One-Step Soft Chemical Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles under Inert Gas Atmosphere. Magnetic Properties and In Vitro Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Characterization
3. Results
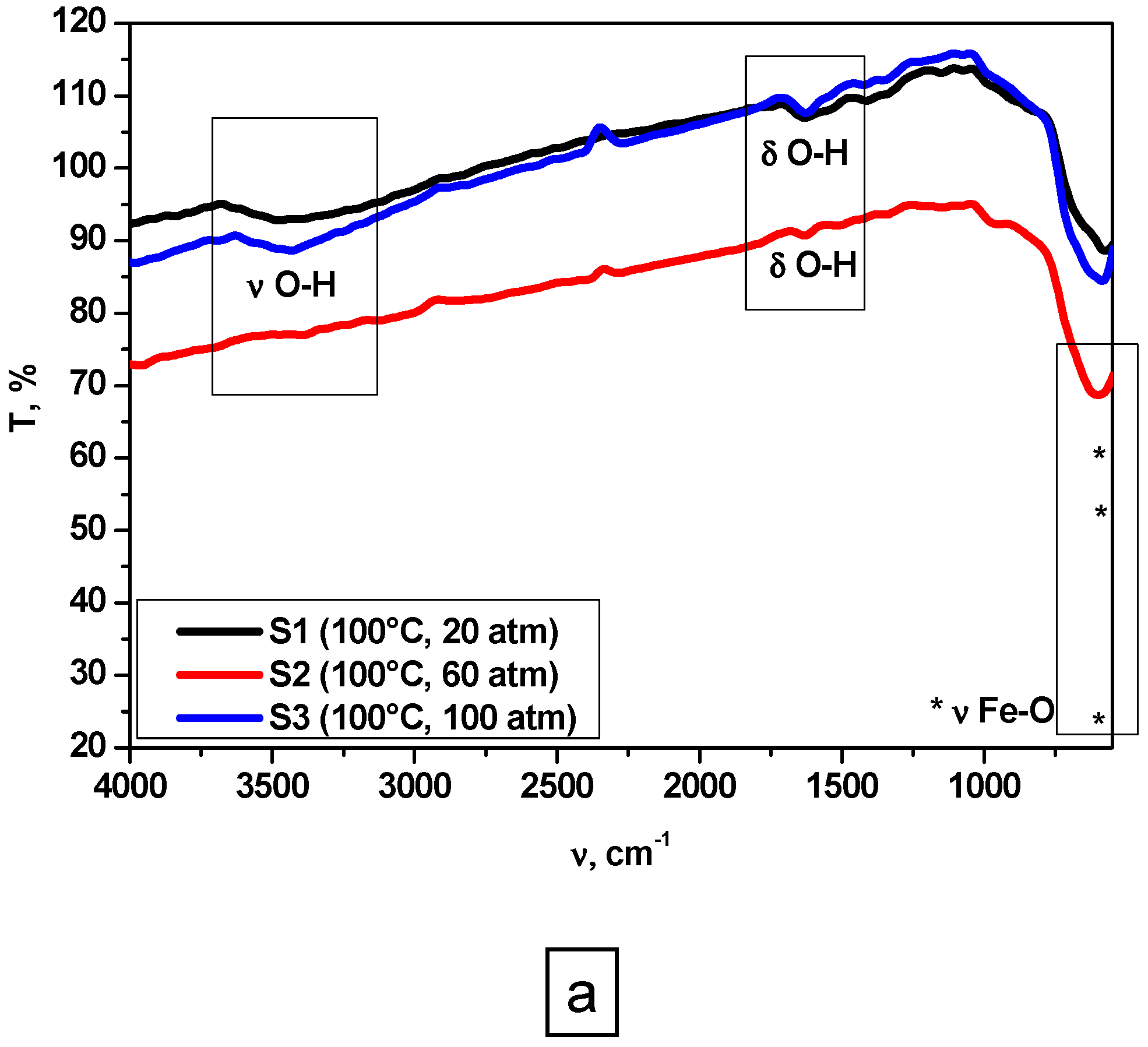
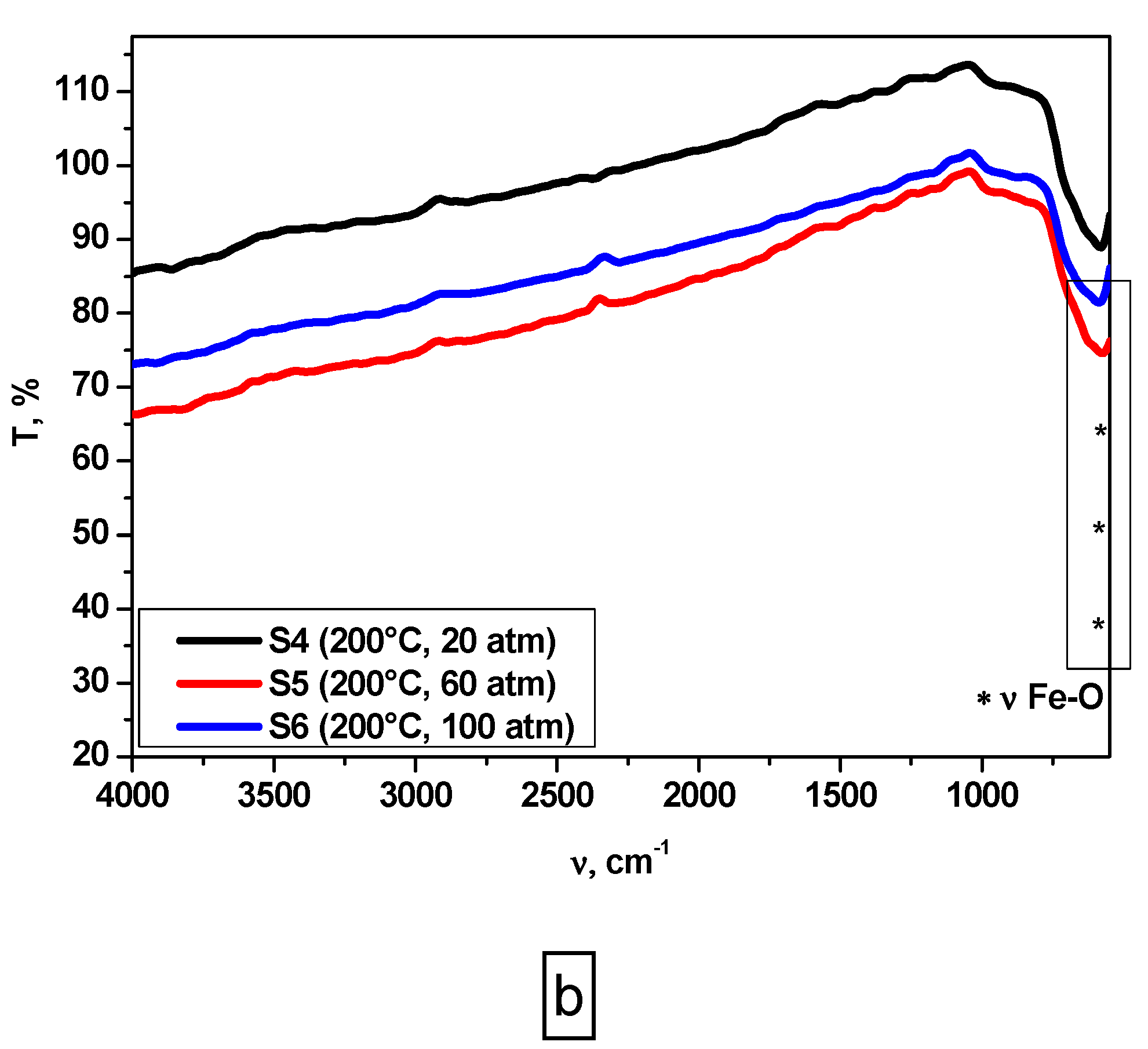
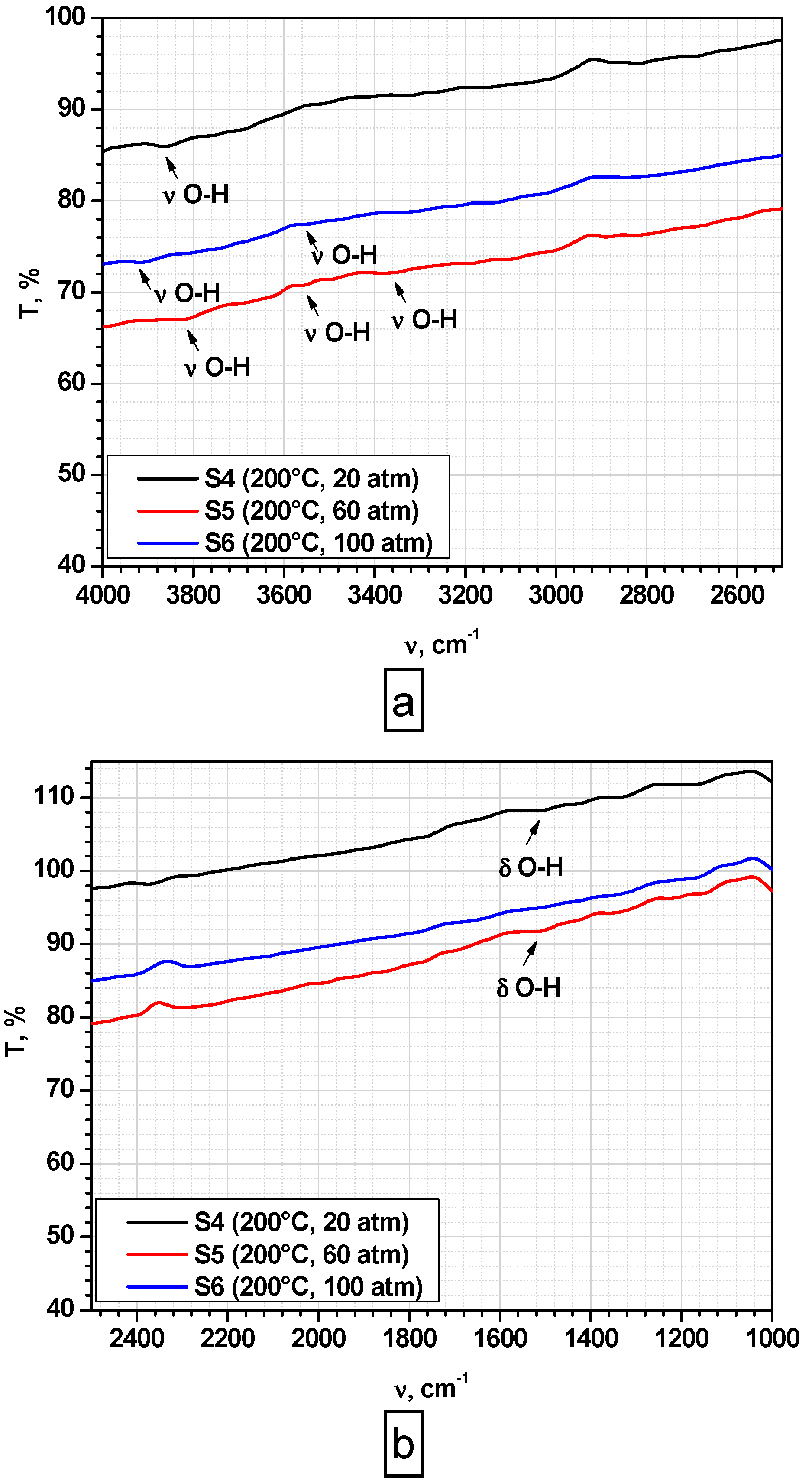
3.1. Fourier-Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Analysis
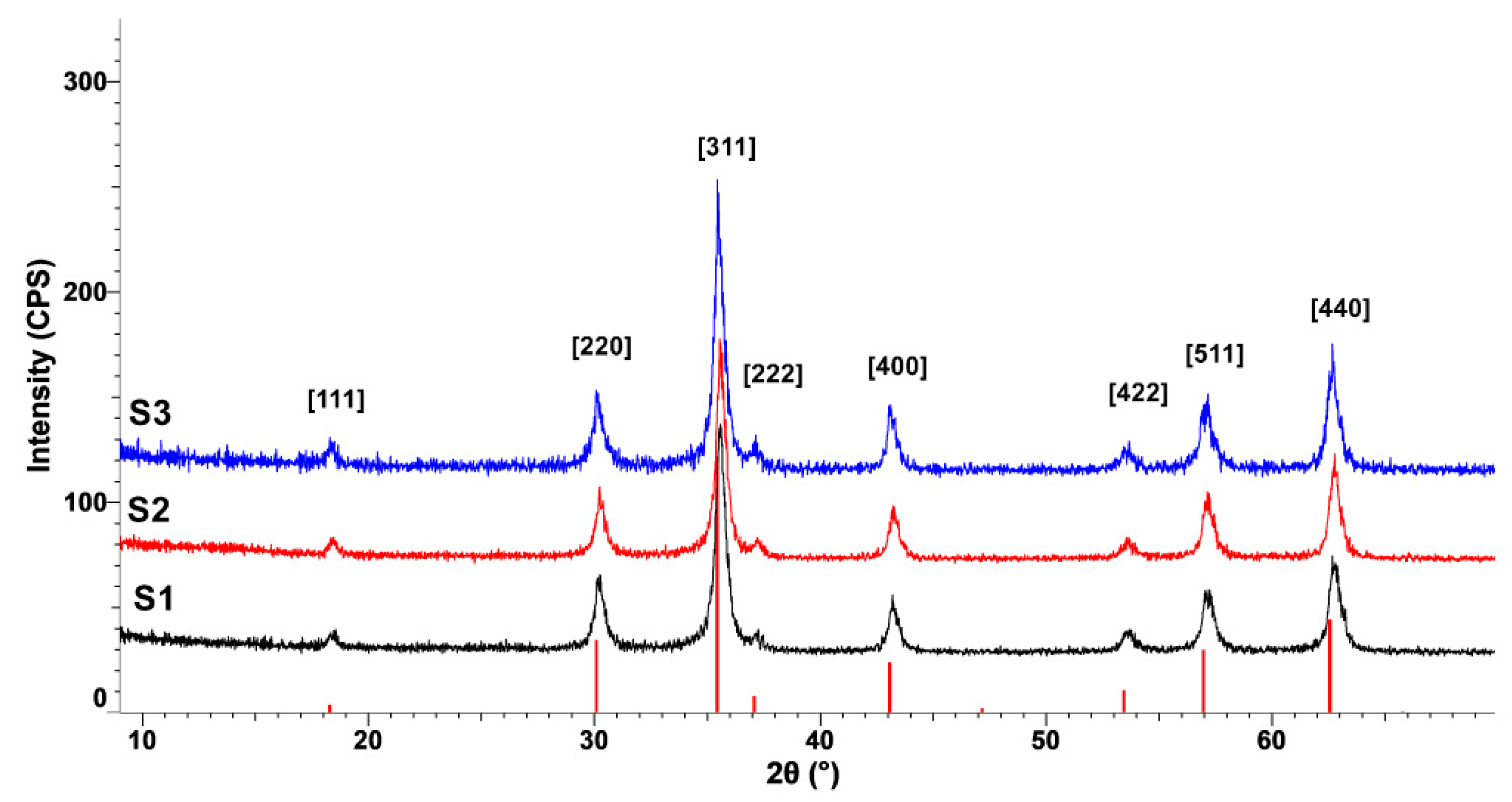
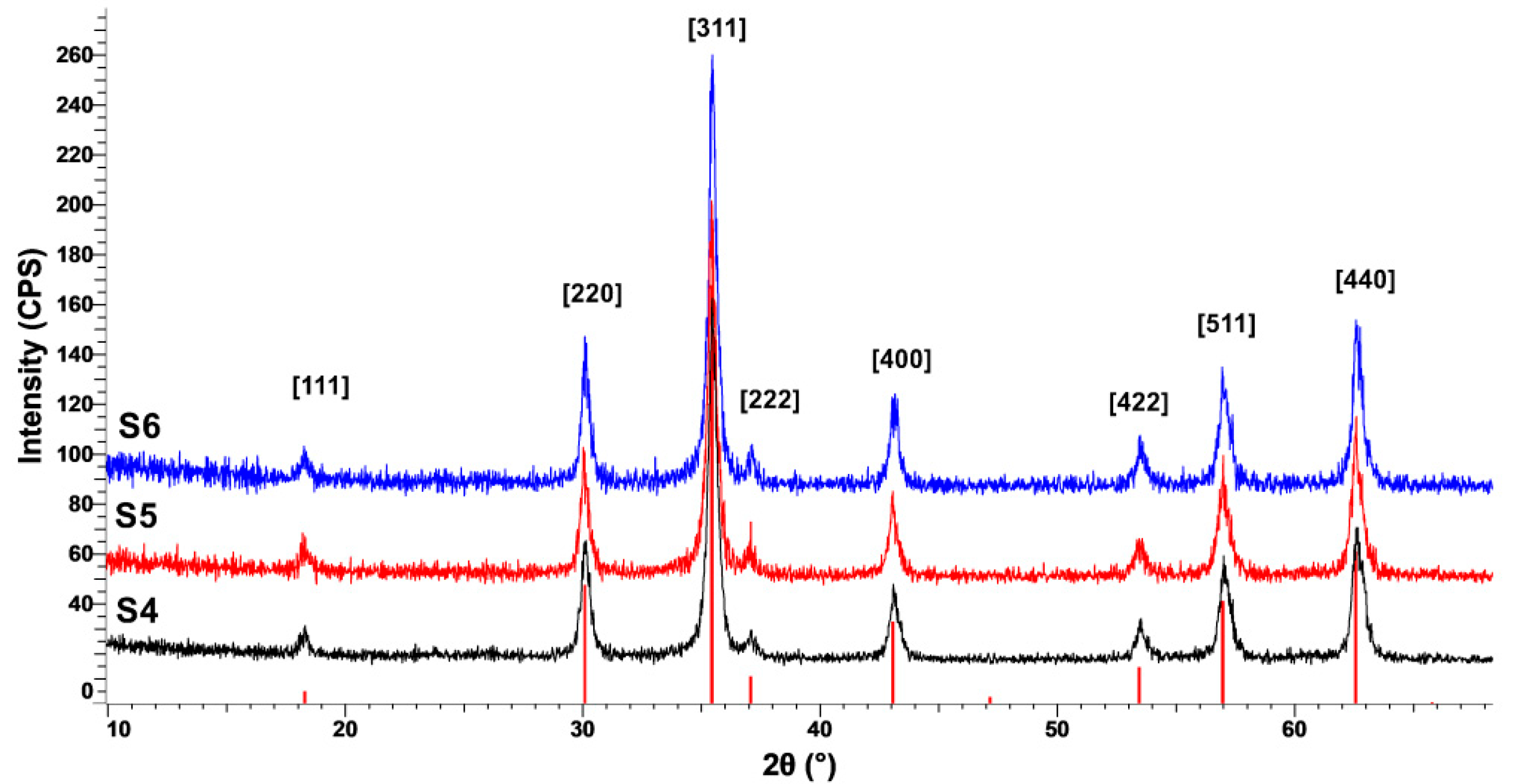
3.2. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Characterization
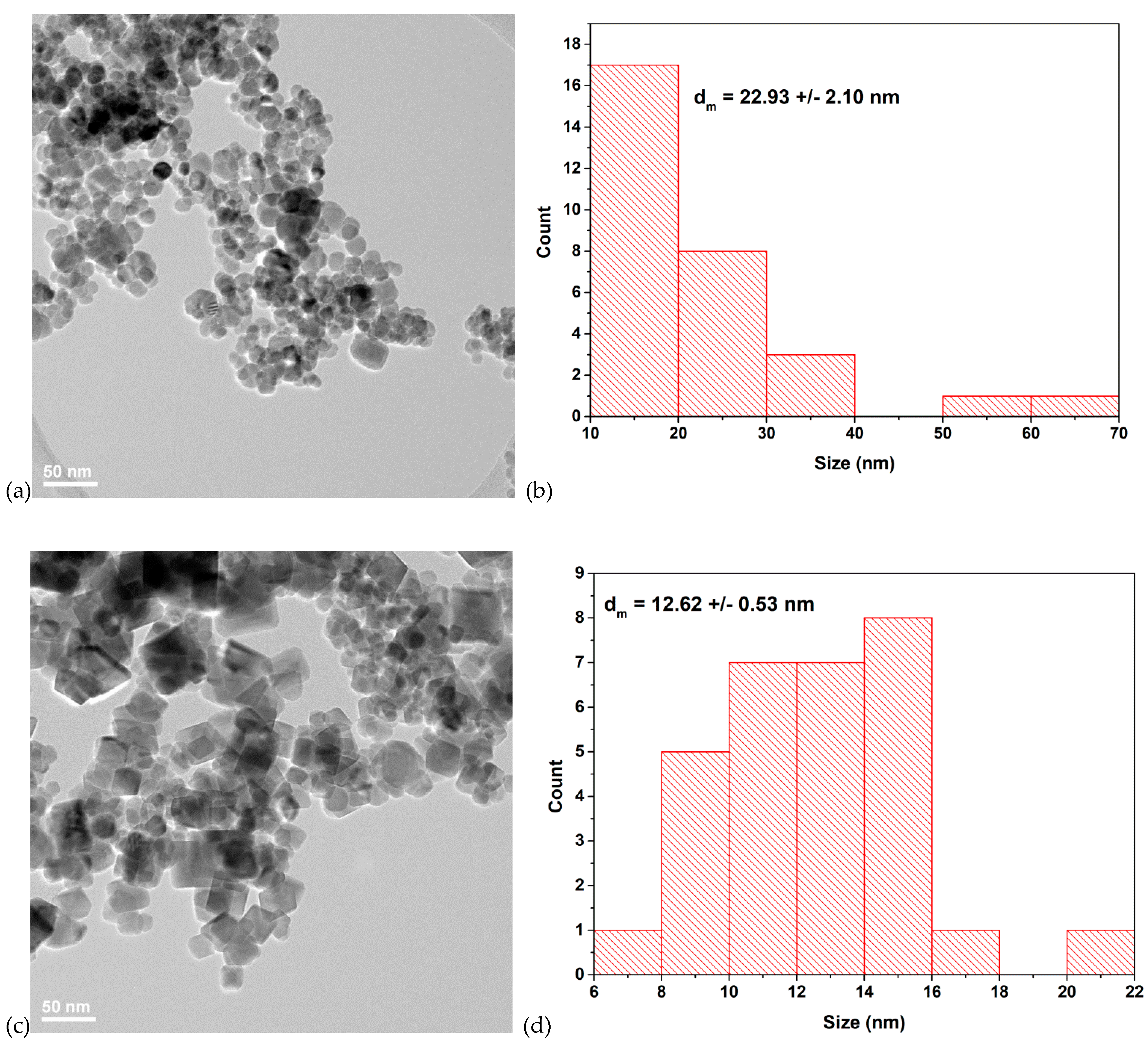
3.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Characterization
3.4. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Measurements
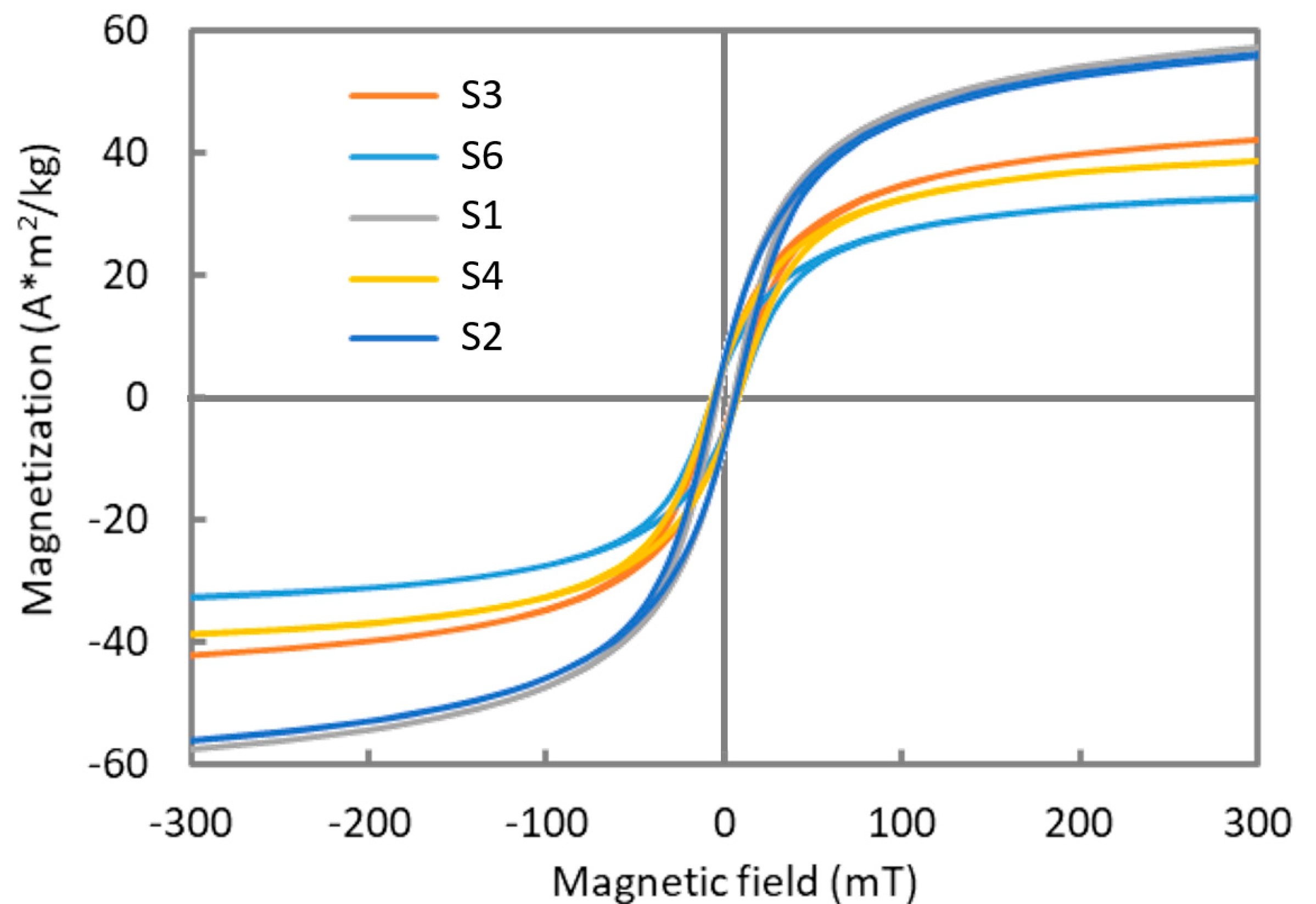
3.5. Magnetic Measurements
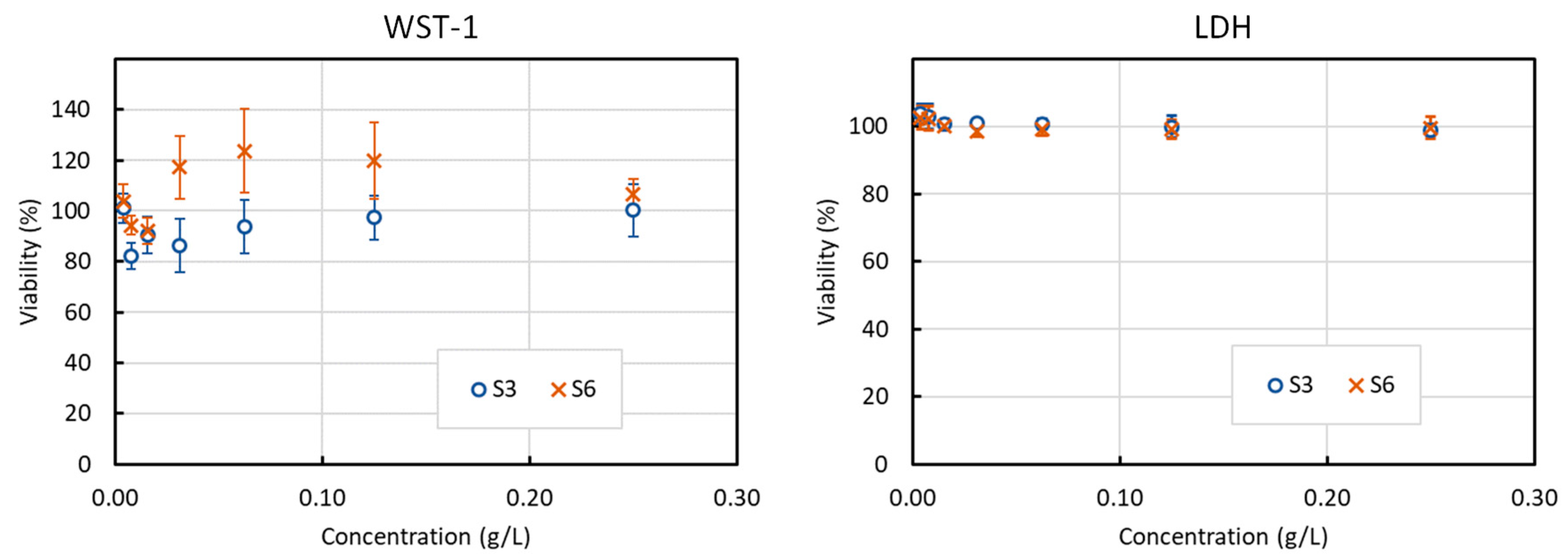
3.6. Toxicity Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nedyalkova, M.; Donkova, B.; Romanova, J.; Tzvetkov, G.; Madurga, S.; Simeonov, V. Iron oxide nanoparticles—In vivo/in vitro biomedical applications and in silico studies. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 249, 192–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, N.; Singh, M. Efficient synthesis of superparamagnetic magnetite nanoparticles under air for biomedical applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 429, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miola, M.; Bellare, A.; Laviano, F.; Gerbaldo, R.; Verné, E. Bioactive superparamagnetic nanoparticles for multifunctional composite bone cements. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 14533–14545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, K.; Bouras, A.; Bozec, D.; Ivkov, R.; Hadjipanayis, C. Magnetic hyperthermia therapy for the treatment of glioblastoma: A review of the therapy’s history, efficacy and application in humans. Int. J. Hyperth. 2018, 34, 1316–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalil, W.B.F.; Pentón-Madrigal, A.; Mello, A.; Carneiro, F.A.; Soares, R.M.; Baptista, L.S.; Sinnecker, J.P.; De Oliveira, L.A.S. Low toxicity superparamagnetic magnetite nanoparticles: One-pot facile green synthesis for biological applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Cho, S.H.; Seong, H. Multifunctional ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as a theranostic agent. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 520, 892–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miola, M.; Ferraris, S.; Pirani, F.; Multari, C.; Bertone, E.; Rožman, K.Ž.; Kostevšek, N.; Verné, E. Reductant-free synthesis of magnetoplasmonic iron oxide-gold nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 15258–15265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.L.; Lim, S.; Ong, H.C.; Chong, W.T. Research progress on iron oxide-based magnetic materials: Synthesis techniques and photocatalytic applications. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 9–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darroudi, M.; Hakimi, M.; Goodarzi, E.; Oskuee, R.K. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs): Green preparation, characterization and their cytotoxicity effects. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 14641–14645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Joh, D.Y.; Al-Zaki, A.; Stangl, M.; Murty, S.; Davis, J.J.; Baumann, B.C.; Alonso-Basanta, M.; Kao, G.D.; Tsourkas, A.; et al. Theranostic Application of Mixed Gold and Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticle Micelles in Glioblastoma Multiforme. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raucher, D.; Dragojevic, S.; Ryu, J. Macromolecular Drug Carriers for Targeted Glioblastoma Therapy: Preclinical Studies, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliramaji, S.; Zamanian, A.; Sohrabijam, Z. Characterization and Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles by Innovative Sonochemical Method. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2015, 11, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Sakthivel, R.; Behura, R.; Mishra, B.K.; Das, D. Synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles from mineral waste. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 645, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suppiah, D.D.; Hamid, S.B.A. One step facile synthesis of ferromagnetic magnetite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 414, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitin, A.; Fedorova, M.; Naumenko, V.; Shchetinin, I.; Abakumov, M.; Erofeev, A.; Gorelkin, P.; Meshkov, G.; Beloglazkina, E.; Ivanenkov, Y.; et al. Synthesis, characterization and MRI application of magnetite water-soluble cubic nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 441, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez, F.; Campo, T.; Cotto, M.; Polanco, R.; Roque, R.; Fierro, P.; Sanz, J.M.; Elizalde, E.; Morant, C. Synthesis and Characterization of Monodisperse Magnetite Hollow Microspheres. Soft Nanosci. Lett. 2011, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, J.; Faivre, D. Iron solubility, colloids and their impact on iron (oxyhydr)oxide formation from solution. Earth Sci. Rev. 2015, 150, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muradova, A.G.; Zaytseva, M.P.; Sharapaev, A.I.; Yurtov, E.V. Influence of temperature and synthesis time on shape and size distribution of Fe3O4 nanoparticles obtained by ageing method. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 509, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, S.; Parekh, K.; Pandey, B. Influence of crystallite size on the magnetic properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 678, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asuha, S.; Suyala, B.; Siqintana, X.; Zhao, S. Direct synthesis of Fe3O4 nanopowder by thermal decomposition of Fe–urea complex and its properties. J. Alloy. Compd. 2011, 509, 2870–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stimphil, E.; Nagesetti, A.; Guduru, R.; Stewart, T.; Rodzinski, A.; Liang, P.; Khizroev, S. Physics considerations in targeted anticancer drug delivery by magnetoelectric nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2017, 4, 021101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Asuha, S. One-pot synthesis of magnetite nanopowder and their magnetic properties. Powder Technol. 2010, 197, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauch, C.; Späth, S.; Ballweg, T.; Luxenhofer, R.; Mandel, K. Nanostructured micro-raspberries from superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Studying agglomeration degree and redispersibility of nanoparticulate powders via magnetisation measurements. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2017, 505, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nourafkan, E.; Asachi, M.; Gao, H.; Raza, G.; Wen, D. Synthesis of stable iron oxide nanoparticle dispersions in high ionic media. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 50, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselova, I.P.; Safronov, A.P.; Samatov, O.M.; Beketov, I.V.; Medvedev, A.I.; Kurlyandskaya, G.V. Water based suspensions of iron oxide obtained by laser target evaporation for biomedical applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 415, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klekotka, U.; Satuła, D.; Spassov, S.; Kalska-Szostko, B. Surfactant dependence on physicochemical properties of magnetite nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 537, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azcona, P.; Zysler, R.; Lassalle, V. Simple and novel strategies to achieve shape and size control of magnetite nanoparticles intended for biomedical applications. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 504, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altan, C.L.; Gurten, B.; Sadza, R.; Yenigul, E.; Sommerdijk, N.A.J.M.; Bucak, S. Poly(acrylic acid)-directed synthesis of colloidally stable single domain magnetite nanoparticles via partial oxidation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 416, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthana, D.S.; Namratha, K.; Byrappa, K.; Yathirajan, H.S. Facile one-step fabrication of magnetite particles under mild hydrothermal conditions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 378, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozel, F.; Kockar, H.; Karaagac, O. Growth of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles by Hydrothermal Process: Effect of Reaction Parameters on the Nanoparticle Size. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2015, 28, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, M.; Piticescu, R.M.; Vasile, E.; Taloi, D.; Petriceanu, M.; Stoiciu, M.; Badilita, V. The Influence of Synthesis Parameters on FeO(OH)/Fe2O3 Formation by Hydrothermal Techniques. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung B 2010, 65, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cursaru, L.M.; Piticescu, R.M.; Dragut, D.V.; Tudor, I.A.; Kuncser, V.; Iacob, N.; Stociu, F. The Influence of Synthesis Parameters on Structural and Magnetic Properties of Iron Oxide Nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-H.; Rozhkova, E.A.; Ulasov, I.V.; Bader, S.D.; Rajh, T.; Lesniak, M.S.; Novosad, V. Biofunctionalized magnetic-vortex microdiscs for targeted cancer-cell destruction. Nat. Mater. 2009, 9, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naud, C.; Thébault, C.; Carrière, M.; Hou, Y.; Morel, R.; Berger, F.; Dieny, B.; Joisten, H. Cancer treatment by magneto-mechanical effect of particles, a review. Nanoscale Adv. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, D.; Agrawal, D.C. Synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles under oxidizing environment and their stabilization in aqueous and non-aqueous media. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 308, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Lü, X.; Shu, H.; Xie, J.; Zhang, H. Microwave-assisted synthesis of perovskite ReFeO3 (Re: La, Sm, Eu, Gd) photocatalyst. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2010, 171, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janbutrach, Y.; Hunpratub, S.; Swatsitang, E. Ferromagnetism and optical properties of La1−xAlxFeO3 nanopowders. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.; Hneda, M.L.; Fernandez-Outon, L.E.; De Sousa, E.M.B.; Ardisson, J.D. Synthesis and characterization of nanocomposites based on rare-earth orthoferrites and iron oxides for magnetic hyperthermia applications. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 17920–17929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoia, M.; Istratie, R.; Păcurariu, C. Investigation of magnetite nanoparticles stability in air by thermal analysis and FTIR spectroscopy. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 125, 1185–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, L.M.; Piticescu, R.M.; Petriceanu, M.; Ottaviani, M.F.; Cangiotti, M.; Vasile, E.; Dîrtu, M.M.; Wolff, M.; Garcia, Y.; Schinteie, G.; et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of nanostructured hybrids based on iron oxide and branched PEI polymers. Influence of high pressure on structure and morphology. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 161, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deriu, M.A.; Popescu, L.M.; Ottaviani, M.F.; Danani, A.; Piticescu, R.M. Iron oxide/PAMAM nanostructured hybrids: Combined computational and experimental studies. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 1996–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, M.; Byrappa, K. Hydrothermal processing of materials: Past, present and future. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 2085–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heider, F.; Williams, W. Note on temperature dependence of exchange constant in magnetite. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1988, 15, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Kartikowati, C.W.; Horie, S.; Ogi, T.; Iwaki, T.; Okuyama, K. Correlation between particle size/domain structure and magnetic properties of highly crystalline Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unni, M.; Uhl, A.; Savliwala, S.; Savitzky, B.H.; Dhavalikar, R.; Garraud, N.; Arnold, D.P.; Kourkoutis, L.F.; Andrew, J.; Rinaldi, C. Thermal decomposition synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles with diminished magnetic dead layer by controlled addition of oxygen. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 2284–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, R.M.; Thorat, N.D.; Shete, P.B.; Bedge, P.A.; Gavde, S.; Joshi, M.G.; Tofail, S.A.M.; Bohara, R.A. Comprehensive cytotoxicity studies of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2018, 13, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample Name | Synthesis Conditions |
|---|---|
| S1 | 100 °C/20 atm |
| S2 | 100 °C/60 atm |
| S3 | 100 °C/100 atm |
| S4 | 200 °C/20 atm |
| S5 | 200 °C/60 atm |
| S6 | 200 °C/100 atm |
| Sample Name | Synthesis Conditions | Mean Particle Size (Hydrodynamic Diameter), nm | Median Particle Size, nm | % of Median Sized Particles from All Size Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 100 °C/20 atm | 231 | 141.8 | 5.9 |
| S2 | 100 °C/60 atm | 421.4 | 396.1 | 24.3 |
| S3 | 100 °C/100 atm | 324.8 | 396.1 | 14.8 |
| S4 | 200 °C/20 atm | 517.5 | 531.2 | 26.1 |
| S5 | 200 °C/60 atm | 692 | 615.1 | 22.6 |
| S6 | 200 °C/100 atm | 539.6 | 615.1 | 20.4 |
| Sample name | T | P | Mr/Ms | Ms | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| °C | atm | mT | Am2/kg | nm | nm | |||
| S1 | 100 | 20 | 4 | 0.09 | 63.3 | 20670 | 10.4 | 4.0 |
| S2 | 100 | 60 | 6 | 0.11 | 62.6 | 20097 | 10.3 | 4.8 |
| S3 | 100 | 100 | 5 | 0.11 | 46.0 | 20377 | 11.5 | 3.9 |
| S4 | 200 | 20 | 7 | 0.15 | 40.8 | 24897 | 12.8 | 2.9 |
| S6 | 200 | 100 | 7 | 0.15 | 35.2 | 24815 | 13.4 | 3.9 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cursaru, L.M.; Piticescu, R.M.; Dragut, D.V.; Morel, R.; Thébault, C.; Carrière, M.; Joisten, H.; Dieny, B. One-Step Soft Chemical Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles under Inert Gas Atmosphere. Magnetic Properties and In Vitro Study. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081500
Cursaru LM, Piticescu RM, Dragut DV, Morel R, Thébault C, Carrière M, Joisten H, Dieny B. One-Step Soft Chemical Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles under Inert Gas Atmosphere. Magnetic Properties and In Vitro Study. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(8):1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081500
Chicago/Turabian StyleCursaru, Laura Madalina, Roxana Mioara Piticescu, Dumitru Valentin Dragut, Robert Morel, Caroline Thébault, Marie Carrière, Hélène Joisten, and Bernard Dieny. 2020. "One-Step Soft Chemical Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles under Inert Gas Atmosphere. Magnetic Properties and In Vitro Study" Nanomaterials 10, no. 8: 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081500
APA StyleCursaru, L. M., Piticescu, R. M., Dragut, D. V., Morel, R., Thébault, C., Carrière, M., Joisten, H., & Dieny, B. (2020). One-Step Soft Chemical Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles under Inert Gas Atmosphere. Magnetic Properties and In Vitro Study. Nanomaterials, 10(8), 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081500








