Growth of Multiorientated Polycrystalline MoS2 Using Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Reactions
Abstract
1. Introduction
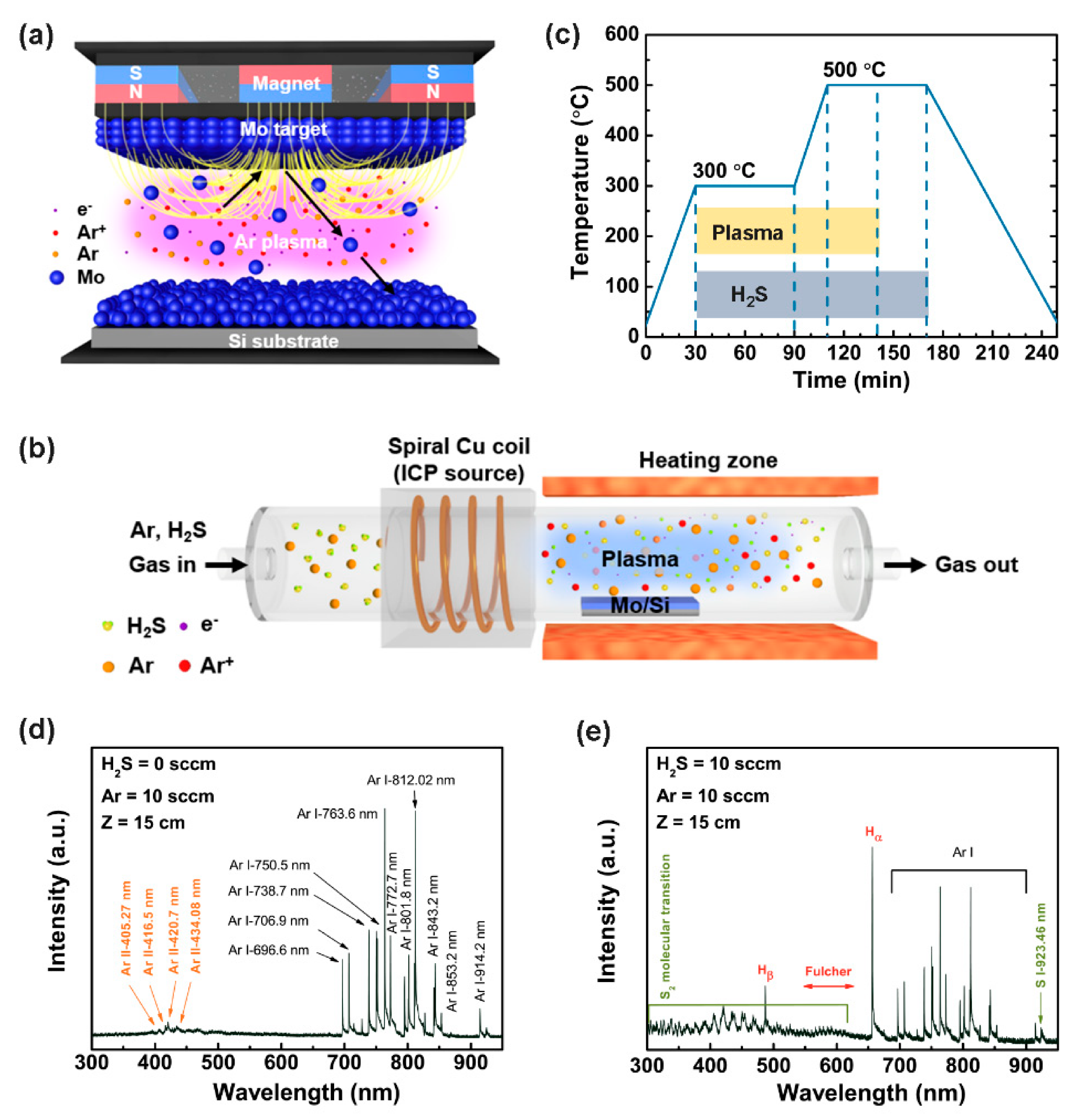
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Growth of MoS2
2.2. Characterization
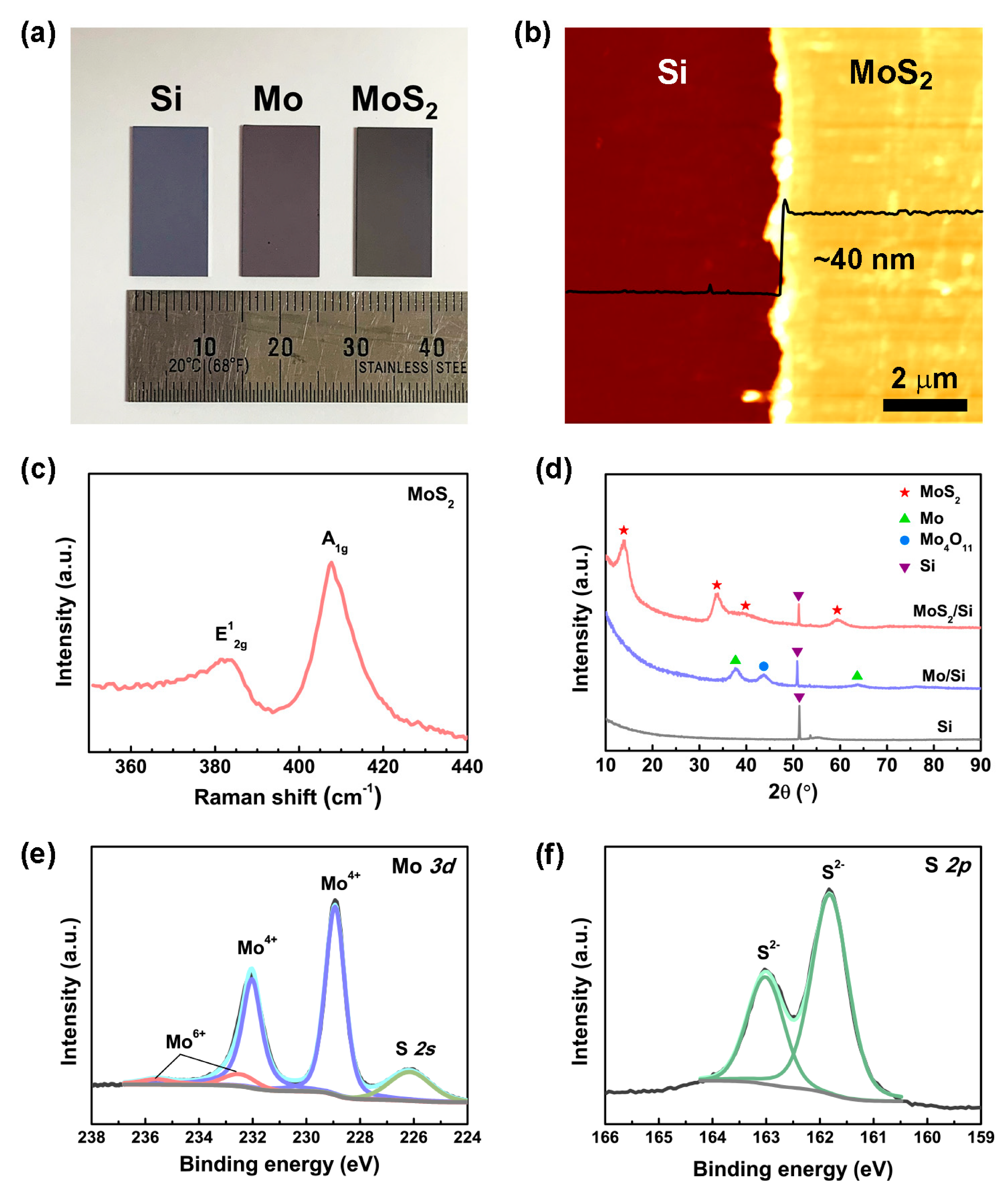
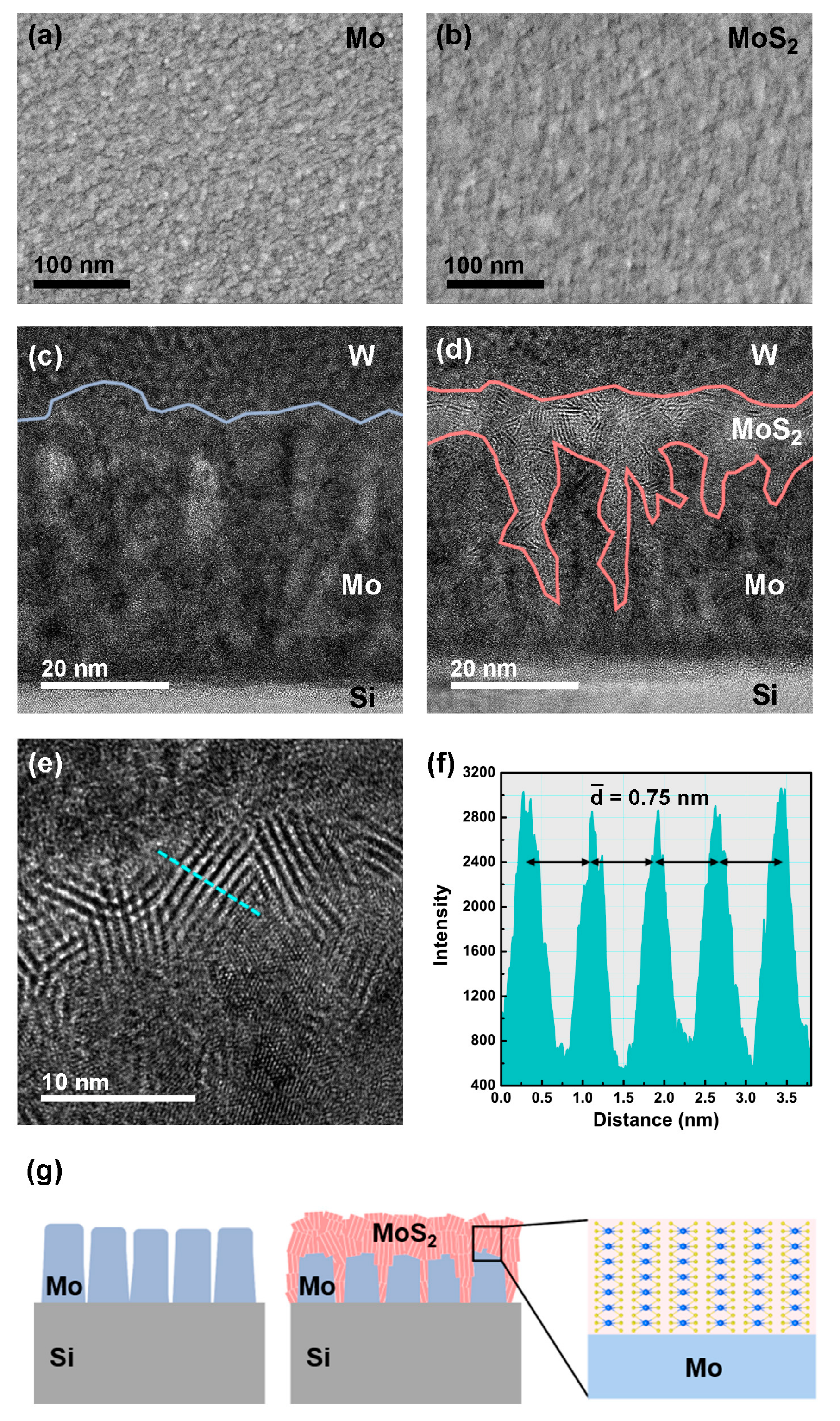
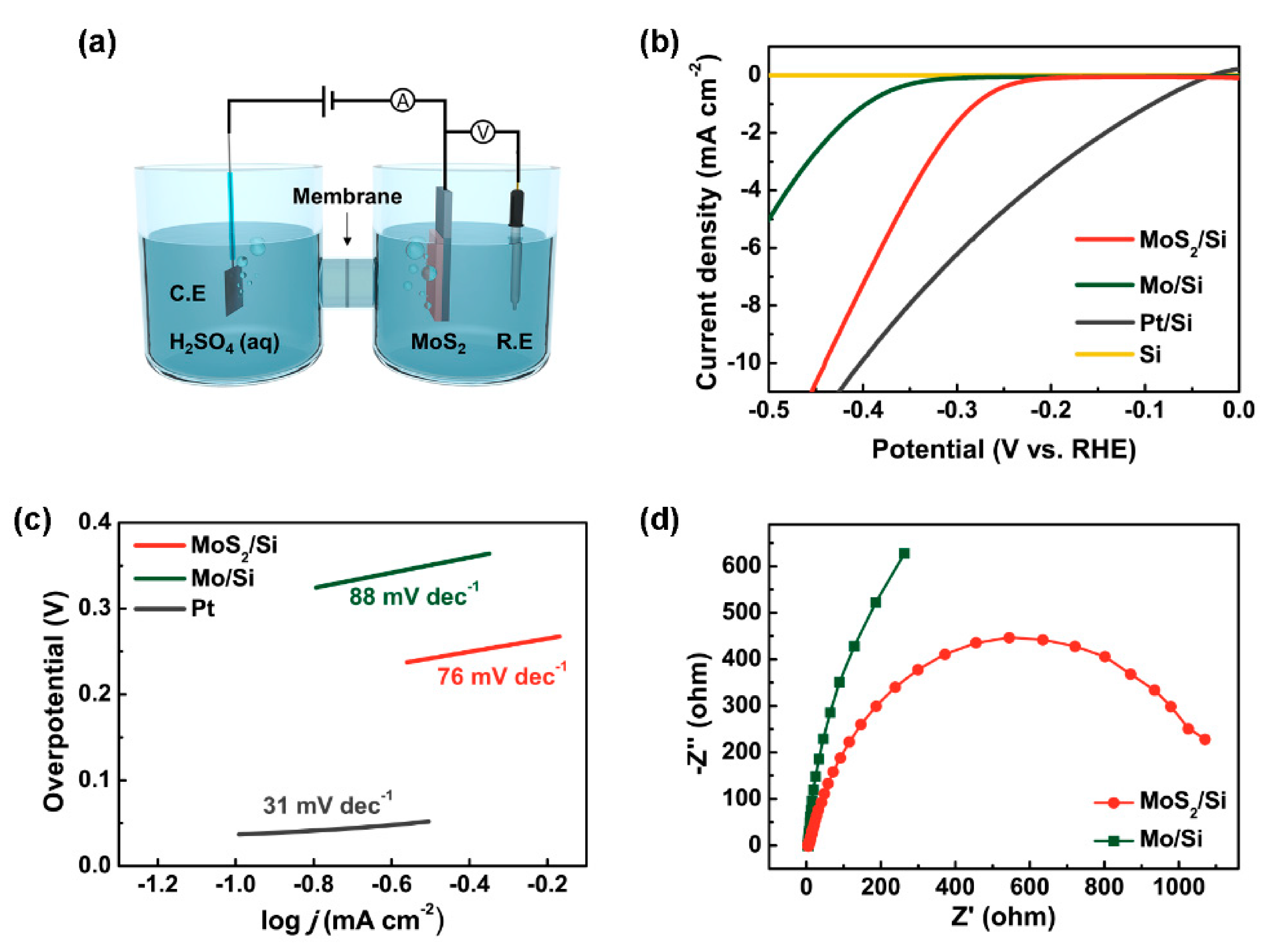
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schloegl, R. Energy: Fuel for thought. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 772–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masters, G.M. Renewable and Efficient Electric Power Systems; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dresselhaus, M.S.; Thomas, I. Alternative energy technologies. Nature 2001, 414, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breen, J.P.; Burch, R.; Coleman, H.M. Metal-catalysed steam reforming of ethanol in the production of hydrogen for fuel cell applications. Appl. Catal. B 2002, 39, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Guio, C.G.; Stern, L.A.; Hu, X. Nanostructured hydrotreating catalysts for electrochemical hydrogen evolution. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 6555–6569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, M.G.; Warren, E.L.; McKone, J.R.; Boettcher, S.W.; Mi, Q.; Santori, E.A.; Lewis, N.S. Solar water splitting cells. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 6446–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmalzried, H. Chemical Kinetics of Solids; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Conway, B.E.; Tilak, B.V. Interfacial processes involving electrocatalytic evolution and oxidation of H2, and the role of chemisorbed H. Electrochim. Acta 2002, 47, 3571–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinnemann, B.; Moses, P.G.; Bonde, J.; Jørgensen, K.P.; Nielsen, J.H.; Horch, S.; Chorkendorff, I.; Nørskov, J.K. Biomimetic hydrogen evolution: MoS2 nanoparticles as catalyst for hydrogen evolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 5308–5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, T.F.; Jørgensen, K.P.; Bonde, J.; Nielsen, J.H.; Horch, S.; Chorkendorff, I. Identification of active edge sites for electrochemical H2 evolution from MoS2 nanocatalysts. Science 2007, 317, 100–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhu, H.; Yang, X. Amorphous carbon supported MoS2 nanosheets as effective catalysts for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 10680–10685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Wang, R.; Sun, X.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, J.; Lou, X.W.; Xie, Y. Defect-rich MoS2 ultrathin nanosheets with additional active edge sites for enhanced electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5807–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Duan, X.; Wang, C.; Duan, X.; Wang, S. Plasma-engineered MoS2 thin-film as an efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 7470–7473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merki, D.; Fierro, S.; Vrubel, H.; Hu, X. Amorphous molybdenum sulfide films as catalysts for electrochemical hydrogen production in water. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Huang, S.-Y.; Li, Y.; Steinmann, S.N.; Yang, W.; Cao, L. Layer-dependent electrocatalysis of MoS2 for hydrogen evolution. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnanasekar, P.; Periyanagounder, D.; Kulandaivel, J. Vertically Aligned MoS2 nanosheets on graphene for highly stable electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reactions. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 2439–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Kong, F.; Yin, G.; Lv, Z.; Sun, X.; Shi, H.; Gao, B. Enhanced hydrogen evolution reaction activity of hydrogen-annealed vertical MoS2 nanosheets. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 14369–14376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, S.; Salamone, M.M.; Robertson, A.W.; Nayak, S.; Kim, H.; Tsang, S.C.E.; Pasta, M.; Warner, J.H. Edge-enriched 2D MoS2 thin films grown by chemical vapor deposition for enhanced catalytic performance. ACS Catal. 2016, 7, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Jackson, D.H.; Lee, D.; Choi, M.; Kim, T.W.; Jeong, S.Y.; Chae, H.J.; Kim, H.W.; Park, N.; Chang, H. In Situ electrochemical activation of atomic layer deposition coated MoS2 basal planes for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1701825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.A.; Bae, C.; Lee, S.; Kim, M.; Montero-Moreno, J.M.; Park, J.H.; Shin, H. Edge-on MoS2 thin films by atomic layer deposition for understanding the interplay between the active area and hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 7604–7614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, S.T.; Macdonald, J.E. Contact and support considerations in the hydrogen evolution reaction activity of petaled MoS2 electrodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 25185–25192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralikrishna, S.; Manjunath, K.; Samrat, D.; Reddy, V.; Ramakrishnappa, T.; Nagaraju, D.H. Hydrothermal synthesis of one-steps for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 89389–89396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.U.; Bark, H.; Jeon, M.; Ryu, G.H.; Lee, Z.; Yeom, G.Y.; Kim, K.; Jung, J.; et al. Low-temperature synthesis of large-scale molybdenum disulfide thin films directly on a plastic substrate using plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 5223–5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, Z.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J.H.; Yu, K.H.; Yan, J.H.; Cen, K.F. Plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition synthesis of vertically oriented graphene nanosheets. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 5180–5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, P.M.; Perini, C.J.; Chiu, J.; Gupta, A.; Ray, H.S.; Chen, H.; Wenzel, K.; Snyder, E.; Wagner, B.K.; Ready, J.; et al. Plasma-assisted synthesis of MoS2. 2D Mater. 2017, 5, 015005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, B.B.; Han, J.G.; Kersten, H. Shaping thin film growth and microstructure pathways via plasma and deposition energy: A detailed theoretical, computational and experimental analysis. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 5591–5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesel, A.; Kovac, J.; Primc, G.; Junkar, I.; Mozetic, M. Effect of H2S plasma treatment on the surface modification of a polyethylene terephthalate surface. Materials 2016, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yap, C.C.R.; Tay, B.K.; Edwin, T.H.T.; Olivier, A.; Baillargeat, D. From bulk to monolayer MoS2: Evolution of Raman scattering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 1385–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.M.D.; Cui, N.; McKinley, A. An XPS study of the surface modification of natural MoS2 following treatment in an RF-oxygen plasma. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1998, 134, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratore, C.; Hu, J.J.; Wang, B.; Haque, M.A.; Bultman, J.E.; Jespersen, M.L.; Shamberger, P.J.; McConney, M.E.; Naguy, R.D.; Voevodin, A.A. Continuous ultra-thin MoS2 films grown by low-temperature physical vapor deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 261604–261609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Singh, J.; Vikraman, D.; Singh, A.K.; Iqbal, M.Z.; Khan, M.F.; Kumar, P.; Choi, D.-C.; Song, W.; An, K.-S.; et al. Large-area, continuous and high electrical performances of bilayer to few layers MoS2 fabricated by RF sputtering via post-deposition annealing method. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30791–30804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eda, G.; Yamaguchi, H.; Voiry, D.; Fujita, T.; Chen, M.; Chhowalla, M. Photoluminescence from chemically exfoliated MoS2. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 5111–5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, N.; Park, J.; Hwang, J.Y.; Choi, W. Growth of large-scale and thickness-modulated MoS2 nanosheets. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 21215–21222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, J.; Bark, H.; Oh, I.K.; Ryu, G.H.; Lee, Z.; Kim, H.; Cho, J.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Lee, C. Synthesis of wafer-scale uniform molybdenum disulfide films with control over the layer number using a gas phase sulfur precursor. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 2821–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Lee, C.S. Interlayer nanoarchitectonics of two-dimensional transition-metal dichalcogenides nanosheets for energy dtorage and conversion applications. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1700571–1700601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasamani, K.D.; Alimohammadi, F.; Sun, Y. Interlayer-expanded MoS2. Mater. Today 2017, 20, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, C. Ultrafine Pt nanoparticles decorated MoS2 nanosheets with significantly improved hydrogen evolution activity. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 241, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benck, J.D.; Hellstern, T.R.; Kibsgaard, J.; Chakthranont, P.; Jaramillo, T.F. Catalyzing the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) with molybdenum sulfide nanomaterials. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 3957–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Li, Y. Recent advances in heterogeneous electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 14942–14962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Xia, B.Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X. Recent development of molybdenum sulfides as advanced electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 1693–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Guo, H.; Chen, W.; Yuan, J.; Martinez, U.; Gupta, G.; Mohite, A.; Ajayan, P.M.; Lou, J. Unveiling active sites for the hydrogen evolution reaction on monolayer MoS2. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1701955–1701962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Gong, Y.; Lin, J.; Li, B.; He, Y.; Pantelides, S.T.; Zhou, W.; Vajtai, R.; Ajayan, P.M. Defects engineered monolayer MoS2 for improved hydrogen evolution reaction. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Jung, J.; Ko, T.Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.-I.; Nah, J.; Ryu, S.; Nam, K.T.; Lee, M.H. Catalytic synergy effect of MoS2/reduced graphene oxide hybrids for a highly efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 5480–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.-C.; Dai, H.; Wang, Q.; Yang, R.; Yu, H.; Liao, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, W.; Wei, Z.; et al. Boundary activated hydrogen evolution reaction on monolayer MoS2. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Lin, Y.; Dong, H.; Dai, W.; Chen, X.; Qu, X.; Zhang, X. One-step hydrothermal fabrication of three-dimensional MoS2 nanoflower using polypyrrole as template for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheem, Y.; Han, Y.; Lee, K.H.; Choi, S.-M.; Myung, N.V. Synthesis of hierarchical MoO2/MoS2 nanofibers for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 105605–105611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Guio, C.G.; Hu, X.L. Amorphous molybdenum sulfides as hydrogen evolution catalysts. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2671–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, D.; Qiao, Q.; Yu, Y.; Peterson, D.; Zafar, A.; Kumar, R.; Curtarolo, S.; Hunte, F.; Shannon, S.; et al. All the catalytic active sites of MoS2 for hydrogen evolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 16632–16638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Sun, M.; Wu, X.; Zhou, S.; Deng, X.; Xie, Z.; Xiao, L.; Jiang, L.; Huang, Q. (B, N)-Doped 3D porous graphene–CNTs synthesized by chemical vapor deposition as a bi-functional catalyst for ORR and HER. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 26934–26937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; McCrory, C.C.; Ferrer, I.M.; Peters, J.C.; Jaramillo, T.F. Benchmarking nanoparticulate metal oxide electrocatalysts for the alkaline water oxidation reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 3068–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benck, J.D.; Chen, Z.; Kuritzky, L.Y.; Forman, A.J.; Jaramillo, T.F. Amorphous molybdenum sulfide catalysts for electrochemical hydrogen production: Insights into the origin of their catalytic activity. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 1916–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.R.; Chan, M.K.Y.; Sun, Y.G. Edge-terminated molybdenum disulfide with a 9.4-Å interlayer spacing for electrochemical hydrogen production. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7493–7501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, N.; Kim, J.; Oh, J.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Sahu, B.B.; Han, J.G.; Kim, S. Growth of Multiorientated Polycrystalline MoS2 Using Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Reactions. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081465
Liu N, Kim J, Oh J, Nguyen QT, Sahu BB, Han JG, Kim S. Growth of Multiorientated Polycrystalline MoS2 Using Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Reactions. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(8):1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081465
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Na, Jeonghun Kim, Jeonghyeon Oh, Quang Trung Nguyen, Bibhuti Bhusan Sahu, Jeong Geon Han, and Sunkook Kim. 2020. "Growth of Multiorientated Polycrystalline MoS2 Using Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Reactions" Nanomaterials 10, no. 8: 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081465
APA StyleLiu, N., Kim, J., Oh, J., Nguyen, Q. T., Sahu, B. B., Han, J. G., & Kim, S. (2020). Growth of Multiorientated Polycrystalline MoS2 Using Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Reactions. Nanomaterials, 10(8), 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081465





