Humidity-Mediated Anisotropic Proton Conductivity through the 1D Channels of Co-MOF-74
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
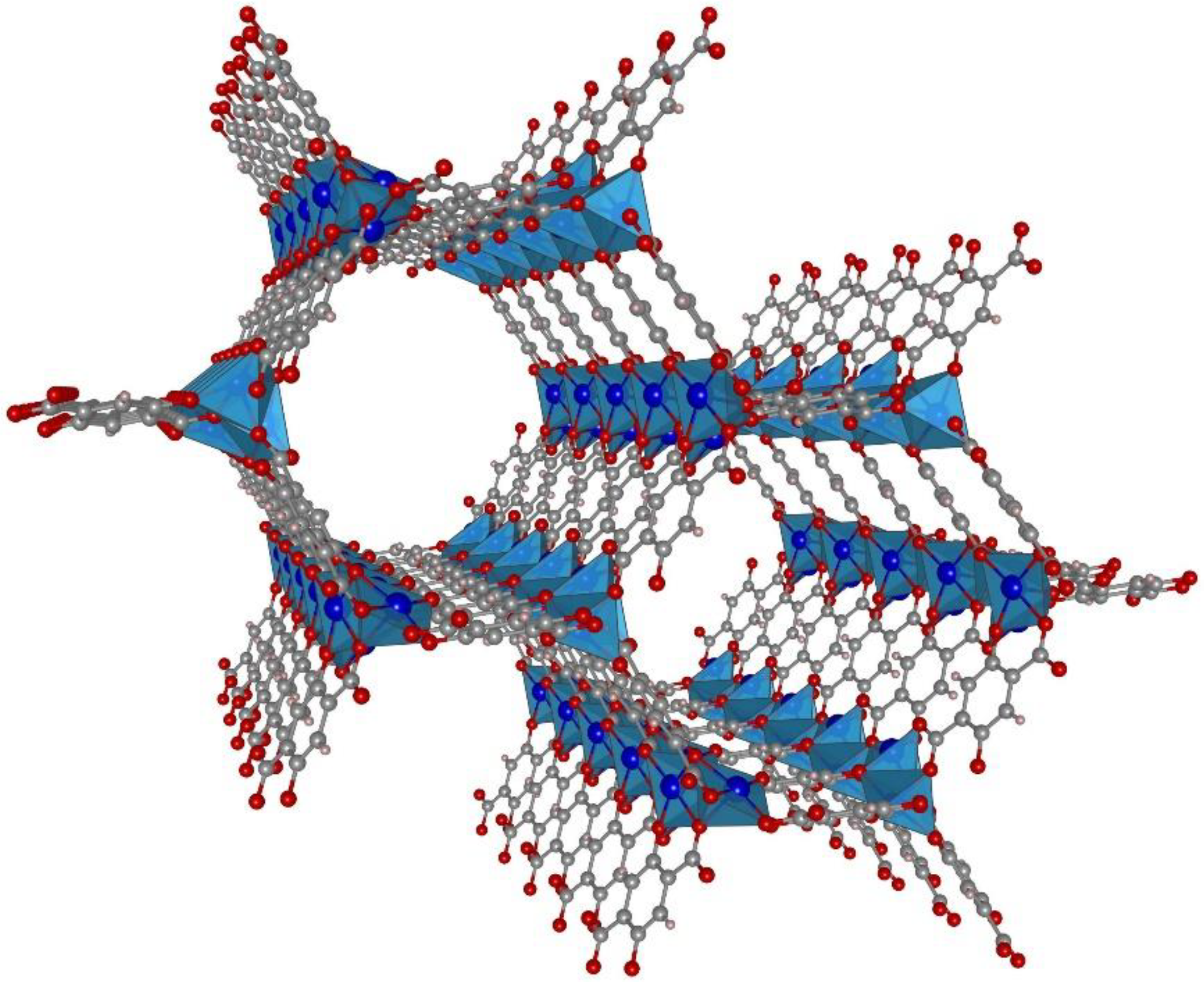
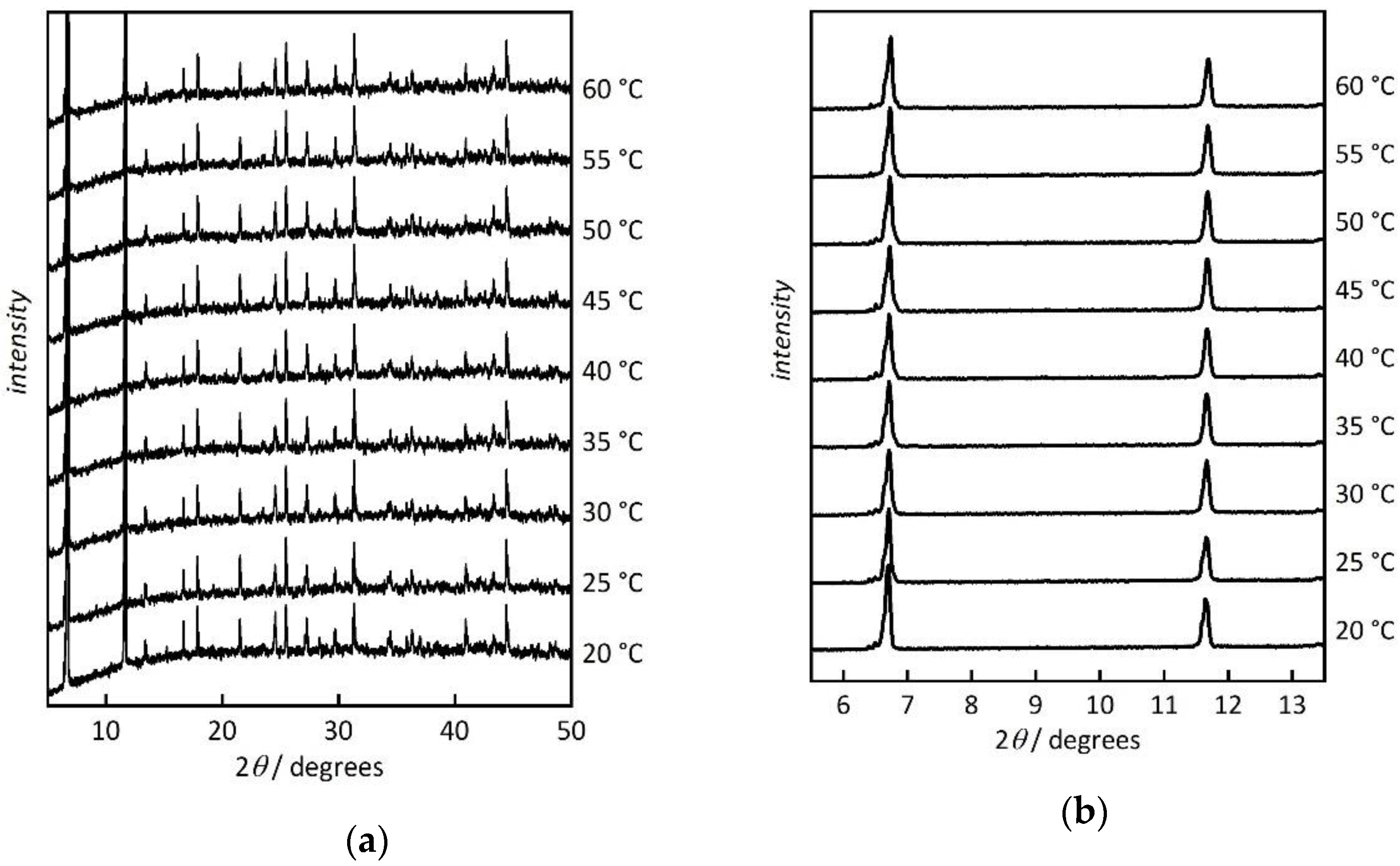
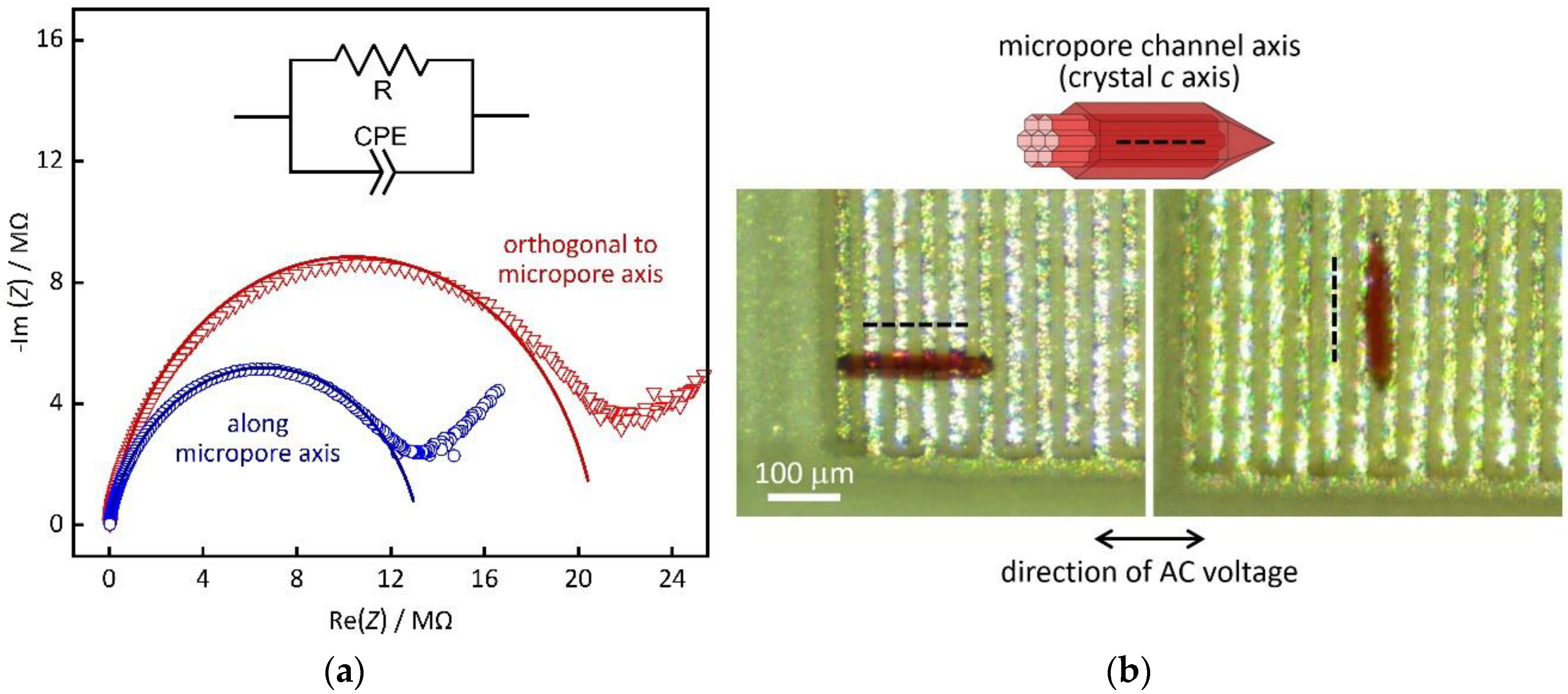
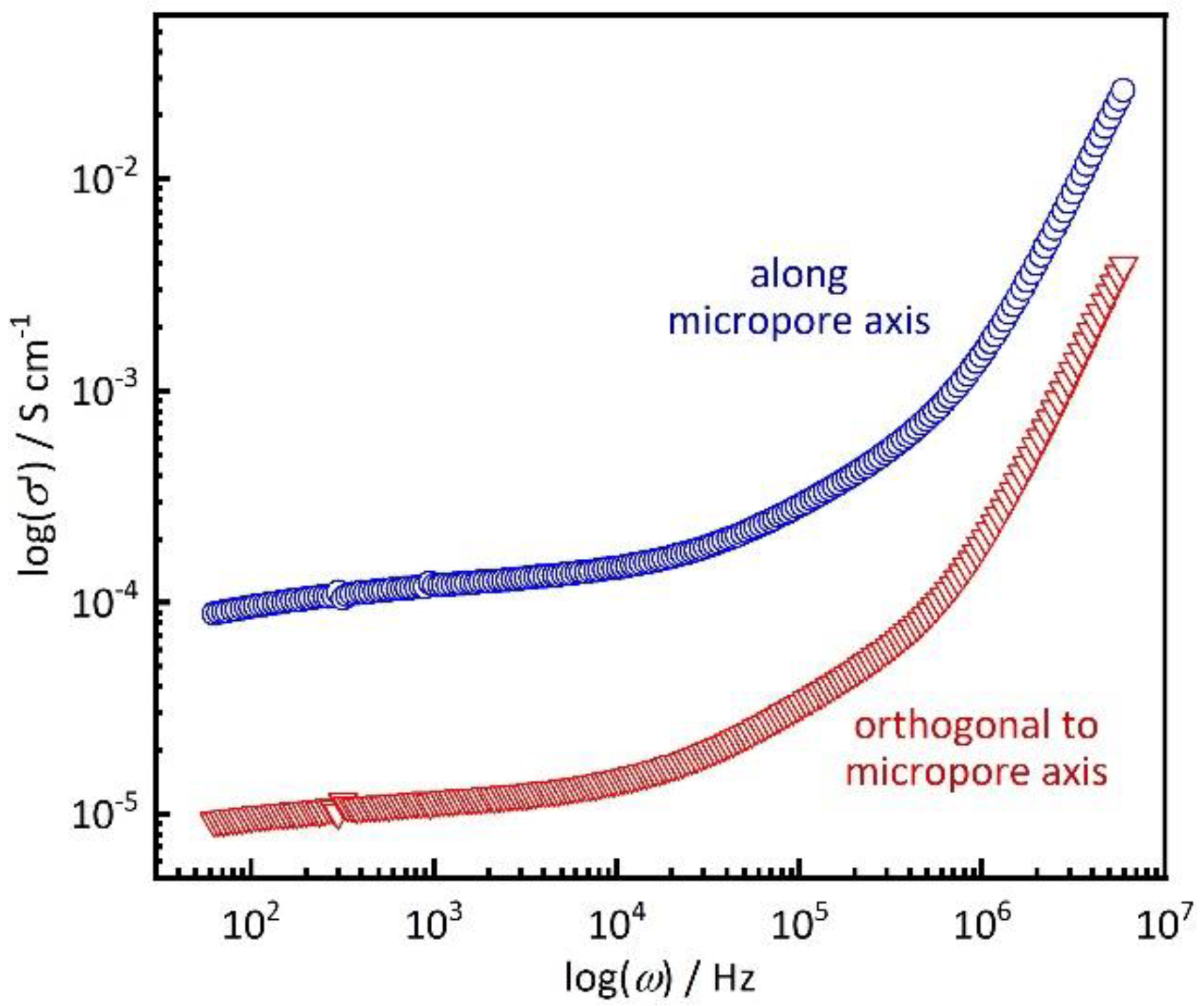
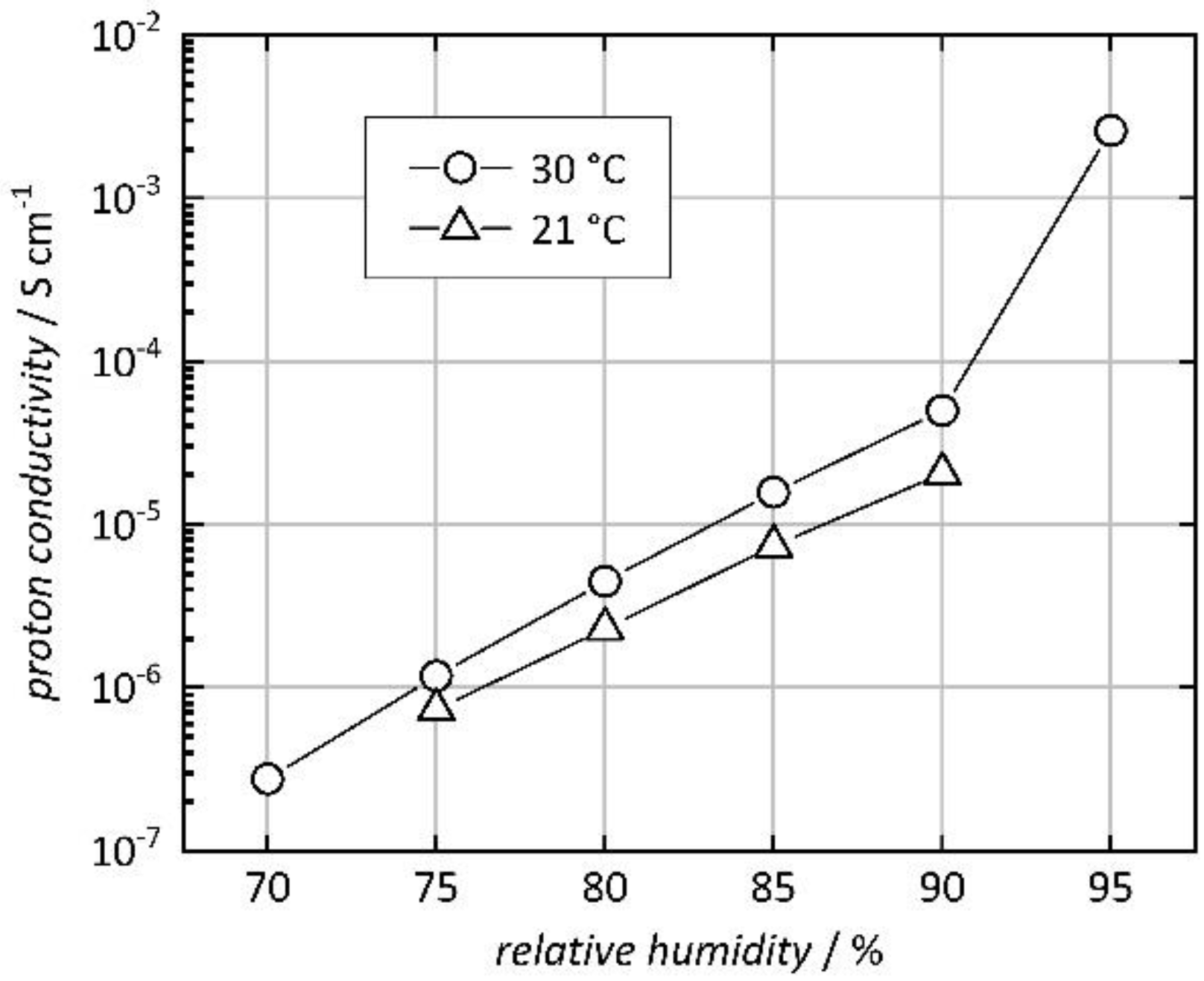
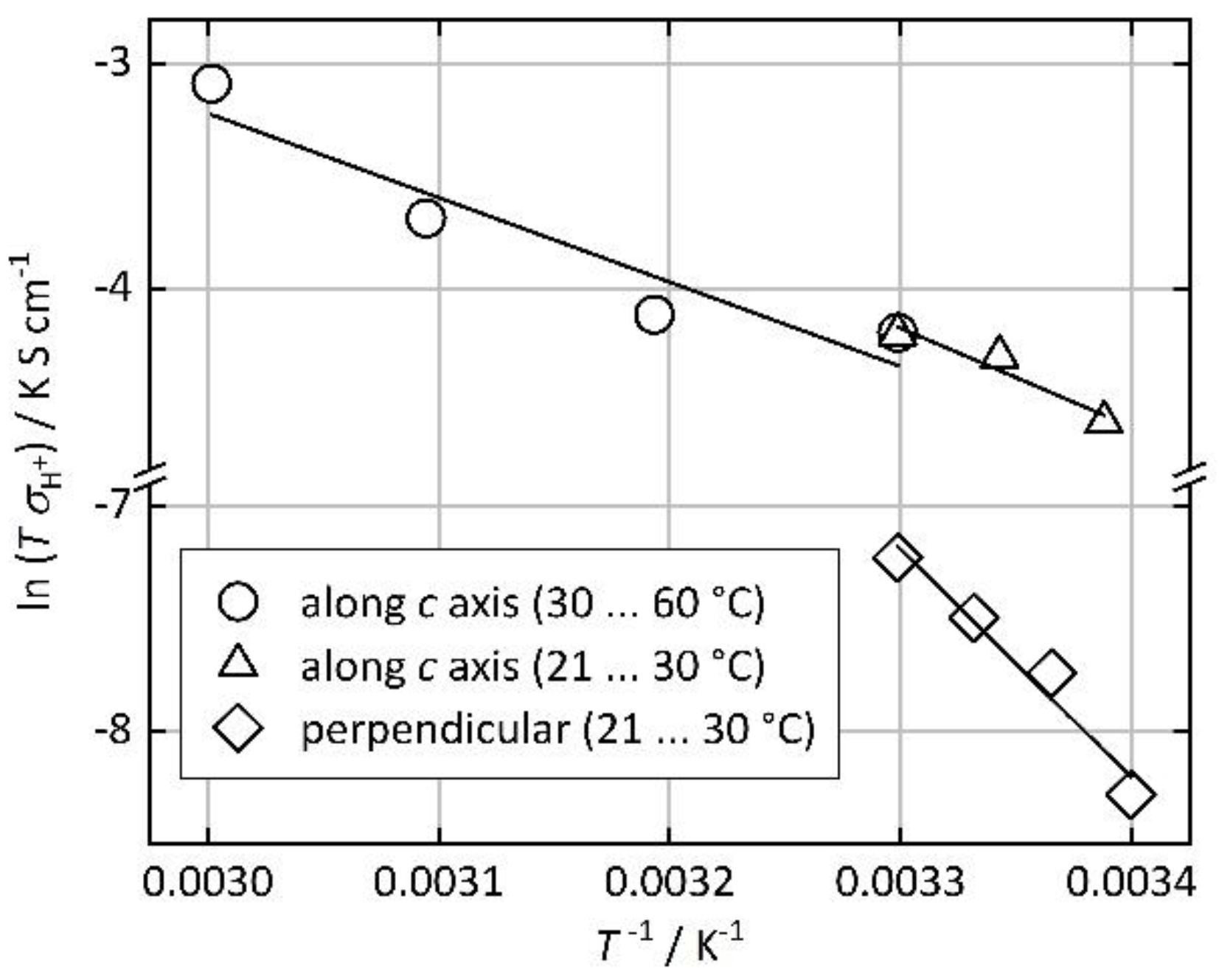
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- U.S. Energy Information Administration. International Energy Outlook 2019 (IEO2019); U.S. Energy Information Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; pp. 17–32. [Google Scholar]
- Fabbri, E.; Pergolesi, D.; Traversa, E. Materials challenges toward proton-conducting oxide fuel cells: A critical review. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 4355–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachsman, E.D.; Lee, K.T. Lowering the Temperature of Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Science 2011, 334, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraytsberg, A.; Ein-Eli, Y. Review of Advanced Materials for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 7303–7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Mogni, L.V.; Miller, E.C.; Railsback, J.G.; Barnett, S.A. A Perspective on Low-Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 1602–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majlan, E.H.; Rohendi, D.; Dauda, W.R.W.; Husaini, T.; Haque, M.A. Electrode for proton exchange membrane fuel cells: A review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2018, 89, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitwieser, M.; Klingele, M.; Vierrath, S.; Zengerle, R.; Thiele, S. Tailoring the Membrane-Electrode Interface in PEM Fuel Cells: A Review and Perspective on Novel Engineering Approaches. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1701257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Zhao, C. In Situ and Operando Characterization of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1901900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, R.S.L.; Rozendal, R.A.; Zhang, K.; Ladewig, B.P. Cost effective cation exchange membranes: A review. Chem. Eng. Res. 2012, 90, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamrock, S.J.; Yandrasits, M.A. Proton Exchange Membranes for Fuel Cell Applications. J. Macromol. Sci. Part C Polym. Rev. 2006, 46, 219–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, G.K.H.; Taylor, J.M.; Kim, S. Proton Conduction with Metal-Organic Frameworks. Science 2013, 341, 354–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Otsubo, K.; Makiura, R.; Kitagawa, H. Designer coordination polymers: Dimensional crossover architectures and proton conduction. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6655–6669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaswamy, P.; Wong, N.E.; Shimizu, G.K.H. MOFs as proton conductors—Challenges and opportunities. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5913–5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tominaka, S.; Cheetham, A.K. Intrinsic and extrinsic proton conductivity in metal-organic frameworks. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 54382–54387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarkar, S.S.; Unni, S.M.; Sharma, A.; Kurungot, S.; Ghosh, S.K. Two-in-One: Inherent Anhydrous and Water-Assisted High Proton Conduction in a 3D Metal-Organic Framework. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 2638–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, P.Z.; Li, A.; Wiggin, S.B.; Tao, A.; Maloney, A.G.P.; Wood, P.A.; Ward, S.C.; Fairen-Jimenez, D. Development of a Cambridge Structural Database Subset: A Collection of Metal-Organic Frameworks for Past, Present, and Future. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 2618–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Wan, S.; Yang, J.; Kurmoo, M.; Zeng, M.-H. Recent advances in post-synthetic modification of metal–organic frameworks: New types and tandem reactions. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 378, 500–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, S.; Kitaura, R.; Noro, S. Functional porous coordination polymers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 2334–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferey, G. Hybrid porous solids: Past, present, future. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 191–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranchemontagne, D.J.; Mendoza-Cortés, J.L.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Secondary building units, nets and bonding in the chemistry of metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1257–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaja, A.U.; Trukhan, N.; Müller, U. Industrial applications of metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1284–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, H.; Cordova, K.E.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. The Chemistry and Applications of Metal-Organic Frameworks. Science 2013, 341, 1230444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietzel, P.D.C.; Morita, Y.; Blom, R.; Fjellvåg, H. An In Situ High-Temperature Single-Crystal Investigation of a Dehydrated Metal-Organic Framework Compound and Field-Induced Magnetization of One-Dimensional Metal-Oxygen Chains. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 6354–6358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosi, N.L.; Kim, J.; Eddaoudi, M.; Chen, B.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Rod Packings and Metal−Organic Frameworks Constructed from Rod-Shaped Secondary Building Units. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 1504–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmelik, C.; Mundstock, A.; Dietzel, P.D.C.; Caro, J. Idiosyncrasies of Co2(dhtp): In situ-annealing by methanol. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 183, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valvekens, P.; Vandichel, M.; Waroquier, M.; Van Speybroeck, V.; De Vos, D. Metal-dioxidoterephthalate MOFs of the MOF-74 type: Microporous basic catalysts with well-defined active sites. J. Catal. 2014, 317, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietzel, P.D.C.; Besikiotis, V.; Blom, R. Application of metal-organic frameworks with coordinatively unsaturated metal sites in storage and separation of methane and carbon dioxide. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 7362–7370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, I.; Mundstock, A.; Hinrichs, D.; Himstedt, R.; Knebel, A.; Reinhardt, C.; Dorfs, D.; Caro, J. The Interaction of Guest Molecules with Co-MOF-74: A Vis/NIR and Raman Approach. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 7434–7439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauss, I.; Mundstock, A.; Treger, M.; Lange, K.; Hwang, S.; Chmelik, C.; Rusch, P.; Bigall, N.C.; Pichler, T.; Shiozawa, H.; et al. Metal–Organic Framework Co-MOF-74-Based Host–Guest Composites for Resistive Gas Sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 14175–14181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Lee, E.J.; Song, D.; Jeong, N.C. High Proton Mobility with High Directionality in Isolated Channels of MOF-74. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 35354–35360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momma, K.; Izumi, F. VESTA 3 for three-dimensional visualization of crystal, volumetric and morphology data. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2011, 44, 1272–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, A.; Wagner, T.; Wöhlbrandt, S.; Stock, N.; Tiemann, M. Proton Conduction in a Single Crystal of a Phosphonato-Sulfonate-Based Coordination Polymer: Mechanistic Insight. ChemPhysChem 2020, 21, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonino, F.; Chavan, S.; Vitillo, J.G.; Groppo, E.; Agostini, G.; Lamberti, C.; Dietzel, P.D.C.; Prestipino, C.; Bordiga, S. Local Structure of CPO-27-Ni Metallorganic Framework upon Dehydration and Coordination of NO. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 4957–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zuhra, Z.; Qin, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tang, F.; Mu, C. Confinement of microporous MOF-74(Ni) within mesoporous γ-Al2O3 beads for excellent ultra-deep and selective adsorptive desulfurization performance. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 176, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietzel, P.D.C.; Johnsen, R.E.; Blom, R.; Fjellvåg, H. Structural Changes and Coordinatively Unsaturated Metal Atoms on Dehydration of Honeycomb Analogous Microporous Metal–Organic Frameworks. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 2389–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canivet, J.; Fateeva, A.; Guo, Y.; Coasne, B.; Farrusseng, D. Water adsorption in MOFs: Fundamentals and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5594–5617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øien-Ødegaard, S.; Shearer, G.C.; Wragg, D.S.; Lillerud, K.P. Pitfalls in metal–organic framework crystallography: Towards more accurate crystal structures. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4867–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, M.; Suh, K.; Kim, H.; Kim, Y.; Selvapalam, N.; Kim, K. High and Highly Anisotropic Proton Conductivity in Organic Molecular Porous Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 7870–7873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaka, S.; Henke, S.; Cheetham, A.K. Coordination polymers of alkali metal trithiocyanurates: Structure determinations and ionic conductivity measurements using single crystals. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2013, 15, 9400–9407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, S.H.; Chen, X.X.; Lu, J.; Fu, Z.H.; Li, Y.; Xu, G.; Zheng, F.K.; Guo, G.C. Highly Anisotropic and Water Molecule-Dependent Proton Conductivity in a 2D Homochiral Copper(II) Metal-Organic Framework. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 2321–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunzen, H.; Javed, A.; Klawinski, D.; Lamp, A.; Grzywa, M.; Kalytta-Mewes, A.; Tiemann, M.; von Nidda, H.-A.K.; Wagner, T.; Volkmer, D. Anisotropic Water-Mediated Proton Conductivity in Large Iron(II) Metal–Organic Framework Single Crystals for Proton-Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuer, K.-D. Proton Conductivity: Materials and Applications. Chem. Mater. 1996, 8, 610–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Javed, A.; Strauss, I.; Bunzen, H.; Caro, J.; Tiemann, M. Humidity-Mediated Anisotropic Proton Conductivity through the 1D Channels of Co-MOF-74. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10071263
Javed A, Strauss I, Bunzen H, Caro J, Tiemann M. Humidity-Mediated Anisotropic Proton Conductivity through the 1D Channels of Co-MOF-74. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(7):1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10071263
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaved, Ali, Ina Strauss, Hana Bunzen, Jürgen Caro, and Michael Tiemann. 2020. "Humidity-Mediated Anisotropic Proton Conductivity through the 1D Channels of Co-MOF-74" Nanomaterials 10, no. 7: 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10071263
APA StyleJaved, A., Strauss, I., Bunzen, H., Caro, J., & Tiemann, M. (2020). Humidity-Mediated Anisotropic Proton Conductivity through the 1D Channels of Co-MOF-74. Nanomaterials, 10(7), 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10071263






