Zn-Doped Calcium Copper Titanate Synthesized via Rapid Laser Sintering of Sol-Gel Derived Precursors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
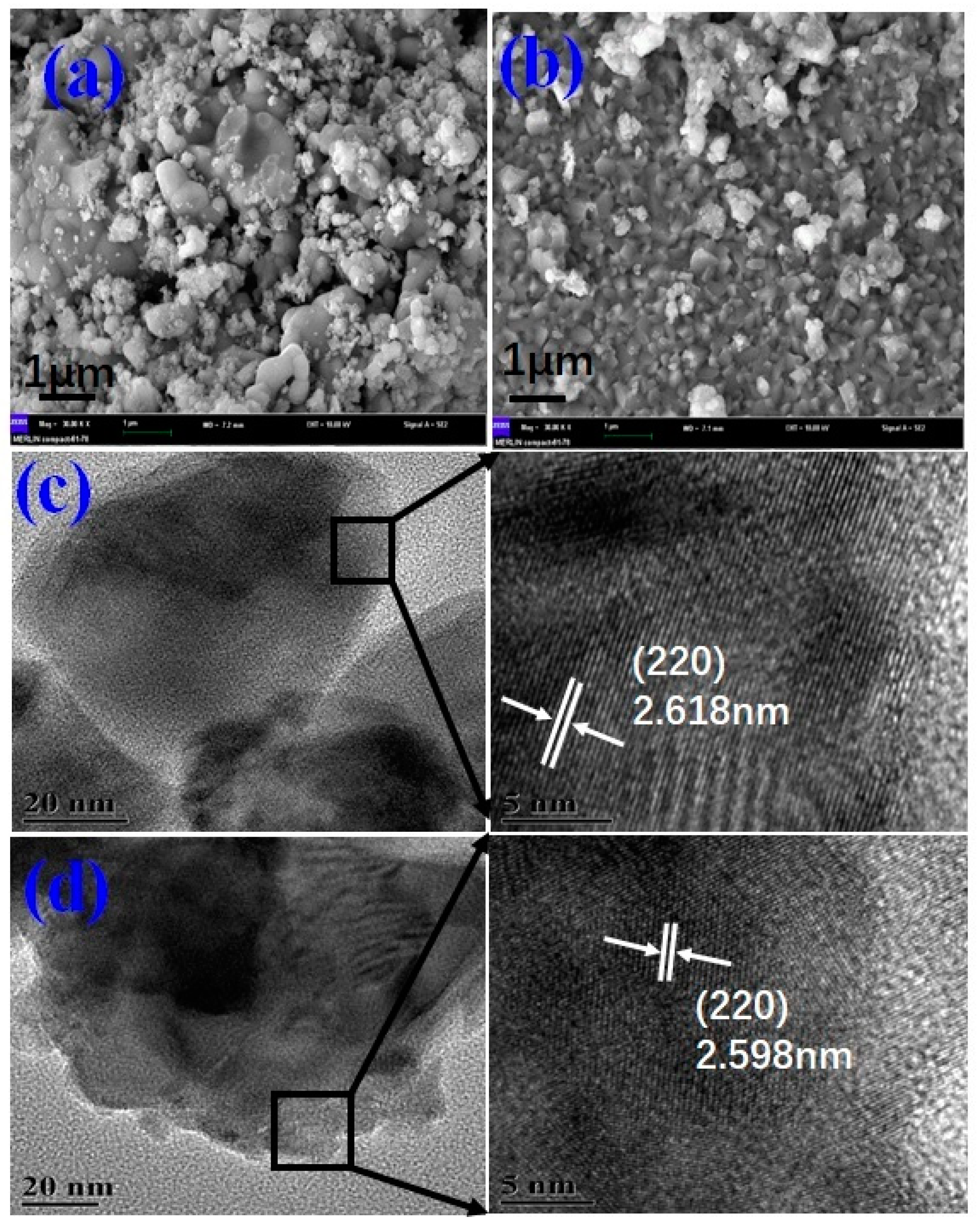
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmadipour, M.; Ain, M.F.; Ahmad, Z.A. A Short Review on Copper Calcium Titanate (CCTO) Electroceramic: Synthesis, Dielectric Properties, Film Deposition, and Sensing Application. Nano-Micro Lett. 2016, 8, 291–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irvine, J.T.S.; Sinclair, D.C.; West, A.R. Electroceramics: Characterization by Impedance Spectroscopy. Adv. Mater. 1990, 2, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-C.; Zhang, M.-N.; Xu, K.-B.; Wang, G.-J. Origin of High-Temperature Relaxor-Like Behavior in CaCu3Ti4O12. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 034109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashokbabu, A.; Thomas, P. Structural, thermal and dielectric behavior of Polyaryletherketone (PAEK)/CaCu3Ti4O12(CCTO). Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 25052–25059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Hao, W.; Lei, Z.; Tian, M. The dielectric properties of CCTO ceramics prepared via different quick quenching methods. Mater. Res. Bull. 2019, 115, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Yu, S.; Sun, R.; Du, R. Nano- and microsize effect of CCTO fillers on the dielectric behavior of CCTO/PVDF composites. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 5593–5602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, M.A.; Li, D.; Duan, N.; Reisner, B.A.; Sleight, A. High Dielectric Constant in ACu3Ti4O12 and ACu3Ti3FeO12 Phases. J. Solid State Chem. 2000, 151, 323–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, T.B.; Sinclair, D.C.; West, A.R. Giant Barrier Layer Capacitance Effects in CaCu3Ti4O12 Ceramics. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1321–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-W.; Koh, J.-H. Enhanced dielectric properties of Ag-doped CCTO ceramics for energy storage devices. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 9493–9497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, D.C.; Adams, T.B.; Morrison, F.D.; West, A.R. CaCu3Ti4O12: One-step internal barrier layer capacitor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 2153–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, T.; Alizadeh, A.P. Microstructure and dielectric properties of CCTO glass-ceramic prepared by the melt-quenching method. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 19316–19322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, T.B.; Sinclair, D.C.; West, A.R. Characterization of grain boundary impedances in fine- and coarse-grained CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 89, 3129–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Lin, X.; Li, J.; Fisher, J.G.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Cheng, X. Enhanced dielectric properties and discharged energy density of composite films using submicron PZT particles. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 15331–15337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, F.; Rivera, R.; Villamagua, L.; Maldonado, J. DFT modelling of ethanol on BaTiO3(001) surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 456, 276–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herle, J.V.; Vasquez, R. Conductivity of Mn and Ni-doped stabilized zirconia electrolyte. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 24, 1177–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Kumar, D.; Singh, R.K.; Venkataraman, H.; Eisenstadt, W.R. Improvement in electrical and dielectric behavior of (Ba, Sr) TiO3 thin films by Ag doping. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 61, 7305–7307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amhil, S.; Choukri, E.; Moumen, S.B.; Bourial, A.; Essaleh, L. Evidence of large hopping polaron conduction process in Strontium doped Calcium Copper Titanate ceramics. Phys. B: Condens. Matter 2019, 556, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.; Huang, C.; Patterson, E.A.; Cann, D.P.; Alberta, E.F.; Kwon, S.; Hackenberger, W.S.; Cann, D.P. The effect of Cr2O3, Nb2O5 and ZrO2 doping on the dielectric properties of CaCu3Ti4O12. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Meng, J.; Li, L. Non-Ohmic behavior of copper-rich CCTO thin film prepared through magnetron sputtering method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 9266–9272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Pu, Y.P.; Wu, H.D.; Chen, K.; Xu, N. Influence of sintering atmosphere on dielectric properties and microstructure of CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, S525–S528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, Y.L.; Young, H.K.; Kyoung, J.C.; Sung, M.J.; Sang, I.Y. Effect of copper-oxide segregation on the dielectric properties of CaCu3Ti4O12 thin films fabricated by pulsed-laser deposition. Thin Solid Films 2010, 518, 5711–5714. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.Q.; Kim, H.E. Microstructure and electrical properties of sol–gel derived Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)0.7Ti0.3O3 thin films with single perovskite phase. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 41, 6768–6772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.L.; Wu, A.Y.; Yin, S.T. Structure, Properties, and Impedance Spectroscopy of CaCu3Ti4O12 Ceramics Prepared by Sol–Gel Process. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 91, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.; Stennett, M.C.; Hyatt, N.C.; Pokorny, J.; Prado-Gonjal, J.; Li, M.; Sinclair, D.C. Effects of sintering temperature on the internal barrier layer capacitor (IBLC) structure in CaCu3Ti4O12 (CCTO) ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 32, 3313–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valim, D.; Souza Filho, A.G.; Freire, P.T.C.; Fagan, S.B.; Ayala, A.P.; Mendes Filho, J.; Almeida, A.F.L.; Fechine, P.B.A.; Sombra, A.S.B.; Staun Olsen, J.; et al. Raman scattering and x-ray diffraction studies of polycrystalline CaCu3Ti4O12 under high-pressure. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 70, 132103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhouma, S.; SaÎd, S.; Autret, C.; de Almeida-Didry, S.; Amrani, M.E.I.; Megriche, A. Comparative studies of pure, Sr-doped, Ni-doped and co-doped CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics: Enhancement of dielectric properties. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 717, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolev, N.; Bontchev, R.P.; Jacobson, A.J.; Popov, V.N.; Hadjiev, V.G.; Litvinchuk, A.P.; Iliev, M.N. Raman spectroscopy of CaCu3Ti4O12. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 66, 132102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, P.R.; Tararan, R.; Parra, R.; Joanni, E.; Ramirez, M.A.; Ribeiro, W.C.; Longo, E.; Varela, J. A polaronic stacking fault defect model for CaCu3Ti4O12 material: An approach for the origin of the huge dielectric constant and semiconducting coexistent features. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 055404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Lai, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, S.; Huang, Z.; Han, J. Influence of sintering conditions on microstructure and electrical properties of CaCu3Ti4O12 (CCTO) ceramics. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 650, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Xue, F.; Guo, P.; Luo, Z.; Xin, Z.; Li, W. Multiferroic properties of BiFeO3–Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3 solid solution. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 9435–9441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongbai, P.; Meeporn, K.; Yamwong, T.; Maensiri, S. Extreme Effects of Na Doping on Microstructure, Giant Dielectric Response and Dielectric Relaxation Behavior in CaCu3Ti4O12 Ceramics. Mater. Lett. 2013, 106, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senda, S.; Rhouma, S.; Torkani, E.; Mefriche, A.; Autret, C. Effect of nickel substitution on electrical and microstructural properties of CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramic. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 698, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida-Didry, S.; Nomel, M.M.; Autret, C.; Honstettre, C.; Lucas, A.; Pacreau, F.; Gervais, F. Control of grain boundary in alumina doped CCTO showing colossal permittivity by core-shell approach. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 38, 3182–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dela Rubia, M.A.; Leret, P.; del Campo, A.; Alonso, R.E.; López-Garcia, A.R.; Fernández, J.F.; de Frutos, J. Dielectric behaviour of Hf-doped CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics obtained by conventional synthesis and reactive sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 32, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, X.; Fan, Y.; Yang, T.; Yuan, H. Dielectric Properties of Zn-Doped CCTO Ceramics by Sol-Gel Method. Adv. Mater. Res. Vols. 2011, 197, 302–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.; Rai, U.S.; Mandal, K.D.; Sin, B.C.; Lee, S.I.; Lee, Y. Dielectric, AC-impedance, modulus studies on 0.5BaTiO3 0.5CaCu3Ti4O12 nano-composite ceramic synthesized by one-pot, glycine-assisted nitrate-gel route. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 10073–10083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadipour, M.; Cheah, W.K.; Ain, M.F.; Rao, K.V.; Ahmad, Z.A. Effects of deposition temperatures and substrates on microstructure and optical properties of sputtered CCTO thin film. Mater. Lett. 2018, 210, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, W.; Płocharski, J.; Przyłuski, J.; Głowinkowski, S.; Pajak, Z. Impedance spectroscopy and phase structure of PEO NaI complexes. Solid State Ion. 1998, 28, 1014–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, O.K.; Malhotra, L.K. Studies of ambient dependent electrical behavior of nanocrystalline SnO2 thin films using impedance spectroscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 7457–7465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao-Yu, G.; Ji, Z.; Rui-Xue, W.; Xian-Zhu, D.; Lei, S.; Zheng-bin, G.; Shan-Tao, Z. ZnO-enhanced electrical properties of Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3-based incipient ferroelectrics. J. Am. Ceram. 2017, 100, 5659–5667. [Google Scholar]


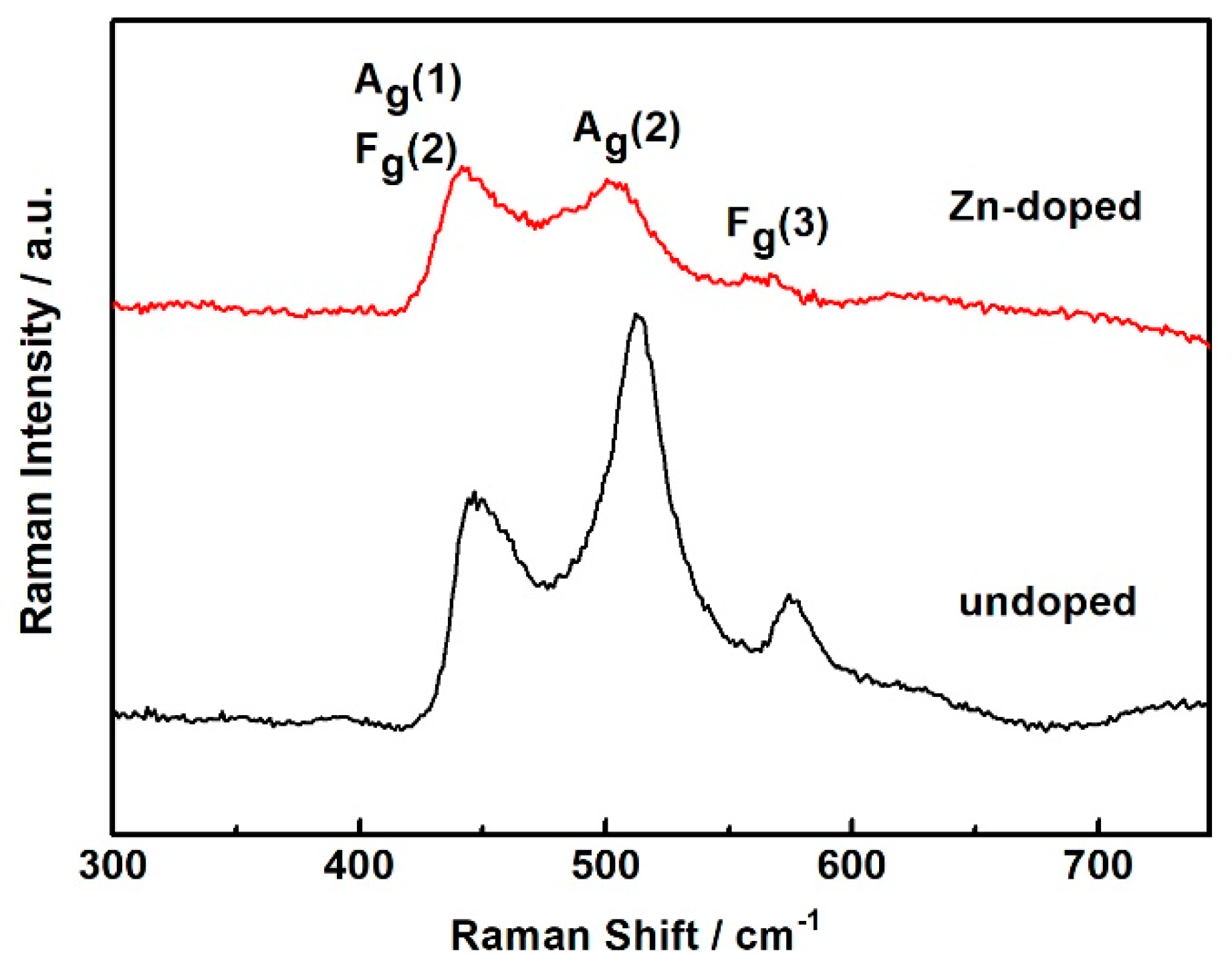
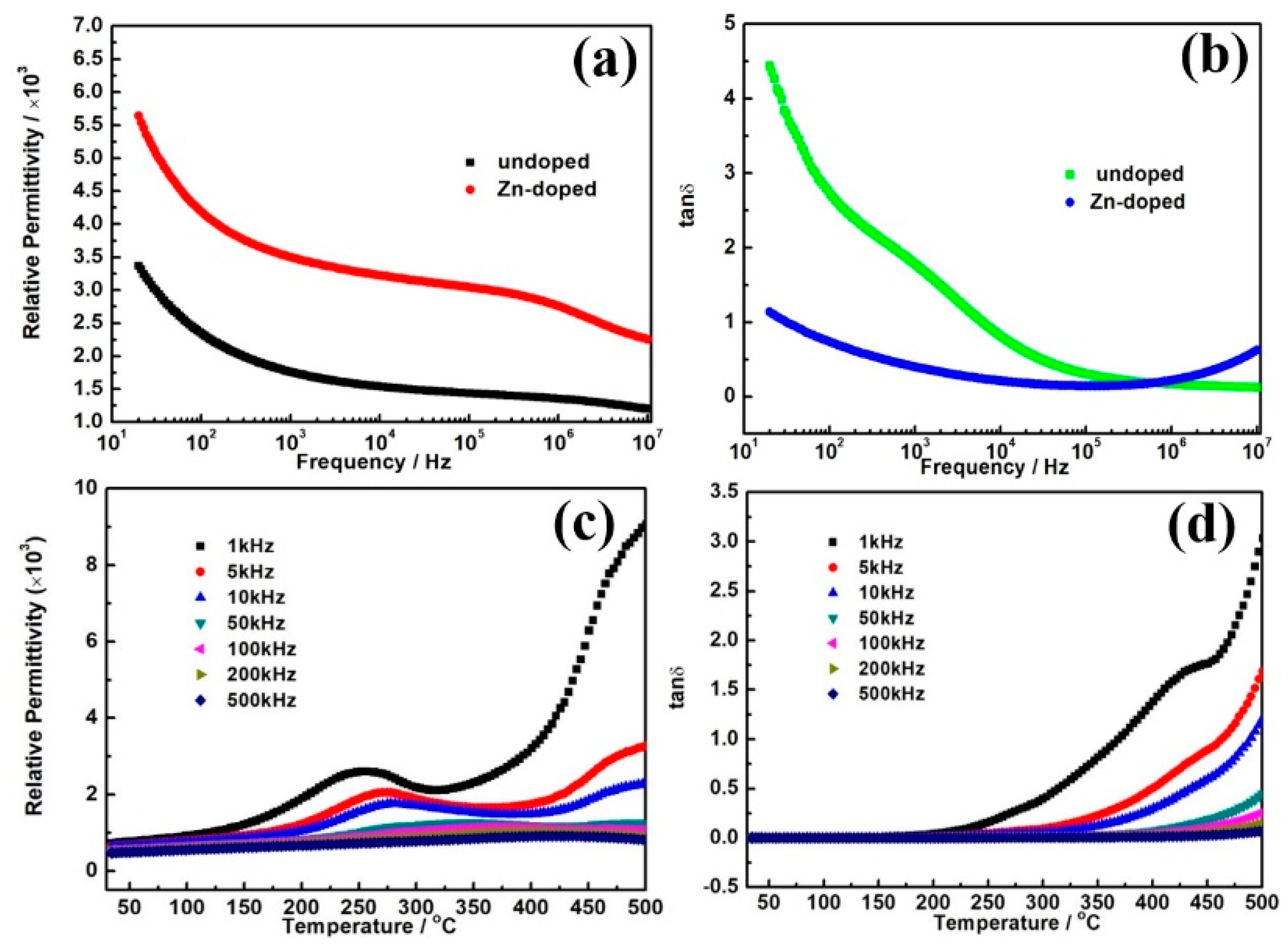
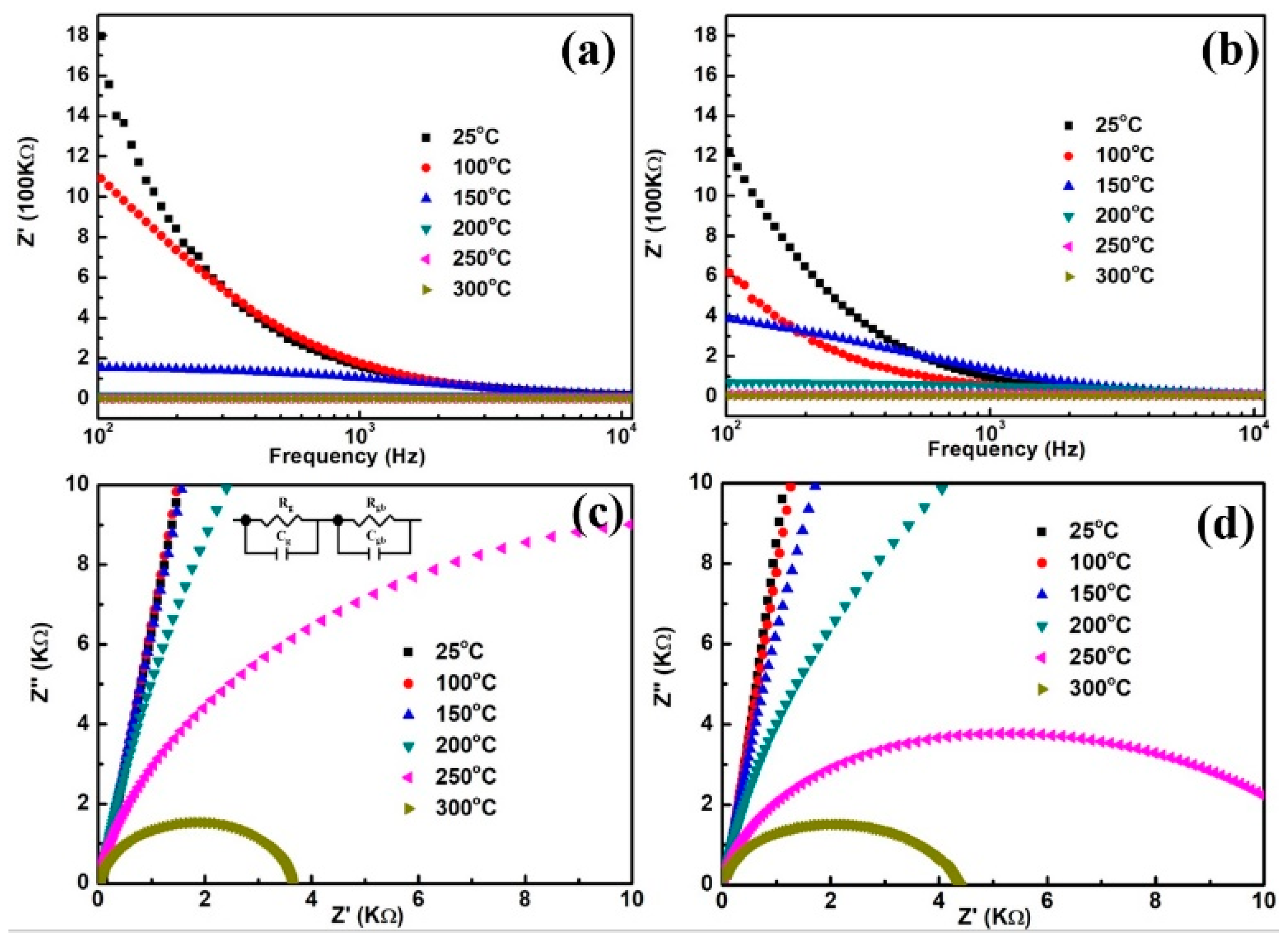
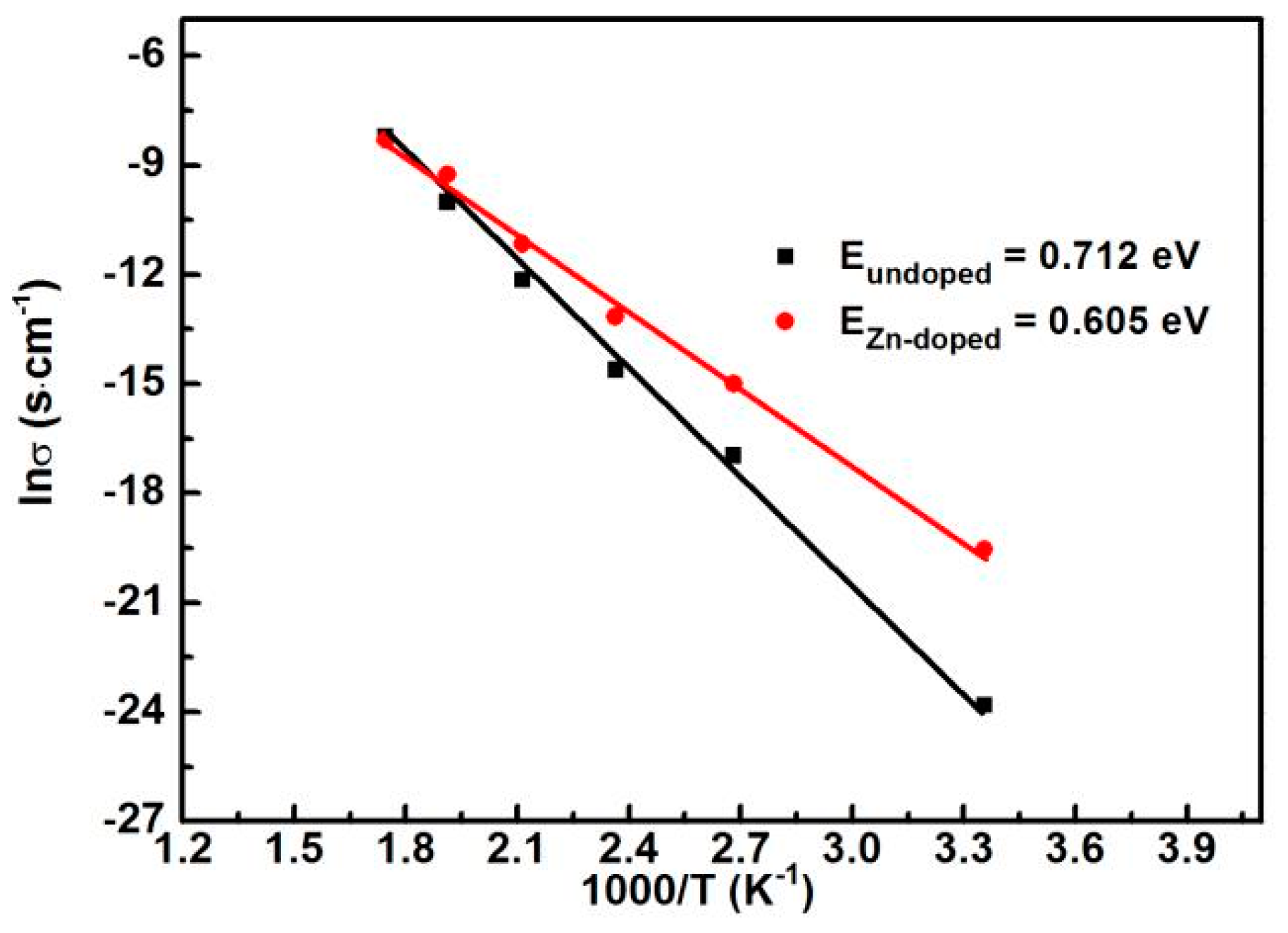
| Temperature (°C) | Undoped | Zn-Doped | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rg (Ω) | Rgb (Ω) | Rg (Ω) | Rgb (Ω) | |
| 25 | 906.7 | 8,998,000,000 | 837.4 | 312,700,000 |
| 100 | 422.7 | 23,223,000 | 406.9 | 3,288,100 |
| 150 | 223.8 | 2,225,400 | 276.2 | 512,790 |
| 200 | 105.9 | 188,050 | 102.2 | 70,520 |
| 250 | 90.5 | 22,282 | 50.6 | 10,454 |
| 300 | 50.0 | 3660 | 40.2 | 4076 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Li, Y.; He, J.; Zeng, H. Zn-Doped Calcium Copper Titanate Synthesized via Rapid Laser Sintering of Sol-Gel Derived Precursors. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061163
Huang Y, Qiao Y, Li Y, He J, Zeng H. Zn-Doped Calcium Copper Titanate Synthesized via Rapid Laser Sintering of Sol-Gel Derived Precursors. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(6):1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061163
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yanwei, Yu Qiao, Yangyang Li, Jiayang He, and Heping Zeng. 2020. "Zn-Doped Calcium Copper Titanate Synthesized via Rapid Laser Sintering of Sol-Gel Derived Precursors" Nanomaterials 10, no. 6: 1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061163
APA StyleHuang, Y., Qiao, Y., Li, Y., He, J., & Zeng, H. (2020). Zn-Doped Calcium Copper Titanate Synthesized via Rapid Laser Sintering of Sol-Gel Derived Precursors. Nanomaterials, 10(6), 1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061163





