Calligraphed Selective Plasmonic Arrays on Paper Platforms for Complementary Dual Optical “ON/OFF Switch” Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis of Anisotropic Gold Nanoparticles in Aqueous Solution
2.3. Preparation of the Calligraphed Plasmonic Paper Platforms
2.4. Preparation of Charged Isolated Plasmonic Lines
2.5. Characterization Techniques
3. Results
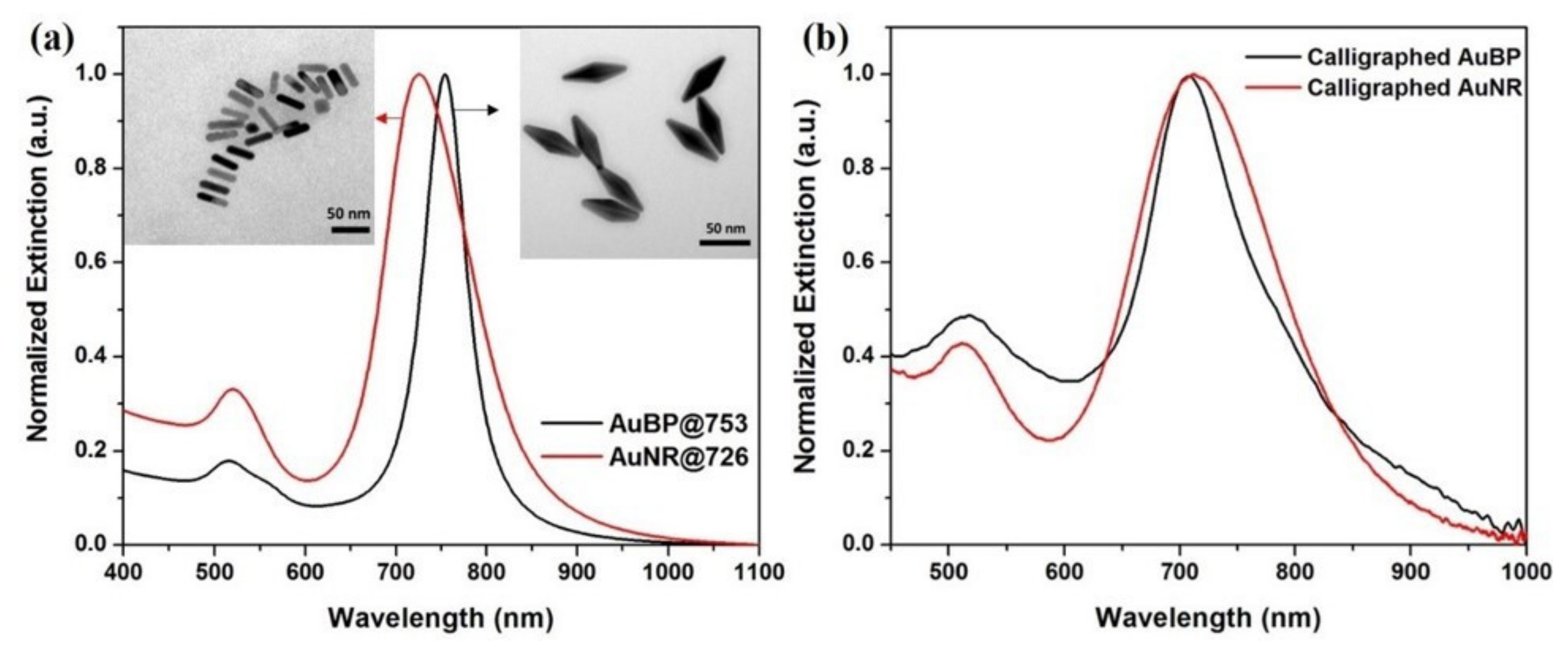
3.1. Optical/Morphological Characterization of the Colloidal and Calligraphed Anisotropic Nanoparticles
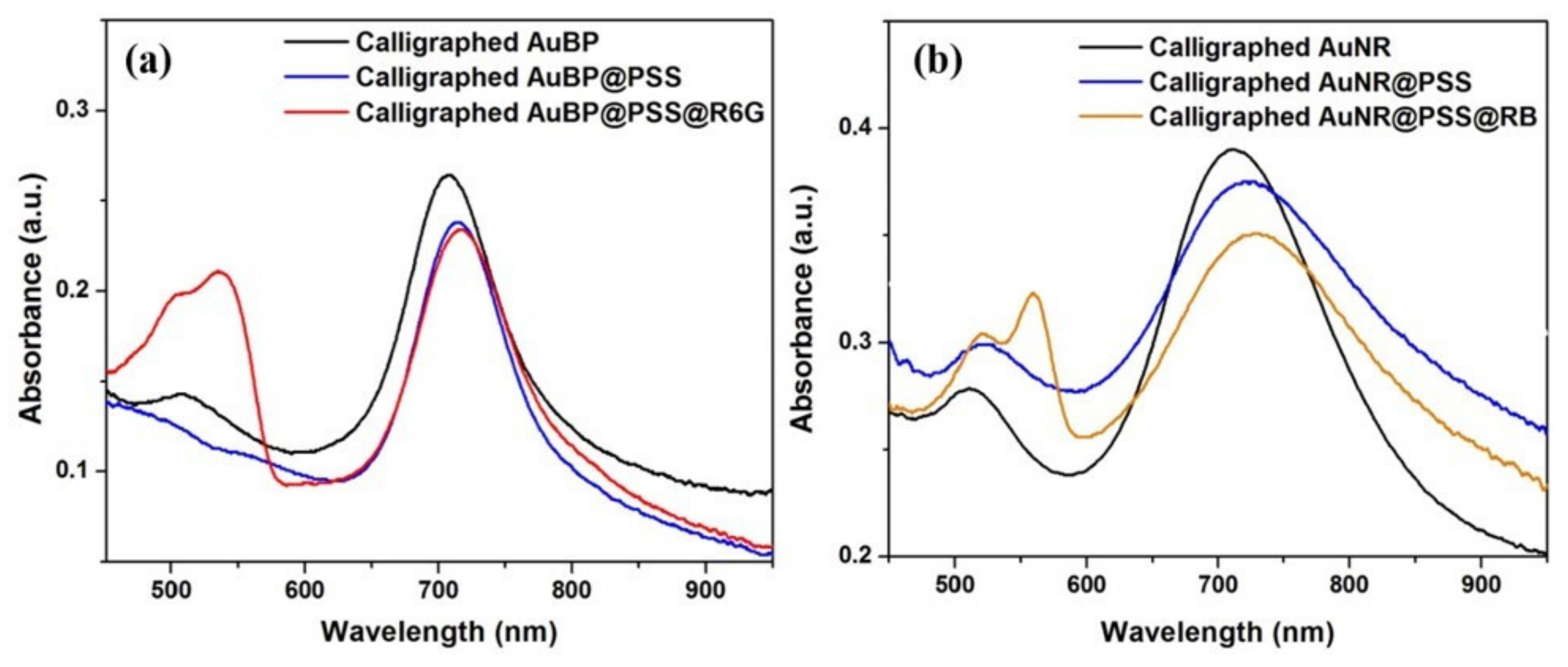
3.2. Bulk LSPR Sensing Performance of the Calligraphed Anisotropic Nanoparticles
3.3. Calligraphed Plasmonic Array as Multiplex LSPR Charge-Selective Detection Scheme
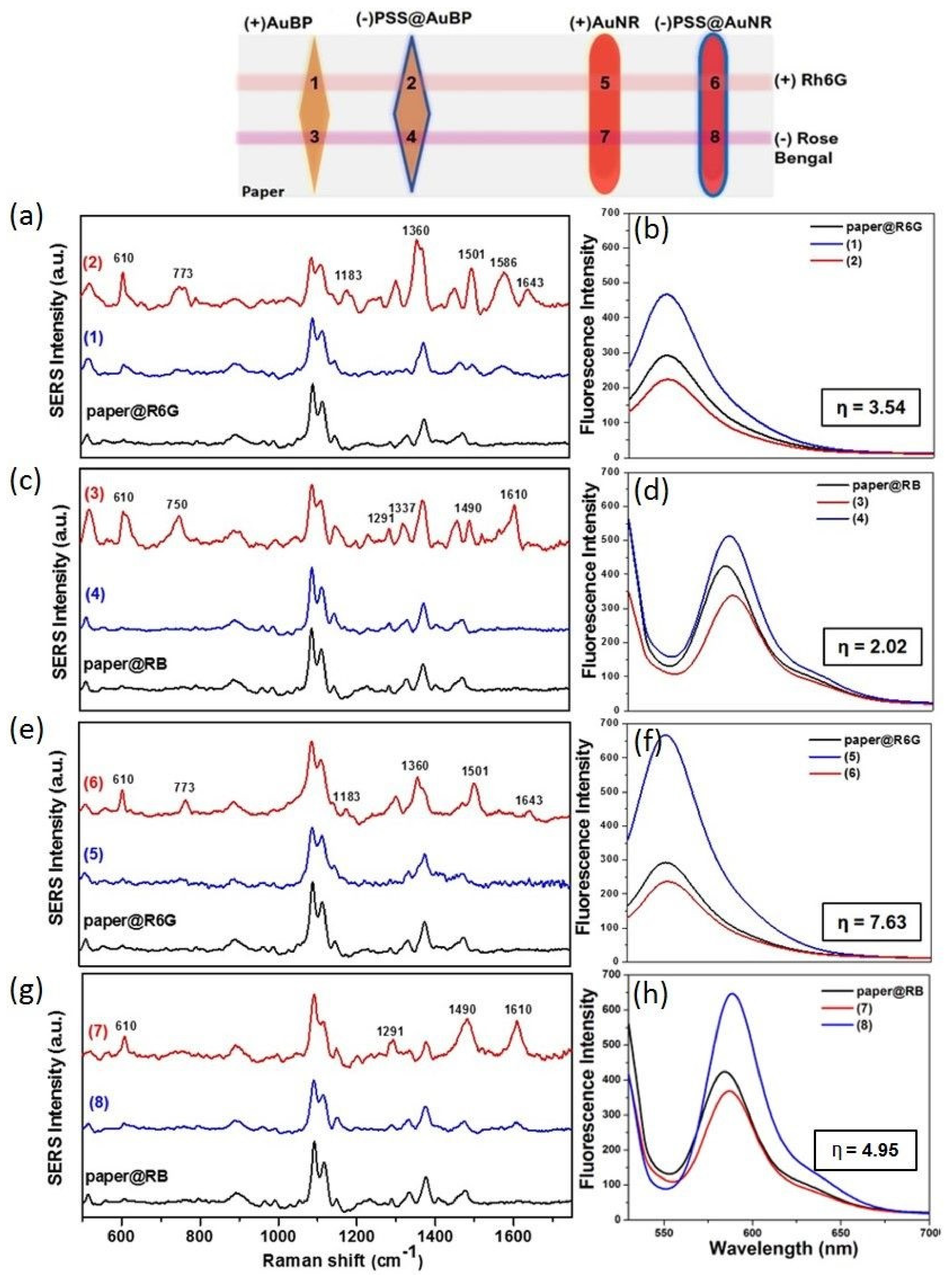
3.4. Dual SERS-MEF “On/Off Switch” Sensing
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nam, J.-M.; Thaxton, C.S.; Mirkin, C.A. Nanoparticle-Based Bio-Bar Codes for the Ultrasensitive Detection of Proteins. Science 2003, 301, 1884–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Luo, W.; Wang, Z.; Guo, X.; Steigerwald, M.L.; Fang, X. Single-Molecule Detection of Proteins Using Aptamer-Functionalized Molecular Electronic Devices. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 2496–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, R.G.; Grabar, K.C.; Allison, K.J.; Bright, R.M.; Davis, J.A.; Guthrie, A.P.; Hommer, M.B.; Jackson, M.A.; Smith, P.C.; Walter, D.G.; et al. Self-Assembled Metal Colloid Monolayers: An Approach to SERS Substrates. Science 1995, 267, 1629–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente, A.T.; Araújo, A.; Mendes, M.J.; Nunes, D.; Oliveira, M.J.; Sanchez-Sobrado, O.; Ferreira, M.P.; Águas, H.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R. Multifunctional cellulose-paper for light harvesting and smart sensing applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 3143–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, H.; Bae, S.H.; Cao, S.; Wang, Z.; Raman, B.; Singamaneni, S. Gold-Nanorod-Based Plasmonic Nose for Analysis of Chemical Mixtures. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 3897–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosier-Boss, P.A. Review of SERS Substrates for Chemical Sensing. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.; Cardinal, M.F.; Kleinman, S.L.; Greeneltch, N.G.; Frontiera, R.R.; Blaber, M.G.; Schatz, G.C.; Duyne, R.P.V. High-performance SERS substrates: Advances and challenges. MRS Bull. 2013, 38, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.H.; Lee, J.U.; Song, S.; Kim, S.; Choi, Y.J.; Sim, S.J. A label-free, ultra-highly sensitive and multiplexed SERS nanoplasmonic biosensor for miRNA detection using a head-flocked gold nanopillar. Analyst 2019, 144, 1768–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.; Kook, Y.-M.; Lee, K.; Koh, W.-G. Metal enhanced fluorescence (MEF) for biosensors: General approaches and a review of recent developments. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 111, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chance, R.R.; Prock, A.; Silbey, R. Comments on the classical theory of energy transfer. J. Chem. Phys. 1975, 62, 2245–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordes, T.; Moerner, W.; Orrit, M.; Needham, L.-M.; Sekatskii, S.; Faez, S.; Goswami, H.P.; Clark, A.; Meixner, A.J.; Piatkowski, L.; et al. Superresolution techniques, biophysics with nanostructures, and fluorescence energy transfer: General discussion. Faraday Discuss. 2015, 184, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakowicz, J.R.; Ray, K.; Chowdhury, M.; Szmacinski, H.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Nowaczyk, K. Plasmon-controlled fluorescence: A new paradigm in fluorescence spectroscopy. Analyst 2008, 133, 1308–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Kim, S.; Nam, J.-M. Plasmonically Engineered Nanoprobes for Biomedical Applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 14509–14525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campu, A.; Lerouge, F.; Chateau, D.; Chaput, F.; Baldeck, P.; Parola, S.; Maniu, D.; Craciun, A.M.; Vulpoi, A.; Astilean, S.; et al. Gold NanoBipyramids Performing as Highly Sensitive Dual-Modal Optical Immunosensors. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 8567–8575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardehkhorram, R.; Bonaccorsi, S.; Zhu, H.; Gonçales, V.R.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Lee, N.A.; Tilley, R.D.; Gooding, J.J. Intrinsic and well-defined second generation hot spots in gold nanobipyramids versus gold nanorods. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 7707–7710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabudean, A.M.; Focsan, M.; Astilean, S. Gold Nanorods Performing as Dual-Modal Nanoprobes via Metal-Enhanced Fluorescence (MEF) and Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS). J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 12240–12249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fothergill, S.M.; Joyce, C.; Xie, F. Metal enhanced fluorescence biosensing: From ultra-violet towards second near-infrared window. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 20914–20929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.-W.; Qiao, S.; Pan, J.-B.; Kang, B.; Xu, J.-J.; Chen, H.-Y. A paper-based SERS test strip for quantitative detection of Mucin-1 in whole blood. Talanta 2018, 179, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez, S.; Morales-Narváez, E. Nanoplasmonics in Paper-Based Analytical Devices. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nery, E.W.; Kubota, L.T. Sensing approaches on paper-based devices: A review. Anal Bioanal Chem 2013, 405, 7573–7595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petryayeva, E.; Algar, W.R. Proteolytic Assays on Quantum-Dot-Modified Paper Substrates Using Simple Optical Readout Platforms. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 8817–8825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogundare, S.A.; van Zyl, W.E. A review of cellulose-based substrates for SERS: Fundamentals, design principles, applications. Cellulose 2019, 26, 6489–6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.T.; Lantigua, D.; Meka, A.; Taing, S.; Pandher, M.; Camci-Unal, G. Paper-Based Sensors: Emerging Themes and Applications. Sensors 2018, 18, 2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parolo, C.; Merkoçi, A. Paper-based nanobiosensors for diagnostics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 42, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susu, L.; Campu, A.; Craciun, A.M.; Vulpoi, A.; Astilean, S.; Focsan, M. Designing Efficient Low-Cost Paper-Based Sensing Plasmonic Nanoplatforms. Sensors 2018, 18, 3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Tadepalli, S.; Hyun Park, S.; Liu, K.-K.; Morrissey, J.J.; Kharasch, E.D.; Naik, R.R.; Singamaneni, S. Bioplasmonic calligraphy for multiplexed label-free biodetection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 59, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campu, A.; Susu, L.; Orzan, F.; Maniu, D.; Craciun, A.M.; Vulpoi, A.; Roiban, L.; Focsan, M.; Astilean, S. Multimodal Biosensing on Paper-Based Platform Fabricated by Plasmonic Calligraphy Using Gold Nanobypiramids Ink. Front. Chem. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoobakht, B.; El-Sayed, M.A. Preparation and Growth Mechanism of Gold Nanorods (NRs) Using Seed-Mediated Growth Method. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 1957–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, J.R.G.; Manchon, D.; Lerouge, F.; Cottancin, E.; Lermé, J.; Bonnet, C.; Chaput, F.; Mosset, A.; Pellarin, M.; Parola, S. Synthesis, electron tomography and single-particle optical response of twisted gold nano-bipyramids. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 145707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Guyot-Sionnest, P. Mechanism of Silver(I)-Assisted Growth of Gold Nanorods and Bipyramids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 22192–22200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Hankus, M.E.; Tian, L.; Pellegrino, P.M.; Singamaneni, S. Plasmonic paper as a highly efficient SERS substrate. In Proceedings of the Chemical, Biological, Radiological, Nuclear, and Explosives (CBRNE) Sensing XIII, International Society for Optics and Photonics, Baltimore, MD, USA, 24–27 April 2012; Volume 8358, p. 835815. [Google Scholar]
- Azizi Samir, M.A.S.; Alloin, F.; Dufresne, A. Review of Recent Research into Cellulosic Whiskers, Their Properties and Their Application in Nanocomposite Field. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, J.; Trügler, A.; Jakab, A.; Hohenester, U.; Sönnichsen, C. The Optimal Aspect Ratio of Gold Nanorods for Plasmonic Bio-sensing. Plasmonics 2010, 5, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; She, Z.; Su, H.; Kerman, K.; Kraatz, H.-B. Effects of bipyramidal gold nanoparticles and gold nanorods on the detection of immunoglobulins. Analyst 2016, 141, 6080–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.N.; Gao, Y.; Mahjouri-Samani, M.; Black, P.N.; Allen, J.; Mitchell, M.; Xiong, W.; Zhou, Y.S.; Jiang, L.; Lu, Y.F. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy using gold-coated horizontally aligned carbon nanotubes. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 205702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.S.; Yang, M. Sensitive and Reproducible Gold SERS Sensor Based on Interference Lithography and Electrophoretic Deposition. Sensors 2018, 18, 4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Pilar Rodríguez-Torres, M.; Díaz-Torres, L.A.; Romero-Servin, S. Heparin Assisted Photochemical Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles and Their Performance as SERS Substrates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 19239–19252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhuo, X.; Li, S.; Ruan, Q.; Xu, Q.-H.; Wang, J. Production of Monodisperse Gold Nanobipyramids with Number Percentages Approaching 100% and Evaluation of Their Plasmonic Properties. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2015, 3, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Analyte | SERS Signal (cm−1) | Band Assignment |
|---|---|---|
| R6G | 610 773 1183 1360 1501 1586 1643 | C–C–C ring in-plane vibration C–H out-of-plane bending C–H and N–H bending of xanthenes ring aromatic C–C stretching aromatic C–C stretching aromatic C–C stretching aromatic C–C stretching |
| RB | 610 750 1291 1337 1490 1547 1612 | C–C–C ring in-plane vibration C-Cl stretching CCC deformation in ring and C–H deformation C–C stretching in ring C=C asymmetric stretching in ring C–C stretching in ring C=C symmetric stretching in ring |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Susu, L.; Campu, A.; Astilean, S.; Focsan, M. Calligraphed Selective Plasmonic Arrays on Paper Platforms for Complementary Dual Optical “ON/OFF Switch” Sensing. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061025
Susu L, Campu A, Astilean S, Focsan M. Calligraphed Selective Plasmonic Arrays on Paper Platforms for Complementary Dual Optical “ON/OFF Switch” Sensing. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(6):1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061025
Chicago/Turabian StyleSusu, Laurentiu, Andreea Campu, Simion Astilean, and Monica Focsan. 2020. "Calligraphed Selective Plasmonic Arrays on Paper Platforms for Complementary Dual Optical “ON/OFF Switch” Sensing" Nanomaterials 10, no. 6: 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061025
APA StyleSusu, L., Campu, A., Astilean, S., & Focsan, M. (2020). Calligraphed Selective Plasmonic Arrays on Paper Platforms for Complementary Dual Optical “ON/OFF Switch” Sensing. Nanomaterials, 10(6), 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061025







