Electrokinetically-Driven Assembly of Gold Colloids into Nanostructures for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Gold Nanoparticle Preparation
2.3. Conductivity Experiments
2.4. Microchip Fabrication
2.5. Chip Modification and Nanoparticle Deposition
2.6. Surface Characterization
2.7. Biotin-Streptavidin Assay
2.8. Chemical Detection: Dropcasting
2.9. Raman Measurements and Spectral Processing
2.10. COMSOL Simulation
3. Results
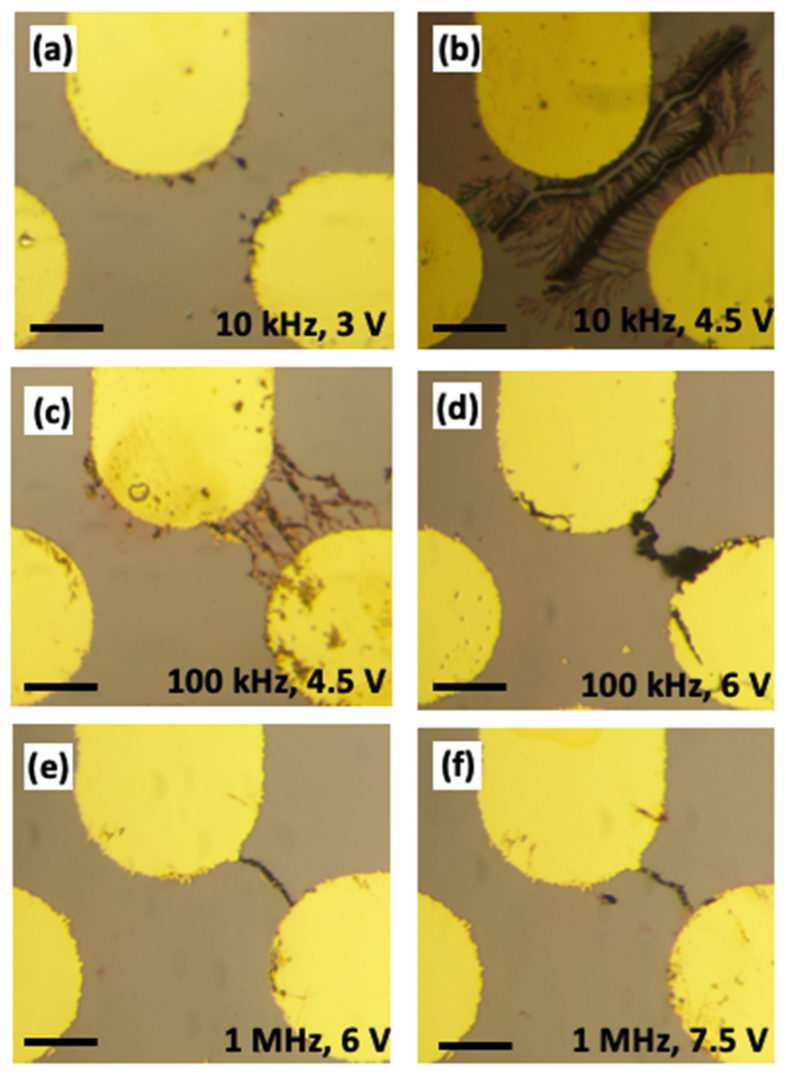
3.1. The Effect of AC Frequency on Gold Nanostructure Assembly
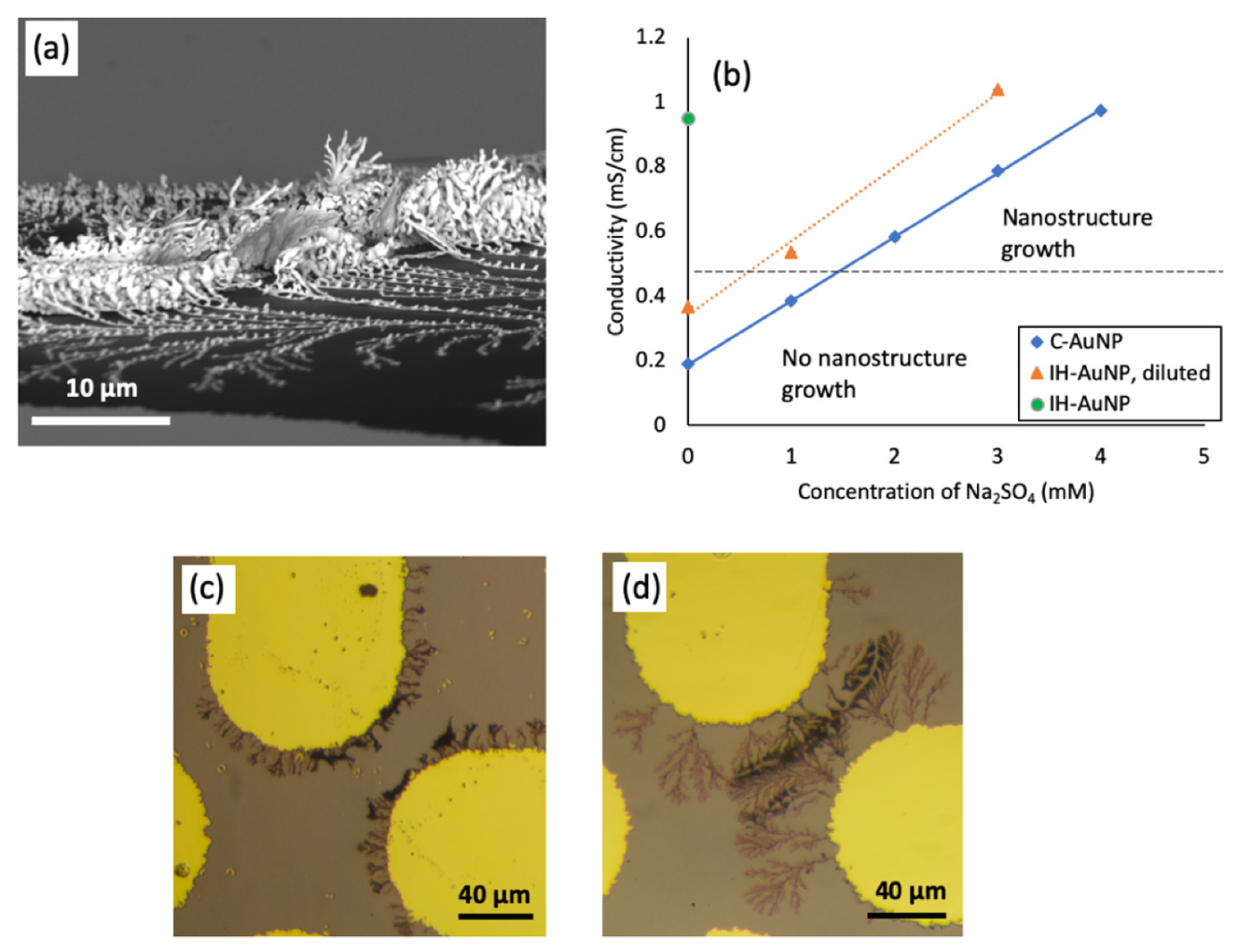
3.2. The Effect of Medium Conductivity on Nanostructure Assembly
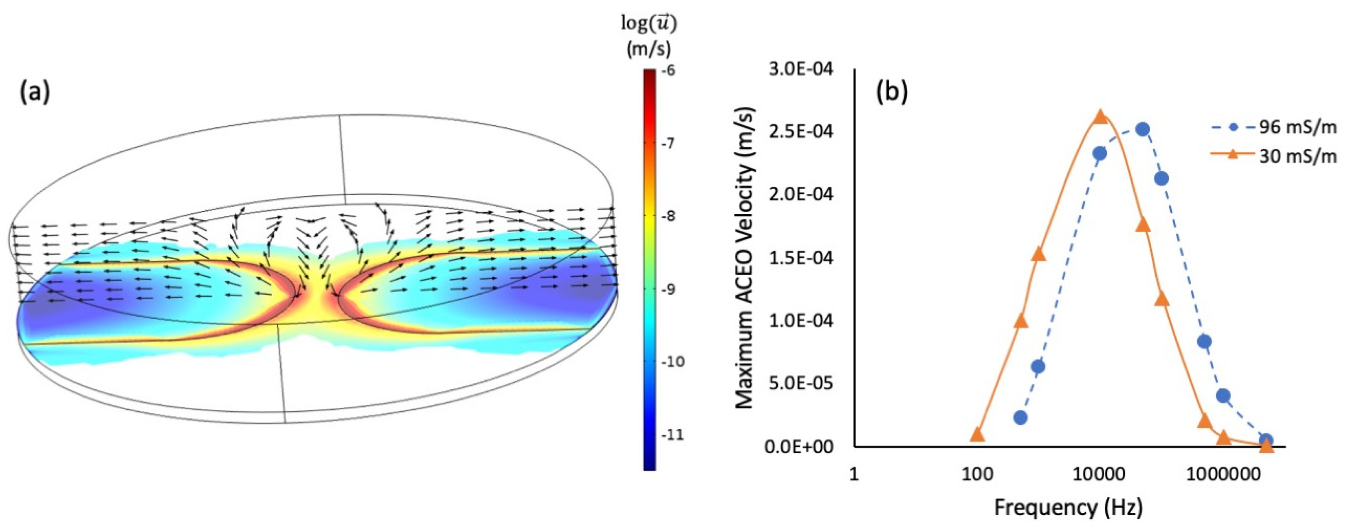
3.3. Simulation and Discussion of the Phenomenon of Nanostructure Growth
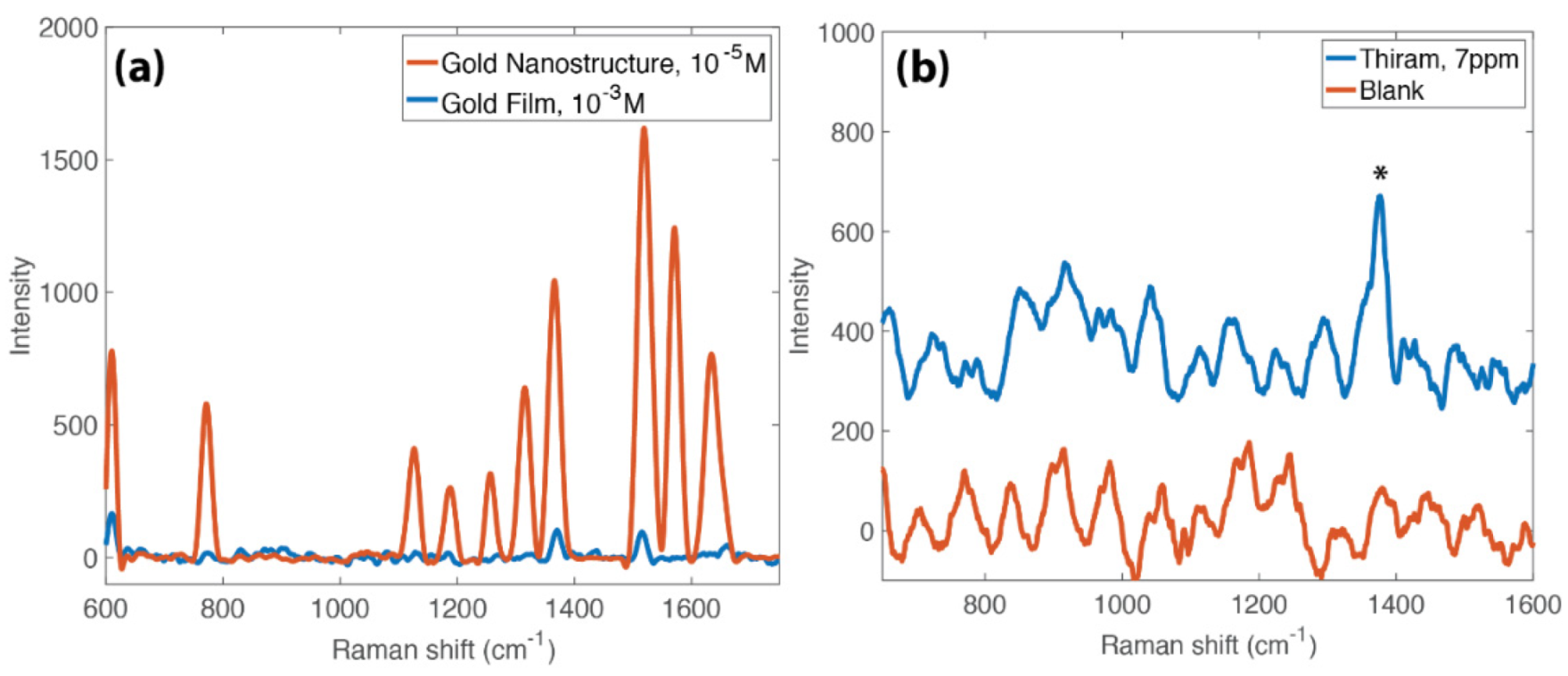
3.4. SERS Activity of the Nanostructures
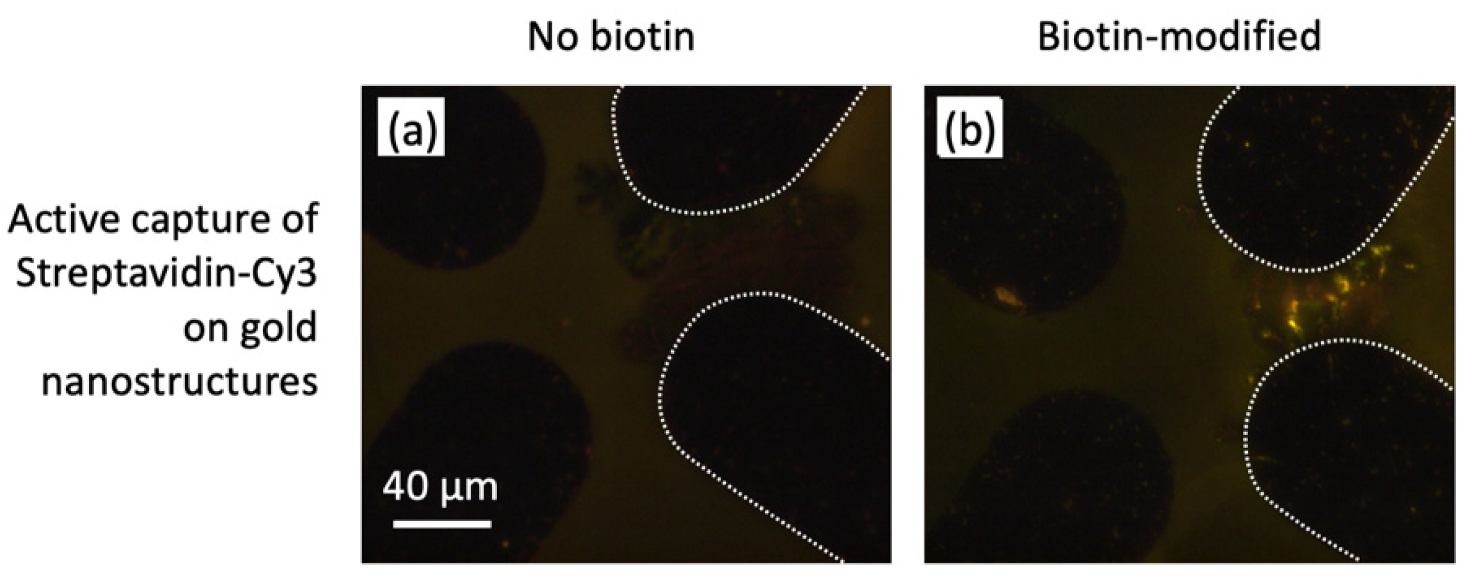
3.5. Nanostructure Functionalization
3.6. Concentration Amplification Effect
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, E.; Dent, G. Modern Raman Spectroscopy—A Practical Approach; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: West Sussex, UK, 2005; ISBN 9780471497943. [Google Scholar]
- Bantz, K.C.; Meyer, A.F.; Wittenberg, N.J.; Im, H.; Kurtuluş, O.; Lee, S.H.; Lindquist, N.C.; Oh, S.-H.; Haynes, C.L. Recent progress in SERS biosensing. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 11551–11567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.-Y.; Yi, J.; Li, J.-F.; Ren, B.; Wu, D.-Y.; Panneerselvam, R.; Tian, Z.-Q. Nanostructure-based plasmon-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for surface analysis of materials. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Andrade, G.F.S.; Brolo, A.G. A review on the fabrication of substrates for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy and their applications in analytical chemistry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 693, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dies, H.; Raveendran, J.; Escobedo, C.; Docoslis, A. In situ assembly of active surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates via electric field-guided growth of dendritic nanoparticle structures. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 7847–7857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dies, H.; Siampani, M.; Escobedo, C.; Docoslis, A.; Dies, H.; Siampani, M.; Escobedo, C.; Docoslis, A. Direct Detection of Toxic Contaminants in Minimally Processed Food Products Using Dendritic Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Substrates. Sensors 2018, 18, 2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dies, H.; Raveendran, J.; Escobedo, C.; Docoslis, A. Rapid identification and quantification of illicit drugs on nanodendritic surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 257, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, M.; Han, Y.; Stanley, S.K.; Stafford, C.M.; Du, H.; Sukhishvili, S. SERS not to Be Taken for Granted in the Presence of Oxygen. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 7480–7481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyagi, Y.; Kajikawa, K. Optical Properties of Advanced Materials; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; ISBN 9783642335273. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, N.H.; Lee, S.J.; Moskovits, M. Aptamer-Mediated Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Intensity Amplification. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 4181–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, K.H.; Velev, O.D. Control and Modeling of the Dielectrophoretic Assembly of On-Chip Nanoparticle Wires. Langmuir 2004, 20, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Busnaina, A.; Selvarasah, S.; Somu, S.; Wei, M.; Mead, J.; Chen, C.L.; Aceros, J.; Makaram, P.; Dokmeci, M.R. Directed assembly of gold nanoparticle nanowires and networks for nanodevices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.J.; Andrews, M.K.; Marlow, B.K. Chaining and dendrite formation of gold particles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 130–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretschmer, R.; Fritzsche, W. Pearl Chain Formation of Nanoparticles in Microelectrode Gaps by Dielectrophoresis. Langmuir 2004, 20, 11797–11801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherukulappurath, S.; Lee, S.H.; Campos, A.; Haynes, C.L.; Oh, S.-H. Rapid and Sensitive in Situ SERS Detection Using Dielectrophoresis. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.W.; White, I.M. Inkjet printed surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy array on cellulose paper. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 9626–9630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, M.J.; Quaresma, P.; Peixoto de Almeida, M.; Araújo, A.; Pereira, E.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R.; Franco, R.; Águas, H. Office paper decorated with silver nanostars—An alternative cost effective platform for trace analyte detection by SERS. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, D.-K.; Jeon, K.-S.; Hwang, J.-H.; Kim, H.; Kwon, S.; Suh, Y.D.; Nam, J.-M. Highly uniform and reproducible surface-enhanced Raman scattering from DNA-tailorable nanoparticles with 1-nm interior gap. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuithschick, M.; Birnbaum, A.; Witte, S.; Sztucki, M.; Vainio, U.; Pinna, N.; Rademann, K.; Emmerling, F.; Kraehnert, R.; Polte, J. Turkevich in New Robes: Key Questions Answered for the Most Common Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7052–7071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, N.G.; Ramos, A.; González, A.; Morgan, H.; Castellanos, A. Fluid flow induced by nonuniform ac electric fields in electrolytes on microelectrodes. III. Observation of streamlines and numerical simulation. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Phys. Plasmas Fluids Relat. Interdiscip. Top. 2002, 66, 026305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, H.; Green, N.G. AC Electrokinetics: Colloids and Nanoparticles; Research Studies Press Ltd.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Jacob, E.; Garik, P. The formation of patterns in non-equilibrium growth. Nature 1990, 343, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Yan, J.; Ye, Q.; Zhou, F. Template-Free and Direct Electrochemical Deposition of Hierarchical Dendritic Gold Microstructures: Growth and Their Multiple Applications. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 15617–15624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, H.A. The Motion and Precipitation of Suspensoids in Divergent Electric Fields. J. Appl. Phys. 1951, 22, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.; García-Sánchez, P.; Morgan, H. AC electrokinetics of conducting microparticles: A review. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 24, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, N.G.; Ramos, A.; González, A.; Morgan, H.; Castellanos, A. Fluid flow induced by nonuniform ac electric fields in electrolytes on microelectrodes. I. Experimental measurements. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 61, 4011–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Wang, C.; Ding, H.; Shao, J.; Ding, Y. AC electric field induced dielectrophoretic assembly behavior of gold nanoparticles in a wide frequency range. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 370, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierhart, B.C.; Howitt, D.G.; Chen, S.J.; Smith, R.L.; Collins, S.D. Frequency dependence of gold nanoparticle superassembly by dielectrophoresis. Langmuir 2007, 23, 12450–12456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, Z.; Bo, R.; Wang, Y.; Motta, N.; Chen, H.; Tricoli, A. Self-assembly of Au nano-islands with tuneable organized disorder for highly sensitive SERS. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 6308–6316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Jayachandran, M. The self-assembling of DNA-templated Au nanoparticles into nanowires and their enhanced SERS and catalytic applications. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 16486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Bai, X.; Zheng, L. Ultrafast Preparation of Three-Dimensional Dendritic Gold Nanostructures in Aqueous Solution and Their Applications in Catalysis and SERS. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 14641–14647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Aulakh, J.S.; Malik, A.K. Thiram: Degradation, applications and analytical methods. J. Environ. Monit. 2003, 5, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, S.; Escobedo, C.; Sabat, R.G. Crossed Surface Relief Gratings as Nanoplasmonic Biosensors. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leebeeck, A.; Kumar, L.K.S.; de Lange, V.; Sinton, D.; Gordon, R.; Brolo, A.G. On-Chip Surface-Based Detection with Nanohole Arrays. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4094–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dies, H.; Bottomley, A.; Nicholls, D.L.; Stamplecoskie, K.; Escobedo, C.; Docoslis, A. Electrokinetically-Driven Assembly of Gold Colloids into Nanostructures for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040661
Dies H, Bottomley A, Nicholls DL, Stamplecoskie K, Escobedo C, Docoslis A. Electrokinetically-Driven Assembly of Gold Colloids into Nanostructures for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(4):661. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040661
Chicago/Turabian StyleDies, Hannah, Adam Bottomley, Danielle Lilly Nicholls, Kevin Stamplecoskie, Carlos Escobedo, and Aristides Docoslis. 2020. "Electrokinetically-Driven Assembly of Gold Colloids into Nanostructures for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering" Nanomaterials 10, no. 4: 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040661
APA StyleDies, H., Bottomley, A., Nicholls, D. L., Stamplecoskie, K., Escobedo, C., & Docoslis, A. (2020). Electrokinetically-Driven Assembly of Gold Colloids into Nanostructures for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Nanomaterials, 10(4), 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040661