NH3 Plasma-Treated Magnesium Doped Zinc Oxide in Biomedical Sensors with Electrolyte–Insulator–Semiconductor (EIS) Structure for Urea and Glucose Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
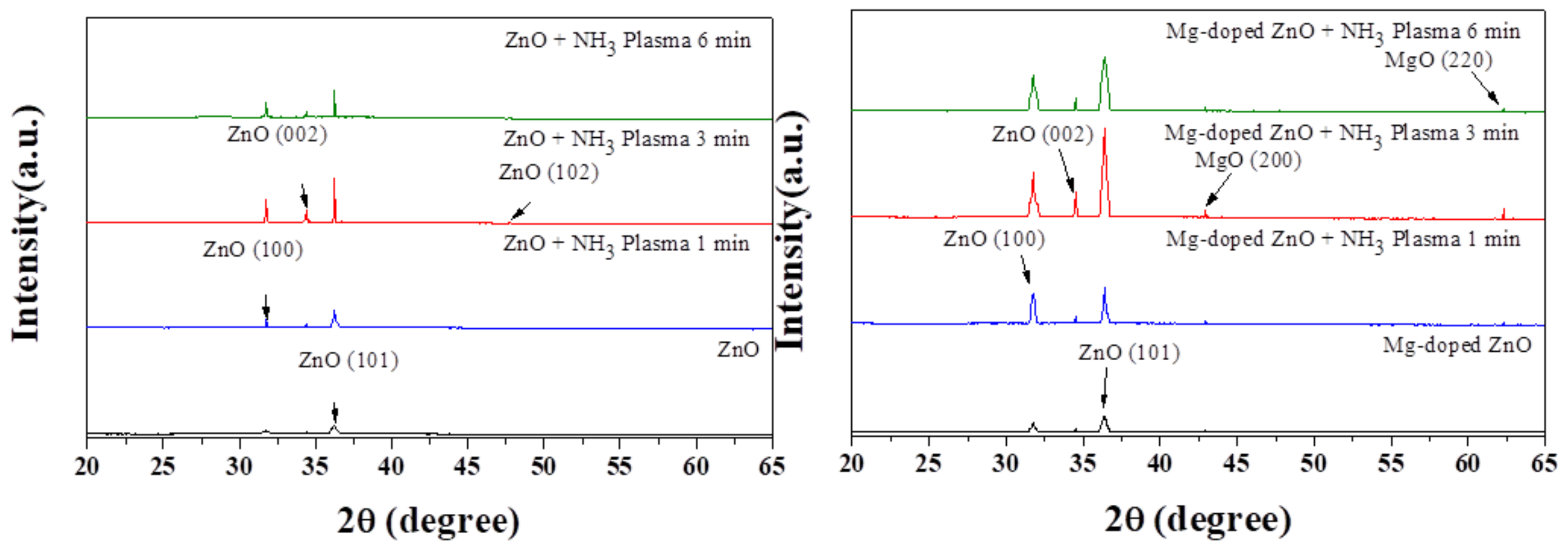
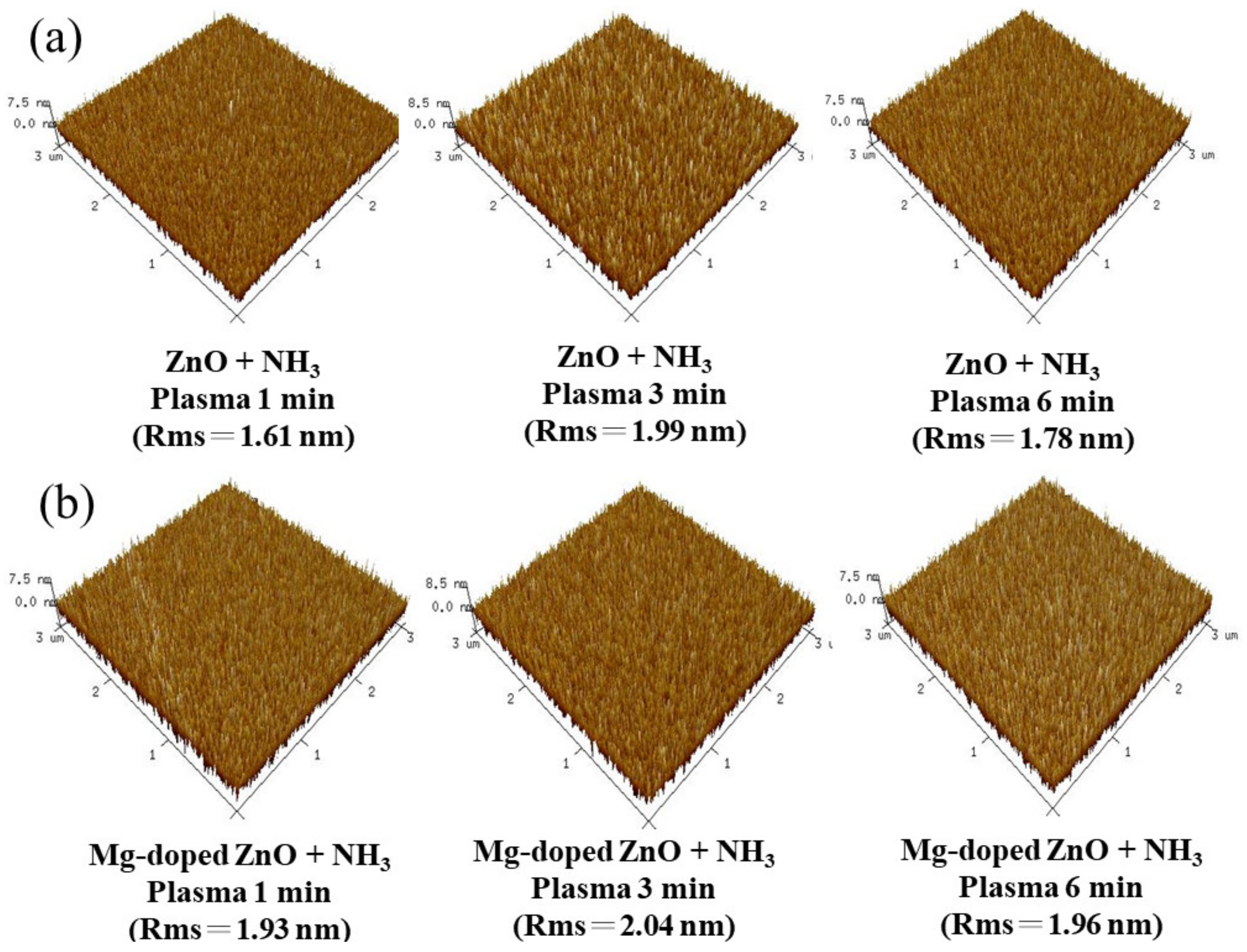
3.1. Physical Characteristics
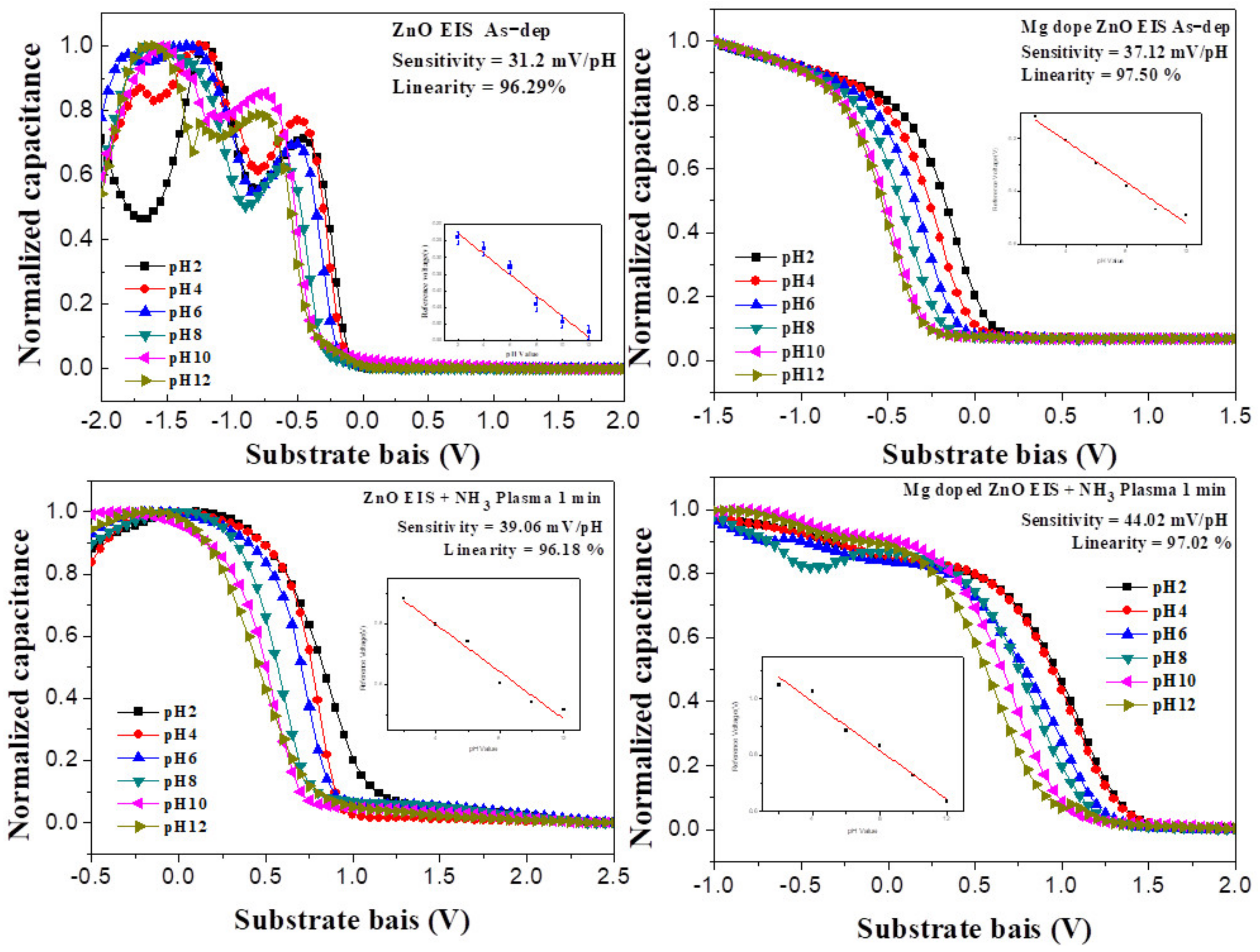
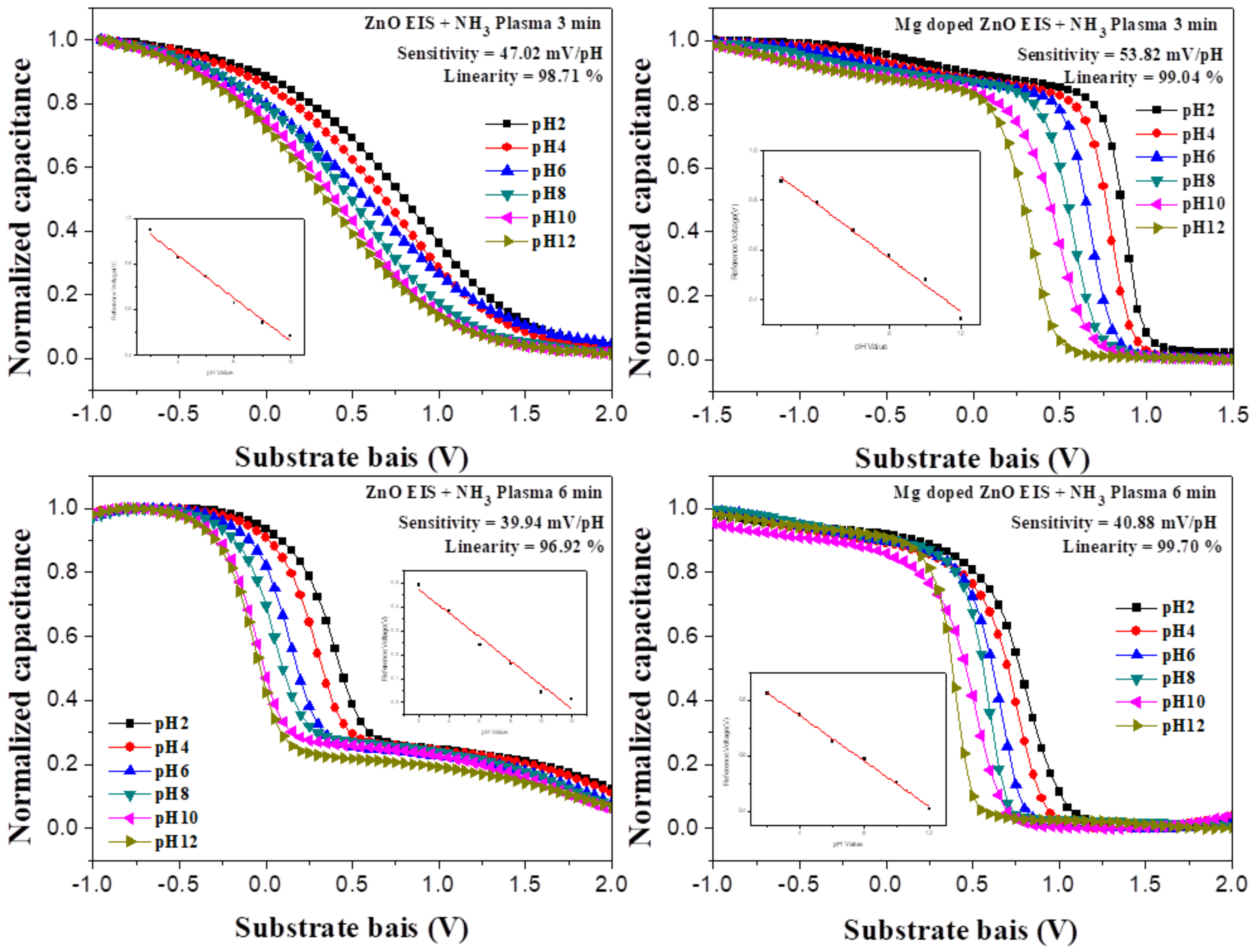
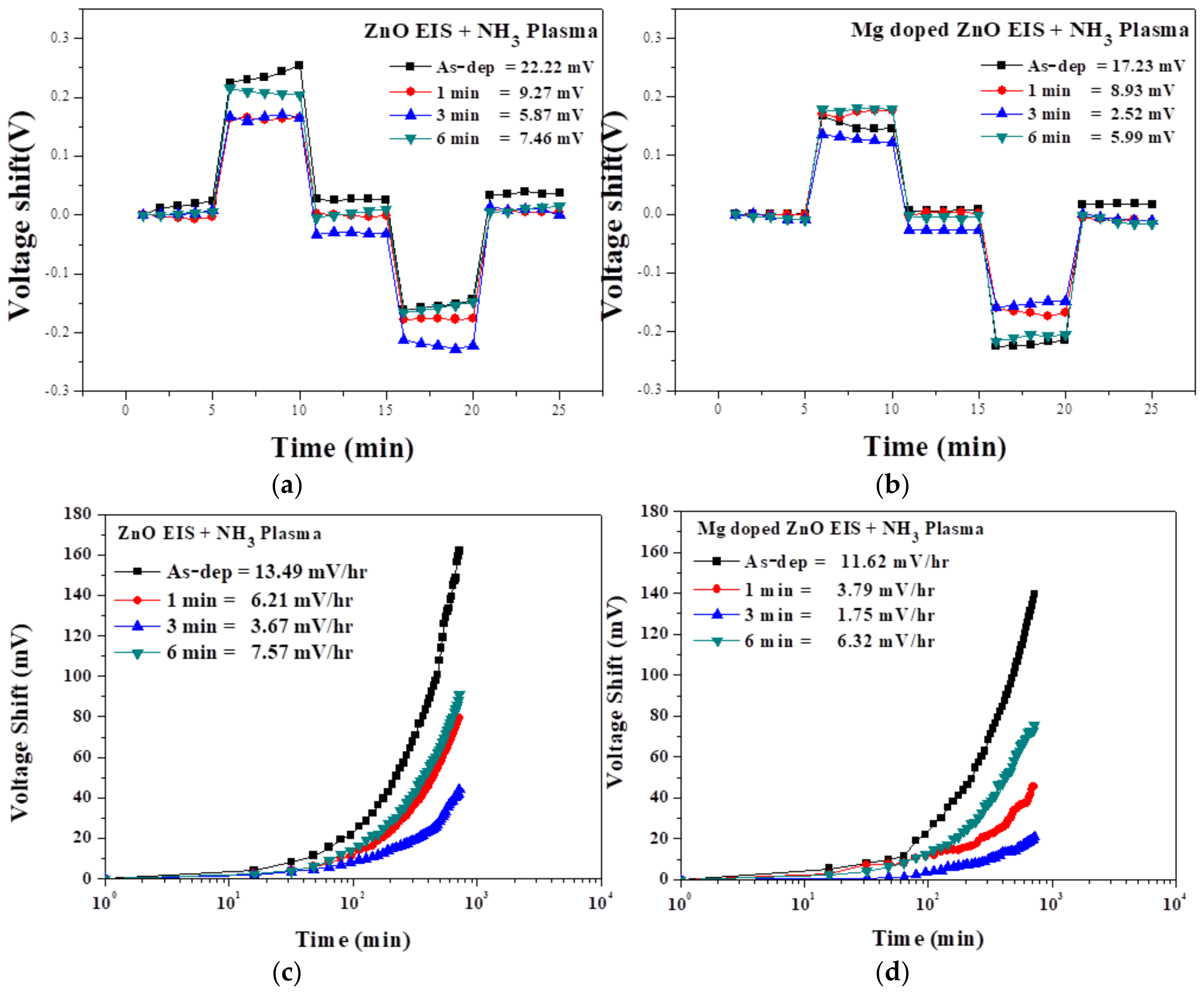
3.2. Sensing Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yates, D.E.; Levine, S.; Healy, T.W. Site-binding model of the electrical double layer at the oxide/water interface. Phys. Chem. Condens. Phases 1974, 70, 1807–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergveld, P. Development of an ion-sensitive solid-state device for neurophysiological measurements. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1970, 1, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C.H.; Chen, H.; Lee, M.L.; Liu, C.C.; Ueng, H.Y.; Chu, Y.C.; Chen, C.B.; Chang, K.M. Effects of N2 and O2 annealing on the multianalyte biosensing characteristics of CeO2-based electrolyte–insulator–semiconductor structures. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 194, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C.H.; Chen, H.; Kuo, L.T.; Wang, J.C.; Chen, Y.T.; Chu, Y.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Lai, C.S.; Chang, S.W.; Chang, C.W. Multi-analyte biosensors on a CF4 plasma treated Nb2O5-based film with an extended gate field effect transistor structure. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 194, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, E. A novel hydrogen peroxide sensor based on horseradish peroxidase immobilized on colloidal Au modified ITO electrode. Electrochem. Commun. 2004, 6, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.W.; Kim, H.K.; Wamer, W.G. Photogenerated reactive oxygen species and charge carriers in ZnO/Au hybrid nanostructures are correlated with enhanced photocatalytic and antibacterial activity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, R.K.; Khanna, R.; Sharma, G.L.; Pavunny, S.P.; Katiyar, R.S. Hydrogen sensing properties of copper-doped zinc oxide thin films. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 7021–7028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.H.; Mao, S.; Feick, H.; Yan, H.; Wu, Y.; Kind, H.; Weber, E.; Russo, R.; Yang, P. Room-temperature ultraviolet nanowire nanolasers. Science 2002, 292, 1897–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yu, J.; Lv, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, F. Preparation and characterization of Mg-doped ZnO thin films by sol–gel method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 3710–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Splendid One-Dimensional Nanostructures of Zinc Oxide: A New Nanomaterial Family for Nanotechnology. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 1987–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Vyas, R.; Sharma, N.; Singh, V.; Singh, A.; Kataria, V.; Gupta, B.K.; Vijay, Y.K. Highly efficient green light harvesting from Mg doped ZnO nanoparticles: Structural and optical studies. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 552, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, C.H.; Woo, H.S.; Abdel-Hady, F.; Wazzan, A.A.; Leea, J.H. Vapor-phase growth of urchin-like Mg-doped ZnO nanowire networks and their application to highly sensitive and selective detection of ethanol. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 223, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılınç, N.; Arda, L.; Öztürk, S.; Öztürk, Z.Z. Structure and electrical properties of Mg-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Cryst. Res. Technol. 2010, 45, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, C.J.; Prabakar, K.; Karthick, S.N.; Hemalatha, K.V.; Son, M.K.; Kim, H.J. Banyan Root Structured Mg-Doped ZnO Photoanode Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 2600–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtomo, A.; Kawasaki, M.; Koida, T.; Masubuchi, K.; Koinuma, H.; Sakurai, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; Yasuda, T.; Segawa, Y. MgxZn1−xO as a II–VI widegap semiconductor alloy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 72, 2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.M.; Wang, I.S.; Lin, Y.T.; Huang, C.H.; Lu, T.F.; Lue, C.E.; Pijanowska, D.G.; Hua, M.Y.; Lai, C.S. Low cost and flexible electrodes with NH3 plasma treatments in extended gate field effect transistors for urea detection. Sens. Actuators B 2013, 187, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuravlev, K.K.; Hlaing Oo, W.M.; McCluskey, M.D.; Huso, J.; Morrison, J.L.; Bergman, L. X-ray diffraction of MgxZn1−xO and ZnO nanocrystals under high pressure. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106, 013511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senol, S.D.; Erdem, M. Hydrothermal synthesis of Li co-doped Zn0.98Mg0.02O nanoparticles and their structural, optical and electrical properties. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 10929–10934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Hudson, M.S.L.; Pandey, S.K.; Tiwari, R.S.; Srivastava, O.N. Structural and hydrogenation studies of ZnO and Mg doped ZnO nanowires. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 3748–3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogar, S.; Khan, W.; Khan, F.; Kim, S.D. Effect of NH3 plasma treatment on the transient characteristics of ZnO nanorod-gated AlGaN/GaN high electron mobility transistor-based UV sensors. Thin Solid Films 2017, 642, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, W.; Fu, K.; Yu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, S.; Song, L.; Deng, X.; Xing, Z.; et al. AlGaN/GaN MIS-HEMTs of very-low Vth hysteresis and current collapse with in-situ pre-deposition plasma nitridation and LPCVD-Si3N4 gate insulator. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2017, 38, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hierro, A.; Ringel, S.A.; Hansen, M.; Speck, J.S.; Mishra, U.K.; DenBaars, S.P. Hydrogen passivation of deep levels in n-GaN. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 77, 1499–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Liu, Z.; Guan, Z.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Deng, Z.; Teng, F.; Tang, A. Chloride-Passivated Mg-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles for Improving Performance of Cadmium-Free, Quantum-Dot Light-Emitting Diodes. ACS Photon. 2018, 5, 3704–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.S.; Lim, D.; Han, H.; Sokolov, A.S.; Jeon, Y.R.; Choi, C. Influence of in-situ NH3 plasma passivation on the electrical characteristics of Ga-face n-GaN MOS capacitor with atomic layer deposited HfO2. Solid State Electron. 2018, 149, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergveld, P. Thirty years ISFETOLOGY: What happened in the past 30 years and what may happen in the next 30 years. Sens. Actuators B 2003, 88, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorramshahi, V.; Karamdel, J.; Yousefi, R. High acetic acid sensing performance of Mg-doped ZnO/rGO nanocomposites. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 7034–7043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousse, L.J.; de Rooij, N.F.; Bergveld, P. Operation of chemically sensitive field effect sensors, as function of the properties of the insulator/electrolyte interface. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1983, 30, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlodder, E.; Witt, H.T. Stoichiometry of Proton Release from the Catalytic Center in Photosynthetic Water Oxidation. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 30387–30392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, J.; Gao, Y.; Li, M.; Kuang, D.; Li, Y.; Xue, J.S.; Zhang, T.; Yu, Z. Impact of NH3 plasma treatment for solution-processed indium oxide thin-film transistors with low thermal budget. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 817, 152720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.S.; Lue, C.E.; Yang, C.M.; Jao, J.H.; Tai, C.C. New pH-sensitive TaOxNy films prepared by NH3 plasma surface treatment and nitrogen incorporated reactive sputtering. Sens. Actuators B 2008, 130, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C.H.; Chang, C.W.; Chen, Y.T.; Su, W.M.; Lu, C.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Chen, H. Influence of NH3 plasma and Ti doping on pH-sensitive CeO2 electrolyte-insulator semiconductor biosensors. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.; Lou, B.S.; Her, J.L.; Pang, S.T.; Pan, T.M. Super Nernstian pH response and enzyme-free detection of glucose using sol-gel derived RuOx on PET flexible-based extended-gate field-effect transistor. Sens. Actuators B 2019, 298, 126837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Park, I.; Hao, Z.; Holman, H.Y.N.; Pisano, A.P. Quantitative Studies of Long-Term Stable, Top-Down Fabricated Silicon Nanowire pH Sensors. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2012, 107, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.C.; Chang, K.P.; Liao, C.H.; Chang, R.D.; Lai, C.S.; Chang, L.C. Low-damage NH3 plasma treatment on SiO2 tunneling oxide of chemically-synthesized gold nanoparticle nonvolatile memory. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2016, 16, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.F.; Kao, C.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Liu, C.S.; Liu, Y.W. Comparison Between Performances of In2O3 and In2TiO5-Based EIS Biosensors Using Post Plasma CF4 Treatment Applied in Glucose and Urea Sensing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigante, S.; Scarbolo, P.; Wipf, M.; Stoop, R.L.; Bedner, K.; Buitrago, E.; Bazigos, A.; Bouvet, D.; Calame, M.; Nenberger, C.S.; et al. Sensing with Advanced Computing Technology: Fin Field-Effect Transistors with High-k Gate Stack on Bulk Silicon. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4872–4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.F.; Kao, C.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Liu, Y.W.; Wang, C.H. The electrical and physical characteristics of Mg-doped ZnO sensing film in EIS (electrolyte-insulator-semiconductor) for glucose sensing applications. Results Phys. 2020, 16, 102976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieneker, L.M.; Bakker, S.J.L.; de Boer, R.A.; Navis, G.J.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Joosten, M.M. Low potassium excretion but not high sodium excretion is associated with increased risk of developing chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2016, 90, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parpia, A.S.; L’Abbe, M.; Goldstein, M.; Arcand, J.; Magnuson, B.; Darling, P.B. The impact of additives on the phosphorus, potassium, and sodium content of commonly consumed meat, poultry, and fish products among patients with chronic kidney disease. J. Renal Nutr. 2018, 28, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.C.; Huang, Y.P. Fabrication and stability analysis for the sodium ion sensor. Sens. Lett. 2008, 6, 920–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.T.; Lin, Y.T.; Leu, Y.C.; Hu, C.Y. Enzyme immobilization on nitrocellulose film for pH-EGFET type biosensors. Sens. Actuators B 2010, 148, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmanian, R.; Mozaffari, S.A. Electrochemical fabrication of ZnO-polyvinyl alcohol nanostructured hybrid film for application to urea biosensor. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 207, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Electrochemical glucose biosensors. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claussen, J.C.; Franklin, A.D.; Haque, A.U.; Porterfield, D.M.; Fisher, T.S. Electrochemical Biosensor of Nanocube-Augmented Carbon Nanotube Networks. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, W.H.; Wang, C.W.; Pang, C.T.; Pan, T.M. Enzymatic Glucose Biosensor Based on TbYxOy Electrolyte-Insulator-Semiconductor. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, B445–B452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C.H.; Chen, H.; Liu, C.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Chen, Y.T.; Chu, Y.C. Electrical, material and multianalyte-sensitive characteristics of thermal CeO2/SiO2-stacked oxide capacitors. Thin Solid Films 2014, 570, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C.H.; Chen, H.; Ling, L.M.; Liu, C.C.; Ueng, H.Y.; Cheng, C.Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Chang, K.M. Multianalyte biosensor based on pH-sensitive ZnO electrolyte-insulator-semiconductor structures. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 184701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.H.; Cheng, C.H.; Lai, C.S.; Pan, T.M. Structural properties and sensing performance of high-k Sm2O3 film-based electrolyte-insulator-semiconductor for pH and urea detection. Sens. Actuators B 2009, 138, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.L.; Wang, J.C.; Kao, C.H.; Chen, H.; Lin, C.Y.; Chang, C.W.; Mahanty, R.K.; Lin, C.F.; Chang, K.M. Comparison of ZnO and Ti-doped ZnO sensing film applied in electrolyte-insulator-semiconductor structure. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 6081–6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C.H.; Chen, H.; Hou, F.Y.S.; Chang, S.W.; Chang, C.W.; Lai, C.S.; Chen, C.P.; He, Y.Y.; Lin, S.R.; Hsieh, K.M.; et al. Fabrication of multianalyte CeO2 nanograin electrolyte-insulator-semiconductor biosensors by using CF4 plasma treatment. Sens. Biosens. Res. 2015, 5, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sensing Film | Glucose (2~7 mM) | Urea (5~40 mM) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| TbYxOy APTES+GA | 4.81 mV/mM | - | [44] |
| CeO2 | 4.74 mV/mM | 2.49 mV/mM | [45] |
| ZnO | 3.14 mV/mM | 1.81 mV/mM | [46] |
| Sm2O3 | - | 2.45 mV/mM | [47] |
| Ti-ZnO | 6.42 mV/mM | 1.4~3.62 mV/mM | [48] |
| CeO withCF4 plasma | 5.83 mV/mM | 2.30 mV/mM | [49] |
| In2TiO5 with CF4 plasma | 6.63 mV/mM | 2.69 mV/mM | [34] |
| MZO with NH3 plasma | 10.73 mV/mM | 8.39 mV/mM | This study |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, C.F.; Kao, C.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Chen, K.L.; Lin, Y.H. NH3 Plasma-Treated Magnesium Doped Zinc Oxide in Biomedical Sensors with Electrolyte–Insulator–Semiconductor (EIS) Structure for Urea and Glucose Applications. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030583
Lin CF, Kao CH, Lin CY, Chen KL, Lin YH. NH3 Plasma-Treated Magnesium Doped Zinc Oxide in Biomedical Sensors with Electrolyte–Insulator–Semiconductor (EIS) Structure for Urea and Glucose Applications. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(3):583. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030583
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Chun Fu, Chyuan Haur Kao, Chan Yu Lin, Kuan Lin Chen, and Yun Hao Lin. 2020. "NH3 Plasma-Treated Magnesium Doped Zinc Oxide in Biomedical Sensors with Electrolyte–Insulator–Semiconductor (EIS) Structure for Urea and Glucose Applications" Nanomaterials 10, no. 3: 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030583
APA StyleLin, C. F., Kao, C. H., Lin, C. Y., Chen, K. L., & Lin, Y. H. (2020). NH3 Plasma-Treated Magnesium Doped Zinc Oxide in Biomedical Sensors with Electrolyte–Insulator–Semiconductor (EIS) Structure for Urea and Glucose Applications. Nanomaterials, 10(3), 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030583




