Silver Nanoparticles-Composing Alginate/Gelatine Hydrogel Improves Wound Healing In Vivo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Production of AgNPs-Composing Alginate/Gelatin Hydrogel
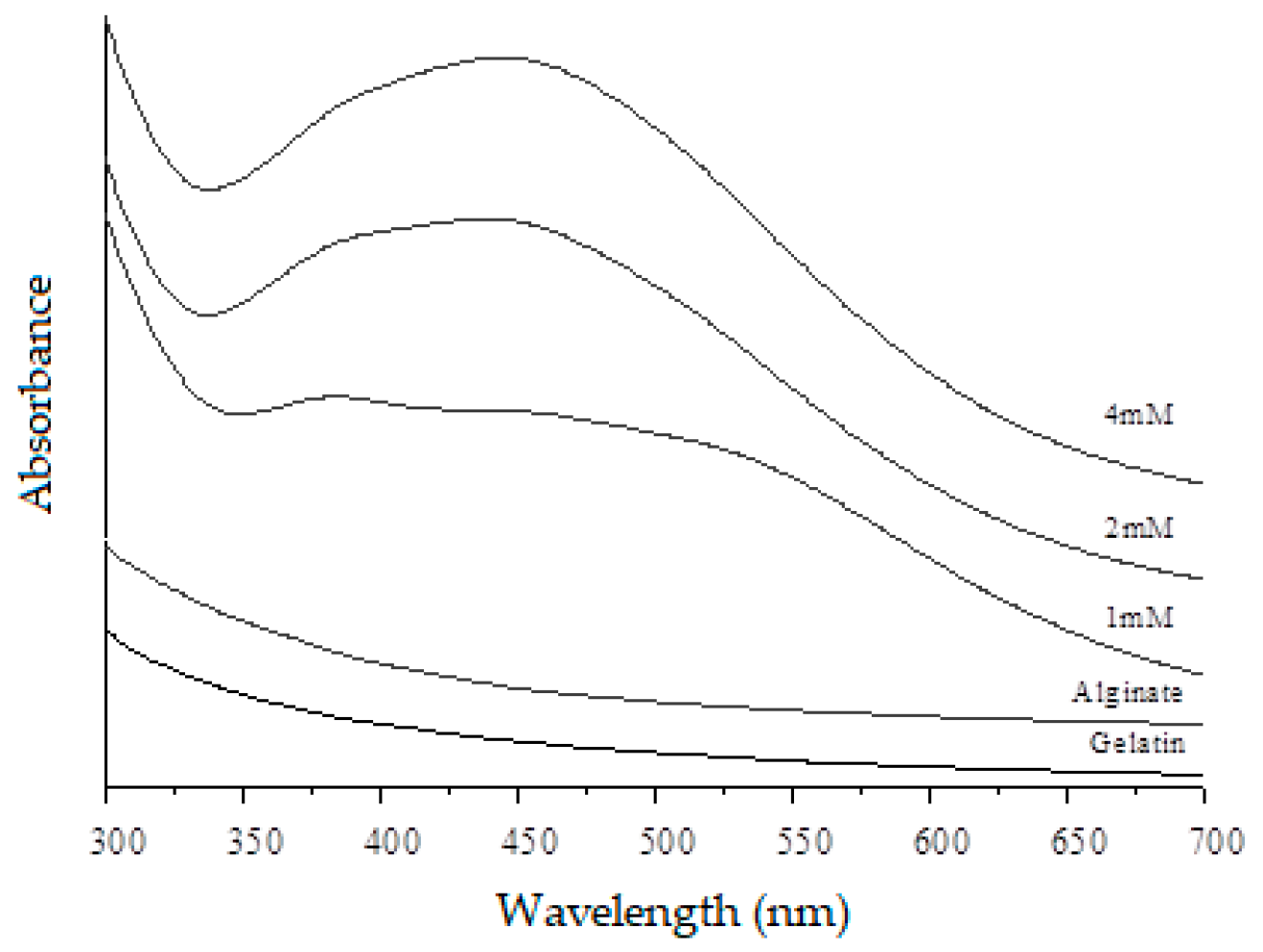
2.3. UV–VIS Spectrophotometer Analysis
2.4. Fourier-Transform Infra-Red Analysis
2.5. Thermal Analysis
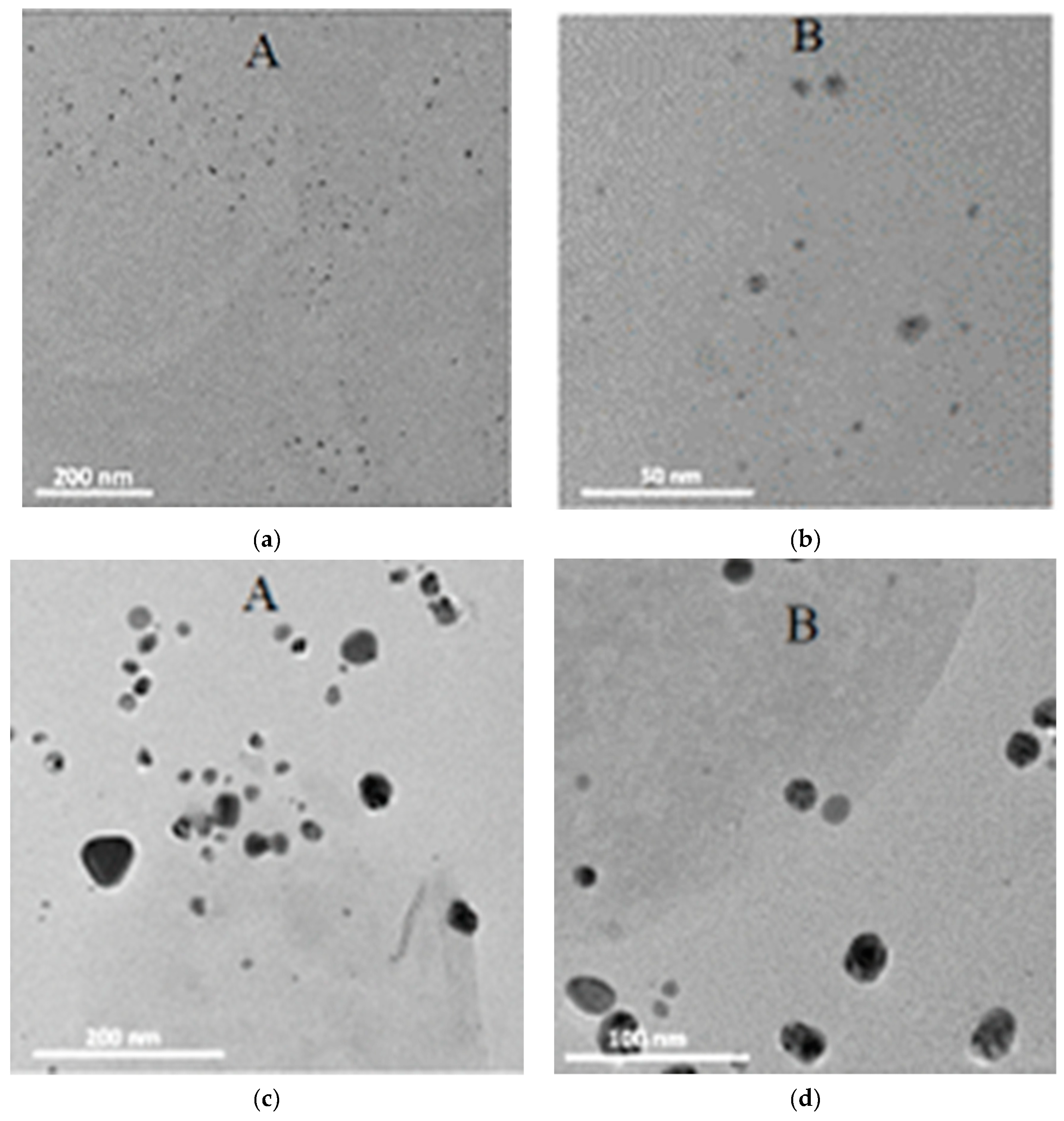
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.7. Biological Assays
2.7.1. Viability Assays
2.7.2. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
2.7.3. Wound Healing Test
2.7.4. Histomorphology Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Winter, G.D. Formation of the scab and the rate of epithelisation of superficial wounds in the skin of the young domestic pig. 1962. Discussion. J. Wound Care 1995, 4, 366–367. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, G.D. Formation of the scab and the rate of epithelization of superficial wounds in the skin of the young domestic pig. Nature 1962, 193, 293–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maneerung, T.; Tokura, S.; Rujiravanit, R. Impregnation of silver nanoparticles into bacterial cellulose for antimicrobial wound dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 72, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Venditti, A.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Kregiel, D.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Santini, A.; Souto, E.B.; Novellino, E.; et al. The Therapeutic Potential of Apigenin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debone, H.S.; Lopes, P.S.; Severino, P.; Yoshida, C.M.P.; Souto, E.B.; da Silva, C.F. Chitosan/Copaiba oleoresin films for would dressing application. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 555, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, C.; Panda, C.R.; Bhaskara, P.K.; Sasmal, A.; Shekhar, S.; Sen, A.K.J.P.B. Physicochemical and antimicrobial properties of sodium alginate/gelatin-based silver nanoformulations. Polym. Bull. 2017, 74, 689–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, P.; da Silva, C.F.; Andrade, L.N.; de Lima Oliveira, D.; Campos, J.; Souto, E.B. Alginate Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery and Targeting. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 1312–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilkar Erdagi, S.; Asabuwa Ngwabebhoh, F.; Yildiz, U. Genipin crosslinked gelatin-diosgenin-nanocellulose hydrogels for potential wound dressing and healing applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jia, H.; Cheng, Q.; Pan, F.; Jiang, Z. Sodium alginate–gelatin polyelectrolyte complex membranes with both high water vapor permeance and high permselectivity. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 375, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Bures, P.; Leobandung, W.; Ichikawa, H. Hydrogels in pharmaceutical formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Cheng, J.; Yu, K. In situ reduction of silver nanoparticles by gelatin to obtain porous silver nanoparticle/chitosan composites with enhanced antimicrobial and wound-healing activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 121, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-López, E.; Gomes, D.; Esteruelas, G.; Bonilla, L.; Lopez-Machado, A.L.; Galindo, R.; Cano, A.; Espina, M.; Ettcheto, M.; Camins, A.; et al. Metal-Based Nanoparticles as Antimicrobial Agents: An Overview. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashour, A.A.; Raafat, D.; El-Gowelli, H.M.; El-Kamel, A.H. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using cranberry powder aqueous extract: characterization and antimicrobial properties. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 7207–7221. [Google Scholar]
- Iravani, S.; Korbekandi, H.; Mirmohammadi, S.; Zolfaghari, B. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Chemical, physical and biological methods. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 9, 385–406. [Google Scholar]
- Bollella, P.; Schulz, C.; Favero, G.; Mazzei, F.; Ludwig, R.; Gorton, L.; Antiochia, R. Green synthesis and characterization of gold and silver nanoparticles and their application for development of a thirdgeneration lactose biosensor. Electroanalysis 2017, 29, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamoun, E.A.; Kenawy, E.-R.S.; Chen, X. A review on polymeric hydrogel membranes for wound dressing applications: PVA-based hydrogel dressings. J. Adv. Res. 2017, 8, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, S. Natural Polymers Vs Synthetic Polymer. In Natural Polymer Drug Delivery Systems; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 95–118. [Google Scholar]
- Mogoşanu, G.D.; Grumezescu, A.M. Natural and synthetic polymers for wounds and burns dressing. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 463, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, Z.; Thu, H.E.; Shuid, A.N.; Katas, H.; Hussain, F. Recent advances in polymer-based wound dressings for the treatment of diabetic foot ulcer: An overview of state-of-the-art. Curr. Drug Targets 2018, 19, 527–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Sun, X.; Liang, L.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.N. Gelatin-Based Hydrogels Blended with Gellan as an Injectable Wound Dressing. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 4766–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Z.; Li, T.; Zhang, W.; Liang, Y. Carboxymethyl chitosan/gelatin/hyaluronic acid blended-membranes as epithelia transplanting scaffold for corneal wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 192, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trostrup, H.; Holstein, P.; Karlsmark, T.; Moser, C.; Agren, M.S. Uncontrolled gelatin degradation in non-healing chronic wounds. J. Wound Care 2018, 27, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojkovska, J.; Djurdjevic, Z.; Jancic, I.; Bufan, B.; Milenkovic, M.; Jankovic, R.; Miskovic-Stankovic, V.; Obradovic, B. Comparative in vivo evaluation of novel formulations based on alginate and silver nanoparticles for wound treatments. J. Biomater. Appl. 2018, 32, 1197–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aderibigbe, B.A.; Buyana, B. Alginate in Wound Dressings. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rescignano, N.; Hernandez, R.; Lopez, L.D.; Calvillo, I.; Kenny, J.M.; Mijangos, C. Preparation of alginate hydrogels containing silver nanoparticles: a facile approach for antibacterial applications. Polym. Int. 2016, 65, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organization for Standardization. 10993–5: 2009 Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices–Part 5: Tests for in Vitro Cytotoxicity. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva. 2009. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/36406.html (accessed on 22 February 2020).
- Rigon, R.B.; Goncalez, M.L.; Severino, P.; Alves, D.A.; Santana, M.H.A.; Souto, E.B.; Chorilli, M. Solid lipid nanoparticles optimized by factorial design for skin administration: Cytotoxicity in NIH3T3 fibroblasts. Colloids Surf. B 2018, 171, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, P.; Chaud, M.V.; Shimojo, A.; Antonini, D.; Lancelloti, M.; Santana, M.H.; Souto, E.B. Sodium alginate-cross-linked polymyxin B sulphate-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: Antibiotic resistance tests and HaCat and NIH/3T3 cell viability studies. Colloids Surf. B 2015, 129, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Souto, S.B.; Zielinska, A.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Santini, A.; Horbańczuk, O.K.; Atanasov, A.G.; Marques, C.; Andrade, L.N.; et al. Perillaldehyde 1,2-epoxide loaded SLN-tailored mAb: Production, physicochemical characterization and in vitro cytotoxicity profile in MCF-7 cell lines. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 161. [Google Scholar]
- Smart, J.I.; Corey, G.R.; Stryjewski, M.E.; Wang, W.; Barriere, S.L. Assessment of minimum inhibitory concentrations of telavancin by revised broth microdilution method in phase 3 hospital-acquired pneumonia/ventilator-associated pneumonia clinical isolates. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2016, 5, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barreto, R.S.; Quintans, J.S.; Barreto, A.S.; Albuquerque-Júnior, R.L.; Galvão, J.G.; Gonsalves, J.K.; Nunes, R.S.; Camargo, E.A.; Lucca-Júnior, W.; Soares, R.C. Improvement of wound tissue repair by chitosan films containing borneol, a bicyclic monoterpene alcohol, in rats. Int. Wound J. 2016, 13, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Ribeiro, A.F.; Ferreira, M.I.; Teixeira, M.C.; Shimojo, A.A.M.; Soriano, J.L.; Naveros, B.C.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Souto, S.B.; et al. New Nanotechnologies for the Treatment and Repair of Skin Burns Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Ramontja, J. Sodium alginate stabilized silver nanoparticles–silica nanohybrid and their antibacterial characteristics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 712–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyliszczak, B.; Drabczyk, A.; Kudlacik-Kramarczyk, S.; Bialik-Was, K.; Kijkowska, R.; Sobczak-Kupiec, A. Preparation and cytotoxicity of chitosan-based hydrogels modified with silver nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B 2017, 160, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lustosa, A.; de Jesus Oliveira, A.C.; Quelemes, P.V.; Placido, A.; da Silva, F.V.; Oliveira, I.S.; de Almeida, M.P.; Amorim, A.; Delerue-Matos, C.; de Oliveira, R.C.M.; et al. In Situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles in a hydrogel of carboxymethyl cellulose with phthalated-cashew gum as a promising antibacterial and healing agent. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez Chabala, L.F.; Cuartas, C.E.E.; López, M.E.L. Release behavior and antibacterial activity of chitosan/alginate blends with aloe vera and silver nanoparticles. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianconi, L.; Calo, L.; Mennuni, M.; Santini, L.; Morosetti, P.; Azzolini, P.; Barbato, G.; Biscione, F.; Romano, P.; Santini, M. n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids for the prevention of arrhythmia recurrence after electrical cardioversion of chronic persistent atrial fibrillation: a randomized, double-blind, multicentre study. Europace 2011, 13, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiad, I.; El-Sukkary, M.M.; Soliman, E.; El-Awady, M.Y.; Shaban, S.M. In situ and green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their biological activity. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 3430–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavendish, M.; Nalone, L.A.; Barbosa, T.C.; Barbosa, R.M.; Costa, S.P.M.; Nunes, R.; da Silva, C.F.; Chaud, M.V.; Souto, E.B.; Hollanda, L.; et al. Study of pre-formulatiom and development of solid lipid nanoparticles containing perillyl alcohol. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.F.; Monteiro, J.P.; Bonafé, E.G.; Gerola, A.P.; Silva, C.T.P.; Girotto, E.M.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C. Bactericidal activity of hydrogel beads based on N,N,N-trimethyl chitosan/alginate complexes loaded with silver nanoparticles. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2015, 26, 1129–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, N.; Kakati, D.K. Smart porous microparticles based on gelatin/sodium alginate polyelectrolyte complex. J. Food Eng. 2013, 117, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabadini, R.C.; Martins, V.C.; Pawlicka, A. Synthesis and characterization of gellan gum: chitosan biohydrogels for soil humidity control and fertilizer release. Cellulose 2015, 22, 2045–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalai, J.; Nallamuthu, T. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: characterization and determination of antibacterial potency. Appl. Nanosci. 2016, 6, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rescignano, N.; Fortunati, E.; Montesano, S.; Emiliani, C.; Kenny, J.; Martino, S.; Armentano, I. PVA bio-nanocomposites: a new take-off using cellulose nanocrystals and PLGA nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 99, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palza, H.; Delgado, K.; Curotto, N. Synthesis of copper nanostructures on silica-based particles for antimicrobial organic coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 357, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanmani, P.; Rhim, J.-W. Physicochemical properties of gelatin/silver nanoparticle antimicrobial composite films. Food Chem. 2014, 148, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazar, V. Quorum sensing in biofilms—How to destroy the bacterial citadels or their cohesion/power? Anaerobe 2011, 17, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periasamy, S.; Joo, H.-S.; Duong, A.C.; Bach, T.-H.L.; Tan, V.Y.; Chatterjee, S.S.; Cheung, G.Y.; Otto, M. How Staphylococcus aureus biofilms develop their characteristic structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekkawy, A.I.; El-Mokhtar, M.A.; Nafady, N.A.; Yousef, N.; Hamad, M.A.; El-Shanawany, S.M.; Ibrahim, E.H.; Elsabahy, M. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles for topical applications: effect of surface coating and loading into hydrogels. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 759–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashmore, D.; Chaudhari, A.; Barlow, B.; Barlow, B.; Harper, T.; Vig, K.; Miller, M.; Singh, S.; Nelson, E.; Pillai, S. Evaluation of E. coli inhibition by plain and polymer-coated silver nanoparticles. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. S. Paulo 2018, 60, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, G.; Hussain, T.; Chauhan, G.; Garg, T.; Goyal, A.K. Collagen nanofiber containing silver nanoparticles for improved wound-healing applications. J. Drug Targeting 2016, 24, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.D.; Houreld, N.N.; Kroukamp, E.M.; Abrahamse, H. Cellular imaging and bactericidal mechanism of green-synthesized silver nanoparticles against human pathogenic bacteria. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2018, 178, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, T.; Nigusse, T.; Dhanaraju, M.D. Silver nanoparticles as real topical bullets for wound healing. J. Am. Coll. Clin. Wound Spec. 2011, 3, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasi, P.; Schoubben, A.; Giovagnoli, S.; Rossi, C.; Ricci, M. Lipid nanoparticles for drug delivery to the brain: in vivo veritas. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2009, 5, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarusha, L.; Paoletti, S.; Travan, A.; Marsich, E. Alginate membranes loaded with hyaluronic acid and silver nanoparticles to foster tissue healing and to control bacterial contamination of non-healing wounds. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2018, 29, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.P.; Kim, Y.J.; Singh, P.; Huo, Y.; Soshnikova, V.; Markus, J.; Ahn, S.; Chokkalingam, M.; Lee, H.A.; Yang, D.C. Biosynthesis of gold and silver chloride nanoparticles mediated by Crataegus pinnatifida fruit extract: in vitro study of anti-inflammatory activities. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 46, 1530–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Wong, K.K.; Ho, C.M.; Lok, C.N.; Yu, W.Y.; Che, C.M.; Chiu, J.F.; Tam, P.K. Topical delivery of silver nanoparticles promotes wound healing. ChemMedChem 2007, 2, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Yao, P.; Lee, E.; Greenhalgh, D.; Soulika, A.M. Interferon-gamma inhibits healing post scald burn injury. Wound Repair Regener. 2012, 20, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattyasovszky, S.G.; Mausbach, S.; Ritz, U.; Wollstadter, J.; Schmidtmann, I.; Baranowski, A.; Drees, P.; Rommens, P.M.; Hofmann, A. Cytokine Interferon-gamma suppresses the function of capsule myofibroblasts and induces cell apoptosis. J. Orthopaedic Res. Off. Publ. Orthopaedic Res. Soc. 2017, 35, 2524–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhao, Y.; Simonenko, V.; Xu, J.J.; Liu, K.; Wang, D.; Shi, J.; Zhong, T.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, L.; et al. Simultaneous silencing of TGF-beta1 and COX-2 reduces human skin hypertrophic scar through activation of fibroblast apoptosis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 80651–80665. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Lee, P.y.; Ho, C.m.; Lui, V.C.; Chen, Y.; Che, C.m.; Tam, P.K.; Wong, K.K. Silver nanoparticles mediate differential responses in keratinocytes and fibroblasts during skin wound healing. ChemMedChem 2010, 5, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Bacteria | Gelatin | Sodium Alginate | AgNO3 | Hydrogel 1 mM | Hydrogel 2 mM | Hydrogel 4 mM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gram-negative Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | Bacterial Growth | Bacterial Growth | No bacterial growth | 1.050 µg.mL−1 | 1.050 µg.mL−1 | 00.50 µg.mL−1 |
| Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | Bacterial Growth | Bacterial Growth | No bacterial growth | 130 µg.mL−1 | 130 µg.mL−1 | 53.0 µg.mL−1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diniz, F.R.; Maia, R.C.A.P.; de Andrade, L.R.M.; Andrade, L.N.; Vinicius Chaud, M.; da Silva, C.F.; Corrêa, C.B.; de Albuquerque Junior, R.L.C.; Pereira da Costa, L.; Shin, S.R.; et al. Silver Nanoparticles-Composing Alginate/Gelatine Hydrogel Improves Wound Healing In Vivo. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020390
Diniz FR, Maia RCAP, de Andrade LRM, Andrade LN, Vinicius Chaud M, da Silva CF, Corrêa CB, de Albuquerque Junior RLC, Pereira da Costa L, Shin SR, et al. Silver Nanoparticles-Composing Alginate/Gelatine Hydrogel Improves Wound Healing In Vivo. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(2):390. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020390
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiniz, Flavia Resende, Romerito Cesar A. P. Maia, Lucas Rannier M. de Andrade, Luciana Nalone Andrade, Marco Vinicius Chaud, Classius Ferreira da Silva, Cristiane Bani Corrêa, Ricardo Luiz C. de Albuquerque Junior, Luiz Pereira da Costa, Su Ryon Shin, and et al. 2020. "Silver Nanoparticles-Composing Alginate/Gelatine Hydrogel Improves Wound Healing In Vivo" Nanomaterials 10, no. 2: 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020390
APA StyleDiniz, F. R., Maia, R. C. A. P., de Andrade, L. R. M., Andrade, L. N., Vinicius Chaud, M., da Silva, C. F., Corrêa, C. B., de Albuquerque Junior, R. L. C., Pereira da Costa, L., Shin, S. R., Hassan, S., Sanchez-Lopez, E., Souto, E. B., & Severino, P. (2020). Silver Nanoparticles-Composing Alginate/Gelatine Hydrogel Improves Wound Healing In Vivo. Nanomaterials, 10(2), 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020390













