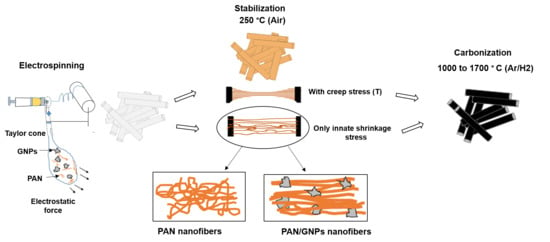
Graphene Nanoplatelet (GNPs) Doped Carbon Nanofiber (CNF) System: Effect of GNPs on the Graphitic Structure of Creep Stress and Non-Creep Stress Stabilized Polyacrylonitrile (PAN)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material & Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Carbon Nanofibers and Graphene Nanoplatelets (GNPs) Doped Carbon Nanofiber System
2.3. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussions
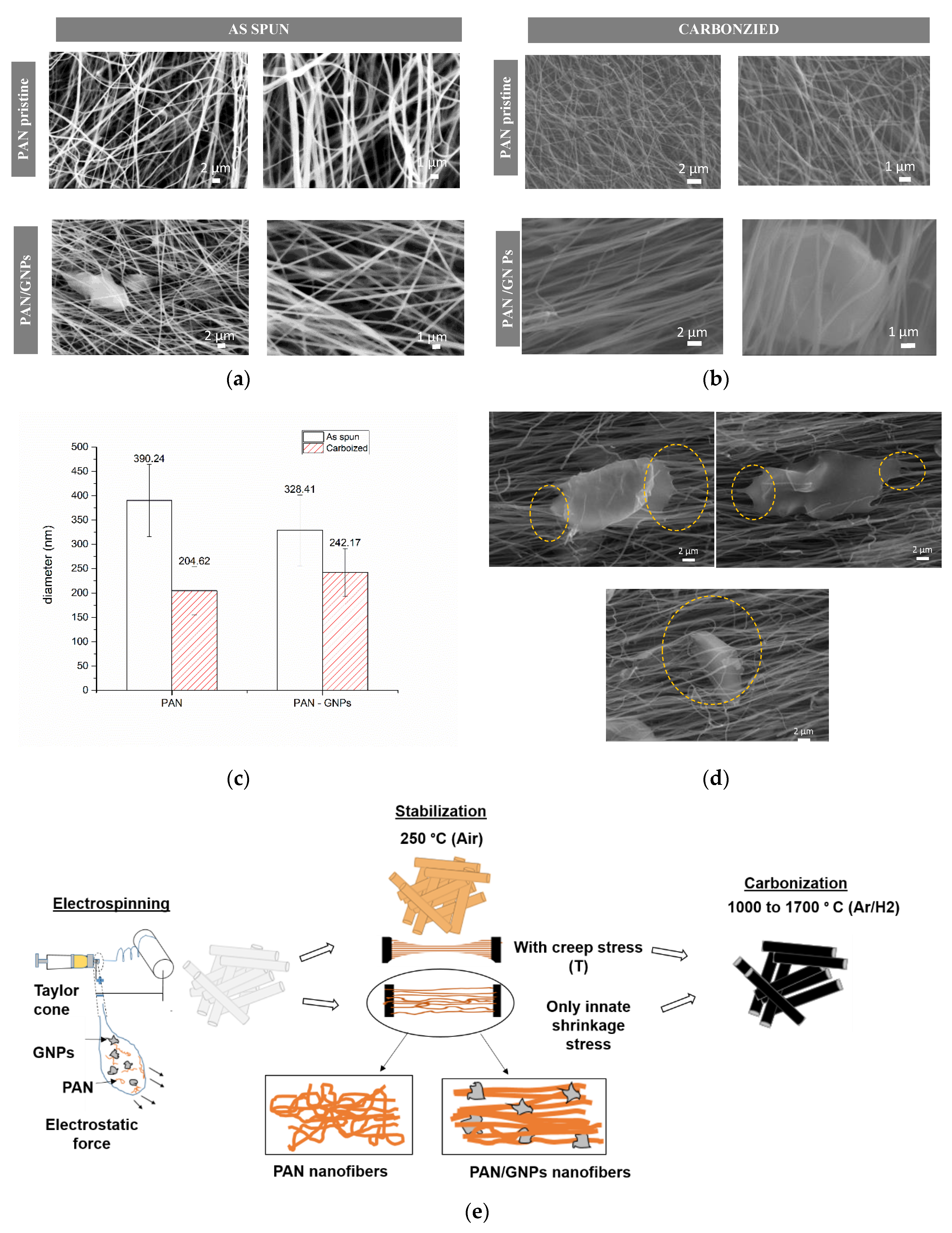
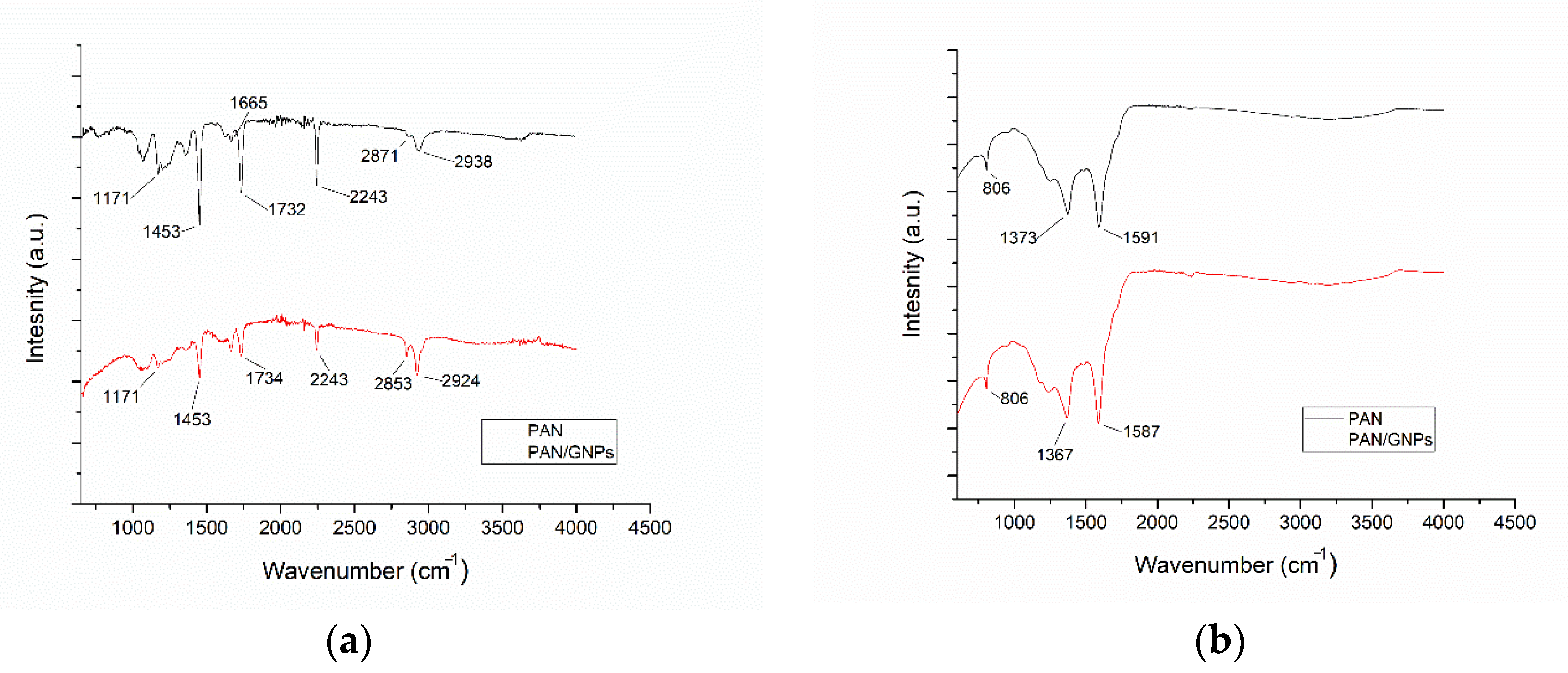
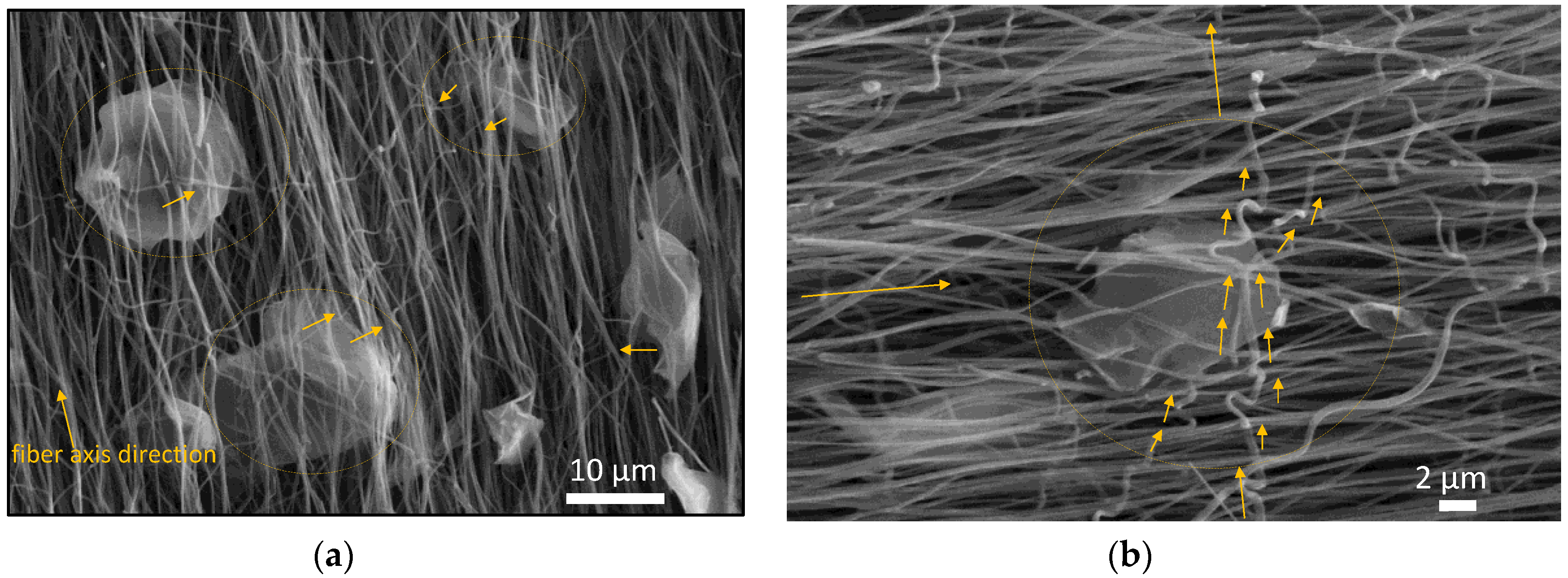
3.1. Morphology and Molecular Structure of As-Spun and Stabilized Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) and PAN/GNPs
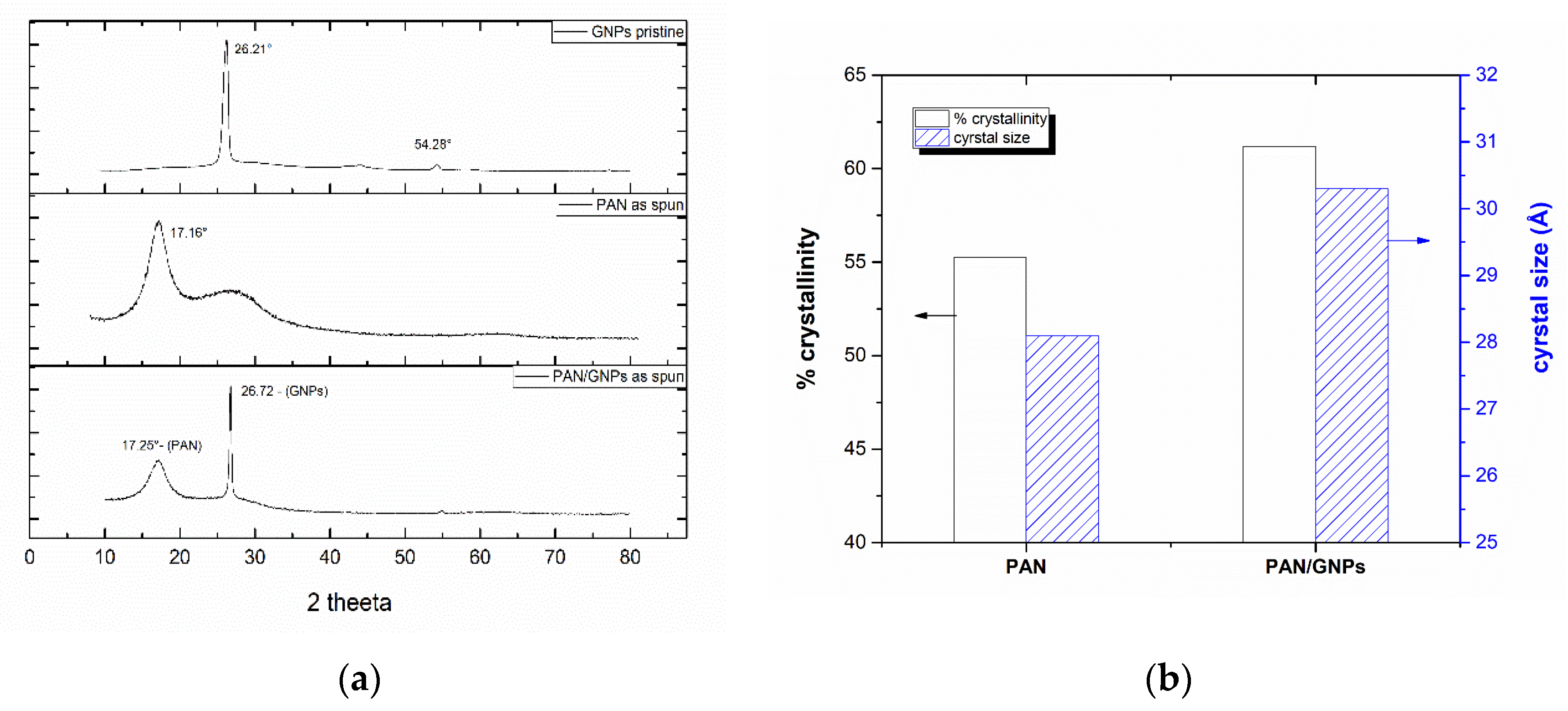
3.2. Carbonization and Graphitic Structure of PAN and GNPs Doped PAN
3.3. Electrical Conductivity of Pristine and GNPs Doped PAN Nanofiber Mats
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hammel, E.; Tang, X.; Trampert, M.; Schmitt, T.; Mauthner, K.; Eder, A.; Pötschke, P. Carbon nanofibers for composite applications. Carbon 2004, 42, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, T. Carbon Nanofibers: Synthesis, Properties and Applications. In Polymer Nanocomposites Based on Inorganic and Organic Nanomaterials; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 63–88. [Google Scholar]
- Prilutsky, S.; Zussman, E.; Cohen, Y. Carbonization of electrospun poly (acrylonitrile) nanofibers containing multiwalled carbon nanotubes observed by transmission electron microscope with in situ heating. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2010, 48, 2121–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greil, P. Perspectives of nano-carbon based engineering materials. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2015, 17, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadiv, R.; Shachar, G.; Peretz-Damari, S.; Varenik, M.; Levy, I.; Buzaglo, M.; Ruse, E.; Regev, O. Performance of nano-carbon loaded polymer composites: Dimensionality matters. Carbon 2018, 126, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kumar, S. Recent progress in fabrication, structure, and properties of carbon fibers. Polym. Rev. 2012, 52, 234–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, M.; Yang, Y.; Kang, F. Carbon nanofibers prepared via electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2547–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.K.; Lai, K.; Liu, W.; Yao, M.; Sun, R.J. Preparation of carbon nanofibres through electrospinning and thermal treatment. Polym. Int. 2009, 58, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataraj, S.; Yang, K.; Aminabhavi, T. Polyacrylonitrile-based nanofibers—A state-of-the-art review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 487–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, T.H.; Ting, H.Y.; Lin, C.H. Thermal stabilization of polyacrylonitrile fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1988, 35, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.B.; Dreyer, B.; Renz, F.; Tegenkamp, C.; Sindelar, R. Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile Based Carbon Nanofibers: The Role of Creep Stress towards Cyclization and Graphitization. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Naraghi, M. Effect of templating graphitization on electrical conductivity of electrospun carbon nanofiber. In Proceedings of the 58th AIAA/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference, Grapevine, TX, USA, 9–13 January 2017; p. 0796. [Google Scholar]
- Chawla, S.; Cai, J.; Naraghi, M. Mechanical tests on individual carbon nanofibers reveals the strong effect of graphitic alignment achieved via precursor hot-drawing. Carbon 2017, 117, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilatela, J.J.; Eder, D. Nanocarbon composites and hybrids in sustainability: A review. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 456–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Lou, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, R.; Liang, Q.; Huang, Z. Electrospinning fabrication and in situ mechanical investigation of individual graphene nanoribbon reinforced carbon nanofiber. Carbon 2017, 114, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papkov, D.; Beese, A.M.; Goponenko, A.; Zou, Y.; Naraghi, M.; Espinosa, H.D.; Saha, B.; Schatz, G.C.; Moravsky, A.; Loutfy, R. Extraordinary improvement of the graphitic structure of continuous carbon nanofibers templated with double wall carbon nanotubes. ACS Nano 2012, 7, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papkov, D.; Goponenko, A.; Compton, O.C.; An, Z.; Moravsky, A.; Li, X.Z.; Nguyen, S.T.; Dzenis, Y.A. Improved graphitic structure of continuous carbon nanofibers via graphene oxide templating. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 5763–5770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ra, E.J.; An, K.H.; Kim, K.K.; Jeong, S.Y.; Lee, Y.H. Anisotropic electrical conductivity of MWCNT/PAN nanofiber paper. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2005, 413, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burchell, T.D. Carbon Materials for Advanced Technologies; Elsevier: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, A.; Syväjärvi, M. Graphene Materials: Fundamentals and Emerging Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Mahalingam, S.; Amir, A.; Porwal, H.; Reece, M.J.; Naglieri, V.; Colombo, P.; Edirisinghe, M. Novel preparation, microstructure, and properties of polyacrylonitrile-based carbon nanofiber–graphene nanoplatelet materials. ACS Omega 2016, 1, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, S.; Thomsen, C. Raman spectroscopy of graphite. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2004, 362, 2271–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merel, P.; Tabbal, M.; Chaker, M.; Moisa, S.; Margot, J. Direct evaluation of the sp3 content in diamond-like-carbon films by XPS. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1998, 136, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.C.; Meyer, J.; Scardaci, V.; Casiraghi, C.; Lazzeri, M.; Mauri, F.; Piscanec, S.; Jiang, D.; Novoselov, K.; Roth, S. Raman spectrum of graphene and graphene layers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 187401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, G.; Lu, C.; Ling, L.; Hao, A.; He, F. Influence of tension on the oxidative stabilization process of polyacrylonitrile fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 96, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.J. New perspectives on the structure of graphitic carbons. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2005, 30, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harris, P.J.; Tsang, S.C. High-resolution electron microscopy studies of non-graphitizing carbons. Philos. Mag. A 1997, 76, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, M.S.A.; Ismail, A.F.; Mustafa, A. A review of heat treatment on polyacrylonitrile fiber. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 1421–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S.; Kumar, C.S.; Korvink, J.G.; Kübel, C. Evolution of glassy carbon microstructure: In situ transmission electron microscopy of the pyrolysis process. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pesin, L. Review Structure and properties of glass-like carbon. J. Mater. Sci. 2002, 37, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.; Cameán, I.; García, A.B. Graphitization thermal treatment of carbon nanofibers. Carbon 2013, 59, 2–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprojanz, J.; Dreyer, B.; Wehr, M.; Wiegand, J.; Baringhaus, J.; Koch, J.; Renz, F.; Sindelar, R.; Tegenkamp, C. Highly anisotropic electric conductivity in PAN-based carbon nanofibers. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2017, 29, 494002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
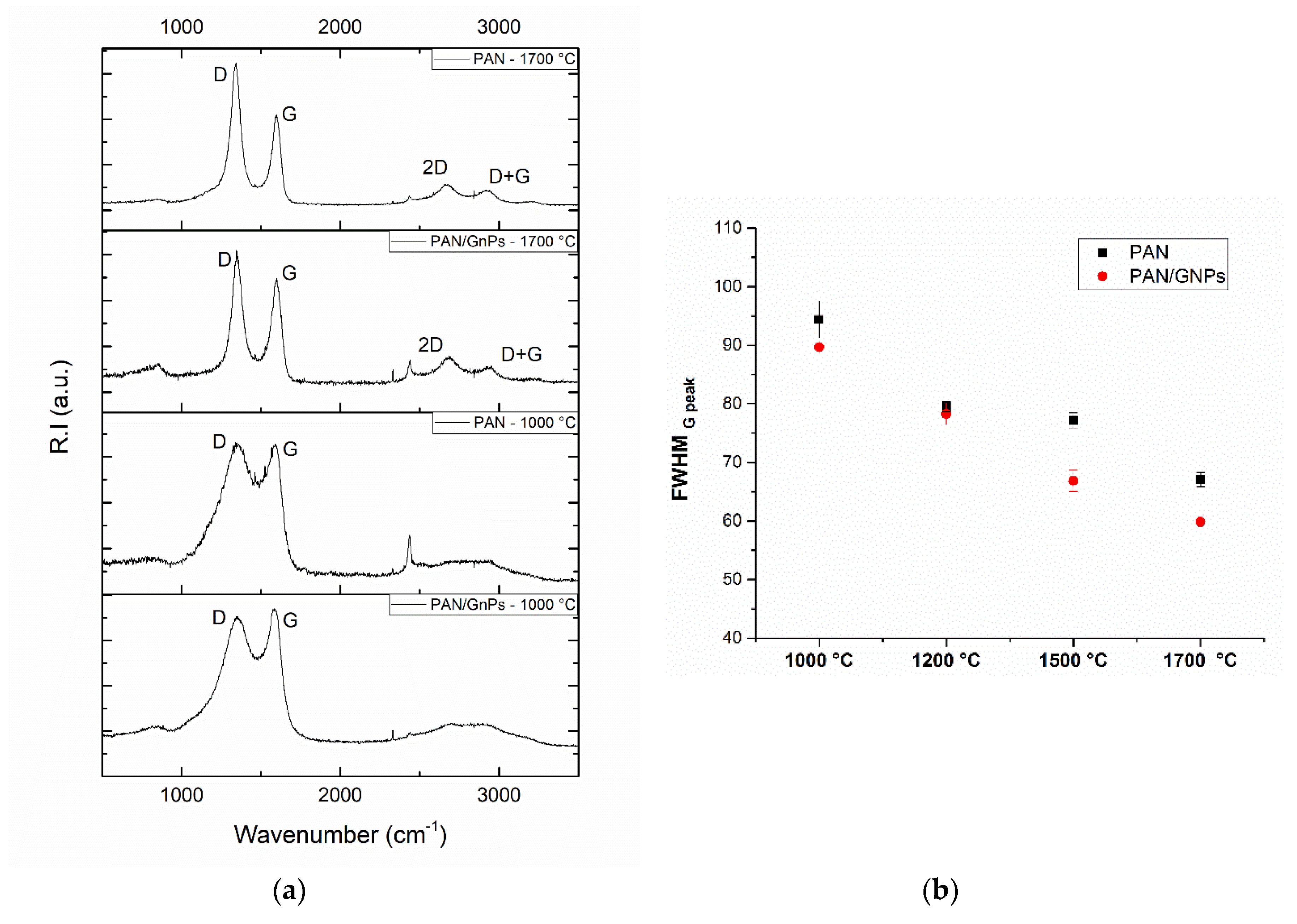
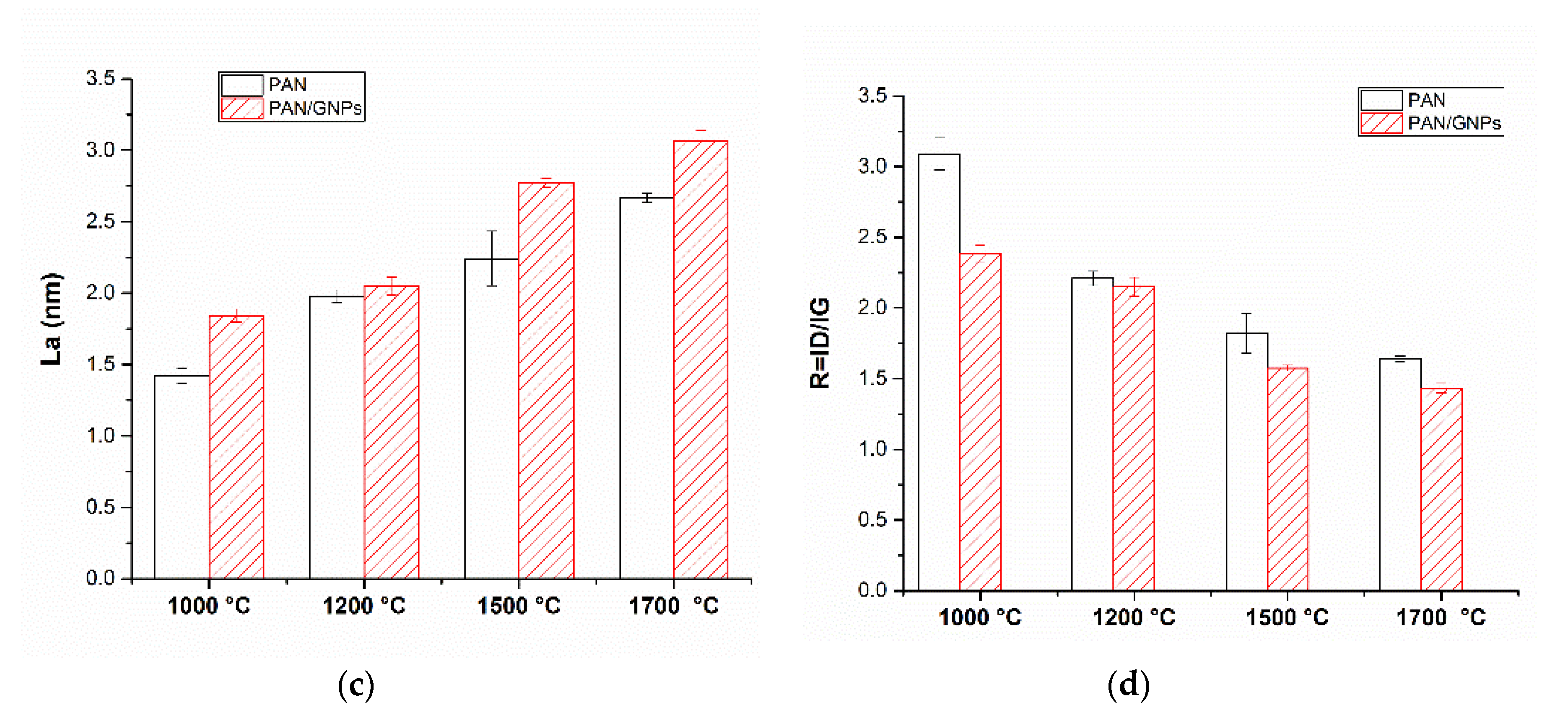

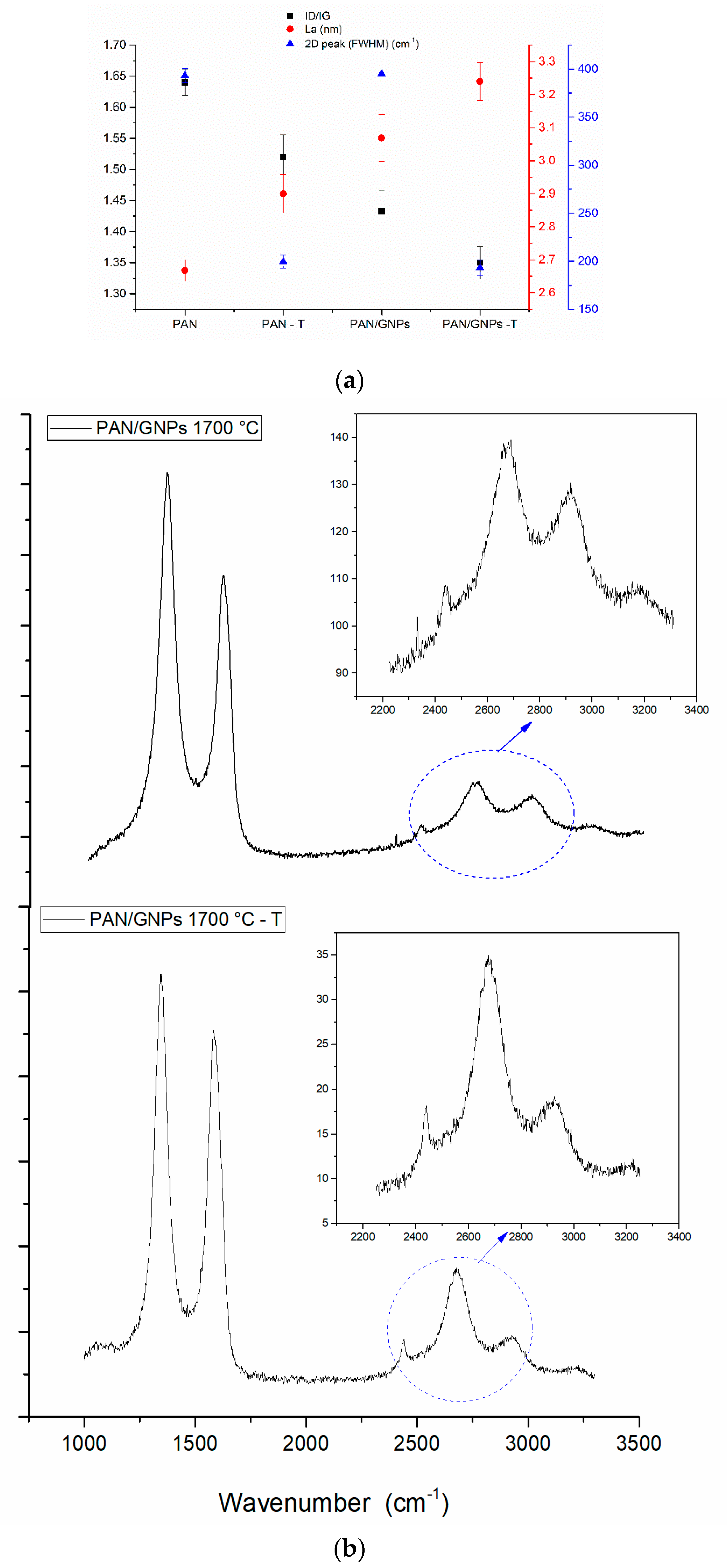
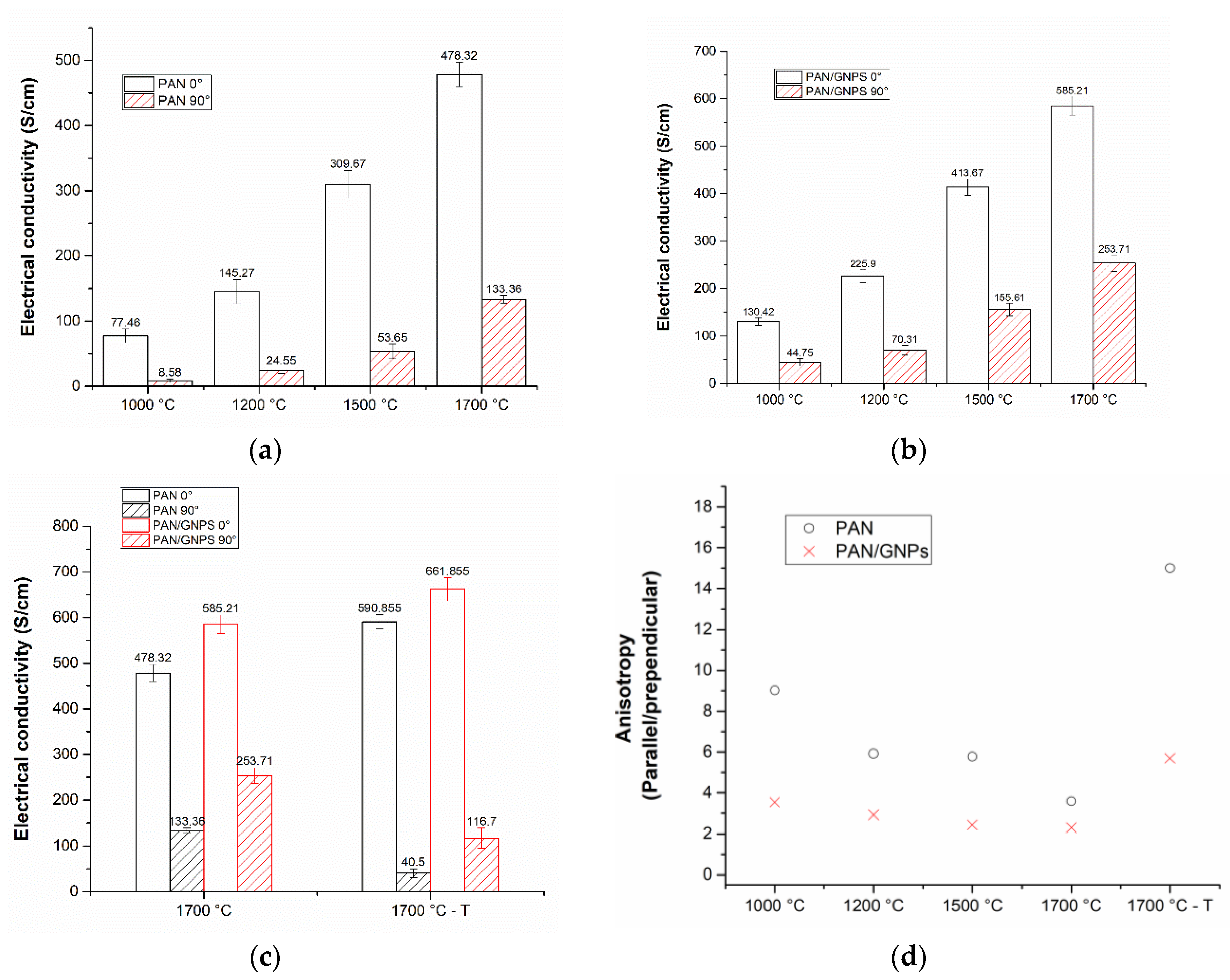
| Sample | Lc (nm) | FWHM (002) |
|---|---|---|
| PAN–1000 °C | 1.38 | 5.82 |
| PAN–1200 °C | 1.96 | 5.01 |
| PAN–1500 °C | 2.01 | 4.65 |
| PAN–1700 °C | 2.03 | 3.98 |
| PAN/GNPs–1000 °C | 1.68 | 5.14 |
| PAN/GNPs–1200 °C | 2.2 | 3.64 |
| PAN/GNPs–1500 °C | 2.33 | 3.45 |
| PAN/GNPs–1700 °C | 2.47 | 3.25 |
| PAN–1700 °C–T | 2.07 | 3.88 |
| PAN/GNPs–1700 °C–T | 2.58 | 3.12 |
| Sample | sp2/sp3 Ratio | sp2 Fraction |
|---|---|---|
| PAN–1000 °C | 1.22 | 54.8% |
| PAN/GNPs–1000 °C | 1.50 | 59% |
| PAN–1700 °C | 1.57 | 61.89% |
| PAN/GNPs–1700 °C | 1.81 | 64.45% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bin Ali, A.; Renz, F.; Koch, J.; Tegenkamp, C.; Sindelar, R. Graphene Nanoplatelet (GNPs) Doped Carbon Nanofiber (CNF) System: Effect of GNPs on the Graphitic Structure of Creep Stress and Non-Creep Stress Stabilized Polyacrylonitrile (PAN). Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020351
Bin Ali A, Renz F, Koch J, Tegenkamp C, Sindelar R. Graphene Nanoplatelet (GNPs) Doped Carbon Nanofiber (CNF) System: Effect of GNPs on the Graphitic Structure of Creep Stress and Non-Creep Stress Stabilized Polyacrylonitrile (PAN). Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(2):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020351
Chicago/Turabian StyleBin Ali, Annas, Franz Renz, Julian Koch, Christoph Tegenkamp, and Ralf Sindelar. 2020. "Graphene Nanoplatelet (GNPs) Doped Carbon Nanofiber (CNF) System: Effect of GNPs on the Graphitic Structure of Creep Stress and Non-Creep Stress Stabilized Polyacrylonitrile (PAN)" Nanomaterials 10, no. 2: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020351
APA StyleBin Ali, A., Renz, F., Koch, J., Tegenkamp, C., & Sindelar, R. (2020). Graphene Nanoplatelet (GNPs) Doped Carbon Nanofiber (CNF) System: Effect of GNPs on the Graphitic Structure of Creep Stress and Non-Creep Stress Stabilized Polyacrylonitrile (PAN). Nanomaterials, 10(2), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020351