Abstract
Tm-Tb co-substituted Co-Ni nanospinel ferrites (NSFs) as (Co0.5Ni0.5) [TmxTbxFe2−2x]O4 (x = 0.00–0.05) NSFs were attained via the ultrasound irradiation technique. The phase identification and morphologies of the NSFs were explored using X-rays diffraction (XRD), selected area electron diffraction (SAED), and transmission and scanning electronic microscopes (TEM and SEM). The magnetization measurements against the applied magnetic field (M-H) were made at 300 and 10 K with a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). The various prepared nanoparticles revealed a ferrimagnetic character at both 300 and 10 K. The saturation magnetization (Ms), the remanence (Mr), and magneton number () were found to decrease upon the Tb-Tm substitution effect. On the other hand, the coercivity (Hc) was found to diminish with increasing x up to 0.03 and then begins to increase with further rising Tb-Tm content. The Hc values are in the range of 346.7–441.7 Oe at 300 K to 4044.4–5378.7 Oe at 10 K. The variations in magnetic parameters were described based on redistribution of cations, crystallites and/or grains size, canting effects, surface spins effects, super-exchange interaction strength, etc. The observed magnetic results indicated that the synthesized (Co0.5Ni0.5)[TmxTbxFe2−x]O4 NSFs could be considered as promising candidates to be used for room temperature magnetic applications and magnetic recording media.
1. Introduction
The complex oxides of transition metals are attractive both from a practical application [1,2,3] and from the point of view of studying the fundamental physical phenomena [4,5,6]. Close attention to these compounds appeared due to the interconnection of structural, charge, and spin interactions [7]. Multiferroics are the most relevant for research in the physics and chemistry of condensed matter [8,9,10]. Ferrites stand out among the most promising multiferroics [11,12,13].
The broad field of science and technology of spinel ferrite materials has been established [14,15,16]. Certainly, magnetic nanocrystal ferrites have the potentials for use as raw material for various technological industries processes, such as in non-volatile memory devices, spintronics, and energy storage devices [17,18,19], and also in bio-implementations, such as medical imaging, nano-drug delivery, and sensing [20,21]. The structure of spinel cubic ferrite contains a divalent cation (often transition metals) in addition to ferric ion, represented as Me2+Fe23+O4, where metals are bound by oxygen to form a face-centered cubic closed packing. Each of the cations resides either at tetrahedral A or an octahedral B lattice site [22]. Ferrites and derivatives are known for their broad ferromagnetic resonance linewidth, moreover, owing to their exceptionally high magnetic and dielectric loss, these crystals are regarded as crucial particularly in the area of electromagnetic interference and low observable technology (LOT) [23,24,25].
Typically, a candidate material for use as an electromagnetic resonance absorber should have (i) broad magnetic resonance bandwidth, large values of (ii) permeability, and (iii) permittivity [23,25]. NiCoFe3O4 nanomaterials are reported to have a low coercivity (1.20 Oe) and high values of saturation magnetic flux density (2.1 T) [26] and Curie temperature (~527 °C), high permeability and permittivity, and low value of magnetocrystalline anisotropy and appreciable resistivity (~105–104 ohm/cm). In addition, it is well known that both Co- and Ni are inverse spinels, that exhibit homogeneous distribution in the A and B lattice sites; thus, their magnetic features are attributed to antiferromagnetic coupling amongst the tetrahedral and octahedral sublattices [27,28]. Furthermore, nickel substituted cobalt ferrites demonstrate good chemical stability and thus found applications as a binder and as magnetic filler in electromagnetic shielding nanocomposites [29,30,31]. Moreover, it is generally anticipated that rare-earth substituted spinel ferrites, in many cases, would show a superior electric and magnetic character when compared with the pristine spinel counterpart [32].
The bottom-up chemical synthesis routes commonly employed to prepare magnetic nano ferrites include co-precipitation, thermal decomposition, microemulsion, hydrothermal, and polyol methods [33,34,35,36]. Although these techniques yield materials with a narrow size distribution, precise control of the structural morphology, surface area, and size/size distribution during the chemical reaction is challenging [37]. Additionally, large scale production of uniformly sized magnetic nanoparticles is crucial since many advanced technological applications are sensitive not only to nano-sized crystals but a material with crystals size consistency [38]. For instance, studies have shown that size/size distribution is a major factor that determines the mechanical and thermal stability of magnetic nanofluid that are used as heat transfer media [39]. Fortunately, a strict size control can be achieved through the sonochemical approach. This technique follows the acoustic cavitation phenomenon [37], where the reaction mixture is subjected to ultrasound treatment at high temperature and pressure. Consequently, the reaction is quenched by rapid cooling followed by the application of strong shock waves and microjets [37,40]. This process hinders secondary nucleation and offers excellent size/size distribution. In addition, the sonochemical method is inexpensive, environmentally benign, effective, and most importantly, produces magnetic nanocrystal with a better magnetic response.
Spinel ferrites substituted with rare-earth ions have been reported by numerous research groups. Biasi and co-workers investigated the magnetocrystalline anisotropy of NiCoxFe2−xO4. The report shows that, except for pristine NiFe2O4, all the samples had a positive value of magnetocrystalline anisotropy, which increases monotonically as more Co is introduced, the material, and thus, may have a practical application as magnetic material [41]. Zhang et al. [42] considered the magnetic properties of LaxNiCoFe2−xO4 (x = 0.025–0.125) synthesized via a sol-gel method, the substitution of La3+ effectively decreases the coercivity and increases the magnetization. On the other hand, Srinivasamurthy et al. [32] explored the phase and magnetic features of Ce-Sm doped Co-Ni nano spinel ferrite. They found that the magnetic measurements increased with increasing the dopant due to the improved superexchange interaction of A-B. Moreover, Hossain et al. [43] reported magnetic characteristics of Ni0.7Zn0.2Co0.1Fe2−xGdxO4 (x = 0.00–0.12). Their findings showed that the saturation magnetization reduced while coercivity improved with adding Gd. Almessiere et al. implemented a research on magnetic merits of CoTmxFe2−xO4 (0.0 ≤ x ≤ 0.08) and CoTbxFe2−xO4 (x ≤ 0.10) NPs. Influence of synthesis method on structure and microstructural analysis was observed for nanosized substituted spinels [44]. The outcome of these studies demonstrated a strong influence of Tm and Tb individually on magnetic features of Co ferrites [45].
Although Tm and Tb are reported to influence the magnetic behaviors of ferrites solids [44,45], no clear trend of physicochemical properties due to substitution can be found thus far. Moreover, a bimetallic substitution into NiCoFe2O4 is scarcely explored. Herein, we introduced a rare earth Tb3+ and Tm3+ as (Co0.5Ni0.5)[TmxTbxFe2−2x]O4 via ultrasonic technique. The material is characterized and studied the magnetic behavior as a function of the concentration of rare-earth dopants.
2. Materials and Methods
Ultrasound irradiation was employed to produce (Co0.5Ni0.5)[TmxTbxFe2−2x]O4 (x = 0.00–0.05) NSFs. The Ni(NO3)2·6H2O, Co(NO3)2·6H2O, Tm2O3, Tb4O7, and Fe(NO3)3·9H2O are employed as sources of the metals. Initially, an appropriate amount of Tm2O3 and Tb4O7 were first dissolved in 10 mL acid solution containing concentrated HCl and HNO3, the admixture was carefully heated up at 200 °C through continued stirring for 1 h. Secondly, a required quantity of metal nitrates was thawed in 60 mL deionized (DI) H2O. Subsequently, the Tm2O3 and Tb4O7 solution was gradually adding to the nitrate solution, and the resultants solution stirred at room temperature. The pH was adjusted to 11 using an ammonia solution. The precursor mixture was undergoing ultrasound irradiation by ultrasonic homogenizer for 40 min and 20 kHz. The solid product was purified by washing using distilled water several times until a neutral pH is achieved. The solid is finally dried at 60 °C overnight to obtain NSFs [46,47].
The XRD Benchtop Rigaku Miniflex (Cu Kα line) was applied to identify the structure of the NSFs. The morphology and composition of the samples were analyzed using FEI Titan ST SEM and TEM equipped with an EDX spectrometer. Quantum Design PPMS DynaCool-9 coupled with VSM head was applied to study the magnetic properties of the products.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structure
Figure 1 depicts the XRD powder pattern of (Co0.5Ni0.5)[TmxTbxFe2−2x]O4 (x = 0.00–0.05) NSFs. The characteristic peaks of the NSFs adequately matched with the JCPDS Card No 22-1086, and thus indicated the successful crystallization of the single phase of Co-Ni spinel ferrites. In addition, the Rietveld refinement revealed the absence of any trace rare earth oxides, suggesting the purity of the synthesized NSFs. It can be observed that, that the most intense peak at 2θ = 34.96° (x = 0.01–0.05) with a crystal plane (311) is shifted to a higher diffraction angle while x is increasing. Moreover, this peak becomes slightly broaden when increasing the ratio of the substituted ion; this is a characteristic of crystals with small particle size. Hence, the introduction of more Tm and Tb into the solid solution of the spinel ferrites hinders the crystal growth. A similar observation has been reported, where substitution using Gm3+, Sm3+ and Eu3+ resulted in a crystallite size reduction of Ni-Co ferrite [48]. On the other hand, cell parameters, cell volume, crystallite sizes, goodness fit (χ2), and R-factors have been evaluated via refinement through Match3 and a Full Proof program of X-ray experimental data as included in Table 1—lattice parameter (a), volume of unit cell (V), and average crystal size determined from XRD patterns (DXRD). A decrease in cell parameters and cell volume was observed when increasing the content of Tm3+ and Tb3+ (x = 0.0–0.05), this could be due to the deformation in spinel crystal by larger rTm3+ (0.88 Å) and rTb3+ (0.92 Å) in comparison with rFe3+(0.64 Å) which caused depositary in the grain boundary and hinders the cell parameters growth [49]. The crystal sizes were computed with the Debye–Scherer formula by considering the maximum peak (311) and found in the range of 11–13 nm.
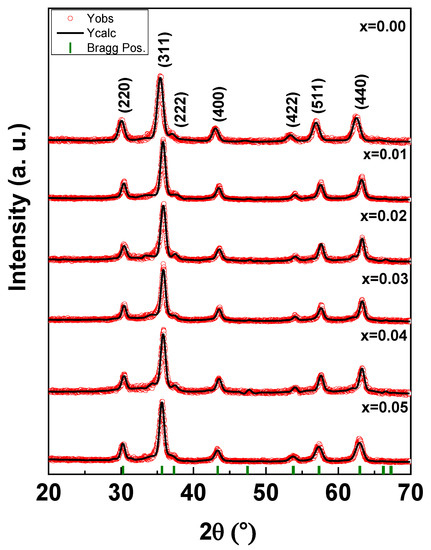
Figure 1.
XRD powder patterns of (Co0.5Ni0.5)[TmxTbxFe2−2x]O4 (x = 0.00–0.05) NSFs at room temperature.

Table 1.
Refined structural parameters and cation distribution calculations for (Co0.5Ni0.5)[TmxTbxFe2−2x]O4 (x = 0.00–0.05) NSFs.
Bertaut method applied to investigate cation occupancy of Co0.5Ni0.5TmxTbxFe2−2xO4 NSFs based on XRD data as following [50].
where and are the practical and calculated intensities, respectively, for reflection (hkl). The ratio of XRD lines, I220/I440, and I422/I400 were used for calculating the cation distribution with the planes that sensitive to the cation distribution [50,51]. It is well-known that Spinel ferrites contain a crystallographic site, specifically Octahedral (B) and Tetrahedral (A). Table 1 listed the cation distribution of Co0.5Ni0.5TmxTbxFe2−2xO4 system. The results revealed that for each value of x, the Fe3+, Ni2+, and Co2+ ions occupied the A-site and B-site. Both Tm3+ and Tb3+ cations are found that they occupied B-site only due to their higher ionic radii [52].
3.2. Surface Morphology
The morphological examination was conducted using SEM and the images for (Co0.5Ni0.5)[TmxTbxFe2−2x]O4 (x = 0.00, 0.01, 0.03 and 0.05) NSFs were depicted in Figure 2. The crystals exhibited spherical shape morphology with an agglomerated appearance obviously due to ferrimagnetic character. Overall, the sample displayed an appreciable distribution of particle size, in the range 15 nm that agreed with the XRD analysis. Of note, the sample with the highest Tb3+ and Tm3+ doping (x = 0.5) contains some irregularly shaped nanocrystals, these crystals agglomerates and produce a secondary grain with a size range of 200–500 nm. The elemental weight percentage of (Co0.5Ni0.5)[TmxTbxFe2−2x]O4 (x = 0.02 and 0.05) NSFs were evaluated using EDX elemental and mapping as shown in Figure 3. The EDX spectrum of all samples have verified the occurrence of Co, Ni, Tm, Tb, O and Fe elements in products. This also indicated the efficiency of the ultrasound synthesis method.
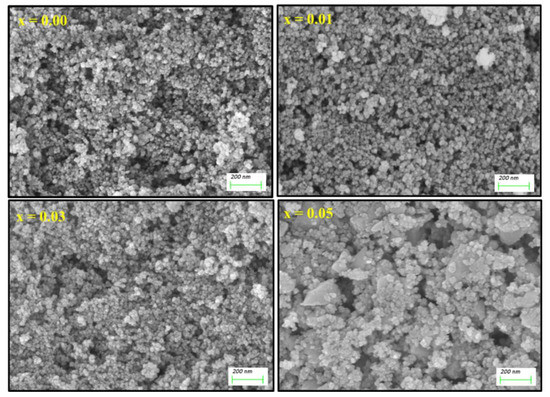
Figure 2.
SEM images of (Co0.5Ni0.5)[TmxTbxFe2−2x]O4 NSFs with x = 0.00, 0.01, 0.03 and 0.05.
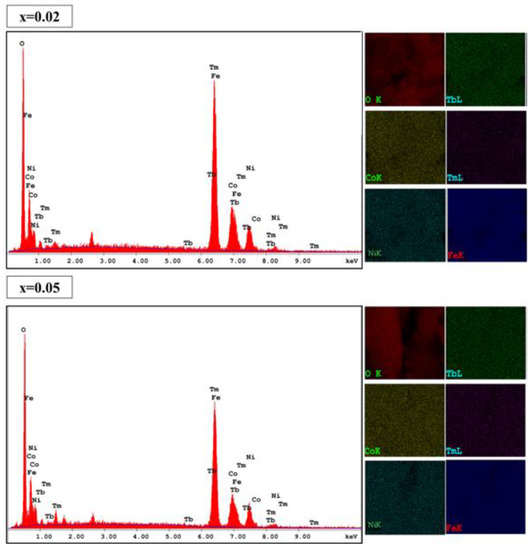
Figure 3.
EDX spectra and elemental mappings of (Co0.5Ni0.5)[TmxTbxFe2−2x]O4 NSFs with x = 0.02 and 0.05.
To further study the structure, morphology, and particle size, TEM and SAED were employed on Co0.5Ni0.5)[TmxTbxFe2−2x]O4 (x = 0.02 and 0.05) NSFs as seen in Figure 4. The TEM images disclosed the aggregation of cubic and spherical particles. Thus, observation of TEM images confirmed the uniformity of the particles. The particle size distribution histogram were calculated via Image J software and found that DXRD of products have been within the range of 9–15 nm (Figure 4). The SAED showed a spotty bright ring with different intensities that confirmed the purity of the spinel NSFs ferrites structure. Accordingly, the index planes are consented with the XRD results.
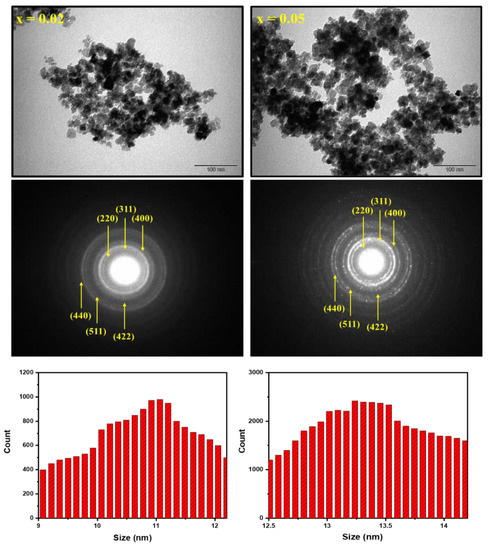
Figure 4.
TEM, SAED, and size distribution histograms of (Co0.5Ni0.5)[TmxTbxFe2−2x]O4 NSFs with x = 0.02 and 0.05.
3.3. Magnetic Properties
The experiments of magnetization versus the implemented magnetic field, M-H, were made at two selected temperatures (300 and 10 K). M-H hysteresis loops of unsubstituted and Tb/Tm-substituted Co-Ni spinel ferrites are existing in Figure 5 and Figure 6, respectively. The insets in Figure 5 show magnified regions near the origin (H = 0 kOe) so that the coercivity will be more visible. At both measurement temperatures, the different produced products displayed an opened M-H hysteresis loops with a clear and large coercivity, which reveal the ferrimagnetic (FM) behavior of various samples at 300 and 10 K. It is slightly obvious in various M-H hysteresis loops that the magnetization was not saturated easily even if the applied field is high. This observation is largely ascribed to the disordered or canted spins at the surface of NSFs, which are hard to be aligned along the direction of the field, which in turn will cause a non-saturated magnetization in the nanoparticles. In the following discussions, we referred to the magnetization at the maximum applied field as the saturation magnetization. Furthermore, Figure 6 showed a clear distortion in the region close to H = 0 kOe of M-H hysteresis loops performed at a lower temperature. Such distortion in M-H hysteresis loops is associated with a phenomenon of spins freezing, owing to the considerable time dependency of the remanent magnetization [53].
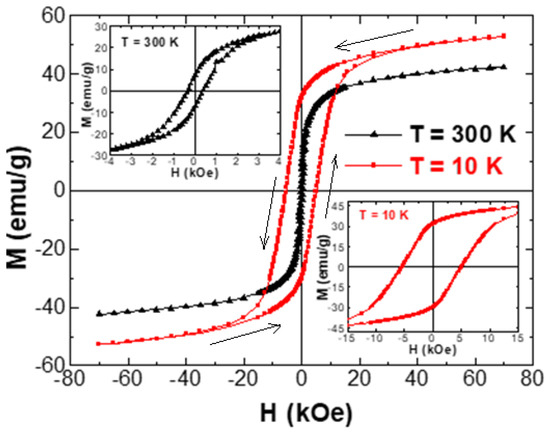
Figure 5.
Magnetization versus applied magnetic field performed at T = 300 and 10 K for Co0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4 NSFs. The insets show magnified views of the region near the origin (H = 0 kOe).
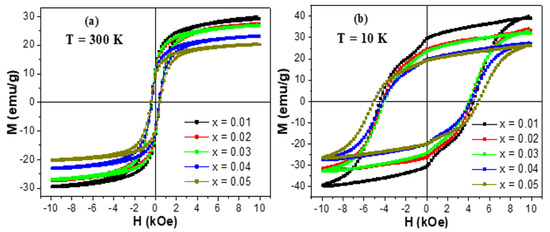
Figure 6.
M-H hysteresis loops of (Co0.5Ni0.5)[TmxTbxFe2−x]O4 NSFs with x = 0.01–0.05 performed at: (a) T = 300 K and (b) T = 10 K.
The several magnetic parameters are concluded from the performed M-H measurements and are offered in Figure 7. The variations of the saturation magnetization (Ms) with respect to Tm-Tb amounts at 300 and 10 K are displayed in Figure 7a. It is clear that Ms value enhances with the reduction in the temperature of nanoparticles from 300 K down to 10 K. Generally, Ms below the Curie temperature (Tc) obeys the Bloch’s law (Equation (2)) for bulky ferrimagnetic/ferromagnetic systems [54]:
where is the Ms value at , is the Bloch’s constant, is the Bloch’s exponent, and is the temperature at which . In line with this equation, when the temperature is decreasing, the magnetization will increase. Accordingly, the improvement in Ms values at lower temperatures compared to those at 300 K has essentially resulted from the reduction in the thermal fluctuations at lower temperatures [55,56]. Furthermore, the improvement in magnetization is accredited to the enhancement of spins order at the surface of Tb-Tm substituted Co0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4 nanoparticles [57]. Indeed, the spins moment of shells could additionally contribute to the resultant magnetization at lower temperatures, thus improving the total magnetization of NSFs [57].
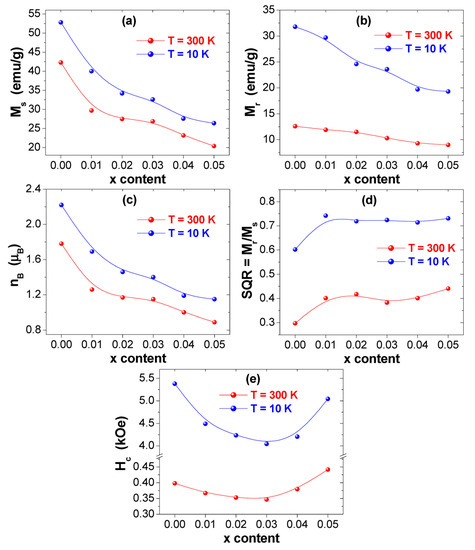
Figure 7.
Variations of various deduced magnetic parameters of (Co0.5Ni0.5)[TmxTbxFe2−2x]O4 with x = 0.00–0.05) NSFs at T = 300 and 10 K: (a) Ms, (b) Mr, (c) , (d) SQR = Mr/Ms, (e) Hc.
The non-substituted sample (i.e., Co0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4) displayed Ms values of about ~42.3 and ~52.8 emu/g at T = 300 and 10 K, correspondingly. These registered values are lower than those attained in bulk Co0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4 system. These lower Ms values can be ascribed to the structural distortions in the surface such as dead surface layers and random spins canting in comparison to the bulk for which it can diminish the number of contributing moments [58,59,60]. Furthermore, the difference in the site occupancy of different cations in nanoparticulate and bulky systems is responsible for the dissimilarity in Ms values [61]. In fact, Co0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4 NPs do not exhibit an inverse spinel structure type like in bulk compounds, but they have a mixed spinel structure type. Consequently, this leads to the observed decrease in the Ms value. Nevertheless, the Ms values observed in our samples are larger than those found in Co-Ni spinel ferrite NSFs produced via sol-gel auto-combustion approach [62,63] and mechanochemical technique [64]. Almost near Ms values are observed in Co-Ni spinel ferrite NSFs generated through a one-pot modified-solvothermal approach [30].
Ms decreases at both 300 and 10 K as a function of Tm-Tb contents. Ms value decreases from ~42.3 to ~20.4 emu/g at 300 K and from ~52.8 to ~26.4 emu/g at 10 K. The minimum Ms values of ~20.4 and ~26.4 emu/g, respectively, at 300 and 10 K are belonging to the composition with x = 0.05. Generally, the magnetic properties of spinel ferrite nanoparticles are significantly influenced by the microstructure, the composition, the crystallites size, and the distribution of cations between the B- and A-sites in spinel structure [65,66,67]. Firstly, it was found that Ms decreases at both 300 and 10 K as a function of grains/crystallites size. The variation in Ms value could be also described based on the experimental values of the magneton number () per formula unit in Bohr magneton (). The expression of is given as following [68]:
The determined values are presented in Figure 7c. It is obvious that , at both measurement temperatures 300 and 10 K, decreases with the rise in Tb3+ and Tm3+ contents, which reflect that the A-B superexchange interactions are weakened due to co-substitution effect. As evident from Figure 7a,c, the values of Ms and exposed similar tendencies as a function of Tb3+ and Tm3+ content.
The coercive fields (Hc) deduced from M-H loops are presented in Figure 7e. One can remarkably observe an increase in the coercivity of all prepared nanoparticles with the diminution in the temperature from 300 down to 10 K, which indicates that the prepared nanoparticles become magnetically harder at very low temperatures. The Hc values for various synthesized products improve from 346.7–441.7 Oe at 300 K to 4044.4–5378.7 Oe at 10 K. The coercivity is a sensitive characteristic to the temperature of a product. In fact, additional magnetic moments are frozen within anisotropic directions at very low temperatures. Hence, the observed increment trend in Hc values is generally assigned to the effects of thermal fluctuations of the blocked moments across the anisotropy barriers. The effect of spins freezing is predominant at lower temperatures mainly below the blocking temperature (TB). This could develop because of the exchange coupling among the spins of the core and the surface. The coercive field (Hc), for an assemblage of non-interacting three-dimensional single domain magnetic (SDM) NSFs and in a temperature interval lower than TB, can be expressed as follow [69,70]:
This expression is well-known as the Kneller’s law. It is a simple model form of thermal activation of the moments of nanoparticles across the anisotropy barriers. In Equation (4), the constant is the value of at . It is evident from this equation that Hc value increases with the decrease in the temperature below TB. This indicates that the effects of thermal activation of the nanoparticle moments across the anisotropy barriers are prominent at lower temperatures. Nevertheless, one should also take into account that the anisotropy effect could have a great influence when one is investigating the nanoparticles at lower temperatures. Hence, other factors (in addition to the improvement of anisotropy), such as the intrinsic structural characteristics of NSFs comprising the volume distribution, the interactions between particles, and the random anisotropy, could also affect the thermal dependency of Hc in the case of NSFs [71].
In the current investigation, the variation of Hc values at both 300 and 10 K could be explained based on the cations redistribution at the octahedral and tetrahedral sites and on the change of grains/crystallites size [47,65]. The non-substituted Co0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4 NSFs displayed Hc values of ~398.2 and ~5378.7 Oe at 300 and 10 K, respectively. Initially, Hc diminishes with the increase of Tb-Tm content up to x = 0.03. Afterward, it increases with further increasing Tb-Tm substituting contents. Largely, the variation in coercivity for nanoparticles is proportional to the crystallites/grains size [72]. At Tb-Tm substitution content lower than 0.3, it is noticed that Hc decreases with the decrease in grains/crystallites size as found in XRD and SEM investigations. However, for x ≥ 0.3, the coercivity and grains/crystallites size does not follow each other. The redistribution of cations at A and B- sites greatly influences the Hc of the Co-Ni ferrite NSFs. Accordingly, the improvement of Hc at higher Tb-Tm content (i.e., x ≥ 0.3) could be attributed to the existence of Co2+ and Ni2+ cations at the B-sites that lead to great values of magnetic anisotropy and coercivity because of the strong L–S coupling of bivalent+ cations at B-site. According to the observed results, the synthesized (Co0.5Ni0.5)[TmxTbxFe2−x]O4 NSFs could be considered as promising candidates to be used for room temperature magnetic applications and magnetic recording media [73].
The variations of the Mr value and the squareness ratio (SQR = Mr/Ms) against Tm-Tb contents are displayed in Figure 7b,d. It is observed that both Mr and SQR values for different samples increase with reducing the temperature from 300 down to 10 K, which indicates that the strength of the magnetic anisotropy intensifies at lower temperatures [74]. The Mr values are around ~12.6 and ~31.8 emu/g, respectively, at 300 and 10 K for un-substituted sample (x = 0.00). As observed in Figure 7a,b, the variations in Mr and Ms values exposed similar tendency versus Tb3+ and Tm3+ contents. Indeed, Mr values are maximum for the non-substituted Co0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4 NPs and then decreased upon Tb-Tm co-substitution. As shown via the morphological observations, the densities of grains of the diverse prepared products are very close. Therefore, the decline in Mr values is largely dependent on the evolution of Ms and the net alignment of grains magnetization induced by weak exchange interactions between particles. According to the Stoner–Wohlfarth concept for non-interacting particles with randomly oriented easy axes, SQR is around ~0.8 for cubic anisotropy and ~0.5 for uniaxial anisotropy [74]. Furthermore, a SQR value lower than 0.5 reflects that a multi-magnetic domain (MMD) structure is formed in which the motion of domain walls permits for an easier change in the orientation with the applied field, whereas, SQR value ≥0.5 implies that the system is around the single magnetic domain (SMD) size [75,76]. As shown in Figure 7d, SQR values for the synthesized products are in the interval of 0.298–0.441 (i.e., lower than 0.5) at T = 300 K, indicating that these products display a MMD structure with uniaxial anisotropy. However, SQR values are exceeding the value of 0.5 at 10 K but are still lower than 0.8, which implies that these products have a virtually SMD structure with the coexistence of cubic and uniaxial anisotropy.
4. Conclusions
The interdependence of Tm-Tb on the phase and magnetic features of Co-Ni NSFs as a new study has been presented. (Co0.5Ni0.5)[TmxTbxFe2−2x]O4 (x = 0.00–0.05) NSFs. NSFs were produced via ultrasound irradiation procedure. X-ray diffraction presented a single-phase formation of NSFs. It was found that the cell parameters decrease with the rise in the content of substitution ions. The morphology and grain size were estimated by SEM and TEM. The M-H hysteresis loops of various prepared nanoparticles showed a ferrimagnetic behavior at both measurement temperatures 300 and 10K. It was found that Ms, Mr, decreased as a function of Tb-Tm content. Hc values decreased with the increase of x content up to 0.03 and then increased with the further rise of Tb-Tm content. The variations in these magnetic parameters are successfully described based on the redistribution of cations, variations crystallites and/or grains size, canting effects, surface spins effects, super-exchange interaction strength, etc. The obtained magnetic results are found to be encouraging for the possible use of these products in room temperature magnetic applications and magnetic recording media.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A.A., Y.S., S.V.T., D.A.V. and A.V.T.; methodology, M.A.A., Y.S., and A.B.; data curation, İ.A.A. and S.E.S.; formal analysis, B.Ö. and İ.E.; investigation, Y.S., M.A.A. and A.V.T.; writing—original draft, Y.S., M.A.A., A.B., S.V.T. and A.V.T.; writing—review and editing, Y.S., M.A.A., S.V.T., D.A.V. and A.V.T.; supervision, M.A.A., Y.S., A.M. and A.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors greatly acknowledge the financial support from the Deanship of Scientific Research of Imam Abdulrahman Bin Faisal University (Dammam—Saudi Arabia) through the Grant No. 2020-164-IRMC. Present work was partially supported by RFBR (project 20-08-00716).
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Institute for Research and Medical Consultations (IMRC) of Imam Abdulrahman Bin Faisal University (IAU—Saudi Arabia) for providing lab facilities.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Guo, H.-H.; Zhou, D.; Du, C.; Wang, P.-J.; Liu, W.-F.; Pang, L.-X.; Wang, Q.-P.; Su, J.-Z.; Singh, C.; Trukhanov, S. Temperature stable Li2Ti0.75(Mg1/3Nb2/3)0.25O3-based microwave dielectric ceramics with low sintering temperature and ultra-low dielectric loss for dielectric resonator antenna applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 4690–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukenbayev, K.; Korolkov, I.V.; Tishkevich, D.I.; Kozlovskiy, A.L.; Trukhanov, S.V.; Gorin, Y.G.; Shumskaya, E.E.; Kaniukov, E.Y.; Vinnik, D.A.; Zdorovets, M.V.; et al. Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for Complex Targeted Delivery and Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.M.; Panina, L.V.; Trukhanova, E.L.; Darwish, M.A.; Morchenko, A.T.; Zubar, T.I.; Trukhanov, S.V.; Trukhanov, A.V. Structural, electric and magnetic properties of (BaFe11.9Al0.1O19)1-x-(BaTiO3)x composites. Comp. Part B Eng. 2019, 174, 107054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketsko, V.A.; Beresnev, E.N.; Kop’eva, M.A.; Rjabkova, L.V.; Baranchicov, A.E.; Stognij, A.I.; Trukhanov, A.V.; Kuznetsov, N.T. Specifics of the pyrohydrolytic and solid-phase syntheses of solid solutions in the (MgGa2O4)x(MgFe2O4)1-x system. Rus. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 55, 427–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nipan, G.D.; Ketsko, V.A.; Stognij, A.I.; Trukhanov, A.V.; Kol’tsova, T.N.; Kop’eva, M.A.; Elesina, L.V.; Kuznetsov, T.N. Properties of Mg(Fe1-XGaX)2O4+δ Solid solutions in stable and metastable state. Inorg. Mater. 2010, 46, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, C.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, H.; Ni, Y.; Pocs, C.A.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, F.; Hoffmann, C.; Wang, X.; Lee, M.; et al. Quantum liquid from strange frustration in the trimer magnet Ba4Ir3O10. NPJ Quantum Mater. 2020, 5, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpinsky, D.V.; Silibin, M.V.; Trukhanov, S.V.; Trukhanov, A.V.; Zhaludkevich, A.L.; Latushka, S.I.; Zhaludkevich, D.V.; Khomchenko, V.A.; Alikin, D.O.; Abramov, A.S.; et al. Peculiarities of the crystal structure evolution of BiFeO3-BaTiO3 ceramics across structural phase transitions. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarev, R.V.; Moskvin, A.S.; Kalashnikova, A.M.; Rasing, T. Charge transfer transitions in multiferroic BiFeO3 and related ferrite insulators. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 235128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodouop, F.K.; Fouokeng, G.C.; Ateuafack, M.E.; Tchoffo, M.; Fai, L.C. Metamagnetoelectric effect in multiferroics A2Cu2Mo3O12 (A=Rb and Cs) quantum spin chain. Phys. B 2020, 598, 412455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silveira Lacerda, L.H.; de Lazaro, S.R. Magneto-optical coupling and Kerr effect in PbNiO3, PbCrO3, and PbMnO3 multiferroics: An excited-states approach. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 514, 167176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trukhanov, S.V.; Trukhanov, A.V.; Kostishin, V.G.; Panina, L.V.; Kazakevich, I.S.; Turchenko, V.A.; Kochervinskiy, V.V. Coexistence of spontaneous polarization and magnetization in substituted M-type hexaferrites BaFe12–xAlxO19 (x ≤ 1.2) at room temperature. JETP Lett. 2016, 103, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchenko, V.; Trukhanov, A.; Trukhanov, S.; Balasoiu, M.; Lupu, N. Correlation of crystalline and magnetic structures of barium ferrites with dual ferroic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 477, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchenko, V.; Kostishyn, V.G.; Trukhanov, S.; Damay, F.; Porcher, F.; Balasoiu, M.; Lupu, N.; Bozzo, B.; Fina, I.; Trukhanov, A.; et al. Crystal and magnetic structures, magnetic and ferroelectric properties of strontium ferrite partially substituted with in ions. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 821, 153412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakovenko, O.S.; Matzui, L.Y.; Vovchenko, L.L.; Lozitsky, O.V.; Prokopov, O.I.; Lazarenko, O.A.; Zhuravkov, A.V.; Oliynyk, V.V.; Launets, V.L.; Trukhanov, S.V.; et al. Electrophysical properties of epoxy-based composites with graphite nanoplatelets and magnetically aligned magnetite. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2018, 661, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, M.A.; Trukhanov, A.V.; Senatov, O.S.; Morchenko, A.T.; Saafan, S.A.; Astapovich, K.A.; Trukhanov, S.V.; Trukhanova, E.L.; Pilyushkin, A.A.; Sombra, A.S.B.; et al. Investigation of AC-measurements of epoxy/ferrite composites. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trukhanov, A.V.; Astapovich, K.A.; Turchenko, V.A.; Almessiere, M.A.; Slimani, Y.; Baykal, A.; Sombra, A.S.B.; Zhou, D.; Jotania, R.B.; Singh, C.; et al. Influence of the dysprosium ions on structure, magnetic characteristics and origin of the reflection losses in the Ni-Co spinels. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 841, 155667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F. An Overview of surface-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles: Preparation and application for wastewater treatment. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 6805–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ortega, A.; Lottini, E.; Fernandez, C.d.J.; Sangregorio, C. Exploring the magnetic properties of cobalt-ferrite nanoparticles for the development of a rare-earth-free permanent magnet. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 4048–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Li, M.; Xiao, C.; Ding, D.; Gao, G.; Ding, S. Tunable growth of perpendicular cobalt ferrite nanosheets on reduced graphene oxide for energy storage. Nanotechnology 2016, 28, 055401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbab, A.S.; Jordan, E.K.; Wilson, L.B.; Yocum, G.T.; Lewis, B.K.; Frank, J.A. In Vivo trafficking and targeted delivery of magnetically labeled stem cells. Hum. Gene Ther. 2004, 15, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloag, L.; Mehdipour, M.; Chen, D.; Tilley, R.D.; Gooding, J.J. Advances in the application of magnetic nanoparticles for sensing. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1904385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, T.S.; Kadhim, F.J. Effect depositions parameters on the characteristics of Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4 nanocomposite films prepared by DC reactive magnetron Co-sputtering technique. Iraqi J. Phys. 2020, 18, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, V.G. Modern microwave ferrites. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 48, 1075–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, G.; Liu, Y.; Cui, T.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Guan, J. Tunable dielectric properties and excellent microwave absorbing properties of elliptical Fe3O4 nanorings. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 072905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datt, G.; Kotabage, C.; Abhyankar, A. Ferromagnetic resonance of NiCoFe2O4 nanoparticles and microwave absorption properties of flexible NiCoFe2O4–carbon black/poly(vinyl alcohol) composites. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 20699–20712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaka, T.; Takai, M.; Hayashi, K.; Ohashi, K.; Saito, M.; Yamada, K. A soft magnetic CoNiFe film with high saturation magnetic flux density and low coercivity. Nature 1998, 392, 796–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffari, M.; Amighian, J.; Darsheshdar, E. Magnetic and structural studies of nickel-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles, synthesized by the sol-gel method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 350, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, T.P.; Fay, M.W.; Zhu, Y.; Brown, P.D. Hydrothermal synthesis of mixed cobalt-nickel ferrite nanoparticles. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2012, 371, 012074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscas, G.; Yaacoub, N.; Concas, G.; Sayed, F.; Hassan, R.S.; Greneche, J.-M.; Cannas, C.; Musinu, A.; Foglietti, V.; Casciardi, S. Evolution of the magnetic structure with chemical composition in spinel iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 13576–13585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datt, G.; Bishwas, M.S.; Raja, M.M.; Abhyankar, A. Observation of magnetic anomalies in one-step solvothermally synthesized nickel–cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 5200–5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahgat, M.; Paek, M.-K.; Park, C.-H.; Pak, J.-J. Thermal synthesis of nanocrystalline (CoxNi1-x)yFe1-y KOVAR alloy through gaseous reduction of mixed oxides. Mater. Trans. 2008, 49, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasamurthy, K.; Angadi, V.J.; Kubrin, S.; Matteppanavar, S.; Kumar, P.M.; Rudraswamy, B. Evidence of enhanced ferromagnetic nature and hyperfine interaction studies of Ce-Sm doped Co-Ni ferrite nanoparticles for microphone applications. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 18878–18885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiri, S.; Sertkol, M.; Guner, S.; Gungunes, H.; Batoo, K.; Saleh, T.A.; Sozeri, H.; Almessiere, M.A.; Manikandan, A.; Baykal, A. Hydrothermal synthesis of CoyZnyMn1-2yFe2O4 nanoferrites: Magneto-optical investigation. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 5751–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auwal, I.; Erdemi, H.; Sözeri, H.; Güngüneş, H.; Baykal, A. Magnetic and dielectric properties of Bi3+ substituted SrFe12O19 hexaferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 412, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, D.; Ding, J.; Xue, J.-M. Synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles by thermal decomposition: Time, temperature, surfactant and solvent effects. Func. Mater. Lett. 2008, 1, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biehl, P.; Von der Lühe, M.; Dutz, S.; Schacher, F.H. Synthesis, characterization, and applications of magnetic nanoparticles featuring polyzwitterionic coatings. Polymers 2018, 10, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Nkurikiyimfura, I.; Pan, Z. Sonochemical synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. Comm. 2015, 202, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, M.; Yamini, Y.; Rezaee, M. Magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, stabilization, functionalization, characterization, and applications. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2010, 7, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkurikiyimfura, I.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Z. Effect of chain-like magnetite nanoparticle aggregates on thermal conductivity of magnetic nanofluid in magnetic field. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2013, 44, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchegiani, G.; Imperatori, P.; Mari, A.; Pilloni, L.; Chiolerio, A.; Allia, P.; Tiberto, P.; Suber, L. Sonochemical synthesis of versatile hydrophilic magnetite nanoparticles. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2012, 19, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Biasi, R.S.; de Souza Lopes, R.D. Magnetocrystalline anisotropy of NiCoFe2O4 nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 9315–9318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, A.; Zhao, X.; Suo, N.; Yu, L.; Zuo, Z. Structural and magnetic properties of La3+ ion doped Ni-Cu-Co nano ferrites prepared by sol-gel auto-combustion method. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 2019, 90, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Khan, M.; Nahar, A.; Ali, M.; Matin, M.; Hoque, S.; Hakim, M.; Jamil, A. Tailoring the properties of Ni-Zn-Co ferrites by Gd3+ substitution. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 497, 165978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almessiere, M.A.; Trukhanov, A.V.; Khan, F.A.; Slimani, Y.; Tashkandi, N.; Turchenko, V.A.; Zubar, T.I.; Tishkevich, D.I.; Trukhanov, S.V.; Panina, L.V.; et al. Correlation between microstructure parameters and anti-cancer activity of the [Mn0.5Zn0.5](EuxNdxFe2-2x)O4 nanoferrites produced by modified sol-gel and ultrasonic methods. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 7346–7354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadaqat, A.; Almessiere, M.; Slimani, Y.; Guner, S.; Sertkol, M.; Albetran, H.; Baykal, A.; Shirsath, S.E.; Ozcelik, B.; Ercan, I. Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Tb3+ substituted Co nanoferrites prepared via sonochemical approach. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 22538–22546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almessiere, M.; Slimani, Y.; Guner, S.; Sertkol, M.; Korkmaz, A.D.; Shirsath, S.E.; Baykal, A. Sonochemical synthesis and physical properties of Co0.3Ni0.5Mn0.2EuxFe2−xO4 nano-spinel ferrites. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 58, 104654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almessiere, M.; Slimani, Y.; Kurtan, U.; Guner, S.; Sertkol, M.; Shirsath, S.E.; Akhtar, S.; Baykal, A.; Ercan, I. Structural, magnetic, optical properties and cation distribution of nanosized Co0.7Zn0.3TmxFe2−xO4 (0.0≤x≤0.04) spinel ferrites synthesized by ultrasonic irradiation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 58, 104638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanbir, K.; Ghosh, M.P.; Singh, R.K.; Kar, M.; Mukherjee, S. Effect of doping different rare earth ions on microstructural, optical, and magnetic properties of nickel-cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, A.; Mande, V.K.; Kadam, S.; Kadam, R.; Shirsath, S.E.; Borade, R.B. Influence of gadolinium (Gd3+) ion substitution on structural, magnetic and electrical properties of cobalt ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 840, 155669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirsath, S.E.; Mane, M.; Yasukawa, Y.; Liu, X.; Morisako, A. Chemical tuning of structure formation and combustion process in CoDy0.1Fe1.9O4 nanoparticles: Influence@pH. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2013, 15, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirsath, S.E.; Mane, M.L.; Yasukawa, Y.; Liu, X.; Morisako, A. Self-ignited high temperature synthesis and enhanced super-exchange interactions of Ho3+–Mn2+–Fe3+–O2− ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 2347–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, L.; Aparicio, M.; Jitianu, A. Handbook of Sol-Gel Science and Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, H.; Msomi, J.; Moyo, T.; Dolo, J.; Lančok, A. Mössbauer and magnetic studies of Mn0.1Sr0.2Co0.7Fe2O4 nanoferrite. Hyperfine Interact. 2011, 203, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloch, F. Zur Theorie des Ferromagnetismus. Zeitschrift für Physik 1930, 61, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trukhanov, A.V.; Algarou, N.A.; Slimani, Y.; Almessiere, M.A.; Baykal, A.; Tishkevich, D.I.; Vinnik, D.A.; Vakhitov, M.G.; Klygach, D.S.; Silibin, M.V.; et al. Peculiarities of the microwave properties of hard-soft functional composites SrTb0.01Tm0.01Fe11.98O19-AFe2O4 (A = Co, Ni, Zn, Cu and Mn). RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 32638–32651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almessiere, M.A.; Slimani, Y.; Gungunes, H.; Manikandan, A.; Baykal, A. Investigation of the effects of Tm3+ on the structural, microstructural, optical, and magnetic properties of Sr hexaferrites. Res. Phys. 2019, 13, 102166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, L.; Kolesnichenko, V.; Caruntu, D.; Chou, N.; O’Connor, C.; Spinu, L. Magnetic properties of ultrafine cobalt ferrite particles. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 7486–7488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A., Jr.; e Silva, F. High temperature magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 172505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J. Noncollinear spin structures. Can. J. Phys. 1987, 65, 1210–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimani, Y.; Almessiere, M.; Nawaz, M.; Baykal, A.; Akhtar, S.; Ercan, I.; Belenli, I. Effect of bimetallic (Ca, Mg) substitution on magneto-optical properties of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 6021–6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagomi, F.; Da Silva, S.; Garg, V.; Oliveira, A.; Morais, P.; Franco, A., Jr.; Lima, E. The influence of cobalt population on the structural properties of CoxFe3−xO4. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 09M514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffari, F.; Kameli, P.; Rahimi, M.; Ahmadvand, H.; Salamati, H. Effects of Co-substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of NiCoxFe2−xO4 ferrite nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 7352–7358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algarou, N.A.; Slimani, Y.; Almessiere, M.A.; Sadaqat, A.; Trukhanov, A.V.; Gondal, M.A.; Hakeem, A.S.; Trukhanov, S.V.; Vakhitov, M.G.; Klygach, D.S.; et al. Functional Sr0.5Ba0.5Sm0.02Fe11.98O4/x(Ni0.8Zn0.2Fe2O4) hard-soft ferrite nanocomposites: Structure, magnetic and microwave properties. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chermahini, M.D.; Baghbaderani, H.A.; Shahraki, M.M.; Kazazi, M. Low temperature sintering of magnetic Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4 ceramics prepared from mechanochemically synthesized nanopowders. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 5491–5495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Y.; Shirage, P.M. Highest coercivity and considerable saturation magnetization of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles with tunable band gap prepared by thermal decomposition approach. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 4840–4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almessiere, M.; Slimani, Y.; Güner, S.; Baykal, A.; Ercan, I. Effect of dysprosium substitution on magnetic and structural properties of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Rare Earths 2019, 37, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimani, Y.; Almessiere, M.; Güner, S.; Tashkandi, N.; Baykal, A.; Sarac, M.; Nawaz, M.; Ercan, I. Calcination effect on the magneto-optical properties of vanadium substituted NiFe2O4 nanoferrites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 9143–9154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimani, Y.; Unal, B.; Almessiere, M.; Korkmaz, A.D.; Shirsath, S.E.; Yasin, G.; Trukhanov, A.; Baykal, A. Investigation of structural and physical properties of Eu3+ ions substituted Ni0.4Cu0.2Zn0.4Fe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles prepared via sonochemical approach. Res. Phys. 2020, 17, 103061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaz, K.; Mumtaz, A.; Hasanain, S.; Bertino, M. Temperature dependent coercivity and magnetization of nickel ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 2199–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimani, Y.; Almessiere, M.; Güner, S.; Kurtan, U.; Shirsath, S.E.; Baykal, A.; Ercan, I. Magnetic and microstructural features of Dy3+ substituted NiFe2O4 nanoparticles derived by sol-gel approach. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 2020, 95, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, O.; Labarta, A.; Batlle, X. Exchange bias phenomenology and models of core/shell nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2008, 8, 2761–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimani, Y.; Almessiere, M.; Korkmaz, A.D.; Guner, S.; Güngüneş, H.; Sertkol, M.; Manikandan, A.; Yildiz, A.; Akhtar, S.; Shirsath, S.E. Ni0.4Cu0.2Zn0.4TbxFe2-xO4 nanospinel ferrites: Ultrasonic synthesis and physical properties. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 59, 104757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tegus, O.; Brück, E.; Buschow, K.; De Boer, F. Transition-metal-based magnetic refrigerants for room-temperature applications. Nature 2002, 415, 150–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, N.S.; Moyo, T. Temperature dependence of coercivity and magnetization of Sr1/3Mn1/3Co1/3Fe2O4 ferrite nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2016, 29, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, C.C.; Kagdi, A.R.; Jotania, R.B.; Upadhyay, A.; Sandhu, C.S.; Shirsath, S.E.; Meena, S.S. Structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of Co-Zr substituted M-type calcium hexagonal ferrite nanoparticles in the presence of α-Fe2O3 phase. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 17812–17823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almessiere, M.; Slimani, Y.; Korkmaz, A.; Taskhandi, N.; Sertkol, M.; Baykal, A.; Shirsath, S.E.; Ercan, İ.; Ozcelik, B. Sonochemical synthesis of Eu3+ substituted CoFe2O4 nanoparticles and their structural, optical and magnetic properties. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 58, 104621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).