Effects of Mg and Sb Substitution on the Magnetic Properties of Magnetic Field Annealed MnBi Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental and Calculations
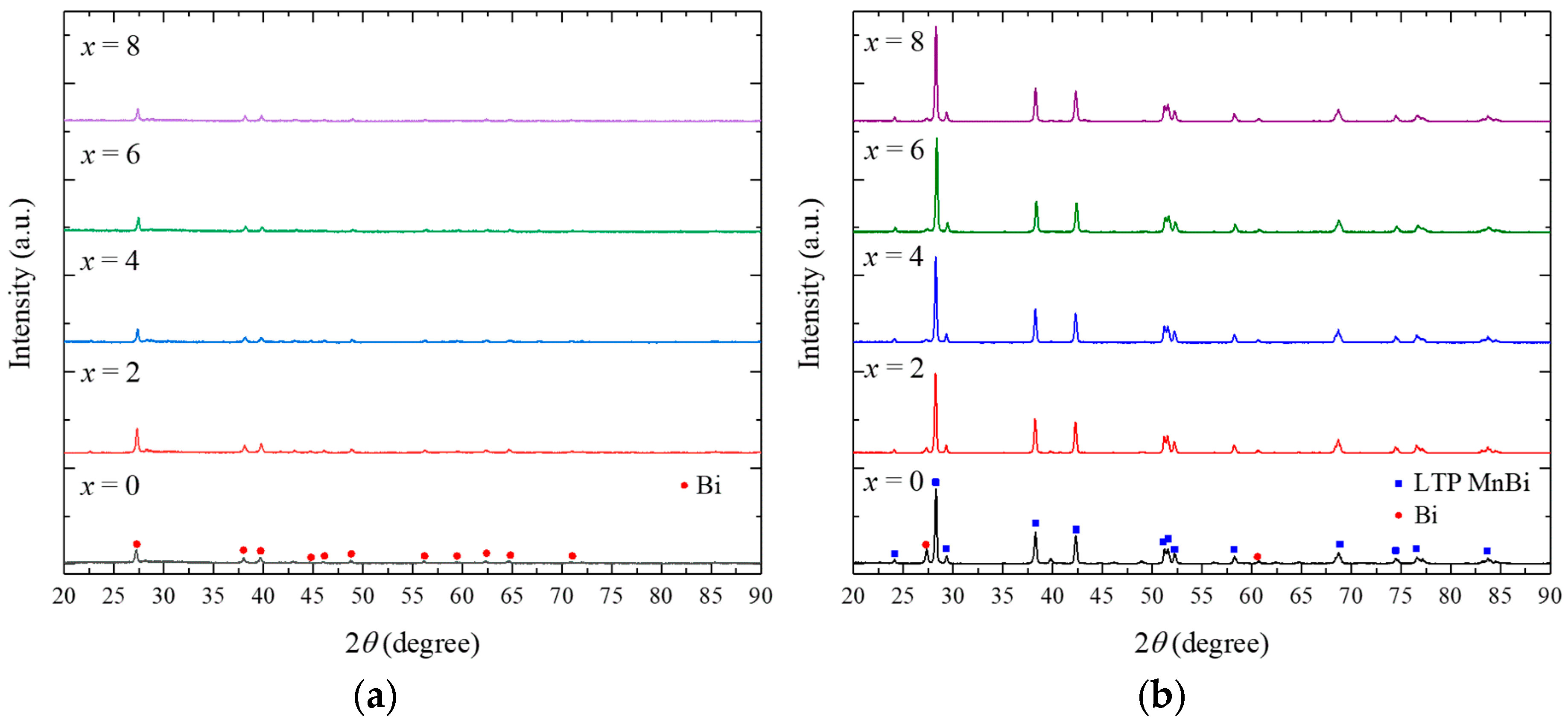
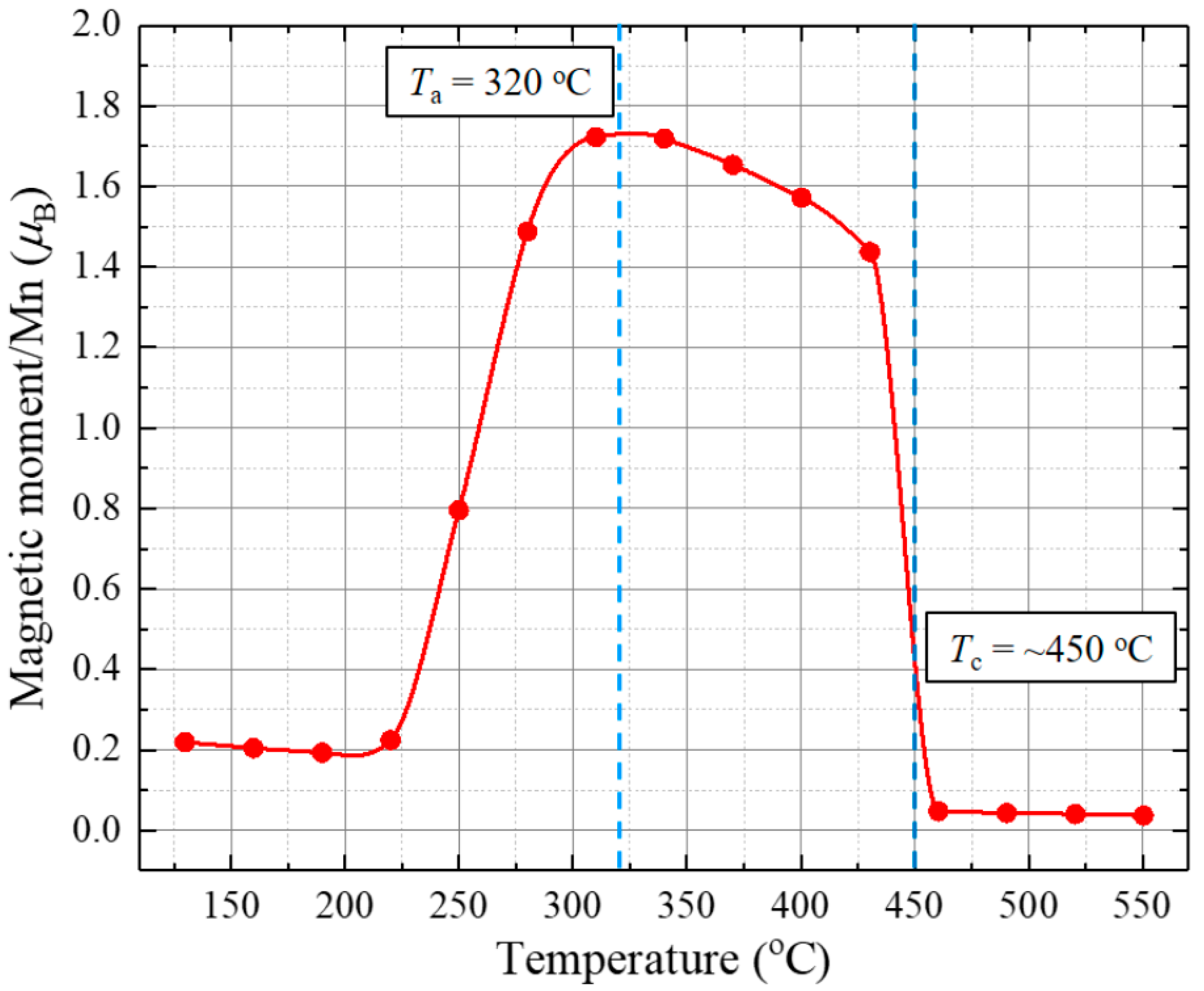
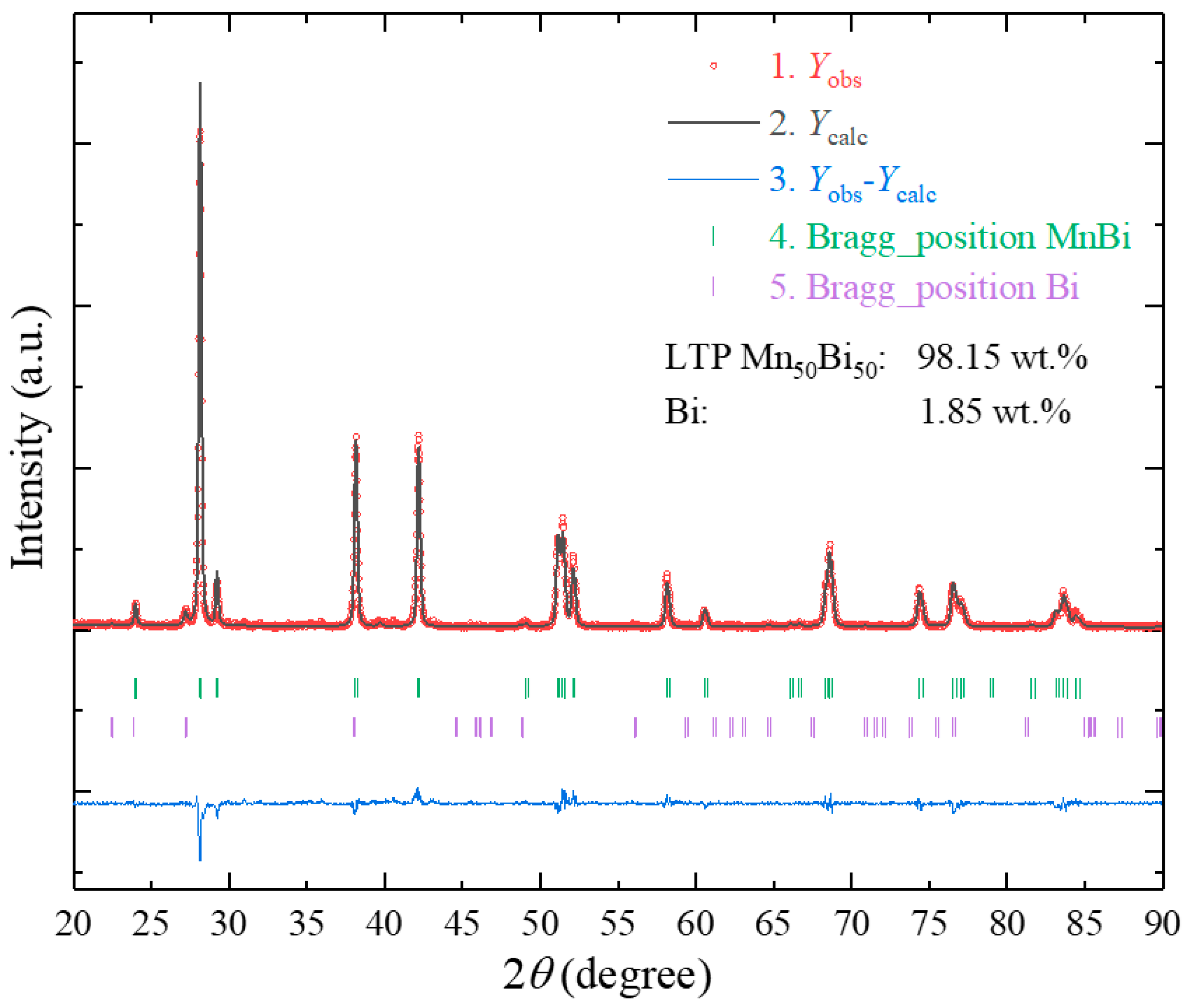
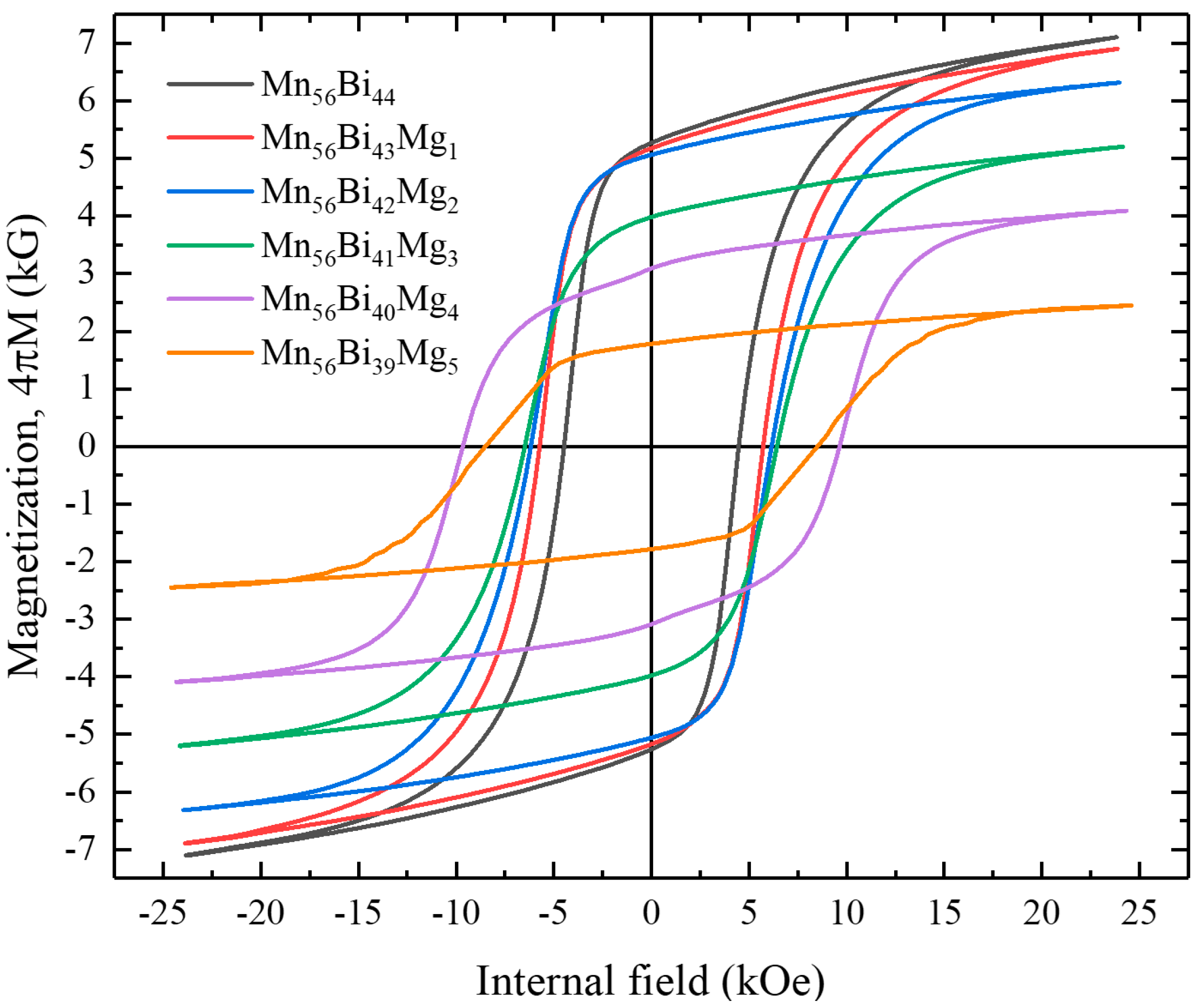
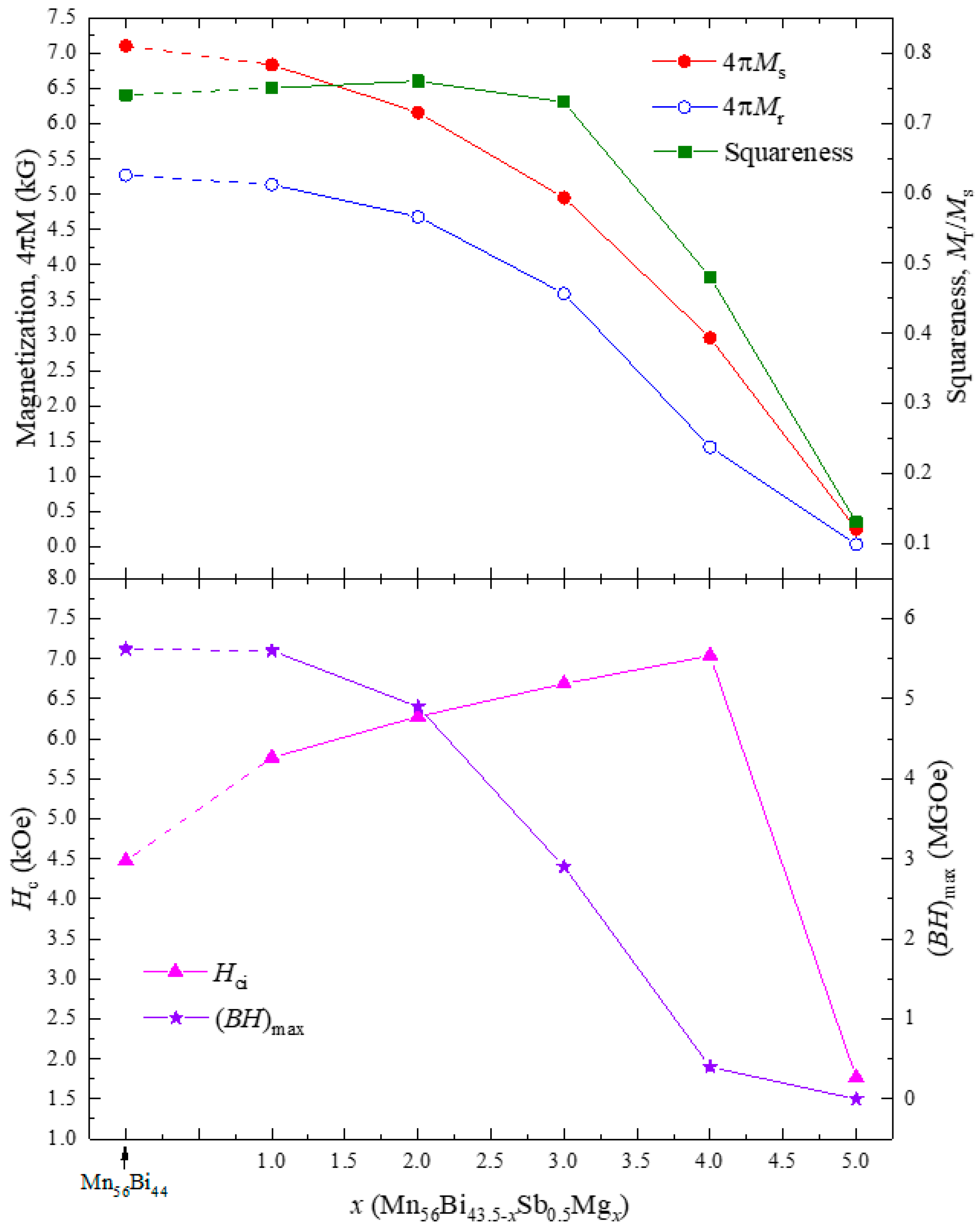
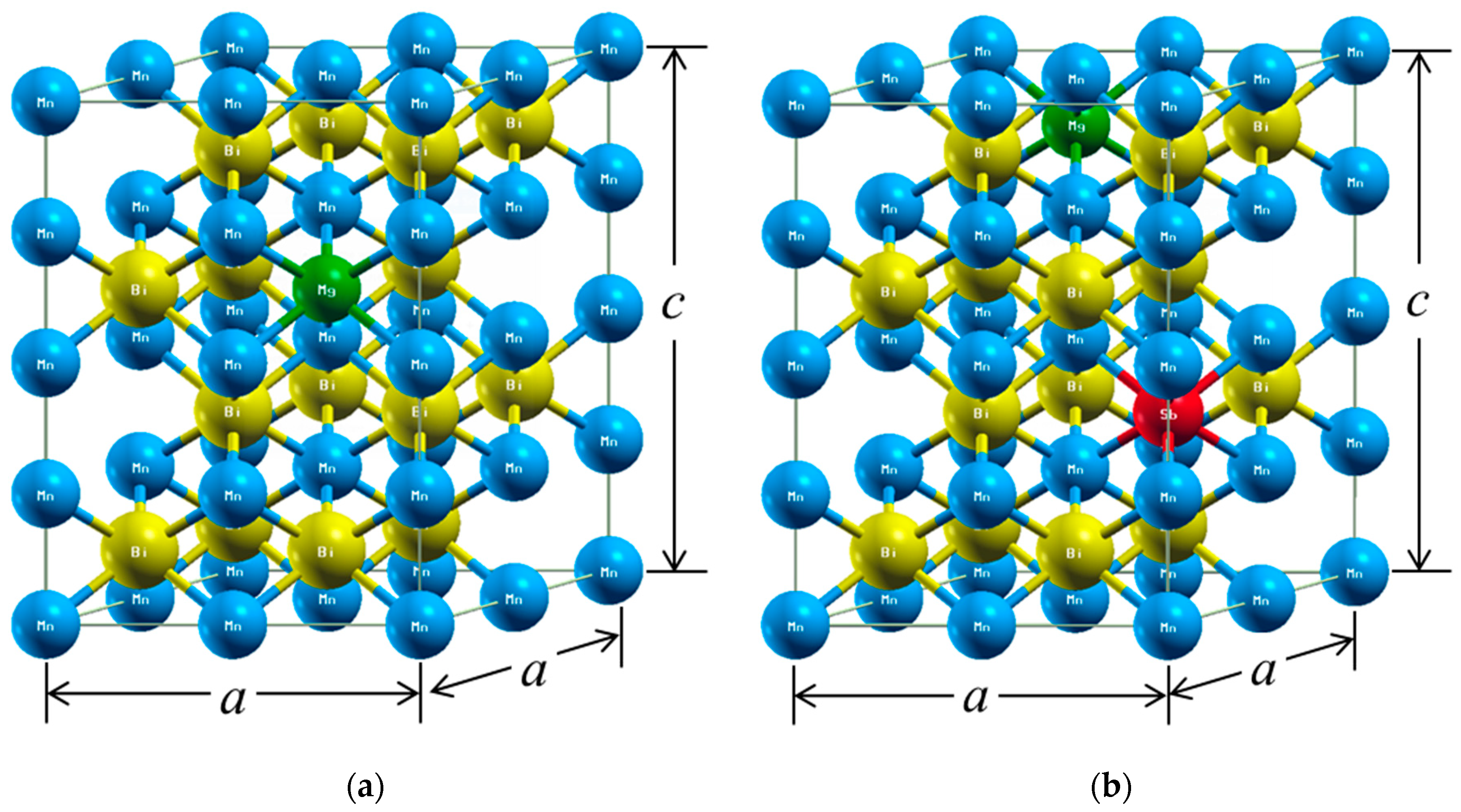
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vagati, A. The Synchronous Reluctance Solution: A New Alternative in AC drives. In Proceedings of the IECON’94–20th Annual Conference of IEEE Industrial Electronics, Bologna, Italy, 5–9 September 1994; Volume 1, pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Lipo, T.A. Synchronous reluctance machines-a viable alternative for AC drives? Electr. Mach. Power Syst. 1991, 19, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rama Rao, N.V.; Gabay, A.M.; Hadjipanayis, G.C. Anisotropic fully dense MnBi permanent magnet with high energy product and high coercivity at elevated temperatures. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 062001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Huang, Y.L.; Hou, Y.H.; Shi, Z.Q.; Yan, X.T.; Zhong, Z.C.; Wang, G.P. Microstructure and magnetic properties of MnBi alloys with high coercivity and significant anisotropy prepared by surfactant assisted ball milling. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 473, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnasamy, C.; Jasinski, M.M.; Ulmer, A.; Li, W.; Hadjipanayis, G.; Liu, J. Mn-Bi magnetic powders with high coercivity and magnetization at room temperature. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 3641–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Park, J.; Lim, J.T.; Kim, J.-W.; Li, O.L.; Choi, C.-J. Effect of phase purity on enhancing the magnetic properties of Mn-Bi alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2021, 517, 167344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Choi, J.P.; Li, G.; Polikarpov, E.; Darsell, J.; Overman, N.; Olszta, M.; Schreiber, D.; Bowden, M.; Droubay, T.; et al. Thermal stability of MnBi magnetic materials. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2014, 26, 064212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Moon, H.; Jung, H.; Kim, S.-M.; Lee, H.-S.; Choi-Yim, H.; Lee, W. Magnetic properties of large-scaled MnBi bulk magnets. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 708, 1245–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.B.; Yelon, W.B.; James, W.J.; Cai, Q.; Kornecki, M.; Roy, S.; Ali, N.; L’Heritier, P. Crystal structure, magnetic properties and electronic structure of the MnBi intermetallic compound. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2002, 14, 6509–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudyal, N.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Nguyen, V.V.; Ma, Y.; Gandha, K.; Elkins, K.; Liu, J.P.; Sun, K.; Kramer, M.J.; et al. Processing of MnBi bulk magnets with enhanced energy product. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 056004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Hong, Y.-K.; Lee, J.; Lee, W.; Kim, S.-G.; Choi, C.-J. Electronic structure and maximum energy product of MnBi. Metals 2014, 4, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Kim, J.-W.; Si, P.-Z.; Qian, H.-D.; Shin, Y.; Wang, X.; Park, J.; Li, O.L.; Wu, Q.; Ge, H.; et al. Effects of Ga-doping on the microstructure and magnetic properties of MnBi alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 769, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuma, A.; Manabe, Y.; Kota, Y. First principles calculation of magnetocrystalline anisotropy energy of MnBi and MnBi1-xSnx. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2013, 82, 073704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.-D.; Park, J.; Lim, J.T.; Yang, Y.; Si, P.-Z.; Kim, J.W.; Choi, C.-J.; Cho, K.M. Magnetic properties of MnBi bulk magnets with NaCl and C addition. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 115213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qian, H.; Si, P.-Z.; Yang, Y.; Choi, C.-J.; Park, J.; Wang, X.; Ge, H.; Shinde, K.P.; Chung, K. Structure and magnetic properties of MnBi nanoparticles prepared by laser ablation and arc-discharge method. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54, 2301005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, H.; Ohnaka, I.; Yamamoto, Y.; Tokieda, K.; Kishio, K. Formation of crystallographically aligned BiMn grains by semi-solid processing of rapidly solidified Bi-Mn alloys under a magnetic field. Mater. Trans. 2003, 44, 2207–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.-M.; Li, X.; Deng, K.; Wang, H.; Zhuang, Y. Solidification structures of Bi-Mn alloys under a high magnetic field. J. Shanghai Univ. 2006, 10, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, R.; Mitsui, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Uda, S.; Koyama, K. In-field annealing and quenching for ferromagnetic MnBi under 19 T. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2019, 55, 1000204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsui, Y.; Abematsu, K.; Umetsu, R.Y.; Takahashi, K.; Koyama, K. Magnetic field effects on liquid-phase reactive sintering of MnBi. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 400, 304–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Kharel, P.; George, T.; Li, X.Z.; Mukherjee, P.; Valloppilly, S.; Sellmyer, D.J. Grain alignment due to magnetic-field annealing in MnBi:Bi nanocomposites. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 455002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, P.Z.; Yang, Y.; Yao, L.L.; Qian, H.D.; Ge, H.L.; Park, J.; Chung, K.C.; Choi, C.J. Magnetic-field-enhanced reactive synthesis of MnBi from Mn nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 476, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, T. Magnet Steel Containing Nickel and Aluminium. U.S. Patent 2,027,994, 14 January 1936. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Balasubramanian, B.; Kharel, P.; Pahari, R.; Valloppilly, S.R.; Li, X.; Yue, L.; Skomski, R.; Sellmyer, D.J. High energy product of MnBi by field annealing and Sn alloying. APL Mater. 2019, 7, 121111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, A.M.; Hadjipanayis, G.C.; Cui, J. Effect of Sb substitution on crystal structure, texture and hard magnetic properties of melt-spun MnBi alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 792, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, A.M.; Hadjipanayis, G.C.; Cui, J. New anisotropic MnBi permanent magnets by field-annealing of compacted melt-spun alloys modified with Mg and Sb. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 495, 165860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, A.M.; Hadjipanayis, G.C. Effect of Mg content in melt-spun Mn–Bi–Mg–Sb–In alloys on the structure and properties of field-annealed magnets. IEEE Magn. Lett. 2020, 11, 7503304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, A.M.; Hadjipanayis, G.C.; Cui, J. Development of rare-earth-free bulk magnets with energy product up to 12 MGOe in field annealed Mn–Bi–Mg–In–Sb alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 822, 153663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaha, P.; Schwarz, K.; Madsen, G.; Kvasnicka, D.; Luitz, J. WIEN2k: An Augmented Plane Wave Plus Local Orbitals Program for Calculating Crystal Properties; Vienna University of Technology: Vienna, Austria, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, B.W. Neutron diffraction study of the structures and magnetic properties of manganese bismuthide. Phys. Rev. 1956, 104, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T. Contribution to the equilibrium phase diagram of the Mn-Bi system near MnBi. J. Appl. Phys. 1974, 45, 2358–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, N.R.; Singh, N.; Singh, S.K.; Gahtori, B.; Mishra, S.K.; Dhar, A.; Awana, V.P.S. Appreciable magnetic moment and energy density in single-step normal route synthesized MnBi. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 2013, 26, 3161–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J.M.D. Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 401–404. [Google Scholar]
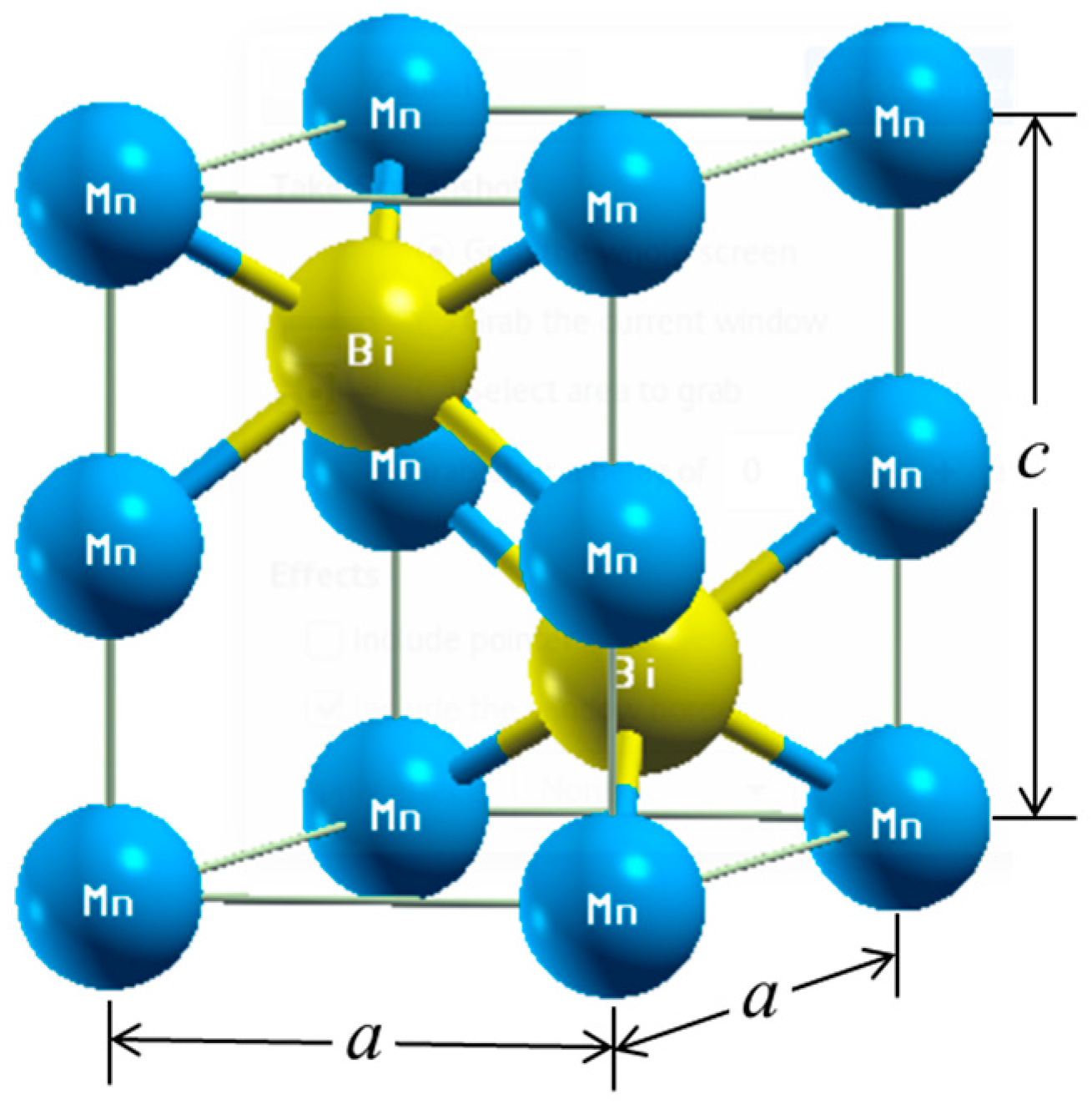



| Materials | Mn | Bi | Mg | Sb | Interstitial, Int. | Total Magnetic Moments, μB | Anisotropy Constant, K (×106 J/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MnBi | 3.571 | −0.103 | - | - | 0.104 | 7.044 | −0.850 |
| MnMg | 2.331 | - | 0.002 | - | 0.006 | 0.067 | 19.690 |
| Mn16Bi15Mg | 3.577 | −0.108 | −0.071 | - | 0.790 | 56.371 | −0.898 |
| Mn16Bi15Sb | 3.573 | −0.121 | - | −0.124 | 0.741 | 56.210 | 6.042 |
| Mn16Bi14SbMg | 3.579 | −0.134 | −0.071 | −0.131 | 0.784 | 56.368 | −0.441 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, H.-D.; Yang, Y.; Lim, J.T.; Kim, J.-W.; Choi, C.-J.; Park, J. Effects of Mg and Sb Substitution on the Magnetic Properties of Magnetic Field Annealed MnBi Alloys. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112265
Qian H-D, Yang Y, Lim JT, Kim J-W, Choi C-J, Park J. Effects of Mg and Sb Substitution on the Magnetic Properties of Magnetic Field Annealed MnBi Alloys. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(11):2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112265
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Hui-Dong, Yang Yang, Jung Tae Lim, Jong-Woo Kim, Chul-Jin Choi, and Jihoon Park. 2020. "Effects of Mg and Sb Substitution on the Magnetic Properties of Magnetic Field Annealed MnBi Alloys" Nanomaterials 10, no. 11: 2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112265
APA StyleQian, H.-D., Yang, Y., Lim, J. T., Kim, J.-W., Choi, C.-J., & Park, J. (2020). Effects of Mg and Sb Substitution on the Magnetic Properties of Magnetic Field Annealed MnBi Alloys. Nanomaterials, 10(11), 2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112265






