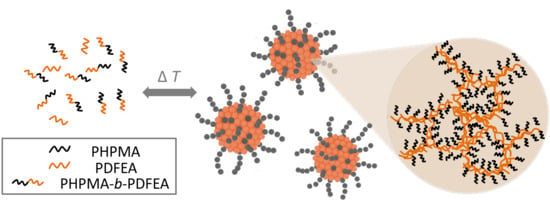
Internal Structure of Thermoresponsive Physically Crosslinked Nanogel of Poly[N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide]-Block-Poly[N-(2,2-difluoroethyl)acrylamide], Prominent 19F MRI Tracer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
2.3. Small-Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS)
2.4. Small-Angle Neutron Scattering (SANS)
2.5. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
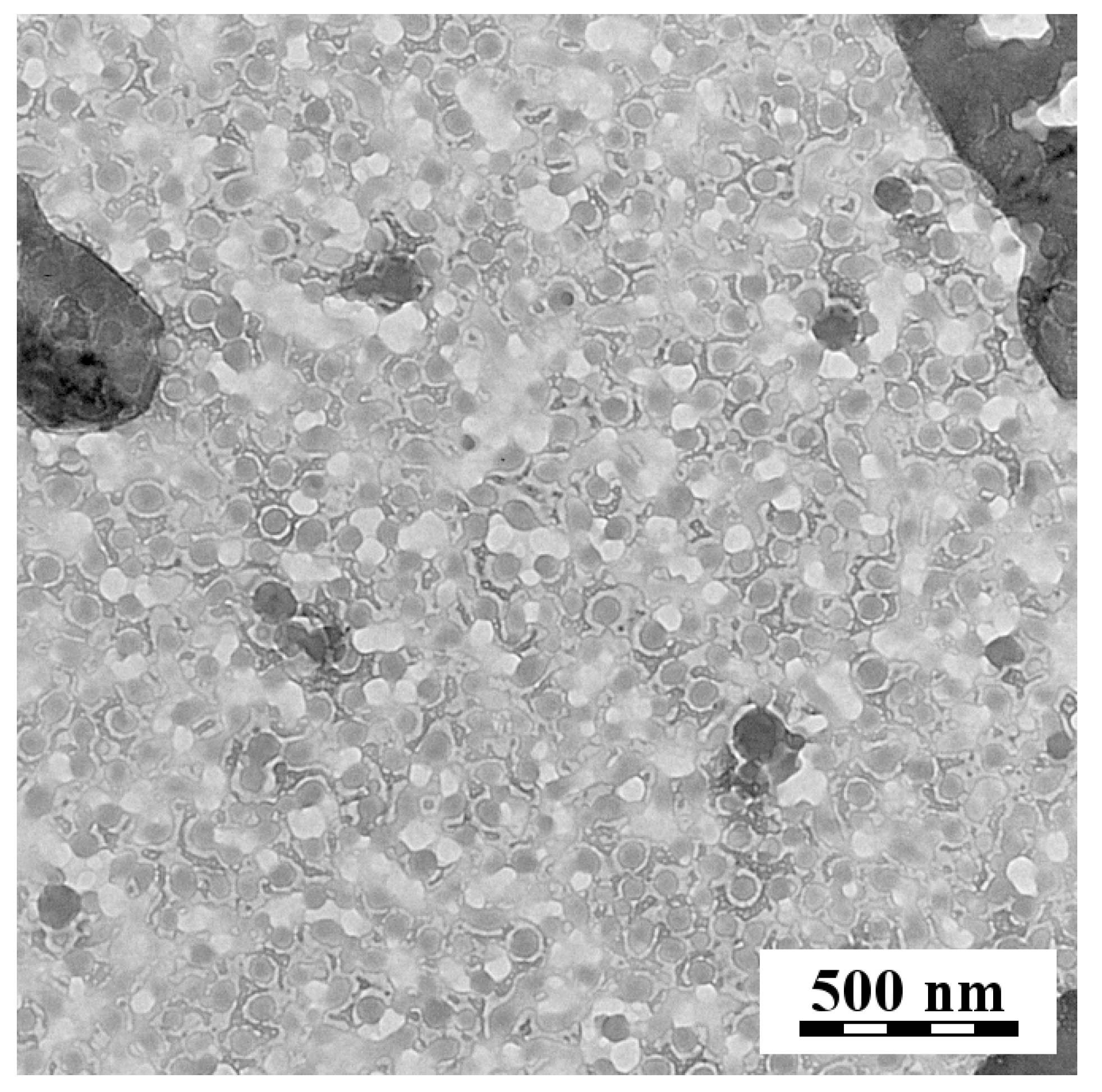
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
3.2. Small-Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS)
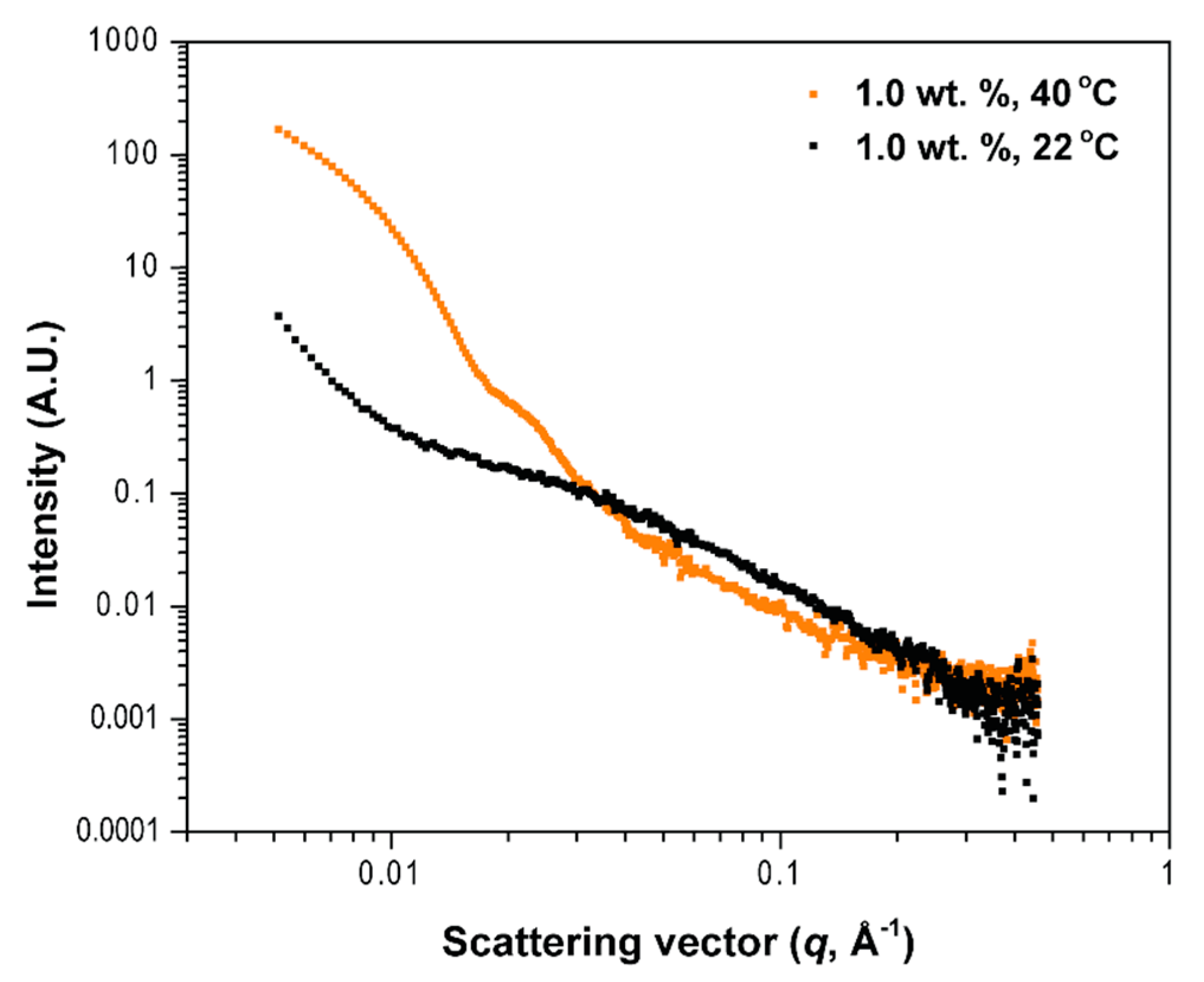
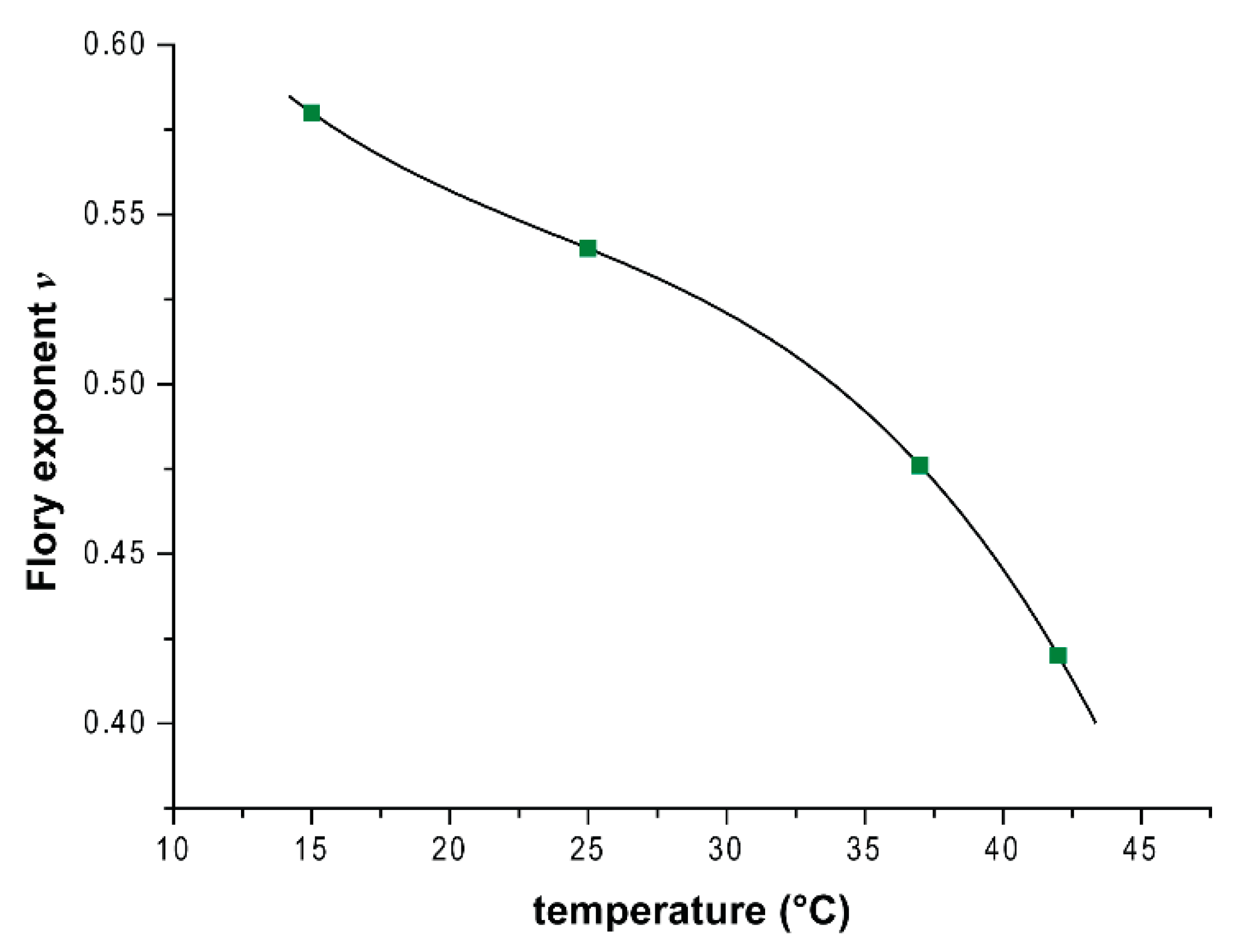
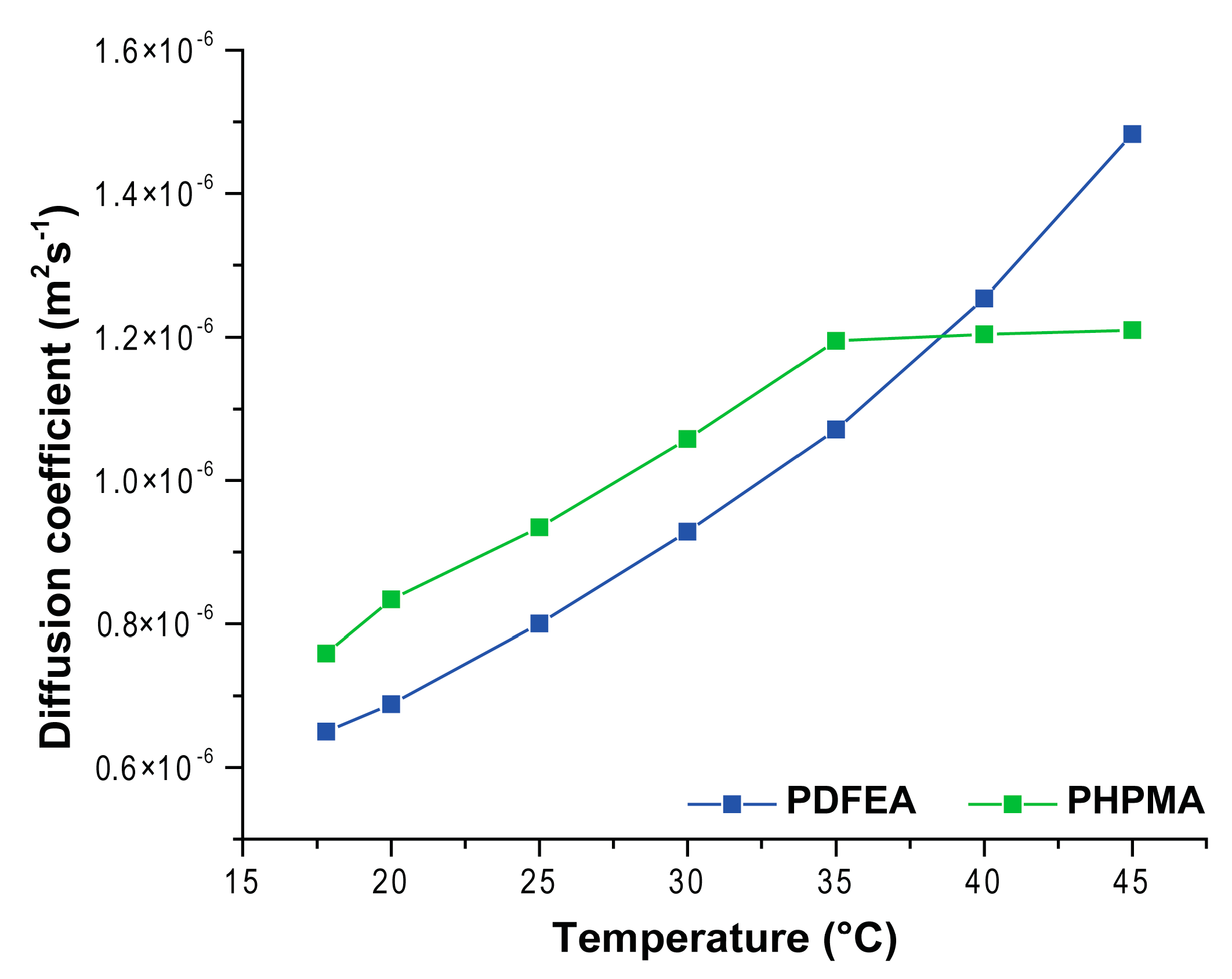
3.3. Small-Angle Neutron Scattering (SANS)
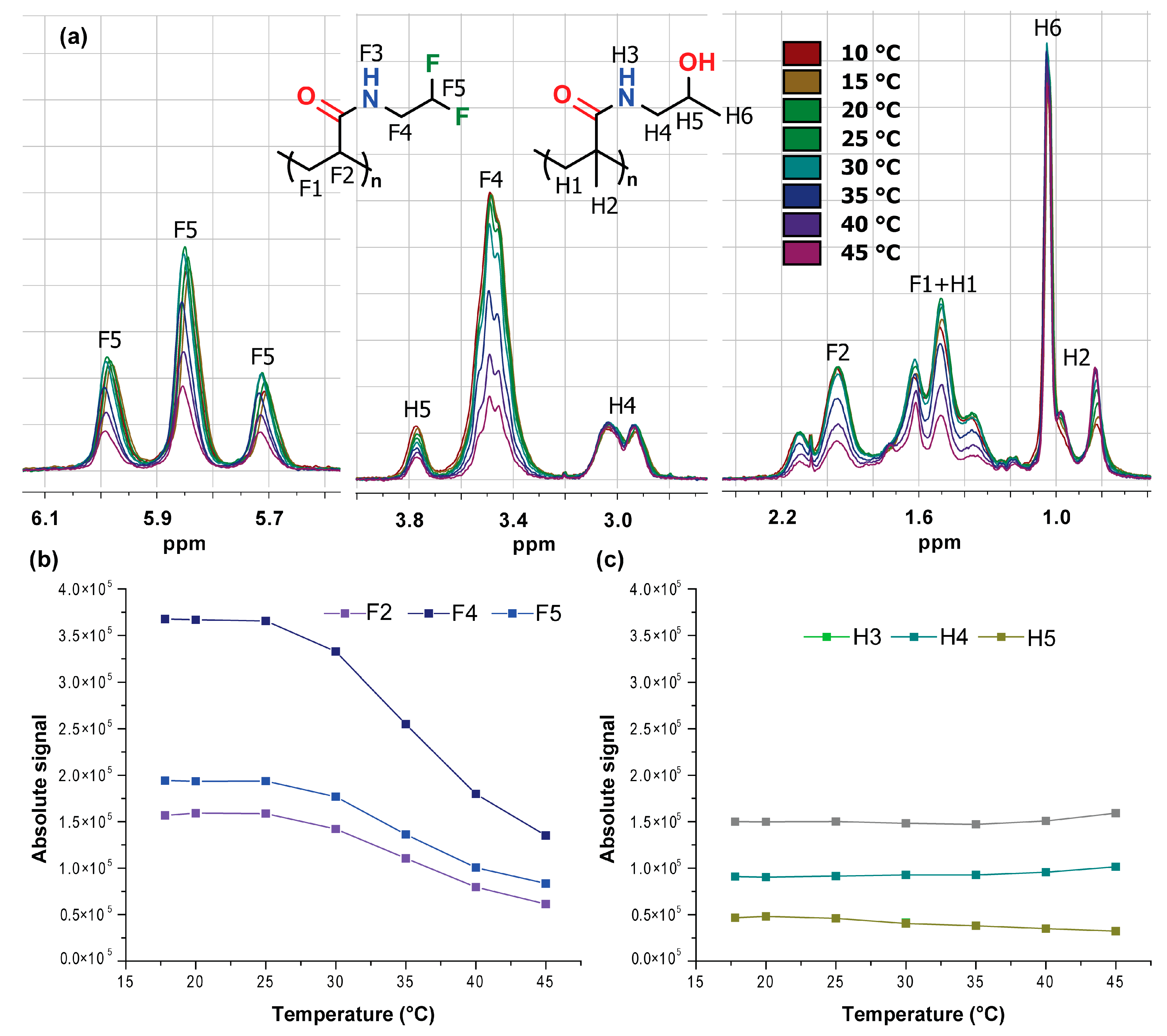
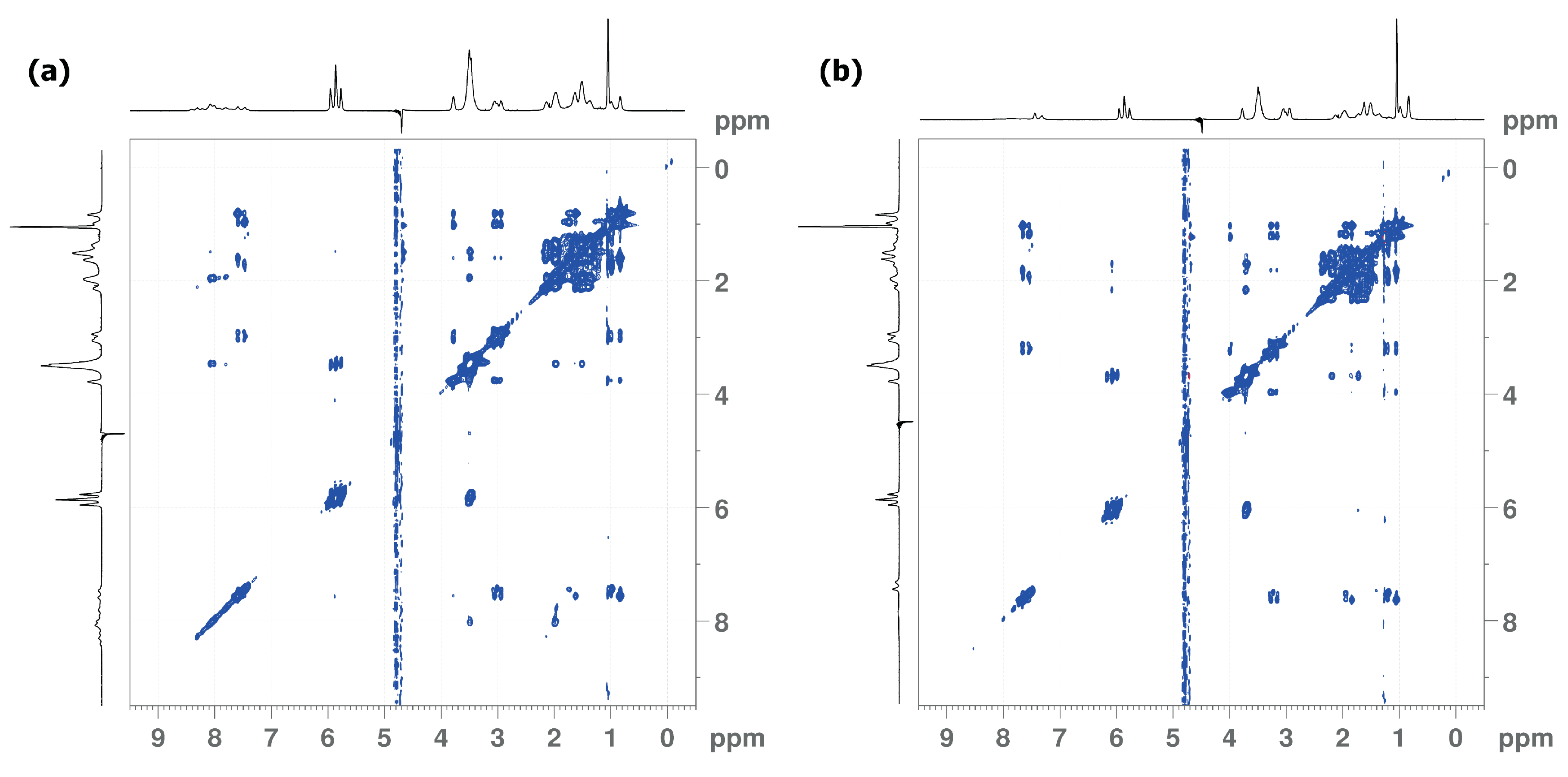
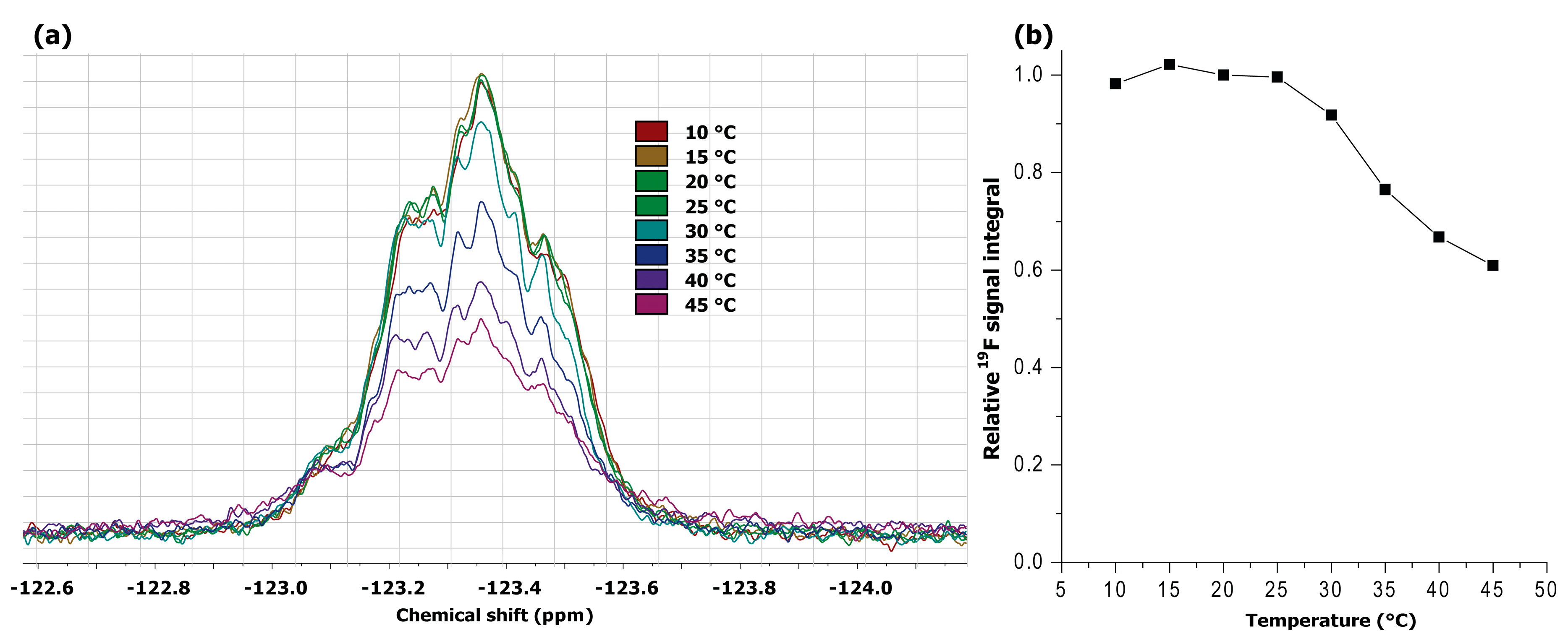
3.4. 1H and 19F NMR Measurements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hashemi, R.H.; Bradley, W.G.; Lisanti, C.J. MRI: The Basics; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Cabello, J.; Barnett, B.P.; Bottomley, P.A.; Bulte, J.W.M. Fluorine (19F) MRS and MRI in Biomedicine. NMR Biomed. 2011, 24, 114–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jirak, D.; Galisova, A.; Kolouchova, K.; Babuka, D.; Hruby, M. Fluorine Polymer Probes for Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Quo Vadis? Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2019, 32, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahrens, E.T.; Rothbächer, U.; Jacobs, R.E.; Fraser, S.E. A Model for MRI Contrast Enhancement Using T1 Agents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 8443–8448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahrens, E.T.; Helfer, B.M.; O’Hanlon, C.F.; Schirda, C. Clinical Cell Therapy Imaging Using a Perfluorocarbon Tracer and Fluorine-19 MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 72, 1696–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staal, X.; Koshkina, O.; Srinivas, M. 11-In Vivo 19-Fluorine Magnetic Resonance Imaging. In Fluorine in Life Sciences: Pharmaceuticals, Medicinal Diagnostics, and Agrochemicals; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 397–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, M.S.; Gaudet, J.M.; Foster, P.J. Fluorine-19 MRI Contrast Agents for Cell Tracking and Lung Imaging. Magn. Reson. Insights 2015, 8 (Suppl. 1), 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillis, E.P.; Eastman, K.J.; Hill, M.D.; Donnelly, D.J.; Meanwell, N.A. Applications of Fluorine in Medicinal Chemistry. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 8315–8359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Heeswijk, R.B.; Pilloud, Y.; Flögel, U.; Schwitter, J.; Stuber, M. Fluorine-19 Magnetic Resonance Angiography of the Mouse. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolouchova, K.; Sedlacek, O.; Jirak, D.; Babuka, D.; Blahut, J.; Kotek, J.; Vit, M.; Trousil, J.; Konefał, R.; Janouskova, O.; et al. Self-Assembled Thermoresponsive Polymeric Nanogels for 19F MR Imaging. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 3515–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolouchova, K.; Jirak, D.; Groborz, O.; Sedlacek, O.; Ziolkowska, N.; Vit, M.; Sticova, E.; Galisova, A.; Svec, P.; Trousil, J.; et al. Implant-Forming Polymeric 19F MRI-Tracer with Tunable Dissolution. J. Control. Release 2020, 327, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babuka, D.; Kolouchova, K.; Hruby, M.; Groborz, O.; Tosner, Z.; Zhigunov, A.; Stepanek, P. Investigation of the Internal Structure of Thermoresponsive Diblock Poly(2-Methyl-2-Oxazoline)-b-Poly[N-(2,2-Difluoroethyl)Acrylamide] Copolymer Nanoparticles. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 121, 109306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlacek, O.; Jirak, D.; Galisova, A.; Jager, E.; Laaser, J.E.; Lodge, T.P.; Stepanek, P.; Hruby, M. 19F Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Injectable Polymeric Implants with Multiresponsive Behavior. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 4892–4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, S.K. Nanoparticles in Modern Medicine: State of the Art and Future Challenges. Int. J. Nanomed. 2007, 2, 129–141. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Gu, F.X.; Chan, J.M.; Wang, A.Z.; Langer, R.S.; Farokhzad, O.C. Nanoparticles in Medicine: Therapeutic Applications and Developments. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 83, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H.; Wu, J.; Sawa, T.; Matsumura, Y.; Hori, K. Tumor Vascular Permeability and the EPR Effect in Macromolecular Therapeutics: A Review. J. Control. Release 2000, 65, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lim, Y.T.; Soltesz, E.G.; De Grand, A.M.; Lee, J.; Nakayama, A.; Parker, J.A.; Mihaljevic, T.; Laurence, R.G.; Dor, D.M.; et al. Near-Infrared Fluorescent Type II Quantum Dots for Sentinel Lymph Node Mapping. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akerman, M.E.; Chan, W.C.W.; Laakkonen, P.; Bhatia, S.N.; Ruoslahti, E. Nanocrystal Targeting in Vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 12617–12621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Cui, Y.; Levenson, R.M.; Chung, L.W.K.; Nie, S. In Vivo Cancer Targeting and Imaging with Semiconductor Quantum Dots. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, Y.-M.; Jun, Y.; Song, H.-T.; Kim, S.; Choi, J.; Lee, J.-H.; Yoon, S.; Kim, K.; Shin, J.-S.; Suh, J.-S.; et al. In Vivo Magnetic Resonance Detection of Cancer by Using Multifunctional Magnetic Nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12387–12391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, G.; Tiwari, R.; Sriwastawa, B.; Bhati, L.; Pandey, S.; Pandey, P.; Bannerjee, S.K. Drug Delivery Systems: An Updated Review. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2012, 2, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, T.M.; Cullis, P.R. Drug Delivery Systems: Entering the Mainstream. Science 2004, 303, 1818–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, R. The Dawning Era of Polymer Therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jaeghere, F.; Allémann, E.; Kubel, F.; Galli, B.; Cozens, R.; Doelker, E.; Gurny, R. Oral Bioavailability of a Poorly Water Soluble HIV-1 Protease Inhibitor Incorporated into PH-Sensitive Particles: Effect of the Particle Size and Nutritional State. J. Control. Release 2000, 68, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, A. The Use of Mucoadhesive Polymers in Ocular Drug Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1595–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Kong, X.; Behera, A.K.; Hellermann, G.R.; Lockey, R.F.; Mohapatra, S.S. Chitosan IFN-Gamma-PDNA Nanoparticle (CIN) Therapy for Allergic Asthma. Genet. Vaccines Ther. 2003, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popovic, N.; Brundin, P. Therapeutic Potential of Controlled Drug Delivery Systems in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 314, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlachetzki, F.; Zhang, Y.; Boado, R.J.; Pardridge, W.M. Gene Therapy of the Brain: The Trans-Vascular Approach. Neurology 2004, 62, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pridgen, E.M.; Langer, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. Biodegradable, Polymeric Nanoparticle Delivery Systems for Cancer Therapy. Nanomedicine 2007, 2, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.; Lee, J.H.; Shin, T.H.; Cheon, J. Theranostic Magnetic Nanoparticles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamrungsap, S.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, T.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Fu, T.; Tan, W. Nanotechnology in Therapeutics: A Focus on Nanoparticles as a Drug Delivery System. Nanomedicine 2012, 7, 1253–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, M.; Okano, T. Intelligent Thermoresponsive Polymeric Micelles for Targeted Drug Delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2006, 16, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S. Recent Research and Development in Synthetic Polymer-Based Drug Delivery Systems. J. Chem. Res. 2004, 2004, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knop, K.; Hoogenboom, R.; Fischer, D.; Schubert, U.S. Poly(Ethylene Glycol) in Drug Delivery: Pros and Cons as Well as Potential Alternatives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6288–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, M.; Lautenschlaeger, C.; Kempe, K.; Tauhardt, L.; Schubert, U.S.; Fischer, D. Poly(2-Ethyl-2-Oxazoline) as Alternative for the Stealth Polymer Poly(Ethylene Glycol): Comparison of in Vitro Cytotoxicity and Hemocompatibility. Macromol. Biosci. 2012, 12, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker, B.S.; Sumerlin, B.S. Poly(N-(2-Hydroxypropyl) Methacrylamide)-Based Nanotherapeutics. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 1566–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Rosa, V.R. Poly(2-Oxazoline)s as Materials for Biomedical Applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2014, 25, 1211–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedláček, O.; Černoch, P.; Kučka, J.; Konefal, R.; Štěpánek, P.; Vetrík, M.; Lodge, T.P.; Hrubý, M. Thermoresponsive Polymers for Nuclear Medicine: Which Polymer Is the Best? Langmuir 2016, 32, 6115–6122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanazs, A.; Armes, S.P.; Ryan, A.J. Self-Assembled Block Copolymer Aggregates: From Micelles to Vesicles and Their Biological Applications. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2009, 30, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakeš, J. Regularized Positive Exponential Sum (REPES) Program-A Way of Inverting Laplace Transform Data Obtained by Dynamic Light Scattering. Collect. Czech. Chem. Commun. 1995, 60, 1781–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štěpánek, P. Chapter 4: Data Analysis in Dynamic Light Scattering. In Dynamic Light Scattering; Brown, W., Ed.; Oxford science publications: Oxford, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Kieffer, J.; Karkoulis, D. PyFAI, a Versatile Library for Azimuthal Regrouping. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 425, 202012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breßler, I.; Kohlbrecher, J.; Thünemann, A.F. SASfit: A Tool for Small-Angle Scattering Data Analysis Using a Library of Analytical Expressions. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2015, 48, 1587–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doucet, M.; Cho, J.H.; Alina, G.; Bakker, J.; Bouwman, W.; Butler, P.; Campbell, K.; Gonzales, M.; Heenan, R.; Jackson, A.; et al. SasView Version 4.2; Zenodo: Berlin, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findeisen, M.; Brand, T.; Berger, S. A 1H-NMR Thermometer Suitable for Cryoprobes. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2006, 45, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Bigam, C.G.; Yao, J.; Abildgaard, F.; Dyson, H.J.; Oldfield, E.; Markley, J.L.; Sykes, B.D. 1H, 13C and 15N Chemical Shift Referencing in Biomolecular NMR. J. Biomol. NMR 1995, 6, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, K.E.; Smith, M.A.; Shaka, A.J. Adjustable, Broadband, Selective Excitation with Uniform Phase. J. Magn. Reson. 2002, 155, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wu, C. Light-Scattering Study of Coil-to-Globule Transition of a Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) Chain in Deuterated Water. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 4299–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuzer, L.P.; Widmann, T.; Hohn, N.; Wang, K.; Bießmann, L.; Peis, L.; Moulin, J.-F.; Hildebrand, V.; Laschewsky, A.; Papadakis, C.M.; et al. Swelling and Exchange Behavior of Poly(Sulfobetaine)-Based Block Copolymer Thin Films. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 3486–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Peng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Deng, J.; Lu, L.; Cai, Y. Effect of Molecular Structure on Thermoresponsive Behaviors of Pyrrolidone-Based Water-Soluble Polymers. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 4041–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Fu, W.; Li, Z.; Zhao, B. Multi-Responsive Polymethacrylamide Homopolymers Derived from Tertiary Amine-Modified l-Alanine. Polymer 2016, 101, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodge, T.P.; Bang, J.; Hanley, K.J.; Krocak, J.; Dahlquist, S.; Sujan, B.; Ott, J. Origins of Anomalous Micellization in Diblock Copolymer Solutions. Langmuir 2003, 19, 2103–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
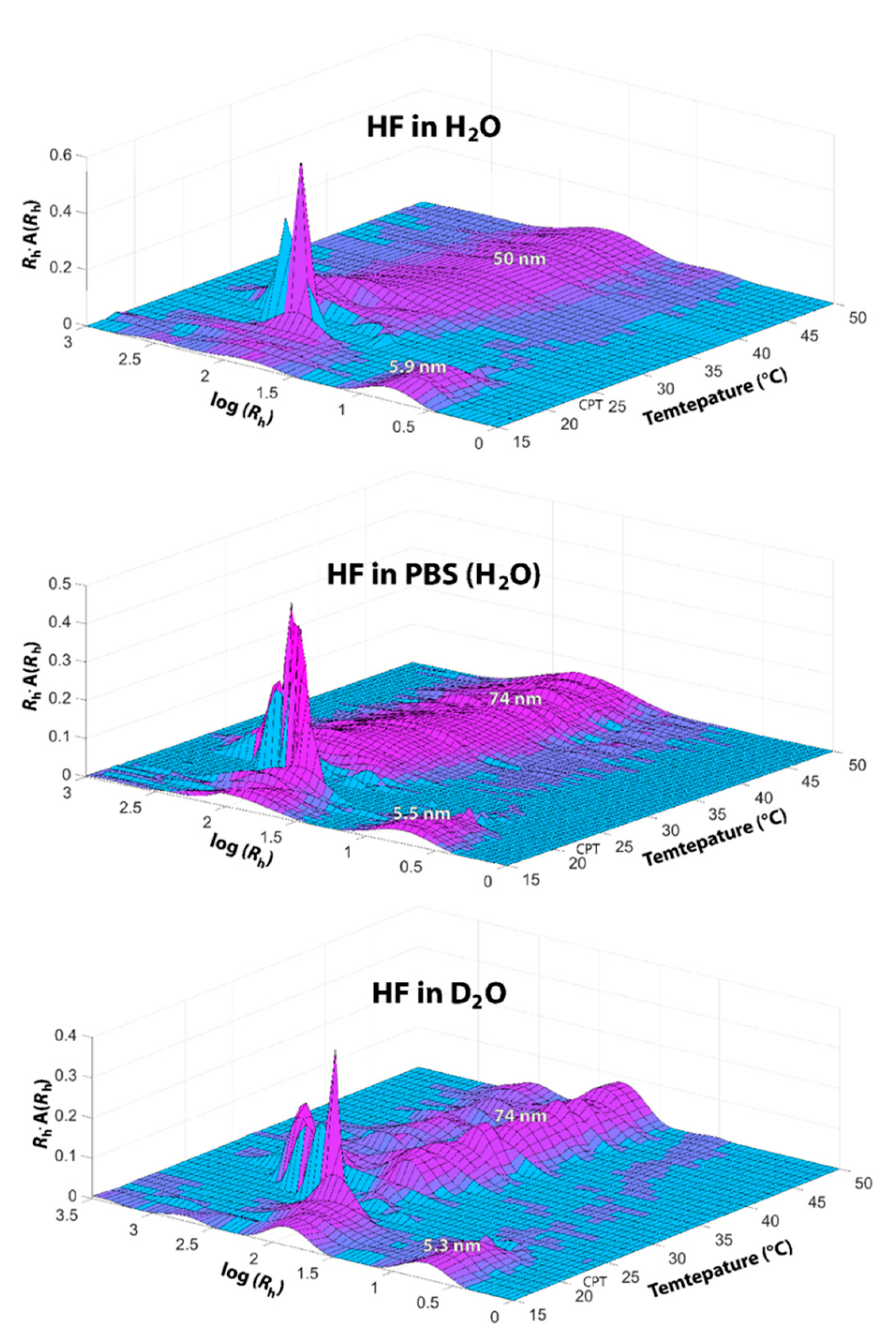

| Solvent | Unimers | Assemblies | CPT (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rh ± σRh (nm) | Rh ± σRh (nm) | ||
| H2O | 5.9 ± 0.4 | 50 ± 6 | 23 |
| PBS | 5.5 ± 0.3 | 74 ± 7 | 21 |
| D2O | 5.3 ± 0.3 | 74 ± 5 | 23 |
| Solvent | Unimers | Assemblies | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| μ (nm) | μ − σ (nm) | μ + σ (nm) | μ (nm) | μ − σ (nm) | μ + σ (nm) | |
| H2O | 6.0 | 4.0 | 9.1 | 52 | 24 | 117 |
| PBS (H2O) | 5.7 | 3.5 | 9.1 | 75 | 34 | 165 |
| D2O | 5.8 | 3.6 | 9.3 | 83 | 41 | 165 |
| t (°C) | T1 (ms) | T2 (ms) |
|---|---|---|
| 20.0 | 363 ± 66 | 142 ± 9 |
| 37.0 | 452 ± 9 | 127 ± 8 |
| 45.0 | 462 ± 14 | 178 ± 9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Babuka, D.; Kolouchova, K.; Groborz, O.; Tosner, Z.; Zhigunov, A.; Stepanek, P.; Hruby, M. Internal Structure of Thermoresponsive Physically Crosslinked Nanogel of Poly[N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide]-Block-Poly[N-(2,2-difluoroethyl)acrylamide], Prominent 19F MRI Tracer. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112231
Babuka D, Kolouchova K, Groborz O, Tosner Z, Zhigunov A, Stepanek P, Hruby M. Internal Structure of Thermoresponsive Physically Crosslinked Nanogel of Poly[N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide]-Block-Poly[N-(2,2-difluoroethyl)acrylamide], Prominent 19F MRI Tracer. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(11):2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112231
Chicago/Turabian StyleBabuka, David, Kristyna Kolouchova, Ondrej Groborz, Zdenek Tosner, Alexander Zhigunov, Petr Stepanek, and Martin Hruby. 2020. "Internal Structure of Thermoresponsive Physically Crosslinked Nanogel of Poly[N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide]-Block-Poly[N-(2,2-difluoroethyl)acrylamide], Prominent 19F MRI Tracer" Nanomaterials 10, no. 11: 2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112231
APA StyleBabuka, D., Kolouchova, K., Groborz, O., Tosner, Z., Zhigunov, A., Stepanek, P., & Hruby, M. (2020). Internal Structure of Thermoresponsive Physically Crosslinked Nanogel of Poly[N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide]-Block-Poly[N-(2,2-difluoroethyl)acrylamide], Prominent 19F MRI Tracer. Nanomaterials, 10(11), 2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112231