Synthesis of Oxide Iron Nanoparticles Using Laser Ablation for Possible Hyperthermia Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frey, N.A.; Peng, S.; Cheng, K.; Sun, S. Magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, functionalization, and applications in bioimaging and magnetic energy storage. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2532–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrand, A.M.; Rahman, M.F.; Hussain, S.M.; Schlager, J.J.; Smith, D.A.; Ali, S.F. Metal-based nanoparticles and their toxicity assessment. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2010, 2, 544–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.-H.; Juang, R.-S. Biochemical and biomedical applications of multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles: A review. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2011, 13, 4411–4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassoued, A.; Lassoued, M.S.; Dkhil, B.; Ammar, S.; Gadri, A. Synthesis, photoluminescence and Magnetic properties of iron oxide (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles through precipitation or hydrothermal methods. Phys. E Low-Dimensional Syst. Nanostruct. 2018, 101, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, M. Superparamagnetism: Theory and Applications. Superparamagn. Theory Appl. 2012, 22, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Akbarzadeh, A.; Samiei, M.; Davaran, S. Magnetic nanoparticles: Preparation, physical properties, and applications in biomedicine. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonsen, G.; Strand, M.; Øye, G. Potential applications of magnetic nanoparticles within separation in the petroleum industry. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 165, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomoucka, J.; Drbohlavova, J.; Huska, D.; Adam, V.; Kizek, R.; Hubalek, J. Magnetic nanoparticles and targeted drug delivering. Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 62, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karade, V.C.; Dongale, T.D.; Sahoo, S.C.; Kollu, P.; Chougale, A.; Patil, P.S.; Patil, P. Effect of reaction time on structural and magnetic properties of green-synthesized magnetic nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2018, 120, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, D.; Giustetto, R.; Hoser, A. Structure of magnetite (Fe3O4) above the Curie temperature: A cation ordering study. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2011, 39, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.; Langell, M. XPS analysis of oleylamine/oleic acid capped Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a function of temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 303, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcena, C.; Sra, A.K.; Gao, J. Applications of Magnetic Nanoparticles in Biomedicine. Nanoscale Magn. Mater. Appl. 2009, 167, 591–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorio-Jáuregui, K. “Item 1025/494 | Repositorio CIQA”, Ciqa.repositorioinstitucional.mx. 2020. Available online: http://ciqa.repositorioinstitucional.mx/jspui/handle/1025/494 (accessed on 12 September 2020).
- Lassoued, A.; Lassoued, M.S.; Dkhil, B.; Ammar, S.; Gadri, A. Synthesis, structural, morphological, optical and magnetic characterization of iron oxide (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles by precipitation method: Effect of varying the nature of precursor. Phys. E Low-Dimensional Syst. Nanostruct. 2018, 97, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marathe, K.; Doshi, P. Magnetic nanoparticles: Preparation, physical properties, and applications in biomedicine. IEEE Int. Conf. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2015, 2015, 2550–2555. [Google Scholar]
- Bantz, C.; Koshkina, O.; Lang, T.; Galla, H.-J.; Kirkpatrick, C.J.; Stauber, R.H.; Maskos, M. The surface properties of nanoparticles determine the agglomeration state and the size of the particles under physiological conditions. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 1774–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Yao, Y.; Tang, G. Controlled-synthesis, characterization, and magnetic properties of Fe3O4 nanostructures. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2007, 89, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolghadr, S.; Kimiagar, S.; Davarpanah, A.M. Magnetic property of α-Fe2O3-GO nanocomposite. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarjuna, R.; Challagulla, S.; Ganesan, R.; Roy, S. High rates of Cr (VI) photoreduction with magnetically recoverable nano-Fe3O4@Fe2O3/Al2O3 catalyst under visible light. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirtoaje, C.; Petrescu, E.; Stan, C.; Creanga, D. Ferromagnetic nanoparticles suspensions in twisted nematic. Phys. E Low-Dimensional Syst. Nanostruct. 2016, 79, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.W. Laser Ablation in Liquids: Applications in the Synthesis of Nanocrystals. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2007, 38, 648–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillán, J.M.J.; Arboleda, D.M.; Coral, D.F.; Van Raap, M.F.; Muraca, D.; Schinca, D.C.; Scaffardi, L.B. Optical and Magnetic Properties of Fe Nanoparticles Fabricated by Femtosecond Laser Ablation in Organic and Inorganic Solvents. ChemPhysChem 2017, 18, 1192–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svetlichnyi, V.A.; Shabalina, A.V.; Lapin, I.N.; Goncharova, D.A.; Kharlamova, T.S.; Stadnichenko, A.I. Comparative study of magnetite nanoparticles obtained by pulsed laser ablation in water and air. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 468, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, R.A.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Abdulrahman, S.A.; Marzoog, T.R. Antibacterial activity of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles synthesized by laser ablation in liquid. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 53, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, A.; Maier-Hauff, K. Magnetic Nanoparticles for Intracranial Thermotherapy. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2007, 7, 4604–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasemian, A.R.; Almasi-Kashi, M.; Ramazani, A. Surfactant-free synthesis and magnetic hyperthermia investigation of iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles at different reaction temperatures. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 230, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Gökce, B.; Barcikowski, S. Laser Synthesis and Processing of Colloids: Fundamentals and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 3990–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plata, L. Caracterización de suspensiones coloidales de nanopartículas metálicas sintetizadas por ablación láser de pulsos ultracortos. Ph.D. Thesis, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas, La Plata, Argentina, 18 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Riabinina, D.; Chaker, M.; Margot, J. Dependence of gold nanoparticle production on pulse duration by laser ablation in liquid media. Nanotechnol. 2012, 23, 135603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, V.; Meneghetti, M. What controls the composition and the structure of nanomaterials generated by laser ablation in liquid solution? Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 3027–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, S.; França, R.; Moreau-Bélanger, L.; Sacher, E. Confirmation of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Peak Attributions of Nanoparticulate Iron Oxides, Using Symmetric Peak Component Line Shapes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 10711–10718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H. Re: What are the Major Sources of Carbon Peaks in XPS Spectra of Non-Carbonous Samples? 2016. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/post/What_are_the_major_sources_of_carbon_peaks_in_XPS_spectra_of_non-carbonous_samples/58555ceb615e276a3f466071/citation/download (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- García-Benjume, M.L.; Espitia-Cabrera, M.I.; Contreras-García, M.E. Hierarchical macro-mesoporous structures in the system TiO2-Al2O3, obtained by hydrothermal synthesis using Tween-20® as a directing agent. Mater. Charact. 2009, 60, 1482–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayatnasab, Z.; Abnisa, F.; Daud, W.M.A.W. Review on magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic nanofluid hyperthermia application. Mater. Des. 2017, 123, 174–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutz, S.; Hergt, R. Magnetic nanoparticle heating and heat transfer on a microscale: Basic principles, realities and physical limitations of hyperthermia for tumour therapy. Int. J. Hyperth. 2013, 29, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimisadr, S.; Aslibeiki, B.; Asadi, R. Magnetic hyperthermia properties of iron oxide nanoparticles: The effect of concentration. Phys. C Supercond. 2018, 549, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanier, O.; Korotych, O.I.; Monsalve, A.G.; Wable, D.; Savliwala, S.; Grooms, N.W.F.; Nacea, C.; Tuitt, O.R.; Dobson, J. Evaluation of magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic fluid hyperthermia. Int. J. Hyperth. 2019, 36, 686–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

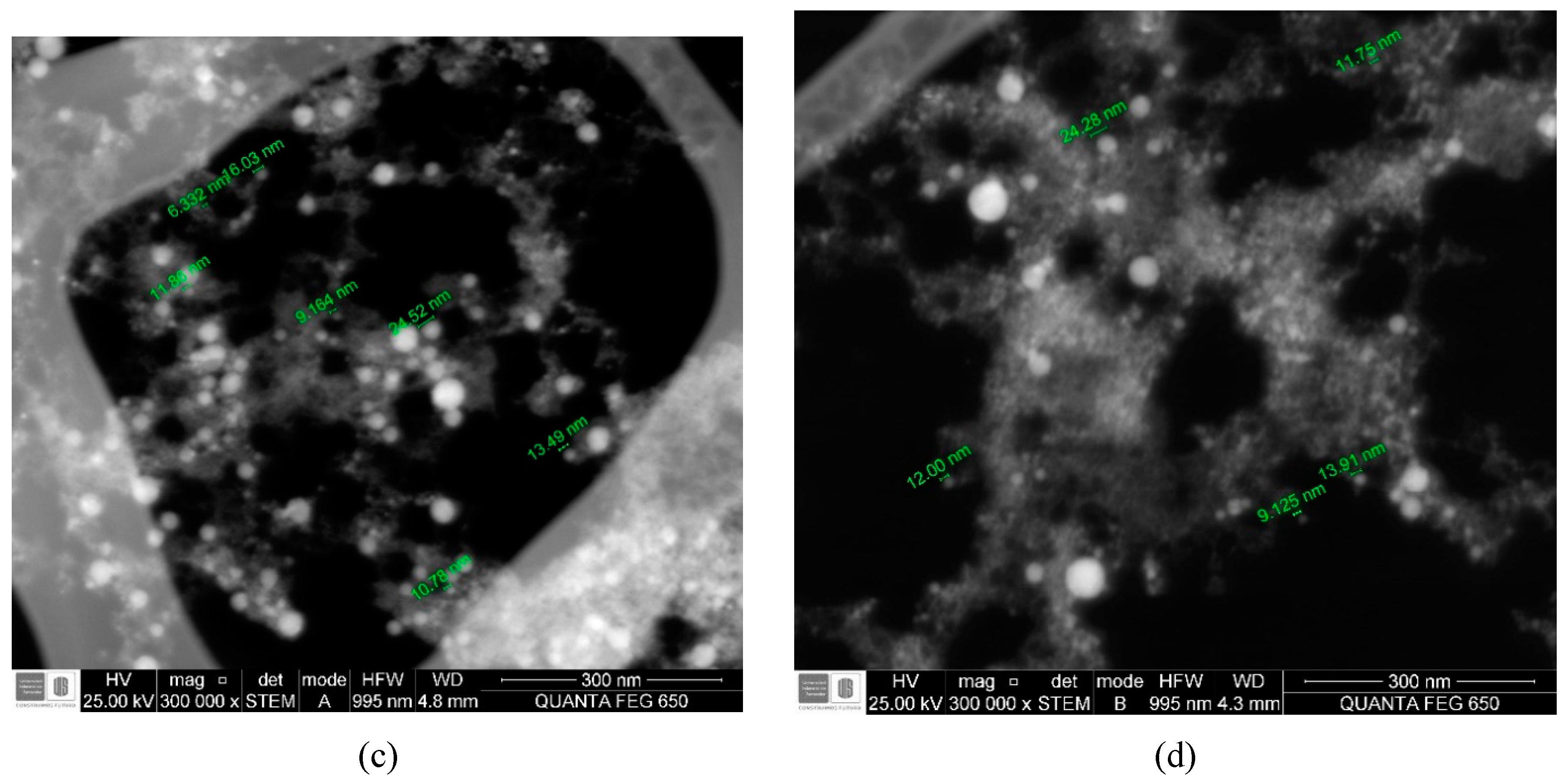
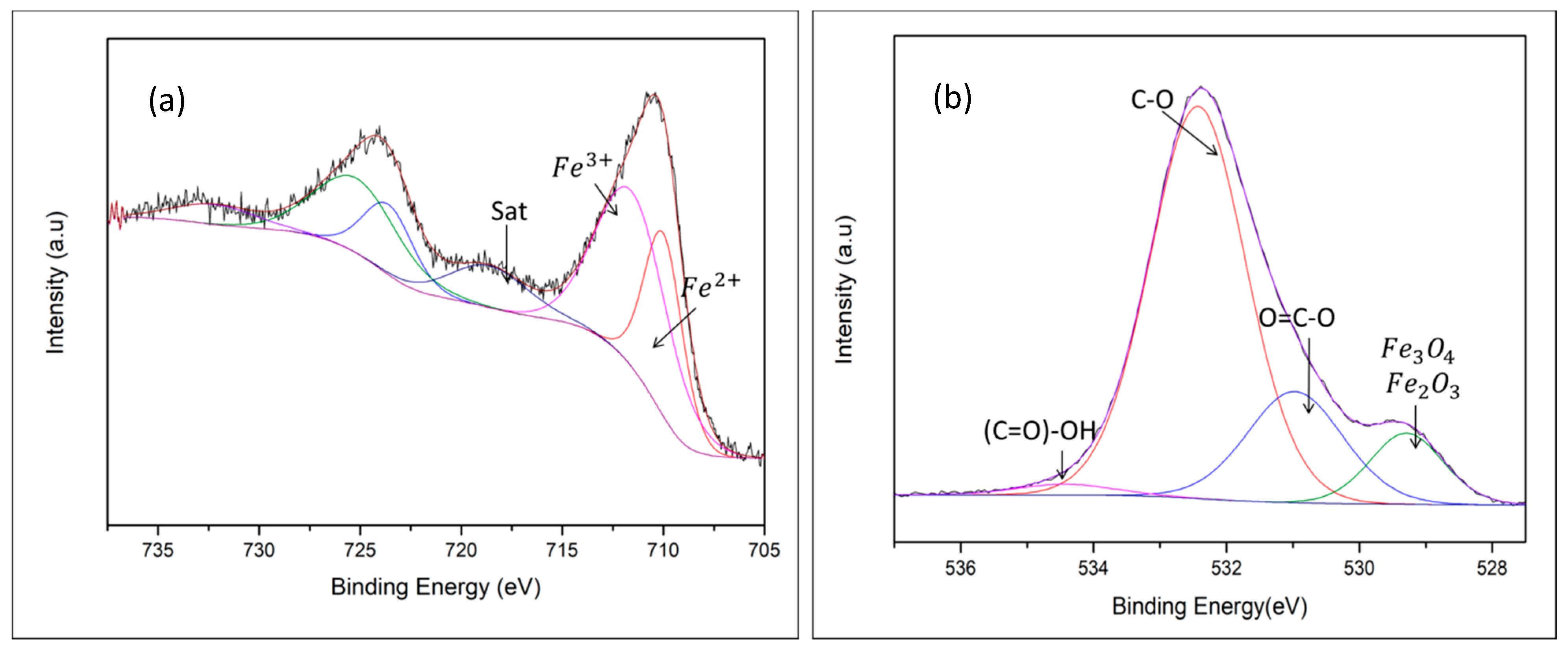
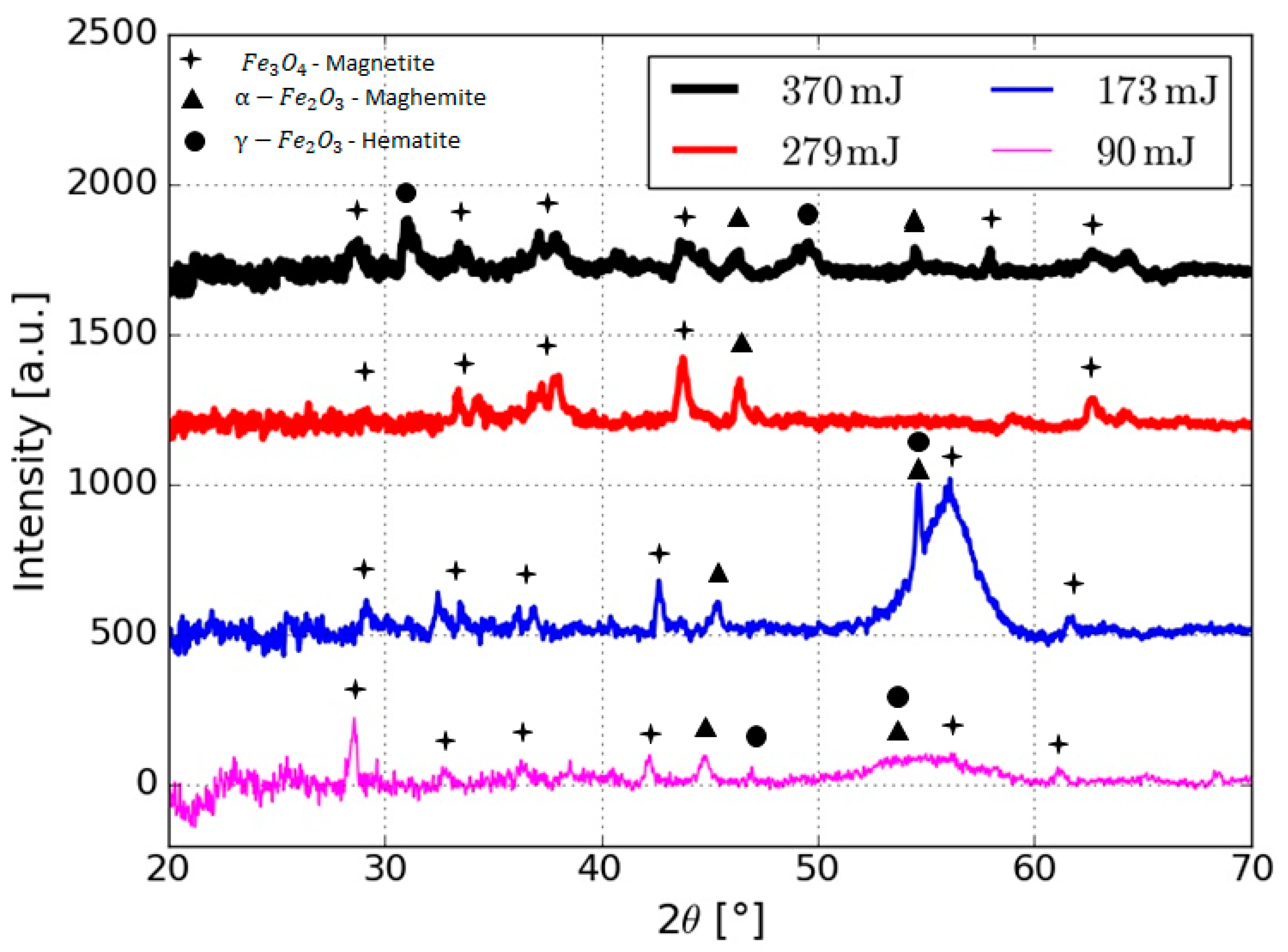
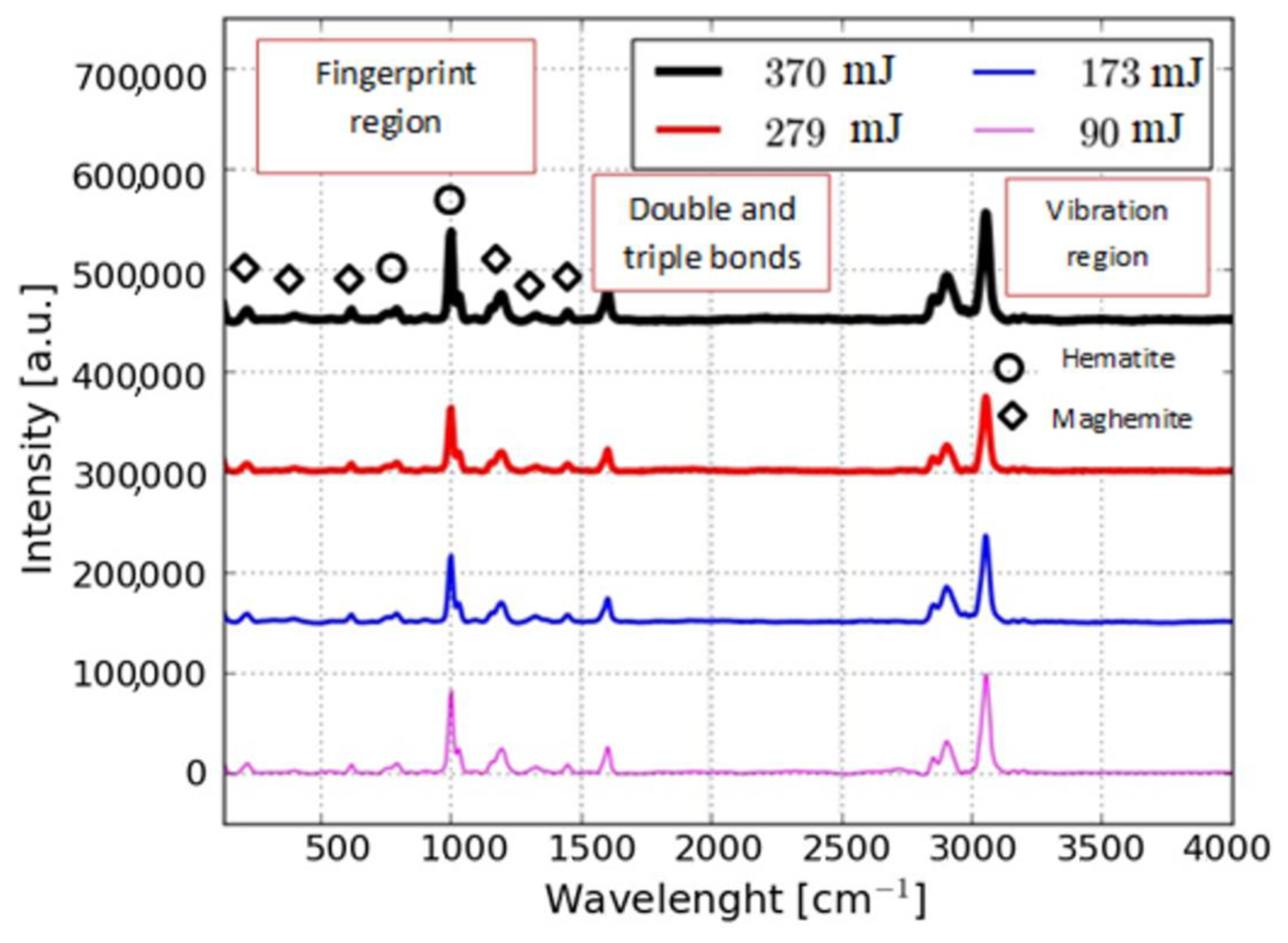
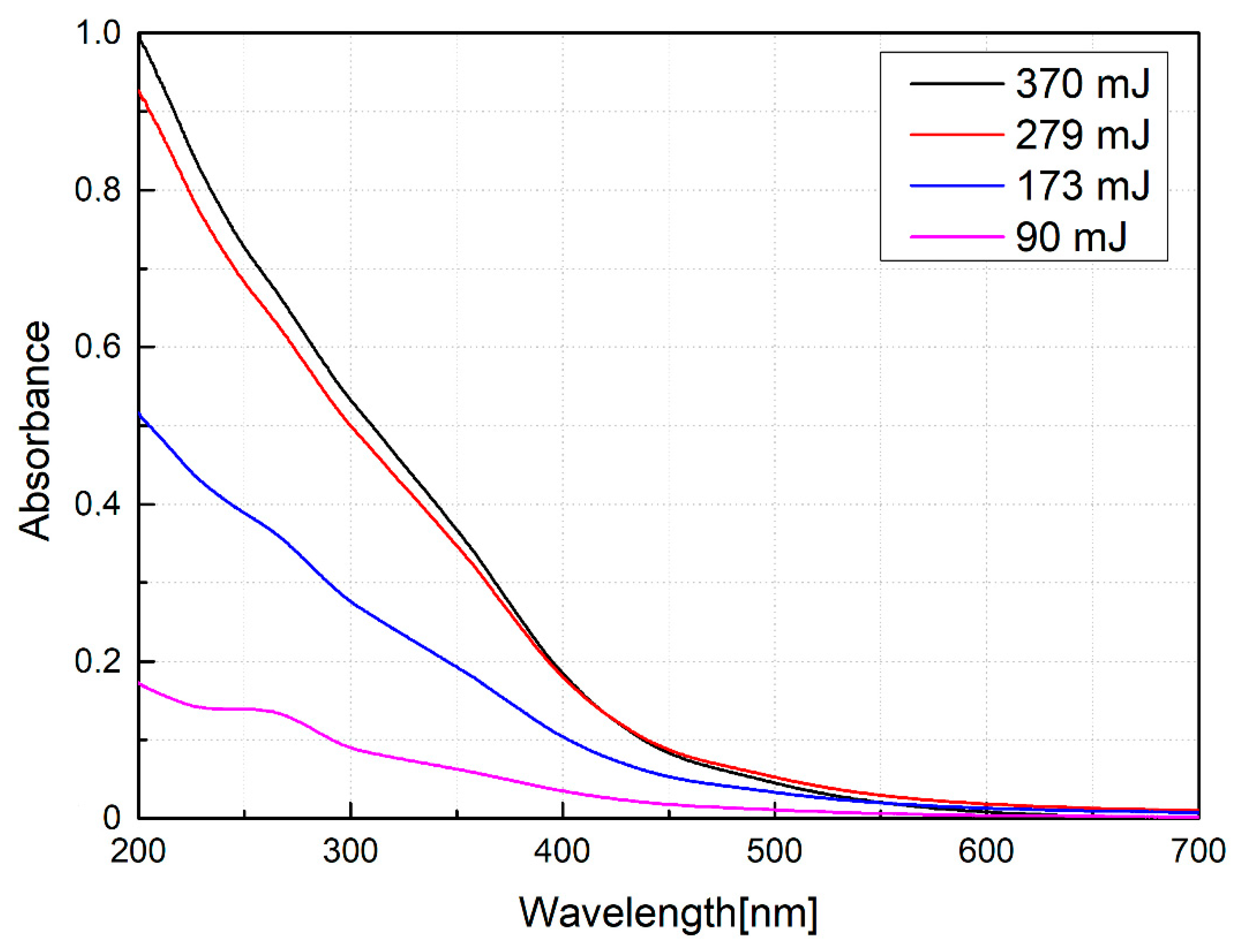
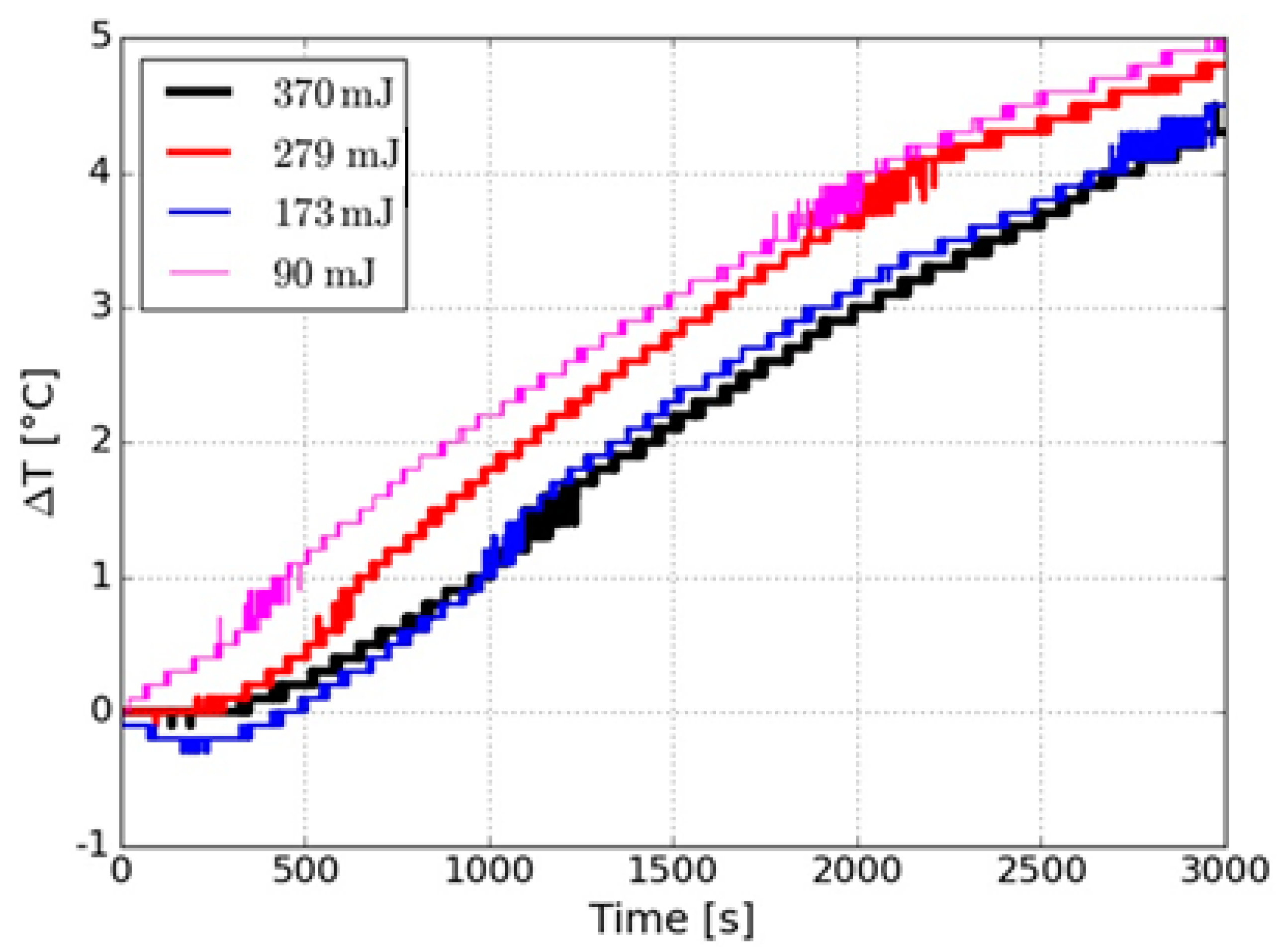
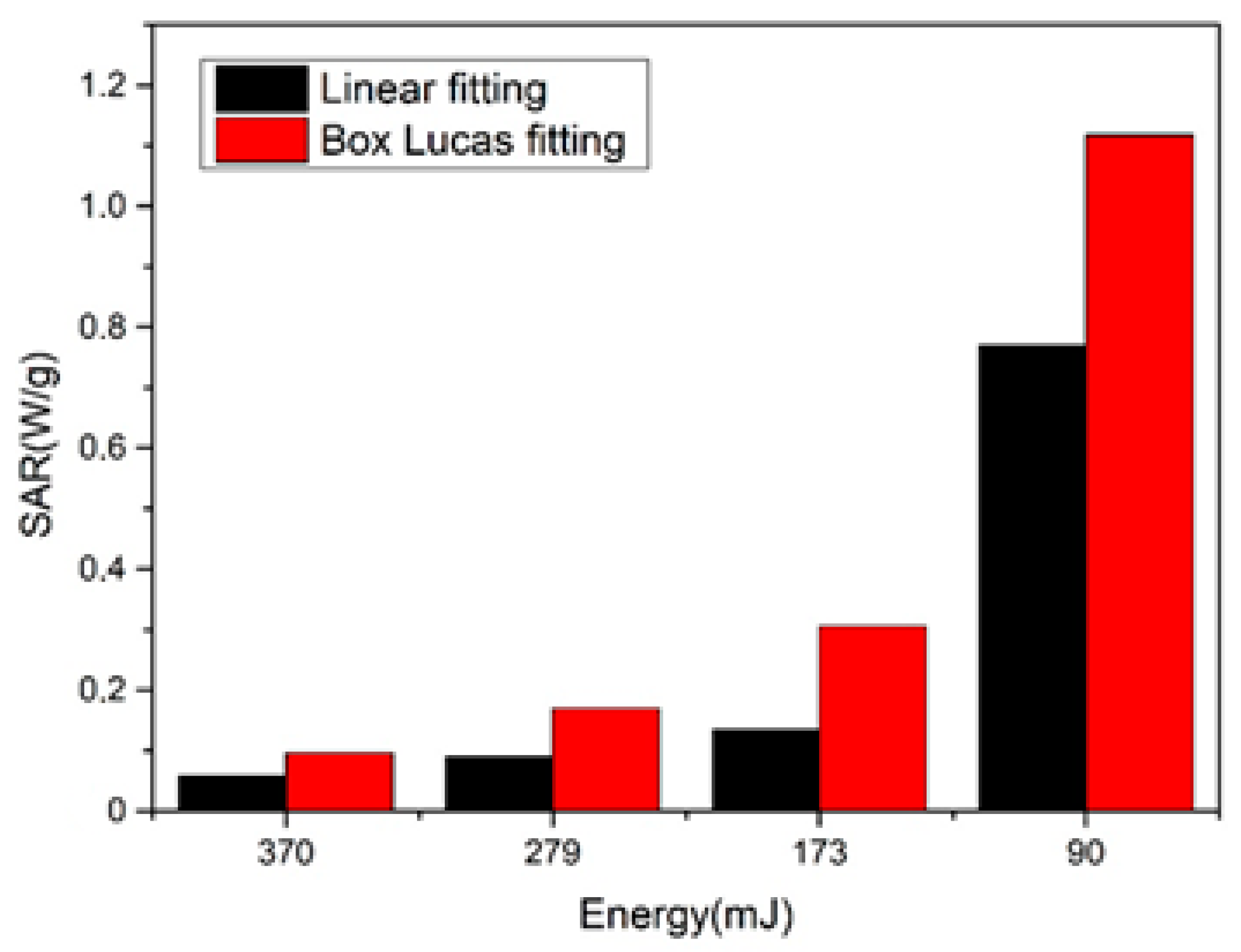
| Energy (mJ) | DLS Measurements | STEM Measurements | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Size (nm) | Standard Deviation (nm) | Average Size (nm) | Standard Deviation (nm) | |
| 370 | 25.868 | 4.189 | 16.827 | 6.044 |
| 279 | 65.363 | 6.680 | 15.695 | 4.854 |
| 173 | 42.176 | 25.585 | 14.870 | 8.347 |
| 90 | 25.900 | 0.761 | 18.719 | 12.825 |
| Sample | At% (EDS) | |
|---|---|---|
| Fe | O | |
| 90 mJ | 5.2 | 94.8 |
| 173 mJ | 9.3 | 90.7 |
| 279 mJ | 10 | 90 |
| 370 mJ | 9.9 | 90.1 |
| Peak | Assignation | Area under the Curve (cm−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90 mJ | 173 mJ | 279 mJ | 370 mJ | ||
| 224.83 | Hematite | 1.6 | 2.47 | 1.72 | 1.85 |
| 410.90 | Hematite | 0.47 | 3.87 | 0.67 | 1.04 |
| 626.73 | Hematite | 1.13 | 1.85 | 1.05 | 1.19 |
| 797.91 | Maghemite | 2.27 | 4.01 | 2.49 | 2.33 |
| 1004.82 | Maghemite | 12.99 | 14.19 | 12.53 | 11.56 |
| 1190.88 | Hematite | 8.17 | 9.18 | 7.87 | 8.16 |
| 1317.40 | Hematite | 1.71 | 3.14 | 1.32 | 1.12 |
| 1451.38 | Hematite | 1.29 | 1.84 | 1.46 | 1.17 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rivera-Chaverra, M.J.; Restrepo-Parra, E.; Acosta-Medina, C.D.; Mello, A.; Ospina, R. Synthesis of Oxide Iron Nanoparticles Using Laser Ablation for Possible Hyperthermia Applications. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2099. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112099
Rivera-Chaverra MJ, Restrepo-Parra E, Acosta-Medina CD, Mello A, Ospina R. Synthesis of Oxide Iron Nanoparticles Using Laser Ablation for Possible Hyperthermia Applications. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(11):2099. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112099
Chicago/Turabian StyleRivera-Chaverra, María J., Elisabeth Restrepo-Parra, Carlos D. Acosta-Medina, Alexandre. Mello, and Rogelio. Ospina. 2020. "Synthesis of Oxide Iron Nanoparticles Using Laser Ablation for Possible Hyperthermia Applications" Nanomaterials 10, no. 11: 2099. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112099
APA StyleRivera-Chaverra, M. J., Restrepo-Parra, E., Acosta-Medina, C. D., Mello, A., & Ospina, R. (2020). Synthesis of Oxide Iron Nanoparticles Using Laser Ablation for Possible Hyperthermia Applications. Nanomaterials, 10(11), 2099. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112099







