Does Intraoral Scanning at the Subgingival Finish Line Affect the Accuracy of Interim Crowns?
Abstract
1. Introduction
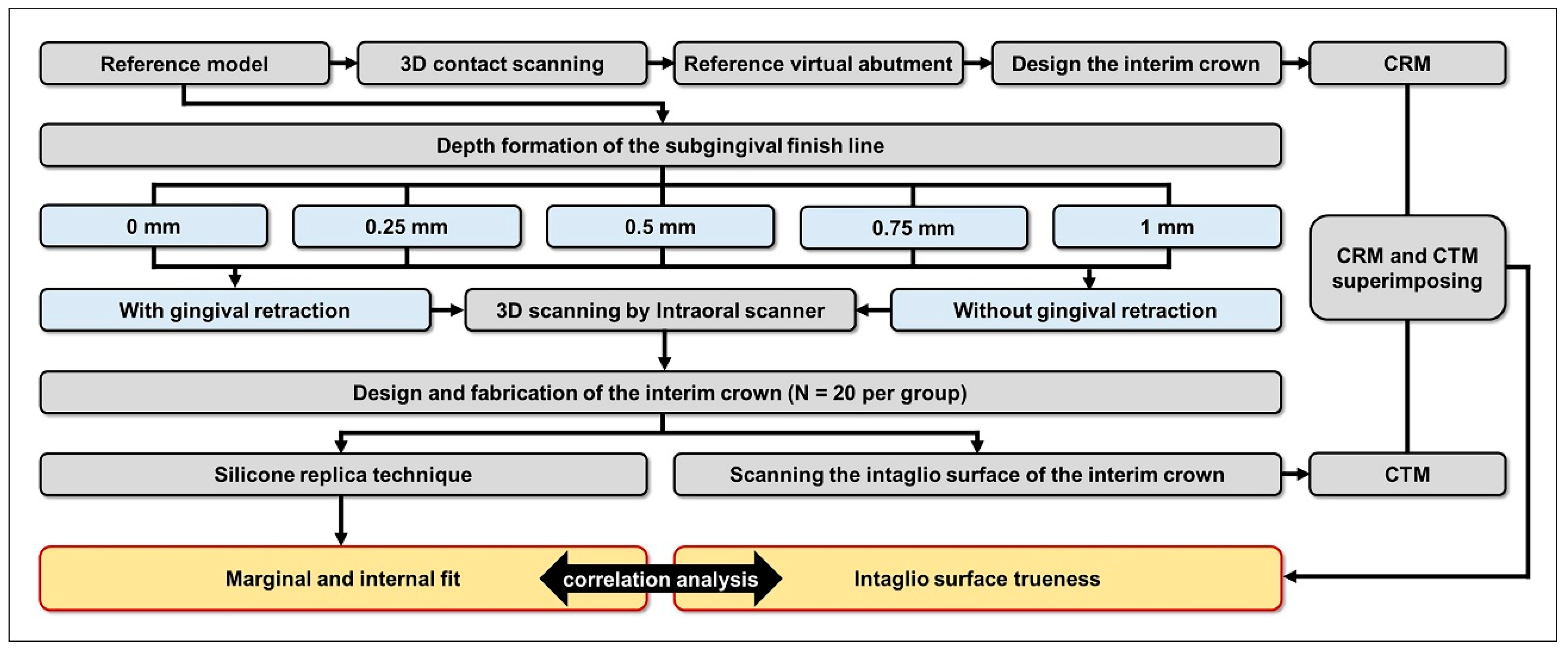
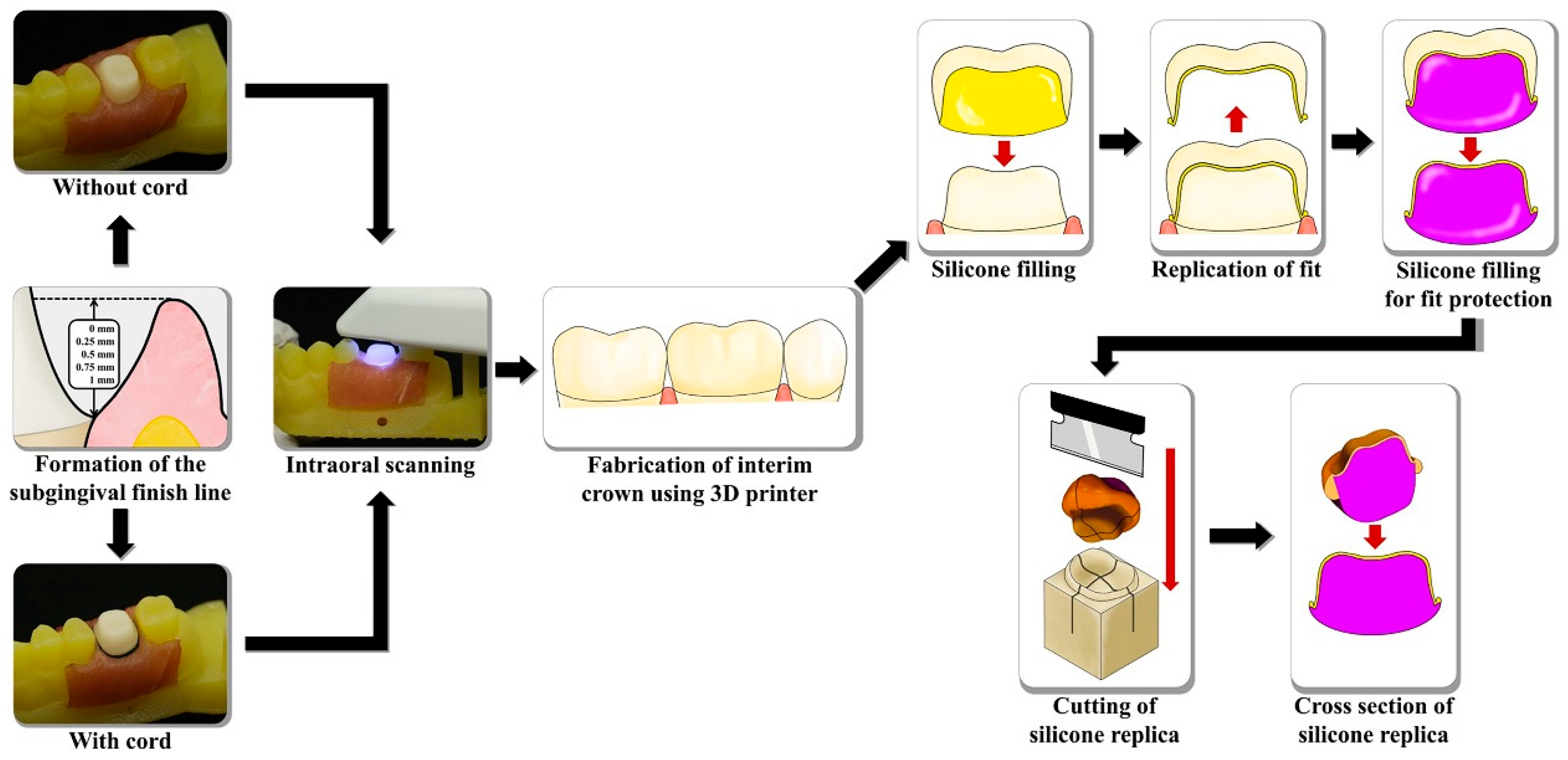
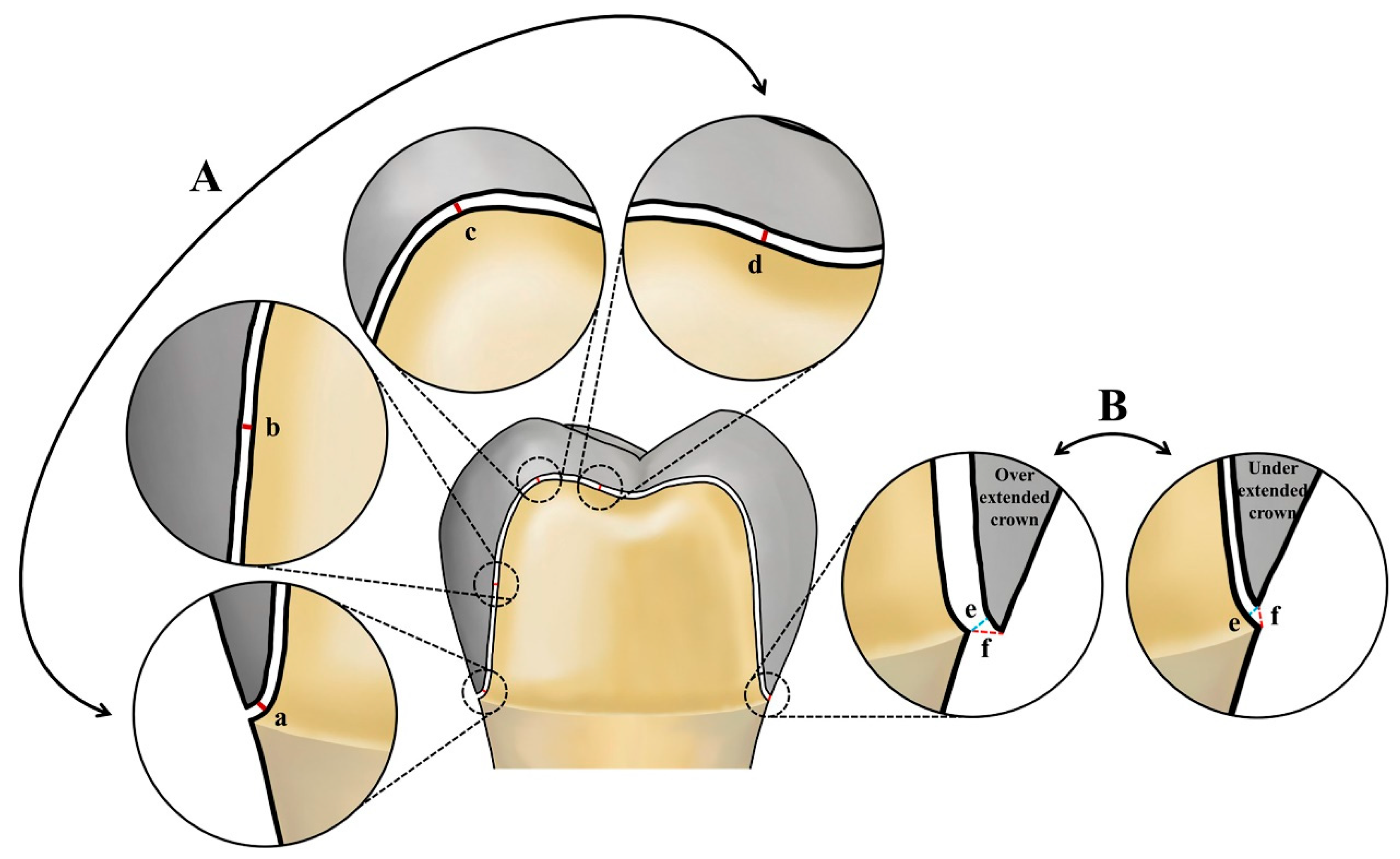
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Güth, J.F. Potential of innovative digital technologies and CAD/CAM composites in complex cases with change in the VDO. Int. J. Esthet. Dent. 2017, 12, 274–285. [Google Scholar]
- Shembesh, M.; Ali, A.; Finkelman, M.; Weber, H.P.; Zandparsa, R. An in vitro comparison of the marginal adaptation accuracy of CAD/CAM restorations using different impression systems. J. Prosthodont. 2017, 26, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joós-Kovács, G.; Vecsei, B.; Körmendi, S.; Gyarmathy, V.A.; Borbély, J.; Hermann, P. Trueness of CAD/CAM digitization with a desktop scanner—An in vitro study. BMC Oral Health 2019, 19, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güth, J.F.; Keul, C.; Stimmelmayr, M.; Beuer, F.; Edelhoff, D. Accuracy of digital models obtained by direct and indirect data capturing. Clin. Oral Investig. 2013, 17, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, G.J. Will digital impressions eliminate the current problems with conventional impressions? J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2008, 139, 761–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, R.; Galli, M.; Chen, Z.; Mendonça, G.; Meirelles, L.; Wang, H.-L.; Chan, H.-L. Intraoral scanning reduces procedure time and improves patient comfort in fixed prosthodontics and implant dentistry: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Investig. 2021, 25, 6517–6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayama, H.; Fueki, K.; Wadachi, J.; Wakabayashi, N. Trueness and precision of digital impressions obtained using an intraoral scanner with different head size in the partially edentulous mandible. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2018, 62, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Betensky, R.A.; Gianneschi, G.E.; Gallucci, G.O. Accuracy of digital versus conventional implant impressions. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2015, 26, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joda, T.; Zarone, F.; Ferrari, M. The complete digital workflow in fixed prosthodontics: A systematic review. BMC Oral Health 2017, 17, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.Y.; Esguerra, R.J.; Chia, V.A.P.; Tan, Y.H.; Tan, K.B.C. Three-dimensional accuracy of digital static interocclusal registration by three intraoral scanner systems. J. Prosthodont. 2018, 27, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revilla-León, M.; Sicilia, E.; Agustín-Panadero, R.; Gómez-Polo, M.; Kois, J.C. Clinical evaluation of the effects of cutting off, overlapping, and rescanning procedures on intraoral scanning accuracy. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2023, 130, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Polo, M. Influence of rescanning mesh holes and stitching procedures on the complete-arch scanning accuracy of an intraoral scanner: An in vitro study. J. Dent. 2021, 110, 103690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revilla-León, M.; Subramanian, S.G.; Özcan, M.; Krishnamurthy, V.R. Clinical study of the influence of ambient light scanning conditions on the accuracy (trueness and precision) of an intraoral scanner. J. Prosthodont. 2020, 29, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Button, H.; Kois, J.C.; Barmak, A.B.; Zeitler, J.M.; Rutkunas, V.; Revilla-León, M. Scanning accuracy and scanning area discrepancies of intraoral digital scans acquired at varying scanning distances and angulations among 4 different intraoral scanners. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2023, 132, 1044–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, L.N.; Thompson, G.A.; Cho, S.H.; Berzins, D.W.; Ahn, K.W. Die spacer thickness reproduction for central incisor crown fabrication with combined computer-aided design and 3D printing technology: An in vitro study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2015, 113, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, K.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, K.B. Marginal and internal fit and intaglio surface trueness of temporary crowns fabricated with stereolithography, digital light processing, and milling technology. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2022, 35, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, K.; Yu, B.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Son, Y.T.; Lee, K.B. Comparison of intaglio surface adjustment in the oral cavity for lithium disilicate crowns fabricated using different scanners. J. Prosthodont. 2021, 30, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesse, H.; Ulstein, D.M.Å.; Vaage, M.M.; Øilo, M. Internal and marginal fit of cobalt-chromium fixed dental prostheses fabricated with 3 different techniques. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2015, 114, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, J.W. The estimation of cement film thickness by an in vivo technique. Br. Dent. J. 1971, 131, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felton, D.A.; Kanoy, B.E.; Bayne, S.A.; Wirthman, G.P. Effect of in vivo crown margin discrepancies on periodontal health. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1991, 65, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, J.E.; Nalbandian, J.; Sanford, C.; Bailit, H. Effect of restoration quality on periodontal health. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1985, 53, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, Y.; Park, S.; Park, J.W.; Kim, K.M.; Park, Y.B.; Roh, B.D. Evaluation of the marginal and internal discrepancies of CAD-CAM endocrowns with different cavity depths: An in vitro study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 117, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Yu, H.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Gao, B. Trueness analysis of zirconia crowns fabricated with 3-dimensional printing. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 121, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.Y.; Son, K.; Lee, K.B. Evaluation of intaglio surface trueness and margin quality of interim crowns in accordance with the build angle of stereolithography apparatus 3-dimensional printing. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2021, 126, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakmak, G.; Cuellar, A.R.; Donmez, M.B.; Schimmel, M.; Abou-Ayash, S.; Lu, W.-E.; Yilmaz, B. Effect of printing layer thickness on the trueness and margin quality of 3D-printed interim dental crowns. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ender, A.; Attin, T.; Mehl, A. In vivo precision of conventional and digital methods of obtaining complete-arch dental impressions. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 115, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamac, E.; Toksavul, S.; Toman, M. Clinical marginal and internal adaptation of CAD/CAM milling, laser sintering, and cast metal ceramic crowns. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2014, 112, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowley, J.F.; Sun, A.F.; Barouch, K.K. Effect of margin location on crown preparation resistance form. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2004, 92, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, A.; Shenoy, N.; Babannavar, R. Periodontal considerations determining the design and location of margins in restorative dentistry. J. Interdisc. Dent. 2012, 2, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, K.; Son, Y.T.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, K.B. Marginal and internal fit and intaglio surface trueness of interim crowns fabricated from tooth preparation of four finish line locations. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, K.; Lee, K.B. Effect of finish line locations of tooth preparation on the accuracy of intraoral scanners. Int. J. Comput. Dent. 2021, 24, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Tal, H.; Soldinger, M.; Dreiangel, A.; Pitaru, S. Periodontal response to long-term abuse of the gingival attachment by supracrestal amalgam restorations. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1989, 16, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padbury, A.; Eber, R.; Wang, H.L. Interactions between the gingiva and the margin of restorations. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2003, 30, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.T.; Son, K.; Lee, K.B. Trueness of intraoral scanners according to subgingival depth of abutment for fixed prosthesis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting-shu, S.; Jian, S. Intraoral digital impression technique: A review. J. Prosthodont. 2015, 24, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedelcu, R.; Olsson, P.; Nyström, I.; Rydén, J.; Thor, A. Accuracy and precision of 3 intraoral scanners and accuracy of conventional impressions: A novel in vivo analysis method. J. Dent. 2018, 69, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güth, J.F.; Edelhoff, D.; Schweiger, J.; Keul, C. A new method for the evaluation of the accuracy of full-arch digital impressions in vitro. Clin. Oral Investig. 2016, 20, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotti, J.; Neiva, G.; Kao, D.; Nummikoski, P.; Platt, J. Evaluation of the repeatability of digital and conventional impression techniques using a reference model. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 117, 340–345. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, R.J.Y.; Park, J.M.; Shim, J.S. Accuracy of 9 intraoral scanners for complete-arch image acquisition: A qualitative and quantitative evaluation. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 120, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markarian, R.A.; Bui, A.; Pham, A.; Ferracane, J.L.; Sharp, S.M. Effect of finish line location on the marginal and internal fit of crowns fabricated with digital and conventional workflows. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2021, 125, 623.e1–623.e6. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, Y.; Son, K.; Lee, K.B. Correlation between fit and internal surface trueness of three-unit zirconia prostheses fabricated using a CAD/CAM system: In vitro study. Materials 2022, 15, 6380. [Google Scholar]
- Imburgia, M.; Logozzo, S.; Hauschild, U.; Veronesi, G.; Mangano, C.; Mangano, F.G. Accuracy of four intraoral scanners in oral implantology: A comparative in vitro study. BMC Oral Health 2017, 17, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latham, J.; Ludlow, M.; Mennito, A.; Kelly, A.; Evans, Z.; Renne, W. Effect of scan pattern and storage on the trueness and precision of four intraoral digital impression systems. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 123, 106–112. [Google Scholar]
- Batmaz, I.; Arslan, M.; Altundasar, E.; Tuncel, I. Evaluation of the effects of scanner type and scanning strategy on the accuracy of digital impressions of preparations for all-ceramic crowns. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2021, 33, 229–236. [Google Scholar]
- Revilla-León, M.; Sadeghpour, M.; Özcan, M. A review of the applications of additive manufacturing technologies used to fabricate metal and ceramic dental restorations. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2020, 32, 260–267. [Google Scholar]
- Alharbi, N.; Wismeijer, D.; Osman, R.B. Additive manufacturing techniques in prosthodontics: Where do we currently stand? A critical review. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2017, 30, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michou, S.; Ozcan, M.; Papageorgiou, S.N.; Kiliaridis, S. Impact of soft tissue simulation on the accuracy of digital impressions for edentulous jaws. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 2103–2111. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.H.; Kim, N.; Park, J.M.; Lee, J.Y. Accuracy of intraoral digital impressions compared to conventional impressions in in-vitro studies: A systematic review. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2021, 13, 192–204. [Google Scholar]
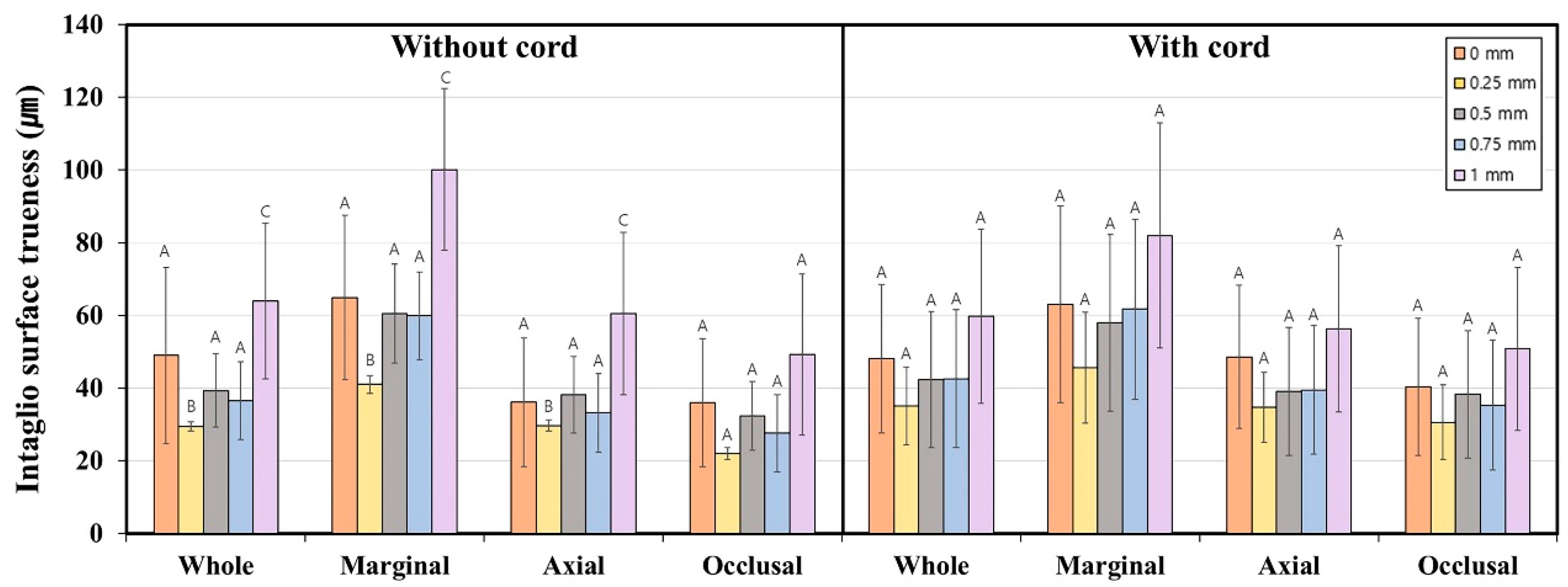
| Region Type | Finish Line Depth (mm) | Cord Type | Mean | SD | 95% CI | p * | Without Cord; p ** | With Cord; p *** | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||||
| Whole region | 0 | Without cord | 49.0 | 48.6 | 31.2 | 69.6 | 0.421 | <0.001 ** (1 mm > 0.75, 0.5, 0 mm > 0.25 mm) | 0.334 |
| With cord | 48.1 | 40.9 | 28.9 | 67.3 | |||||
| 0.25 | Without cord | 29.4 | 2.6 | 28.2 | 30.5 | 0.243 | |||
| With cord | 35.1 | 21.5 | 25.0 | 45.2 | |||||
| 0.5 | Without cord | 39.3 | 20.2 | 29.9 | 48.8 | 0.754 | |||
| With cord | 42.3 | 37.4 | 24.8 | 59.9 | |||||
| 0.75 | Without cord | 36.5 | 21.4 | 26.5 | 46.5 | 0.532 | |||
| With cord | 42.6 | 37.8 | 24.9 | 60.3 | |||||
| 1.0 | Without cord | 64.0 | 42.9 | 43.9 | 84.1 | 0.771 | |||
| With cord | 59.8 | 47.9 | 37.3 | 82.2 | |||||
| Marginal region | 0 | Without cord | 64.9 | 45.2 | 34.4 | 85.4 | 0.678 | <0.001 ** (1 mm > 0.75, 0.5, 0 mm > 0.25 mm) | 0.248 |
| With cord | 63.1 | 54.1 | 37.7 | 88.4 | |||||
| 0.25 | Without cord | 41.0 | 4.8 | 38.7 | 43.2 | 0.505 | |||
| With cord | 45.6 | 30.5 | 31.3 | 59.9 | |||||
| 0.5 | Without cord | 60.5 | 27.4 | 47.7 | 73.3 | 0.842 | |||
| With cord | 58.0 | 48.6 | 35.3 | 80.7 | |||||
| 0.75 | Without cord | 59.9 | 24.2 | 48.5 | 71.2 | 0.885 | |||
| With cord | 61.7 | 49.6 | 38.5 | 84.9 | |||||
| 1.0 | Without cord | 100.1 | 44.5 | 79.3 | 121.0 | 0.294 | |||
| With cord | 82.0 | 61.8 | 53.1 | 111.0 | |||||
| Axial region | 0 | Without cord | 36.1 | 35.3 | 24.9 | 57.2 | 0.541 | <0.001 ** (1 mm > 0.75, 0.5, 0 mm > 0.25 mm) | 0.329 |
| With cord | 48.6 | 39.4 | 30.2 | 67.0 | |||||
| 0.25 | Without cord | 29.7 | 3.2 | 28.2 | 31.2 | 0.263 | |||
| With cord | 34.7 | 19.3 | 25.6 | 43.7 | |||||
| 0.5 | Without cord | 38.2 | 21.0 | 28.3 | 48.0 | 0.919 | |||
| With cord | 39.1 | 35.3 | 22.6 | 55.6 | |||||
| 0.75 | Without cord | 33.2 | 21.6 | 23.1 | 43.3 | 0.502 | |||
| With cord | 39.5 | 35.3 | 22.9 | 56.0 | |||||
| 1.0 | Without cord | 60.5 | 44.5 | 39.7 | 81.3 | 0.771 | |||
| With cord | 56.3 | 45.7 | 34.9 | 77.7 | |||||
| Occlusal region | 0 | Without cord | 36.0 | 35.3 | 24.9 | 57.2 | 0.084 | 0.314 | 0.473 |
| With cord | 40.4 | 37.7 | 22.8 | 58.1 | |||||
| 0.25 | Without cord | 22.0 | 3.3 | 20.5 | 23.6 | 0.071 | |||
| With cord | 30.6 | 20.4 | 21.1 | 40.2 | |||||
| 0.5 | Without cord | 32.3 | 18.9 | 23.5 | 41.2 | 0.504 | |||
| With cord | 38.3 | 35.1 | 21.9 | 54.7 | |||||
| 0.75 | Without cord | 27.6 | 21.2 | 17.7 | 37.5 | 0.414 | |||
| With cord | 35.3 | 35.8 | 18.5 | 52.0 | |||||
| 1.0 | Without cord | 49.3 | 44.3 | 28.6 | 70.0 | 0.914 | |||
| With cord | 50.8 | 44.9 | 29.8 | 71.8 | |||||
| Finish Line Depth (mm) | Marginal and Internal Fit | Cord Type | Mean | SD | 95% CI | p * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||
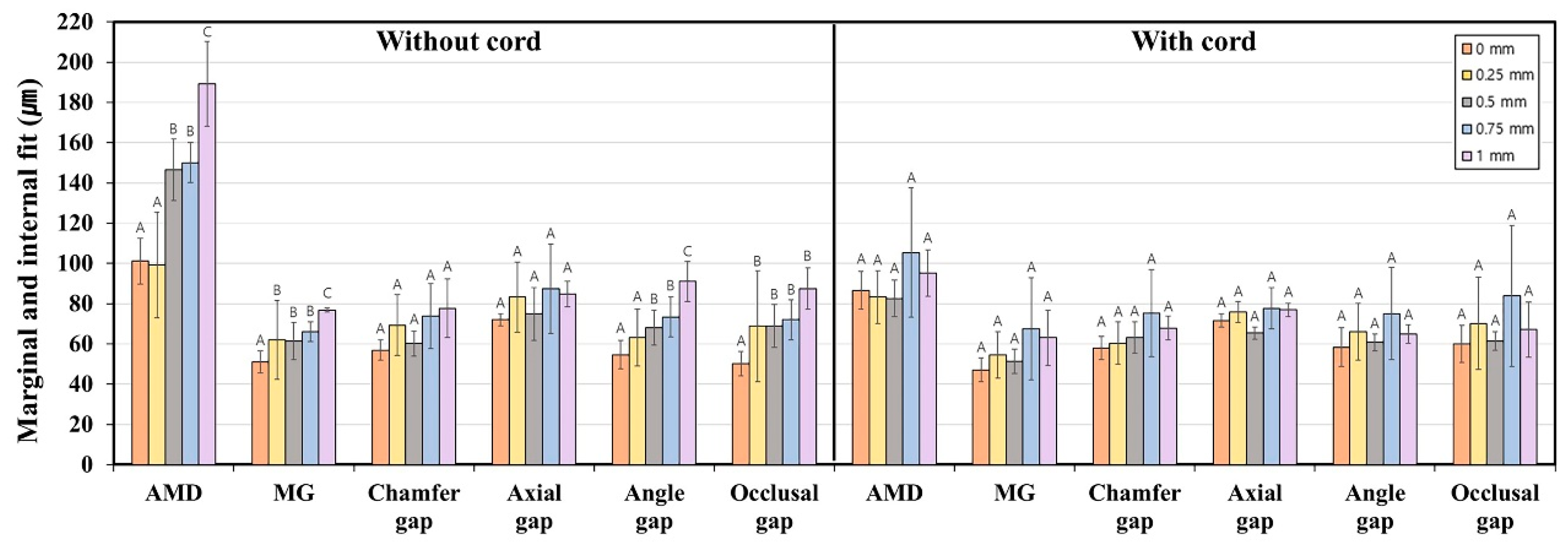
| 0 | AMD | Without cord | 101.1 | 22.7 | 90.5 | 111.7 | 0.034 * |
| With cord | 86.6 | 18.9 | 77.7 | 95.4 | |||
| MG | Without cord | 51.0 | 11.1 | 45.8 | 56.1 | 0.293 | |
| With cord | 47.1 | 11.9 | 41.5 | 52.7 | |||
| Chamfer gap | Without cord | 56.9 | 10.1 | 52.1 | 61.6 | 0.757 | |
| With cord | 57.9 | 11.7 | 52.5 | 63.4 | |||
| Axial gap | Without cord | 72.0 | 5.9 | 69.3 | 74.7 | 0.853 | |
| With cord | 71.6 | 6.8 | 68.4 | 74.8 | |||
| Angle gap | Without cord | 54.6 | 14.2 | 48.0 | 61.2 | 0.492 | |
| With cord | 58.3 | 19.3 | 49.3 | 67.4 | |||
| Occlusal gap | Without cord | 50.2 | 12.3 | 44.4 | 55.9 | 0.058 | |
| With cord | 59.9 | 18.5 | 51.2 | 68.6 | |||
| 0.25 | AMD | Without cord | 99.2 | 52.4 | 74.7 | 123.8 | 0.229 |
| With cord | 83.2 | 26.2 | 71.0 | 95.5 | |||
| MG | Without cord | 62.0 | 39.1 | 43.7 | 80.3 | 0.46 | |
| With cord | 54.5 | 23.0 | 43.7 | 65.2 | |||
| Chamfer gap | Without cord | 69.3 | 30.4 | 55.0 | 83.5 | 0.289 | |
| With cord | 60.4 | 20.9 | 50.6 | 70.2 | |||
| Axial gap | Without cord | 83.3 | 34.9 | 66.9 | 99.6 | 0.365 | |
| With cord | 75.8 | 10.3 | 71.0 | 80.6 | |||
| Angle gap | Without cord | 63.1 | 28.4 | 49.8 | 76.4 | 0.757 | |
| With cord | 65.9 | 28.3 | 52.6 | 79.1 | |||
| Occlusal gap | Without cord | 68.8 | 54.9 | 43.1 | 94.5 | 0.933 | |
| With cord | 70.2 | 46.0 | 48.6 | 91.7 | |||
| 0.5 | AMD | Without cord | 146.6 | 30.5 | 132.3 | 160.9 | <0.001 * |
| With cord | 82.6 | 18.0 | 74.2 | 91.0 | |||
| MG | Without cord | 61.4 | 18.5 | 52.8 | 70.1 | 0.048 * | |
| With cord | 51.3 | 12.2 | 45.6 | 57.0 | |||
| Chamfer gap | Without cord | 60.2 | 12.3 | 54.5 | 66.0 | 0.522 | |
| With cord | 63.1 | 15.6 | 55.8 | 70.4 | |||
| Axial gap | Without cord | 74.9 | 26.3 | 62.6 | 87.2 | 0.125 | |
| With cord | 65.4 | 6.0 | 62.6 | 68.2 | |||
| Angle gap | Without cord | 68.1 | 17.2 | 60.0 | 76.1 | 0.096 | |
| With cord | 60.7 | 8.4 | 56.8 | 64.7 | |||
| Occlusal gap | Without cord | 69.0 | 21.3 | 59.0 | 78.9 | 0.15 | |
| With cord | 61.4 | 9.4 | 57.0 | 65.8 | |||
| 0.75 | AMD | Without cord | 150.1 | 19.7 | 140.9 | 159.3 | 0.005 * |
| With cord | 105.4 | 64.6 | 75.2 | 135.7 | |||
| MG | Without cord | 66.0 | 9.9 | 61.3 | 70.6 | 0.898 | |
| With cord | 67.5 | 50.9 | 43.6 | 91.3 | |||
| Chamfer gap | Without cord | 73.9 | 32.3 | 58.8 | 89.0 | 0.913 | |
| With cord | 75.2 | 43.2 | 55.0 | 95.4 | |||
| Axial gap | Without cord | 87.3 | 44.4 | 66.5 | 108.1 | 0.387 | |
| With cord | 77.7 | 20.6 | 68.1 | 87.3 | |||
| Angle gap | Without cord | 73.3 | 19.8 | 64.0 | 82.6 | 0.875 | |
| With cord | 75.1 | 45.7 | 53.7 | 96.5 | |||
| Occlusal gap | Without cord | 72.0 | 20.0 | 62.6 | 81.4 | 0.475 | |
| With cord | 83.8 | 70.3 | 50.9 | 116.7 | |||
| 1.0 | AMD | Without cord | 189.1 | 42.2 | 169.3 | 208.8 | <0.001 * |
| With cord | 95.2 | 22.9 | 84.5 | 106.0 | |||
| MG | Without cord | 76.8 | 20.2 | 67.3 | 86.2 | 0.082 | |
| With cord | 63.1 | 27.4 | 50.3 | 76.0 | |||
| Chamfer gap | Without cord | 77.6 | 29.1 | 63.9 | 91.2 | 0.177 | |
| With cord | 67.9 | 12.0 | 62.2 | 73.5 | |||
| Axial gap | Without cord | 84.7 | 12.8 | 78.7 | 90.7 | 0.02 * | |
| With cord | 76.9 | 6.5 | 73.9 | 80.0 | |||
| Angle gap | Without cord | 91.0 | 19.8 | 81.8 | 100.3 | <0.001 * | |
| With cord | 64.9 | 9.2 | 60.6 | 69.2 | |||
| Occlusal gap | Without cord | 87.4 | 20.5 | 77.8 | 97.0 | 0.012 * | |
| With cord | 67.1 | 27.5 | 54.3 | 80.0 | |||
| Without cord; p ** | AMD; <0.001 ** (1 mm > 0.75, 0.5 mm > 0.25, 0 mm) | MG; 0.011 ** (1 mm > 0.75, 0.5, 0.25 mm > 0 mm) | Chamfer gap; 0.056 | Axial gap; 0.374 | Angle gap; <0.001 ** (1 mm > 0.75, 0.5 mm > 0.25, 0 mm) | Occlusal gap; 0.005 ** (1, 0.75, 0.5, 0.25 mm > 0 mm) | |
| With cord; p *** | AMD; 0.195 | MG; 0.156 | Chamfer gap; 0.168 | Axial gap; 0.050 | Angle gap; 0.314 | Occlusal gap; 0.360 | |
| Trueness | Marginal Fit | Internal Fit | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marginal Region | AMD | MG | Chamfer Gap | Axial Gap | Angle Gap | Occlusal Gap | |
| Without cord | Pearson’s correlation coefficient | 0.439 | - | - | - | 0.268 | 0.232 |
| Correlation level * | Moderate | - | - | - | Weak | Weak | |
| p ** | 0.001 | 0.184 | 0.246 | 0.134 | 0.007 | 0.02 | |
| With cord | Pearson’s correlation coefficient | - | - | - | - | 0.297 | 0.288 |
| Correlation level * | - | - | - | - | Weak | Weak | |
| p ** | 0.548 | 0.387 | 0.275 | 0.056 | 0.003 | 0.004 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Son, Y.-T.; Son, K.; Lee, J.-M.; Lee, K.-B. Does Intraoral Scanning at the Subgingival Finish Line Affect the Accuracy of Interim Crowns? J. Funct. Biomater. 2025, 16, 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16090309
Son Y-T, Son K, Lee J-M, Lee K-B. Does Intraoral Scanning at the Subgingival Finish Line Affect the Accuracy of Interim Crowns? Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2025; 16(9):309. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16090309
Chicago/Turabian StyleSon, Young-Tak, Keunbada Son, Ji-Min Lee, and Kyu-Bok Lee. 2025. "Does Intraoral Scanning at the Subgingival Finish Line Affect the Accuracy of Interim Crowns?" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 16, no. 9: 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16090309
APA StyleSon, Y.-T., Son, K., Lee, J.-M., & Lee, K.-B. (2025). Does Intraoral Scanning at the Subgingival Finish Line Affect the Accuracy of Interim Crowns? Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 16(9), 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16090309








