Photothermal Release by Melanin-like Nanoparticles: Biomedical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Natural and Biomimetic Melanin
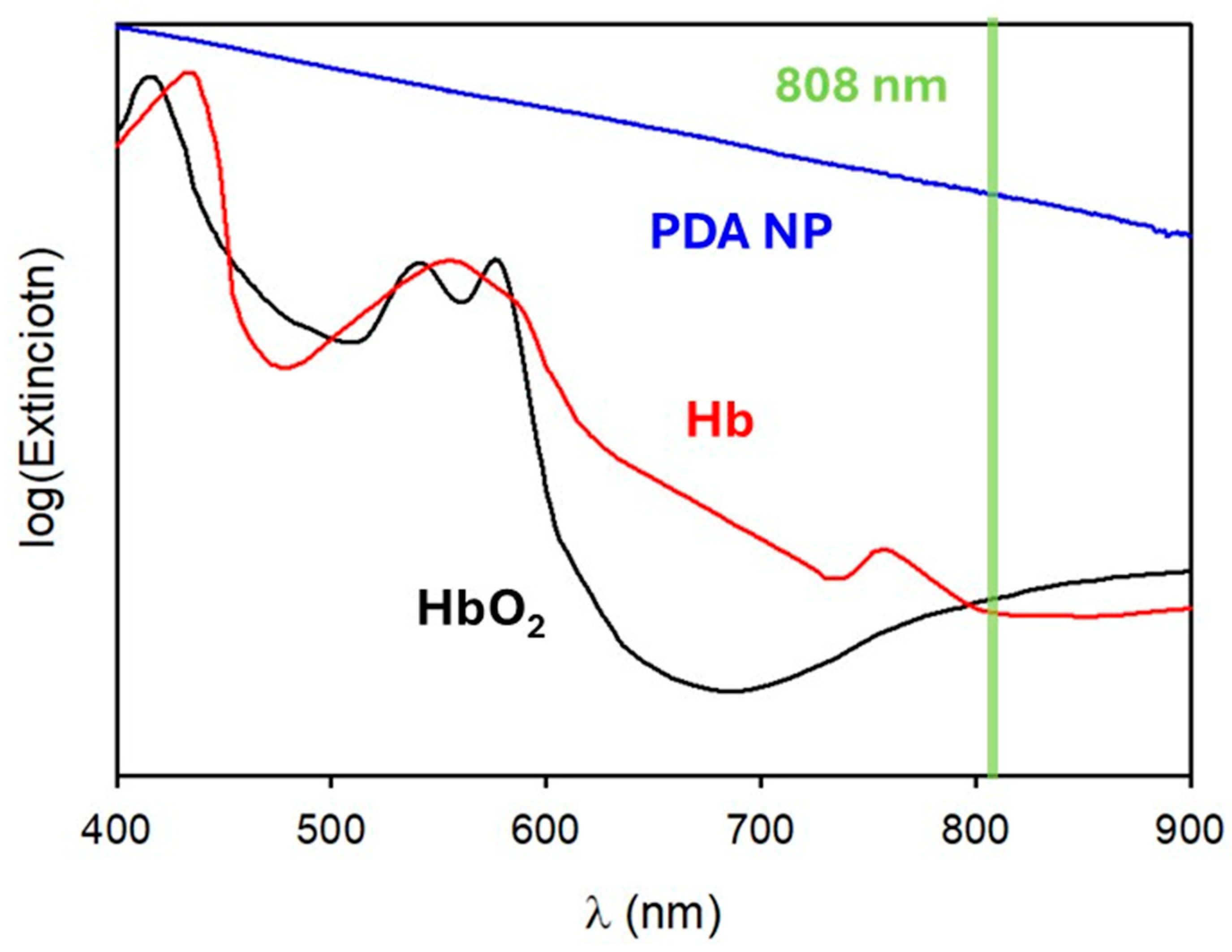
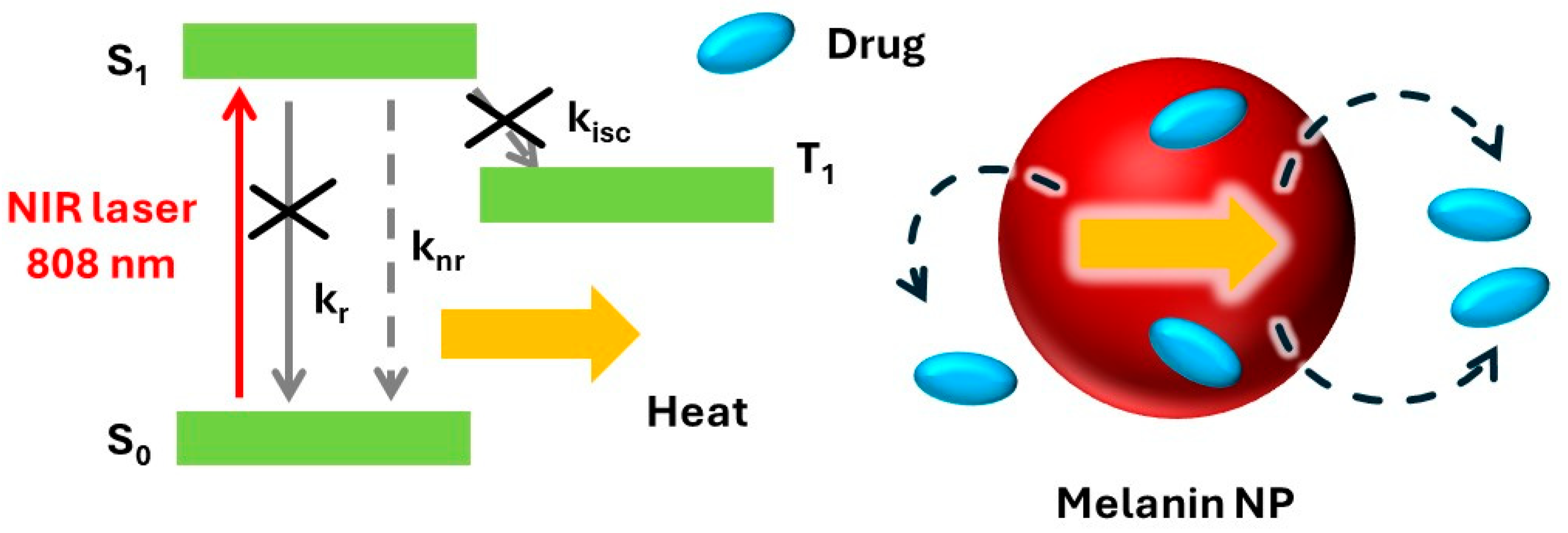
1.2. Photothermal Processes
1.3. Photoacoustic Imaging
1.4. Photothermal Release
2. Cancer Treatment
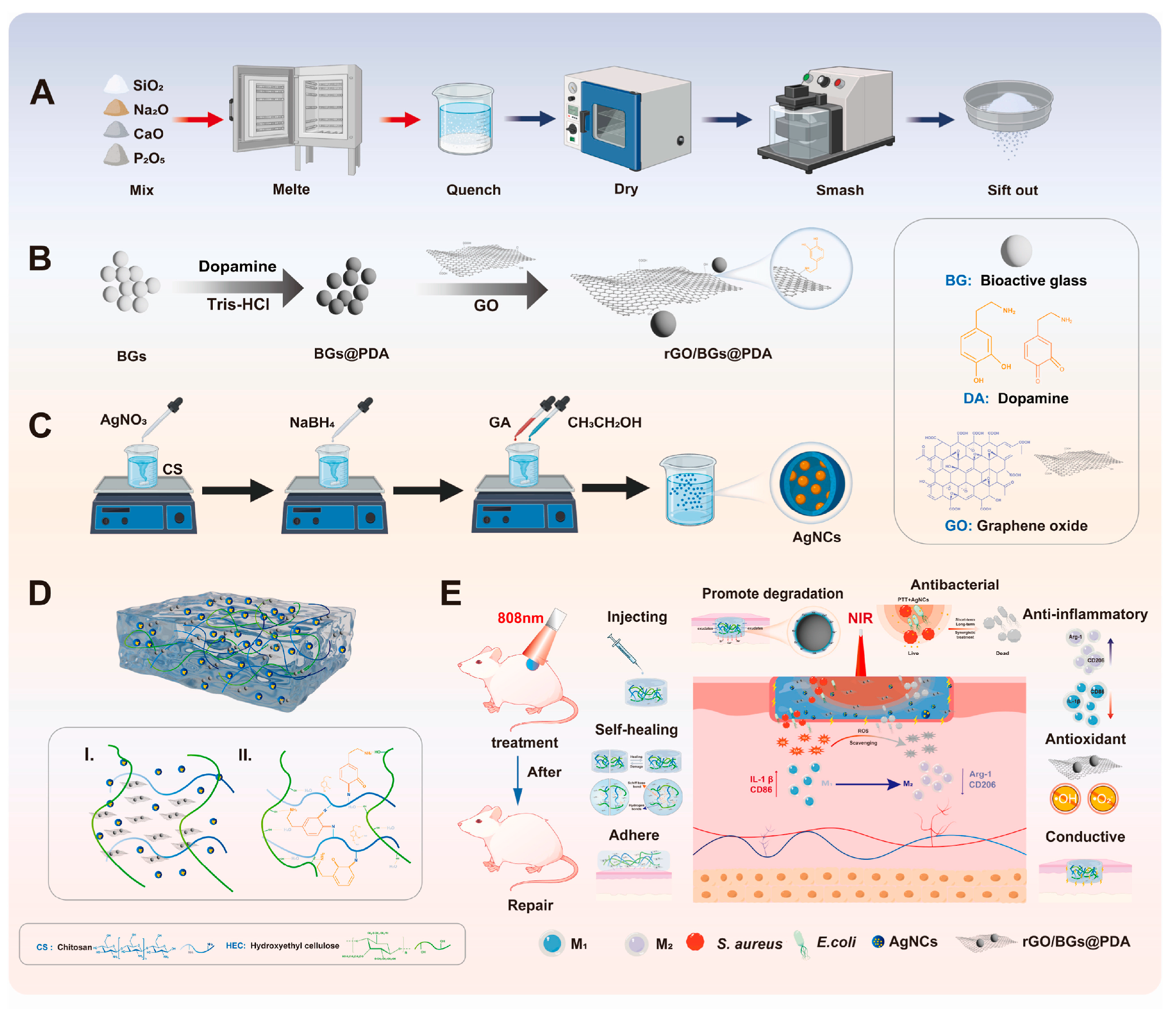
3. Antibacterial Applications
4. Other Applications
5. Future Perspectives
5.1. What Local Temperature Is Reached?
5.2. How Does Local Temperature Change over Time?
5.3. Are Different Experimental Results Comparable?
5.4. The Role of Chemistry and Photochemistry
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, W.; Zhou, X.; McCallum, N.C.; Hu, Z.; Ni, Q.Z.; Kapoor, U.; Heil, C.M.; Cay, K.S.; Zand, T.; Mantanona, A.J.; et al. Unraveling the Structure and Function of Melanin through Synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 2622–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corani, A.; Huijser, A.; Gustavsson, T.; Markovitsi, D.; Malmqvist, P.A.; Pezzella, A.; D’Ischia, M.; Sundström, V. Superior photoprotective motifs and Mechanisms in eumelanins uncovered. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 11626–11635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menichetti, A.; Mordini, D.; Vicenzi, S.; Pane, A.; Montalti, M. Unexplored Mechanisms of Photoprotection: Synergistic Light Absorption and Antioxidant Activity of Melanin. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micillo, R.; Panzella, L.; Iacomino, M.; Prampolini, G.; Cacelli, I.; Ferretti, A.; Crescenzi, O.; Koike, K.; Napolitano, A.; D’Ischia, M. Eumelanin broadband absorption develops from aggregation-modulated chromophore interactions under structural and redox control. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menichetti, A.; Mordini, D.; Montalti, M. Melanin and Light. Chem. Eur. J. 2024, 30, e202400461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakamatsu, K.; Ito, S. Recent Advances in Characterization of Melanin Pigments in Biological Samples. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ischia, M.; Napolitano, A.; Pezzella, A.; Meredith, P.; Sarna, T. Chemical and structural diversity in eumelanins: Unexplored bio-optoelectronic materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 3914–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Ischia, M.; Wakamatsu, K.; Cicoira, F.; Di Mauro, E.; Garcia-Borron, J.C.; Commo, S.; Galván, I.; Ghanem, G.; Kenzo, K.; Meredith, P.; et al. Melanins and melanogenesis: From pigment cells to human health and technological applications. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2015, 28, 520–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ischia, M.; Wakamatsu, K.; Napolitano, A.; Briganti, S.; Garcia-Borron, J.C.; Kovacs, D.; Meredith, P.; Pezzella, A.; Picardo, M.; Sarna, T.; et al. Melanins and melanogenesis: Methods, standards, protocols. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2013, 26, 616–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, P.; Sarna, T. The physical and chemical properties of eumelanin. Pigment Cell Res. 2006, 19, 572–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, F.R.; Grieco, C.; Kohler, B. Ultrafast spectral hole burning reveals the distinct chromophores in eumelanin and their common photoresponse. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 1248–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieco, C.; Kohl, F.R.; Kohler, B. Ultrafast Radical Photogeneration Pathways in Eumelanin. Photochem. Photobiol. 2023, 99, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petropoulos, V.; Mavridi-Printezi, A.; Menichetti, A.; Mordini, D.; Kabacinski, P.; Gianneschi, N.C.; Montalti, M.; Maiuri, M.; Cerullo, G. Sub-50 fs Formation of Charge Transfer States Rules the Fate of Photoexcitations in Eumelanin-Like Materials. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2024, 15, 3639–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulos, V.; Mordini, D.; Montorsi, F.; Akturk, M.; Menichetti, A.; Olivati, A.; Petrozza, A.; Morandi, V.; Maiuri, M.; Gianneschi, N.C.; et al. Photochemical Pathways and Light-Enhanced Radical Scavenging Activity of 1,8-Dihydroxynaphthalene Allomelanin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 10031–10043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, K.-Y.; Fischer, M.C.; Warren, W.S. Understanding the Role of Aggregation in the Broad Absorption Bands of Eumelanin. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 12050–12061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarna, T. Photodynamics of Melanin Radicals: Contribution to Photoprotection by Melanin. Photochem. Photobiol. 2023, 99, 866–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szewczyk, G.; Zadlo, A.; Sarna, M.; Ito, S.; Wakamatsu, K.; Sarna, T. Aerobic photoreactivity of synthetic eumelanins and pheomelanins: Generation of singlet oxygen and superoxide anion. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2016, 29, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavridi-Printezi, A.; Giordani, S.; Menichetti, A.; Mordini, D.; Zattoni, A.; Roda, B.; Ferrazzano, L.; Reschiglian, P.; Marassi, V.; Montalti, M. The dual nature of biomimetic melanin. Nanoscale 2023, 16, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Lyu, M.; Huang, Q.; Suo, M.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Duo, Y.; Fan, K. Stellate Plasmonic Exosomes for Penetrative Targeting Tumor NIR-II Thermo-Radiotherapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 36928–36937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Chen, H.; Huang, C.; Li, G.; Wang, X.; Jiang, W.; Fan, K. H2O2 Self-Producing Single-Atom Nanozyme Hydrogels as Light-Controlled Oxidative Stress Amplifier for Enhanced Synergistic Therapy by Transforming “Cold” Tumors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2110268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolmans, D.E.J.G.J.; Fukumura, D.; Jain, R.K. Photodynamic therapy for cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H.; Wu, J.; Sawa, T.; Matsumura, Y.; Hori, K. Tumor vascular permeability and the EPR effect in macromolecular therapeutics: A review. J. Control. Release 2000, 65, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalti, M.; Cantelli, A.; Battistelli, G. Nanodiamonds and silicon quantum dots: Ultrastable and biocompatible luminescent nanoprobes for long-term bioimaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4853–4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, B.; Park, J.Y.; Tung, C.H.; Kim, I.H.; Choi, Y. Gold nanorod-photosensitizer complex for near-infrared fluorescence imaging and photodynamic/photothermal therapy in vivo. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Sunil, D.; Ningthoujam, R.S. Hypoxia-responsive nanoparticle based drug delivery systems in cancer therapy: An up-to-date review. J. Control. Release 2020, 319, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Jain, P.K.; El-Sayed, I.H.; El-Sayed, M.A. Plasmonic photothermal therapy (PPTT) using gold nanoparticles. Lasers Med. Sci. 2008, 23, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ai, K.; Liu, J.; Deng, M.; He, Y.; Lu, L. Dopamine-Melanin Colloidal Nanospheres: An Efficient Near-Infrared Photothermal Therapeutic Agent for In Vivo Cancer Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.V.; Hu, S. Photoacoustic tomography: In vivo imaging from organelles to organs. Science 2012, 335, 1458–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wang, L.V. Photoacoustic imaging in biomedicine. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2006, 77, 041101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, F.; Menichetti, A.; Degli Esposti, L.; Montesi, M.; Panseri, S.; Bassi, G.; Montalti, M.; Lazzarini, L.; Adamiano, A.; Iafisco, M. Fluorescent Carbon Dots from Food Industry By-Products for Cell Imaging. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Zanden, S.Y.; Qiao, X.; Neefjes, J. New insights into the activities and toxicities of the old anticancer drug doxorubicin. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 6095–6111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Efficient Co-Delivery of Metformin and Ammonia Borane via a Hollow Mesoporous Polydopamine Nanogenerator for Enhanced Chemo-Photothermal Therapy against Melanoma. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 17, 7462–7477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, B.; Ni, J.; Xiang, Y.; He, Z. Combined Chemo-and Photothermal Therapies of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Using Polydopamine/Au Hollow Nanospheres Loaded with Doxorubicin. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 9597–9612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezk, A.I.; Lee, J.; Kim, B.S.; Chun, S. Strategically Designed Bifunctional Polydopamine Enwrapping Polycaprolactone-Hydroxyapatite-Doxorubicin Composite Nanofibers for Osteosarcoma Treatment and Bone Regeneration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 22946–22957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Lan, J.; Li, Z.; Zeng, R.; Ding, Y.; Pan, W. Mesoporous polydopamine (MPDA)-based drug delivery system for oral chemo-photothermal combinational therapy of orthotopic colon cancer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 281, 136618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, P.; Tang, J.; Xue, Y.; Luo, H.; Dai, R.; Jin, J.; Liu, J. 3D printed heterogeneous hybrid hydrogel scaffolds for sequential tumor photothermal-chemotherapy and wound healing. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 5648–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Wei, X.; Chen, B.; Luo, Y. 3D printed hydrogel/PCL core/shell fiber scaffolds with NIR-triggered drug release for cancer therapy and wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2021, 131, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Q.; He, D.; Ding, L.; Kong, F.; He, P.; Huang, J.; Guo, J.; Brinker, C.J.; Luo, G.; Zhu, W.; et al. Microneedle Patches Integrated with Biomineralized Melanin Nanoparticles for Simultaneous Skin Tumor Photothermal Therapy and Wound Healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2113269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Cheng, H.; Wang, Z.; Miao, Z.; Zhang, F.; Chen, J.; Wang, G.; Tao, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. “Carrier-drug” layer-by-layer hybrid assembly of biocompatible polydopamine nanoparticles to amplify photo-chemotherapy. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 13740–13754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, C.; Zou, Y.; Gao, G.; Sun, L.; Yu, B.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Han, M. Photothermal combined with intratumoral injection of annonaceous acetogenin nanoparticles for breast cancer therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 213, 112426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, M.; Archana, P.R.; Mumbrekar, K.D. Exploring baicalein: A natural flavonoid for enhancing cancer prevention and treatment. Heliyon 2024, 10, e40809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Lv, R.; Hao, N.; Wang, H.; Lv, Y.; Li, Y.; Ji, Y.; Liu, Y. Fabrication of pH/photothermal-responsive ZIF-8 nanocarriers loaded with baicalein for effective drug delivery and synergistic chem-photothermal effects. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 668, 131401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Shi, W.; Wu, Y.; Kong, L.; Gao, J.; Kong, Y. A stimuli-responsive drug delivery system based on konjac glucomannan, carboxymethyl chitosan and mesoporous polydopamine nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 292, 139196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Qian, C.; Ma, L.; Guo, P.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, F.; Yang, D. High-stabilized polydopamine modified low eutectic fatty acids based on near-infrared response for breast cancer therapy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2021, 220, 112213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, H.; Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Bao, Y.; Jian, M.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Meng, X. Photothermal induced chemo-immunological synergistic therapy for anaplastic thyroid carcinoma treatment. Mater. Des. 2023, 229, 111859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepp, O.; and Kroemer, G. Is ferroptosis immunogenic? The devil is in the details! OncoImmunology 2022, 11, 2127273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Yang, J.; Kang, R.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Z.; Yang, N.; Liu, Z.; Jia, Z.; Zhou, X.; Shen, Q. Biomimetic bacteria-derived nanoclusters enhance ferroptosis cancer immunotherapy through synergistic CRISPR-photothermo modulation. Nano Today 2024, 55, 102213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Zhang, W.; Yang, M.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L. Near-infrared light-enhanced polydopamine-based multifunctional nanoparticles for combination of chemodynamic and NO gas therapy in the treatment of osteosarcoma. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 289, 138946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, K.; Singh, S.; Itakura, S.; Hashimoto, M.; Kusamori, K.; Nishikawa, M. Reactive oxygen species augmented polydopamine-chlorin e6 nanosystem for enhanced chemo/photothermal/photodynamic therapy: A synergistic trimodal combination approach in vitro & in vivo. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 283, 137236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, T.; Jiang, J.; Chen, C.; Lv, Y.; Cao, T.; Cao, P.; Zhan, Q. Temperature-responsive two-dimensional polydopamine hydrogel: Preparation, mechanisms, and applications in cancer treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282, 136891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getachew, G.; Tien, Y.C.; Kan, T.C.; Dirersa, W.B.; Wibrianto, A.; Orchirbat, S.; Chang, J.; Rasal, A.S.; Gurav, V.; Kizhepat, S.; et al. Defect-passivated metal halide perovskite quantum dots stabilized into biodegradable porous polydopamine nanoparticles for photothermal/chemodynamic/gas therapy of cancer. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 467, 143560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shi, L.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qian, Y.; Yang, D.; Zheng, J. Aptamer induced nanosystem with dynamically self-monitoring and in-situ imaging for breast cancer therapy. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 384, 133611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Kong, X.; Meng, J.; Zhang, X. Dual-Responsive Triple-Synergistic Fe-MOF for Tumor Theranostics. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 9003–9013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, J. MRI-guided dual-responsive anti-tumor nanostructures for synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy and chemodynamic therapy. Acta Biomater. 2023, 158, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, S.; Ren, K.; Mu, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Dong, J.; et al. Polydopamine Nanostructure-Enhanced Water Interaction with pH-Responsive Manganese Sulfide Nanoclusters for Tumor Magnetic Resonance Contrast Enhancement and Synergistic Ferroptosis-Photothermal Therapy. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 3369–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Dun, Y.; Xie, L.; Jiang, W.; Sun, X.; Hu, P.; Zheng, S.; Yu, Y. Preparation of doxorubicin-loaded porous iron Oxide@ polydopamine nanocomposites for MR imaging and synergistic photothermal–chemotherapy of cancer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 208, 112107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.K.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.C.; Lee, C.S. MnCO3-mineralized polydopamine nanoparticles as an activatable theranostic agent for dual-modality imaging-guided photothermal therapy of cancers. Theranostics 2022, 12, 6762–6778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Yu, X.; Zhang, C.; Du, H.; Yang, S.; Wang, H.; Zhu, J.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, M. Facile fabrications of poly (acrylic acid)-mesoporous zinc phosphate/polydopamine Janus nanoparticles as a biosafe photothermal therapy agent and a pH/NIR-responsive drug carrier. Acta Biomater. 2024, 187, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Chen, W.; Wang, C.; Jiang, K.; Zhu, J.; Lu, R.; Lin, Z.; Cao, Z.; Zheng, J. A mesoporous theranostic platform for ultrasound and photoacoustic dual imaging-guided photothermal and enhanced starvation therapy for cancer. Acta Biomater. 2024, 183, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Kong, L.; Tian, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, X.; Dang, W.; Xing, B.; Zhang, Q.; Pang, X.; Hu, Z.; et al. Photoacoustic imaging-guided triple-responsive nanoparticles with tumor hypoxia relief for improving chemotherapy/ photothermal/photodynamic synergistic therapy against breast cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 164, 114928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, G.; Dai, S.; Li, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Ou, S.; Jin, Z.; Wu, J.; Liu, L.; Huang, G. Losartan-IR820-Loaded Polydopamine Nanoparticles for CO2-Generating Ultrasound Imaging-Guided Photothermal/Photodynamic Therapies of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 12300–12311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Dong, W.; Zhao, S.; Du, T.; Wang, Y.; Yao, J.; Liu, Z.; Sun, D.; Zhang, M. An injectable adhesive antibacterial hydrogel wound dressing for infected skin wounds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 134, 112584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Huang, J.; Zhao, J.; Yue, T.; Shenyang, W.; Xu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, Y. pH-responsive cationic guar gum-based multifunctional hydrogel with silver nanoenzymes: Combined photothermal antibacterial therapy and antioxidant properties for MRSA infected wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 292, 139201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Ye, A.; Jiang, L.; Lu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Huang, R.; Du, S.; Dong, X.; Huang, T.; Li, P.; et al. Photothermal-enhanced silver nanocluster bioactive glass hydrogels for synergistic antimicrobial and promote wound healing. Mater. Today Bio 2025, 30, 101439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Sun, J.; Xu, J.; Li, D. Near-Infrared Light-Mediated Cyclodextrin Metal–Organic Frameworks for Synergistic Antibacterial and Anti-Biofilm Therapies. Small 2023, 19, 2300199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Feng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yi, B.; Li, W.; Zeng, X.; Xu, H. Coral-like AgNPs hybrided MOFs modulated with biopolymer polydopamine for synergistic antibacterial and biofilm eradication. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282, 137080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shang, H.; Xiong, Y.; Luan, Y.; Wang, D.; Du, X. Silver/jellyfish-like mesoporous polydopamine nanomotor with concentration-dependent synergistic antibacterial activity. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 505, 159367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, Z.; Lin, S.; Ni, W.; Sun, Z.; Shen, D.; Zhu, J.; Liu, L.; et al. NIR-Activated Hydrogel with Dual-Enhanced Antibiotic Effectiveness for Thorough Elimination of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 17, 2952–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Fan, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Lin, W.; Yi, G.; Feng, X. Adhesive polydopamine-based photothermal hybrid hydrogel for on-demand lidocaine delivery, effective anti-bacteria, and prolonged local long-lasting analgesia. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, D.; Rinoldi, C.; Nakielski, P.; Du, J.; Haghighat Bayan, M.A.; Zargarian, S.S.; Pruchniewski, M.; Li, X.; Strojny-Cieślak, B.; Ding, B.; et al. Injectable and self-healable nano-architectured hydrogel for NIR-light responsive chemo- and photothermal bacterial eradication. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 12, 1905–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Xu, N.; Wang, X.; Shi, L.; Huang, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Ni, T.; Yang, Z.; Guo, W. Mesoporous polydopamine/copper sulfide hybrid nanocomposite for highly efficient NIR-triggered bacterial inactivation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277, 134238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Wang, J.; Xiong, Q.; Xu, Y.; Xuan, S.; Leung, K.C.F.; Fang, Q. Dipolar-hollowed α-Fe2O3@Au/Polydopamine nanospindle for photothermal-photodynamic coupling antibacterial and drug-delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 281, 136615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, Q.; Tang, L.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liu, X.; Lin, D.; Zhou, G. A multifunctional hydrogel with mild photothermal antibacterial and antioxidant properties based on quercetin and dopamine-coated zinc oxide nanoparticles for healing bacteria-infected wound. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 497, 154518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Wan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Sun, X.; Qi, M.; Cheng, S.; Li, C.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, L.; Dong, B.; et al. Near-infrared-activated nanohybrid coating with black phosphorus/zinc oxide for efficient biofilm eradication against implant-associated infections. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 134935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, L.; He, Y.; Wang, L.; Deng, Z.; Liu, J.; Peng, D.; Ding, T.; Lu, L.; Ding, Y.; et al. Polydopamine Nanosheets Doped Injectable Hydrogel with Nitric Oxide Release and Photothermal Effects for Bacterial Ablation and Wound Healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2101476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhang, W.; Ding, D.; Liu, G.; Cheng, N. Multifunctional chitosan/alginate hydrogel incorporated with bioactive glass nanocomposites enabling photothermal and nitric oxide release activities for bacteria-infected wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 232, 123445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jia, D.; Qiao, J.; Peng, X.; Zhou, C.; Yang, Y. Controlled Nitric Oxide-Releasing Nanovehicles for Enhanced Infected Wound Healing: A Study on PDA@BNN6 Encapsulated in GelMA Hydrogel. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 11499–11516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Ma, J.; Meng, S.; Zou, H.; Wang, H.; Zhou, M. Functionalized Mesoporous Polydopamine Nanocarrier with Near-Infrared Laser-Trigged NO Release and Photothermal Effects for the Killing of Pathogenic Bacteria. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 10429–10441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Tian, Y.; Wu, X.; Zeng, M.; Wu, C.; Wei, D.; Luo, H.; Sun, J.; Ding, J.; Fan, H. Temperature and light dual-responsive hydrogels for anti-inflammation and wound repair monitoring. J. Mater. Chem. B 2025, 13, 2855–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Huang, X.; Li, H.; Ren, F.; Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Tong, Y.; Ran, P. Bacterial lipase-responsive polydopamine nanoparticles for detection and synergistic therapy of wound biofilms infection. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 270, 132350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Q.; Ran, P.; Xie, S.; Wei, J.; Li, X. Pyroelectric Janus nanomotors for synergistic electrodynamic-photothermal-antibiotic therapies of bacterial infections. Acta Biomater. 2023, 162, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, T.V.; Deb Dutta, S.; Patel, D.K.; Ganguly, K.; Lim, K.T. Electrospinning near infra-red light-responsive unzipped CNT/PDA nanofibrous membrane for enhanced antibacterial effect and rapid drug release. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 612, 155949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alinezhad, V.; Esmaeilzadeh, K.; Bagheri, H.; Zeighami, H.; Kalantari-Hesari, A.; Jafari, R.; Makvandi, P.; Xu, Y.; Mohammadi, H.; Shahbazi, M.A.; et al. Engineering a platelet-rich plasma-based multifunctional injectable hydrogel with photothermal, antibacterial, and antioxidant properties for skin regeneration. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 11, 5872–5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quni, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, M.; Zhang, L.; You, J.; Cui, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Li, D.; et al. NF-κB-Signaling-Targeted Immunomodulatory Nanoparticle with Photothermal and Quorum-Sensing Inhibition Effects for Efficient Healing of Biofilm-Infected Wounds. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 25757–25772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Fang, W.; Xu, S.; Luo, H.; Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Tong, Y.; Zhao, L. Synergistic quorum sensing inhibition and mild-temperature photothermal therapy of integrated nanoplatform for implant-associated biofilm infections. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2024, 663, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhao, J.; Fan, D. A dissolving microneedle patch for Antibiotic/Enzymolysis/Photothermal triple therapy against bacteria and their biofilms. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 437, 135475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Chan, Y.K.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Liang, K.; Deng, Y. Photo-Activated Nanofibrous Membrane with Self-Rechargeable Antibacterial Function for Stubborn Infected Cutaneous Regeneration. Small 2022, 18, 2105988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, X.; Meng, L.; Zhao, L.; Kong, L.; Pan, S.; Che, Y. Tunicate cellulose nanocrystals strengthened injectable stretchable hydrogel as multi-responsive enhanced antibacterial wound dressing for promoting diabetic wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 343, 122426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhao, B.; Li, M.; Wang, H.; Zhu, J.; Li, Q.; Gao, H.; Feng, Q.; Cao, X. Microenvironment responsive nanocomposite hydrogel with NIR photothermal therapy, vascularization and anti-inflammation for diabetic infected wound healing. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 26, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.S.; Gao, Y.; Rui, B.Y.; Li, X.R.; Liu, P.L.; Han, Z.Y.; Wei, Z.Y.; Zhang, C.R.; Wang, F.; Dawes, H.; et al. Double-network hydrogel enhanced by SS31-loaded mesoporous polydopamine nanoparticles: Symphonic collaboration of near-infrared photothermal antibacterial effect and mitochondrial maintenance for full-thickness wound healing in diabetes mellitus. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 27, 409–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chu, L.; Meng, X.; Ye, L.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, P. Photoactivated Hydrogel Therapeutic System with MXene-Based Nanoarchitectonics Potentiates Endogenous Bone Repair Through Reshaping the Osteo-Vascularization Network. Small 2024, 20, 2403003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.; Yang, L.; Li, W.; Chen, K.; Shang, L.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, Y. Mussel-inspired multi-bioactive microsphere scaffolds for bone defect photothermal therapy. Mater. Today Bio 2024, 29, 101363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wang, D.; He, Y.; Tao, B.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Tan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, J.; Yang, W.; et al. A HAase/NIR responsive surface on titanium implants for treating bacterial infection and improving osseointegration. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 143, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.Y.; Liu, Z.H.; Yu, H.D.; Chen, A.J.; Du, Z.; Cai, Y.R.; Fu, X.X.; Jin, S.E.; Chen, J.L.; Zhou, Z.K.; et al. Multifunctional mesoporous polydopamine near-infrared photothermal controlled release of kartogenin for cartilage repair. Mater. Des. 2023, 231, 112007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ge, W.; Ma, Z.; Ji, G.; Wang, M.; Zhou, G.; Wang, X. Use of mesoporous polydopamine nanoparticles as a stable drug-release system alleviates inflammation in knee osteoarthritis. APL Bioeng. 2022, 6, 026101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.W.; Lu, Q.J.; Chen, Y.J.; Hou, Y.K.; Zou, Y.M.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, W.H.; Yuan, L.X.; Chen, J.X. NIR-PTT/ROS-Scavenging/Oxygen-Enriched Synergetic Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis by a pH-Responsive Hybrid CeO2-ZIF-8 Coated with Polydopamine. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8, 3361–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, L.; Wang, Y.; Sha, D.; Li, G.; Wei, Z.; Liu, C.; Yuan, Y.; Song, D. A biomimetic and bioactive scaffold with intelligently pulsatile teriparatide delivery for local and systemic osteoporosis regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 19, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
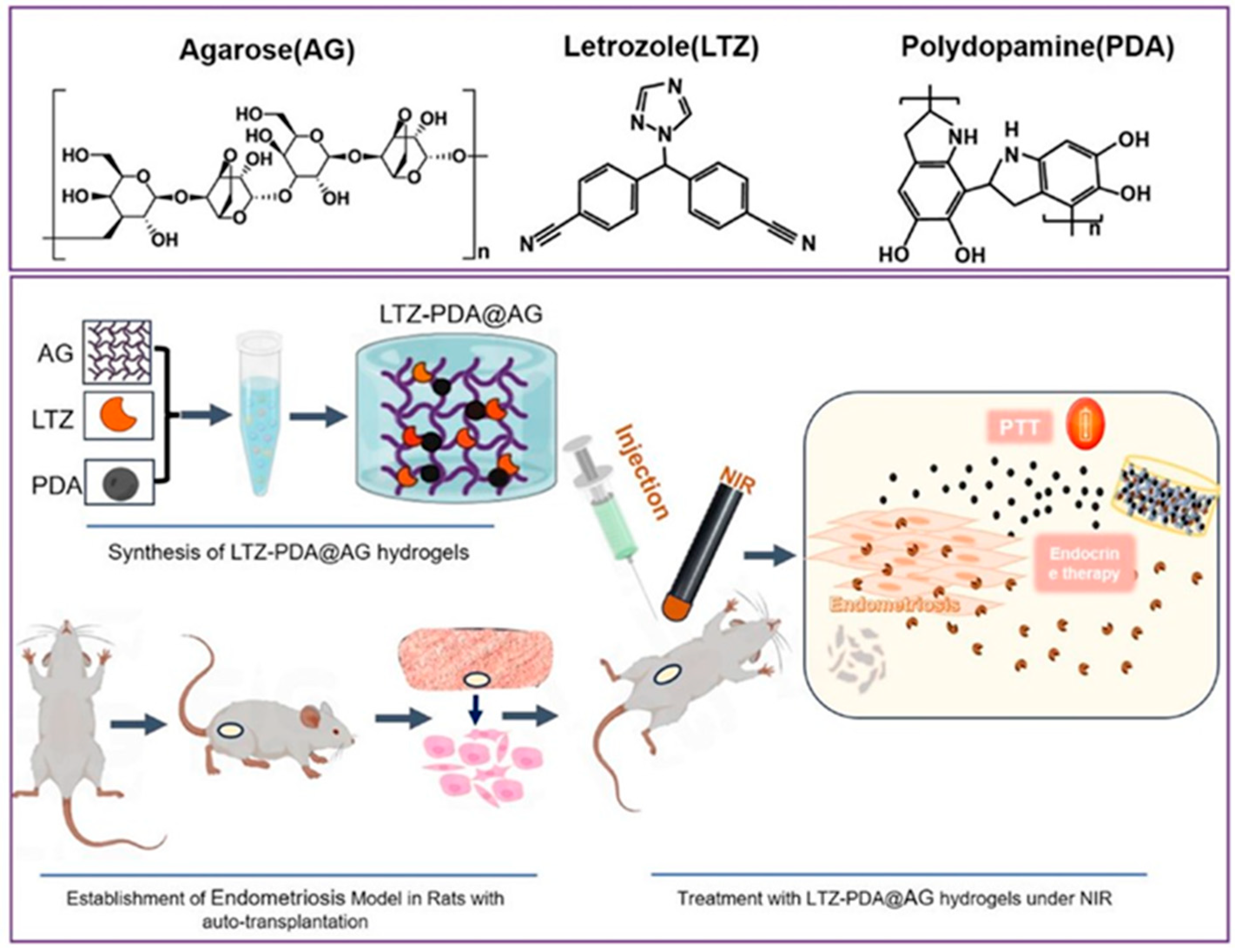
- Tian, W.; Wang, C.; Chu, R.; Ge, H.; Sun, X.; Li, M. Injectable hydrogel nanoarchitectonics with near-infrared controlled drug delivery for in situ photothermal/endocrine synergistic endometriosis therapy. Biomater. Res. 2023, 27, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Fei, F.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Gong, Y.; Chen, X.; Zheng, Y.; Tan, B.; Xu, C.; Xie, H.; et al. Nanoengineered on-demand drug delivery system improves efficacy of pharmacotherapy for epilepsy. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabm3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, K.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, W.; Song, Z.; Wang, W.; Han, H. Biomimetic Nanoplatelets to Target Delivery Hirudin for Site-Specific Photothermal/Photodynamic Thrombolysis and Preventing Venous Thrombus Formation. Small 2022, 18, 2203184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.; Spaeth, P.; Kar, A.; Baaske, M.D.; Khatua, S.; Orrit, M. Photothermal Microscopy: Imaging the Optical Absorption of Single Nanoparticles and Single Molecules. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 16414–16445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baffou, G.; Bordacchini, I.; Baldi, A.; Quidant, R. Simple experimental procedures to distinguish photothermal from hot-carrier processes in plasmonics. Light Sci. Appl. 2020, 9, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baffou, G.; Quidant, R.; García de Abajo, F.J. Nanoscale Control of Optical Heating in Complex Plasmonic Systems. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-d.; Wolfbeis, O.S.; Meier, R.J. Luminescent probes and sensors for temperature. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7834–7869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauzzi, D.; Pattacini, R.; Delferro, M.; Dini, F.; Di Natale, C.; Paolesse, R.; Bonacchi, S.; Montalti, M.; Zaccheroni, N.; Calvaresi, M.; et al. Temperature-Dependent Fluorescence of Cu5 Metal Clusters: A Molecular Thermometer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 9662–9665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guernelli, M.; Bakalis, E.; Mavridi-Printezi, A.; Petropoulos, V.; Cerullo, G.; Zerbetto, F.; Montalti, M. Photothermal motion: Effect of low-intensity irradiation on the thermal motion of organic nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 7233–7241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Disease | Imaging | Agents | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Melanoma | - | Met and Ammonia Borane | [32] |
| Non-small cell lung cancer | FL | DOX | [33] |
| Osteosarcoma | - | DOX | [34] |
| Colon cancer | FL | DOX | [35] |
| Melanoma | - | DOX | [36] |
| Cancer | - | DOX | [37] |
| Skin tumors | - | Melanin NP, SiO44− | [38] |
| Breast cancer | Fluorescence | DOX | [39] |
| Breast cancer | - | ACGs | [40] |
| Lung cancer | - | BA | [42] |
| Breast cancer | - | Curcumin | [43] |
| Breast cancer | Photothermal | DOX | [44] |
| Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma | FL/Photothermal | DOX, double-stranded CpG oligodeoxynucleotides | [45] |
| Cancer | - | T7 polypeptide-engineered bacterial outer membrane vesicles | [47] |
| Osteosarcoma | - | L-Arg, ICG, H2O2 | [48] |
| Breast cancer | - | Ce6, PTX | [49] |
| Breast cancer | Photothermal | ZnPc, SPC | [50] |
| Breast cancer | FL | CsPbBr3 quantum dots | [51] |
| Breast cancer | FL, Photothermal | CuO2 | [52] |
| Breast cancer | - | DOX | [53] |
| Cancer | MR | DOX | [54] |
| Cancer | MR | Manganese sulfide nanoclusters, H2S | [55] |
| Breast cancer | MR | DOX | [56] |
| Breast cancer | FL/MR | MnCO3-mineralized PDA NP | [57] |
| Breast cancer | FL | DOX | [58] |
| Colon carcinoma | Ultrasound/PA | GOx, PFP | [59] |
| Breast cancer | Photoacoustic | DOX | [60] |
| Triple-Negative Breast Cancer | Ultrasound | CQ, ICG | [61] |
| Matrix | Agents | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogel | AgNPs | [62] |
| Hydrogel | AgNPs | [63] |
| Hydrogel | rGO/BG/AgNC | [64] |
| - | MOFs/AgNPs | [65] |
| - | MOFs/AgNPs | [66] |
| Hydrogel | Ag Nanomotors | [67] |
| Hydrogel | AgNPs/Levofloxacin | [68] |
| Hydrogel | AgNPs/Lidocaine | [69] |
| Hydrogel | Ketoprofene | [70] |
| - | Cu2-xS NP | [71] |
| - | α-Fe2O3@Au NPs | [72] |
| Hydrogel | ZnO NPs, quercetin, quaternary ammonium salt chitosan | [73] |
| Ti substrates | BP NS, ZnO NW | [74] |
| Hydrogel | BNN6 (NO donor) | [75] |
| Hydrogel | BNN6 (NO donor)/BG NPs | [76] |
| Hydrogel | BNN6 (NO donor) | [77] |
| Hydrogel | SNP (NO donor) | [78] |
| Hydrogel | BNN6 (NO donor) | [79] |
| - | Ciprofloxacin | [80] |
| - | Janus pyroelectric NPs, ciprofloxacin | [81] |
| Electrospun polycaprolactone | uCNT | [82] |
| Hydrogel | PRP | [83] |
| Macrophage membrane | Naringenin | [84] |
| Hyaluronic acid coating | Luteolin | [85] |
| Microneedle patches | Levofloxacin, α-amylase | [86] |
| Electrospun polycaprolactone | Mxene/Ag3PO4 | [87] |
| Hydrogel | QCS-PBA, tunicate cellulose crystals, insulin drugs | [88] |
| Hydrogel | Metformin | [89] |
| Hydrogel | SS31 | [90] |
| Disease | Agents | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Bone regeneration | MXene NS, aFGF | [91] |
| Bone regeneration | MAP | [92] |
| Bacterial infection and poor osseointegration in titanium implants | Ciprofloxacin | [93] |
| Cartilage repair | Kartogenin | [94] |
| Chronic joint osteoarthritis | RCGD423 | [95] |
| Chronic joint rheumatoid arthritis | CeO2-doped ZIF-8 | [96] |
| Osteoporosis | Teriparatide | [97] |
| Endometriosis | LTZ | [98] |
| Epilepsy | PHT | [99] |
| Venous thrombosis | Hirudin | [100] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Menichetti, A.; Vicenzi, S.; Pane, A.; Mordini, D.; Mancin, F.; Montalti, M. Photothermal Release by Melanin-like Nanoparticles: Biomedical Applications. J. Funct. Biomater. 2025, 16, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16070243
Menichetti A, Vicenzi S, Pane A, Mordini D, Mancin F, Montalti M. Photothermal Release by Melanin-like Nanoparticles: Biomedical Applications. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2025; 16(7):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16070243
Chicago/Turabian StyleMenichetti, Arianna, Silvia Vicenzi, Agata Pane, Dario Mordini, Fabrizio Mancin, and Marco Montalti. 2025. "Photothermal Release by Melanin-like Nanoparticles: Biomedical Applications" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 16, no. 7: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16070243
APA StyleMenichetti, A., Vicenzi, S., Pane, A., Mordini, D., Mancin, F., & Montalti, M. (2025). Photothermal Release by Melanin-like Nanoparticles: Biomedical Applications. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 16(7), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16070243







