Bubble-Based Drug Delivery Systems: Next-Generation Diagnosis to Therapy
Abstract
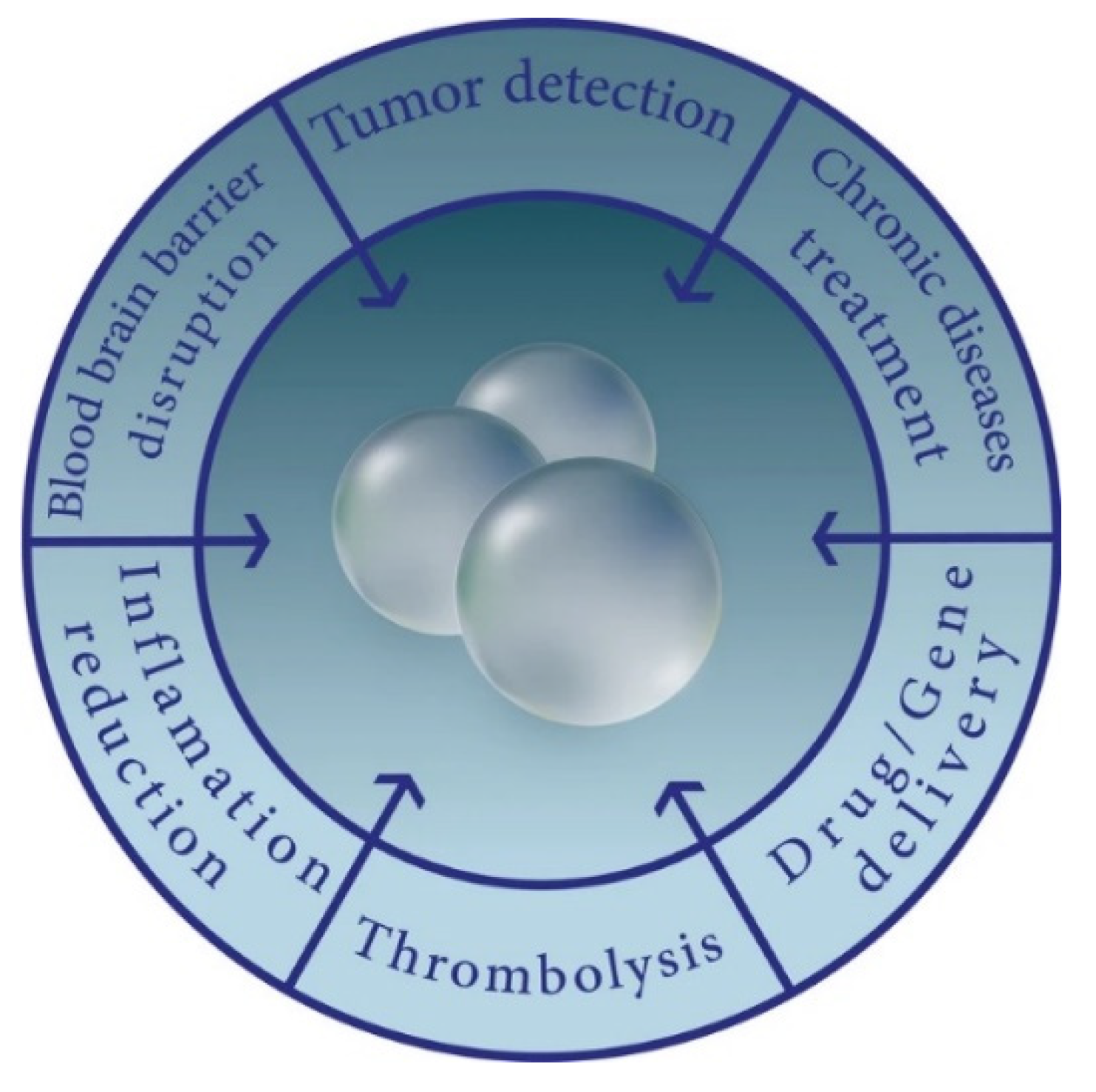
1. Introduction
Innovation in Micro/Nanobubbles for Drug/Gene Delivery and Imaging
2. Drug and Gene Delivery Overview
3. Bubbles in Practice
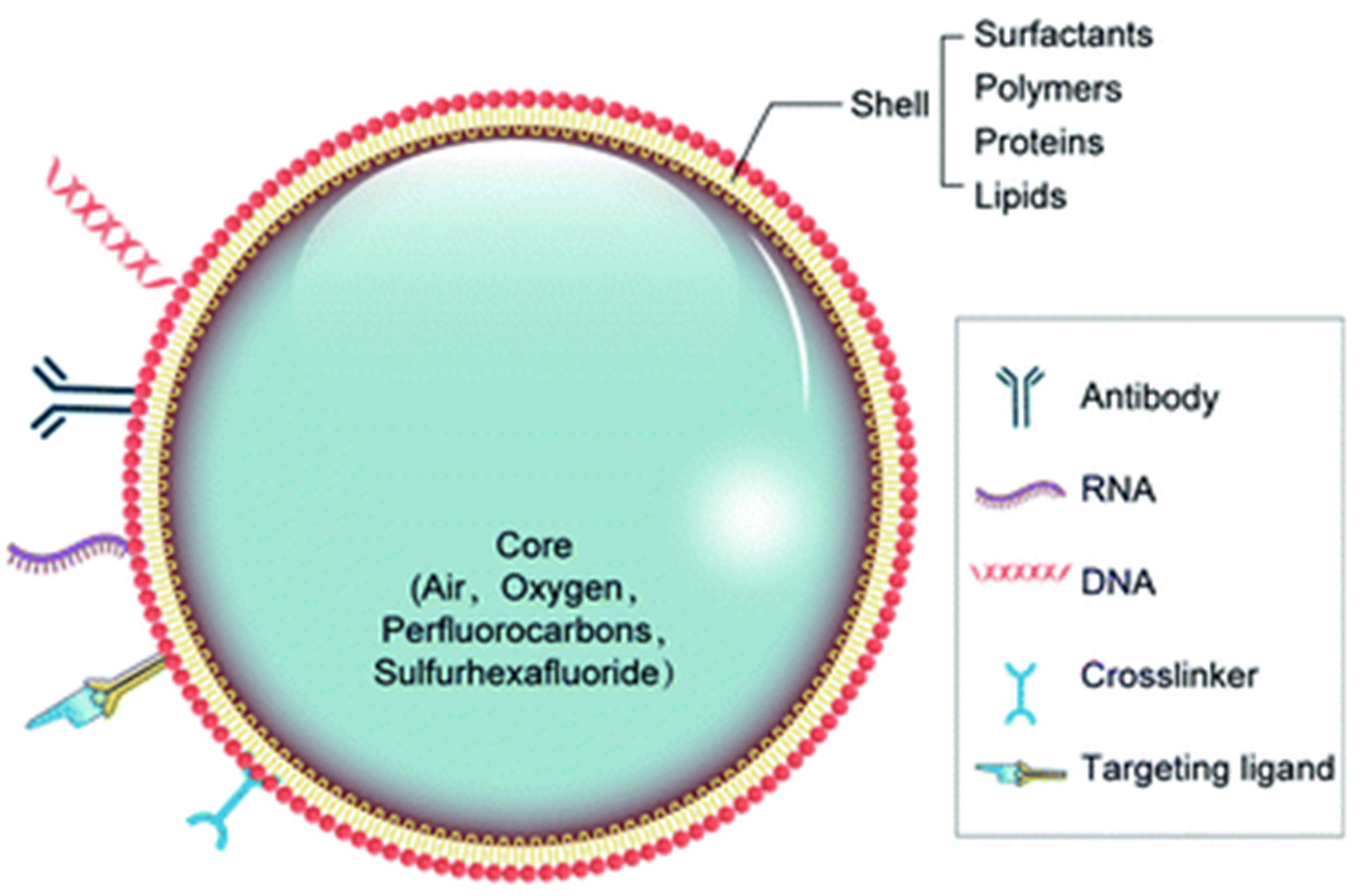
3.1. Bubble Types and Materials
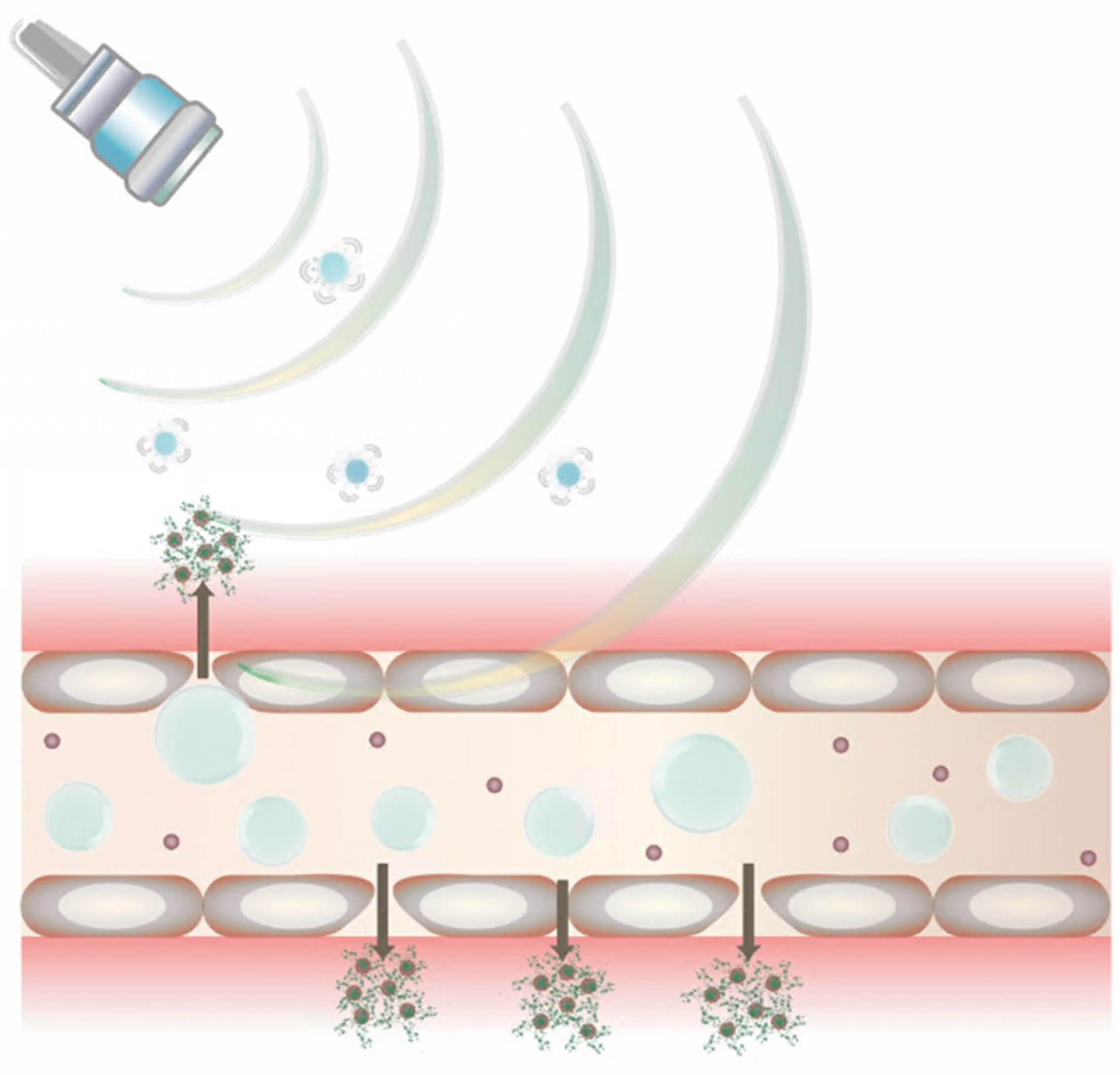
3.2. Ultrasound-Mediated Drug and Gene Delivery Using Bubbles
3.3. Bubbles in Image-Guided Drug Delivery
3.4. Challenges in Bubble-Based Image-Guided Drug Delivery
3.5. Bubbles in Gene Delivery
4. General Bubble Administration
5. Medical Bubble Applications
5.1. Cancer
5.2. Osteoporosis
5.3. Management of Acute Medical Conditions
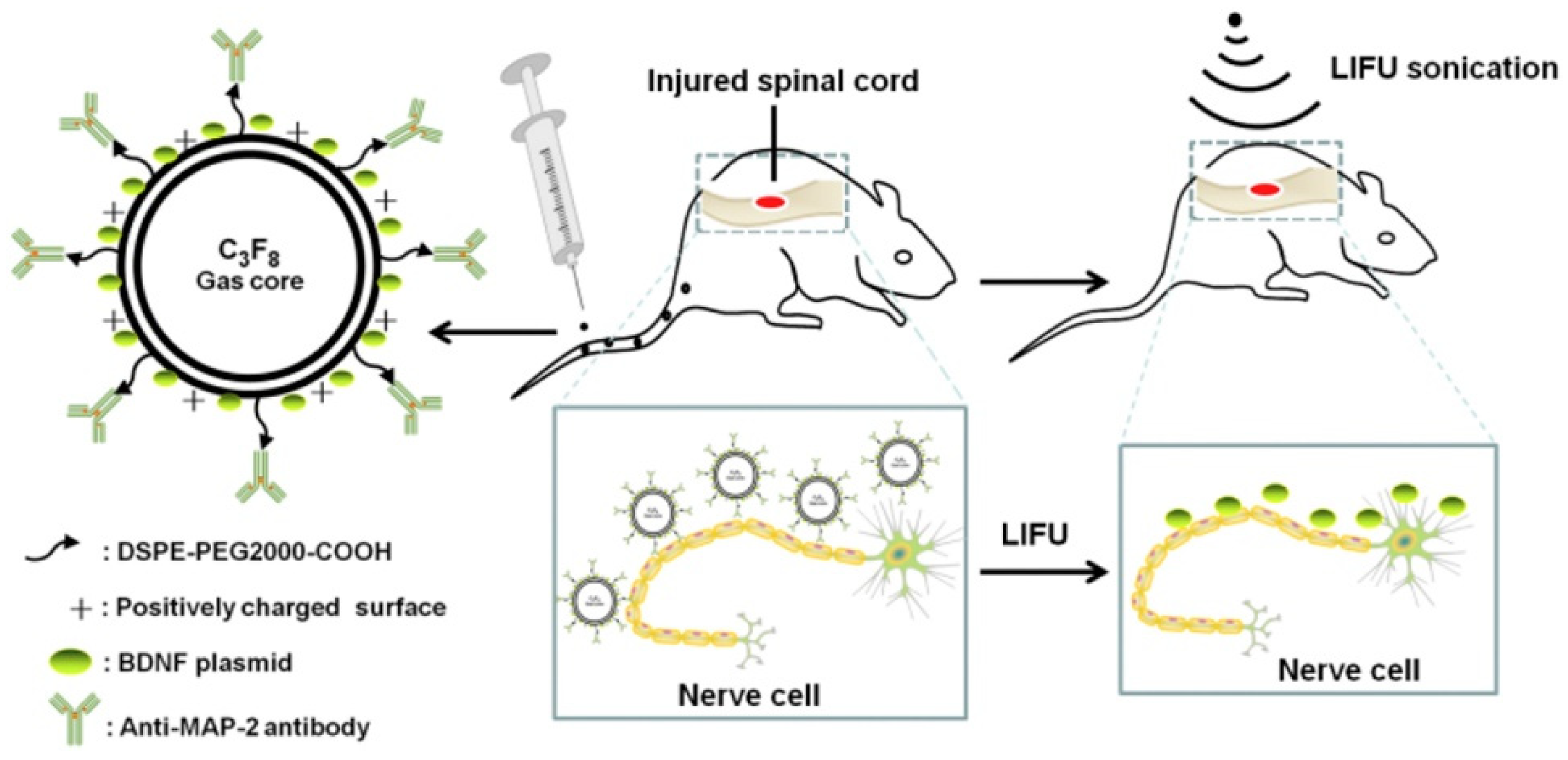
5.3.1. Blood–Brain Barrier
5.3.2. Lung-Targeted Delivery
6. Bubbles in Clinical Trials
7. Bubble Challenges and Opportunities
7.1. Microbubble Design
7.2. Endothelial Barrier
7.3. Blood–Brain Barrier
7.4. Immunological Barrier
8. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Endo-Takahashi, Y.; Negishi, Y. Gene and oligonucleotide delivery via micro- and nanobubbles by ultrasound exposure. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2022, 44, 100445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalli, R.; Soster, M.; Argenziano, M. Nanobubbles: A promising efficienft tool for therapeutic delivery. Ther. Deliv. 2016, 7, 117–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirsi, S.R.; Borden, M.A. Microbubble compositions, properties and biomedical applications. Bubble Sci. Eng. Technol. 2009, 1, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo-Takahashi, Y.; Negishi, Y. Microbubbles and Nanobubbles with Ultrasound for Systemic Gene Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalli, R.; Bisazza, A.; Lembo, D. Micro- and nanobubbles: A versatile non-viral platform for gene delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 456, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, A.; Blum, N.T.; Goodwin, A.P. Colloids, nanoparticles, and materials for imaging, delivery, ablation, and theranostics by focused ultrasound (FUS). Theranostics 2019, 9, 2572–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Ren, X.; Nie, F.; Li, T.; Lv, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y. Current advances in ultrasound-combined nanobubbles for cancer-targeted therapy: A review of the current status and future perspectives. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 12915–12928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paknahad, A.A.; Kerr, L.; Wong, D.A.; Kolios, M.C.; Tsai, S.S.H. Biomedical nanobubbles and opportunities for microfluidics. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 32750–32774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, R.-K. Ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction in gene therapy: A new tool to cure human diseases. Genes Dis. 2016, 4, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooiman, K.; Roovers, S.; Langeveld, S.A.G.; Kleven, R.T.; Dewitte, H.; O’Reilly, M.A.; Escoffre, J.-M.; Bouakaz, A.; Verweij, M.D.; Hynynen, K.; et al. Ultrasound-Responsive Cavitation Nuclei for Therapy and Drug Delivery. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2020, 46, 1296–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presset, A.; Bonneau, C.; Kazuyoshi, S.; Nadal-Desbarats, L.; Mitsuyoshi, T.; Bouakaz, A.; Kudo, N.; Escoffre, J.M.; Sasaki, N. Endothelial cells, first target of drug delivery using microbubble-assisted ultra-sound. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2020, 46, 1565–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shar, A.; Aboutalebianaraki, N.; Misiti, K.; Sip, Y.Y.L.; Zhai, L.; Razavi, M. A novel ultrasound-mediated nanodroplet-based gene delivery system for osteoporosis treatment. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2022, 41, 102530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henley, S.J.; Ward, E.M.; Scott, S.; Ma, J.; Anderson, R.N.; Firth, A.U.; Thomas, C.C.; Islami, F.; Weir, H.K.; Lewis, D.R.; et al. Annual Report to the Nation on the Status of Cancer, Part I: National Cancer Statistics. Cancer 2020, 126, 2225–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Cheng, X.; Li, J. Lipid nanobubbles as an ultrasound-triggered artesunate delivery system for imaging-guided, tumor-targeted chemotherapy. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 1841–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessone, F.; Argenziano, M.; Grillo, G.; Ferrara, B.; Pizzimenti, S.; Barrera, G.; Cravotto, G.; Guiot, C.; Stura, I.; Cavalli, R.; et al. Low-dose curcuminoid-loaded in dextran nanobubbles can prevent metastatic spreading in prostate cancer cells. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 214004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Wang, G.; Hou, X.; Kala, S.; Qiu, Z.; Wong, K.F.; Cao, F.; Sun, L. Biogenic nanobubbles for effective oxygen delivery and enhanced photodynamic therapy of cancer. Acta Biomater. 2020, 108, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Luo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Ran, H.; Wang, Z.; Guo, D. Magnetic nanobubbles with potential for targeted drug delivery and trimodal imaging in breast cancer: An in vitro study. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 991–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marano, F.; Argenziano, M.; Frairia, R.; Adamini, A.; Bosco, O.; Rinella, L.; Fortunati, N.; Cavalli, R.; Catalano, M.G. Doxorubicin-Loaded Nanobubbles Combined with Extracorporeal Shock Waves: Basis for a New Drug Delivery Tool in Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 2016, 26, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.-H.; Chan, Y.-C.; Liu, R.-S.; Hsiao, M. A selective drug delivery system based on phospholipid-type nanobubbles for lung cancer therapy. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 2689–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, B.; Smith, G.L.; Gerin, J.L.; Purcell, R.H. Live recombinant vaccinia virus protects chimpanzees against hepatitis B. Nature 1984, 311, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Dong, L.; Liang, S.; Wei, X.; Wang, Y.; Chang, L.; Guo, K.; Wu, H.; Chang, Y.; Yin, Y.; et al. Ultrasound-triggered drug delivery for glioma therapy through gambogic acid-loaded nanobubble-microbubble complexes. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 150, 113042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Guo, X.; Xiu, W.; Liu, Y.; Ren, L.; Xiao, H.; Yang, F.; Gao, Y.; Xu, C.; Wang, L. Accelerating thrombolysis using a precision and clot-penetrating drug delivery strategy by nanoparticle-shelled microbubbles. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz8204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Jiang, D.; Wu, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, R. Ultrasound-mediated nanobubble destruction (UMND) facilitates the delivery of VEGFR2-targeted CD-TK-loaded cationic nanobubbles in the treatment of bladder cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 146, 1415–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Cheng, W.; Li, S.; Wu, B.; Leng, X.; Xu, S.; Tian, J. Novel cell-penetrating peptide-loaded nanobubbles synergized with ultrasound irradiation enhance EGFR siRNA delivery for triple negative Breast cancer therapy. Colloids Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2016, 146, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Liu, J.; Meng, Z.; Li, Y.; Hong, Y.; Wang, L.; He, L.; Hu, B.; Zheng, Y.; Li, T.; et al. Ultrasound-assisted C3F8-filled PLGA nanobubbles for enhanced FGF21 delivery and improved prophylactic treatment of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Acta Biomater. 2021, 130, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, Y.K.; Kim, S.W. Recent advances in the development of gene delivery systems. Biomater. Res. 2019, 23, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega-Vásquez, P.; Mosier, N.S.; Irudayaraj, J. Nanoscale Drug Delivery Systems: From Medicine to Agriculture. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvi, S.B.; Ahmed, S.; Sridharan, D.; Naseer, Z.; Pracha, N.; Wang, H.; Boudoulas, K.D.; Zhu, W.; Sayed, N.; Khan, M. De novo Drug Delivery Modalities for Treating Damaged Hearts: Current Challenges and Emerging Solutions. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 742315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.R.; del Pilar Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S.; et al. Nano based drug delivery systems: Recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 20, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A. Microsphere: A promising approach for drug delivery. J. Appl. Pharm. Res. 2019, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanovic, M.; Arsenijevic, A.; Milovanovic, J.; Kanjevac, T.; Arsenijevic, N. Nanoparticles in Antiviral Therapy. In Antimicrobial Nanoarchitectonics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 383–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigata, M.; Meinert, C.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Bock, N. Hydrogels as Drug Delivery Systems: A Review of Current Characterization and Evaluation Techniques. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanaswamy, R.; Torchilin, V.P. Hydrogels and Their Applications in Targeted Drug Delivery. Molecules 2019, 24, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jangjou, A.; Meisami, A.H.; Jamali, K.; Niakan, M.H.; Abbasi, M.; Shafiee, M.; Salehi, M.; Hosseinzadeh, A.; Amani, A.M.; Vaez, A. The promising shadow of microbubble over medical sciences: From fighting wide scope of prevalence disease to cancer eradication. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 28, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Yang, L.; Chen, F.; Gu, N. Drug delivery system based on nanobubbles. Interdiscip. Mater. 2022, 1, 471–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alheshibri, M.; Al Baroot, A.; Shui, L.; Zhang, M. Nanobubbles and nanoparticles. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 55, 101470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alheshibri, M.; Craig, V.S.J. Differentiating between Nanoparticles and Nanobubbles by Evaluation of the Compressibility and Density of Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 21998–22007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Leon, A.; Perera, R.; Nittayacharn, P.; Cooley, M.; Jung, O.; Exner, A.A. Chapter three—Ultrasound contrast agents and delivery systems in cancer detection and therapy. In Advances in Cancer Research; Broome, A.-M., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; Volume 139, pp. 57–84. [Google Scholar]
- Perera, R.H.; Wu, H.; Peiris, P.; Hernandez, C.; Burke, A.; Zhang, H.; Exner, A.A. Improving performance of nanoscale ultrasound contrast agents using N,N-diethylacrylamide stabilization. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2016, 13, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudakovskaya, P.G.; Barmin, R.A.; Kuzmin, P.S.; Fedotkina, E.P.; Sencha, A.N.; Gorin, D.A. Microbubbles Stabilized by Protein Shell: From Pioneering Ultrasound Contrast Agents to Advanced Theranostic Systems. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deprez, J.; Lajoinie, G.; Engelen, Y.; De Smedt, S.; Lentacker, I. Opening doors with ultrasound and microbubbles: Beating biological barriers to promote drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 172, 9–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helbert, A.; Gaud, E.; Segers, T.; Botteron, C.; Frinking, P.; Jeannot, V. Monodisperse versus Polydisperse Ultrasound Contrast Agents: In Vivo Sensitivity and safety in Rat and Pig. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2020, 46, 3339–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Deng, C.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Lv, Q.; Han, W.; Xie, M. The Optimized Fabrication of a Novel Nanobubble for Tumor Imaging. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exner, A.A.; Kolios, M.C. Bursting microbubbles: How nanobubble contrast agents can enable the future of medical ultrasound molecular imaging and image-guided therapy. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 54, 101463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Counil, C.; Abenojar, E.; Perera, R.; Exner, A.A. Extrusion: A New Method for Rapid Formulation of High-Yield, Monodisperse Nanobubbles. Small 2022, 18, 2200810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Deng, S.; Zhao, R.; Nie, X.; Liu, Y. Effect of Nanobubble Evolution on Hydrate Process: A Review. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 28, 948–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lohse, D. Perspectives on surface nanobubbles. Biomicrofluidics 2014, 8, 041301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Hu, J. Generation and stability of bulk nanobubbles: A review and perspective. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 53, 101439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, W.G.; Husseini, G.A.; Staples, B.J. Ultrasonic drug delivery—A general review. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2004, 1, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carovac, A.; Smajlovic, F.; Junuzovic, D. Application of Ultrasound in Medicine. Acta Inform. Medica 2011, 19, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Zhao, P.; Deng, Y.; Liu, Y. Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Delivery through Micro/Nanobubble-Assisted Ultrasound. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kida, H.; Nishimura, K.; Ogawa, K.; Watanabe, A.; Feril, L.B.; Irie, Y.; Endo, H.; Kawakami, S.; Tachibana, K. Nanobubble Mediated Gene Delivery in Conjunction With a Hand-Held Ultrasound Scanner. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J. The Enhanced Permeability and Retention (EPR) Effect: The Significance of the Concept and Methods to Enhance Its Application. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, L.D. Nonthermal effects of therapeutic ultrasound: The frequency resonance hypothesis. J. Athl. Train. 2002, 37, 293–299. [Google Scholar]
- Legay, M.; Gondrexon, N.; Le Person, S.; Boldo, P.; Bontemps, A. Enhancement of Heat Transfer by Ultrasound: Review and Recent Advances. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 2011, 670108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Shirai, Y.; Sugawa, S. Free-Radical Generation from Bulk Nanobubbles in Aqueous Electrolyte Solutions: ESR Spin-Trap Observation of Microbubble-Treated Water. Langmuir 2021, 37, 5005–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Hwang, J.; Lee, K.; Choi, Y.; Seo, Y.; Jeon, H.; Hong, J.W.; Choi, J. Anti-Tumor Drug-Loaded Oxygen Nanobubbles for the Degradation of HIF-1α and the Upregulation of Reactive Oxygen Species in Tumor Cells. Cancers 2019, 11, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gampa, G.; Talele, S.; Kim, M.; Mohammad, A.; Griffith, J.; Elmquist, W.F. Chapter 9—Influence of transporters in treating cancers in the cns. In Drug Efflux Pumps in Cancer Resistance Pathways: From Molecular Recognition and Characterization to Possible Inhibition Strategies in Chemotherapy; Sosnik, A., Bendayan, R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; Volume 7, pp. 277–301. [Google Scholar]
- Prabhakar, A.; Banerjee, R. Nanobubble Liposome Complexes for Diagnostic Imaging and Ultrasound-Triggered Drug Delivery in Cancers: A Theranostic Approach. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 15567–15580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsha Virsingh, S.; Rafik Yakub, S.; Chandrashekhar, A.D. Using microbubbles as targeted drug delivery to improve aids. In Pharmaceutical Formulation Design; Usama, A., Juber, A., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2019; Chapter 6. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Lin, W.; Liu, H.; Deng, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Fu, X.; Yang, Y. Ultrasound-responsive nanobubbles contained with peptide–camptothecin conjugates for targeted drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2015, 23, 2756–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Grainger, D.W. Developing siRNA therapies to address osteoporosis. Ther. Deliv. 2013, 4, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şanlıer, H.; Ak, G.; Yılmaz, H.; Ünal, A.; Bozkaya, .F.; Tanıyan, G.; Yıldırım, Y.; Türkyılmaz, G.Y. Development of Ultrasound-Triggered and Magnetic-Targeted Nanobubble System for Dual-Drug Delivery. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 108, 1272–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernot, S.; Klibanov, A.L. Microbubbles in ultrasound-triggered drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1153–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Cornel, E.J.; Du, J. Ultrasound-responsive polymer-based drug delivery systems. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 1323–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlaxca, J.L.; Rychak, J.J.; Ernst, P.B.; Konkalmatt, P.R.; Shevchenko, T.I.; Pizzaro, T.T.; Rivera-Nieves, J.; Klibanov, A.L.; Lawrence, M.B. Ultrasound-based molecular imaging and specific gene delivery to mesenteric vasculature by endothelial adhesion molecule targeted microbubbles in a mouse model of Crohn’s disease. J. Control. Release 2013, 165, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Deng, Q.; Hu, B.; Wang, Y.-J.; Chen, J.-L.; Cui, J.-J.; Cao, S.; Song, H.-N. Ultrasound combined with targeted cationic microbubble-mediated angiogenesis gene transfection improves ischemic heart function. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 2293–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, J.; Hu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, J. Noninvasive, targeted gene therapy for acute spinal cord injury using LIFU-mediated BDNF-loaded cationic nanobubble destruction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 496, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åslund, A.K.; Berg, S.; Hak, S.; Mørch, Y.; Torp, S.H.; Sandvig, A.; Widerøe, M.; Hansen, R.; Davies, C.D.L. Nanoparticle delivery to the brain—By focused ultrasound and self-assembled nanoparticle-stabilized microbubbles. J. Control. Release 2015, 220, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omata, D.; Unga, J.; Suzuki, R.; Maruyama, K. Lipid-based microbubbles and ultrasound for therapeutic application. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 154–155, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.-Y.; Chen, C.C.; Tung, Y.-S.; Olumolade, O.O.; Konofagou, E.E. Effects of the microbubble shell physicochemical properties on ultrasound-mediated drug delivery to the brain. J. Control. Release 2015, 212, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jawadi, S.; Thakur, S.S. Ultrasound-responsive lipid microbubbles for drug delivery: A review of preparation techniques to optimise formulation size, stability and drug loading. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 585, 119559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yan, K.; Shen, L.; Yang, W.; Gong, J.; Ding, K. Clinical study of ultrasound and microbubbles for enhancing chemotherapeutic sensitivity of malignant tumors in digestive system. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 30, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nittayacharn, P.; Yuan, H.-X.; Hernandez, C.; Bielecki, P.; Zhou, H.; Exner, A.A. Enhancing Tumor Drug Distribution With Ultrasound-Triggered Nanobubbles. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 3091–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, E.; Liu, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, Z.; Song, L.; Zhu, B.; Wu, X.; Liu, J.; Zhao, D.; Li, Y. Advances in COVID-19 mRNA vaccine development. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengstie, M.A. Viral Vectors for the in Vivo Delivery of CRISPR Components: Advances and Challenges. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 895713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, E.A.; Lee, J.; Hotta, A. Delivery of CRISPR-Cas tools for in vivo genome editing therapy: Trends and challenges. J. Control. Release 2022, 342, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitta, J.; Howard, C.M. Applications of Ultrasound-Mediated Drug Delivery and Gene Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-J.; Zhou, Q.; Cao, S.; Hu, B.; Deng, Q.; Jiang, N.; Cui, J. Efficient gene therapy with a combination of ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction and PEI/DNA/NLS complexes. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 7685–7691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Xu, M.; Cao, Z.; Li, W.; Chen, L.; Xie, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, J. Ultrasound-Assisted miR-122-Loaded Polymeric Nanodroplets for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Gene Therapy. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 17, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kida, H.; Feril, L.B.; Irie, Y.; Endo, H.; Itaka, K.; Tachibana, K. Influence of Nanobubble Size Distribution on Ultrasound-Mediated Plasmid DNA and Messenger RNA Gene Delivery. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 855495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Ma, J.; Guan, L.; Mu, Y. General Characteristics of Microbubble-Adenovirus Vectors Carrying Genes. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 2020, 14, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Huang, S.; Yi, Y.; Bao, S. Ultrasound microbubble-mediated CRISPR/Cas9 knockout of C-erbB-2 in HEC-1A cells. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 47, 2199–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
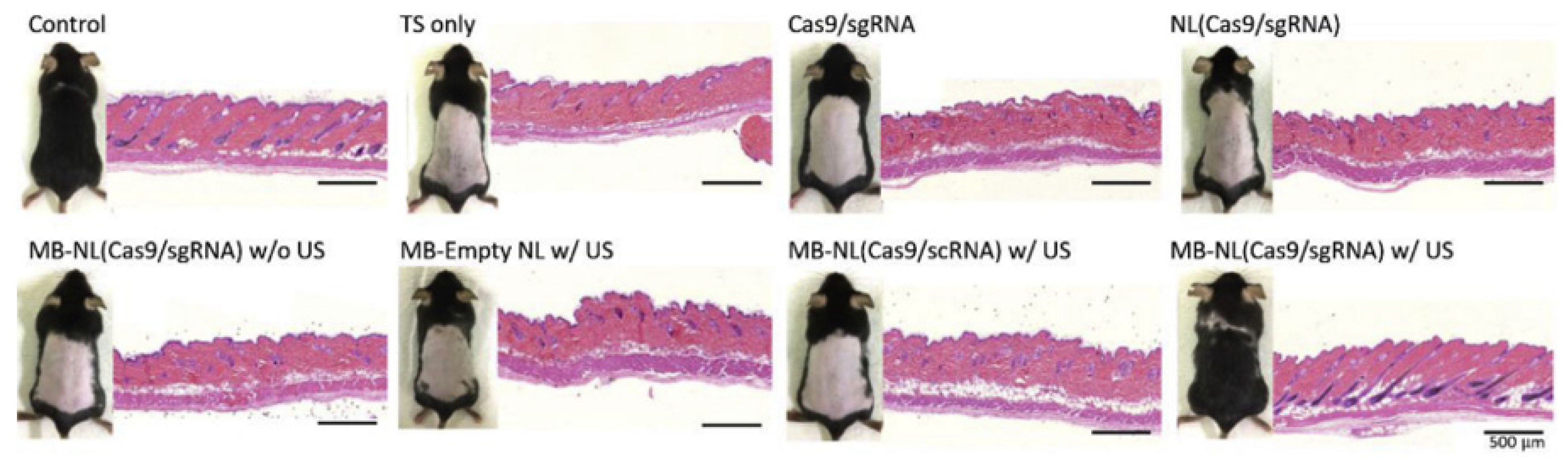
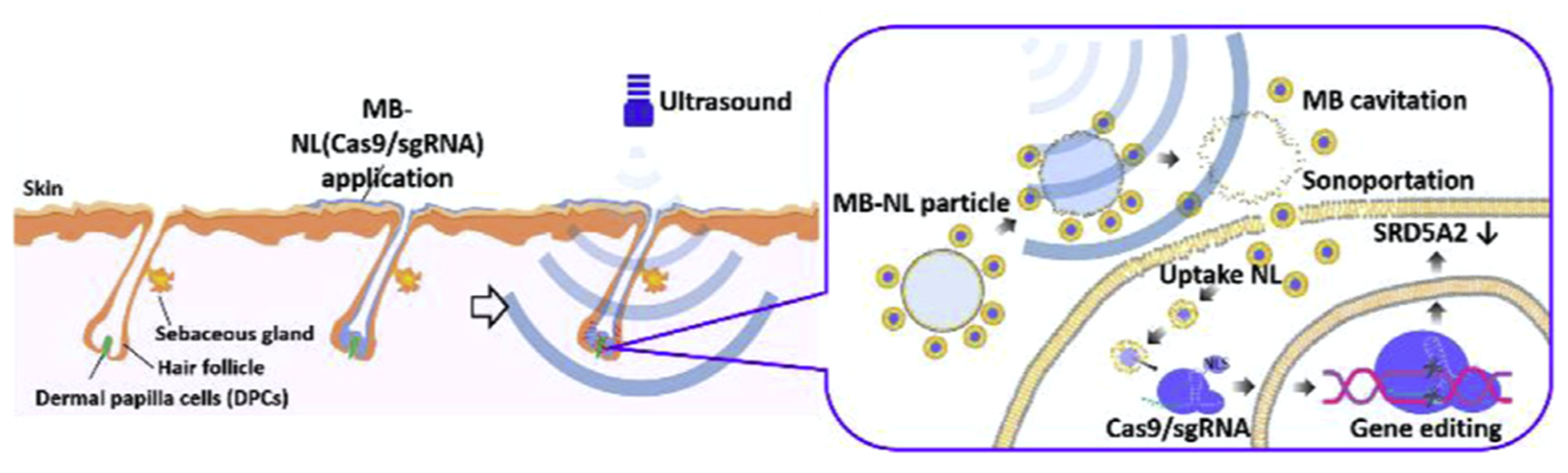
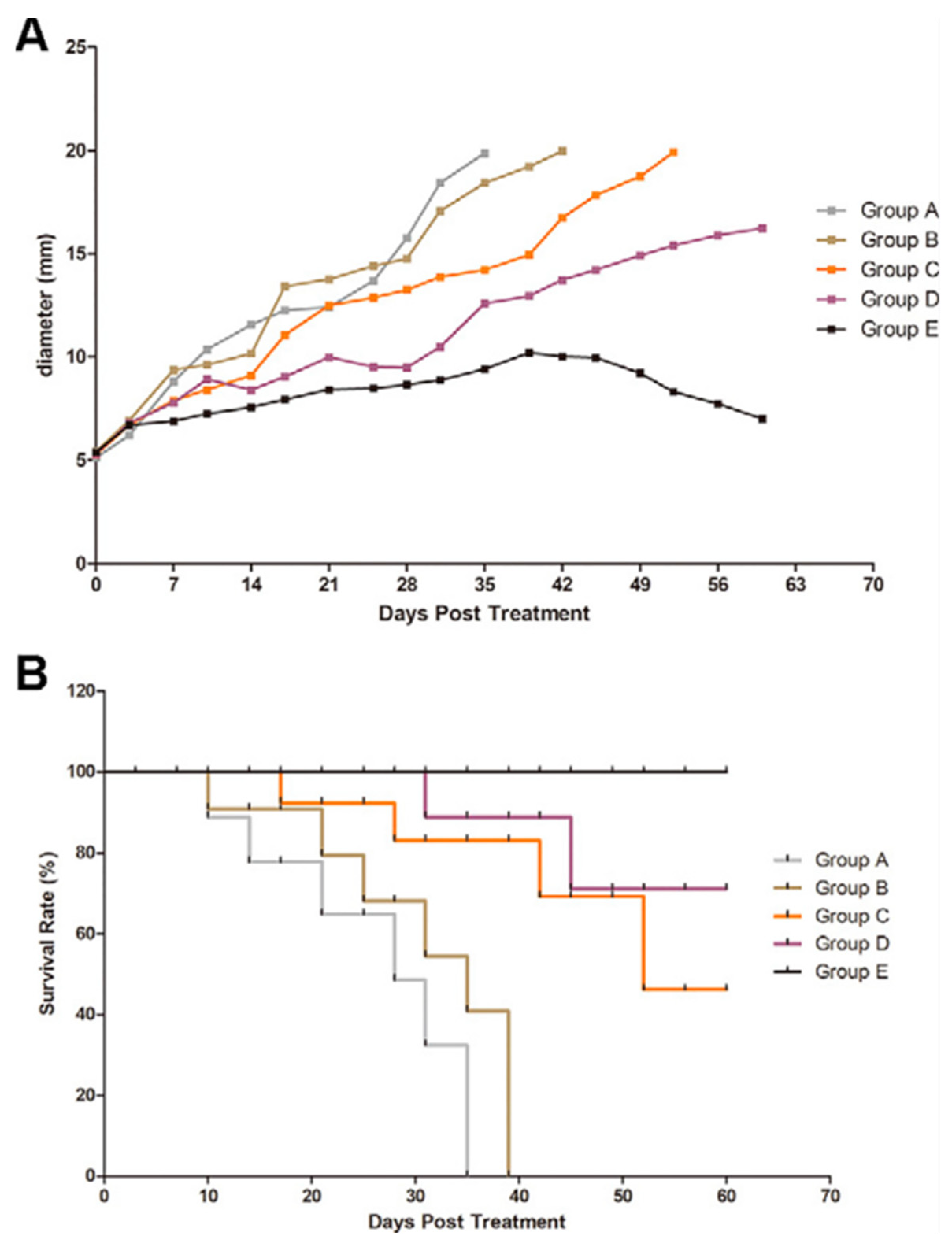
- Ryu, J.-Y.; Won, E.-J.; Lee, H.A.R.; Kim, J.H.; Hui, E.; Kim, H.P.; Yoon, T.-J. Ultrasound-activated particles as CRISPR/Cas9 delivery system for androgenic alopecia therapy. Biomaterials 2020, 232, 119736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Shang, H.; Liang, X.; Sun, Y.; Jing, H.; Han, X.; Cheng, W. Preparation of novel targeting nanobubbles conjugated with small interfering RNA for concurrent molecular imaging and gene therapy in vivo. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 14129–14136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Wu, P.; Zhou, D.; Huang, J.; Qin, M.; Yang, X.; Wan, M.; Zong, Y. Ultrasound-Mediated Gene Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Pre-microRNA Plasmid-Loaded Nanodroplets. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 46, 90–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Hossack, J.A.; Klibanov, A.L. Targeting of microbubbles: Contrast agents for ultrasound molecular imaging. J. Drug Target. 2018, 26, 420–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Ye, D.; Chien, C.-Y.; Yue, Y.; Chen, H. Comparison of Sonication Patterns and Microbubble Administration Strategies for Focused Ultrasound-Mediated Large-Volume Drug Delivery. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 69, 3449–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Cai, L.; Nie, M.; Shang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Cheerios Effect Inspired Microbubbles as Suspended and Adhered Oral Delivery Systems. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2004184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corthésy, B.; Bioley, G. Lipid-Based Particles: Versatile Delivery Systems for Mucosal Vaccination against Infection. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corthésy, B.; Bioley, G. Gas-filled microbubbles: Novel mucosal antigen-delivery system for induction of anti-pathogen’s immune responses in the gut. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corthésy, B.; Bioley, G. Therapeutic intranasal instillation of allergen-loaded microbubbles suppresses experimental allergic asthma in mice. Biomaterials 2017, 142, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Shin, S.; Shukla, N.; Kim, K.; Park, M.-H. Effects of Nanobubbles in Dermal Delivery of Drugs and Cosmetics. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
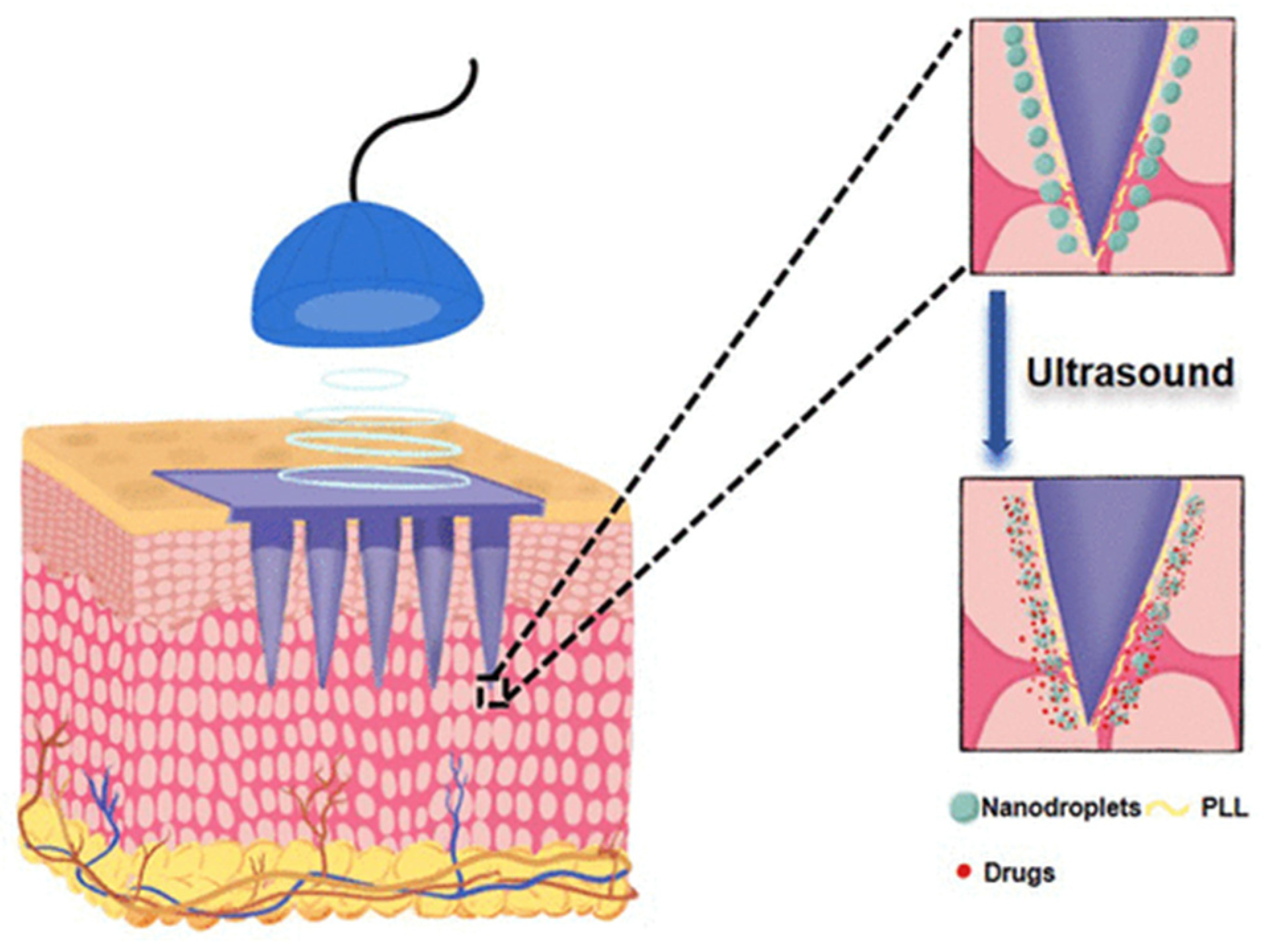
- Shao, S.; Wang, S.; Ren, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Pi, H.; Sun, Y.; Dong, C.; Weng, L.; Gao, Y.; et al. Layer-by-Layer Assembly of Lipid Nanobubbles on Microneedles for Ultrasound-Assisted Transdermal Drug Delivery. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Msc, M.L.; Weiderpass, E.; Soerjomataram, I. The ever-increasing importance of cancer as a leading cause of premature death worldwide. Cancer 2021, 127, 3029–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, M.A. Ultrasound-guided Microbubble in the Treatment of Cancer: A Mini Narrative Review. Cureus 2018, 10, e3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Wang, J.; Luo, J.; Li, H. Ultrasound-mediated destruction of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) targeted and paclitaxel loaded microbubbles for inhibition of human breast cancer cell MCF-7 proliferation. Mol. Cell. Probes 2019, 46, 101415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Mei, H.; Gao, Y.; Xie, X.; Nie, H.; Li, T.; Zhang, H.; Jia, L. Co-delivery of oxygen and erlotinib by aptamer-modified liposomal complexes to reverse hypoxia-induced drug resistance in lung cancer. Biomaterials 2017, 145, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yin, M.; Zhu, S.; Liu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, R.X.; Chang, S. Ultrasound-mediated destruction of oxygen and paclitaxel loaded lipid microbubbles for combination therapy in hypoxic ovarian cancer cells. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 28, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Bing, C.; Xi, Y.; Shah, B.; Exner, A.A.; Chopra, R. Influence of Nanobubble Concentration on Blood–Brain Barrier Opening Using Focused Ultrasound Under Real-Time Acoustic Feedback Control. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 45, 2174–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macor, P.; Durigutto, P.; Argenziano, M.; Smith-Jackson, K.; Capolla, S.; Di Leonardo, V.; Marchbank, K.; Tolva, V.S.; Semeraro, F.; Ammollo, C.T.; et al. Plasminogen activator-coated nanobubbles targeting cellbound β2-glycoprotein I as a novel thrombus-specific thrombolytic strategy. Haematologica 2022, 108, 1861–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanwal, R.; Joshi, K.; Ditmans, M.; Tsai, S.S.; Lee, W.L. Ultrasound and microbubbles for targeted drug delivery to the lung endo-thelium in ards: Cellular mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 803. Available online: https://mdpi-res.com/d_attachment/biomedicines/biomedicines-09-00803/article_deploy/biomedicines-09-00803-v2.pdf?version=1626149980 (accessed on 15 October 2022). [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, A.; Dalvi, S.V.; Gupta, G.; Khanna, N. Effect of PEGylation on performance of protein microbubbles and its comparison with lipid microbubbles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Du, J. On the origin and regulation of ultrasound responsiveness of block copolymer nanoparticles. Sci. China Chem. 2019, 63, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Pulsipher, K.W.; Chattaraj, R.; Hammer, D.A.; Sehgal, C.M.; Lee, D. Engineering the Echogenic Properties of Microfluidic Microbubbles Using Mixtures of Recombinant Protein and Amphiphilic Copolymers. Langmuir 2019, 35, 10079–10086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helfield, B.; Chen, X.; Watkins, S.C.; Villanueva, F.S. Biophysical insight into mechanisms of sonoporation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9983–9988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beekers, I.; Vegter, M.; Lattwein, K.R.; Mastik, F.; Beurskens, R.; van der Steen, A.F.; de Jong, N.; Verweij, M.D.; Kooiman, K. Opening of endothelial cell–cell contacts due to sonoporation. J. Control. Release 2020, 322, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumbaca, D.; Wong, A.; Drake, E.; Ii, A.E.R.; Lin, B.C.; Stephan, J.-P.; Desnoyers, L.; Shen, B.-Q.; Dennis, M.S. Highly specific off-target binding identified and eliminated during the humanization of an antibody against FGF receptor 4. mAbs 2011, 3, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmann, J.K.; Kimura, R.H.; Deshpande, N.; Lutz, A.M.; Cochran, J.R.; Gambhir, S.S. Targeted Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Imaging of Tumor Angiogenesis with Contrast Microbubbles Conjugated to Integrin-Binding Knottin Peptides. J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiro, O.; Aguilar, R.J.; Tejera, E.; Megías, D.; de Torres-Alba, F.; Evangelista, A.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. Specific Targeting of Human Inflamed Endothelium and In Situ Vascular Tissue Transfection by the Use of Ultrasound Contrast Agents. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2009, 2, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goertz, D.E. An overview of the influence of therapeutic ultrasound exposures on the vasculature: High intensity ultrasound and microbubble-mediated bioeffects. Int. J. Hyperth. 2015, 31, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, C.J.; ter Haar, G.R.; Rivens, I.H.; Giussani, D.A.; Lees, C.C. Pathophysiological mechanisms of high-intensity focused ultrasound-mediated vascular occlusion and relevance to non-invasive fetal surgery. J. R. Soc. Interface 2014, 11, 20140029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Tao, L.; Cao, X.; Chen, L. The solute carrier transporters and the brain: Physiological and pharmacological implications. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 15, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.-H.; Harvey, B.K.; Borden, M.A. State-of-the-art of microbubble-assisted blood-brain barrier disruption. Theranostics 2018, 8, 4393–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, Z.I.; Kim, S.; Jikaria, N.; Qureshi, F.; Milo, B.; Lewis, B.K.; Bresler, M.; Burks, S.R.; Frank, J.A. Disrupting the blood–brain barrier by focused ultrasound induces sterile inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 114, E75–E84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, D.; Oakden, W.; Hynynen, K. Investigating the effects of dexamethasone on blood-brain barrier permeability and inflammatory response following focused ultrasound and microbubble exposure. Theranostics 2020, 10, 1604–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioley, G.; Bussat, P.; Lassus, A.; Schneider, M.; Terrettaz, J.; Corthésy, B. The phagocytosis of gas-filled microbubbles by human and murine antigen-presenting cells. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, M.; Kawakami, S.; Kono, Y.; Un, K.; Higuchi, Y.; Maruyama, K.; Hashida, M. Enhancement of the anti-tumor effect of DNA vaccination using an ultra-sound-responsive mannose-modified gene carrier in combination with doxorubicin-encapsulated pegylated liposomes. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 475, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Un, K.; Kawakami, S.; Suzuki, R.; Maruyama, K.; Yamashita, F.; Hashida, M. Suppression of Melanoma Growth and Metastasis by DNA Vaccination Using an Ultrasound-Responsive and Mannose-Modified Gene Carrier. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strati, P. Car t-cell therapy: Which product for which patient? Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2022, 139, 3673–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study | Identifier | Condition | Intervention | Enrollment | Primary Outcome and Results | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contrast-enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS) For Intraoperative Spinal Cord Injury | NCT05530798 | Spine Disease and degeneration; Spinal Stenosis and Injury; Spinal Cord Diseases, Injuries, and Compression | Device: Definity US Contrast | 20 | Use of contrast enhanced US to identify discrete areas of perfusion changes in the spinal cord of subjects undergoing spinal cord decompression | Not Yet Recruiting |
| Feasibility of the Vapor Nanobubble Technology for Malaria Diagnostics (MalariaSense) | NCT02672228 | Malaria | Device: MalariaSense device | 208 | Hemozoin-generated vapor NB (H-VNB) amplitude thresholds among malaria infected and uninfected individuals | Completed (2015) |
| The Effect of RNS60 on ALS Biomarkers (RNS60) | NCT03456882 | Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) | Drug: RNS60 | 142 | Pharmacodynamic biomarkers to measure the effect of RNS60 treatment on selected pharmacodynamic biomarkers in ALS patients concurrently treated with riluzole. | Completed (2020) |
| Micro/Nanobubbles (MNBs) for Treatment of Acute and Chronic Wounds | NCT05169814 | Open Wound Wound Heal | Drug: Irrigation: MNB and Other: 0.9% Normal Saline Drug: Negative Pressure Wound Therapy with Instillation: MNB and Other: 0.9% Normal Saline | 40 |
| Recruiting |
| Study | Identifier | Condition | Intervention | Enrollment | Primary Outcome and Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sonazoid™ vs. SonoVue® for Focal Liver Lesions during Pre- and Post-CEUS | NCT03335566 | Liver Lesions | Drug: I.V bolus Sonazoid™ Drug: I.V bolus SonoVue® | 424 (214 completed Sonazoid and 203 completed SonoVue) | % of Participants with accuracy improvement post- vs. pre-contrast US examination of liver lesions as malignant or benign against reference diagnosis (RD). Assessments were performed by 3 blinded readers.
|
| CEUS for Complex Kidney Lesion Diagnosis in Patients With Chronic Kidney Diseases (CKD) | NCT03196076 | CKD and Cystic Kidney Disease | Drug: Perflutren | 25 (5 healthy subjects and 20 with kidney lesions) | # of Participants With Change in Radiologist’s Lesion Evaluation to determine whether a lesion has progressed, regressed, or is stable.
|
| Sonothrombolysis in Patients With ST—segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI) | NCT03092089 | STEMI | Drug: Definity Device: Myocardial Contrast Echocardiography Procedure: Reperfusion therapy with PPCI | 15 |
|
| Detection of High Grade Prostate Cancer With Subharmonic US Imaging | NCT02967458 | Prostatic Neoplasm | Drug: Perflutren Lipid Microsphere Intravenous Suspension | 55 |
|
| Real-Time Myocardial Perfusion Echocardiography (RMPE) for Coronary Allograft Vasculopathy | NCT02880137 | Cardiac Allograft Vasculopathy | Drug: Perflutren Lipid Microsphere Definity Procedure: RTMPE IV biologically—inert MBs | 36 | # of subjects with a perfusion defect identified using the following:
|
| CEUS of the Kidney (CEUS-CKD) | NCT02684435 | CKD; Cystic Kidney Disease | Drug: Perflutren lipid microsphere | 63 |
|
| Noninvasive Subharmonic Aided Pressure Estimation of Portal Hypertension (HTN) | NCT02489045 | Liver Diseases Portal Hypertension | Drug: Subharmonic aided pressure estimation (SHAPE) measurement (Sonazoid US contrast agent) | 178 (125 completed) (53 not completed) |
|
| CEUS Sentinel Lymph Node Imaging With Guided Biopsy in Breast Cancer Patients | NCT02321527 | Breast Cancer | Drug: Perflutren Protein-Type A Microspheres Injectable Suspension Device: CEUS Procedure: Biopsy + Radioactive Seed Placement | 21 (20 completed) (1 not completed) | # of Breast Cancer Participants With Sentinel Lymph Nodes (SLN) Identification Using the CEUS Technique: 20/21 participants (95.2%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kancheva, M.; Aronson, L.; Pattilachan, T.; Sautto, F.; Daines, B.; Thommes, D.; Shar, A.; Razavi, M. Bubble-Based Drug Delivery Systems: Next-Generation Diagnosis to Therapy. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14070373
Kancheva M, Aronson L, Pattilachan T, Sautto F, Daines B, Thommes D, Shar A, Razavi M. Bubble-Based Drug Delivery Systems: Next-Generation Diagnosis to Therapy. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2023; 14(7):373. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14070373
Chicago/Turabian StyleKancheva, Mihaela, Lauren Aronson, Tara Pattilachan, Francesco Sautto, Benjamin Daines, Donald Thommes, Angela Shar, and Mehdi Razavi. 2023. "Bubble-Based Drug Delivery Systems: Next-Generation Diagnosis to Therapy" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 14, no. 7: 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14070373
APA StyleKancheva, M., Aronson, L., Pattilachan, T., Sautto, F., Daines, B., Thommes, D., Shar, A., & Razavi, M. (2023). Bubble-Based Drug Delivery Systems: Next-Generation Diagnosis to Therapy. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 14(7), 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14070373










