Bioprinted 3D Bionic Scaffolds with Pancreatic Islets as a New Therapy for Type 1 Diabetes—Analysis of the Results of Preclinical Studies on a Mouse Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
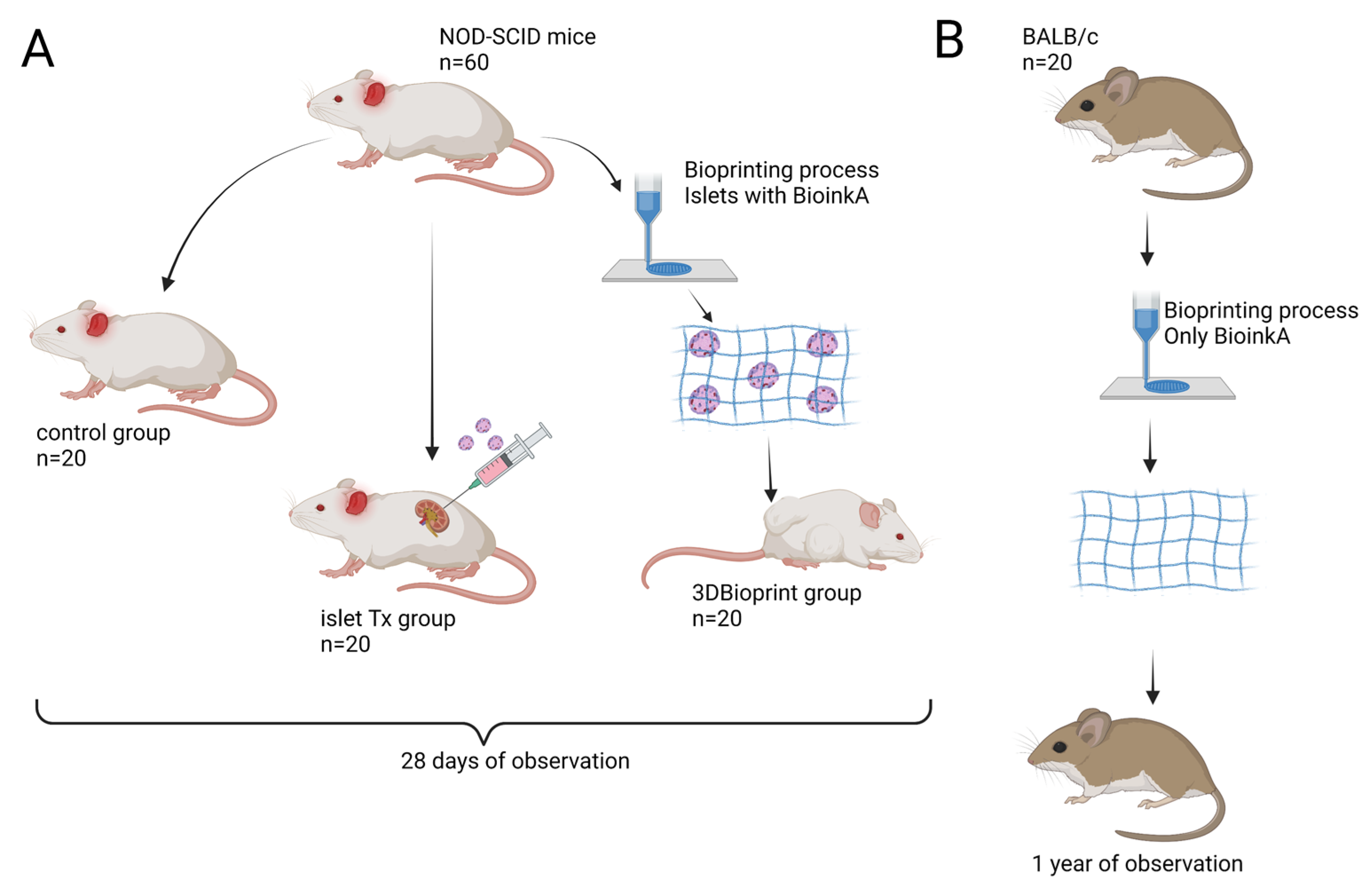
2.1. Research Model and Transplantation
2.2. Bioink Preparation
2.3. Source of Porcine Pancreatic Islets
2.4. Three-Dimensional Bioprinting of Bionic Petals
2.5. Blood Analytical Research
2.5.1. Glucose Measurement
2.5.2. Peptide-C Measurement
2.6. Microscopic Analysis
2.6.1. Immunohistochemistry and Imaging of Bionic Scaffolds and Kidney
2.6.2. DAPI Staining of Nuclei
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Body Weight Measurements
3.2. Mean Fasting Glucose Analysis
3.3. Mean Fasting Mice C-Peptide Results
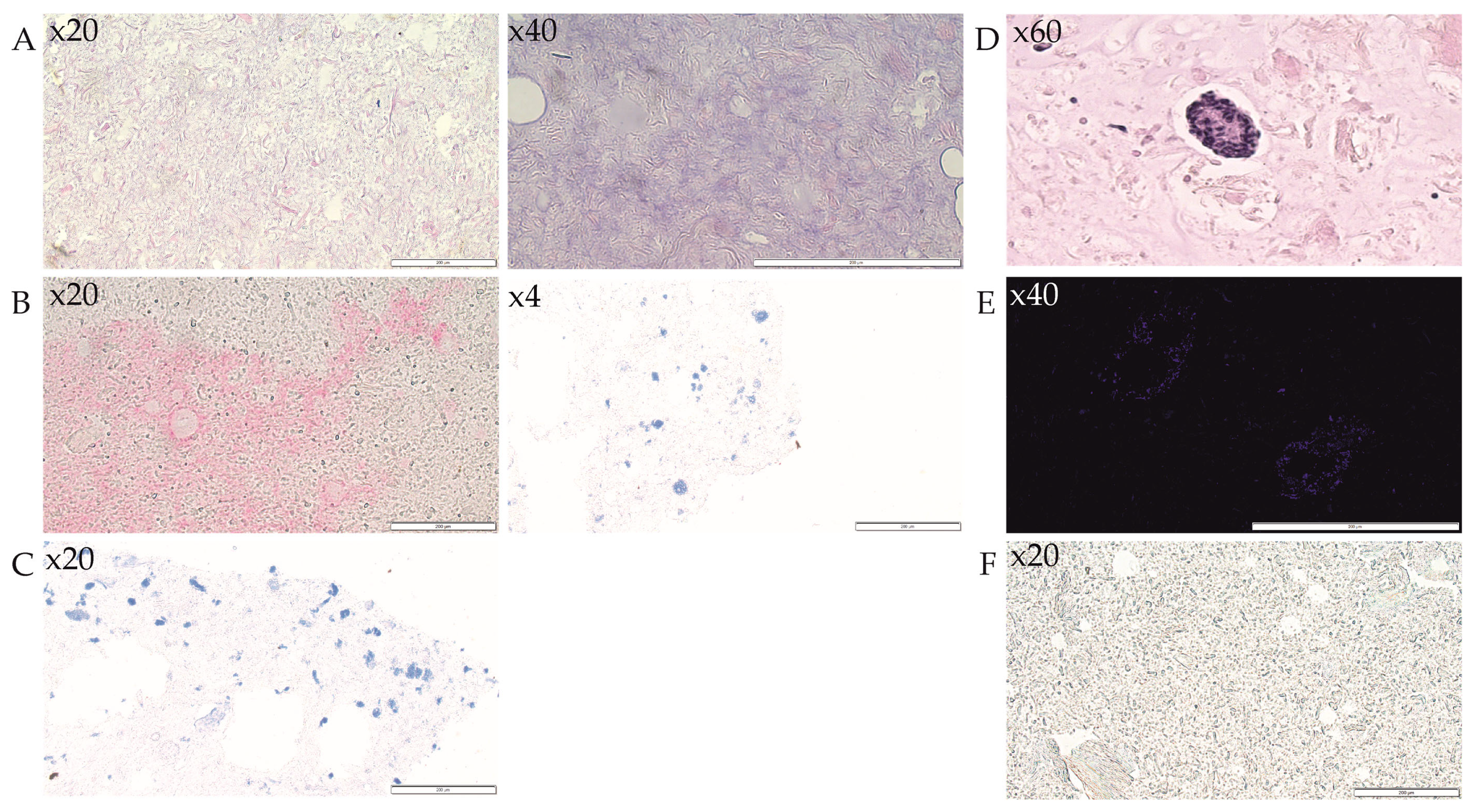
3.4. Analysis of 3D-Bioprinted Scaffolds
3.5. Analysis of Islets Transplanted under the Renal Capsule
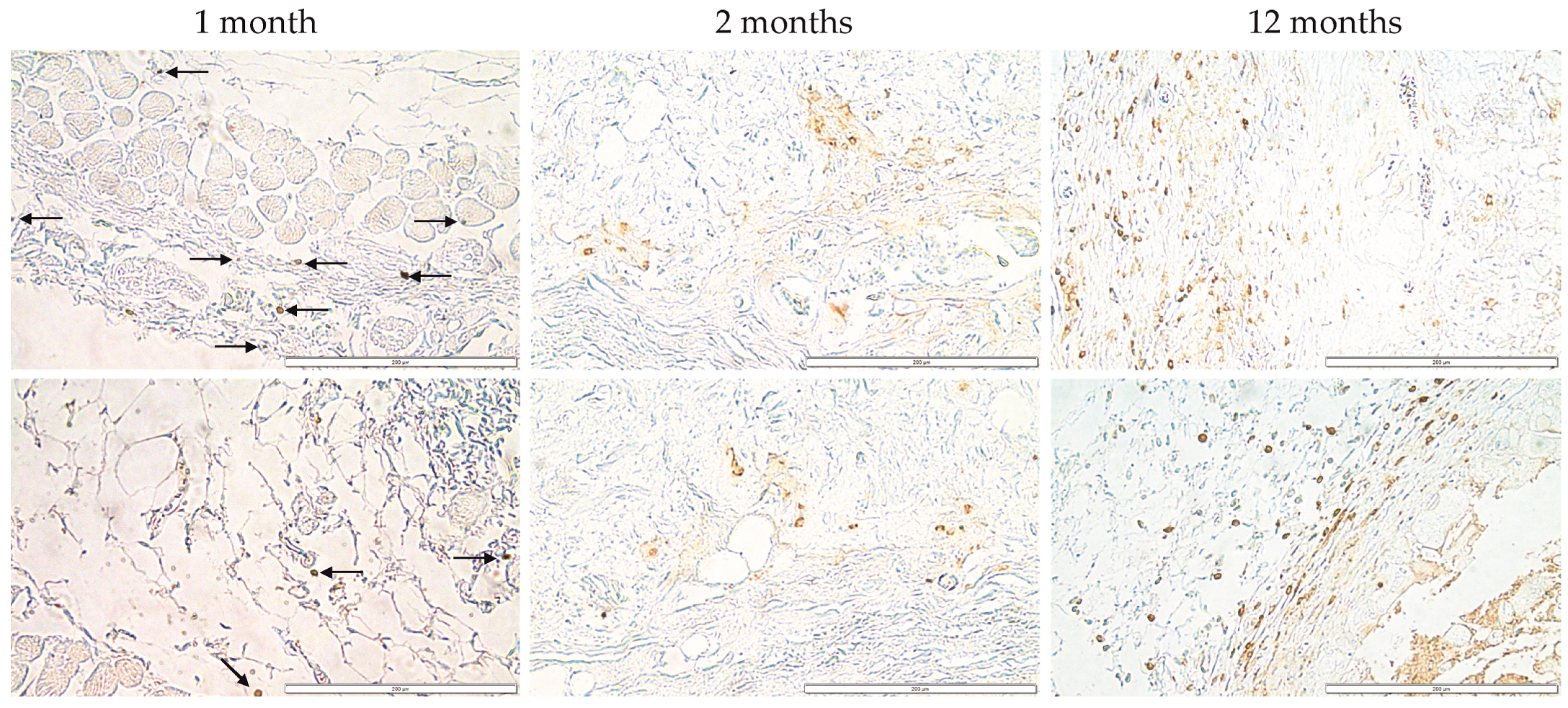
3.6. Immunohistochemical Analysis of Monocytes and Macrophages (MOMA) within the Bionic Scaffolds and Postoperative Tissues from Mice
3.7. Immunohistochemical Analysis of Lymphocytes (CD45) within the Bionic Scaffolds and Postoperative Tissues from Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, J.; Kang, K.; Drogemuller, C.J.; Wallace, G.G.; Coates, P.T. Bioprinting an Artificial Pancreas for Type 1 Diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2019, 19, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalbach, L.; Roma, L.P.; Schmitt, B.M.; Becker, V.; Körbel, C.; Wrublewsky, S.; Pack, M.; Später, T.; Metzger, W.; Menger, M.M.; et al. Improvement of islet transplantation by the fusion of islet cells with functional blood vessels. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e12616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, R.P.H.; Meyer, J.; Muller, Y.D.; Szot, G.L.; Bédat, B.; Andres, A.; Massé, N.; Lablanche, S.; Puppa, G.; Bosco, D.; et al. Pancreas collagen digestion during islet of Langerhans isolation—A prospective study. Transpl. Int. 2020, 33, 1516–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroni, L.; Burdick, J.A.; Highley, C.; Lee, S.J.; Morimoto, Y.; Takeuchi, S.; Yoo, J.J. Biofabrication strategies for 3D in vitro models and regenerative medicine. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Pr, A.K.; Yoo, J.J.; Zahran, F.; Atala, A.; Lee, S.J. A Photo-Crosslinkable Kidney ECM-Derived Bioink Accelerates Renal Tissue Formation. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1800992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H. Oxidative Stress in Pancreatic Beta Cell Regeneration. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 1930261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.; Kim, T.G.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, S.-W.; Kwon, S.-M.; Cho, D.-W. Tailoring mechanical properties of decellularized extracellular matrix bioink by vitamin B2-induced photo-crosslinking. Acta Biomater. 2016, 33, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J. 3D Bioprinting and In Vitro Cardiovascular Tissue Modeling. Bioengineering 2017, 4, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidov, T.; Efraim, Y.; Hayam, R.; Oieni, J.; Baruch, L.; Machluf, M. Extracellular Matrix Hydrogels Originated from Different Organs Mediate Tissue-Specific Properties and Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Piazza, E.; Pandolfi, E.; Cacciotti, I.; Del Fattore, A.; Tozzi, A.E.; Secinaro, A.; Borro, L. Bioprinting Technology in Skin, Heart, Pancreas and Cartilage Tissues: Progress and Challenges in Clinical Practice. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2021, 18, 10806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klak, M.; Łojszczyk, I.; Berman, A.; Tymicki, G.; Adamiok-Ostrowska, A.; Sierakowski, M.; Olkowski, R.; Szczepankiewicz, A.A.; Kamiński, A.; Dobrzyń, A.; et al. Impact of Porcine Pancreas Decellularization Conditions on the Quality of Obtained dECM. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klak, M.; Kosowska, K.; Bryniarski, T.; Łojszczyk, I.; Dobrzański, T.; Tymicki, G.; Filip, A.; Szczepankiewicz, A.A.; Olkowski, R.; Kosowska, A.; et al. Bioink based on the dECM for 3D bioprinting of bionic tissue, the first results obtained on murine model. Bioprinting 2022, 28, e00233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.J.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Improving Bioscience Research Reporting: The ARRIVE Guidelines for Reporting Animal Research. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Säljö, K.; Orrhult, L.S.; Apelgren, P.; Markstedt, K.; Kölby, L.; Gatenholm, P. Successful engraftment, vascularization, and In vivo survival of 3D-bioprinted human lipoaspirate-derived adipose tissue. Bioprinting 2020, 17, e00065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Tao, J.; Huang, Y.; Wu, W.; Li, Y.; Zhou, K.; Wei, X.; et al. Noninvasive in vivo 3D bioprinting. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba7406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amoroso, M.; Apelgren, P.; Säljö, K.; Montelius, M.; Orrhult, L.S.; Engström, M.; Gatenholm, P.; Kölby, L. Functional and morphological studies of in vivo vascularization of 3D-bioprinted human fat grafts. Bioprinting 2021, 23, e00162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klak, M.; Kowalska, P.; Dobrzański, T.; Tymicki, G.; Cywoniuk, P.; Gomółka, M.; Kosowska, K.; Bryniarski, T.; Berman, A.; Dobrzyń, A.; et al. Bionic Organs: Shear Forces Reduce Pancreatic Islet and Mammalian Cell Viability during the Process of 3D Bioprinting. Micromachines 2021, 12, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klak, M.; Bryniarski, T.; Kowalska, P.; Gomolka, M.; Tymicki, G.; Kosowska, K.; Cywoniuk, P.; Dobrzanski, T.; Turowski, P.; Wszola, M. Novel Strategies in Artificial Organ Development: What is the Future of Medicine? Micromachines 2020, 11, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wszoła, M.; Klak, M.; Kosowska, K.; Berman, A.; Idaszek, J.; Majdańska, E.; Dobrzański, T.; Kowalska, P.; Gomółka, M. Towards 3D-Bioprinting of Bionic Pancreas: Influence of the Bioink Composition during 3D Bioprinting of Pancreatic Scaffolds on the Functionality and Viability of Pancreatic Islets. Transpl. Int. 2019, 32, 80. [Google Scholar]
- Klak, M.; Gomółka, M.; Dobrzański, T.; Tymicki, G.; Cywoniuk, P.; Kowalska, P.; Kosowska, K.; Bryniarski, T.; Berman, A.; Dobrzyń, A.; et al. Irradiation with 365 nm and 405 nm wavelength shows differences in DNA damage of swine pancreatic islets. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.J. The use of animal models in diabetes research. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 166, 877–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wszola, M.; Klak, M.; Kosowska, A.; Tymicki, G.; Berman, A.; Adamiok-Ostrowska, A.; Olkowska-Truchanowicz, J.; Uhrynowska-Tyszkiewicz, I.; Kaminski, A. Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes in a Mouse Model (BALB/c) Is Not an Effective Model for Research on Transplantation Procedures in the Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, M.L.; Janecek, J.L.; Kittredge, J.A.; Hering, B.J.; Schuurman, H.-J. The streptozotocin-induced diabetic nude mouse model: Differences between animals from different sources. Comp. Med. 2011, 61, 356–360. [Google Scholar]
- Wennberg, L.; Sundberg, B.; Ekdahl-Nilsson, K.; Korsgren, O. C-Peptide determinations in islet xenotransplantation: A study in the pig-to-mouse model. Cell Transplant. 2001, 10, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs-Tulleneers-Thevissen, D.; Chintinne, M.; Ling, Z.; Gillard, P.; Schoonjans, L.; Delvaux, G.; Strand, B.L.; Gorus, F.; Keymeulen, B.; Pipeleers, D.; et al. Sustained function of alginate-encapsulated human islet cell implants in the peritoneal cavity of mice leading to a pilot study in a type 1 diabetic patient. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 1605–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, S.; Flatt, A.J.; Bennett, D.; Crookston, R.; Pimkova, M.; Birtles, L.; Pernet, A.; Wood, R.C.; Burling, K.; Barker, P.; et al. The impact of islet mass, number of transplants, and time between transplants on graft function in a national islet transplant program. Am. J. Transplant. 2021, 22, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuch, B.E.; Keogh, G.W.; Williams, L.J.; Wu, W.; Foster, J.L.; Vaithilingam, V.; Philips, R. Safety and Viability of Microencapsulated Human Islets Transplanted Into Diabetic Humans. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1887–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, M.; Iizuka, N.; Fujita, Y.; Sawamoto, O.; Matsumoto, S. Effects of encapsulated porcine islets on glucose and C-peptide concentrations in diabetic nude mice 6 months after intraperitoneal transplantation. Xenotransplantation 2017, 24, e12313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; Abalovich, A.; Wechsler, C.; Wynyard, S.; Elliott, R.B. Clinical Benefit of Islet Xenotransplantation for the Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes. Ebiomedicine 2016, 12, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; Tan, P.; Baker, J.; Durbin, K.; Tomiya, M.; Azuma, K.; Doi, M.; Elliott, R. Clinical Porcine Islet Xenotransplantation Under Comprehensive Regulation. Transplant. Proc. 2014, 46, 1992–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazda, L.S.; Vinerean, H.V.; Laramore, M.A.; Hall, R.D.; Carraway, J.W.; Smith, B.H. No Evidence of Viral Transmission following Long-Term Implantation of Agarose Encapsulated Porcine Islets in Diabetic Dogs. J. Diabetes Res. 2014, 2014, 727483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosimi, S.; Marchetti, P.; Giannarelli, R.; Masiello, P.; Bombara, M.; Carmellini, M.; Mosca, F.; Arvia, C.; Navalesi, R. Insulin release in response to glucose from isolated mouse, rat, porcine, bovine, and human pancreatic islets. Transplant. Proc. 1994, 26, 3421–3422. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, S.; Shimoda, M. Current situation of clinical islet transplantation from allogeneic toward xenogeneic. J. Diabetes 2020, 12, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Tucker-Burden, C.; Cauffiel, S.M.D.; Barry, A.K.; Iwakoshi, N.N.; Weber, C.J.; Safley, S.A. Long-Term Metabolic Control of Autoimmune Diabetes in Spontaneously Diabetic Nonobese Diabetic Mice by Nonvascularized Microencapsulated Adult Porcine Islets. Transplantation 2009, 88, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, B.; Lee, E.-J.; Ahn, S.M.; Kim, G.; Lee, S.H.; Ji, D.-Y.; Kang, J.-T. Production of genetically modified pigs expressing human insulin and C-peptide as a source of islets for xenotransplantation. Transgenic Res. 2019, 28, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gradel, A.K.J.; Kildegaard, J.; Porsgaard, T.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Refsgaard, H.H.F. Food intake rather than blood glucose levels affects the pharmacokinetic profile of insulin aspart in pigs. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2021, 128, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahrén, B.; Thomaseth, K.; Pacini, G. Reduced insulin clearance contributes to the increased insulin levels after administration of glucagon-like peptide 1 in mice. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 2140–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galili, U. Interaction of the natural anti-Gal antibody with α-galactosyl epitopes: A major obstacle for xenotransplantation in humans. Immunol. Today 1993, 14, 480–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenbaum, C.J.; Palmer, J.P. Insulin Antibodies and Insulin Autoantibodies. Diabet. Med. 1991, 8, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iizuka, N.; Nishimura, M.; Fujita, Y.; Sawamoto, O.; Matsumoto, S. The pharmacokinetics of porcine C-peptide after intraperitoneal injection. Xenotransplantation 2019, 26, e12505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penchala, S.C.; Miller, M.R.; Pal, A.; Dong, J.; Madadi, N.R.; Xie, J.; Joo, H.; Tsai, J.; Batoon, P.; Samoshin, V.; et al. A biomimetic approach for enhancing the in vivo half-life of peptides. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, D.J.; Kim, A.; Miller, K.; Hara, M. Pancreatic islet plasticity: Interspecies comparison of islet architecture and composition. Islets 2010, 2, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowther, N.J.; Gotfredsen, C.F.; Moody, A.J.; Green, I.C. Porcine Islet Isolation, Cellular Composition and Secretory Response. Horm. Metab. Res. 1989, 21, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, D.; Hering, B.J.; El-Ouaghlidi, A.; Jahr, H.; Brandhorst, H.; Brandhorst, D.; Vietzke, R.; Federlin, K.; Bretzel, R.G. Isokinetic gradient centrifugation prolongs survival of pig islets xenografted into mice. J. Mol. Med. 1999, 77, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matveyenko, A.V.; Veldhuis, J.D.; Butler, P.C.; Farmer, T.D.; Jenkins, E.C.; O’Brien, T.P.; McCoy, G.A.; Havlik, A.E.; Nass, E.R.; Nicholson, W.E.; et al. Measurement of pulsatile insulin secretion in the rat: Direct sampling from the hepatic portal vein. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2008, 295, E569–E574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjaervold, N.K.; Knai, K.; Elvemo, N. Some oscillatory phenomena of blood glucose regulation: An exploratory pilot study in pigs. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duin, S.; Schütz, K.; Ahlfeld, T.; Lehmann, S.; Lode, A.; Ludwig, B.; Gelinsky, M. 3D Bioprinting of Functional Islets of Langerhans in an Alginate/Methylcellulose Hydrogel Blend. Adv. Health Mater. 2019, 8, e1801631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchioli, G.; van Gurp, L.; van Krieken, P.P.; Stamatialis, D.; Engelse, M.; van Blitterswijk, C.A.; Karperien, M.B.J.; de Koning, E.; Alblas, J.; Moroni, L.; et al. Fabrication of three-dimensional bioplotted hydrogel scaffolds for islets of Langerhans transplantation. Biofabrication 2015, 7, 025009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idaszek, J.; Volpi, M.; Paradiso, A.; Quoc, M.N.; Górecka, Ż.; Klak, M.; Tymicki, G.; Berman, A.; Wierzbicki, M.; Jaworski, S.; et al. Alginate-based tissue-specific bioinks for multi-material 3D-bioprinting of pancreatic islets and blood vessels: A step towards vascularized pancreas grafts. Bioprinting 2021, 24, e00163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Control | Day 0 | Day 7 | Day 14 | Day 28 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 0 | - | 0.7527 | 0.8746 | 0.3526 |
| Day 7 | 0.7527 | - | 0.6374 | 0.5313 |
| Day 14 | 0.8746 | 0.6374 | - | 0.2813 |
| Day 28 | 0.3526 | 0.5313 | 0.2813 | - |
| IsletTX | Day 0 | Day 7 | Day 14 | Day 28 |
| Day 0 | - | 0.0194 | 0.0883 | 0.3316 |
| Day 7 | 0.0194 | - | 0.4156 | 0.1175 |
| Day 14 | 0.0883 | 0.4156 | - | 0.4156 |
| Day 28 | 0.3316 | 0.1175 | 0.4156 | - |
| 3D bioprint | Day 0 | Day 7 | Day 14 | Day 28 |
| Day 0 | - | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Day 7 | <0.0001 | - | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Day 14 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | - | 0.5750 |
| Day 28 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.5750 | - |
| Control | Day 0 | Day 7 | Day 14 | Day 28 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 0 | - | 0.1586 | 0.0576 | 0.0653 |
| Day 7 | 0.1586 | - | 0.5619 | 0.6092 |
| Day 14 | 0.0576 | 0.5619 | - | 0.9441 |
| Day 28 | 0.0653 | 0.6092 | 0.9441 | - |
| IsletTX | Day 0 | Day 7 | Day 14 | Day 28 |
| Day 0 | - | 0.0001 | 0.2605 | 0.1774 |
| Day 7 | 0.0001 | - | 0.0010 | 0.0016 |
| Day 14 | 0.2605 | 0.0010 | - | 0.8053 |
| Day 28 | 0.1774 | 0.0016 | 0.8053 | - |
| 3D bioprint | Day 0 | Day 7 | Day 14 | Day 28 |
| Day 0 | - | <0.0001 | 0.0005 | 0.0002 |
| Day 7 | <0.0001 | - | 0.3223 | 0.7562 |
| Day 14 | 0.0005 | 0.3223 | - | 0.4885 |
| Day 28 | 0.0002 | 0.7562 | 0.4885 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klak, M.; Wszoła, M.; Berman, A.; Filip, A.; Kosowska, A.; Olkowska-Truchanowicz, J.; Rachalewski, M.; Tymicki, G.; Bryniarski, T.; Kołodziejska, M.; et al. Bioprinted 3D Bionic Scaffolds with Pancreatic Islets as a New Therapy for Type 1 Diabetes—Analysis of the Results of Preclinical Studies on a Mouse Model. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14070371
Klak M, Wszoła M, Berman A, Filip A, Kosowska A, Olkowska-Truchanowicz J, Rachalewski M, Tymicki G, Bryniarski T, Kołodziejska M, et al. Bioprinted 3D Bionic Scaffolds with Pancreatic Islets as a New Therapy for Type 1 Diabetes—Analysis of the Results of Preclinical Studies on a Mouse Model. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2023; 14(7):371. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14070371
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlak, Marta, Michał Wszoła, Andrzej Berman, Anna Filip, Anna Kosowska, Joanna Olkowska-Truchanowicz, Michał Rachalewski, Grzegorz Tymicki, Tomasz Bryniarski, Marta Kołodziejska, and et al. 2023. "Bioprinted 3D Bionic Scaffolds with Pancreatic Islets as a New Therapy for Type 1 Diabetes—Analysis of the Results of Preclinical Studies on a Mouse Model" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 14, no. 7: 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14070371
APA StyleKlak, M., Wszoła, M., Berman, A., Filip, A., Kosowska, A., Olkowska-Truchanowicz, J., Rachalewski, M., Tymicki, G., Bryniarski, T., Kołodziejska, M., Dobrzański, T., Ujazdowska, D., Wejman, J., Uhrynowska-Tyszkiewicz, I., & Kamiński, A. (2023). Bioprinted 3D Bionic Scaffolds with Pancreatic Islets as a New Therapy for Type 1 Diabetes—Analysis of the Results of Preclinical Studies on a Mouse Model. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 14(7), 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14070371








