The Peroxidase-like Nanocomposites as Hydrogen Peroxide-Sensitive Elements in Cholesterol Oxidase-Based Biosensors for Cholesterol Assay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Synthesis of HRP-like NZs
2.3. Evaluation of HRP-like Activity of the Synthesized NZs
2.4. Construction of Amperometric Biosensors
2.5. Study of H2O2-Sensing Ability of the Electrodes, Modified with Peroxidase-like NPs
2.6. Modification of GCE with nPt
2.7. Construction and Characterization of Bionanoelectrodes
2.8. Analysis of CHOL in Serum
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the Nanocomposites Most Sensitive to Hydrogen Peroxide
3.2. Platinization of GCE for Construction of H2O2- and Cholesterol-Sensitive Sensors
3.3. Construction and Analytical Properties of ChOx/NZs-Based Bionanosensors
3.3.1. Construction of Unmodified ChOx/NZs-Based Bionanosensors
3.3.2. Construction and Bioanalytical Properties of Bionanosensors Based on ChOx and nCuFe Using Platinized GCE
3.4. Analytical Properties of the Constructed Bionanosensor
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, J.; Yang, H.; Song, B.L. Mechanisms and regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, W.Y.; Hartmann, H.; Ling, S.C. Central nervous system cholesterol metabolism in health and disease. IUBMB Life 2022, 74, 826–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Report of the Formal Meeting of Member States to Conclude the Work on the Comprehensive Global Monitoring Framework, Including Indicators, and a Set of Voluntary Global Targets for the Prevention and Control of Communicable Diseases. 2012. Available online: http://apps.who.int/gb/NCDs/pdf/A_NCD_2-en (accessed on 4 June 2023).
- Jung, E.; Kong, S.Y.; Ro, Y.S.; Ryu, H.H.; Shin, S.D. Serum Cholesterol Levels and Risk of Cardiovascular Death: A Systematic Review and a Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Wu, S.; Xie, L. Colorimetric Detection of Cholesterol Based on the Peroxidase-Like Activity of Metal-Organic Framework MIL-101 (Cr). ChemistrySelect 2021, 6, 7143–7149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, L.; Dash, K.; Sashidhar, R.B. Selective and sensitive detection of cholesterol using intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of biogenic palladium nanoparticles. Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 2021, 3, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.N.; Sun, X.T.; Chen, L.; Xu, Z.R. Boron nitride nanosheet/CuS nanocomposites as mimetic peroxidase for sensitive colorimetric detection of cholesterol. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 246, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briones, M.; Busó-Rogero, C.; Catalán-Gómez, S.; García-Mendiola, T.; Pariente, F.; Redondo-Cubero, A.; Lorenzo, M.E. ZnO nanowire-based fluorometric enzymatic assays for lactate and cholesterol. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmida, H.M.; Bertucci, P.; Franzò, L.; Massoud, R.; Cortese, C.; Lala, A.; Federici, G. Simultaneous determination of plasmatic phytosterols and cholesterol precursors using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) with selective ion monitoring (SIM). J. Chromatogr. B 2006, 842, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lütjohann, D.; Björkhem, I.; Friedrichs, S.; Kerksiek, A.; Lövgren-Sandblom, A.; Geilenkeuser, W.J.; Schött, H.F. First international descriptive and interventional survey for cholesterol and non-cholesterol sterol determination by gas-and liquid-chromatography–Urgent need for harmonisation of analytical methods. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 190, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojo, K.; Hakamata, H.; Ito, A.; Kotani, A.; Furukawa, C.; Hosokawa, Y.Y.; Kusu, F. Determination of total cholesterol in serum by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1166, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, K.; Zhang, P.; Wang, W.; Dai, T.; Li, L. Determination of total cholesterol in serum by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Asian J. Chem. 2014, 26, 2646–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Harada, A.; Toh, R.; Kubo, T.; Miwa, K.; Kim, J.; Kiriyama, M.; Iino, T.; Nishikawa, Y.; Uno, S.; et al. Fully automated immunoassay for cholesterol uptake capacity to assess high-density lipoprotein function and cardiovascular disease risk. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narwal, V.; Deswal, R.; Batra, B.; Kalra, V.; Hooda, R.; Sharma, M.; Rana, J.S. Cholesterol biosensors: A review. Steroids 2019, 143, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Malhotra, R.; Malhotra, B.D.; Grover, S.K. Co-immobilization of cholesterol oxidase and horseradish peroxidase in a sol–gel film. Anal. Chim. Acta 2000, 414, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, B.; Narwal, V.; Ahlawat, J.; Sharma, M. An amperometric cholesterol biosensor based on immobilization of cholesterol oxidase onto titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Sens. Int. 2021, 2, 100111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.-W.; Sampson, N.S. Cholesterol oxidase senses subtle changes in lipid bilayer structure. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Li, X.; Kim, J.; Lim, B.O.; Ahammad, A.J.S.; Lee, J.-J. A cholesterol biosensor based on a bi-enzyme immobilized on conducting poly(thionine) film. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 202, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, A.K.; Sinhamahapatra, A.; Prakash, S.; Chaudhari, J.; Shahi, V.K.; Panda, A.B. Porous ZnO microtubes with excellent cholesterol sensing and catalytic properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wan, L.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Q.; Jiao, K. Highly sensitive and selective cholesterol biosensor based on direct electron transfer of hemoglobin. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 383, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Nan, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Zheng, L.; Lu, X. Hydrophobic ionic liquid immoblizing cholesterol oxidase on the electrodeposited Prussian blue on glassy carbon electrode for detection of cholesterol. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 90, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooda, V.; Gahlaut, A. Amperometric cholesterol determination using HRP incorporated carbon paste electrode. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Asia 2020, 17, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, K.; Sarkar, P.; Bhattacharyay, D.; Majumdar, P. One step electrode fabrication for direct electron transfer cholesterol biosensor based on composite of polypyrrole, green reduced graphene oxide and cholesterol oxidase. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 2719–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Rajeev, R.; Benny, L.; Sudhakar, Y.N.; Varghese, A.; Hegde, G. Recent advances in carbon nanotubes-based biocatalysts and their applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 297, 102542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Xie, C.; Wang, J.; Meng, A.; Zhang, F. Direct electrochemistry of cholesterol oxidase immobilized on chitosan–graphene and cholesterol sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 208, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Wu, R.; Chen, H.; Wang, H.; Nan, W. Highly sensitive cholesterol biosensor based on electron mediator thionine and cubic-shaped Cu2O nanomaterials. Microchem. J. 2023, 185, 108201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haritha, V.S.; Kumar, S.S.; Rakhi, R.B. Amperometric cholesterol biosensor based on cholesterol oxidase and Pt-Au/MWNTs modified glassy carbon electrode. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 50, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravind, S.S.J.; Baby, T.T.; Arockiadoss, T.; Rakhi, R.B.; Ramaprabhu, S. A cholesterol biosensor based on gold nanoparticles decorated functionalized graphene nanoplatelets. Thin Solid Film. 2011, 519, 5667–5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Zhang, L.; Chai, Y.; Yuan, R. Electrochemistry of cholesterol biosensor based on a novel Pt–Pd bimetallic nanoparticle decorated graphene catalyst. Talanta 2013, 109, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, U.; Das, A.B. Nanomaterials towards fabrication of cholesterol biosensors: Key roles and design approaches. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, M.; Hou, Y.; Huang, W.; Yao, C.; Wu, Q. An Au nanocomposite based biosensor for determination of cholesterol. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 3480–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevik, E.; Cerit, A.; Gazel, N.; Yildiz, H.B. Construction of an amperometric cholesterol biosensor based on DTP (aryl) aniline conducting polymer bound cholesterol oxidase. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 2445–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M.; Srivastava, S.K.; Nirala, N.R.; Prakash, R. A chitosan-based polyaniline–Au nanocomposite biosensor for determination of cholesterol. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.J.; O’Reilly, E.J.; Moriarty, R.D.; Bertoncello, P.; Keyes, T.E.; Forster, R.J.; Dennany, L. A cholesterol biosensor based on the NIR electrogenerated-chemiluminescence (ECL) of water-soluble CdSeTe/ZnS quantum dots. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 157, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soorya, V.C.; Berchmans, S. Cu-Pt-Bi Nanocomposite modified glassy carbon electrode for dual mode H2O2 and cholesterol sensing. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, B435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.P.; Miyazaki, C.M.; Mascagni, D.B.; Ferreira, M. Layer-by-layer films of gold nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes for improved amperometric detection of cholesterol. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 5483–5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagappan, M.; Immanuel, S.; Sivasubramanian, R.; Kandaswamy, A. Development of cholesterol biosensor using Au nanoparticles decorated f-MWCNT covered with polypyrrole network. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 2001–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nantaphol, S.; Chailapakul, O.; Siangproh, W. Sensitive and selective electrochemical sensor using silver nanoparticles modified glassy carbon electrode for determination of cholesterol in bovine serum. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, R.S.; Raj, C.R. Enzyme-integrated cholesterol biosensing scaffold based on in situ synthesized reduced graphene oxide and dendritic Pd nanostructure. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 62, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh, T.T.N.; Tam, L.T.; Van Thu, V.; Le, A.T.; Hung, V.P.; Tam, P.D. Nano-rods structured cerium oxide platform for cholesterol biosensor. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 3886–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomi, R.; Cazzolaro, A.; Sansone, A.; Scrimin, P.; Prins, L.J. Detection of enzyme activity through catalytic signal amplification with functionalized gold nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 2307–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Patolsky, F.; Katz, E.; Hainfeld, J.F.; Willner, I. “Plugging into Enzymes”: Nanowiring of redox enzymes by a gold nanoparticle. Science 2003, 299, 1877–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashidi, K.; Mahmoudi, M.; Mohammadi, G.; Zangeneh, M.M.; Korani, S.; Goicoechea, H.C.; Gu, H.W.; Jalalvand, A.R. Simultaneous co-immobilization of three enzymes onto a modified glassy carbon electrode to fabricate a high-performance amperometric biosensor for determination of total cholesterol. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguílaz, M.; Villalonga, R.; Agüí, L.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Gold nanoparticles: Poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride)–carbon nanotubes composites as platforms for the preparation of electrochemical enzyme biosensors: Application to the determination of cholesterol. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2011, 661, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruecha, N.; Rangkupan, R.; Rodthongkum, N.; Chailapakul, O. Novel paper-based cholesterol biosensor using graphene/polyvinylpyrrolidone/polyaniline nanocomposite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 52, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, M.M.; Razalli, R.L.; Tahir, P.M.; Chaibakhsh, N.; Hassani, M.; Mir, M. Optimized fabrication of newly cholesterol biosensor based on nanocellulose. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komathi, S.; Gopalan, A.I.; Kim, S.K.; Anand, G.S.; Lee, K.P. Fabrication of horseradish peroxidase immobilized poly(N-[3-(trimethoxy silyl)propyl]aniline) gold nanorods film modified electrode and electrochemical hydrogen peroxide sensing. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 92, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh, T.T.N.; Van Thu, V.; Dang, H.S.; Pham, V.H.; Tam, P.D. Cerium oxide/polypyrrole nanocomposite as the matrix for cholesterol biosensor. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2021, 2021, 6627645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalan, A.I.; Lee, K.P.; Ragupathy, D. Development of a stable cholesterol biosensor based on multi-walled carbon nanotubes–gold nanoparticles composite covered with a layer of chitosan–room-temperature ionic liquid network. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2211–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Gao, X.; Wang, L.; Wu, Q.; Lin, X. A layer-by-layer assembled and carbon nanotubes/gold nanoparticles-based bienzyme biosensor for cholesterol detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 181, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaçar, C.; Erden, P.E.; Dalkiran, B.; Inal, E.K.; Kiliç, E. Amperometric biogenic amine biosensors based on Prussian blue, indium tin oxide nanoparticles and diamine oxidase– or monoamine oxidase–modified electrodes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 1933–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurup, C.P.; Ahmed, M.U. Nanozymes towards Personalized Diagnostics: A Recent Progress in Biosensing. Biosensors 2023, 13, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerez-Masaquiza, M.D.; Fernández, L.; González, G.; Montero-Jiménez, M.; Espinoza-Montero, P.J. Electrochemical sensor based on prussian blue electrochemically deposited at ZrO2 doped carbon nanotubes glassy carbon modified electrode. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karyakin, A.A.; Karyakina, E.E.; Gorton, L. Amperometric biosensor for glutamate using prussian blue-based “artificial peroxidase” as a transducer for hydrogen peroxide. Anal Chem. 2000, 72, 1720–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stasyuk, N.; Demkiv, O.; Gayda, G.; Zakalskiy, A.; Klepach, H.; Bisko, N.; Gonchar, M.; Nisnevitch, M. Highly porous 3D gold enhances sensitivity of amperometric biosensors based on oxidases and CuCe nanoparticles. Biosensors 2022, 12, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demkiv, O.; Gayda, G.; Stasyuk, N.; Brahinetz, O.; Gonchar, M.; Nisnevitch, M. Nanomaterials as redox mediators in laccase-based amperometric biosensors for catechol assay. Biosensors 2022, 12, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibirnyj, W.; Grabek-Lejko, D.; Gonchar, M. The use of enzymes for ethanol, methanol and formaldehyde determination in food products. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2021, 2021, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cheng, H.; Xie, H.; Luo, G.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Sun, W. Platinum nanoparticles decorating a biomass porous carbon nanocomposite-modified electrode for the electrocatalytic sensing of luteolin and application. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 33607–33616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Ni, Y.; Kokot, S. Electrochemical cholesterol sensor based on cholesterol oxidase and MoS2-AuNPs modified glassy carbon electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 233, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadalinezhad, A.; Chen, A. High-performance electrochemical biosensor for the detection of total cholesterol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 4508–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doaga, R.; McCormac, T.; Dempsey, E. Functionalized magnetic nanomaterials for electrochemical biosensing of cholesterol and cholesteryl palmitate. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Lee, J.; Seo, J.; Shin, H. Development of a sensitive electrochemical enzymatic reaction-based cholesterol biosensor using nano-sized carbon interdigitated electrodes decorated with gold nanoparticles. Sensors 2017, 17, 2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eom, K.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Seo, H.W.; Kang, J.Y.; Shim, J.S.; Lee, S.H. Sensitive and non-invasive cholesterol determination in saliva via optimization of enzyme loading and platinum nano-cluster composition. Analyst 2020, 145, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.; Chen, J.; Wan, X.; Tian, J. Direct Electrochemistry of Cholesterol Oxidase Immobilized on PEDOT Functionalized Screen-Printed Electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2023, 170, 027510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.R.; Xu, J.J.; Chen, H.Y. Potassium-doped carbon nanotubes toward the direct electrochemistry of cholesterol oxidase and its application in highly sensitive cholesterol biosensor. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 9378–9385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demkiv, O.; Stasyuk, N.; Serkiz, R.; Gayda, G.; Nisnevitch, M.; Gonchar, M. Peroxidase-Like Metal-Based Nanozymes: Synthesis, Catalytic Properties, and Analytical Application. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cui, L.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, N.; Liang, J.; Li, G. Ultrasensitive cholesterol biosensor based on enzymatic silver deposition on gold nanoparticles modified screen-printed carbon electrode. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 77, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



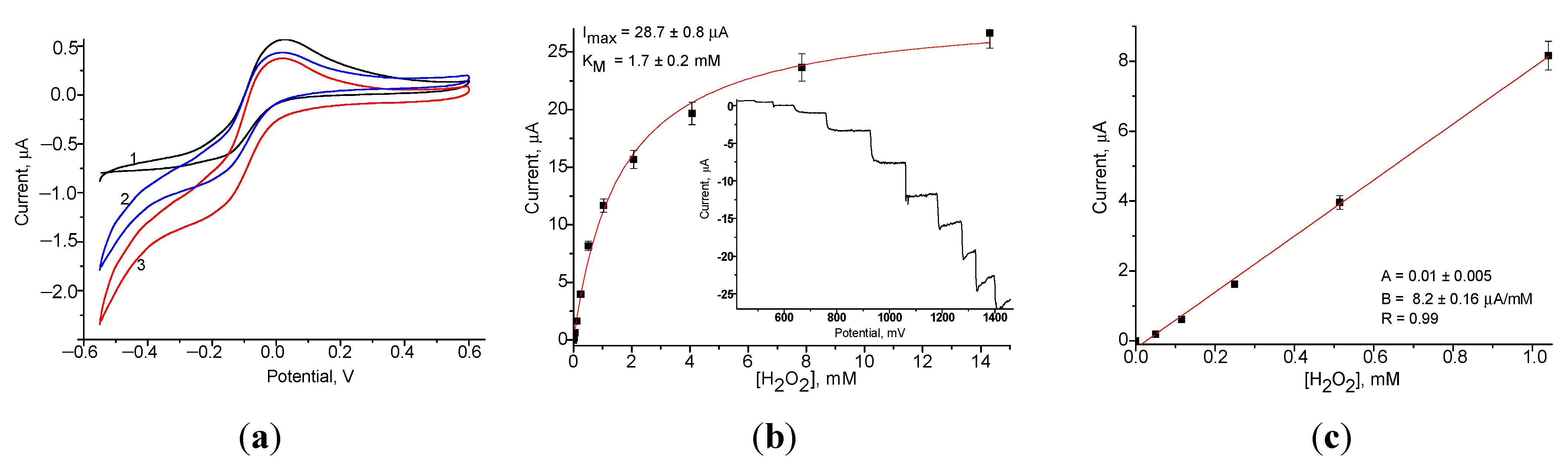

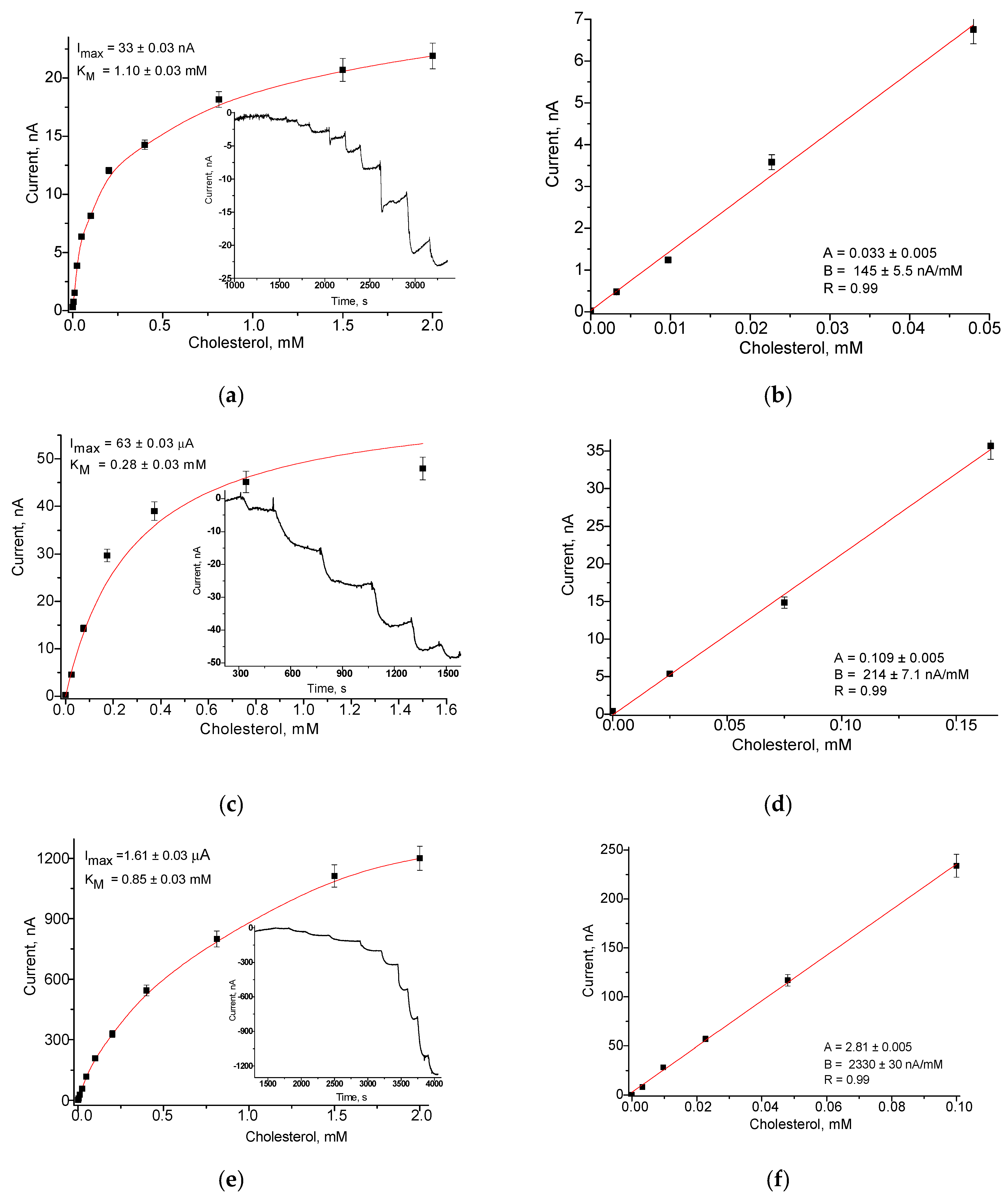
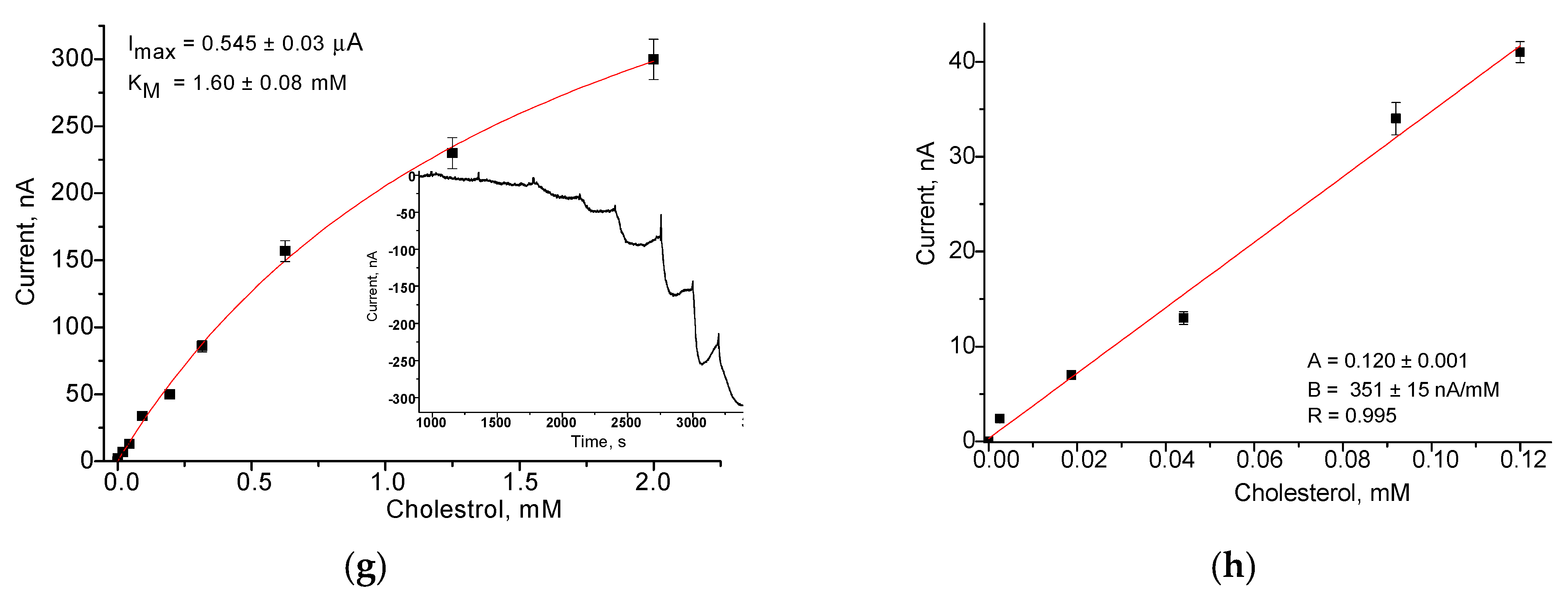


| N | H2O2-Selective Layer | Sensitivity, A·M−1·m−2 | Linear Range, up to mM | Imax, µA | KMapp, mM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | nAuHCF/GCE | 1232 ± 40 | 0.02–3.0 | 41.4 ± 3.2 | 2.4 ± 0.3 |
| 2 | nCuFe/GCE | 1290 ± 7.1 | 0.02–1.4 | 30.3 ± 2.2 | 2.2 ± 0.3 |
| 3 | nCeAu/GCE | 666 ± 7.0 | 0.02–1.6 | 12.5 ± 1.2 | 3.3 ± 0.3 |
| 4 | HRP/GCE | 351 ± 20 | 0.05–0.2 | 4.8 ± 0.2 | 5.9 ± 1.1 |
| Biosensors | Sensitivity, A·M−1·m−2 | LOD µM | Linear Range, mM | KMapp, mM | Potential, V | Redox Agent | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GlOx/nCeAu/GCE | 33 ± 2 | 4 | 0.05 | 1.1 | −0.25 | nCeAu NZs | This work |
| GlOx/nAuHCF/GCE | 63 ± 4 | 4 | 0.18 | 0.2 | −0.25 | nAuHCF NZs | This work |
| ChOx/nCuFe/GCE | 321 ± 12 | 2.8 | 0.003–0.1 | 0.85 | −0.25 | nCuFe NZs | This work |
| GlOx/nPt/GCE | 305 ± 14 | 1.7 | 0.02–0.4 | 2.46 | −0.25 | nPt NZs | This work |
| ChOx/nCuFe/nPt/GCE | 3960 ± 20 | 0.2 | 0.002–0.05 | 0.41 | −0.25 | nCuFe/nPt NZs | This work |
| Ti/NPAu/ChOx–HRP–ChE | 29.33 | 0.01 | 0.97–7.80 | 0.64 | - | HRP | [60] |
| Au-f-MWCNT-PPy-ChOx/GCE | 101.2 | - | 2–8 | 1.66 | 0.6 | K4[Fe(CN)6] | [37] |
| ChOx/Graphene/PVP/PANI | 347.7 | - | 0.05–0.10 | - | 0.6 | PANI | [45] |
| SPE/PANi/CNC/IL/GLU/ChOx | 351.9 | - | 1–12 | - | 0.6 | PANI | [46] |
| ChOx/CS/ZnO@ZnS/GCE | 526.7 | 20 | 0.4–3 | - | 0.3 | K4[Fe(CN)6] | [19] |
| ChOx/TH/Cu2O/GCE | 702 | 0.0018 | 0.01–1 | 0.025 | - | Thionine | [26] |
| ChOx/Fe3O4@PAMAM | 739 | - | 0.1–1.5 | - | 0.6 | K4[Fe(CN)6] | [64] |
| ChOx/Fe3O4@APTES | 1019 | - | 0.1–1 | - | 0.6 | K4[Fe(CN)6] | [64] |
| ChOx/AuNP/carbon IDE | 1203 | 24.6 | 1–10 | - | 0.6 | K4[Fe(CN)6] | [62] |
| Pt-NC/enzyme/Nafion | 1320 | 2 | 0.02–0.48 | - | 0.6 | Pt-NC | [63] |
| ChOx/MoS2-AuNP/GCE | 44,600 (4460 μA mM−1 cm−2) | 0.026 | 0.05–0.048 | 0.325 | - | MoS2-AuNPs | [56] |
| SPE-PEDOT-ChOx-nafion | 1.34 μA·mM−1 | - | 0.05–0.8 | 0.24 | –0.51 | PEDOT | [51] |
| ChOx/KMWNTs/GCE | 2 μA·mM−1 | - | 0.005–0.016 | - | 0.6 | KMWNTs | [65] |
| ChOx/CeO2-NR | 858 | 680 | 1–6.5 | 0.68 | 1.25 | CeO2 | [48] |
| Ag/ChOx/ChE/Au NPs/SPE | 336 | 0.009 | 0.01–15 | - | - | Ag | [66,67] |
| Biosensor Method | Enzymatic Method | |
|---|---|---|
| ChOx/nCuFe/nPt/GCE | ChOx/nCuFe/GCE | |
| 2.25 ± 0.35 | 2.23 ± 0.15 | 2.3 ± 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Demkiv, O.; Nogala, W.; Stasyuk, N.; Grynchyshyn, N.; Vus, B.; Gonchar, M. The Peroxidase-like Nanocomposites as Hydrogen Peroxide-Sensitive Elements in Cholesterol Oxidase-Based Biosensors for Cholesterol Assay. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14060315
Demkiv O, Nogala W, Stasyuk N, Grynchyshyn N, Vus B, Gonchar M. The Peroxidase-like Nanocomposites as Hydrogen Peroxide-Sensitive Elements in Cholesterol Oxidase-Based Biosensors for Cholesterol Assay. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2023; 14(6):315. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14060315
Chicago/Turabian StyleDemkiv, Olha, Wojciech Nogala, Nataliya Stasyuk, Nadiya Grynchyshyn, Bohdan Vus, and Mykhailo Gonchar. 2023. "The Peroxidase-like Nanocomposites as Hydrogen Peroxide-Sensitive Elements in Cholesterol Oxidase-Based Biosensors for Cholesterol Assay" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 14, no. 6: 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14060315
APA StyleDemkiv, O., Nogala, W., Stasyuk, N., Grynchyshyn, N., Vus, B., & Gonchar, M. (2023). The Peroxidase-like Nanocomposites as Hydrogen Peroxide-Sensitive Elements in Cholesterol Oxidase-Based Biosensors for Cholesterol Assay. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 14(6), 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14060315






