Effects of Modulation of the Hedgehog and Notch Signaling Pathways on Osteoblast Differentiation Induced by Titanium with Nanotopography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ti Surface Modification and Characterization
2.2. Selection of the Concentrations of the Hedgehog and Notch Agonists and Antagonists
2.2.1. Preparation of the Hedgehog and Notch Agonists and Antagonists
2.2.2. Isolation and Culture of Osteoblasts
2.2.3. Analysis of Gene Expression by Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.2.4. Analysis of the ALP Activity by Fast Red Staining
2.2.5. Analysis of the Extracellular MATRIX Mineralization by Alizarin Red Staining
2.3. Effects of the Hedgehog Signalling Modulation on Osteoblast Differentiation and Expression of Hedgehog Receptors in Cells Grown on Ti-Control and Ti-Nano
Analysis of the Protein Expression by Western Blot
2.4. Effects of the Notch Signalling Modulation on Osteoblast Differentiation and the Expression of Notch Receptors in Cells Grown on Ti-Control and Ti-Nano
2.5. Effects of the Combination of the Hedgehog and Notch Signalling Modulation on the Gene Expression of Bone Markers in Cells Grown on Ti-Control and Ti-Nano
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
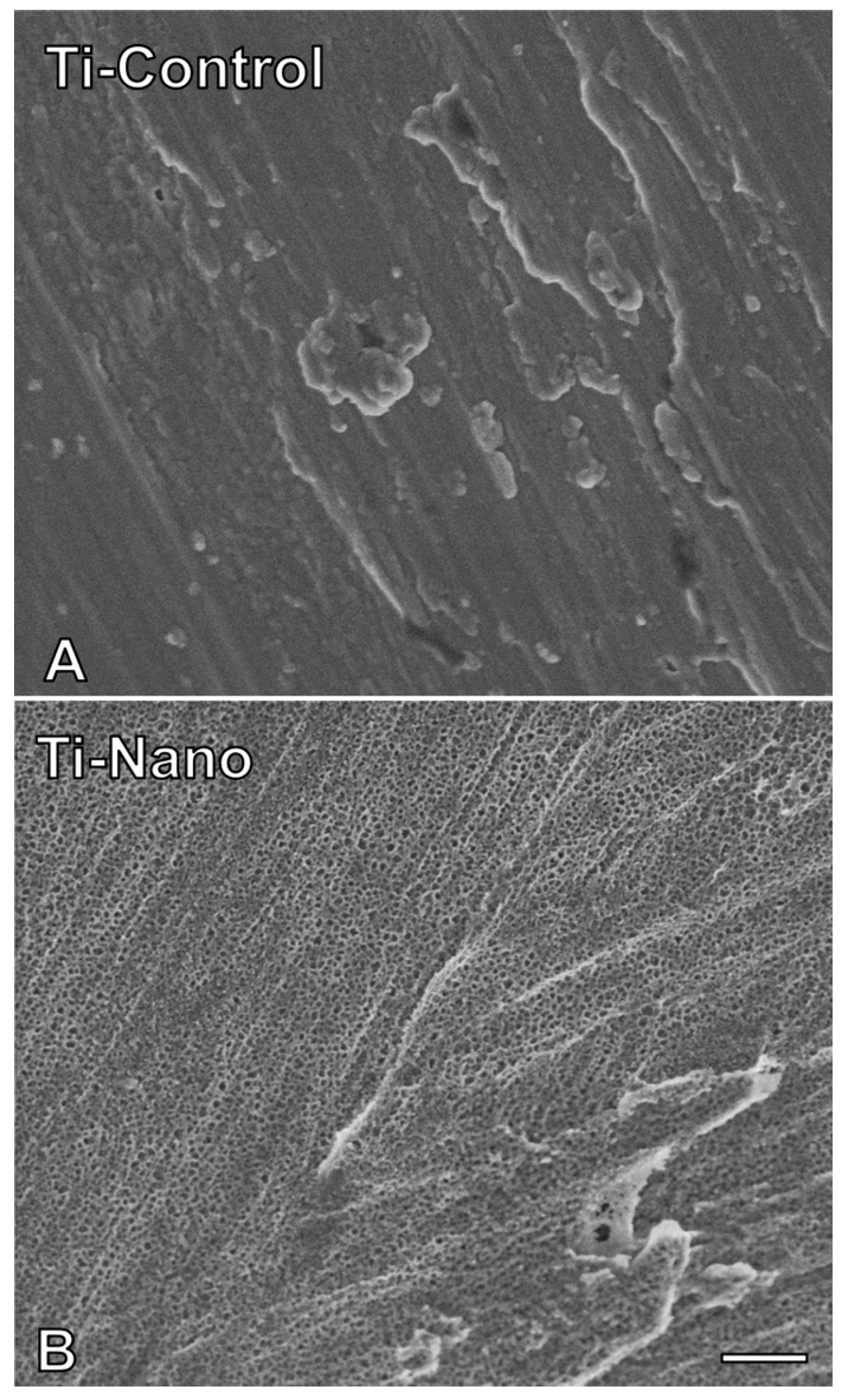
3.1. Ti-Control and Ti-Nano Surfaces
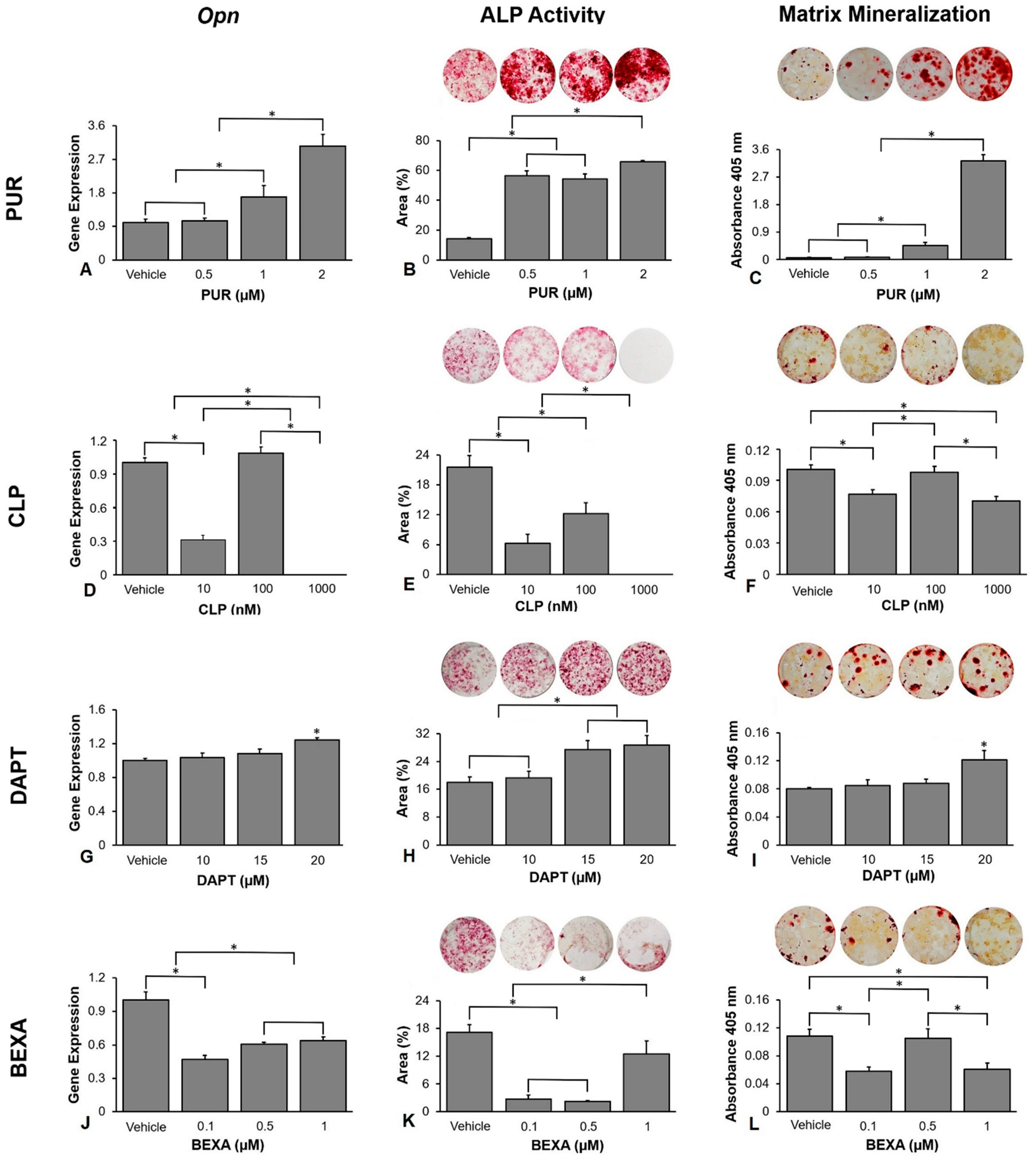
3.2. Selection of the Concentration of the Hedgehog and Notch Agonists and Antagonists
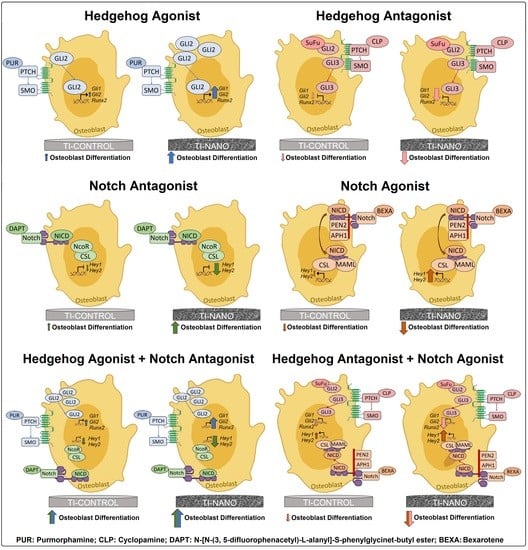
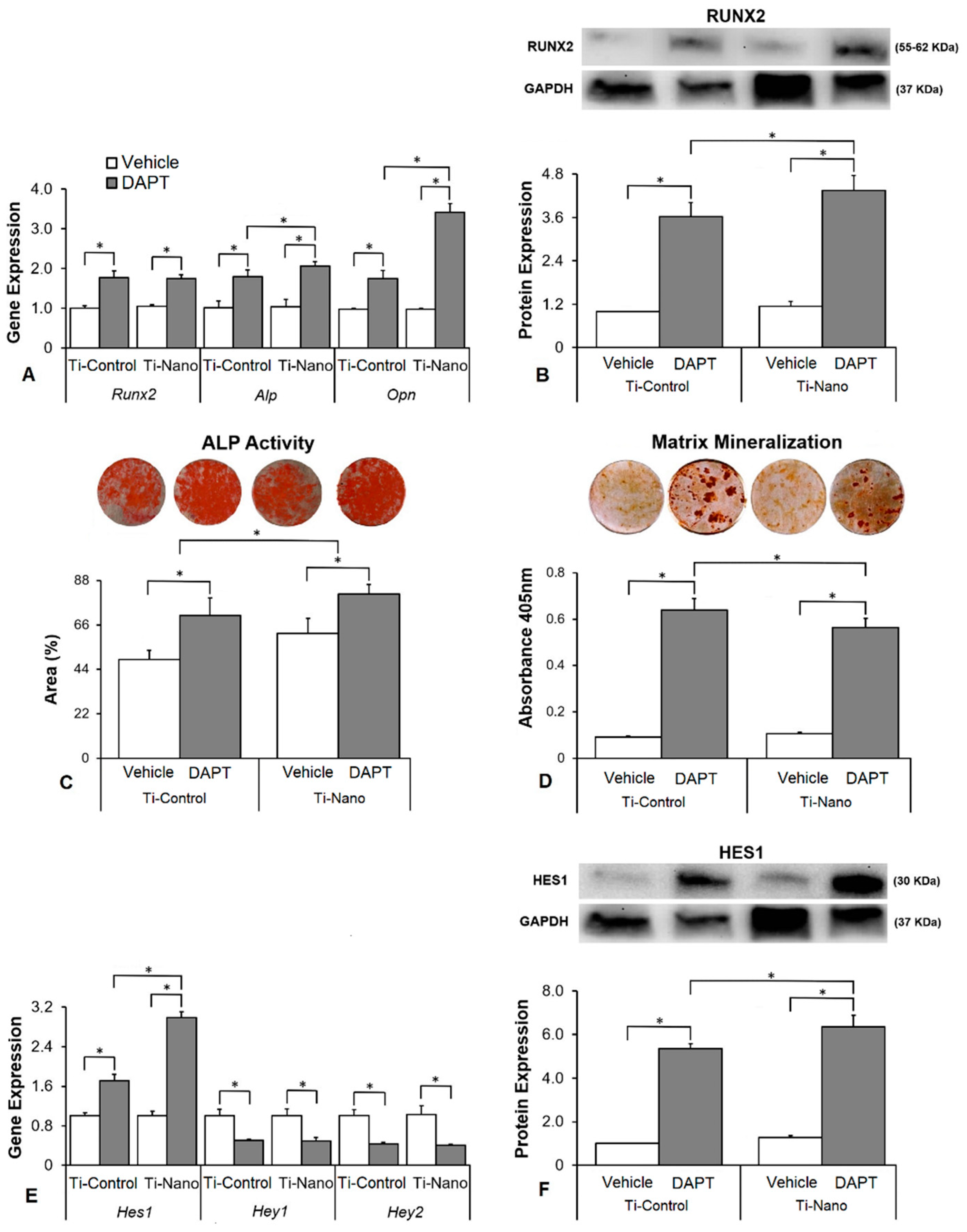
3.3. Effects of the Hedgehog Signalling Modulation on Osteoblast Differentiation and the Expression of Hedgehog Receptors in Cells Grown on Ti-Control and Ti-Nano
3.4. Effects of the Notch Signalling Modulation on Osteoblast Differentiation and the Expression of Notch Receptors in the Cells Grown on Ti-Control and Ti-Nano
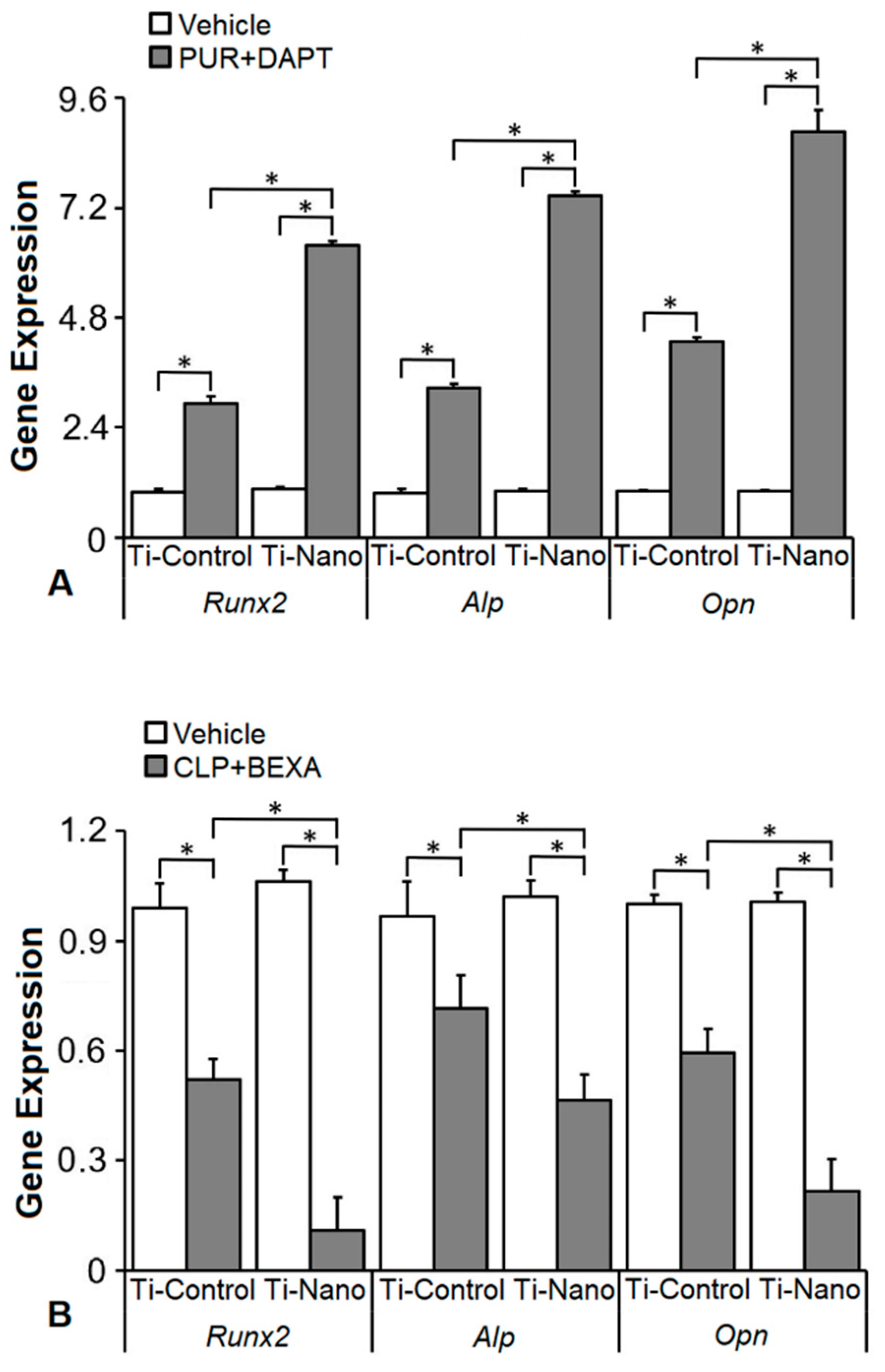
3.5. Effects of the Combination of the Hedgehog and Notch Signalling Modulation on the Gene Expression of Bone Markers in the Cells Grown on Ti-Control and Ti-Nano
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adolpho, L.F.; Lopes, H.B.; Freitas, G.P.; Weffort, D.; Campos Totoli, G.G.; Loyola Barbosa, A.C.; Freire Assis, R.I.; Silverio Ruiz, K.G.; Andia, D.C.; Rosa, A.L.; et al. Human periodontal ligament stem cells with distinct osteogenic potential induce bone formation in rat calvaria defects. Regen. Med. 2022, 17, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, W.; Sinha, K.M.; Yasuda, H.; de Crombrugghe, B. Identification and characterization of microRNAs controlled by the osteoblast-specific transcription factor Osterix. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, A.T.P.; Lopes, H.B.; Oliveira, F.S.; Weffort, D.; Freitas, G.P.; Adolpho, L.F.; Fernandes, R.R.; Rosa, A.L.; Beloti, M.M. The extracellular matrix protein Agrin is expressed by osteoblasts and contributes to their differentiation. Cell Tissue Res. 2021, 386, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Andre, P.; Ye, L.; Yang, Y.-Z. The Hedgehog signalling pathway in bone formation. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2015, 7, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levi, B.; James, A.W.; Nelson, E.R.; Li, S.; Peng, M.; Commons, G.W.; Lee, M.; Wu, B.; Longaker, M.T. Human Adipose-Derived Stromal Cells Stimulate Autogenous Skeletal Repair via Paracrine Hedgehog Signaling with Calvarial Osteoblasts. Stem Cells Dev. 2011, 20, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, L.; Dou, G.; Liu, Y.; Duan, J.; Feng, L.; Deng, S.; et al. Endothelial cells-targeted soluble human Delta-like 4 suppresses both physiological and pathological ocular angiogenesis. Sci. China Life Sci. 2015, 58, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heretsch, P.; Tzagkaroulaki, L.; Giannis, A. Cyclopamine and Hedgehog Signaling: Chemistry, Biology, Medical Perspectives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 3418–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberge, L.; Origa-Alves, A.C.; Rebelatto, C.L.K.; Dallagiovanna, B.; Shigunov, P. Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling pathway affects the expression of miR-20a and miR-3. J. Biotechnol. Biodivers. 2013, 4, 322–332. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, A.; Ullah, N.; Nawaz, T.; Aziz, T. Molecular mechanisms of Sanguinarine in cancer prevention and treatment. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2022. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, C.; Zeng, F.; Xue, M.; Zhang, X. Activation of the Hh pathway in periosteum-derived mesenchymal stem cells induces bone formation in vivo: Implication for postnatal bone repair. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 3100–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelista, M.; Tian, H.; de Sauvage, F.J. The hedgehog signaling pathway in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 5924–5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingham, P.W.; McMahon, A.P. Hedgehog signaling in animal development: Paradigms and principles. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 3059–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaisant, M.; Giorgetti-Peraldi, S.; Gabrielson, M.; Loubat, A.; Dani, C.; Peraldi, P. Inhibition of hedgehog signaling decreases proliferation and clonogenicity of human mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beloti, M.M.; Bellesini, L.S.; Rosa, A.L. Purmorphamine enhances osteogenic activity of human osteoblasts derived from bone marrow mesenchymal cells. Cell Biol. Int. 2005, 29, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloti, M.M.; Bellesini, L.S.; Rosa, A.L. The effect of purmorphamine on osteoblast phenotype expression of human bone marrow mesenchymal cells cultured on titanium. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 4245–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, F.S.; Bellesini, L.S.; Defino, H.L.A.; da Silva Herrero, C.F.; Beloti, M.M.; Rosa, A.L. Hedgehog signaling and osteoblast gene expression are regulated by purmorphamine in human mesenchymal stem cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 113, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ding, S.; Ding, Q.; Gray, N.S.; Schultz, P.G. A small molecule with osteogenesis-inducing activity in multipotent mesenchymal progenitor cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 14520–14521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, S.; Chen, J.K. Purmorphamine activates the Hedgehog pathway by targeting Smoothened. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 2, 29–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Walker, J.; Zhang, J.; Ding, S.; Schultz, P.G. Purmorphamine induces osteogenesis by activation of the hedgehog signaling pathway. Chem. Biol. 2004, 11, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heretsch, P.; Tzagkaroulaki, L.; Giannis, A. Modulators of the hedgehog signaling pathway. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 6613–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, Y.; Katoh, M. Hedgehog target genes: Mechanisms of carcinogenesis induced by aberrant hedgehog signaling activation. Curr. Mol. Med. 2009, 9, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quint, E.; Smith, A.; Avaron, F.; Laforest, L.; Miles, J.; Gaffield, W.; Akimenko, M.-A. Bone patterning is altered in the regenerating zebrafish caudal fin after ectopic expression of sonic hedgehog and bmp2b or exposure to cyclopamine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 8713–8718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, J.M.; Gao, X.; McKay, J.; McKay, R.; Salo, Z.; Graff, J.M. Hedgehog signaling plays a conserved role in inhibiting fat formation. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panepucci, R.A.; Oliveira, L.H.B.; Zanette, D.L.; Viu Carrara, R.d.C.; Araujo, A.G.; Orellana, M.D.; Bonini de Palma, P.V.; Menezes, C.C.B.O.; Covas, D.T.; Zago, M.A. Increased levels of NOTCH1, NF-kappaB, and other interconnected transcription factors characterize primitive sets of hematopoietic stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2010, 19, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radtke, F.; Schweisguth, F.; Pear, W. The Notch “gospel”. EMBO Rep. 2005, 6, 1120–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- High, F.; Epstein, J.A. Signalling Pathways Regulating Cardiac Neural Crest Migration and Differentiation. In Vascular Development; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 152–164. ISBN 978-0-470-31941-3. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, A.; Gessler, M. Delta-Notch—And then? Protein interactions and proposed modes of repression by Hes and Hey bHLH factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 4583–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, V.; Muth, A.N.; Ransom, J.F.; Schluterman, M.K.; Barnes, R.; King, I.N.; Grossfeld, P.D.; Srivastava, D. Mutations in NOTCH1 cause aortic valve disease. Nature 2005, 437, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLarren, K.W.; Lo, R.; Grbavec, D.; Thirunavukkarasu, K.; Karsenty, G.; Stifani, S. The mammalian basic helix loop helix protein HES-1 binds to and modulates the transactivating function of the runt-related factor Cbfa1. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Christakos, S. The vitamin D receptor, Runx2, and the Notch signaling pathway cooperate in the transcriptional regulation of osteopontin. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 40589–40598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamurovic, N.; Cappellen, D.; Rohner, D.; Susa, M. Coordinated activation of notch, Wnt, and transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathways in bone morphogenic protein 2-induced osteogenesis. Notch target gene Hey1 inhibits mineralization and Runx2 transcriptional activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 37704–37715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitranshi, N.; Dheer, Y.; Kumar, S.; Graham, S.L.; Gupta, V. Molecular docking, dynamics, and pharmacology studies on bexarotene as an agonist of ligand-activated transcription factors, retinoid X receptors. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 11745–11760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dishowitz, M.I.; Terkhorn, S.P.; Bostic, S.A.; Hankenson, K.D. Notch signaling components are upregulated during both endochondral and intramembranous bone regeneration. J. Orthop. Res. 2012, 30, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, W.; Xiong, Z.; Cai, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, L.; Tang, W.; Lin, Y.; Tian, W. Effects of γ-secretase inhibition on the proliferation and vitamin D3 induced osteogenesis in adipose derived stem cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 392, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, D.G.; Ferraz, E.P.; Abuna, R.P.F.; de Oliveira, P.T.; Morra, M.; Beloti, M.M.; Rosa, A.L. The effect of collagen coating on titanium with nanotopography on in vitro osteogenesis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2017, 105, 2783–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, J.Y.; Schwartz, Z.; Hummert, T.W.; Schraub, D.M.; Simpson, J.; Lankford, J., Jr.; Dean, D.D.; Cochran, D.L.; Boyan, B.D. Effect of titanium surface roughness on proliferation, differentiation, and protein synthesis of human osteoblast-like cells (MG63). J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1995, 29, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, G.; Mendonça, D.B.S.; Simões, L.G.P.; Araújo, A.L.; Golin, A.L.; Duarte, W.R.; Cooper, L.F.; Aragão, F.J.L. Efeito de superfícies de implantes nano-estruturadas na expressão de genes de osteoblastos e no contato osso-implante in vivo. Rev. Odontológica Bras. Cent. 2010, 19, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverwood, R.K.; Fairhurst, P.G.; Sjöström, T.; Welsh, F.; Sun, Y.; Li, G.; Yu, B.; Young, P.S.; Su, B.; Meek, R.M.D.; et al. Analysis of Osteoclastogenesis/Osteoblastogenesis on Nanotopographical Titania Surfaces. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, A.; Kato, R.; Castro-Raucci, L.; Teixeira, L.; de Oliveira, F.; Bellesini, L.; de Oliveira, P.T.; Hassan, M.; Beloti, M. Nanotopography drives stem cell fate toward osteoblast differentiation through α1β1 integrin signaling pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 115, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bighetti-Trevisan, R.L.; Almeida, L.O.; Castro-Raucci, L.M.S.; Gordon, J.A.R.; Tye, C.E.; Stein, G.S.; Lian, J.B.; Stein, J.L.; Rosa, A.L.; Beloti, M.M. Titanium with nanotopography attenuates the osteoclast-induced disruption of osteoblast differentiation by regulating histone methylation. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 134, 112548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, P.T.; Zalzal, S.F.; Beloti, M.M.; Rosa, A.L.; Nanci, A. Enhancement of in vitro osteogenesis on titanium by chemically produced nanotopography. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2007, 80, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuna, R.P.F.; Oliveira, F.S.; Adolpho, L.F.; Fernandes, R.R.; Rosa, A.L.; Beloti, M.M. Frizzled 6 disruption suppresses osteoblast differentiation induced by nanotopography through the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 8293–8303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, R.B.; Roy, B.; De Oliveira, F.S.; Ferraz, E.P.; De Oliveira, P.T.; Kemper, A.G.; Hassan, M.Q.; Rosa, A.L.; Beloti, M.M. Nanotopography Directs Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Osteoblast Lineage through Regulation of microRNA-SMAD-BMP-2 Circuit. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014, 229, 1690–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, H.B.; Freitas, G.P.; Elias, C.N.; Tye, C.; Stein, J.L.; Stein, G.S.; Lian, J.B.; Rosa, A.L.; Beloti, M.M. Participation of integrin β3 in osteoblast differentiation induced by titanium with nano or microtopography. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2019, 107, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, H.B.; Souza, A.T.P.; Freitas, G.P.; Elias, C.N.; Rosa, A.L.; Beloti, M.M. Effect of focal adhesion kinase inhibition on osteoblastic cells grown on titanium with different topographies. J. Appl. Oral Sci. Rev. FOB 2020, 28, e20190156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Raucci, L.M.S.; Francischini, M.S.; Teixeira, L.N.; Ferraz, E.P.; Lopes, H.B.; de Oliveira, P.T.; Hassan, M.Q.; Rosa, A.L.; Beloti, M.M. Titanium With Nanotopography Induces Osteoblast Differentiation by Regulating Endogenous Bone Morphogenetic Protein Expression and Signaling Pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 117, 1718–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, P.T.; Zalzal, S.F.; Irie, K.; Nanci, A. Early Expression of Bone Matrix Proteins in Osteogenic Cell Cultures. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2003, 51, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambasco de Oliveira, P.; Nanci, A. Nanotexturing of titanium-based surfaces upregulates expression of bone sialoprotein and osteopontin by cultured osteogenic cells. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuna, R.P.F.; Oliveira, F.S.; Ramos, J.I.R.; Lopes, H.B.; Freitas, G.P.; Souza, A.T.P.; Beloti, M.M.; Rosa, A.L. Selection of reference genes for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction studies in rat osteoblasts. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 234, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majors, A.K.; Boehm, C.A.; Nitto, H.; Midura, R.J.; Muschler, G.F. Characterization of human bone marrow stromal cells with respect to osteoblastic differentiation. J. Orthop. Res. 1997, 15, 546–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, C.A.; Gunn, W.G.; Peister, A.; Prockop, D.J. An Alizarin red-based assay of mineralization by adherent cells in culture: Comparison with cetylpyridinium chloride extraction. Anal. Biochem. 2004, 329, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyan, B.D.; Berger, M.B.; Nelson, F.R.; Donahue, H.J.; Schwartz, Z. The Biological Basis for Surface-dependent Regulation of Osteogenesis and Implant Osseointegration. JAAOS-J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2022, 30, e894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Bai, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, R.; Sun, Y.; Hang, R.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Yao, X.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Type I collagen decorated nanoporous network on titanium implant surface promotes osseointegration through mediating immunomodulation, angiogenesis, and osteogenesis. Biomaterials 2022, 288, 121684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Horst, G.; Farih-Sips, H.; Löwik, C.W.G.M.; Karperien, M. Hedgehog stimulates only osteoblastic differentiation of undifferentiated KS483 cells. Bone 2003, 33, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.K.; Taipale, J.; Cooper, M.K.; Beachy, P.A. Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling by direct binding of cyclopamine to Smoothened. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 2743–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, B.Z.; Peng, L.F. Small-molecule modulators of the Sonic Hedgehog signaling pathway. Mol. Biosyst. 2009, 6, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.-F.; Zhu, W.-X.; Liu, T.; He, J.-Q.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J. Cyclopamine functions as a suppressor of benign prostatic hyperplasia by inhibiting epithelial and stromal cell proliferation via suppression of the Hedgehog signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 46, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Androutsellis-Theotokis, A.; Leker, R.R.; Soldner, F.; Hoeppner, D.J.; Ravin, R.; Poser, S.W.; Rueger, M.A.; Bae, S.-K.; Kittappa, R.; McKay, R.D.G. Notch signalling regulates stem cell numbers in vitro and in vivo. Nature 2006, 442, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canalis, E. Notch Signaling in Osteoblasts. Sci. Signal. 2008, 1, pe17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, X.; Mao, F.; Shen, S.; Shentu, Y.; Wang, J.; Lu, S. Bexarotene inhibits the viability of non-small cell lung cancer cells via slc10a2/PPARγ/PTEN/mTOR signaling pathway. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantini, J.; Di Scala, C.; Yahi, N.; Troadec, J.-D.; Sadelli, K.; Chahinian, H.; Garmy, N. Bexarotene blocks calcium-permeable ion channels formed by neurotoxic Alzheimer’s β-amyloid peptides. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2014, 5, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamp, F.; Scheidt, H.A.; Winkler, E.; Basset, G.; Heinel, H.; Hutchison, J.M.; LaPointe, L.M.; Sanders, C.R.; Steiner, H.; Huster, D. Bexarotene Binds to the Amyloid Precursor Protein Transmembrane Domain, Alters Its α-Helical Conformation, and Inhibits γ-Secretase Nonselectively in Liposomes. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 1702–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Huang, Y.; He, J.; Chen, F.; He, Y.; Zhang, W. Role of Hedgehog-Gli1 signaling in the enhanced proliferation and differentiation of MG63 cells enabled by hierarchical micro-/nanotextured topography. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 3267–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Chen, X.; Zheng, X.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; He, J.; Lin, Y. Beta1-integrin/Hedgehog-Gli1 signaling pathway fuels the diameter-dependent osteoblast differentiation on different TiO2 nanotubes: The optimal-diameter nanotubes for osteoblast differentiation. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2021, 137, 106026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Calle, J.; McAndrews, K.; Wu, G.; Orr, A.L.; Ferrari, A.; Tu, X.; Srinivasan, V.; Roodman, G.D.; Ebetino, F.H.; Boeckman, R.K., Jr.; et al. The Notch pathway regulates the bone gain induced by PTH anabolic signaling. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanotti, S.; Smerdel-Ramoya, A.; Stadmeyer, L.; Durant, D.; Radtke, F.; Canalis, E. Notch inhibits osteoblast differentiation and causes osteopenia. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 3890–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calciolari, E.; Hamlet, S.; Ivanovski, S.; Donos, N. Pro-osteogenic properties of hydrophilic and hydrophobic titanium surfaces: Crosstalk between signalling pathways in in vivo models. J. Periodontal Res. 2018, 53, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xie, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, G. Enhanced osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on titanium substrates by inhibiting Notch3. Arch. Oral Biol. 2017, 80, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuhashi, Y.; Itoh, M.; Nara, N.; Tohda, S. Effects of combination of notch inhibitor plus hedgehog inhibitor or Wnt inhibitor on growth of leukemia cells. Anti-Cancer Res. 2011, 31, 893–896. [Google Scholar]



| Gene | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| Opn | GAAGCCTGACCCATCTCAGAA | GTTGCTTGGAAGAGTTTCTTGCTT |
| Runx2 | CGTATTTCAGATGATGACACTGCC | AAATGCCTGGGAACTGCCTG |
| Alp | TACTGCTGATCACTCCCACG | ACCGTCCACCACCTTGTAAC |
| Gli1 | ACCTGCAAACCGTAATCCGT | TCCTAAAGAAGGGCTCATGGTG |
| Gli2 | CCAACCAGAATAAGCAGAACAGC | TGAGATCAGCCAGTTGCTCC |
| Gli3 | AGTCAGCCCTGCGGAATACT | GGGAAATCTGGTGCTGTCCAT |
| Hes1 | ACGACACCGGACAAACCAAA | CGGGAGCTATCTTTCTTAAGTGCAT |
| Hey1 | GCCGACGAGACCGAATCAAT | ATAGTCCATAGCCAGGGCGT |
| Hey2 | CGTGGGGAGCGAGAACAATTA | ATTTATTCGATCCCGACGCCT |
| Eif2β | ACCTCCCTGGAATACTCTGACT | TCGCCCCGTCTTTGATGAAT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Souza, P.G.; Adolpho, L.F.; Lopes, H.B.; Weffort, D.; Souza, A.T.P.; Oliveira, F.S.; Rosa, A.L.; Beloti, M.M. Effects of Modulation of the Hedgehog and Notch Signaling Pathways on Osteoblast Differentiation Induced by Titanium with Nanotopography. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14020079
Souza PG, Adolpho LF, Lopes HB, Weffort D, Souza ATP, Oliveira FS, Rosa AL, Beloti MM. Effects of Modulation of the Hedgehog and Notch Signaling Pathways on Osteoblast Differentiation Induced by Titanium with Nanotopography. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2023; 14(2):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14020079
Chicago/Turabian StyleSouza, Paola Gomes, Leticia Faustino Adolpho, Helena Bacha Lopes, Denise Weffort, Alann Thaffarell Portilho Souza, Fabiola Singaretti Oliveira, Adalberto Luiz Rosa, and Marcio Mateus Beloti. 2023. "Effects of Modulation of the Hedgehog and Notch Signaling Pathways on Osteoblast Differentiation Induced by Titanium with Nanotopography" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 14, no. 2: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14020079
APA StyleSouza, P. G., Adolpho, L. F., Lopes, H. B., Weffort, D., Souza, A. T. P., Oliveira, F. S., Rosa, A. L., & Beloti, M. M. (2023). Effects of Modulation of the Hedgehog and Notch Signaling Pathways on Osteoblast Differentiation Induced by Titanium with Nanotopography. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 14(2), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14020079