Abstract
Autistic individuals often show impairments in cognitive and developmental domains beyond the core symptoms of lower social communication skills and restricted repetitive behaviors. Consequently, the assessment of cognitive and developmental functions constitutes an essential part of the diagnostic evaluation. Yet, evidence on differential validity from intelligence and developmental tests, which are commonly used with autistic individuals, varies widely. In the current study, we investigated the cognitive (i.e., intelligence, executive functions) and developmental (i.e., psychomotor skills, social–emotional skills, basic skills, motivation and attitude, participation during testing) functions of autistic and non-autistic children and adolescents using the Intelligence and Development Scales–2 (IDS-2). We compared 43 autistic (Mage = 12.30 years) with 43 non-autistic (Mage = 12.51 years) participants who were matched for age, sex, and maternal education. Autistic participants showed significantly lower mean values in psychomotor skills, language skills, and the evaluation of participation during testing of the developmental functions compared to the control sample. Our findings highlight that autistic individuals show impairments particularly in motor and language skills using the IDS-2, which therefore merit consideration in autism treatment in addition to the core symptoms and the individuals’ intellectual functioning. Moreover, our findings indicate that particularly motor skills might be rather neglected in autism diagnosis and may be worthy of receiving more attention. Nonsignificant group differences in social–emotional skills could have been due to compensatory effects of average cognitive abilities in our autistic sample.
1. Introduction
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by difficulties in social communication and interaction accompanied by restricted repetitive behaviors, activities, and interests (American Psychiatric Association 2013). The worldwide prevalence of ASD has increased in recent years to approximately 1–2% (Idring et al. 2015; Maenner et al. 2020) and ASD is now considered a comparatively frequent condition (Happé and Frith 2020). Autistic individuals often experience difficulties beyond the core symptoms, such as impairments in cognitive and developmental domains, which in turn predict long-term development (e.g., Howlin and Moss 2012). Information about each individual’s cognitive and developmental abilities is particularly important when it comes to making decisions about access to social services, the selection of appropriate treatment programs, and educational placement (White et al. 2007). Moreover, the amount of provided support is oftentimes determined on the basis of a cognitive assessment (Bowen 2014). According to the criteria of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association 2013) and the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (11th ed.; World Health Organization 2018), clinicians have to report potential difficulties such as intellectual and language impairments in the diagnostic evaluation. Therefore, assessments with intelligence and developmental test batteries—in addition to autism-specific test procedures—represent a core part of the diagnostic process for autistic children and adolescents.
Yet, current tests for children and adolescents mainly allow the assessment of only single characteristics, such as intelligence, at a time and test batteries including multiple cognitive and developmental functions are missing so far. Consequently, when information about several domains or a broad assessment in a diagnostic evaluation is needed, clinicians often have to use various tests. This can be challenging, as the theoretical background and test administration differ widely among tests and dealing with these differences requires resources from the clinician. Moreover, tests build upon different characteristics of standardization samples and thus show less comparable scaled scores. The Intelligence and Development Scales–2 (IDS-2; Grob and Hagmann-von Arx 2018a) is a standardized test battery that assesses cognitive (i.e., intelligence and executive functions) and developmental (i.e., psychomotor skills, social–emotional skills, basic skills, motivation and attitude, and participation during testing) functions in 5- to 20-year-olds. The IDS-2 thus provides a comprehensive picture of an individual’s strengths and difficulties with a single test battery across a wide age range from childhood to adolescence. In addition, the IDS-2 contains clear instructions and structured tasks, and many subtests use a closed-response format, which is particularly important for autistic children because of frequent structural language difficulties (Boucher 2012), making it suitable for administration with autistic individuals. Since the publication of the IDS-2 in 2018, it has often been used in psychological and medical practice in German-speaking countries. Further international adaptations for several other languages are currently in progress or have recently been published (e.g., Dutch, English, Italian, Polish; Grob et al. 2018, 2019, 2021, 2022). In the present study, we aimed to compare autistic children and adolescents to a matched non-autistic control sample on cognitive and developmental functions to study the differential validity of test scores from the IDS-2. By doing so, we can assess whether the IDS-2 is able to distinguish between clinical subgroups and typically developing individuals (Schmidt-Atzert and Amelang 2012).
Although general intellectual functioning varies substantially among autistic individuals, the latest report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention showed that almost 60% of autistic children are classified in the below-average intelligence range (IQ < 85), with about half of these children meeting criteria for intellectual disability (IQ ≤ 70; Maenner et al. 2020). Autistic individuals typically display uneven cognitive profiles, with relative strengths in nonverbal domains (e.g., Coolican et al. 2008; Grondhuis et al. 2018) and in tasks assessing abstract reasoning and visuospatial abilities (Charman et al. 2011; Nader et al. 2016), such as a well-documented peak in the Block Design subtest of the Wechsler Intelligence Scales (e.g., Muth et al. 2014). In contrast, relative weaknesses have been demonstrated in verbal domains, particularly in the Comprehension subtest of the Wechsler Intelligence Scales (e.g., Oliveras-Rentas et al. 2012), and in processing speed and working memory tasks1 (Mayes and Calhoun 2003a; Nader et al. 2016; Oliveras-Rentas et al. 2012).
Autistic individuals often experience further cognitive difficulties on measures assessing executive functions (e.g., Hill 2004). Executive functions include a set of mental top-down regulation and control mechanisms (Miyake and Friedman 2012). In the theory of executive dysfunction, it is assumed that impairments in executive functions are responsible for some of the autism symptoms (Pennington and Ozonoff 1996), such as repetitive behavior (e.g., de Vries and Geurts 2012; Yerys et al. 2009). Demetriou et al. (2018) reported in the largest meta-analysis to date (235 studies) that autistic individuals showed moderate impairments in executive functions, both overall and in subdomains such as cognitive flexibility, fluency, planning, and inhibition,—which are also assessed with the IDS-2 (see Table S1 in the Supplement for an overview)—compared to non-autistic individuals.
Moreover, previous research showed significant impairments in autistic individuals’ motor abilities, beginning in early childhood with deficits in the acquisition of motor milestones, such as later independent walking (e.g., Manicolo et al. 2019), and delays in gross and fine motor skills, for example, diminished object manipulation activity (Libertus et al. 2014; Provost et al. 2007). In a recent meta-analysis of 139 studies with samples of autistic children, adolescents, and young adults, their overall motor ability as well as gross and fine motor skills were strongly impaired in comparison to non-autistic peers (Coll et al. 2020). In line with this result, several studies found that autistic children, compared to non-autistic samples, scored lower on subscales (i.e., manual dexterity, ball skills, and balance) of the Movement Assessment Battery for Children–2 (M-ABC-2; Petermann 2008), which is a test of motor development that contains tasks similar to those in the IDS-2 psychomotor skills domain (Liu and Breslin 2013; Manicolo et al. 2019; Siaperas et al. 2012).
Further, research has shown that lower motor skills of autistic children were significantly associated with poorer social communication skills (MacDonald et al. 2013b). It has been suggested that motor problems might even precede social and communication deficits in autistic individuals because they may limit social participation and interaction with peers during play and may interfere with effective and timely movements, such as turning the head or pointing to something, that are particularly important for joint attention (Bhat et al. 2011). Impairments in social communication and interaction, such as difficulties in social–emotional reciprocity and nonverbal communicative behaviors, as well as in developing, maintaining, and understanding relationships constitute a core diagnostic characteristic of ASD (American Psychiatric Association 2013; World Health Organization 2018). These impairments are reflected in less accurate emotion recognition in human faces, with increased response times (Leung et al. 2022; Yeung 2022), more maladaptive emotion regulation strategies (Cai et al. 2018), including more reliance on others to regulate their emotions (Cibralic et al. 2019), and fewer socially competent behaviors (e.g., Meyer et al. 2009) compared to non-autistic individuals.
Additionally, language difficulties commonly co-occur with autism (Kjellmer et al. 2018). Some autistic individuals do not acquire verbal language at all (Brignell et al. 2018). Among those who develop language, delays often begin in infancy with retardations in the production of first words and in early language comprehension (e.g., Luyster et al. 2007; Mitchell et al. 2006). Moreover, across the preschool years, autistic children exhibit difficulties in phonological awareness skills (e.g., identifying syllables or onset-rimes), with slower development than their non-autistic peers (Dynia et al. 2019). Regarding language production and comprehension (i.e., expressive and receptive language skills, respectively), some studies indicated an atypical pattern, with better expressive and poorer receptive language skills in autistic individuals (e.g., Hudry et al. 2010). However, a meta-analysis examining 74 studies reported that autistic children and adolescents had scores that were approximately 1.5 standard deviations lower in receptive as well as expressive language abilities compared to non-autistic samples (Kwok et al. 2015).
In terms of academic skills, research indicated that autistic students demonstrate variable performance (Keen et al. 2016). Specifically, in previous studies, autistic individuals showed similar basic word-reading skills, such as word recognition, compared to non-autistic peers, but they tended to have difficulties in reading comprehension (for a meta-analysis: Brown et al. 2013). Autistic individuals with higher (vs. lower) reading skills also seemed to demonstrate better writing abilities (Zajic et al. 2020). Studies predominantly indicated deficits in text generation abilities for autistic individuals, while overall intact or slightly impaired spelling skills were reported (Finnegan and Accardo 2018; Mayes and Calhoun 2003a, 2003b). Similarly, the majority of autistic individuals exhibited average competencies in mathematics, such as mathematical problem solving, compared to non-autistic peers or to the norm population in previous research (Chiang and Lin 2007; Titeca et al. 2017; Troyb et al. 2014).
Concerning motivation and attitude, a recent meta-analysis reported that autistic individuals displayed significantly lower levels of conscientiousness than non-autistic individuals (Lodi-Smith et al. 2019). In contrast, less is known regarding achievement motivation in autistic individuals. A few studies reported that autistic individuals encountered problems with self-regulation (e.g., Jahromi et al. 2012; Konstantareas and Stewart 2006) and displayed higher interest in mathematics while simultaneously showing more fear of failure and lower mastery goals (Georgiou et al. 2018). Moreover, autistic children tended to exhibit impaired engagement (Keen 2009), especially in assessment situations where they frequently demonstrated off-task behaviors (Akshoomoff 2006) and a lack of willingness to complete tasks (Mandelbaum et al. 2006).
Previous research has rarely used the IDS-2 in order to test autistic individuals. The only study so far reported in the technical manual of the IDS-2 (Grob and Hagmann-von Arx 2018b) built upon a small sample of autistic children and adolescents (N = 18; Mage = 13 years 4 months, age range 8–17 years; 17 males and 1 female). Findings showed significantly lower group mean values for autistic children and adolescents compared to non-autistic peers in the composite score of social–emotional skills (d = 0.62) and the composite score of psychomotor skills (d = 1.01) of the IDS-2. No differences were found in the composite scores of other domains. However, evidence of possible differences at the level of subtests is currently lacking, as analyses on this level have not been performed. Moreover, the study included mainly children and adolescents with Asperger’s syndrome (n = 13) and no participants with previously diagnosed infantile autism. Given the small sample size, which may have diminished the power to find group differences, and the biased distribution of sex and subtype, it remains unknown to what extent these results can be generalized.
Building on this theoretical background, we pursued two goals for the present study: First, we aimed to extend previous research on various cognitive and developmental functions in autistic children and adolescents using a single test procedure and based on the norms of a large and representative standardization sample. By doing so, our findings will provide a comparable and comprehensive view of participants’ performance in relevant domains. Second, we aimed to add knowledge regarding the differential validity evidence for test scores of the IDS-2 in autistic individuals, as psychological test procedures need to be examined in terms of their scientific quality in order to draw appropriate conclusions based on their test results. Given that previous research had some limitations (Grob and Hagmann-von Arx 2018b), we attempted to overcome these shortcomings by assessing a larger sample, including a more representative mapping of sex and subtypes, and performing analyses at the level of subtests, which have not yet been investigated in this population. We therefore examined possible mean-level differences between a large sample of autistic children and adolescents and a control sample of non-autistic children and adolescents matched by age, sex, and maternal education in the cognitive and developmental functions measured by the IDS-2. We included maternal education as a proxy for socioeconomic status (SES) to control for the fact that more autistic children and adolescents come from families with higher SES than from other SES groups (Thomas et al. 2012; Van Meter et al. 2010).
Taking into consideration the presented literature, we hypothesized that autistic children and adolescents would score lower than the control sample of non-autistic children in the following IDS-2 domains as displayed in Table 1, while we assumed that autistic children and adolescents’ scores would be similar to those of the control sample in the other IDS-2 domains (see Table 1 for a summary).

Table 1.
Summary of our hypotheses.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Procedure
Forty-three autistic children and adolescents (Mage = 12 years 4 months, age range 7–17 years; 35 males and 8 females) were recruited during (n = 18) or after (n = 25) the IDS-2 standardization and validation study with the help of local child and adolescent psychiatric services and hospitals, privately practicing psychiatrists and psychotherapists who are experts in autism diagnoses, and associations for autistic individuals. All included children and adolescents were diagnosed with ASD (infantile autism: n = 11, atypical autism: n = 6, Asperger’s syndrome: n = 24, not specified: n = 2) but were not selected on the basis of specific subtypes. Participants had received the diagnosis on average 4.08 years (SD = 2.61) prior to their participation in the present study. The ratio of males to females corresponded to the distribution of approximately four males to one female diagnosed with ASD in the population (Maenner et al. 2020).
A control sample of 43 non-autistic children and adolescents (Mage = 12 years 6 months, age range 6–20 years; 35 males and 8 females) was drawn from the German standardization and validation sample of the IDS-2 (N = 2030; Mage = 12 years 3 months, age range 5–20 years; 977 males and 1053 females). The control sample was matched by age, sex, and maternal education (as a proxy for SES) and did not differ regarding demographic characteristics from the sample of autistic children and adolescents (see Table 2). Non-autistic children and adolescents were recruited from kindergartens and schools.

Table 2.
Demographic Characteristics of Autistic and Non-Autistic Children and Adolescents.
All participants were individually tested using the IDS-2 by psychologists or trained psychology students. For the administration of the IDS-2 with autistic children and adolescents, we received input from psychiatrists and psychotherapists who specialize in autism. Test administration lasted approximately 4 h and was split into two sessions no longer than 1 week apart upon a participant’s request. Participants were tested either at their homes or in a laboratory at the university. The local ethics committee (Ethics Committee Northwest and Central Switzerland) provided approval and the study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was obtained from participants and/or their parents.
2.2. Instrument
A detailed description of the IDS-2 (Grob and Hagmann-von Arx 2018a) can be found in the Supplemental Material (Table S1). Psychometric properties have been demonstrated in several studies for the standardization sample (Grieder and Grob 2020; Grob and Hagmann-von Arx 2018b). Demographic characteristics were assessed through a parental interview at the beginning of the first test session.
2.3. Statistical Analyses
Analyses were conducted with R (R Core Team 2021). To obtain a non-autistic sample that would be comparable to the autistic sample with respect to demographic characteristics, we performed a matching procedure using the MatchIt package (Ho et al. 2011). We matched the two samples by age (nearest; continuous), sex (exact; 0 = male, 1 = female), and maternal education (nearest; 1 = compulsory school, 2 = apprenticeship, 3 = high school, 4 = higher vocational education, 5 = university degree, 6 = other, 7 = unknown). We calculated independent-samples t tests to investigate mean-level differences between the autistic sample and the non-autistic sample in cognitive and developmental domains using standardized scores (M = 100, SD = 15, for Profile IQ, Full-Scale IQ, Screening IQ, and the seven intelligence group factors; M = 10, SD = 3, for other composite scores and subtests). To reduce the alpha error inflation caused by multiple testing, p values were adjusted with Hommel’s (1988) correction by including p values from all tests simultaneously. Effect sizes were computed (Cohen 1988) and interpreted in accordance with common practice (Cohen’s d; small effect: d ≥ 0.20, medium effect: d ≥ 0.50, large effect: d ≥ 0.80). A post hoc power analysis using G*Power (Faul et al. 2007) revealed that with α = .05 and power = .80, small effects (d = 0.30) could be detected in the present sample (note that this is without accounting for multiple testing). Differences were interpreted as meaningful if they were significant after Hommel’s correction and showed at least a small effect size. In addition, we reported reliabilities for all IDS-2 scores, consisting of Cronbach’s alpha for homogeneous subtests; reliabilities calculated according to a formula of Lienert and Raatz (1998) for composite scores, which are based on intercorrelations and reliabilities of those subtests or tasks that are included in the corresponding score; or retest reliabilities reported in the technical manual of the IDS-2 (Grob and Hagmann-von Arx 2018b) for subtests that contain a single score or consist of heterogeneous tasks.
3. Results
Reliabilities, descriptive statistics, and results of the independent-samples t tests2 are presented in Table 3 for the cognitive functions and in Table 4 for the developmental functions. Reliabilities were high for composite scores and high-to-satisfactory for subtests in both samples.

Table 3.
Reliabilities, Means, Standard Deviations, and t tests of the Cognitive Functions From the Intelligence and Development Scales–2 for Autistic and Non-Autistic Children and Adolescents.

Table 4.
Reliabilities, Means, Standard Deviations, and t tests of the Developmental Functions From the Intelligence and Development Scales–2 for Autistic and Non-Autistic Children and Adolescents.
3.1. Cognitive Functions
Figure 1 displays the means and standard deviations in the cognitive functions of the IDS-2 for the autistic and non-autistic samples. Before controlling for multiple testing, we found significant group differences for the intelligence composite scores: Profile IQ, t(77) = 1.96, p = .027, and Screening IQ, t(82) = 1.80, p = .038, with small effect sizes (d = 0.44 and 0.39, respectively), indicating lower scores for the autistic sample than the control sample. Furthermore, we observed group differences for the intelligence group factors: Auditory Short-Term Memory, t(79) = 2.12, p = .019, and Visuospatial Short-Term Memory, t(79) = 2.70, p = .004, with small-to-medium effect sizes (d = 0.47 and 0.60, respectively), and the corresponding subtests Mixed Digit and Letter Span, t(79) = 2.51, p = .007, and Rotated Shape Memory, t(79) = 2.78, p = .003, with medium effect sizes (d = 0.56 and 0.62, respectively), such that the autistic participants showed lower mean values than the control sample. Moreover, the autistic participants had significantly lower mean values in the executive functions composite score, t(71) = 2.27, p = .013, and the subtests Listing Words, t(73) = 2.38, p = .010, Divided Attention, t(71) = 2.13, p = .019, and Animal Colors, t(72) = 1.70, p = .047. Effect sizes were in the small-to-medium range (d = 0.40 to 0.55). We found no differences between autistic and non-autistic participants in the Full-Scale IQ, t(81) = 1.58, p = .059, in the intelligence group factors Visual Processing, t(80) = 1.46, p = .148, Processing Speed, t(80) = 1.15, p = .126, Abstract Reasoning, t(80) = 0.62, p = .539, Verbal Reasoning, t(81) = 1.48, p = .071, and Long-Term Memory, t(79) = 1.57, p = .060, including corresponding intelligence subtests, and in the executive functions subtest Drawing Routes, t(74) = 0.88, p = .192.
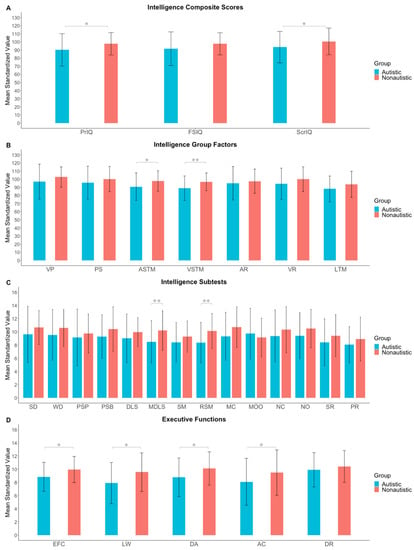
Figure 1.
Means and standard deviations are reported for (A) intelligence composite scores, (B) intelligence group factors, (C) intelligence subtests, and (D) executive functions composite score and subtests of the Intelligence and Development Scales–2 for autistic and non-autistic children and adolescents. Asterisks in grey indicate p values not adjusted with Hommel’s (1988) correction. Asterisks in black indicate p values adjusted according to Hommel (1988). Please note that after this correction, none of the comparisons were significant and therefore, no black asterisks are included in the present graphs. PrIQ = Profile IQ; FSIQ = Full-Scale IQ; ScrIQ = Screening IQ; VP = Visual Processing; PS = Processing Speed; ASTM = Auditory Short-Term Memory; VSTM = Visuospatial Short-Term Memory; AR = Abstract Reasoning; VR = Verbal Reasoning; LTM = Long-Term Memory; SD = Shape Design; WD = Washer Design; PSP = Parrots; PSB = Boxes; DLS = Digit and Letter Span; MDLS = Mixed Digit and Letter Span; SM = Shape Memory; RSM = Rotated Shape Memory; MC = Matrices: Completion; MOO = Matrices: Odd One Out; NC = Naming Categories; NO = Naming Opposites; SR = Story Recall; PR = Picture Recall; EFC = Executive functions composite score; LW = Listing Words; DA = Divided Attention; AC = Animal Colors; DR = Drawing Routes. * p < .05. ** p < .01. *** p < .001.
However, after controlling for multiple testing, the significant differences in intelligence and executive functions fell above the Hommel-corrected p-value threshold (see Table 3).
3.2. Developmental Functions
Figure 2 shows the means and standard deviations in the developmental functions of the IDS-2 for the autistic and non-autistic samples. Before controlling for multiple testing, results indicate that autistic participants scored significantly lower than non-autistic participants in psychomotor skills [composite score, t(81) = 4.60, p < .001; Gross Motor Skills, t(32) = 5.30, p < .001; Fine Motor Skills, t(79) = 3.20, p < .001; Visuomotor Skills, t(81) = 3.01, p = .002] with medium-to-large effect sizes (d = 0.66 to 1.82). We found a similar group difference for participants’ social–emotional skills [composite score, t(82) = 2.71, p = .004; Identifying Emotions, t(32) = 2.07, p = .023; Regulating Emotions, t(82) = 2.37, p = .010; Socially Competent Behavior, t(80) = 2.29, p = .012] with medium effect sizes (d = 0.51 to 0.71), and in language skills [composite score, t(28) = 4.11, p < .001; Phoneme Analysis, t(29) = 3.75, p < .001; Language Expressive, t(28) = 3.31, p = .001; Language Receptive, t(29) = 4.52, p < .001] with large effect sizes (d = 1.22 to 1.63). Furthermore, autistic participants showed significantly lower group mean values than the control sample for the evaluation of participation during the test session of intelligence, t(81) = 2.68, p = .004, executive functions, t(71) = 2.13, p = .018, and developmental functions, t(79) = 3.30, p < .001, with medium effect sizes (d = 0.50 to 0.73). We found no differences in the subtests Logical–Mathematical Reasoning, t(81) = 1.44, p = .153, Reading, t(74) = 1.35, p = .182, Spelling, t(65) = 1.26, p = .212, and in the motivation and attitude domain [composite score, t(46) = 0.11, p = .458; Conscientiousness, t(45) = 0.06, p = .477; Achievement Motivation, t(47) = −0.07, p = .528], indicating similar performance in autistic and non-autistic participants.
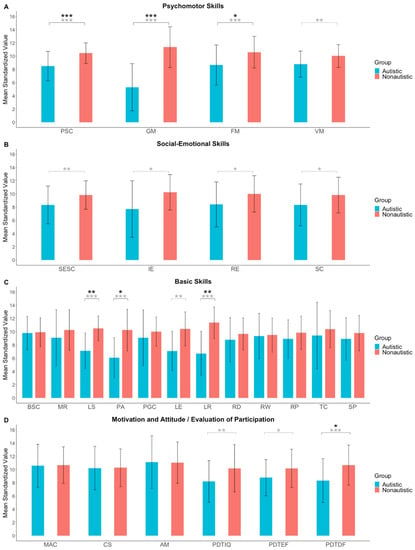
Figure 2.
Means and standard deviations are reported for (A) psychomotor skills composite score and subtests, (B) social–emotional skills composite score and subtests, (C) basic skills composite score and subtests, and (D) motivation and attitude composite score and subtests as well as for the evaluation of participation during testing of the Intelligence and Development Scales–2 for autistic and non-autistic children and adolescents. Asterisks in grey indicate p values not adjusted with Hommel’s (1988) correction. Asterisks in black indicate p values adjusted according to Hommel (1988). PSC = Psychomotor skills composite score; GM = Gross Motor Skills; FM = Fine Motor Skills; VM = Visuomotor Skills; SESC = Social–emotional skills composite score; IE = Identifying Emotions; RE = Regulating Emotions; SC = Socially Competent Behavior; BSC = Basic skills composite score; MR = Logical–Mathematical Reasoning; LS = Language Skills; PA = Phoneme Analysis; PGC = Phoneme–Grapheme Correspondence; LE = Language Expressive; LR = Language Receptive; RD = Reading; RW = Reading Words; RP = Reading Pseudo Words; TC = Text Comprehension; SP = Spelling; MAC = Motivation and attitude composite score; CS = Conscientiousness; AM = Achievement Motivation; PDTIQ = Participation during testing, intelligence; PDTEF = Participation during testing, executive functions; PDTDF = Participation during testing, developmental functions. * p < .05. ** p < .01. *** p < .001.
After controlling for multiple testing, significant group differences remained for the composite score of psychomotor skills (pH < .001) and subtests Gross Motor Skills (pH < .001) and Fine Motor Skills (pH = .046). Moreover, the composite score of language skills remained significant (pH = .008) as well as Phoneme Analysis (pH = .019) and Language Receptive (pH = .003) tasks. Finally, the evaluation of participation during testing of the developmental functions remained significant (pH = .035; see Table 4).3
3.3. Post Hoc Analyses
To assess for age-related differences between children and adolescents, we further performed post hoc analyses separately for children aged 5–10 years (n = 17) and adolescents aged 11–20 years (n = 26). After Hommel’s (1988) correction, autistic children scored significantly lower than non-autistic children in the composite scores of the cognitive functions, the intelligence group factors, Auditory Short-Term Memory, Visuospatial Short-Term Memory, and Verbal Reasoning (including the corresponding subtests) as well as in psychomotor skills, social–emotional skills, and basic skills of the developmental functions (see Tables S3 and S4 in the Supplemental Material for results). We found no significant group differences between autistic and non-autistic adolescents for the cognitive and developmental functions of the IDS-2 after controlling for multiple testing (see Tables S5 and S6 in the Supplemental Material).
4. Discussion
In the present study, we compared autistic children and adolescents to a matched control sample on six cognitive and developmental functions assessed with the IDS-2. Our results provide evidence for differential validity for the IDS-2 test scores in psychomotor skills, language skills, and in the evaluation of participation during testing of the developmental functions, with autistic children and adolescents scoring lower than non-autistic participants in these domains. No group differences were detected in the other domains after controlling for multiple testing. Overall, our findings provide an overview of important cognitive and developmental functions in autistic children and adolescents using a single comprehensive and standardized test battery.
In line with our hypotheses, we found similar performance in autistic and non-autistic participants for the intelligence group factors Visual Processing and Abstract Reasoning, which corresponds to studies reporting relative strengths for autistic individuals in nonverbal domains (e.g., Grondhuis et al. 2018) and in subtests measuring fluid reasoning and visuospatial abilities (Charman et al. 2011; Nader et al. 2016). Specifically, the Shape Design subtest, which is part of the Visual Processing group factor of the IDS-2, requires participants to reproduce presented geometric figures with rectangles and triangles. This task is similar to the Block Design subtest of the Wechsler Intelligence Scales, for which autistic individuals oftentimes show at least comparable performance to non-autistic controls (e.g., Muth et al. 2014).
However, in contrast to our hypotheses and previous research (e.g., Demetriou et al. 2018), no significant group differences emerged for the other cognitive functions scores of the IDS-2 after correcting for multiple testing, even though effect sizes were in the small-to-medium range. This finding suggests that our autistic sample included participants with overall average cognitive abilities. One explanation for this result could be that about half of our autistic participants had been diagnosed with Asperger’s syndrome, which is known for impairments in social interaction and restricted interests, but without deficits in cognitive development (10th ed.; World Health Organization 2016). Moreover, when assessing age-related differences in a set of post hoc analyses, we found that autistic adolescents scored similarly to non-autistic adolescents in the IDS-2, while autistic children obtained significantly lower scores in several domains of the IDS-2 compared to non-autistic children. In particular, group differences between autistic and non-autistic children remained significant after controlling for multiple testing in the composite scores of the intelligence and executive functions domains as well as in the intelligence group factors Verbal Reasoning and Auditory and Visuospatial Short-Term Memory. These results are in line with previous research reporting weaknesses of autistic children in verbal domains (e.g., Oliveras-Rentas et al. 2012) and in working memory tasks (e.g., Mayes and Calhoun 2003a) as the IDS-2 Auditory and Visuospatial Short-Term Memory group factors also include tasks measuring working memory (i.e., [Mixed] Digit and Letter Span—backwards and Rotated Shape Memory; see Table S1 in the Supplement). In addition, autistic children scored lower on motor and language skills, and importantly, also on social–emotional skills. Interestingly, we did not find any differences between autistic and non-autistic participants when focusing on adolescents only. One reason for this finding could be that autistic adolescents have already received support and intervention in crucial developmental areas, whereas the included autistic children may have been recently diagnosed with autism and thus have had little or no treatment to that point. However, it should be noted that these results are based on small sample sizes. Thus, future studies should use larger age-specific samples to investigate developmental effects across childhood and adolescence and simultaneously control for previous interventions.
Autistic participants had significant impairments in overall psychomotor skills as well as lower scores in gross and fine motor skills in the IDS-2 compared to the non-autistic participants. This finding is in line with results of a previous meta-analysis (Coll et al. 2020) and studies using the M-ABC-2 to assess motor abilities (e.g., Manicolo et al. 2019). Motor skills are particularly important for carrying out everyday tasks (e.g., grasping a glass) and performing activities of daily living (MacDonald et al. 2013a), as well as for participating in activities at school or in the community (Oliveira et al. 2021). It has been suggested that one reason for these motor differences may be that autistic individuals encounter problems in the translation of sensory inputs into movements (Hannant et al. 2016). Moreover, structural and functional alterations in motor cortex regions of the brain (Mostofsky et al. 2007; Nebel et al. 2014) and in the cerebellum (Fatemi et al. 2012; Mostofsky et al. 2009) have been detected for autistic individuals, which might explain some of the motor impairments. The strong group difference we observed in gross motor skills, representing the largest effect in our study, is in accordance with previous research (Coll et al. 2020) and may be associated with the high prevalence of autistic individuals exhibiting hypotonia (51%) or motor apraxia (34%; Ming et al. 2007). Hence, autistic individuals tend to experience difficulties especially in movements that require activation of muscles in the entire body including balance, arm movements, and coordination. However, as this subtest is administered only to 5- to 10-year-olds in the IDS-2 and correlational research has shown that autistic children’s motor skills improve with age (Coll et al. 2020), future longitudinal studies are needed to study possible developmental effects. Although it is not compulsory to report potential difficulties in motor skills as part of the diagnostic criteria of ASD, our findings support the importance of assessing psychomotor abilities during the diagnostic evaluation of children and adolescents at increased likelihood of ASD, as they might be crucial for treatment programs (Bhat et al. 2011; Colombo-Dougovito and Block 2019).
As stated in previous studies, we found that autistic children scored lower in language skills, such as in phoneme analysis (Dynia et al. 2019) and receptive language tasks (Kwok et al. 2015), compared to the non-autistic participants. However, we detected no significant group differences after correcting for multiple testing in expressive language tasks. Although a previous meta-analysis showed equally impaired receptive and expressive language skills in autistic individuals (Kwok et al. 2015), our finding is in line with other studies that also indicated an atypical language pattern of autistic individuals with an advantage in expressive over receptive language skills (e.g., Hudry et al. 2010). One reason for this result might be that we used a direct measurement of language skills in our study. Previous research also found this pattern when using a similar test procedure but did not detect any expressive language advantages when using caregiver reports (Ellis Weismer et al. 2010). Given that having better language production than comprehension skills is contrary to what is generally anticipated in typically developing peers, researchers even suggested that this pattern may be unique to autism (e.g., Volden et al. 2011) and therefore could be used for differential diagnosis (Mitchell et al. 2011) and specific interventions (Hudry et al. 2010). Nevertheless, as the expressive and receptive language tasks are conducted only with 5- to 10-year-olds in the IDS-2 and previous studies have reported a decrease in the expressive–receptive discrepancy in older autistic individuals (Kwok et al. 2015; Volden et al. 2011), it could also be that our result was driven by age effects. Because of the diagnostic and therapeutic potential of this finding, future studies should continue to examine this potential discrepancy between expressive and receptive language in autistic individuals across development.
Additionally, we found no significant group differences in tasks measuring phoneme–grapheme correspondence, which is consistent with our finding that autistic participants also scored similarly to the non-autistic control group in the reading and spelling subtests in our study. This result might be explained by the fact that knowledge of letter–sound correspondence is a prerequisite for the development of literacy skills (Carnine et al. 2010) and therefore needs to be intact for average reading and spelling skills. The finding that our autistic participants showed no differences in the basic skills logical–mathematical reasoning, reading, and spelling compared to non-autistic peers is in line with other studies (e.g., Brown et al. 2013; Chiang and Lin 2007). One reason may refer to the fact that most of the autistic participants in our study attended inclusive educational settings. The enrollment in integrative settings can have a positive impact on autistic individuals’ academic skills as individualized education plans in mainstream programs focus more on academic enhancement than in specialized settings which place more emphasis on life competencies and developmental domains (Kurth and Mastergeorge 2010).
Contrary to previous research (e.g., Cai et al. 2018; Yeung 2022), we found no significant group differences for social–emotional skills after correcting for multiple testing. One explanation for this result could be that the tasks assessing social–emotional skills in the IDS-2 mainly measure explicit knowledge, such as naming socially competent behavior in hypothetical social situations, rather than actual behavior in real-life situations. Since we did not observe any group differences in the cognitive functions of the IDS-2 either, it might be that autistic participants could compensate for difficulties in social–emotional skills with higher-level analytical strategies (Harms et al. 2010; Leung et al. 2022). This would be in line with studies reporting that intelligence is positively associated with social–emotional skills (Jones et al. 2011), especially in autistic individuals (Dyck et al. 2006; Salomone et al. 2019; Trevisan and Birmingham 2016). We found further evidence for this assumption in supplementary analyses where we matched the non-autistic control sample by age, sex, and Full-Scale IQ and obtained lower effect sizes for the social–emotional skills composite score as well as for the subtests Identifying Emotions and Regulating Emotions compared to the effect sizes obtained by matching the samples by age, sex, and maternal education (see Table S2 in the Supplemental Material). In addition, time limits in testing procedures might explain part of the nonsignificant group differences in social–emotional skills. Nagy et al. (2021) found impairments only when time limits for responding were applied, and the present tasks assessing social–emotional skills did not have any time restrictions. However, it is important to note that although meta-analyses and reviews show significant deficits in social–emotional abilities of autistic individuals (e.g., Cai et al. 2018; Yeung 2022), several previous studies were also not able to detect impairments in emotion recognition and regulation (e.g., Jones et al. 2011; Mazefsky et al. 2014; Rosset et al. 2008) or reported difficulties only for certain emotions, for example, for negative emotions (e.g., Shanok et al. 2019). To clarify the interplay between explicit knowledge and social–emotional skills in the IDS-2, future research should use multiple methods to assess social–emotional skills and compare the autistic participants’ performance in the IDS-2 with the behavior they demonstrate in real-life social interactions using observational measures. Even though the group differences in the social–emotional skills of the IDS-2 were no longer significant after correcting for multiple testing, it is crucial to mention that effect sizes were within a medium range and comparable to those in a previous meta-analysis (Yeung 2022) which at least tends to indicate differential validity of test scores from the social–emotional skills domain of the IDS-2.
A strength of our study is that we assessed the cognitive and developmental functions using a standardized test procedure with good psychometric properties. Moreover, we used a single test battery based on one standardization sample for the assessment of a broad range of cognitive and developmental domains. In addition, our sample covered a wide age range and was representative of the autistic population, in that the male:female ratio was approximately 4:1 (Maenner et al. 2020), different subtypes were included, and children and adolescents exhibited known comorbid conditions (Leyfer et al. 2006; Salazar et al. 2015). We also consider it a strength that we included participants with intellectual functioning below 70, which represents an understudied subpopulation in autism research (Russell et al. 2019). In addition, by selecting the control sample through a matching procedure, we could control for possible confounding influences of age, sex, and SES.
The present study also has limitations that need to be considered and addressed in future research. First, we relied on diagnostic evaluations carried out by clinical services and experienced psychiatrists and psychotherapists and hence could not consider the standardization and comparability of the diagnoses. Second, we had no information regarding symptom severity or previous treatment programs and could therefore not control for these factors. Third, analyses were conducted at the group level, which limits generalizability to individuals. Finally, although the sample size was larger than in previous studies, an even larger sample of children and adolescents would further increase the power to detect small effects in future studies.
5. Conclusions
In sum, our findings suggest that in particular, motor and language skills as well as achievement motivation rated by the test administrator were impaired in autistic children and adolescents in the IDS-2 compared to non-autistic participants, which provides evidence for differential validity for these domains of the IDS-2. The largest difference was found in gross motor skills. We therefore advise that therapists working with autistic children should gain knowledge in the area of motor and language therapeutic intervention. Speech–language pathologists as well as psychomotor therapists should obtain autism-specific knowledge, so that autistic children with limited motor and language skills receive appropriate therapeutic support regardless of the background of the therapist. Arguably, with optimal training, autistic participants may also perform tasks in the psychomotor and language domains with greater engagement, which, in turn, could have a positive impact on the long-term development of their motor and language abilities. In conclusion, our results highlight important domains beyond the core symptoms of ASD that need to be considered in future research, educational contexts, and clinical assessment and that seem particularly critical for interventions.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jintelligence10040112/s1, Table S1: Description of the Composites, Group Factors, and Subtests of the Intelligence and Development Scales–2, Table S2: Means, Standard Deviations, and t tests of the Developmental Functions From the Intelligence and Development Scales–2 for Autistic and Non-Autistic Children and Adolescents Matched by Age, Sex, and Intelligence, Table S3: Means, Standard Deviations, and t tests of the Cognitive Functions From the Intelligence and Development Scales–2 for Autistic and Non-Autistic Children (Aged 5–10 Years), Table S4: Means, Standard Deviations, and t tests of the Developmental Functions From the Intelligence and Development Scales–2 for Autistic and Non-Autistic Children (Aged 5–10 Years), Table S5: Means, Standard Deviations, and t tests of the Cognitive Functions From the Intelligence and Development Scales–2 for Autistic and Non-Autistic Adolescents (Aged 11–20 Years), Table S6: Means, Standard Deviations, and t tests of the Developmental Functions From the Intelligence and Development Scales–2 for Autistic and Non-Autistic Adolescents (Aged 11–20 Years).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.D.O., W.M., S.G. and A.G.; methodology, S.D.O., W.M. and S.G.; software, S.D.O.; validation, S.D.O., W.M. and S.G.; formal analysis, S.D.O.; investigation, S.D.O.; resources, A.G.; data curation, S.D.O.; writing—original draft preparation, S.D.O.; writing—review and editing, S.D.O., W.M., S.G. and A.G.; visualization, S.D.O.; supervision, A.G.; project administration, A.G.; funding acquisition, A.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee Northwest and Central Switzerland (protocol code: PB_2016-01836 and date of approval: 2 May 2019).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy issues and property rights.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all the children and adolescents for their participation and all the test administrators, especially Miriam Weibel, for their support during data collection. We thank Anita Todd for copyediting the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest, with one exception: A.G. is recipient of royalties for the Intelligence and Development Scales–2 (IDS-2).
Notes
| 1 | According to current models of intelligence (Schneider and McGrew 2018) and executive functions (Miyake et al. 2000), working memory can be understood as a component of intelligence or executive functions. Because working memory is included in the intelligence domain in the IDS-2, we subsumed working memory under the realm of intelligence. |
| 2 | Although the sample size met the robustness criteria for using independent-samples t tests (Eid et al. 2017), we also examined the variables regarding normal distribution and variance homogeneity. Analyses using the Shapiro–Wilk test showed that 12 of the 55 dependent variables may not fulfill the normality assumption. Therefore, we additionally calculated Mann–Whitney U tests for these variables. The results remained largely the same with two exceptions: First, the mean difference in the subtest Identifying Emotions was no longer significant before controlling for multiple testing. Second, the mean difference in the composite score of language skills was no longer significant after controlling for multiple testing. Furthermore, we found that the Levene’s test was significant for fewer than 10 of the dependent variables, indicating unequal variances. Thus, Welch’s t tests were additionally performed. The results were identical to those obtained from the independent-samples t tests. |
| 3 | To control for effects of intelligence, we repeated the independent-samples t tests for the developmental functions with a non-autistic control sample matched by age, sex, and intelligence (Full-Scale IQ). The pattern of results remained largely the same, showing lower group mean values for the autistic participants than for the control sample in the domains psychomotor skills, social–emotional skills, language skills, and participation during testing (see Table S2 in the Supplemental Material for full results). These differences hold when correcting for multiple testing in the domain of psychomotor skills. These post hoc analyses underscore the robustness of our findings. |
References
- Akshoomoff, Natacha. 2006. Use of the Mullen Scales of Early Learning for the Assessment of Young Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Child Neuropsychology 12: 269–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. 2013. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, Anjana N., Rebecca J. Landa, and James C. (Cole) Galloway. 2011. Current Perspectives on Motor Functioning in Infants, Children, and Adults with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Physical Therapy 91: 1116–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucher, Jill. 2012. Research Review: Structural Language in Autistic Spectrum Disorder—Characteristics and Causes. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 53: 219–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, Sonya E. 2014. Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD): State of the States of Services and Supports for People with ASD. Washington, DC: L & M Policy Research. [Google Scholar]
- Brignell, Amanda, Angela T. Morgan, Susan Woolfenden, Felicity Klopper, Tamara May, Vanessa Sarkozy, and Katrina Williams. 2018. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Prognosis of Language Outcomes for Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Autism & Developmental Language Impairments 3: 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, Heather M., Janis Oram-Cardy, and Andrew Johnson. 2013. A Meta-Analysis of the Reading Comprehension Skills of Individuals on the Autism Spectrum. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 43: 932–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Ru Ying, Amanda L. Richdale, Mirko Uljarević, Cheryl Dissanayake, and Andrea C. Samson. 2018. Emotion Regulation in Autism Spectrum Disorder: Where We Are and Where We Need to Go. Autism Research 11: 962–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnine, Douglas W., Jerry Silbert, Edward J. Kame’enui, and Sara G. Tarver. 2010. Direct Instruction Reading, 5th ed. Columbus: Merrill. [Google Scholar]
- Charman, Tony, Andrew Pickles, Emily Simonoff, Susie Chandler, Tom Loucas, and Gillian Baird. 2011. IQ in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders: Data from the Special Needs and Autism Project (SNAP). Psychological Medicine 41: 619–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Hsu-Min, and Yueh-Hsien Lin. 2007. Mathematical Ability of Students with Asperger Syndrome and High-Functioning Autism: A Review of Literature. Autism 11: 547–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibralic, Sara, Jane Kohlhoff, Nancy Wallace, Catherine McMahon, and Valsamma Eapen. 2019. A Systematic Review of Emotion Regulation in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders 68: 101422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, Jacob. 1988. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed. Hillsdale: Erlbaum. [Google Scholar]
- Coll, Sarah-Maude, Nicholas E. V. Foster, Alexa Meilleur, Simona M. Brambati, and Krista L. Hyde. 2020. Sensorimotor Skills in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Meta-Analysis. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders 76: 101570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo-Dougovito, Andrew M., and Martin E. Block. 2019. Fundamental Motor Skill Interventions for Children and Adolescents on the Autism Spectrum: A Literature Review. Review Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 6: 159–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coolican, Jamesie, Susan E. Bryson, and Lonnie Zwaigenbaum. 2008. Brief Report: Data on the Stanford–Binet Intelligence Scales (5th Ed.) in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 38: 190–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vries, Marieke, and Hilde M. Geurts. 2012. Cognitive Flexibility in ASD; Task Switching with Emotional Faces. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 42: 2558–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetriou, Eleni A., Amit Lampit, Daniel S. Quintana, Sharon L. Naismith, Yun J.C. Song, Julia E. Pye, Ian Hickie, and Adam J. Guastella. 2018. Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Meta-Analysis of Executive Function. Molecular Psychiatry 23: 1198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyck, Murray J., Jan P. Piek, David Hay, Leigh Smith, and Joachim Hallmayer. 2006. Are Abilities Abnormally Interdependent in Children With Autism? Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology 35: 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dynia, Jaclyn M., Allison Bean, Laura M. Justice, and Joan N. Kaderavek. 2019. Phonological Awareness Emergence in Preschool Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Autism & Developmental Language Impairments 4: 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, Michael, Mario Gollwitzer, and Manfred Schmitt. 2017. Statistik und Forschungsmethoden [Statistics and Research Methods], 5th ed. Weinheim: Beltz. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis Weismer, Susan, Catherine Lord, and Amy Esler. 2010. Early Language Patterns of Toddlers on the Autism Spectrum Compared to Toddlers with Developmental Delay. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 40: 1259–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, S. Hossein, Kimberly A. Aldinger, Paul Ashwood, Margaret L. Bauman, Charles D. Blaha, Gene J. Blatt, Abha Chauhan, Ved Chauhan, Stephen R. Dager, Price E. Dickson, and et al. 2012. Consensus Paper: Pathological Role of the Cerebellum in Autism. The Cerebellum 11: 777–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, Franz, Edgar Erdfelder, Albert-Georg Lang, and Axel Buchner. 2007. G*Power 3: A Flexible Statistical Power Analysis Program for the Social, Behavioral, and Biomedical Sciences. Behavior Research Methods 39: 175–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnegan, Elizabeth, and Amy L. Accardo. 2018. Written Expression in Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Meta-Analysis. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 48: 868–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, Alexandra, Spyridon-Georgios Soulis, and Danai Rapti. 2018. Motivation in Mathematics of High Functioning Students With Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Journal of Psychology Research 8: 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Grieder, Silvia, and Alexander Grob. 2020. Exploratory Factor Analyses of the Intelligence and Development Scales–2: Implications for Theory and Practice. Assessment 27: 1853–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grob, Alexander, and Priska Hagmann-von Arx. 2018a. Intelligence and Development Scales–2 (IDS-2). Intelligenz- und Entwicklungsskalen für Kinder und Jugendliche [Intelligence and Development Scales for Children and Adolescents]. Bern: Hogrefe. [Google Scholar]
- Grob, Alexander, and Priska Hagmann-von Arx. 2018b. Intelligence and Development Scales–2 (IDS-2). Intelligenz- und Entwicklungsskalen für Kinder und Jugendliche. Manual zu Theorie, Interpretation und Gütekriterien [Intelligence and Development Scales for Children and Adolescents. Manual on Theory, Interpretation and Psychometric Criteria]. Bern: Hogrefe. [Google Scholar]
- Grob, Alexander, Priska Hagmann-von Arx, Aleksandra Jaworowska, Anna Matczak, and Diana Fecenec. 2019. Intelligence and Development Scales-2. Inteligencji i Rozwoju Dla Dzieci i Młodzieży [Intelligence and Development Scales for Children and Adolescents]. Warsaw: Hogrefe. [Google Scholar]
- Grob, Alexander, Priska Hagmann-von Arx, Anna Barnett, Nichola Stuart, and Serena Vanzan. 2021. Intelligence and Development Scales-2 (IDS-2). Intelligence and Development Scales for Children and Adolescents. Oxford: Hogrefe. [Google Scholar]
- Grob, Alexander, Priska Hagmann-von Arx, Rosa Ferri, Monica Rea, and Maria Casagrande. 2022. Intelligence and Development Scales-2. Scale Di Intelligenza e Sviluppo per Bambini e Adolescenti [Intelligence and Development Scales for Children and Adolescents]. Florence: Hogrefe. [Google Scholar]
- Grob, Alexander, Priska Hagmann-von Arx, Selma A. J. Ruiter, Marieke E. Timmerman, and Linda Visser. 2018. Intelligence and Development Scales–2 (IDS-2). Intelligentie- En Ontwikkelingsschalen Voor Kinderen En Jongeren. [Intelligence and Development Scales for Children and Adolescents]. Amsterdam: Hogrefe. [Google Scholar]
- Grondhuis, Sabrina N., Luc Lecavalier, L. Eugene Arnold, Benjamin L. Handen, Lawrence Scahill, Christopher J. McDougle, and Michael G. Aman. 2018. Differences in Verbal and Nonverbal IQ Test Scores in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders 49: 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannant, Penelope, Teresa Tavassoli, and Sarah Cassidy. 2016. The Role of Sensorimotor Difficulties in Autism Spectrum Conditions. Frontiers in Neurology 7: 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Happé, Francesca, and Uta Frith. 2020. Annual Research Review: Looking Back to Look Forward—Changes in the Concept of Autism and Implications for Future Research. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 61: 218–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, Madeline B., Alex Martin, and Gregory L. Wallace. 2010. Facial Emotion Recognition in Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Review of Behavioral and Neuroimaging Studies. Neuropsychology Review 20: 290–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, Elisabeth L. 2004. Executive Dysfunction in Autism. Trends in Cognitive Sciences 8: 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Daniel E., Kosuke Imai, Gary King, and Elizabeth A. Stuart. 2011. MatchIt: Nonparametric Preprocessing for Parametric Causal Inference. Journal of Statistical Software 42: 1–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hommel, Gerhard. 1988. A Stagewise Rejective Multiple Test Procedure Based on a Modified Bonferroni Test. Biometrika 75: 383–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlin, Patricia, and Philippa Moss. 2012. Adults with Autism Spectrum Disorders. The Canadian Journal of Psychiatry 57: 275–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudry, Kristelle, Kathy Leadbitter, Kathryn Temple, Vicky Slonims, Helen McConachie, Catherine Aldred, Patricia Howlin, Tony Charman, and the PACT Consortium. 2010. Preschoolers with Autism Show Greater Impairment in Receptive Compared with Expressive Language Abilities. International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders 45: 681–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idring, Selma, Michael Lundberg, Harald Sturm, Christina Dalman, Clara Gumpert, Dheeraj Rai, Brian K. Lee, and Cecilia Magnusson. 2015. Changes in Prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorders in 2001–2011: Findings from the Stockholm Youth Cohort. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 45: 1766–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, Laudan B., Shantel E. Meek, and Sharman Ober-Reynolds. 2012. Emotion Regulation in the Context of Frustration in Children with High Functioning Autism and Their Typical Peers. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 53: 1250–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, Catherine R. G., Andrew Pickles, Milena Falcaro, Anita J. S. Marsden, Francesca Happé, Sophie K. Scott, Disa Sauter, Jenifer Tregay, Rebecca J. Phillips, Gillian Baird, and et al. 2011. A Multimodal Approach to Emotion Recognition Ability in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 52: 275–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keen, Deb. 2009. Engagement of Children with Autism in Learning. Australasian Journal of Special Education 33: 130–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keen, Deb, Amanda Webster, and Greta Ridley. 2016. How Well Are Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder Doing Academically at School? An Overview of the Literature. Autism 20: 276–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjellmer, Liselotte, Elisabeth Fernell, Christopher Gillberg, and Fritjof Norrelgen. 2018. Speech and Language Profiles in 4- to 6-Year-Old Children with Early Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder without Intellectual Disability. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment 14: 2415–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantareas, M. Mary, and Kelly Stewart. 2006. Affect Regulation and Temperament in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 36: 143–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurth, Jennifer A., and Ann M. Mastergeorge. 2010. Academic and Cognitive Profiles of Students with Autism: Implications for Classroom Practice and Placement. International Journal of Special Education 25: 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kwok, Elaine Y. L., Heather M. Brown, Rachael E. Smyth, and Janis Oram Cardy. 2015. Meta-Analysis of Receptive and Expressive Language Skills in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders 9: 202–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, Florence Yik Nam, Jacqueline Sin, Caitlin Dawson, Jia Hoong Ong, Chen Zhao, Anamarija Veić, and Fang Liu. 2022. Emotion Recognition across Visual and Auditory Modalities in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Developmental Review 63: 101000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyfer, Ovsanna T., Susan E. Folstein, Susan Bacalman, Naomi O. Davis, Elena Dinh, Jubel Morgan, Helen Tager-Flusberg, and Janet E. Lainhart. 2006. Comorbid Psychiatric Disorders in Children with Autism: Interview Development and Rates of Disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 36: 849–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libertus, Klaus, Kelly A. Sheperd, Samuel W. Ross, and Rebecca J. Landa. 2014. Limited Fine Motor and Grasping Skills in 6-Month-Old Infants at High Risk for Autism. Child Development 85: 2218–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lienert, Gustav A., and Ulrich Raatz. 1998. Testaufbau und Testanalyse [Test Design and Test Analysis]. Weinheim: Beltz. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Ting, and Casey M. Breslin. 2013. Fine and Gross Motor Performance of the MABC-2 by Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder and Typically Developing Children. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders 7: 1244–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodi-Smith, Jennifer, Jonathan D. Rodgers, Sara A. Cunningham, Christopher Lopata, and Marcus L. Thomeer. 2019. Meta-Analysis of Big Five Personality Traits in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Autism 23: 556–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyster, Rhiannon, Kristina Lopez, and Catherine Lord. 2007. Characterizing Communicative Development in Children Referred for Autism Spectrum Disorders Using the MacArthur-Bates Communicative Development Inventory (CDI). Journal of Child Language 34: 623–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, Megan, Catherine Lord, and Dale A. Ulrich. 2013a. The Relationship of Motor Skills and Adaptive Behavior Skills in Young Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders 7: 1383–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, Megan, Catherine Lord, and Dale A. Ulrich. 2013b. The Relationship of Motor Skills and Social Communicative Skills in School-Aged Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Adapted Physical Activity Quarterly 30: 271–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maenner, Matthew J., Kelly A. Shaw, Jon Baio, Anita Washington, Mary Patrick, Monica DiRienzo, Deborah L. Christensen, Lisa D. Wiggins, Sydney Pettygrove, Jennifer G. Andrews, and et al. 2020. Prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder among Children Aged 8 Years—Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2016. MMWR Surveillance Summaries 69: 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbaum, David E., Michael Stevens, Eric Rosenberg, Max Wiznitzer, Mitchell Steinschneider, Saul R. Korey, Pauline Filipek, Isabelle Rapin, and Saul R. Korey. 2006. Sensorimotor Performance in School-Age Children with Autism, Developmental Language Disorder, or Low IQ. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 48: 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manicolo, Olivia, Mark Brotzmann, Priska Hagmann-von Arx, Alexander Grob, and Peter Weber. 2019. Gait in Children with Infantile/Atypical Autism: Age-Dependent Decrease in Gait Variability and Associations with Motor Skills. European Journal of Paediatric Neurology 23: 117–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayes, Susan Dickerson, and Susan L. Calhoun. 2003a. Analysis of WISC-III, Stanford-Binet:IV, and Academic Achievement Test Scores in Children with Autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 33: 329–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayes, Susan Dickerson, and Susan L. Calhoun. 2003b. Ability Profiles in Children with Autism: Influence of Age and IQ. Autism 7: 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazefsky, Carla A., Xenia Borue, Taylor N. Day, and Nancy J. Minshew. 2014. Emotion Regulation Patterns in Adolescents with High-Functioning Autism Spectrum Disorder: Comparison to Typically Developing Adolescents and Association with Psychiatric Symptoms. Autism Research 7: 344–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, Christine Sandra, Priska Hagmann-von Arx, and Alexander Grob. 2009. Die Intelligence and Development Scale Sozial-Emotionale Kompetenz (IDS-SEK): Psychometrische Eigenschaften eines Tests zur Erfassung sozial-emotionaler Fähigkeiten [The Intelligence and Development Scale Social-Emotional Competence (IDS-SEK): Psychometric properties of a test to assess social-emotional skills]. Diagnostica 55: 234–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, Xue, Michael Brimacombe, and George C. Wagner. 2007. Prevalence of Motor Impairment in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Brain and Development 29: 565–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, Shelley, Janis Oram Cardy, and Lonnie Zwaigenbaum. 2011. Differentiating Autism Spectrum Disorder from Other Developmental Delays In The First Two Years Of Life. Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews 17: 130–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, Shelley, Jessica Brian, Lonnie Zwaigenbaum, Wendy Roberts, Peter Szatmari, Isabel Smith, and Susan Bryson. 2006. Early Language and Communication Development of Infants Later Diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Journal of Developmental & Behavioral Pediatrics 27: S69–S78. [Google Scholar]
- Miyake, Akira, and Naomi P. Friedman. 2012. The Nature and Organization of Individual Differences in Executive Functions: Four General Conclusions. Current Directions in Psychological Science 21: 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, Akira, Naomi P. Friedman, Michael J. Emerson, Alexander H. Witzki, Amy Howerter, and Tor D. Wager. 2000. The Unity and Diversity of Executive Functions and Their Contributions to Complex ‘Frontal Lobe’ Tasks: A Latent Variable Analysis. Cognitive Psychology 41: 49–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostofsky, Stewart H., Melanie P. Burgess, and Jennifer C. Gidley Larson. 2007. Increased Motor Cortex White Matter Volume Predicts Motor Impairment in Autism. Brain 130: 2117–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostofsky, Stewart H., Stephanie K. Powell, Daniel J. Simmonds, Melissa C. Goldberg, Brian Caffo, and James J. Pekar. 2009. Decreased Connectivity and Cerebellar Activity in Autism during Motor Task Performance. Brain 132: 2413–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muth, Anne, Johannes Hönekopp, and Christine M. Falter. 2014. Visuo-Spatial Performance in Autism: A Meta-Analysis. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 44: 3245–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nader, Anne-Marie, Valérie Courchesne, Michelle Dawson, and Isabelle Soulières. 2016. Does WISC-IV Underestimate the Intelligence of Autistic Children? Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 46: 1582–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, Emese, Louise Prentice, and Tess Wakeling. 2021. Atypical Facial Emotion Recognition in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders: Exploratory Analysis on the Role of Task Demands. Perception 50: 819–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebel, Mary Beth, Suresh E. Joel, John Muschelli, Anita D. Barber, Brian S. Caffo, James J. Pekar, and Stewart H. Mostofsky. 2014. Disruption of Functional Organization within the Primary Motor Cortex in Children with Autism. Human Brain Mapping 35: 567–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, Katherine Simone Caires, Déborah Ebert Fontes, Egmar Longo, Hércules Ribeiro Leite, and Ana Cristina Resende Camargos. 2021. Motor Skills Are Associated with Participation of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 21: 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveras-Rentas, Rafael E., Lauren Kenworthy, Richard B. Roberson, Alex Martin, and Gregory L. Wallace. 2012. WISC-IV Profile in High-Functioning Autism Spectrum Disorders: Impaired Processing Speed Is Associated with Increased Autism Communication Symptoms and Decreased Adaptive Communication Abilities. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 42: 655–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, Bruce F., and Sally Ozonoff. 1996. Executive Functions and Developmental Psychopathology. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 37: 51–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petermann, Franz. 2008. Movement Assessment Battery for Children, 2nd ed. Frankfurt: Pearson Assessment. [Google Scholar]
- Provost, Beth, Brian R. Lopez, and Sandra Heimerl. 2007. A Comparison of Motor Delays in Young Children: Autism Spectrum Disorder, Developmental Delay, and Developmental Concerns. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 37: 321–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. 2021. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing (Version 4.0.3) [Computer Software]. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 13 February 2021).
- Rosset, Delphine B., Cécilie Rondan, David Da Fonseca, Andreia Santos, Brigitte Assouline, and Christine Deruelle. 2008. Typical Emotion Processing for Cartoon but Not for Real Faces in Children with Autistic Spectrum Disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 38: 919–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, Ginny, William Mandy, Daisy Elliott, Rhianna White, Tom Pittwood, and Tamsin Ford. 2019. Selection Bias on Intellectual Ability in Autism Research: A Cross-Sectional Review and Meta-Analysis. Molecular Autism 10: 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, Fernando, Gillian Baird, Susie Chandler, Evelin Tseng, Tony O’sullivan, Patricia Howlin, Andrew Pickles, and Emily Simonoff. 2015. Co-Occurring Psychiatric Disorders in Preschool and Elementary School-Aged Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 45: 2283–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomone, Erica, Daniela Bulgarelli, Evelyne Thommen, Emanuelle Rossini, and Paola Molina. 2019. Role of Age and IQ in Emotion Understanding in Autism Spectrum Disorder: Implications for Educational Interventions. European Journal of Special Needs Education 34: 383–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Atzert, Lothar, and Manfred Amelang. 2012. Psychologische Diagnostik [Psychological Assessment], 5th ed. Berlin: Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, W. Joel, and Kevin S. McGrew. 2018. The Cattell–Horn–Carroll Theory of Cognitive Abilities. In Contemporary Intellectual Assessment: Theories, Tests, and Issues, 4th ed. Edited by Dawn P. Flanagan and Erin M. McDonough. New York: Guilford Press, pp. 73–163. [Google Scholar]
- Shanok, Nathaniel A., Nancy Aaron Jones, and Nikola N. Lucas. 2019. The Nature of Facial Emotion Recognition Impairments in Children on the Autism Spectrum. Child Psychiatry & Human Development 50: 661–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siaperas, Panagiotis, Howard A. Ring, Catherine J. McAllister, Sheila Henderson, Anna Barnett, Peter Watson, and Anthony J. Holland. 2012. Atypical Movement Performance and Sensory Integration in Asperger’s Syndrome. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 42: 718–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, Pauline, Walter Zahorodny, Bo Peng, Soyeon Kim, Nisha Jani, William Halperin, and Michael Brimacombe. 2012. The Association of Autism Diagnosis with Socioeconomic Status. Autism 16: 201–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titeca, Daisy, Herbert Roeyers, and Annemie Desoete. 2017. Early Numerical Competencies in 4- and 5-Year-Old Children with Autism Spectrum. Focus on Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities 32: 279–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, Dominic A., and Elina Birmingham. 2016. Are Emotion Recognition Abilities Related to Everyday Social Functioning in ASD? A Meta-Analysis. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders 32: 24–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troyb, Eva, Alyssa Orinstein, Katherine Tyson, Molly Helt, Inge-Marie Eigsti, Michael Stevens, and Deborah Fein. 2014. Academic Abilities in Children and Adolescents with a History of Autism Spectrum Disorders Who Have Achieved Optimal Outcomes. Autism 18: 233–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Meter, Karla C., Lasse E. Christiansen, Lora D. Delwiche, Rahman Azari, Tim E. Carpenter, and Irva Hertz-Picciotto. 2010. Geographic Distribution of Autism in California: A Retrospective Birth Cohort Analysis. Autism Research 3: 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volden, Joanne, Isabel M. Smith, Peter Szatmari, Susan Bryson, Eric Fombonne, Pat Mirenda, Wendy Roberts, Tracy Vaillancourt, Charlotte Waddell, Lonnie Zwaigenbaum, and et al. 2011. Using the Preschool Language Scale, Fourth Edition to Characterize Language in Preschoolers with Autism Spectrum Disorders. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology 20: 200–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, Susan Williams, Lawrence Scahill, Ami Klin, Kathleen Koenig, and Fred R. Volkmar. 2007. Educational Placements and Service Use Patterns of Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 37: 1403–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. 2016. International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (10th Rev.). Geneva: World Health Organization. Available online: https://icd.who.int/browse10/2019/en (accessed on 5 November 2022).
- World Health Organization. 2018. International Classification of Diseases for Mortality and Morbidity Statistics (11th Rev.). Geneva: World Health Organization. Available online: https://icd.who.int/browse11/l-m/en (accessed on 6 January 2022).
- Yerys, Benjamin E., Gregory L. Wallace, Jennifer L. Sokoloff, Devon A. Shook, Joette D. James, and Lauren Kenworthy. 2009. Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Symptoms Moderate Cognition and Behavior in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Autism Research 2: 322–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, Michael K. 2022. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Facial Emotion Recognition in Autism Spectrum Disorder: The Specificity of Deficits and the Role of Task Characteristics. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews 133: 104518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajic, Matthew C., Emily J. Solari, Ryan P. Grimm, Nancy S. McIntyre, and Peter C. Mundy. 2020. Relationships between Reading Profiles and Narrative Writing Abilities in School-Age Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Reading and Writing 33: 1531–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).