Abstract
Recently, there has been a sharp increase in the production of smart devices and related networks, and consequently the Internet of Things. One concern for these devices, which is constantly becoming more critical, is their protection against attacks due to their heterogeneity and the absence of international standards to achieve this goal. Thus, these devices are becoming vulnerable, with many of them not even showing any signs of malfunction or suspicious behavior. The aim of the present work is to introduce a circuit that is connected in series with the power supply of a smart device, specifically an IP camera, which allows analysis of its behavior. The detection circuit operates in real time (real-time detection), sampling the supply current of the device, processing the sampled values and finally indicating any detection of abnormal activities, based on a comparison to normal operation conditions. By utilizing techniques borrowed by simple power analysis side channel attack, it was possible to detect deviations from the expected operation of the IP camera, as they occurred due to intentional attacks, quarantining the monitored device from the rest of the network. The circuit is analyzed and a low-cost implementation (under 5US$) is illustrated. It achieved 100% success in the test results, showing excellent performance in intrusion detection.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, there is a rapid growth of the Internet-of-Things (IoT) market, as analysts and statisticians have predicted. At the same time, new issues are emerging from the growing number of IoT users, as these Internet-connected devices process, generate and exchange significant volumes of data during their operation. In addition, they create communication between devices and systems, and their users, through different types of networks and different platforms, but they are interconnected in a shared, central and flexible network. IoT devices have been used in various applications, such as smart vehicles, environmental monitoring, personal mobile devices and healthcare, which helps with increasing the volume and the variety of data, including sensitive data such as personal information, managed by these devices and connected systems [1]. Such information (including sensitive data) is becoming susceptible to attempts at stealing, manipulating or destroying data by malicious Internet users (hackers). However, there are other cases in which attempts are made to obstruct the provision of services with the ultimate goal of ransom from the victim, or even to harm the service provider on behalf of a third party. In these “smart devices”, there is a steady increase in attacks, and especially those characterized as advanced persistent threats (APTs) [2], as they are considered the most important threat to the security of information and the systems that support them. Since an IoT device is designed for a single (and usually simple) purpose, thereby limiting the requirements for high processing power and memory, manufacturers and researchers are struggling to meet security needs. Malicious users take advantage of the vulnerabilities of such devices.
A wide range of sophisticated malware is increasingly being identified by computer security technicians and researchers. They must therefore detect and categorize the abnormalities associated with such malware, in order to choose the appropriate method to confront them. These anomalies present themselves as a wide range of potential events, from network abuse (DoS, DDoS attacks, network scans) to unusual network user behavior and even to new, unknown events, and this is a primary challenge for automated detection and anomaly categorization. Specifically, botnets are a set of infected nodes (bots) controlled by command and control (C&C) servers owned by attackers. The frequency of the occurrence of this malware (botnets) and its level of complexity are increasing year after year. This type of malware can have severe adverse effects, including the loss of important data and even tangible assets, such as wealth or ownership titles. Examples of popular IoT malware include the Mirai distributed denial of service (DDoS) [3] worm and VPN Filter, the latter of which is armed with powerful payloads, including some intended for data breach, theft of credentials, etc. This has led to sharp increases in the frequency, size and complexity of attacks in recent years. At the same time, DDoS attacks are becoming more and more complex and sophisticated. However, it has been observed that over time they become cheaper and easier to execute, with hackers taking advantage of the large number of the insecure devices connected to the Internet, thereby critically expanding the available attack surface. The aforementioned types of attacks exist in the landscape of threats for many years, allowing hackers to gain control of devices for directing an orchestrated service request to the targeted victim, in order to eventually make it unavailable. The threat of these attacks causes problems for both business and individual users who are prevented from accessing the digital services they need. The problem has been exacerbated by the outbreak of the global COVID-19 pandemic, which has resulted in people relying more on digital services than ever before [4,5]. One notable fact is that DDoS attacks are now easier than ever, even for hackers with less technical skills. Researchers point out that hackers offer DDoS services starting at an average cost of just a few dollars for a disruption that can last just a few minutes, and DDoS attacks lasting longer can be easily purchased for more money. One of the reasons DDoS attacks have become cheaper and easier to execute is the proliferation of IoT devices. Many IoT products come with default usernames and passwords, which means that it is easy for hackers to control them. Owners of the devices may not realize that they have been compromised and that the traffic they generate is being used to attack the hackers’ targets. DDoS rental services are very popular, as not only can they provide a simple way for cybercriminals to make money, but at the same time the nature of the service makes it difficult to identify the hackers behind them. Organizations can protect themselves from the potential impact of a DDoS attack by being aware of their most critical assets and preparing contingency plans in the event of a DDoS mitigation service failing. Vendors and individual users can play equally important roles in reducing the likelihood of DDoS attacks by avoiding the use of default passwords, making it difficult for cybercriminals to break into devices and make them parts of a botnet. Characteristic is the publication of the company Arbor Networks, which shows a continuous escalation in both the size and frequency of attacks [6], while in another published report [7] it is presented that routers and cameras were the most infected devices, accounting for 75% and 15% of IoT attacks respectively. Therefore, the question of the security of information transmitted via the Internet remains unanswered, with industry and academia increasingly focusing on developing security solutions for IoT devices. Review articles, books and numerous research articles have been published for the detection of anomalies [8,9,10,11], with the very first of them being released almost 40 years ago [12]. The approach (anomalies detection) from some studies is becoming more comprehensive [13,14], while others report more specialized methods for detecting network anomalies, such as PCA (principle component analysis) [15,16], wavelet analysis [17,18], Markov models [19], clustering [20], histograms [21] and entropy [22,23]. Systems that use techniques based on the characteristics of the attacks or their signatures (misuse-based techniques or signature-based techniques) are not able to cope against modern malware. In [24,25] there are deficiencies in anomaly detection, while [26] requires knowledge of the patterns in advance, as they can detect known attacks, but they are still vulnerable to unknown patterns. As a result, the existing signature-focused proposals are unable to deal with unknown attacks, attacks based on new techniques and zero-day attacks (0 day attacks) [27]. In addition to the above, in order to detect a specific attack, a rule needs to be released after it is first created, tested and developed, over a long period of time.
Other research suggests the IoT Botnet Detection System (BDS) or the Network Intrusion Detection System (IDS) [3,28,29]. However, applying these techniques to IoT is difficult due to their particular characteristics, such as constrained-resource devices, specific protocol stacks and standards. Some works [30,31,32,33] suggest and apply machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) techniques to identify unknown botnet attacks, whereas in [34] malware detection systems based on power measurements of mobile systems were proposed. The effort nowadays, by a large part of the scientific community, to find a unified method for detecting network anomalies is remarkable; however, the problem remains unsolved. Given the fact that there are several network anomaly detection techniques that offer considerable solutions, a different approach is needed as a potentially complementary solution to the existing ones.
The approach we propose is based on physically measurable features other than communicated or stored data, such as supply current for detecting abnormalities, which is caused in an IoT device by attempts at controlling the device and adding it to a botnet. The above approach is an effective method for detecting distributed denial of service attacks, as shown by [35,36,37]. The article presents a novel small-area and low-cost circuit for detecting intrusions into an IP camera and monitoring side effects, such as power dissipation. Compared to previous works, this is the first that presents results from a custom-made prototype and not a proof-of-concept circuit embedded on a development board. Based on simple power analysis side-channel attack (SCA) techniques, this work is successfully associated with any increase in network traffic and computer load and excessive idle power resulting from a malicious attempt to access the IoT device. The applicability of this approach targets IP cameras currently, which are the most common targets among the IoT devices and suffered the most DDoS attacks during the last few years. The contribution of this work is the introduction of a novel circuit that is an effective low-cost solution for protecting form botnets the IP cameras and potentially regular IoT devices appropriate for exploitation by edge computing, which is presented for the first time in the international literature. Considering that most IoT devices are sold without any embedded security mechanisms, the proposed circuit offers a generic solution for protecting IP cameras for as low as a small portion of the camera’s cost.
This article is an extension of previous work [37] and presents an economical and effective solution for security in IoT devices, taking advantage of the SCA approach [38] for security reasons (white hacking). Initially, it implements SCA to monitor the power outage of a targeted IoT device, captures its electrical behavior and converts it to data. The proposed solution provides real-time power analysis to detect suspicious behavior of devices connected to the Internet. The aforementioned advantages of the techniques used in this project are combined with the exploitation of the physical characteristics of IoT devices, enclosed in a small circuit, to introduce a new method for intrusion detection on an IoT device, without prior rule knowledge and without the need for an IDS connection. Specifically, the innovation lies in the fact that an external circuit is capable of detecting intrusion attempts without prior knowledge of the monitored IoT device or its functionality. In addition, it is a low-cost, compact and computationally fair solution for enhancing security on IP cameras and potentially household IoT devices.
In summary, the main contributions of this work are:
- The first implementation of a low-cost, small-sized integrated system for monitoring external IoT cognitive devices.
- Improved security for IP cameras against DoS, DDoS and similar attacks.
- It imitates the principles of biometrics that allow the expansion of data collected by external IDS (when connected), similar to that of industrial condition monitoring.
- It is agnostic of network rules or virus patterns, offering stronger confrontation with attacks of unknown nature.
- It is the first use of a spike-detection circuit for enhancing the security of an IP camera, in doing so adopting simple power analysis SCA.
The paper is structured as follows. In Section 2, the proposed approach of the IP camera intrusion detection circuit is presented and then the various experiments performed using the proposed device are described. Section 3 provides the results from the practical application of the experimental setup. Finally, Section 4 completes the work by stating the conclusions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Concept of a DoS Detection Circuit
First of all, let us point out that the operation of the proposed device is based on the well-known technique of simple power analysis SCA, analyzing the behavior of the target device (IP camera) through the monitoring of current intensity. The delimitation of the normal behavior of the device by the administrator is something that must be done and achieved by setting rules for normal and abnormal behavior. These devices, although they are known as "smart," have very limited features, thereby making the modeling process even easier. The assumption for the development of the proposed circuit is that each device has its own physical characteristics, consuming an easy-to-determine amount of power under normal operation. Thus, in the case of an attack on the IP camera, there is a change in the behavior of the device (different operating profile), due to the excessive use of communication and processing resources. The operation of the detection circuit is performed in real time (real-time detection), collecting the information by reading the values of the current of the device and processing it in real time for the detection of abnormal activities.
2.2. Proposed Setup
The DoS attack detection circuit is a standalone circuit, specifically a custom-made board embedding a microcontroller, input/output ports and ground, being that it is properly programmed and placed between the target device and the power supply. The proposed circuit is a prototype of a product and differentiates from other proposed in similar works [35,36,37], in which commercial development boards were used for proof of concept. Its logic is based on the current deviations of the target device in relation to its normal operation. A 1 Ohm resistor was inserted between the first and second measurements, allowing us to calculate the current:
where and are the two reference voltages, as depicted in Figure 1 and R is the 1 Ohm resistor. The layout of the circuit is shown in the figure.
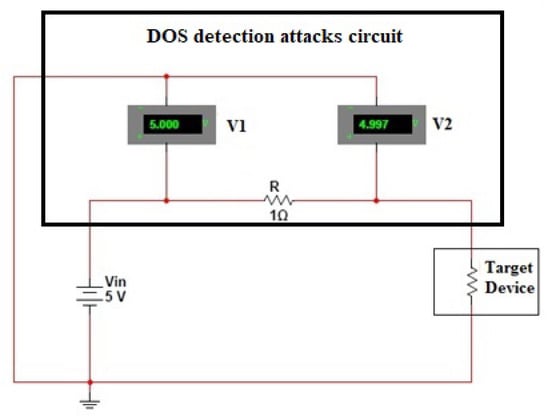
Figure 1.
The layout of the circuit.
Initially, the design was developed on a platform, for the creation of the initial programming through ISP and specifically for the ATmega328P-AU microcontroller. Then the design with the following materials was implemented on a printed circuit board (PCB). The aforementioned ATmega328P-AU microcontroller is a low-power 8-bit CMOS MCU based on AVR-enhanced RISC architecture, allowing the system designer to optimize power consumption versus processing speed. We also used a two-level copper board and a 16-MHz crystal oscillator; one resistor, 0805 SMD 1 kOhm; one resistor, 0805 SMD 1 Ohm; two ceramic capacitors, 0805 SMD, 22 pF and 100 nF; for the restart of the circuit we used a Tact Switch SMD 4.5 × 4.5 mm 3.8 mm 4 pin. Finally, two pin headers, 1 × 3 female and 1 × 6 female right angle were used for the reception of the terminals. In addition, an FTDI module was added for better functionality, which was set to 5 Volts.
The proposed circuit is of low cost and is appropriate for IP cameras, which cost a significant amount of money but do not have a security mechanism embedded. Specifically, the estimated manufacturing cost is estimated to be under USD 5, since this is the cost of the previously described materials. Considering that the IP cameras are the most common targets of botnets and their cost is significantly higher than the cost of the proposed circuit, it is understood that there is no need for sophisticated security mechanisms (hardware or software) in homes or small business; no special skills are required from the owners of IP cameras. A potential expansion of this work is the integration of the circuit using very large scale integration (VLSI) technology and its adoption from the IP cameras’ vendors.
The digital design of the circuit is analyzed in Figure 2. The two levels of the intrusion detection and prevention circuit board are captured through the PCB drawing in Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5, while the final result of the intrusion detection and prevention circuit is shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7.
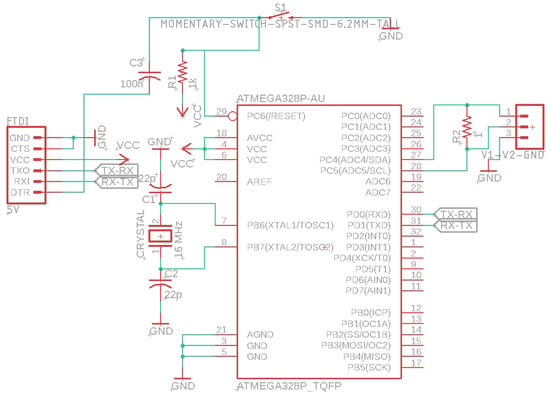
Figure 2.
Digital circuit schematic.
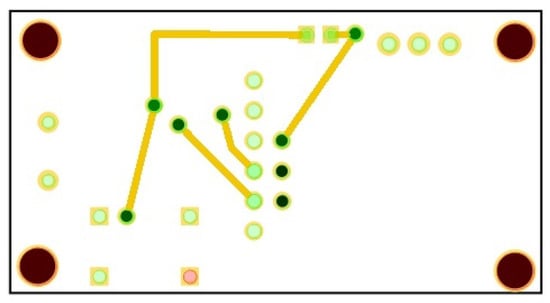
Figure 3.
Schematic of the first level of circuit board.
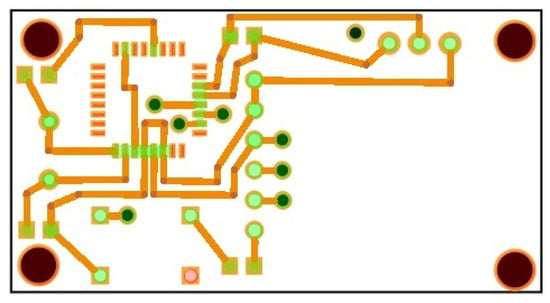
Figure 4.
Schematic of the second level of circuit board.
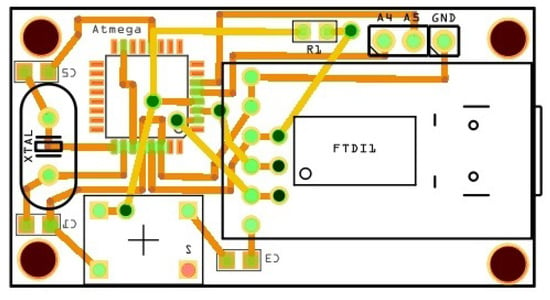
Figure 5.
Schematic of the two-level board with the FTDI.
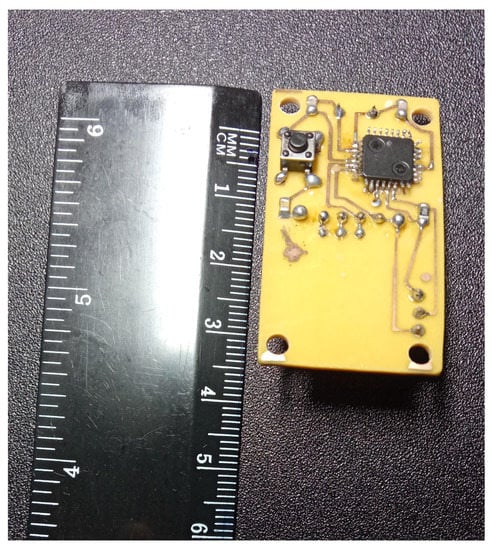
Figure 6.
The first level of the intrusion detection and prevention circuit.
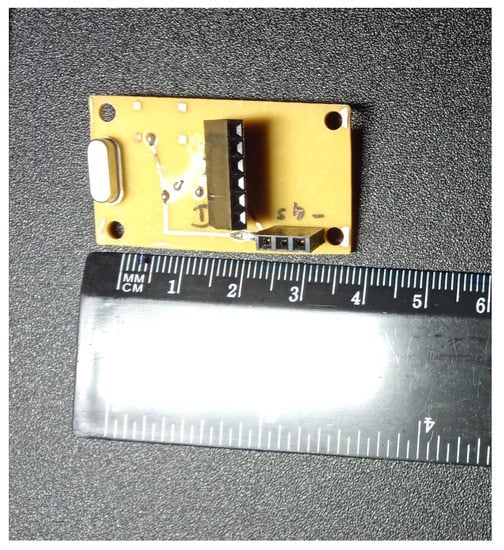
Figure 7.
The second level of the intrusion detection and prevention circuit.
In addition, to smooth out our measurements and avoid noise (spikes) that could have been created by other factors, we applied a filter when programming our software. This signal smoothing technique is called the moving average. From the raw data sequence [, , …, ], we created a corresponding smoothed data sequence. The smoothed point is the mean of an odd number 2n + 1 (n = 1, 2, 3, …) of the raw data sequences , , …, , , , …, , , i.e.,:
2.3. Experiments
In this Subsection, we present the experiments that were performed in order to evaluate our approach. Specifically, we implemented a composite IP camera as a target device, which was based on a Raspberry Pi (RPI) 3 B + micro-controller and an on board 8MP camera. In order to have a realistic display of incidents during a day (24 h), the above device (IP camera) was placed in the main entrance of an indoor house. Then, the proposed circuit was connected in between the power plug of the IP camera and the power supply offered at the home. Using a mobile phone, three DoS attacks were carried out during the day against the targeted IP camera and the results are shown bellow. The tool used was Hummer, and the attacks were carried out on the IP of the target device, specifically on port 8554. The successful execution of the DoS attack flooded the communication channel with a number of packets.
- The first attack took place between 08:30 and 09:00.
- The second attack took place between 17:00 and 17:30.
- The third attack took place between 21:45 and 22:15.
The above attacks were carried out to such an extent that the experiment was not stopped, but the DoS attacks were detected. Otherwise, when the power of the attack was greater, the camera had the problem of refusing to provide services or even terminating it. The values obtained had a sampling rate of:
or
where:
- T is the sampling period;
- is the sampling frequency.
so that the response of the circuit to the detection of DoS attack is immediate (real time).
The sampling rate was selected considering that most attacks require almost 1 s in order to detect the target [39] via WiFi and a few more to perform a successful attack. This means that in a time window of at least 1 sec the circuit should be able to detect attempts of unauthorized access to the IP camera. For this reason the selected sampling rate was 0.1 s and the number of overlapping samples equaled 10, achieving the desired time window of 1 s. The previous selection achieves the goal of detecting unexpected operations, including the scanning of the IP camera’s ports. Furthermore, considering that the maximum operating frequency of the proposed circuit is 16 MHz, it was derived that the application of the software filter does not affect overall performance of the monitoring mechanism.
3. Results
The results that were obtained from the devices of the above experiment are presented and discussed in this section. The only physical feature that was studied was the power supply, from which the detection of a DoS attack is implicitly achieved. The DoS attack detection circuit samples the current of the IoT device (IP camera), as shown in Figure 8. The current of the IP camera, as it may be observed, presents some fluctuations and momentarily exceeds the limits of its normal behavior (spikes are present). However, the above result could indicate normal operation, since the measurements of our values concern physical characteristics which be influenced by unbalanced factors such as some fluctuation of the trend. The capture of the sampled current in Figure 8, presents in a red box the occurrence of the attacks as described in Section 2.3.
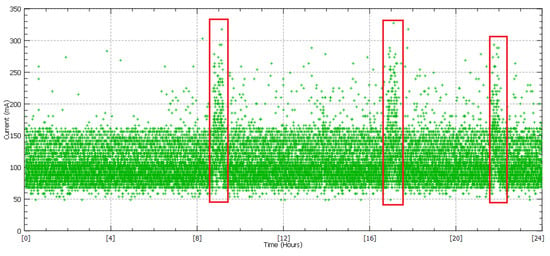
Figure 8.
Current measurements without a software filter.
In order to eliminate potential spikes which are associated with normal operation (potential "benign" spikes) occurring in our measurements, we used the software filters in sequence, with their results being presented in the diagram of the Figure 9.
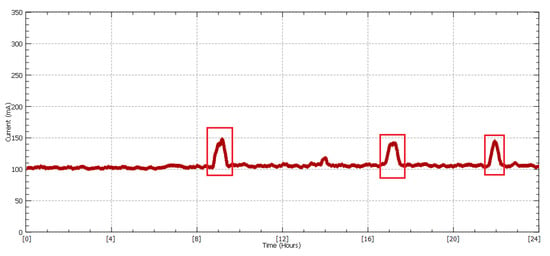
Figure 9.
Current measurements with the first software filter.
Concluding the Results section, we can now observe the processed values of the current in Figure 9, in which the irrelevant spikes have been filtered out from the current signal and the detection of the DoS attack in all three phases of the day is clearly possible. A threshold comparison to the mean value is sufficient to detect the suspicious behavior. Furthermore, extension of the detected region and the consecutive frequency is also another factor for detecting the intrusion, since no intrusion via the network is conducted with a single network packet but rather with a vast number of them, extending the time the attack is performed.
4. Conclusions
This article shows a circuit that is connected externally to the power supply of a device. The purpose of this circuit is to analyze the behavior of the device and detect anomalies, by taking advantage of the SCA technique. The calculation of power dissipation is done in relation to the power supply voltage. By filtering the electrical signals, noise removal is achieved and the circuit is able to detect any abnormality deviating from the expected operation by monitoring the (excessive) power dissipation. The applicability of the proposed circuit is in regard to the IP cameras, which are common targets of botnets, due to the lack of security mechanisms. Thus, the owner should either connect the IP cameras to an IDS or the use of high-cost sophisticated software. Considering further that a vast number of IP cameras are found in households and small businesses, which lack technical support, the introduction of a low-cost solution for intrusion detection and botnet prevention is important. This was the aim of the presented work, which suggests an external circuit based on a simple power analysis SCA approach to detect excessive power dissipation caused due to an attack. Utilizing the received detection signal of the monitored device is of strategic importance, as it can prevent an intrusion or even the inclusion of the IP camera in a botnet. The operation of the detection circuit is performed in real time (real-time detection), giving the optimal result. The results of the experiments showed excellent performance in intrusion detection (100% success). In this scientific area, there is always room for future work, especially since there is a lack of benchmarks. Some of the important possibilities for future work include the addition and combination of a variety of physical features being monitored, and the inclusion of the proposed solution as built-in feature of the IP camera. Furthermore, this work may be used to evaluate its effectiveness in protecting other IoT devices. This work is expected to mark the beginning of the development of an integrated system for VLSI technology that introduces external security systems into home and IoT devices.
Author Contributions
Data curation, D.M.; formal analysis, D.M.; investigation, P.M.; project administration, A.K.; supervision, A.K.; writing— original draft, D.M. and P.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| APTs | Advanced Persistent Threats |
| C&C | Command and Control |
| DDoS | Distributed Denial of Service |
| DoS | Denial of Service |
| IDS | Intrusion Detection System |
| IoT | Internet-of-Things |
| IP | Internet Protocol |
| PCB | Printed Circuit Board |
| SCA | Side Channel Attack |
| SNR | Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
| VLSI | Very Large Scale Integration |
| VPN | Virtual Private Network |
References
- Premsankar, G.; Di Francesco, M.; Taleb, T. Edge computing for the Internet of Things: A case study. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Desmet, L.; Huygens, C. A study on advanced persistent threats. In Proceedings of the IFIP International Conference on Communications and Multimedia Security, Aveiro, Portugal, 25–26 September 2014; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Antonakakis, M.; April, T.; Bailey, M.; Bernhard, M.; Bursztein, E.; Cochran, J.; Durumeric, Z.; Halderman, J.A.; Invernizzi, L.; Kallitsis, M.; et al. Understanding the mirai botnet. In Proceedings of the 26th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 17), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 16–18 August 2017; pp. 1093–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Ospina, J.; Liu, X.; Konstantinou, C.; Dvorkin, Y. On the Feasibility of Load-Changing Attacks in Power Systems during the COVID-19 Pandemic. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 2545–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lallie, H.S.; Shepherd, L.A.; Nurse, J.R.; Erola, A.; Epiphaniou, G.; Maple, C.; Bellekens, X. Cyber security in the age of covid-19: A timeline and analysis of cyber-crime and cyber-attacks during the pandemic. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Helpnetsecurity. Arbor Networks. 2020. Available online: https://www.helpnetsecurity.com/2016/07/19/ddos-attacks-escalate/ (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Symantec. Internet Security Threat Report. 2019. Available online: https://docs.broadcom.com/doc/istr-24-2019-en (accessed on 10 November 2020).
- Witten, I.H.; Frank, E. Data mining: Practical machine learning tools and techniques with Java implementations. ACM Sigmod Rec. 2002, 31, 76–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya, D.K.; Kalita, J.K. Network Anomaly Detection: A Machine Learning Perspective; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, C. Outlier Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Denning, D.E. An intrusion-detection model. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 1987, 2, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, V.; Austin, J. A survey of outlier detection methodologies. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2004, 22, 85–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandola, V.; Banerjee, A.; Kumar, V. Anomaly detection: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2009, 41, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Nguyen, X.; Garofalakis, M.; Jordan, M.I.; Joseph, A.; Taft, N. In-network PCA and anomaly detection. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 3–6 December 2007; pp. 617–624. [Google Scholar]
- Shyu, M.L.; Chen, S.C.; Sarinnapakorn, K.; Chang, L. A Novel Anomaly Detection Scheme Based on Principal Component Classifier; Technical Report; Miami Univ. Coral Gables Fl Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering: Coral Gables, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.; Ghorbani, A.A. Network anomaly detection based on wavelet analysis. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2008, 2009, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Tavallaee, M.; Ghorbani, A.A. Detecting network anomalies using different wavelet basis functions. In Proceedings of the 6th IEEE Annual Communication Networks and Services Research Conference (CNSR 2008), Halifax, NS, Canada, 5–8 May 2008; pp. 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, N.; Zhang, Y.; Borror, C.M. Robustness of the Markov-chain model for cyber-attack detection. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2004, 53, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syarif, I.; Prugel-Bennett, A.; Wills, G. Unsupervised clustering approach for network anomaly detection. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Networked Digital Technologies, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 24–26 April 2012; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 135–145. [Google Scholar]
- Kind, A.; Stoecklin, M.P.; Dimitropoulos, X. Histogram-based traffic anomaly detection. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2009, 6, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellenbach, B.M. Detection, Classification and Visualization of Anomalies Using Generalized Entropy Metrics. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Iglesias, F.; Zseby, T. Entropy-based characterization of internet background radiation. Entropy 2015, 17, 74–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.Y.; Lai, Y.C.; Chen, I.W.; Wang, F.Y.; Tai, W.H. Statistical analysis of false positives and false negatives from real traffic with intrusion detection/prevention systems. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2012, 50, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereziński, P.; Jasiul, B.; Szpyrka, M. An entropy-based network anomaly detection method. Entropy 2015, 17, 2367–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Das, A.; Zhou, J. Usaid: Unifying signature-based and anomaly-based intrusion detection. In Proceedings of the Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Hanoi, Vietnam, 18–20 May 2015; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 702–712. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, T.H.; Lin, Y.D.; Lai, Y.C.; Lin, P.C. Evasion techniques: Sneaking through your intrusion detection/prevention systems. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2011, 14, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarpelão, B.B.; Miani, R.S.; Kawakani, C.T.; de Alvarenga, S.C. A survey of intrusion detection in Internet of Things. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2017, 84, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Guan, L.; Liu, P.; Gao, N.; Lin, J.; Xiang, J. Hey, you, keep away from my device: Remotely implanting a virus expeller to defeat Mirai on IoT devices. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05779. [Google Scholar]
- Letteri, I.; Del Rosso, M.; Caianiello, P.; Cassioli, D. Performance of Botnet Detection by Neural Networks in Software-Defined Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 Italian Conference on Cyber Security (ITASEC), Milan, Italy, 6 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Anthi, E.; Williams, L.; Burnap, P. Pulse: An adaptive intrusion detection for the Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the Living in the Internet of Things: Cybersecurity of the IoT—2018, London, UK, 28–29 March 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, G.D.L.T.; Rad, P.; Choo, K.K.R.; Beebe, N. Detecting Internet of Things attacks using distributed deep learning. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2020, 163, 102662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.; Zhao, H.; Sun, M.; Zhou, G. IoT botnet detection via power consumption modeling. Smart Health 2020, 15, 100103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadri, J.; Chen, T.M.; Blasco, J. A Review of Significance of Energy-Consumption Anomaly in Malware Detection in Mobile Devices. IJCSA 2016, 1, 210–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myridakis, D.; Spathoulas, G.; Kakarountas, A. Supply Current Monitoring for Anomaly Detection on IoT Devices. In Proceedings of the 21st Pan-Hellenic Conference on Informatics, Larisa, Greece, 28–30 September 2017; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Myridakis, D.; Spathoulas, G.; Kakarountas, A.; Schoinianakisy, D.; Lüken, J. Anomaly detection in IoT devices via monitoring of supply current. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 8th International Conference on Consumer Electronics-Berlin (ICCE-Berlin), Berlin, Germany, 2–5 September 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Myridakis, D.; Myridakis, P.; Kakarountas, A. Intrusion Detection and Botnet Prevention Circuit for IoT Devices. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th IEEE South-East Europe Design Automation, Computer Engineering, Computer Networks and Social Media Conference (SEEDA-CECNSM), Corfu, Greece, 25–27 September 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wei, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, K.; Xu, W.; Xu, Q. On code execution tracking via power side-channel. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Vienna, Austria, 24–28 October 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1019–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Ji, X.; Lu, T.; Xu, W. DeWiCam: Detecting Hidden Wireless Cameras via Smartphones. In Proceedings of the 2018 on Asia Conference on Computer and Communications Security, ASIACCS ’18, Incheon, Korea, 4–8 June 2018; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).