Hybrid Nanofluid Flow over a Shrinking Rotating Disk: Response Surface Methodology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Formulation
3. Response Surface Methodology (RSM)
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
- As the mass transfer parameter and the magnitude of the shrinking parameter () increase, the radial velocity profile of the hybrid nanofluid near the disk decreases.
- The increment in the mass transfer parameter and the magnitude of the shrinking parameter improves the profiles of tangential velocity, axial velocity, and temperature.
- The local skin friction coefficient and Nusselt number diminish with the increase in the mass transfer parameter. The injection case demonstrates higher values of these physical quantities of interest than the suction case.
- The increment in the magnitude of the shrinking parameter enhances the local skin friction coefficient and reduces the local Nusselt number.
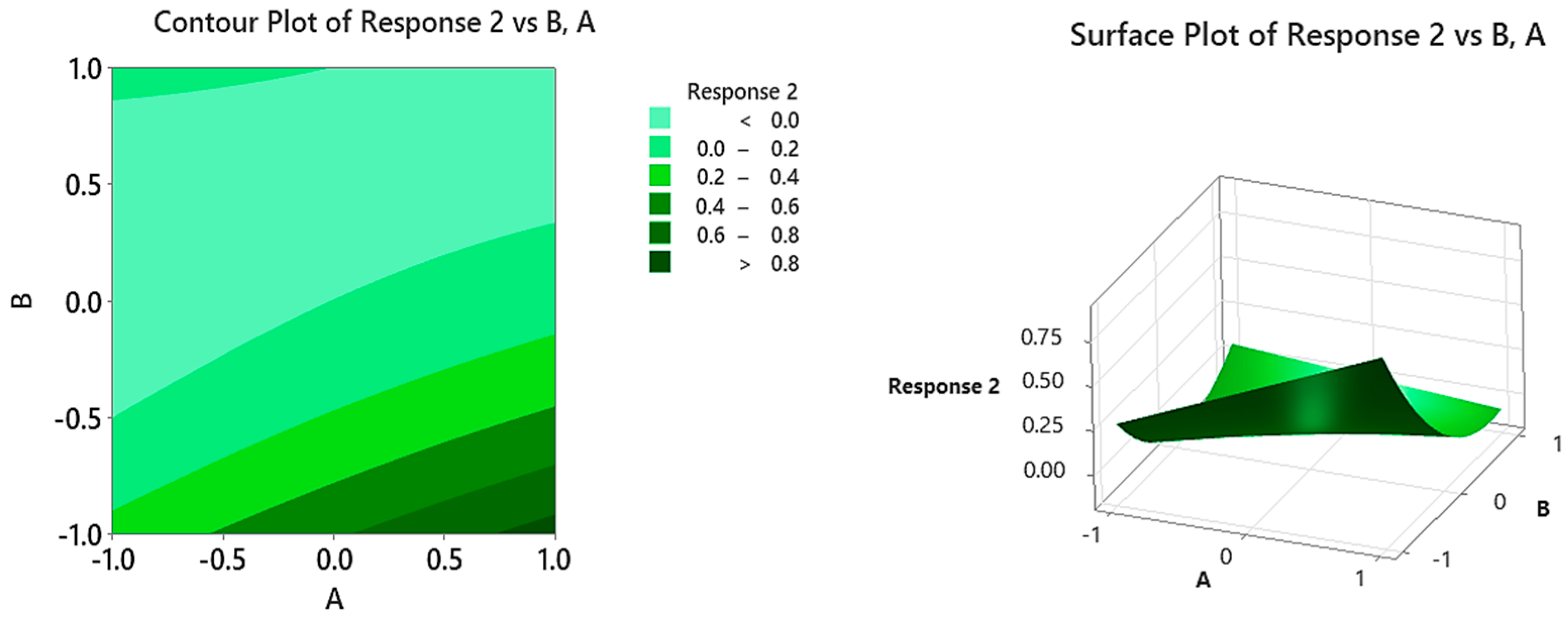
- Based on the RSM, low values of are produced at higher and medium levels of shrinking parameter () and mass transfer parameter. Meanwhile, the highest value of is observed at low levels of these independent parameters.
- High values of occur at lower levels of the mass transfer parameter and higher levels of the shrinking parameter.The local Nusselt number is not significantly impacted by the increase in the shrinking parameter at the moderate level of the mass transfer parameter.
- With a desirability of 66%, the local skin friction coefficient is minimized at 1.528780016, while the local Nusselt number is maximized at 0.888353037 when and .
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gamachu, D.; Ibrahim, W. Mixed Convection Flow of Viscoelastic Ag-Al2O3/Water Hybrid Nanofluid Past a Rotating Disk. Phys. Scr. 2021, 96, 125205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kármán, T.V. Über Laminare Und Turbulente Reibung. ZAMM J. Appl. Math. Mech. Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 1921, 1, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayano, M.S.; Otegbeye, O.; Mathunjwa, J.S. Numerical Simulation Of Nanofluid Flow Due To A Stretchable Rotating Disk. Theor. Appl. Mech. 2023, 50, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Vijay, N.; Bhardwaj, D.; Jindal, R. Flow of Water Conveying Fe3O4 and Mn–ZnFe2O4 Nanoparticles over a Rotating Disk: Significance of Thermophoresis and Brownian Motion. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2023, 574, 170710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puneeth, V.; Aly, E.H.; Pop, I. Nanofluid Flowing over a Rotating Disk That Is Stretching and Permeable: An Unsteady Model. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2023, 37, 23502491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A.; Dawar, A.; Ayaz, M.; Islam, S.; Galal, A.M.; Gul, H. Homotopic Solution of the Chemically Reactive Magnetohydrodynamic Flow of a Hybrid Nanofluid over a Rotating Disk with Brownian Motion and Thermophoresis Effects. ZAMM Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 2023, 103, e202200262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkuhayli, N.A.M. Heat Transfer Analysis of a Hybrid Nanofluid Flow on a Rotating Disk Considering Thermal Radiation Effects. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 49, 103131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Poonia, H.; Areekara, S.; Sabu, A.S.; Mathew, A.; Ali, L. Significance of Irregular Heat Source and Arrhenius Energy on Electro-Magnetohydrodynamic Hybrid Nanofluid Flow over a Rotating Stretchable Disk with Nonlinear Radiation. Numer. Heat. Transf. A Appl. 2024, 85, 1866–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, M. Mixed Convective Magnetized GO-MoS2/H2O Hybrid Nanofluid Flow about a Permeable Rotating Disk. Asia Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 18, e2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lone, S.A.; Anwar, S.; Raizah, Z.; Almusawa, M.Y.; Saeed, A. A Theoretical Investigation of the MHD Water-Based Hybrid Nanofluid Flow over a Convectively Heated Rotating Disk Surface with Velocity Slips and Zero Mass Flux Conditions. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2023, 138, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashi’ie, N.S.; Waini, I.; Zainal, N.A.; Hamzah, K.; Arifin, N.M.; Pop, I. Multiple Solutions and Stability Analysis of Magnetic Hybrid Nanofluid Flow Over a Rotating Disk with Heat Generation. J. Adv. Res. Fluid. Mech. Therm. Sci. 2023, 102, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, N.; Sharma, K. Magnetohydrodynamic Hybrid Nanofluid Flow over a Decelerating Rotating Disk with Soret and Dufour Effects. Multidiscip. Model. Mater. Struct. 2023, 19, 253–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Bakar, S.; Pop, I.; Md Arifin, N. Unsteady Flow of Hybrid Nanofluid over a Permeable Shrinking Inclined Rotating Disk with Radiation and Velocity Slip Effects. Neural Comput. Appl. 2024, 36, 11525–11544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Zaib, A.; Khan, M.I.; Alzahrani, F.; Eldin, S.M. Irreversibility Analysis in Stagnation Point Flow of Tri-Hybrid Nanofluid over a Rotating Disk; Application of Kinetic Energy. J. Indian. Chem. Soc. 2023, 100, 100873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.P.; Kumar, M.; Yaseen, M.; Rawat, S.K. Ternary Hybrid Nanofluid (TiO2−SiO2−MoS2/Kerosene Oil) Flow over a Rotating Disk with Quadratic Thermal Radiation and Cattaneo-Christov Model. J. Cent. S. Univ. 2023, 30, 1262–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patgiri, B.; Paul, A. Inspection of Viscoelastic Ag+Cu+Fe3O4+Al2O3/Kerosene Oil Tetra-Hybrid Nanofluid Flow across a Stretchable Rotating Disk with Exponentially Varying Viscosity. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2024, 18, 2336327. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, I.; Gul, T.; Khan, A. Unsteady Hydromagnetic Flow over an Inclined Rotating Disk through Neural Networking Approach. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varun Kumar, R.S.; Kumar, R.N.; Ben Ahmed, S.; Madhu, J.; Verma, A.; Punith Gowda, R.J. Unsteady Flow of a Ternary Nanofluid over a Slow-Rotating Disk Subject to Uniform Suction and Backpropagated Neural Network. Numer. Heat Transf. Part B Fundam. 2023, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, T.; Ramzan, M.; Howari, F.; Kadry, S.; Chu, Y.M. Application of Response Surface Methodology on the Nanofluid Flow over a Rotating Disk with Autocatalytic Chemical Reaction and Entropy Generation Optimization. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, A.; Sindhu, T.N.; Al-Mdallal, Q.M. A Sensitivity Study on Carbon Nanotubes Significance in Darcy–Forchheimer Flow towards a Rotating Disk by Response Surface Methodology. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, A.; Areekara, S.; Sabu, A.S. Significance of Magnetic Field and Stratification Effects on the Bioconvective Stagnation-Point Flow of Ferro-Nanofluid over a Rotating Stretchable Disk: Four-Factor Response Surface Methodology. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2022, 99, 100615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Ali, A.; Rasheed, K.; Pasha, A.A.; Algarni, S.; Alqahtani, T.; Irshad, K. Application of Response Surface Methodology to Optimize MHD Nanofluid Flow over a Rotating Disk with Thermal Radiation and Joule Heating. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 52, 103715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashi’ie, N.S.; Waini, I.; Hamzah, K.B.; Mukhtar, M.F.; Kasim, A.R.M.; Arifin, N.M.; Pop, I. Numerical Solution and Statistical Analysis of the Unsteady Hybrid Ferrofluid Flow with Heat Generation Subject to a Rotating Disk. ZAMM J. Appl. Math. Mech. Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 2023, 103, e202200384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, F.R.; Tso, C.Y.; Chan, K.C.; Fu, S.C.; Chao, C.Y.H. On Trade-off for Dispersion Stability and Thermal Transport of Cu-Al2O3 Hybrid Nanofluid for Various Mixing Ratios. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 132, 1200–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takabi, B.; Gheitaghy, A.M.; Tazraei, P. Hybrid Water-Based Suspension of Al2O3 and Cu Nanoparticles on Laminar Convection Effectiveness. J. Thermophys. Heat Trans. 2016, 30, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oztop, H.F.; Abu-Nada, E. Numerical Study of Natural Convection in Partially Heated Rectangular Enclosures Filled with Nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2008, 29, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S.; Venkitaraj, K.P.; Selvakumar, P.; Chandrasekar, M. Synthesis of Al2O3-Cu/Water Hybrid Nanofluids Using Two Step Method and Its Thermo Physical Properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 388, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkyilmazoglu, M. Nanofluid Flow and Heat Transfer Due to a Rotating Disk. Comput. Fluids 2014, 94, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X. Flow and Heat Transfer of Nanofluids over a Rotating Disk with Uniform Stretching Rate in the Radial Direction. Propuls. Power Res. 2017, 6, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.E.P.; Wilson, K.B. On the Experimental Attainment of Optimum Conditions. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1951, 13, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanthesh, B.; Thriveni, K.; Rana, P.; Muhammad, T. Radiative Heat Transfer of Nanomaterial on a Convectively Heated Circular Tube with Activation Energy and Nanoparticle Aggregation Kinematic Effects. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 127, 105568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S. Central Composite Design for Response Surface Methodology and Its Application in Pharmacy. In Response Surface Methodology in Engineering Science; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sahoo, P.; Barman, T.K. ANN Modelling of Fractal Dimension in Machining. In Mechatronics and Manufacturing Engineering; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rashidi, M.M.; Abelman, S.; Mehr, N.F. Entropy Generation in Steady MHD Flow Due to a Rotating Porous Disk in a Nanofluid. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 62, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhadri, M.; Raza, J.; Yashkun, U.; Lund, L.A.; Maatki, C.; Khan, S.U.; Kolsi, L. Response Surface Methodology (RSM) and Artificial Neural Network (ANN) Simulations for Thermal Flow Hybrid Nanofluid Flow with Darcy-Forchheimer Effects. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2022, 99, 100607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Independent Parameter | Symbol | Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (−1) | Medium (0) | High (1) | ||
| A | −1.0 | −0.9 | −0.8 | |
| B | −0.6 | −0.1 | 0.4 | |
| Runs | Coded Values | Actual Values | Responses | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | (Response 1) | (Response 2) | |||
| 1 | −1 | −1 | −1.0 | −0.6 | 1.803245471 | 0.232133118 |
| 2 | 1 | −1 | −0.8 | −0.6 | 1.529299905 | 0.975650061 |
| 3 | −1 | 1 | −1.0 | 0.4 | 1.475361873 | 0.000000014 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | −0.8 | 0.4 | 1.229514429 | 0.000001138 |
| 5 | −1 | 0 | −1.0 | −0.1 | 1.642240690 | 0.000228587 |
| 6 | 1 | 0 | −0.8 | −0.1 | 1.380007580 | 0.004928016 |
| 7 | 0 | −1 | −0.9 | −0.6 | 1.659170147 | 0.525530320 |
| 8 | 0 | 1 | −0.9 | 0.4 | 1.346068736 | 0.000000126 |
| 9 | 0 | 0 | −0.9 | −0.1 | 1.504436107 | 0.001106468 |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | −0.9 | −0.1 | 1.504436107 | 0.001106468 |
| 11 | 0 | 0 | −0.9 | −0.1 | 1.504436107 | 0.001106468 |
| 12 | 0 | 0 | −0.9 | −0.1 | 1.504436107 | 0.001106468 |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | −0.9 | −0.1 | 1.504436107 | 0.001106468 |
| Rashidi et al. [34] | Turkyilmazoglu [28] | Present Study | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.510186 | 0.51023262 | 0.510232394 | |
| 0.61589 | 0.61592201 | 0.615921866 | |
| - | 0.93387794 | 0.933877577 |
| Source | DF | Adj SS | Adj MS | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 5 | 0.249759313 | 0.049951863 | 174774.611709837 | 0.000000000 |
| Linear | 2 | 0.249435660 | 0.124717830 | 436370.320105496 | 0.000000000 |
| A | 1 | 0.101927475 | 0.101927475 | 356630.043436460 | 0.000000000 |
| B | 1 | 0.147508184 | 0.147508184 | 516110.596774533 | 0.000000000 |
| Square | 2 | 0.000126277 | 0.000063139 | 220.913397825 | 0.000000474 |
| AA | 1 | 0.000124396 | 0.000124396 | 435.243856915 | 0.000000146 |
| BB | 1 | 0.000008884 | 0.000008884 | 31.084684334 | 0.000837291 |
| 2-Way Interaction | 1 | 0.000197376 | 0.000197376 | 690.591542539 | 0.000000030 |
| AB | 1 | 0.000197376 | 0.000197376 | 690.591542539 | 0.000000030 |
| Error | 7 | 0.000002001 | 0.000000286 | ||
| Lack-of-Fit | 3 | 0.000002001 | 0.000000667 | * | * |
| Pure Error | 4 | 0.000000000 | 0.000000000 | ||
| Total | 12 | 0.249761314 |
| Source | DF | Adj SS | Adj MS | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 5 | 1.000087703 | 0.200017541 | 29.206710770 | 0.000150454 |
| Linear | 2 | 0.594033446 | 0.297016723 | 43.370603881 | 0.000113785 |
| A | 1 | 0.093304904 | 0.093304904 | 13.624451749 | 0.007745032 |
| B | 1 | 0.500728543 | 0.500728543 | 73.116756012 | 0.000059439 |
| Square | 2 | 0.267850314 | 0.133925157 | 19.555851501 | 0.001363026 |
| AA | 1 | 0.001069278 | 0.001069278 | 0.156136818 | 0.704502971 |
| BB | 1 | 0.216321666 | 0.216321666 | 31.587451304 | 0.000798846 |
| 2-Way Interaction | 1 | 0.138203943 | 0.138203943 | 20.180643085 | 0.002824322 |
| AB | 1 | 0.138203943 | 0.138203943 | 20.180643085 | 0.002824322 |
| Error | 7 | 0.047938393 | 0.006848342 | ||
| Lack-of-Fit | 3 | 0.047938393 | 0.015979464 | * | * |
| Pure Error | 4 | 0.000000000 | 0.000000000 | ||
| Total | 12 | 1.048026096 |
| Solution | A | B | Response 2 Fit | Response 1 Fit | Composite Desirability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | −1 | 0.888353037 | 1.528780016 | 0.659986551 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yahaya, R.I.; Arifin, N.M.; Pop, I.; Ali, F.M.; Isa, S.S.P.M. Hybrid Nanofluid Flow over a Shrinking Rotating Disk: Response Surface Methodology. Computation 2024, 12, 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation12070141
Yahaya RI, Arifin NM, Pop I, Ali FM, Isa SSPM. Hybrid Nanofluid Flow over a Shrinking Rotating Disk: Response Surface Methodology. Computation. 2024; 12(7):141. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation12070141
Chicago/Turabian StyleYahaya, Rusya Iryanti, Norihan Md Arifin, Ioan Pop, Fadzilah Md Ali, and Siti Suzilliana Putri Mohamed Isa. 2024. "Hybrid Nanofluid Flow over a Shrinking Rotating Disk: Response Surface Methodology" Computation 12, no. 7: 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation12070141
APA StyleYahaya, R. I., Arifin, N. M., Pop, I., Ali, F. M., & Isa, S. S. P. M. (2024). Hybrid Nanofluid Flow over a Shrinking Rotating Disk: Response Surface Methodology. Computation, 12(7), 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation12070141











