Virtual Combinatorial Library Screening of Quinadoline B Derivatives against SARS-CoV-2 RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Computational Details
2.1.1. Ligand and Protein Preparation
2.1.2. Binding Site Analysis
2.1.3. Molecular Docking and Ligand-Energy Evaluation
2.1.4. Q3-Focused Library Generation
2.1.5. Evaluation of Drug-like Profile
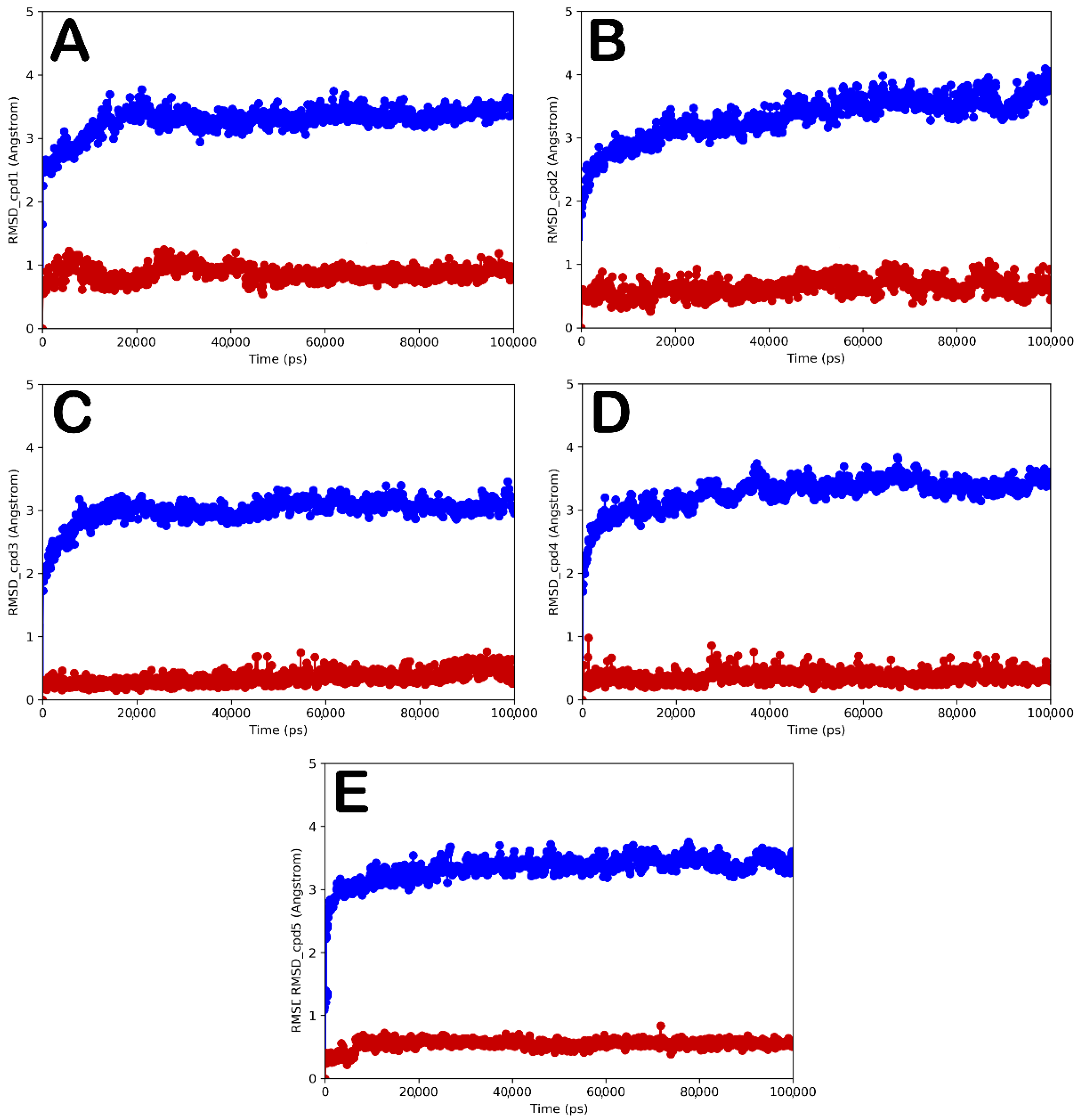
2.1.6. Molecular Dynamics Simulation Details
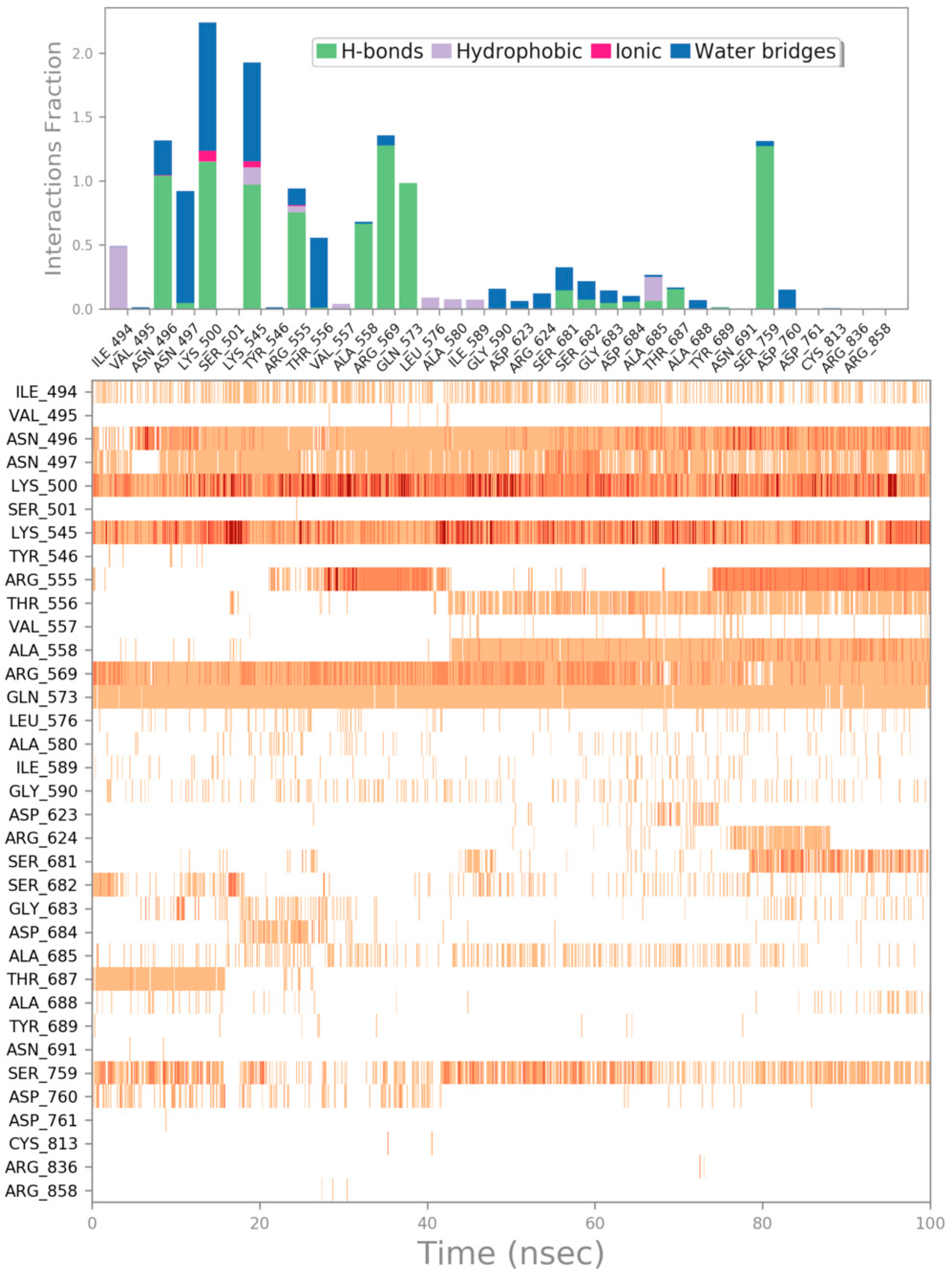
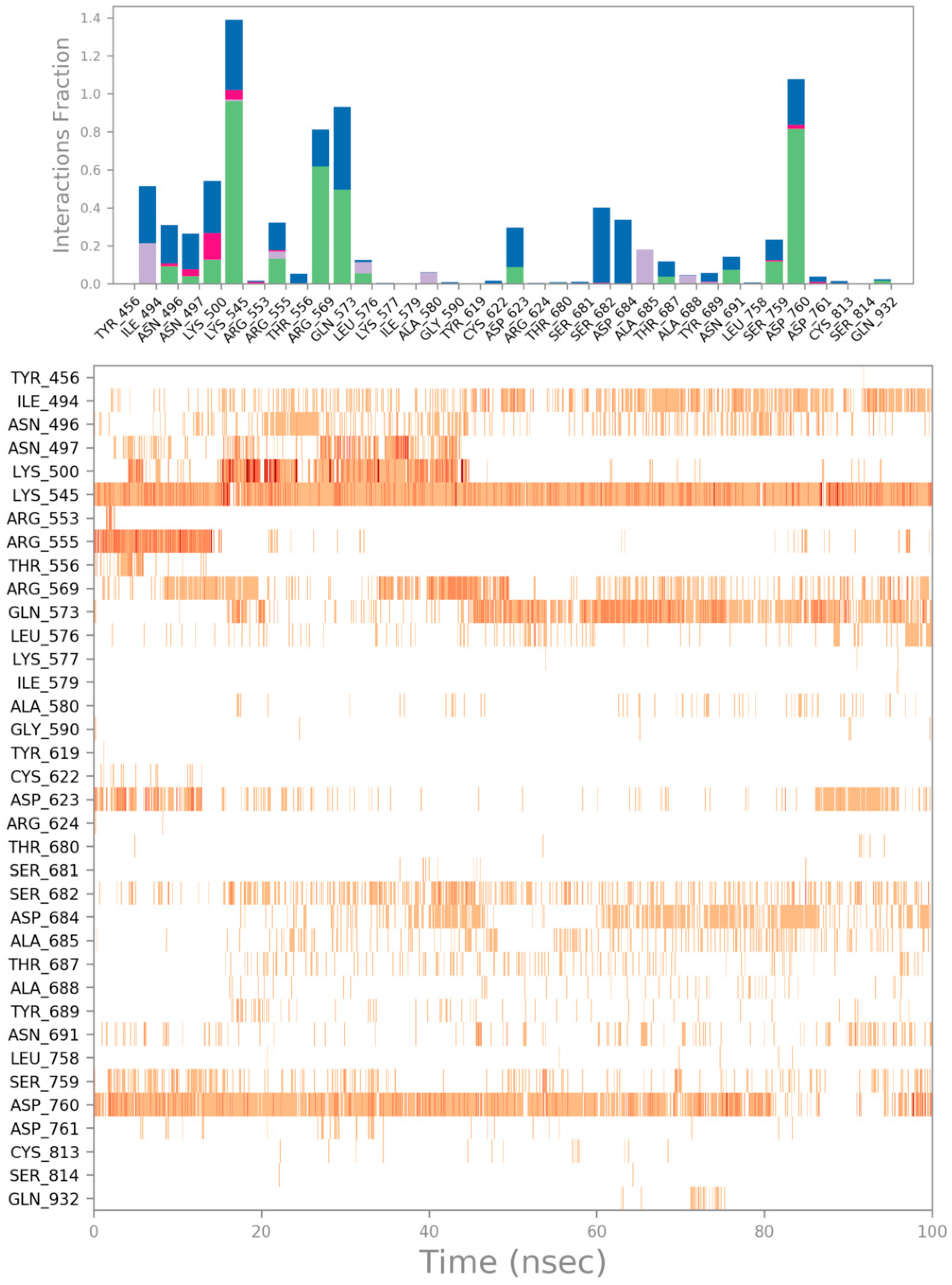
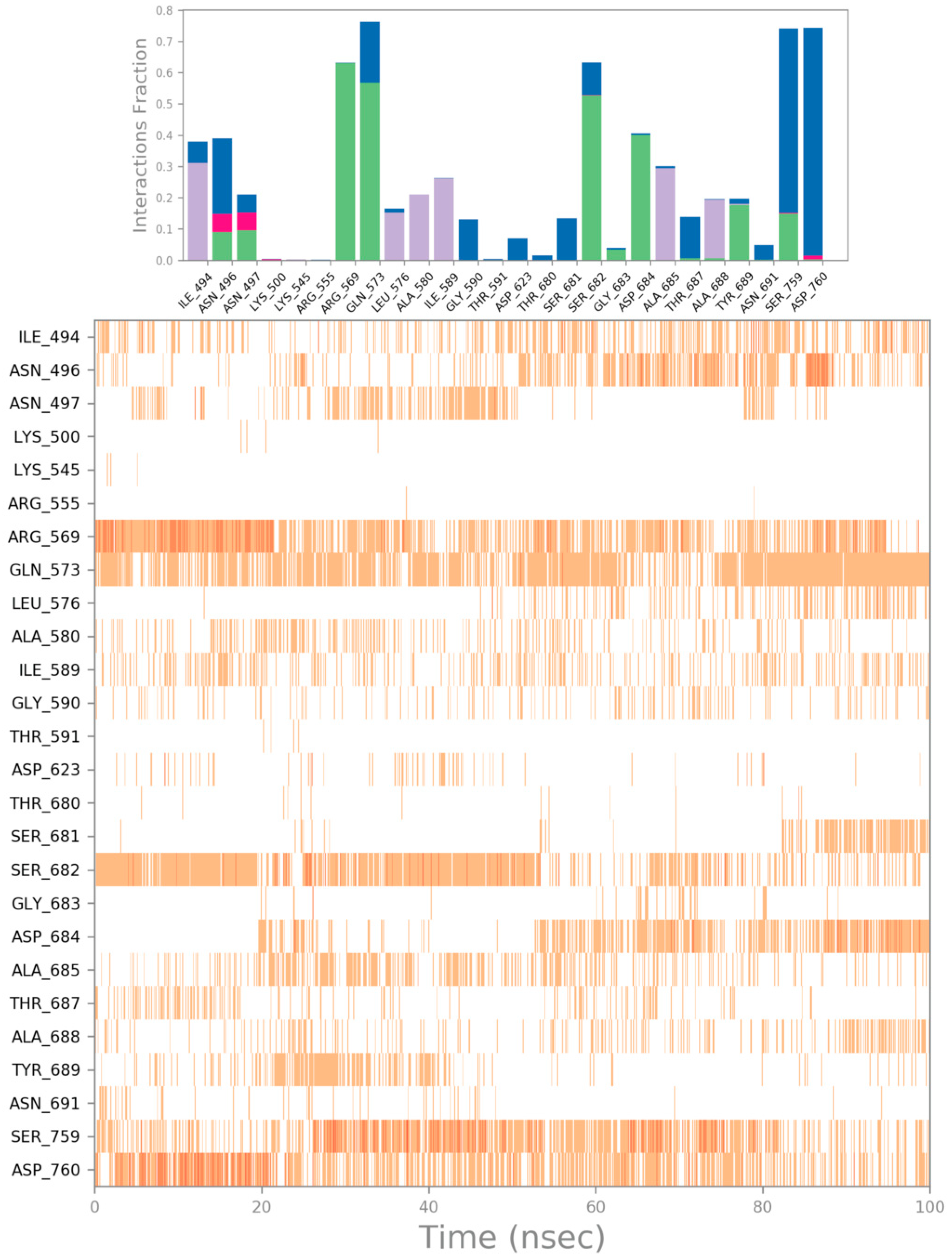
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, F.; Tang, J.; Nussinov, R.; Cheng, F. Artificial intelligence in COVID-19 drug repurposing. Lancet Digit. Health 2020, 2, e667–e676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, L. Turning the Tide: Natural Products and Natural-Product-Inspired Chemicals as Potential Counters to SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdallah, H.M.; El-Halawany, A.M.; Sirwi, A.; El-Araby, A.M.; Mohamed, G.A.; Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Koshak, A.E.; Asfour, H.Z.; Awan, Z.A.; Elfaky, M.A. Repurposing of Some Natural Product Isolates as SARS-COV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors via In Vitro Cell Free and Cell-Based Antiviral Assessments and Molecular Modeling Approaches. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitsillou, E.; Liang, J.; Karagiannis, C.; Ververis, K.; Darmawan, K.K.; Ng, K.; Hung, A.; Karagiannis, T.C. Interaction of small molecules with the SARS-CoV-2 main protease in silico and in vitro validation of potential lead compounds using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2020, 89, 107408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.Y.; Zhang, H.X.; Mezei, M.; Cui, M. Molecular docking: A powerful approach for structure-based drug discovery. Curr. Comput. Aided Drug Des. 2011, 7, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, S.; El-Kafrawy, S.A.; Alandijany, T.A.; Bajrai, L.H.; Shah, A.A.; Dubey, A.; Sahoo, A.K.; Yadava, U.; Kamal, M.A.; Azhar, E.I.; et al. Structure-Based Identification of Natural Products as SARS-CoV-2 M(pro) Antagonist from Echinacea angustifolia Using Computational Approaches. Viruses 2021, 13, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajbabaie, R.; Harper, M.T.; Rahman, T. Establishing an Analogue Based In Silico Pipeline in the Pursuit of Novel Inhibitory Scaffolds against the SARS Coronavirus 2 Papain-Like Protease. Molecules 2021, 26, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhar, Z.; Khan, S.; AlOmar, S.Y.; Alkhuriji, A.; Ahmad, A. ABBV-744 as a potential inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 main protease enzyme against COVID-19. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogi, S.; Ramalho, T.C.; Kuca, K.; Medina-Franco, J.L.; Valko, M. Editorial: In silico Methods for Drug Design and Discovery. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Chaudhary, J.K.; Jain, N.; Chaudhary, P.K.; Khanra, S.; Dhamija, P.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, A.; Handu, S. Role of Structural and Non-Structural Proteins and Therapeutic Targets of SARS-CoV-2 for COVID-19. Cells 2021, 10, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quimque, M.T.; Notarte, K.I.; Adviento, X.A.; Cabunoc, M.H.; de Leon, V.N.; Delos Reyes, F.S.L.; Lugtu, E.J.; Manzano, J.A.; Monton, S.N.; Munoz, J.E.; et al. Polyphenolic Natural Products Active In Silico against SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor Binding Domains and Non-Structural Proteins—A Review. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2022, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Leon, V.N.O.; Manzano, J.A.H.; Pilapil, D.Y.H.t.; Fernandez, R.A.T.; Ching, J.; Quimque, M.T.J.; Agbay, J.C.M.; Notarte, K.I.R.; Macabeo, A.P.G. Anti-HIV reverse transcriptase plant polyphenolic natural products with in silico inhibitory properties on seven non-structural proteins vital in SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2021, 19, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, R.A.; Quimque, M.T.; Notarte, K.I.; Manzano, J.A.; Pilapil, D.Y.t.; de Leon, V.N.; San Jose, J.J.; Villalobos, O.; Muralidharan, N.H.; Gromiha, M.M.; et al. Myxobacterial depsipeptide chondramides interrupt SARS-CoV-2 entry by targeting its broad, cell tropic spike protein. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftab, S.O.; Ghouri, M.Z.; Masood, M.U.; Haider, Z.; Khan, Z.; Ahmad, A.; Munawar, N. Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase as a potential therapeutic drug target using a computational approach. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.; Ikram, S.; Ahmad, F.; Rehman, I.U.; Mushtaq, M. SARS-CoV-2 RNA Dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp)–A drug repurposing study. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, S.K.; Mukhoty, S.; Kundu, H.; Ghosh, S.; Sen, M.K.; Das, S.; Brogi, S. In silico analysis of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of the SARS-CoV-2 and therapeutic potential of existing antiviral drugs. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 135, 104591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quimque, M.T.J.; Notarte, K.I.R.; Fernandez, R.A.T.; Mendoza, M.A.O.; Liman, R.A.D.; Lim, J.A.K.; Pilapil, L.A.E.; Ong, J.K.H.; Pastrana, A.M.; Khan, A.; et al. Virtual screening-driven drug discovery of SARS-CoV2 enzyme inhibitors targeting viral attachment, replication, post-translational modification and host immunity evasion infection mechanisms. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 4316–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Maxwell, D.S.; Tirado-Rives, J. Development and Testing of the OPLS All-Atom Force Field on Conformational Energetics and Properties of Organic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 11225–11236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Yan, L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, L.; Wang, T.; Sun, Q.; Ming, Z.; Zhang, L.; et al. Structure of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from COVID-19 virus. Science 2020, 368, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Capua, A.; Sticozzi, C.; Brogi, S.; Brindisi, M.; Cappelli, A.; Sautebin, L.; Rossi, A.; Pace, S.; Ghelardini, C.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of fluorinated 1,5-diarylpyrrole-3-alkoxyethyl ether derivatives as selective COX-2 inhibitors endowed with anti-inflammatory activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 109, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brindisi, M.; Senger, J.; Cavella, C.; Grillo, A.; Chemi, G.; Gemma, S.; Cucinella, D.M.; Lamponi, S.; Sarno, F.; Iside, C.; et al. Novel spiroindoline HDAC inhibitors: Synthesis, molecular modelling and biological studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 157, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testai, L.; Piragine, E.; Piano, I.; Flori, L.; Da Pozzo, E.; Miragliotta, V.; Pirone, A.; Citi, V.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Brogi, S.; et al. The Citrus Flavonoid Naringenin Protects the Myocardium from Ageing-Dependent Dysfunction: Potential Role of SIRT1. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 4650207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brogi, S.; Brindisi, M.; Butini, S.; Kshirsagar, G.U.; Maramai, S.; Chemi, G.; Gemma, S.; Campiani, G.; Novellino, E.; Fiorenzani, P.; et al. (S)-2-Amino-3-(5-methyl-3-hydroxyisoxazol-4-yl)propanoic Acid (AMPA) and Kainate Receptor Ligands: Further Exploration of Bioisosteric Replacements and Structural and Biological Investigation. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 2124–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frydenvang, K.; Pickering, D.S.; Kshirsagar, G.U.; Chemi, G.; Gemma, S.; Sprogoe, D.; Kaern, A.M.; Brogi, S.; Campiani, G.; Butini, S.; et al. Ionotropic Glutamate Receptor GluA2 in Complex with Bicyclic Pyrimidinedione-Based Compounds: When Small Compound Modifications Have Distinct Effects on Binding Interactions. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 1791–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirous, H.; Chemi, G.; Gemma, S.; Butini, S.; Debyser, Z.; Christ, F.; Saghaie, L.; Brogi, S.; Fassihi, A.; Campiani, G.; et al. Identification of Novel 3-Hydroxy-pyran-4-One Derivatives as Potent HIV-1 Integrase Inhibitors Using in silico Structure-Based Combinatorial Library Design Approach. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chemi, G.; Gemma, S.; Campiani, G.; Brogi, S.; Butini, S.; Brindisi, M. Computational Tool for Fast in silico Evaluation of hERG K(+) Channel Affinity. Front. Chem. 2017, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zaccagnini, L.; Brogi, S.; Brindisi, M.; Gemma, S.; Chemi, G.; Legname, G.; Campiani, G.; Butini, S. Identification of novel fluorescent probes preventing PrP(Sc) replication in prion diseases. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 127, 859–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickolls, J.; Buck, I.; Garland, M.; Skadron, K. Scalable parallel programming with CUDA. Queue 2008, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindisi, M.; Ulivieri, C.; Alfano, G.; Gemma, S.; de Asis Balaguer, F.; Khan, T.; Grillo, A.; Chemi, G.; Menchon, G.; Prota, A.E.; et al. Structure-activity relationships, biological evaluation and structural studies of novel pyrrolonaphthoxazepines as antitumor agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 162, 290–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brogi, S.; Butini, S.; Maramai, S.; Colombo, R.; Verga, L.; Lanni, C.; De Lorenzi, E.; Lamponi, S.; Andreassi, M.; Bartolini, M.; et al. Disease-modifying anti-Alzheimer’s drugs: Inhibitors of human cholinesterases interfering with beta-amyloid aggregation. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2014, 20, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphreys, D.D.; Friesner, R.A.; Berne, B.J. A Multiple-Time-Step Molecular Dynamics Algorithm for Macromolecules. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 6885–6892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, W.G. Canonical dynamics: Equilibrium phase-space distributions. Phys. Rev. A 1985, 31, 1695–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martyna, G.J.; Tobias, D.J.; Klein, M.L. Constant pressure molecular dynamics algorithms. J. Chem. Phys. 1994, 101, 4177–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essmann, U.; Perera, L.; Berkowitz, M.L.; Darden, T.; Lee, H.; Pedersen, L.G. A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 8577–8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cevik, M.; Bamford, C.G.G.; Ho, A. COVID-19 pandemic-a focused review for clinicians. Clin. MicroBiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organic Chemistry Portal. 2021. Available online: http://www.organic-chemistry.org/prog/peo/ (accessed on 25 July 2021).
- Baell, J.B.; Holloway, G.A. New substructure filters for removal of pan assay interference compounds (PAINS) from screening libraries and for their exclusion in bioassays. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2719–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

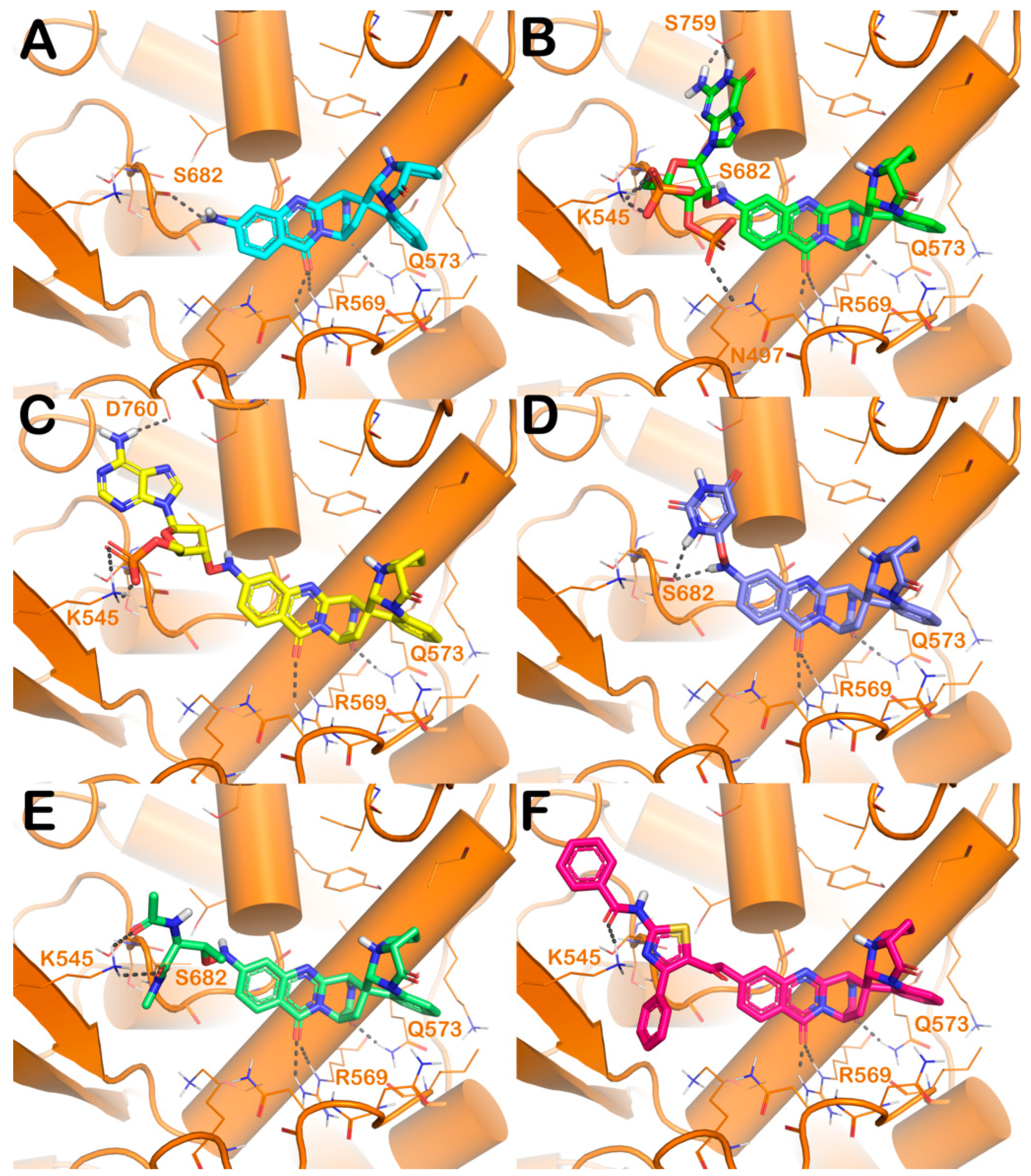
| Cpd | GlideScore (kcal/mol) | ΔGbind (kcal/mol) | Main Contacts | LogPo/w a | Solubility b | GI abs. c | PAINS d | Tumorigenic e | pKi hERG f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −8.71 | −51.1 | H−bonds R569, Q573, S682, N497, S759 salt bridges K545 | −3.72 | High | Low | No | No | 5.03 |
| 2 | −8.47 | −52.3 | H−bonds R569, Q573, K545, D760 | −1.82 | High | Low | No | No | 5.24 |
| 3 | −8.12 | −43.9 | H−bonds R569, Q573, S682 | −0.23 | Moderate | Low | No | No | 5.06 |
| 4 | −7.51 | −44.8 | H−bonds R569, Q573, S682, K545 | −0.27 | Moderate | Low | No | No | 5.35 |
| 5 | −7.46 | −46.3 | H−bonds R569, Q573, K545 cation−π K500, R555 | 3.07 | Poor | Low | No | No | 5.11 |
| 6 | −7.42 | −41.5 | H−bonds R569, Q573, S682 double cation−π K500 | 2.75 | Moderate | High | No | No | 5.32 |
| 7 | −7.38 | −40.6 | H−bonds R569, Q573, S682 double cation−π K500 | 1.67 | Poor | Low | No | No | 5.17 |
| 8 | −7.14 | −41.2 | H−bonds R569, Q573, S682, D684 cation−π K500 | 2.45 | Moderate | High | No | No | 5.51 |
| 9 | −7.08 | −39.1 | H−bonds R569, Q573, S682 | 0.80 | Moderate | Low | No | No | 5.84 |
| 10 | −7.03 | −43.7 | H−bonds R569, Q573, A685, A688 cation−π K545 | 1.32 | Moderate | Low | No | No | 5.63 |
| 11 | −6.97 | −38.8 | H−bonds R569, Q573, S682 cation−π K500 π−π Y689 | 2.50 | Poor | Low | No | No | 4.92 |
| 12 | −6.88 | −40.2 | H−bonds R569, Q573, K545, R555 halogen bonds R624 | 3.02 | Poor | Low | No | No | 5.68 |
| 13 | −6.84 | −42.3 | H−bonds R569, Q573, S682 cation−π K500 | 2.61 | Poor | Low | No | No | 5.26 |
| 14 | −6.81 | −39.4 | H−bonds R569, Q573, S682 cation−π K500 | 1.10 | Moderate | High | No | No | 5.15 |
| 15 | −6.77 | −42.9 | H−bonds R569, Q573, D684 cation−π K545 | 1.05 | Moderate | Low | No | No | 4.93 |
| 16 | −6.71 | −41.0 | H−bonds R569, Q573, S682, K545 | 1.01 | Moderate | High | No | No | 6.21 |
| 17 | −6.59 | −37.1 | H−bonds R569, Q573, S682 π−π Y689 | 2.55 | Poor | Low | No | No | 5.24 |
| 18 | −6.51 | −47.2 | H−bonds R569, Q573, S501 | 1.96 | Poor | Low | No | No | 5.67 |
| 19 | −6.44 | −41.3 | H−bonds R569, Q573, S682 salt bridges D760 | 0.24 | Moderate | High | No | alert: anil_di_alk_A | 5.79 |
| 20 | −6.39 | −33.8 | H−bonds R569, Q573, S682 | 1.84 | Poor | Low | No | No | |
| 21 | −6.37 | −34.9 | H−bonds R569, Q573, S682, K545 | 3.18 | Poor | Low | No | No | 5.47 |
| 22 | −6.36 | −34.3 | H−bonds R569, Q573, S682 halogen bonds K545 | 0.81 | Moderate | Low | No | No | 5.18 |
| 23 | −6.34 | −39.7 | H−bonds R569, Q573 halogen bonds N497 | 1.53 | Poor | Low | No | No | 5.60 |
| 24 | −6.30 | −35.4 | H−bonds R569, Q573, S682 | 0.14 | Moderate | Low | No | No | 5.51 |
| 25 | −6.29 | −40.2 | H−bonds R569, Q573, R553, R555 salt bridges R553, R555 | 1.37 | Moderate | Low | No | No | 4.89 |
| 26 | −6.24 | −39.5 | H−bonds R569, Q573, S682 cation−π K500 | 3.34 | Poor | Low | No | No | 5.54 |
| Q3 | −6.22 | −32.3 | H−bonds R569, Q573, S682 | −0.12 | Moderate | High | No | No | 5.77 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brogi, S.; Quimque, M.T.; Notarte, K.I.; Africa, J.G.; Hernandez, J.B.; Tan, S.M.; Calderone, V.; Macabeo, A.P. Virtual Combinatorial Library Screening of Quinadoline B Derivatives against SARS-CoV-2 RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase. Computation 2022, 10, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation10010007
Brogi S, Quimque MT, Notarte KI, Africa JG, Hernandez JB, Tan SM, Calderone V, Macabeo AP. Virtual Combinatorial Library Screening of Quinadoline B Derivatives against SARS-CoV-2 RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase. Computation. 2022; 10(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation10010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrogi, Simone, Mark Tristan Quimque, Kin Israel Notarte, Jeremiah Gabriel Africa, Jenina Beatriz Hernandez, Sophia Morgan Tan, Vincenzo Calderone, and Allan Patrick Macabeo. 2022. "Virtual Combinatorial Library Screening of Quinadoline B Derivatives against SARS-CoV-2 RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase" Computation 10, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation10010007
APA StyleBrogi, S., Quimque, M. T., Notarte, K. I., Africa, J. G., Hernandez, J. B., Tan, S. M., Calderone, V., & Macabeo, A. P. (2022). Virtual Combinatorial Library Screening of Quinadoline B Derivatives against SARS-CoV-2 RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase. Computation, 10(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation10010007









