TisLLM: Temporal Integration-Enhanced Fine-Tuning of Large Language Models for Sequential Recommendation †
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We highlight the importance of time-series patterns in user preferences and argue that LLMs are inherently suitable for time-series recommendation tasks.
- We introduce a sliding window method to segment user interaction sequences, enriching training samples for model fine-tuning.
- We validate the effectiveness of TisLLM through extensive experiments on multiple datasets.
2. Related Work
2.1. Zero-Shot Recommendation via Prompt Design
2.2. Fine-Tuning LLMs with User Interaction Data
2.3. Leveraging LLMs’ Prior Knowledge for Recommendation
2.4. Learning User-Item Interactions with LLMs
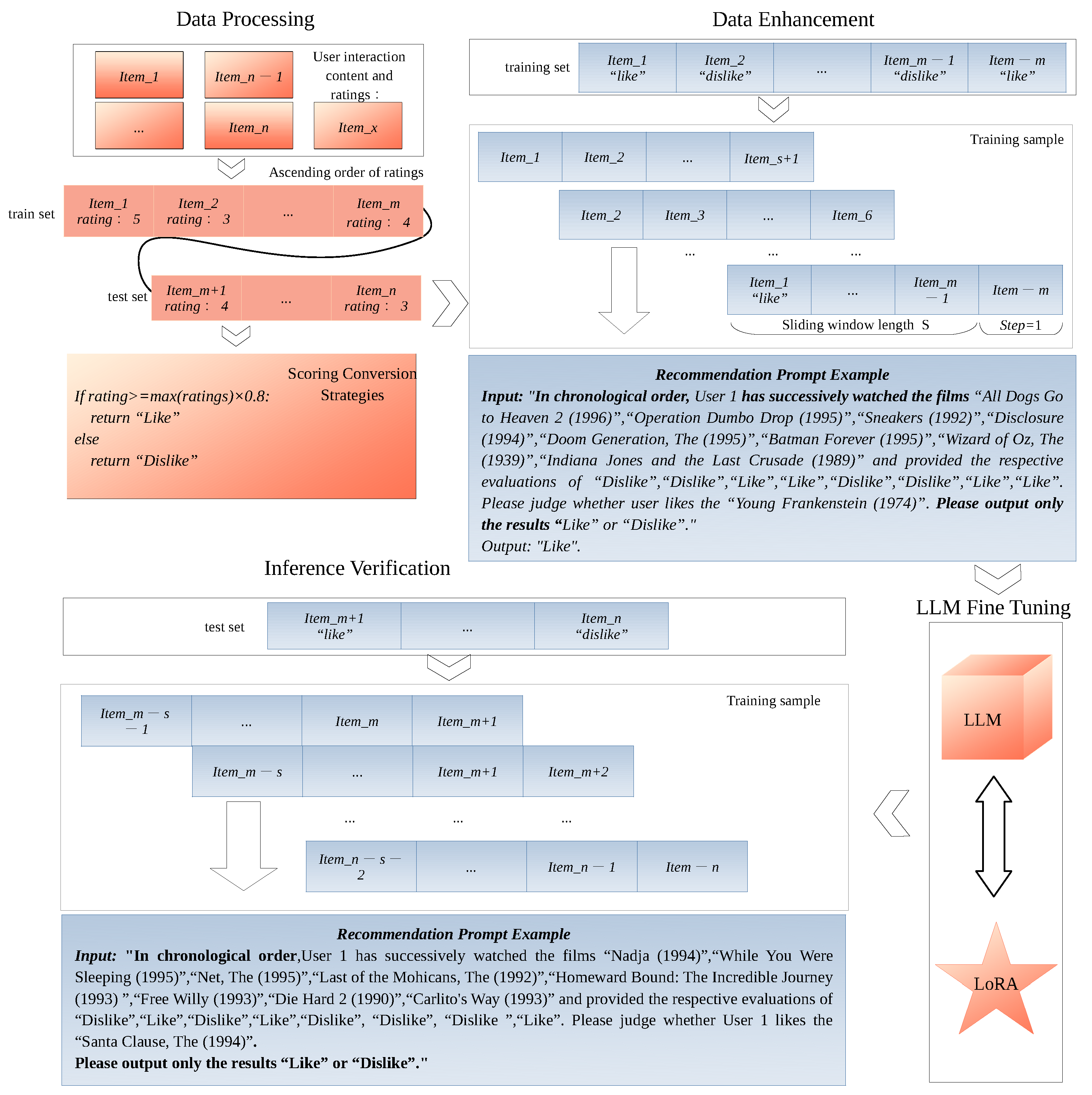
3. Methodology
3.1. Data Processing
3.2. Data Enhancement
| Algorithm 1 Pseudocode for data processing. |
|
3.3. LLM Fine Tuning
3.4. Inference Verification
| Algorithm 2 The fine-tuning data format of TisLLM for recommendation tasks is based on the user’s interaction history and the time series of interacted items, comprising two parts: input and output.The MovieLen dataset and Beauty data were used as examples [28,29]. |
| Recommendation Prompt Example Movie Input: “In chronological order, User 1 has successively watched the films ‘All Dogs Go to Heaven 2 (1996)’, ‘Operation Dumbo Drop (1995)’, ‘Sneakers (1992)’, ‘Disclosure (1994)’, ‘Doom Generation, The (1995)’, ‘Batman Forever (1995)’, ‘Wizard of Oz, The (1939)’, ‘Indiana Jones and the Last Crusade (1989)’, ‘Patton (1970)’, ‘Evil Dead II (1987)’ and provided the respective evaluations of ‘Dislike’, ‘Dislike’, ‘Like’, ‘Like’, ‘Dislike’, ‘Dislike’, ‘Like’, ‘Like’, ‘Dislike’, ‘Dislike’. Please judge whether user likes the ‘Young Frankenstein (1974)’. Please output only the results ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’.” Output: “Like” Recommendation Prompt Example Beauty Input: “In chronological order, User 1 has successively watched the products ‘B001DYLHJA’, ‘B0089JVEPO’, ‘B001G2LWDK’, ‘B005Z41P28’, ‘B0055MYJ0U’ and provided the respective ratings ‘5.0’, ‘1.0’, ‘5.0’, ‘3.0’, ‘4.0’ (with a maximum score of 5 and a minimum score of 1). Please predict the rating (within the range of 1 to 5) that the user will give to the product ‘B00117CH5M’. Please output only the score as the result.” Output: “4” |
4. Experiment
- How does the performance of the TisLLM framework compare to traditional methods?
- What is the impact of the time series component on the performance of the TisLLM framework?
- How does the sliding window length of the time series in the TisLLM framework affect the experimental results?
- What implications does the TisLLM framework have for the interpretability analysis of large language models?
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Baseline Model Comparison Analysis
4.4. Specific Details
4.5. Resource Utilization and Time Efficiency Analysis
4.5.1. Training Phase Analysis
4.5.2. Inference Phase Analysis
4.6. Experimental Results
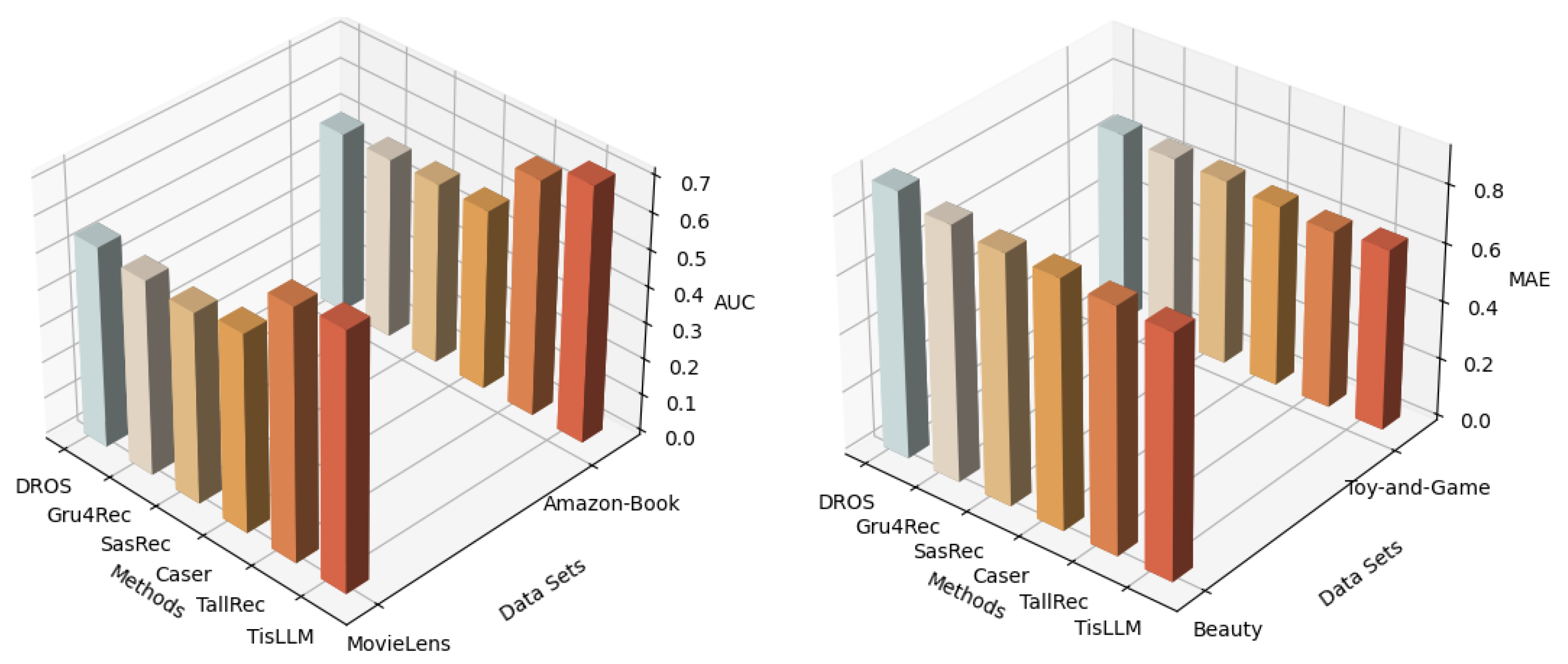
4.6.1. Performance Comparison (RQ1)
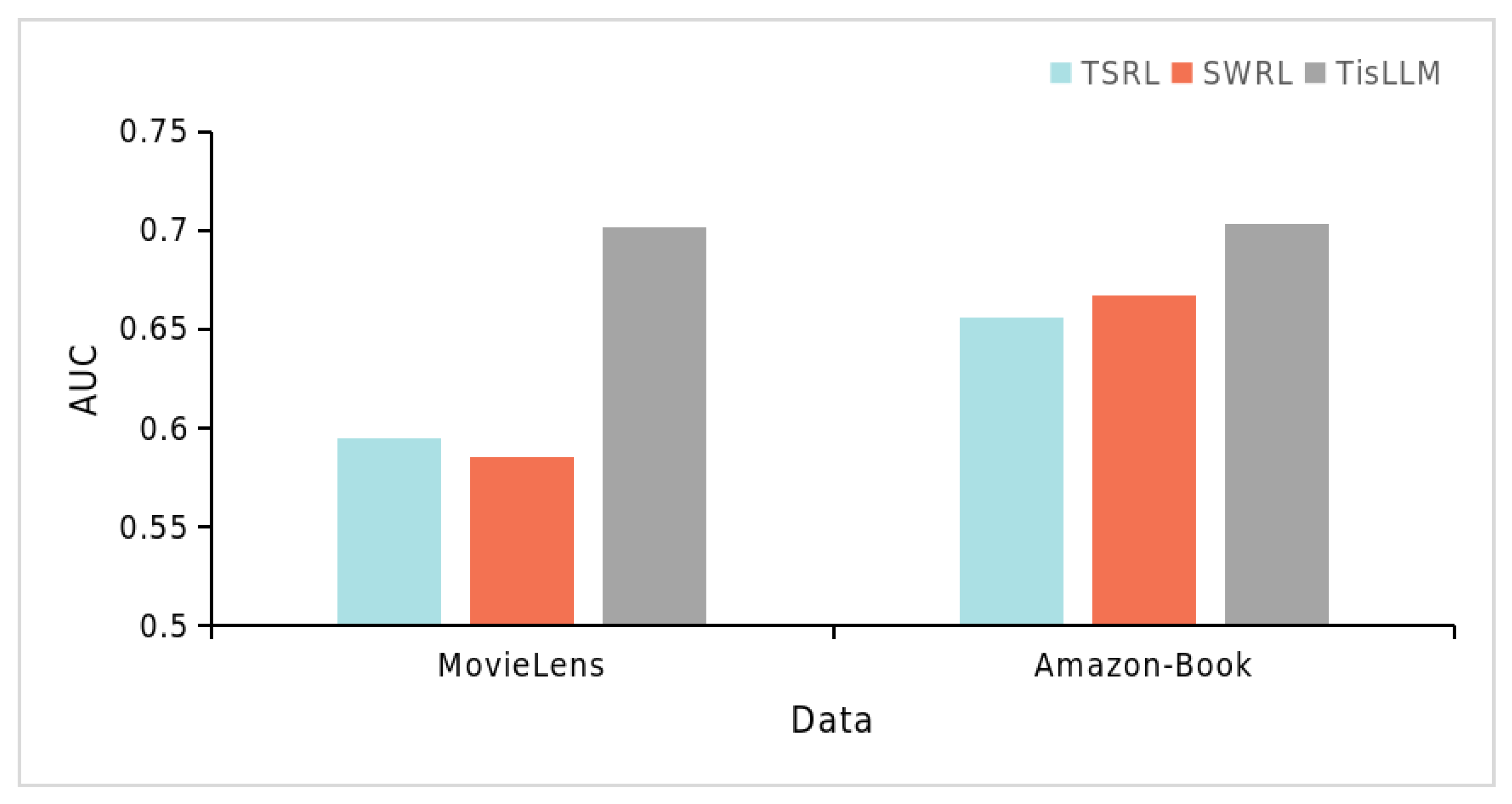
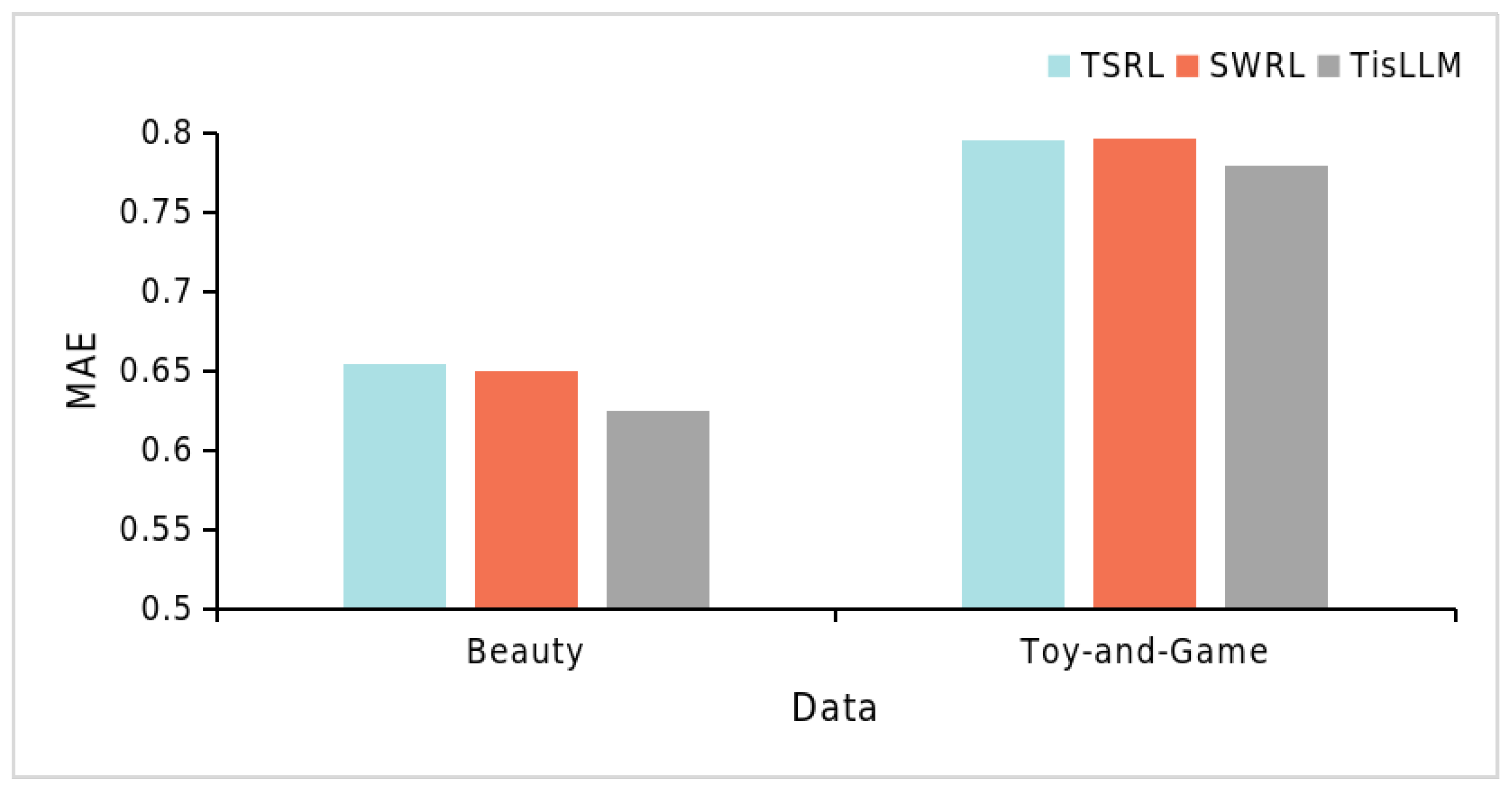
4.6.2. Time Series Impact (RQ2)
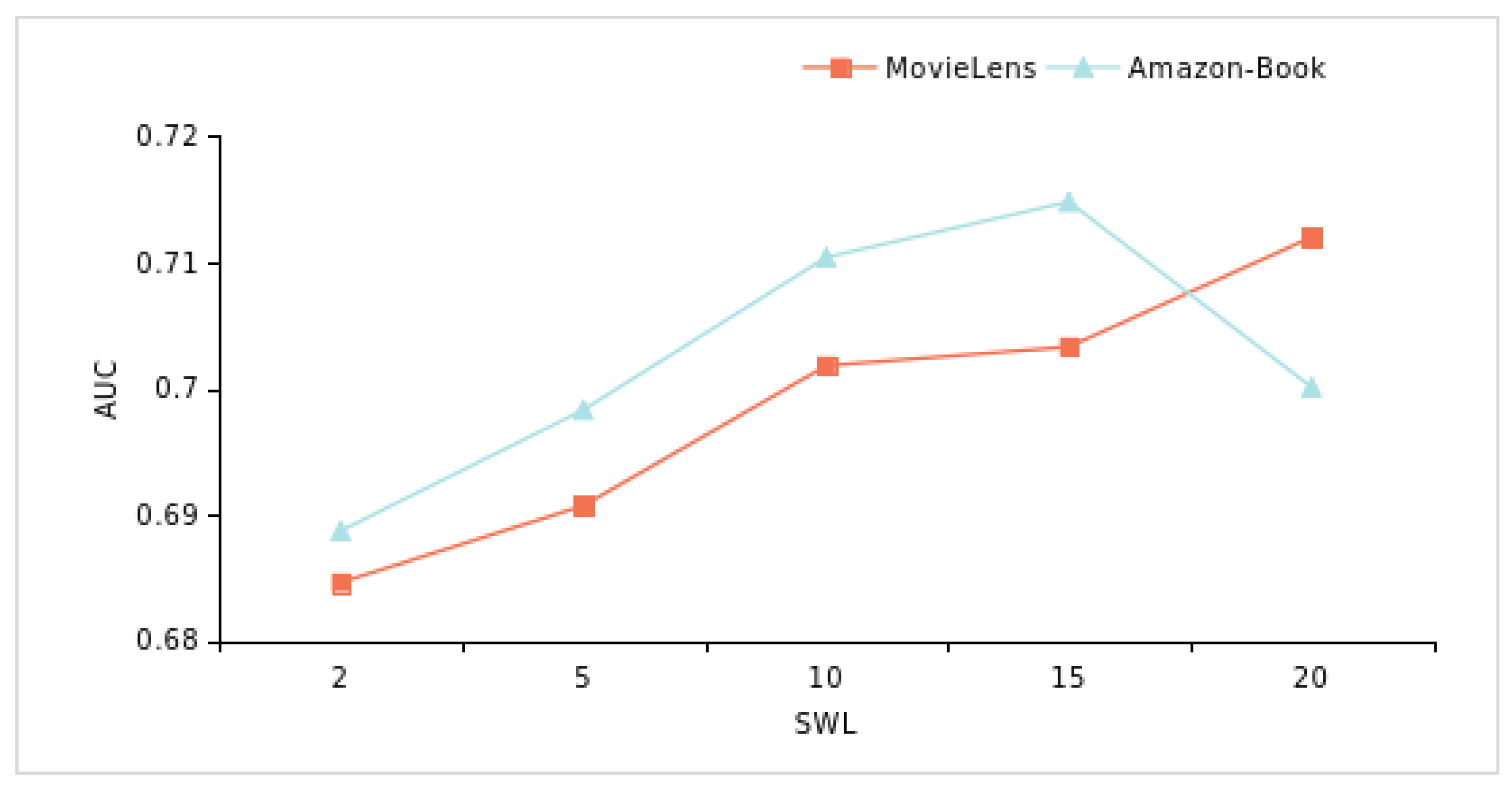
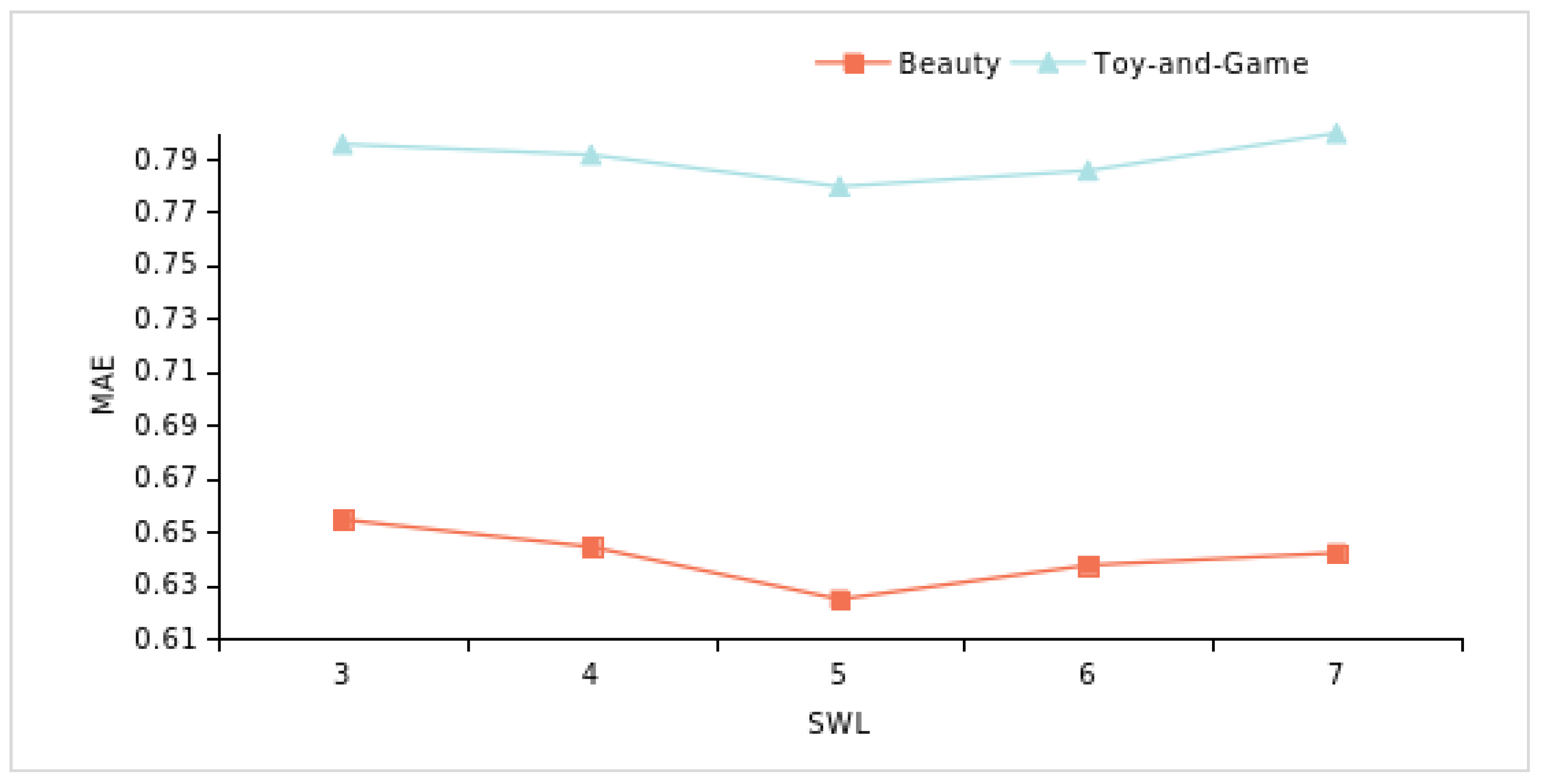
4.6.3. Sliding Window Analysis on Time Series (RQ3)
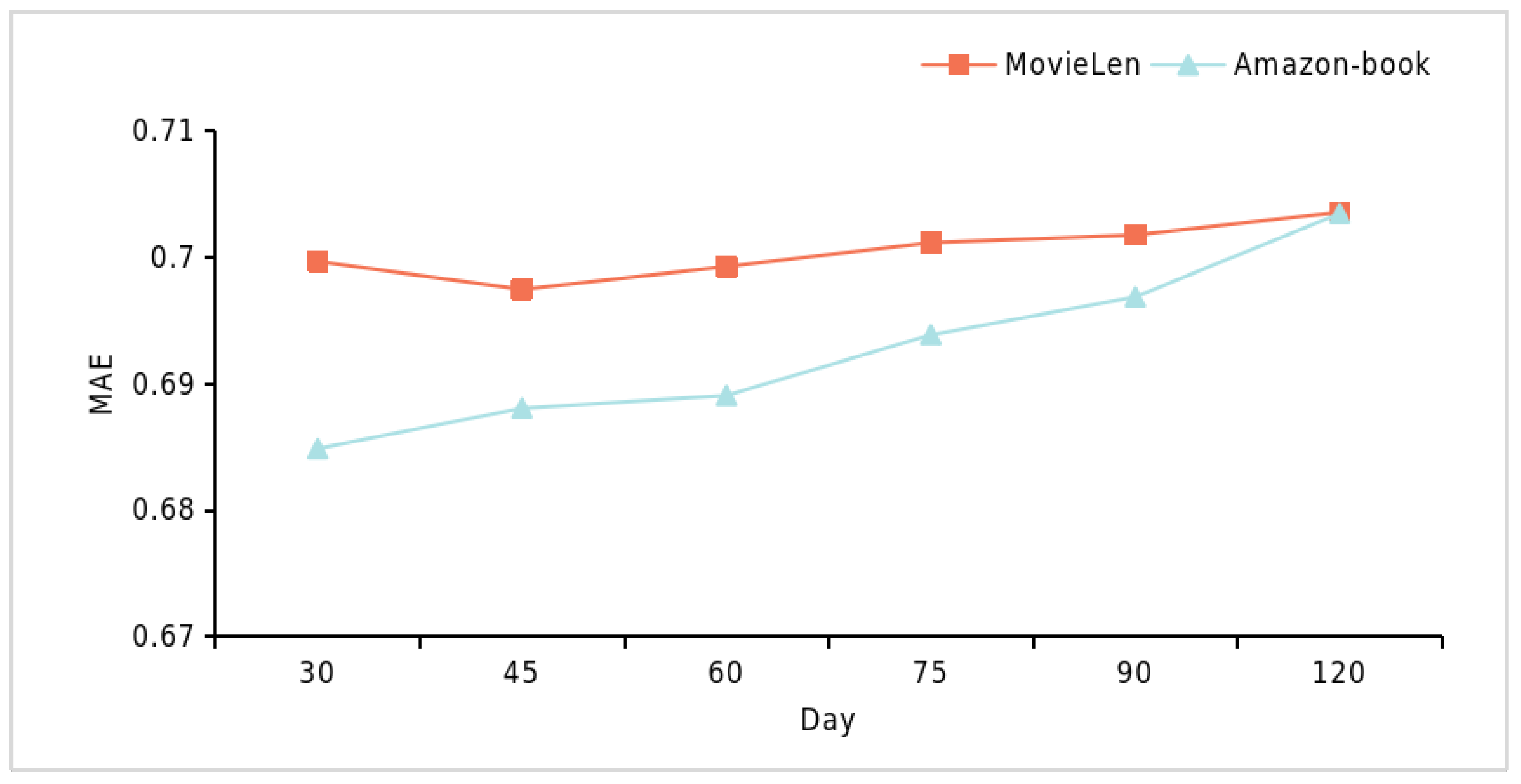
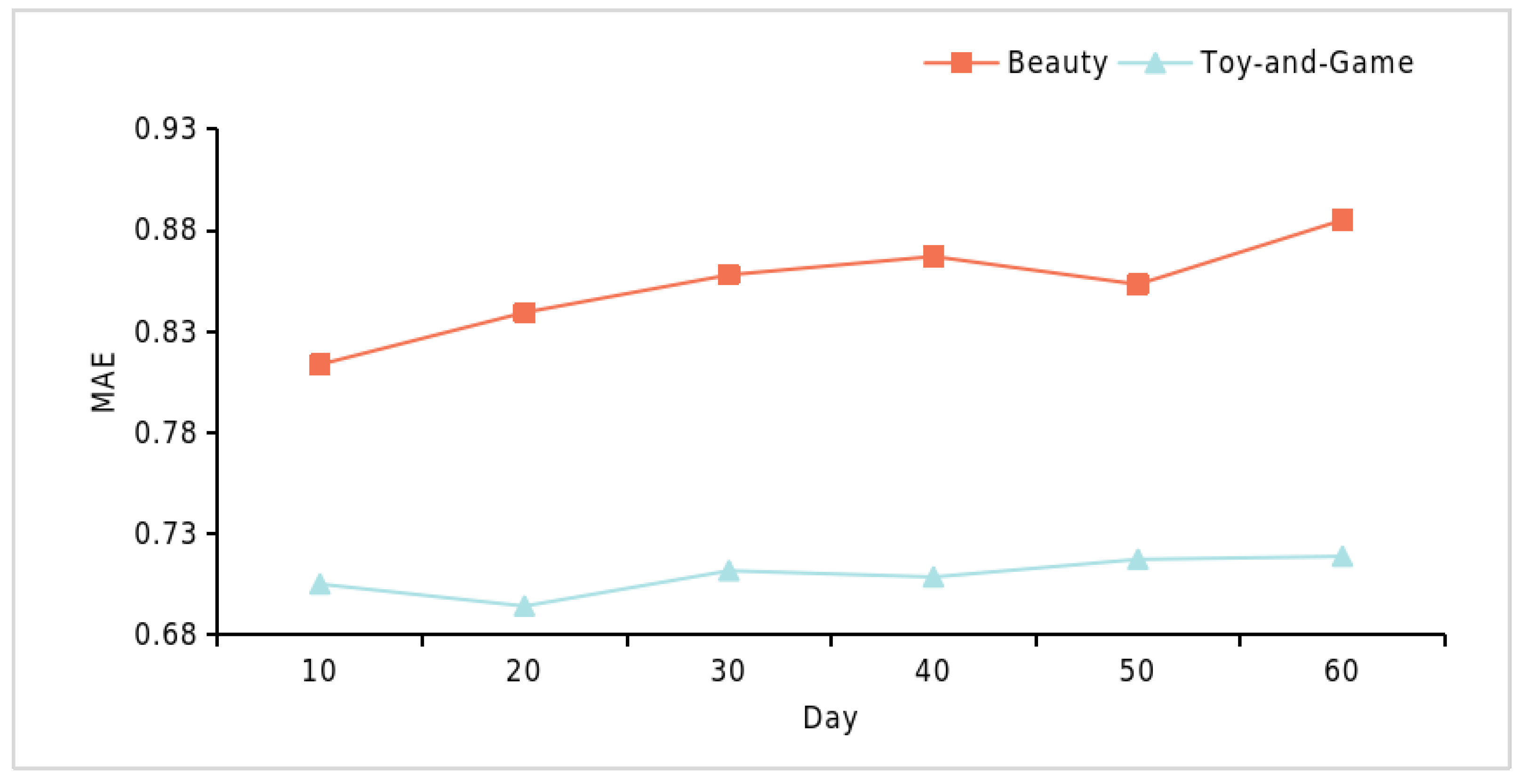
4.6.4. Interpretive Analysis of the TisLLM Framework (RQ4)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, T.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.D.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language models are few-shot learners. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 1877–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, B.; Hou, Y.; Lu, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, W.X.; Chen, M.; Wen, J.R. Adapting large language models by integrating collaborative semantics for recommendation. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 40th International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE), Utrecht, The Netherlands, 13–16 May 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Shan, R.; Zhu, C.; Du, K.; Chen, B.; Quan, S.; Tang, R.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, W. Rella: Retrieval-enhanced large language models for lifelong sequential behavior comprehension in recommendation. In Proceedings of the ACM on Web Conference 2024, Singapore, 13–17 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Xie, R.; Hou, Y.; Zhao, X.; Lin, L.; Wen, J.R. Recommendation as instruction following: A large language model empowered recommendation approach. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 2023, 43, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zheng, Z.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, H.; Gu, H.; Shen, T.; Qin, C.; Zhu, C.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Q.; et al. A survey on large language models for recommendation. World Wide Web 2024, 27, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lim, E.P. Zero-shot next-item recommendation using large pretrained language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.03153. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, F.; Zhang, J.; Bao, K.; Wang, Q.; He, X. Collm: Integrating collaborative embeddings into large language models for recommendation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.19488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Cheng, H.; Liang, Q.; Chen, L.; Han, B. Integrating Large Language Models with Graphical Session-Based Recommendation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.16539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Chua, H.; Liu, H.; Wu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y. Large Language Model with Graph Convolution for Recommendation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.08859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; NeurIPS: San Diego, CA, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, W.C.; McAuley, J. Self-attentive sequential recommendation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), Singapore, 17–20 November 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S.; Yao, Y.; He, B.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, A.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Zhan, M.; Song, L. Integrating large language models into recommendation via mutual augmentation and adaptive aggregation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.13870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bao, K.; Yan, M.; Wang, W.; Feng, F.; He, X. Text-like Encoding of Collaborative Information in Large Language Models for Recommendation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.03210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, K.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Feng, F.; He, X. Tallrec: An effective and efficient tuning framework to align large language model with recommendation. In Proceedings of the 17th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, Singapore, 18–22 September 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, S.; Liu, S.; Fu, Z.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, Y. Recommendation as language processing (rlp): A unified pretrain, personalized prompt & predict paradigm (p5). In Proceedings of the 16th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, New York, NY, USA, 18–23 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Gao, C.; Yuan, S.; Liu, S.; Cai, Q.; Jiang, P. Dlcrec: A novel approach for managing diversity in llm-based recommender systems. In Proceedings of the Eighteenth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Hannover, Germany, 10–14 March 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Mehta, N.; Yi, X.; Keshavan, R.; Heldt, L.; Hong, L.; Chi, E.H.; Sathiamoorthy, M. Aligning Large Language Models with Recommendation Knowledge. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.00245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wu, Q.; Liang, Z.; Han, J.; Ning, X.; Shi, Y.; Lin, W.; Zhang, Y. SLMRec: Distilling large language models into small for sequential recommendation. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2405.17890. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, S.; Hua, W.; Ge, Y.; Tan, J.; Zhang, Y. Genrec: Large language model for generative recommendation. In European Conference on Information Retrieval; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Ma, W.; Sun, P.; Zhang, M.; Ai, Q.; Liu, Y.; Cai, M. Common sense enhanced knowledge-based recommendation with large language model. In International Conference on Database Systems for Advanced Applications; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, B.; Wang, X.; Liu, E.; Wang, X.; Hongyu, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, W.X.; Wen, J.R. DeepRec: Towards a Deep Dive Into the Item Space with Large Language Model Based Recommendation. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.16810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Song, C.; Yi, L.; Cheng, G. TRAWL: External Knowledge-Enhanced Recommendation with LLM Assistance. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.06642. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, F.; Wang, Q.; Feng, F.; He, X. Reason4Rec: Large Language Models for Recommendation with Deliberative User Preference Alignment. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.02061. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Hu, H.; Sha, L.; Xu, C.; Wong, K.F.; Jiang, D. RecInDial: A unified framework for conversational recommendation with pretrained language models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.0747. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, X.; Wei, W.; Xia, L.; Su, L.; Cheng, S.; Wang, J.; Yin, D.; Huang, C. Representation learning with large language models for recommendation. In Proceedings of the ACM on Web Conference 2024, Singapore, 13–17 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Zhou, P.; Lv, R.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, Y. Is chatgpt a good recommender? A preliminary study. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.10149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Chao, W.; Qiu, Z.; Zhu, H.; Xiong, H. Harnessing large language models for text-rich sequential recommendation. In Proceedings of the ACM on Web Conference 2024, Singapore, 13–17 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Harper, F.M.; Konstan, J.A. The MovieLens Datasets: History and Context. ACM Trans. Interact. Intell. Syst. (TiiS) 2015, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAuley, J.; Targett, C.; Shi, Q.; van den Hengel, A. Image-based recommendations on styles and substitutes. In Proceedings of the 38th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval (SIGIR ’15), Santiago, Chile, 9–13 August 2015; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Hidasi, B.; Karatzoglou, A.; Baltrunas, L.; Tikk, D. Session-based recommendations with recurrent neural networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.06939. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Wang, K. Personalized top-n sequential recommendation via convolutional sequence embedding. In Proceedings of the Eleventh ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 5–9 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; He, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Xin, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, X. A generic learning framework for sequential recommendation with distribution shifts. In Proceedings of the 46th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Taipei, Taiwan, 23–27 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- McAuley, J.; Leskovec, J. Hidden factors and hidden topics: Understanding rating dimensions with review text. In Proceedings of the 7th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, Hong Kong, China, 12–16 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P.; Li, J.; Li, G. Research on Collaborative Filtering Recommendation Algorithm Based on Sentiment Analysis and Topic Model. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Big Data and Computing, Guangzhou, China, 10–12 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Noroozi, V.; Yu, P.S. Joint deep modeling of users and items using reviews for recommendation. In Proceedings of the Tenth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Cambridge, UK, 6–10 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Ma, S. Neural attentional rating regression with review-level explanations. In Proceedings of the 2018 World Wide Web Conference, Lyon, France, 23–27 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Lv, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, J. A Deep Recommendation Model with Multi-Layer Interaction and Sentiment Analysis. Data Anal. Knowl. Discov. 2023, 7, 43–57. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, E.J.; Shen, Y.; Wallis, P.; Allen-Zhu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, W. LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2106.09685. [Google Scholar]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. SGDR: Stochastic Gradient Descent with Warm Restarts. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1608.03983. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.; Mou, N.; Fan, Y.; Pi, Q.; Bian, W.; Zhou, C.; Zhu, X.; Gai, K. Deep Interest Evolution Network for Click-Through Rate Prediction. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Volume 33. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, B.; Geng, L.; Ji, J. Time Series Large Language Model for Recommendation System. In Proceedings of the 2025 4th International Conference on Robotics, Artificial Intelligence and Intelligent Control (RAIIC), Chengdu, China, 4–6 July 2025. [Google Scholar]

| Dataset | Number of Users | Number of Ratings | Sparsity |
|---|---|---|---|
| MovieLens | 943 | 100,000 | 0.9363 |
| Amazon-Book | 651 | 99,979 | 0.9966 |
| Beauty | 5123 | 91,824 | 0.9985 |
| Toys-and-Games | 4188 | 74,423 | 0.9985 |
| Equipment Setting | Device Information |
|---|---|
| CPU | 12th Gen Intel(R) Core(TM) i9-12900K |
| GPU | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 24G |
| RAM | 128G KF3200C16D4/32GX DDR4 |
| Operating System | Linux ubuntu 5.15.0-134-generic |
| Programming Language | Python 3.10.14 |
| CUDA | CUDA 11.8 |
| Dataset | Time (hh:mm:ss) | GPU Util. (%) | Power (W) | VRAM Usage (MiB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MovieLens | 41:14:42 | 100 | 348 | 23,399 |
| Amazon-Book | 40:41:40 | 100 | 347 | 22,281 |
| Beauty | 12:16:05 | 83 | 348 | 16,679 |
| Toy-and-Game | 09:30:20 | 73 | 348 | 16,364 |
| Dataset | Time (mm:ss) | GPU Util. (%) | Power (W) | VRAM Usage (MiB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MovieLen | 59:22 | 99 | 349 | 23,436 |
| Amazon-book | 57:34 | 99 | 349 | 22,147 |
| Beauty | 41:27 | 100 | 348 | 14,741 |
| Toy-and-Game | 32:43 | 100 | 348 | 14,618 |
| AUC | ||||||
| Data\Methods | DROS | Gru4Rec | SasRec | Caser | TallRec | TisLLM |
| MovieLens | 0.5502 | 0.5341 | 0.5225 | 0.5420 | 0.6866 | 0.7009 ± 0.0019 |
| Amazon-Book | 0.5021 | 0.4988 | 0.4991 | 0.4959 | 0.6484 | 0.7053 ± 0.0032 |
| MAE | ||||||
| Data\Methods | HFT | SATMCF | DeepConn | NARRE | DeepSami | TisLLM |
| Beauty | 0.9114 | 0.8733 | 0.8550 | 0.8488 | 0.8364 | 0.7773 ± 0.0030 |
| Toy-and-Game | 0.6638 | 0.6499 | 0.6435 | 0.6264 | 0.6127 | 0.6269 ± 0.0022 |
| AUC | |||||
| Dataset | SWL-2 | SWL-5 | SWL-10 | SWL-15 | SWL-20 |
| MovieLens | 0.6846 | 0.6907 | 0.7018 | 0.7033 | 0.7120 |
| Amazon-Book | 0.6887 | 0.6983 | 0.7104 | 0.7148 | 0.7001 |
| MAE | |||||
| Dataset | SWL-3 | SWL-4 | SWL-5 | SWL-6 | SWL-7 |
| Beauty | 0.7953 | 0.7913 | 0.7794 | 0.7854 | 0.7994 |
| Toy-and-Game | 0.6544 | 0.6442 | 0.6245 | 0.6373 | 0.6419 |
| Model | AUC | MAE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MovieLens | Amazon-Book | Beauty | Toy-and-Game | |
| TisLLM | 0.7018 | 0.7033 | 0.6245 | 0.7794 |
| TSRL | 0.5952 | 0.6563 | 0.6545 | 0.7953 |
| SWRL | 0.5855 | 0.6671 | 0.6499 | 0.7968 |
| AUC | ||||||
| Dataset | 30 d | 45 d | 60 d | 75 d | 90 d | 120 d |
| MovieLens | 0.6997 | 0.6975 | 0.6993 | 0.7012 | 0.7018 | 0.7036 |
| Amazon-Book | 0.6849 | 0.6881 | 0.6891 | 0.6939 | 0.6969 | 0.7035 |
| MAE | ||||||
| Dataset | 10 d | 20 d | 30 d | 40 d | 50 d | 60 d |
| Beauty | 0.7052 | 0.6943 | 0.7118 | 0.7087 | 0.7174 | 0.7189 |
| Toy-and-Game | 0.8138 | 0.8395 | 0.8581 | 0.8672 | 0.8534 | 0.8852 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, B.; Geng, L. TisLLM: Temporal Integration-Enhanced Fine-Tuning of Large Language Models for Sequential Recommendation. Information 2025, 16, 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16090818
Zhu X, Li W, Zhang B, Geng L. TisLLM: Temporal Integration-Enhanced Fine-Tuning of Large Language Models for Sequential Recommendation. Information. 2025; 16(9):818. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16090818
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Xiaosong, Wenzheng Li, Bingqiang Zhang, and Liqing Geng. 2025. "TisLLM: Temporal Integration-Enhanced Fine-Tuning of Large Language Models for Sequential Recommendation" Information 16, no. 9: 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16090818
APA StyleZhu, X., Li, W., Zhang, B., & Geng, L. (2025). TisLLM: Temporal Integration-Enhanced Fine-Tuning of Large Language Models for Sequential Recommendation. Information, 16(9), 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16090818








