Leveraging Explainable AI for LLM Text Attribution: Differentiating Human-Written and Multiple LLM-Generated Text
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Advancements in Text Attribution
2.2. Leveraging LLMs for Text Detection
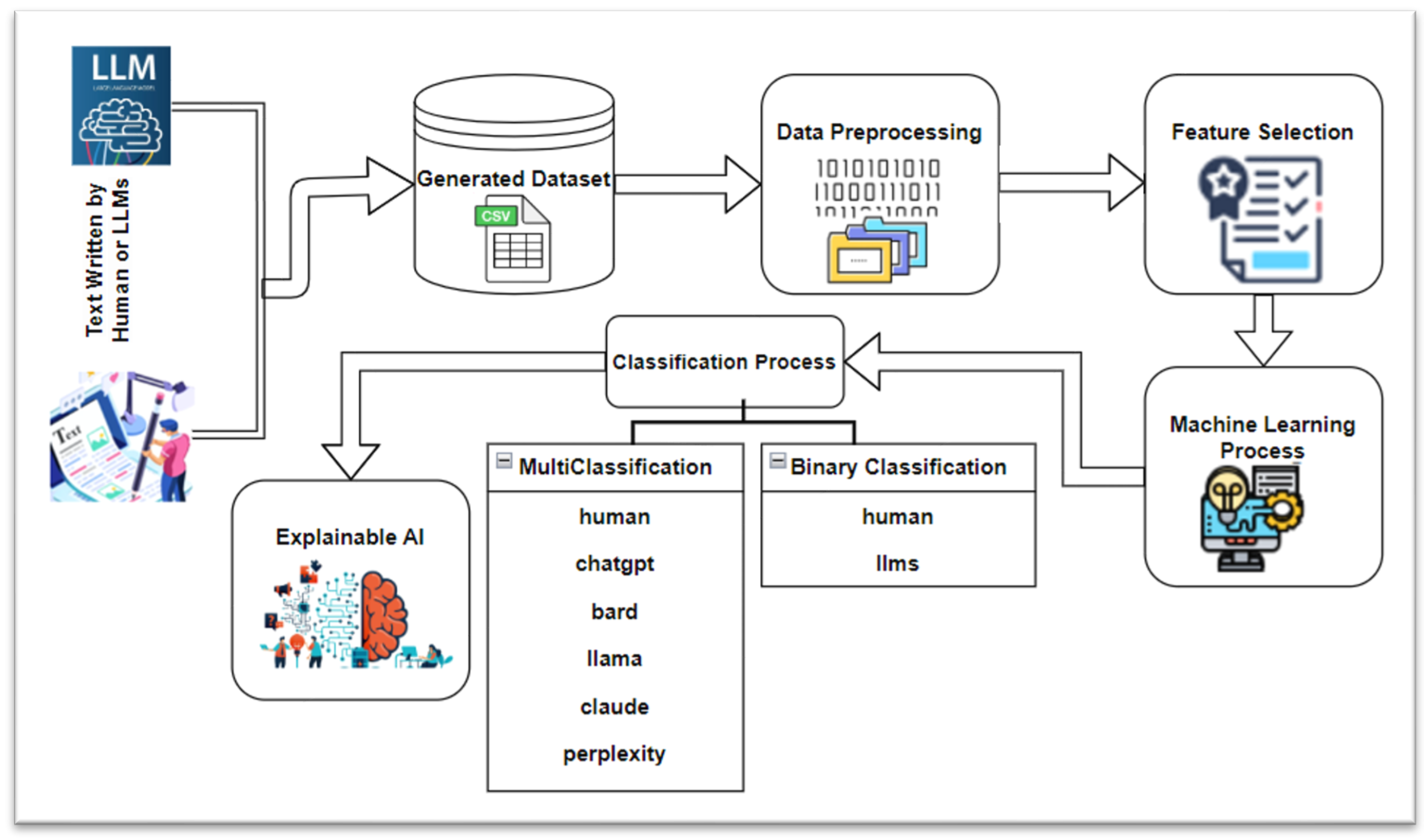
3. Methodology
3.1. Dataset Collation and Generation
- id—A unique identifier for each essay.
- prompt_id—Identifies the prompt for which the essay was produced. Two essays are available: “Car-free cities”, rated “0”; and “Does the electoral college work?” rated “1”.
- text—The essay text itself.
- generated—Whether the essay was written by an LLM (“1”) or by a student (“0”).
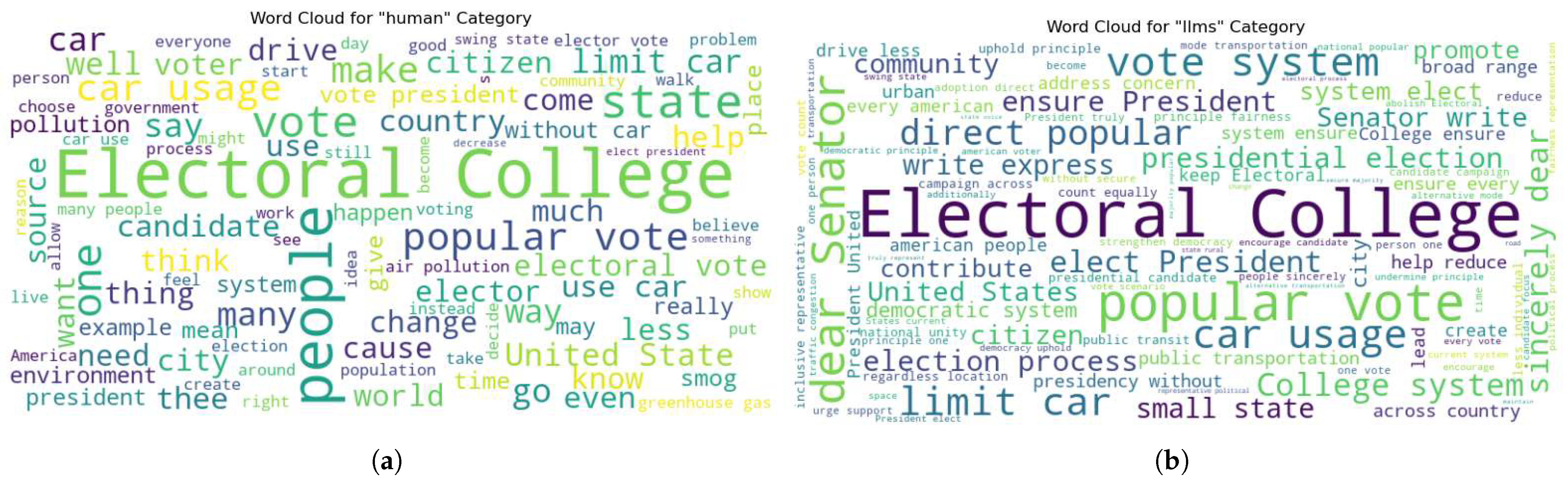
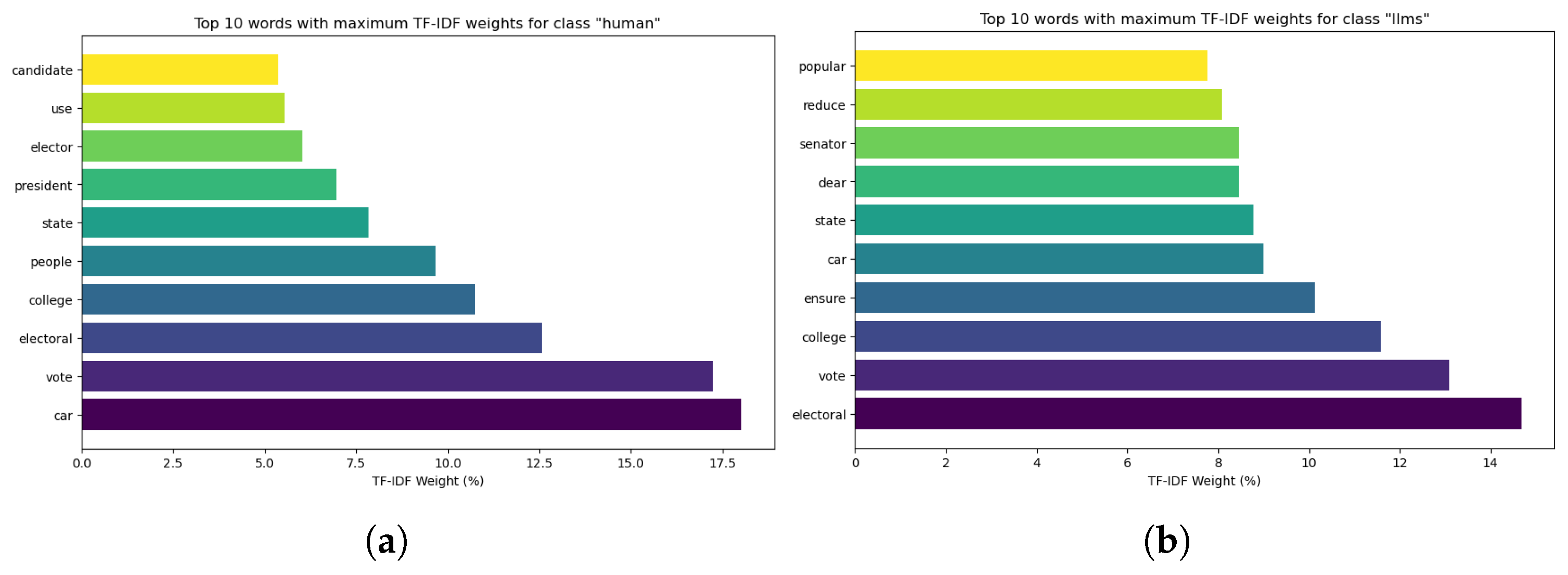
3.2. Data Preprocessing and Feature Selection
| Words Frequency–Human Texts | Words Frequency–LLM Texts | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Word | Count | Percentage % | Word | Count | Percentage % |
| car | 2464 | 2.72 | system | 337 | 2.28 |
| vote | 2163 | 2.39 | electoral | 319 | 2.15 |
| people | 1360 | 1.50 | vote | 317 | 2.14 |
| state | 1121 | 1.24 | college | 303 | 2.05 |
| Electoral | 958 | 1.06 | state | 225 | 1.52 |
| would | 901 | 0.99 | popular | 182 | 1.23 |
| college | 884 | 0.97 | car | 178 | 1.20 |
| not | 767 | 0.85 | ensure | 177 | 1.20 |
| electoral | 750 | 0.83 | would | 161 | 1.09 |
| use | 656 | 0.72 | dear | 150 | 1.01 |
3.3. Classification Algorithms
3.3.1. Binary Classification
3.3.2. Multi-Classification
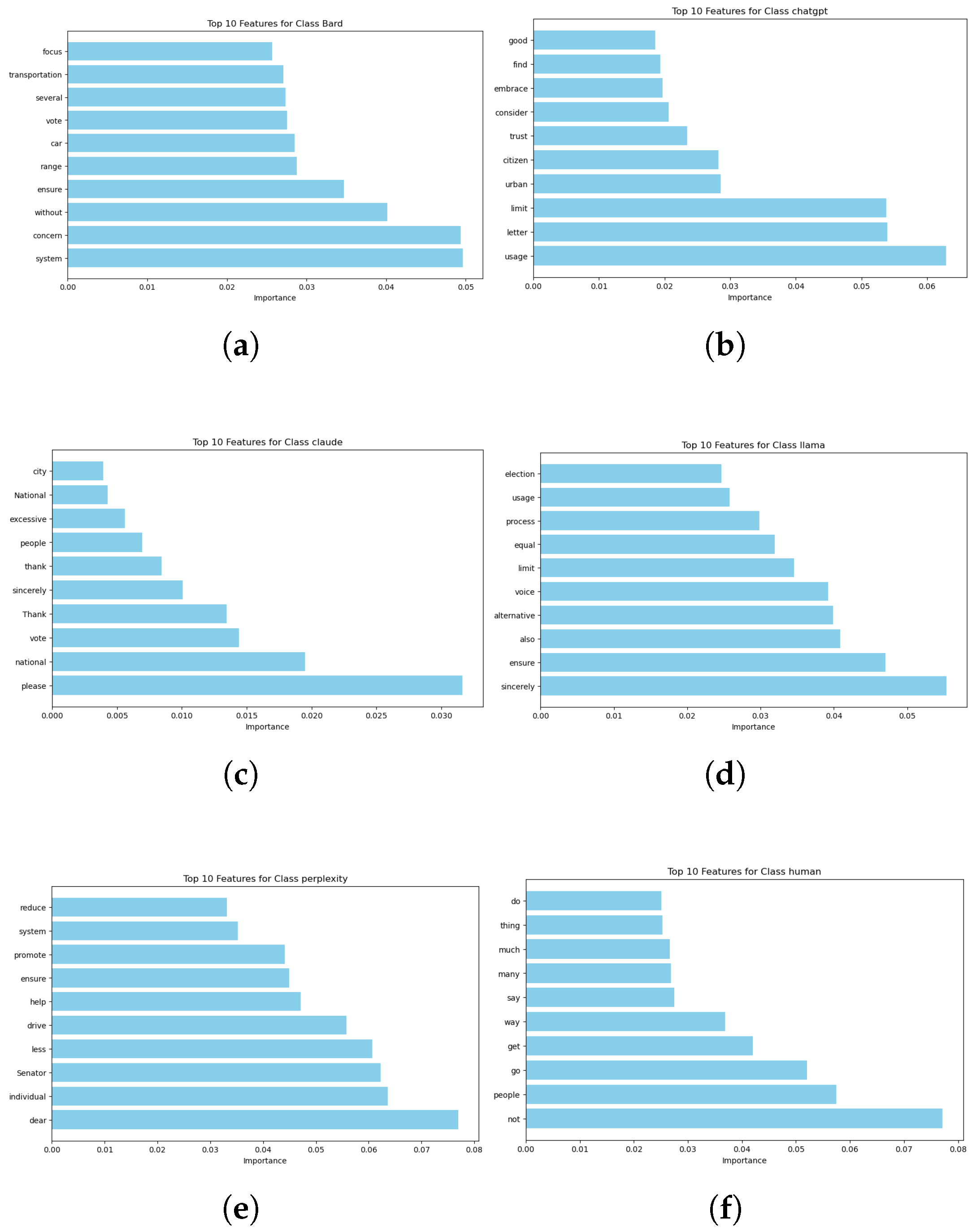
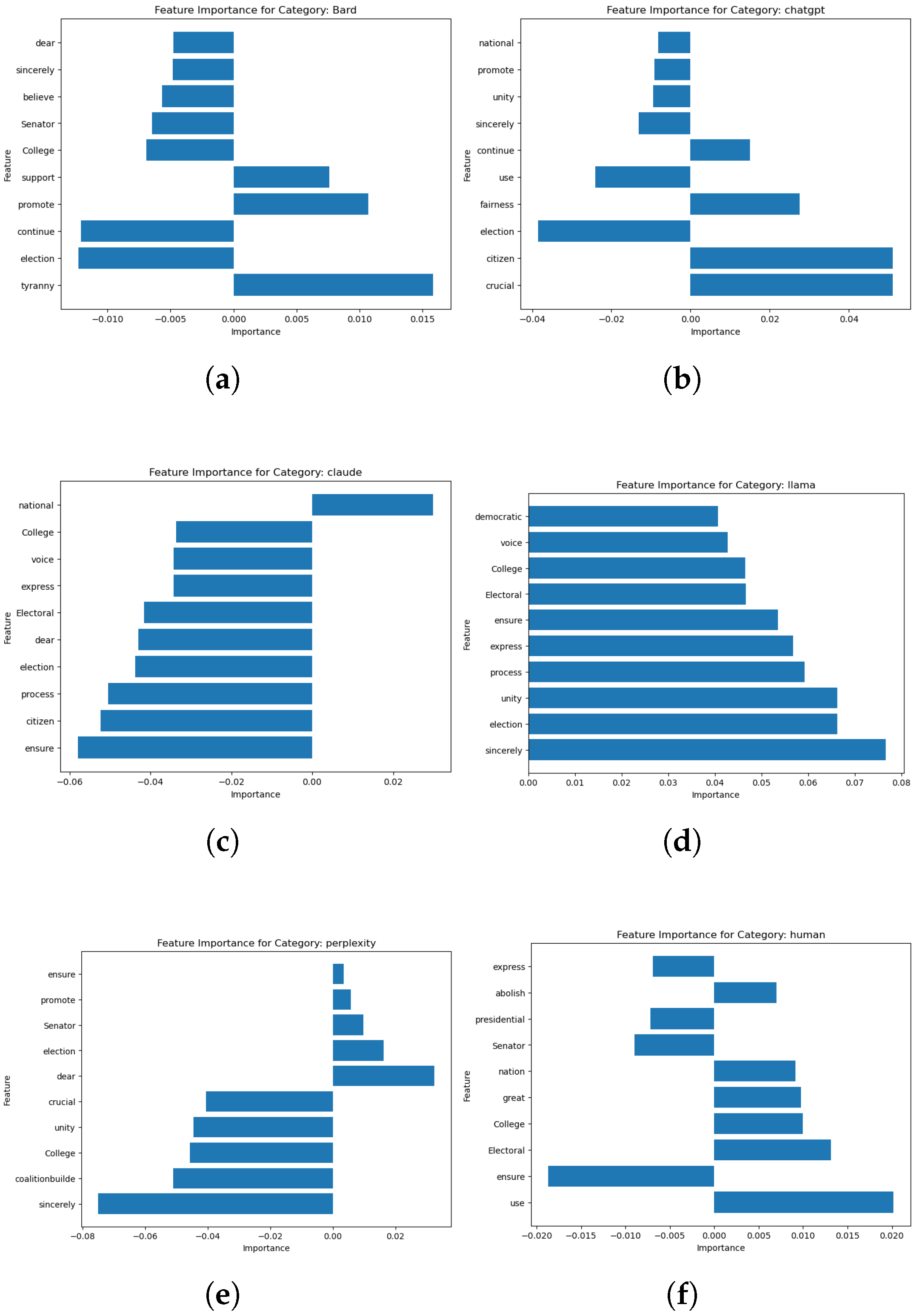
3.4. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI)
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
4.1. Model Evaluation
4.1.1. Binary Classification
| Algorithm | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | 97% | 96% | 95% | 96% |
| XGBoost | 98% | 97% | 98% | 98% |
| RNN | 94% | 93% | 94% | 94% |
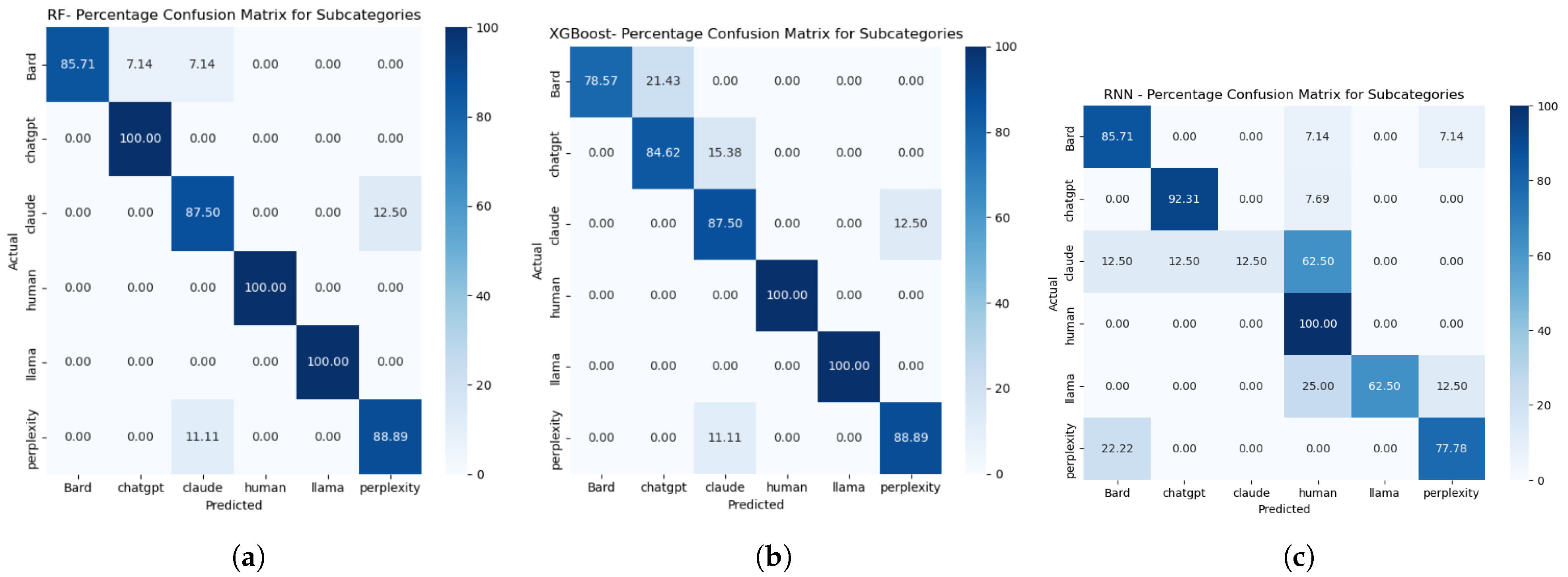
4.1.2. Multi-Classification
| Algorithm | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | 97% | 93% | 94% | 93% |
| XGBoost | 94% | 90% | 90% | 89% |
| RNN | 88% | 90% | 72% | 74% |
4.2. Explainable AI
| Instance Text | True Label | Predicted Label | Prediction Probabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| “dear Senator write express strong support continue use Electoral College presidential election process proud citizen great nation believe crucial maintain principle fairness equality upon democracy found Electoral College ensure small state voice election process promote coalitionbuilde national unity serve vital check tyranny majority implore uphold integrity democratic system reject attempt abolish Electoral College sincerely” | llama | llama | 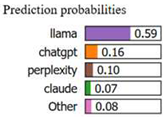 |
4.3. Evaluation
| Class Name | GPTZero Message | AI Text Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Human | “This text is most likely to be written by a human” | 0–10% |
| Different Result | “Our ensemble of detectors predicts different results for this text. Please enter more text for more precise predictions.” | 11–39% |
| Mix | “This text is likely to be a mix of human and AI text” | 40–88% |
| AI | “This text is likely to be written by AI” | 89–100% |
| Not Recognized | “Try typing in some more text (>250 characters) so we can give you accurate results” | The total text is less than 250 characters |
| Class | Human | AI | Mix | Different Result | Not Recognized | Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPTZero | Human | 59 | 1 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 78.3% |
| LLMs | 5 | 35 | 7 | 0 | 5 | ||
| Our Model | Human | 66 | 2 | - | - | - | 97.5% |
| LLMs | 1 | 51 | - | - | - |
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hadi, M.U.; Qureshi, R.; Shah, A.; Irfan, M.; Zafar, A.; Shaikh, M.B.; Akhtar, N.; Wu, J.; Mirjalili, S. A survey on large language models: Applications, challenges, limitations, and practical usage. Authorea Prepr. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, S. Plagiarism and academic misconduct: A systematic review. Desidoc J. Libr. Inf. Technol. 2019, 39, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tami, M.; Ashqar, H.I.; Elhenawy, M. Automated Question Generation for Science Tests in Arabic Language Using NLP Techniques. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.08520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammoudi, M.; Habaybeh, A.; Ashqar, H.I.; Elhenawy, M. Question-Answering (QA) Model for a Personalized Learning Assistant for Arabic Language. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.08519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AopenAI. Introducing ChatGPT. 2023. Available online: https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- Jayaseelan, N. lama 2, A New Intelligent Open Source Language Model. 2024. Available online: https://www.e2enetworks.com/blog/llama-2-the-new-open-source-language-model (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- Team, S. Google Bard: Uses, Limitations, and Tips for More Helpful Answers. 2024. Available online: https://www.semrush.com/blog/google-bard/? (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- Anthropic. Introducing Claude. 2024. Available online: https://www.anthropic.com/index/introducing-claude (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- Perplexity. Introducing PPLX Online LLMs. 2024. Available online: https://blog.perplexity.ai/blog/introducing-pplx-online-llms (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- Radwan, A.; Amarneh, M.; Alawneh, H.; Ashqar, H.I.; AlSobeh, A.; Magableh, A.A.A.R. Predictive analytics in mental health leveraging llm embeddings and machine learning models for social media analysis. Int. J. Web Serv. Res. (IJWSR) 2024, 21, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masri, S.; Raddad, Y.; Khandaqji, F.; Ashqar, H.I.; Elhenawy, M. Transformer Models in Education: Summarizing Science Textbooks with AraBART, MT5, AraT5, and mBART. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.07692. [Google Scholar]
- Jaradat, S.; Nayak, R.; Paz, A.; Ashqar, H.I.; Elhenawy, M. Multitask Learning for Crash Analysis: A Fine-Tuned LLM Framework Using Twitter Data. Smart Cities 2024, 7, 2422–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Chua, M.; Rickard, M.; Lorenzo, A. ChatGPT and large language model (LLM) chatbots: The current state of acceptability and a proposal for guidelines on utilization in academic medicine. J. Pediatr. Urol. 2023, 19, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, D.; Macvean, A.; Hellendoorn, V.; Vasilescu, B.; Myers, B. Using an llm to help with code understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM 46th International Conference on Software Engineering, New York, NY, USA, 14–20 April 2024; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, E.; Janamsetty, R.; Kinares, C.; Koh, C.; Sanchez, A.; Zhan, F.; Ozdemir, M.; Waseem, S.; Yolcu, O.; Dahal, B.; et al. Machine learning models for paraphrase identification and its applications on plagiarism detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Big Knowledge (ICBK), Beijing, China, 10–11 November 2019; pp. 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- AlSallal, M.; Iqbal, R.; Amin, S.; James, A.; Palade, V. An integrated machine learning approach for extrinsic plagiarism detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 9th International Conference on Developments in eSystems Engineering (DeSE), Liverpool, UK, 31 August–2 September 2016; pp. 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Anguita, A.; Beghelli, A.; Creixell, W. Automatic cross-language plagiarism detection. In Proceedings of the 2011 7th International Conference on Natural Language Processing and Knowledge Engineering, Tokushima, Japan, 27–29 November 2011; pp. 173–176. [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi, H.; Goto, T.; Wakatsuki, M.; Nishino, T. A source code plagiarism detecting method using alignment with abstract syntax tree elements. In Proceedings of the 15th IEEE/ACIS International Conference on Software Engineering, Artificial Intelligence, Networking and Parallel/Distributed Computing (SNPD), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 30 June–2 July 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Suleiman, D.; Awajan, A.; Al-Madi, N. Deep learning based technique for plagiarism detection in Arabic texts. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on New Trends in Computing Sciences (ICTCS), Amman, Jordan, 11–13 October 2017; pp. 216–222. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, R.; Chuang, Y.N.; Hu, X. The science of detecting llm-generated text. Commun. Acm 2024, 67, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yang, S.; Zhan, R.; Yuan, Y.; Wong, D.F.; Chao, L.S. A survey on llm-gernerated text detection: Necessity, methods, and future directions. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.14724. [Google Scholar]
- Hayawi, K.; Shahriar, S.; Mathew, S.S. The imitation game: Detecting human and ai-generated texts in the era of large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.12166. [Google Scholar]
- Orenstrakh, M.S.; Karnalim, O.; Suarez, C.A.; Liut, M. Detecting llm-generated text in computing education: A comparative study for chatgpt cases. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.07411. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Ding, X.; Emani, M.; Vanderbruggen, T.; Lin, P.H.; Liao, C. Data race detection using large language models. In Proceedings of the SC’23 Workshops of The International Conference on High Performance Computing, Network, Storage, and Analysis, Denver, CO, USA, 12–17 November 2023; pp. 215–223. [Google Scholar]
- Lab, T.L.A. LLM—Detect AI Generated Text | Kaggle. 2024. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/competitions/llm-detect-ai-generated-text/data (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- Tabassum, A.; Patil, R.R. A survey on text pre-processing & feature extraction techniques in natural language processing. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. (IRJET) 2020, 7, 4864–4867. [Google Scholar]
- Abubakar, H.D.; Umar, M.; Bakale, M.A. Sentiment classification: Review of text vectorization methods: Bag of words, Tf-Idf, Word2vec and Doc2vec. Slu J. Sci. Technol. 2022, 4, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, E.; Friedman, B. Data statements for NLP: Toward Mitigating System Bias and Enabling Better Science. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2018, 6, 587–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GPTZero. GPTZero|The Trusted AI Detector for ChatGPT, GPT-4, and More. 2024. Available online: https://gptzero.me/ (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- Svrluga, S. Princeton Student Creates GPTZero Tool to Detect ChatGPT-Generated Text. 2024. Available online: https://www.washingtonpost.com/education/2023/01/12/gptzero-chatgpt-detector-ai/ (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- Wikipedia. GPTZero. 2024. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GPTZero (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- Habibzadeh, F. GPTZero performance in identifying artificial intelligence-generated medical texts: A preliminary study. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2023, 38, 1516083870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heumann, M.; Kraschewski, T.; Breitner, M.H. ChatGPT and GPTZero in Research and Social Media: A Sentiment-and Topic-Based Analysis. Available online: https://aisel.aisnet.org/amcis2023/sig_hci/sig_hci/6 (accessed on 6 July 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Najjar, A.A.; Ashqar, H.I.; Darwish, O.; Hammad, E. Leveraging Explainable AI for LLM Text Attribution: Differentiating Human-Written and Multiple LLM-Generated Text. Information 2025, 16, 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16090767
Najjar AA, Ashqar HI, Darwish O, Hammad E. Leveraging Explainable AI for LLM Text Attribution: Differentiating Human-Written and Multiple LLM-Generated Text. Information. 2025; 16(9):767. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16090767
Chicago/Turabian StyleNajjar, Ayat A., Huthaifa I. Ashqar, Omar Darwish, and Eman Hammad. 2025. "Leveraging Explainable AI for LLM Text Attribution: Differentiating Human-Written and Multiple LLM-Generated Text" Information 16, no. 9: 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16090767
APA StyleNajjar, A. A., Ashqar, H. I., Darwish, O., & Hammad, E. (2025). Leveraging Explainable AI for LLM Text Attribution: Differentiating Human-Written and Multiple LLM-Generated Text. Information, 16(9), 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16090767








