Robust and Scalable Quantum Repeaters Using Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction and Literature Review
2. Methodology
2.1. System Description
2.2. Cost Function with Frobenius Output Measure
2.3. System Training and Training Pairs
2.4. Noise Simulation
3. Results
4. Conclusions and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dieks, D. Communication by EPR devices. Phys. Lett. A 1982, 92, 271–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wootters, W.K.; Zurek, W.H. A single quantum cannot be cloned. Nature 1982, 299, 802–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briegel, H.J.; Dür, W.; Cirac, J.I.; Zoller, P. Quantum repeaters for communication. arXiv 1998, arXiv:quant-ph/9803056. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.W.; Bouwmeester, D.; Weinfurter, H.; Zeilinger, A. Experimental entanglement swapping: Entangling photons that never interacted. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Patil, A.; Guha, S. Measurement-Based Entanglement Distillation and Constant-Rate Quantum Repeaters over Arbitrary Distances. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.11174. [Google Scholar]
- Azuma, K.; Tamaki, K.; Lo, H.K. All-photonic quantum repeaters. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, K.; Economou, S.; Elkouss, D.; Hilaire, P.; Jiang, L.; Lo, H.K.; Tzitrin, I. Quantum repeaters: From quantum networks to the quantum internet. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2023, 95, 045006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Jie, Q.X.; Li, M.; Wu, S.H.; Wang, Z.B.; Zou, X.B.; Zhang, P.F.; Li, G.; Zhang, T.; Guo, G.C.; et al. Proposal of quantum repeater architecture based on Rydberg atom quantum processors. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.12523. [Google Scholar]
- Zajac, J.M.; Huber-Loyola, T.; Hofling, S. Quantum dots for quantum repeaters. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.13775. [Google Scholar]
- Cussenot, P.; Grivet, B.; Lanyon, B.P.; Northup, T.E.; de Riedmatten, H.; Sørensen, A.S.; Sangouard, N. Uniting Quantum Processing Nodes of Cavity-coupled Ions with Rare-earth Quantum Repeaters Using Single-photon Pulse Shaping Based on Atomic Frequency Comb. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.18704. [Google Scholar]
- Chelluri, S.S.; Sharma, S.; Schmidt, F.; Kusminskiy, S.V.; van Loock, P. Bosonic quantum error correction with microwave cavities for quantum repeaters. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.21569. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, Y.; Azar, M.; Chandra, N.K.; Jin, X.; Cheng, J.; Seshadreesan, K.P.; Liu, J. Quantum repeaters enhanced by vacuum beam guides. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.13397. [Google Scholar]
- Mor-Ruiz, M.F.; Miguel-Ramiro, J.; Wallnöfer, J.; Coopmans, T.; Dür, W. Merging-based quantum repeater. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.04450. [Google Scholar]
- Mastriani, M. Simplified entanglement swapping protocol for the quantum Internet. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayrakci, V.; Ozaydin, F. Quantum Zeno repeaters. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrman, E.C.; Steck, J.E.; Kumar, P.; Walsh, K.A. Quantum algorithm design using dynamic learning. Quantum Inf. Comput. 2008, 8, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Lin, K.; Jain, A.K.; Zhou, J. Transfer Learning in Deep Reinforcement Learning: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 13344–13362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, K.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M.; Wang, D. A survey of transfer learning. J. Big Data 2016, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, N.; Nguyen, N.; Behrman, E.; Steck, J. Experimental pairwise entanglement estimation for an N-qubit system: A machine learning approach for programming quantum hardware. Quantum Inf. Process. 2020, 19, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrman, E.; Steck, J. Multiqubit entanglement of a general input state. Quantum Inf. Comput. 2013, 13, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrman, E.; Nguyen, N.; Steck, J.; McCann, M. Quantum neural computation of entanglement is robust to noise and decoherence. In Quantum Inspired Computational Intelligence; Bhattacharyya, S., Maulik, U., Dutta, P., Eds.; Morgan Kaufmann: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 3–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.H.; Behrman, E.C.; Steck, J.E. Quantum Learning with Noise and Decoherence: A Robust Quantum Neural Network. Quantum Mach. Intell. 2020, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rethinam, M.; Javali, A.; Hart, A.; Behrman, E.; Steck, J. A genetic algorithm for finding pulse sequences for nmr quantum computing. Paritantra—J. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2011, 20, 32–42. [Google Scholar]
- Nola, J.; Sanchez, U.; Murthy, A.K.; Behrman, E.; Steck, J. Training microwave pulses using machine learning. Acad. Quantum 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Lin, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Z.; Ruan, D.; Yin, L.; Long, G.L. Experimental free-space quantum secure direct communication and its security analysis. Photonics Res. 2020, 8, 1522–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Niyato, D.; Hanzo, L. From single-protocol to large-scale multiprotocol quantum networks. IEEE Netw. 2022, 36, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, I.; Nielsen, M. Quantum Computation and Quantum Information; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Roweis, S. Levenberg-Marquardt Optimization. Available online: https://people.duke.edu/~hpgavin/SystemID/References/lm-Roweis.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Levenberg, K. A Method for the Solution of Certain Non-Linear Problems in Least Squares. Q. Appl. Math. 1944, 2, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, D. An Algorithm for Least-Squares Estimation of Nonlinear Parameters. J. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. 1963, 11, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, J.J. The Levenberg-Marquardt Algorithm: Implementation and Theory; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1978; pp. 431–441. [Google Scholar]
- Steck, J.E.; Thompson, N.L.; Behrman, E.C. Programming Quantum Hardware via Levenberg-Marquardt Machine Learning. In Intelligent Quantum Information Processing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Transtrum, M.K.; Sethna, J.P. Improvements to the Levenberg Marquardt algorithm for nonlinear least- squares minimization. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1201.5885. [Google Scholar]
- Transtrum, M.K.; Machta, B.B.; Sethna, J.P. Geometry of nonlinear least squares with applications to sloppy models and optimization. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 83, 036701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottesman, D. An introduction to quantum error correction and fault tolerant quantum computation. Proc. Symp. Appl. Math. 2010, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knill, E.; Laflamme, R.; Zurek, W. Resilient quantum computation: Error models and thresholds. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1998, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgopoulos, K.; Emary, C.; Zuliani, P. Modelling and simulating the noisy behavior of near-term quantum compiuters. Phys. Rev. A 2021, 104, 062432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markiewicz, M.; Puchala, Z.; de Rosier, A.; Laskowski, W.; Zyczkowski, K. Quantum noise generated by local random Hamiltonians. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 95, 032333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, F.; Zhang, W.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y. Analysis on the inherent noise tolerance of feedforward network and one noise-resilient structure. Neural Netw. 2023, 165, 786–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, R.; Nguyen, N.; Behrman, E.; Li, A.; Steck, J. Existence of a robust optimal control process for efficient measurements in a two-qubit system. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2506.19122. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.; Cao, C.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Hou, S.Y.; Xu, P.; Zeng, B. Simulating noisy quantum circuits with matrix product density operators. Phys. Rev. Res. 2021, 3, 023005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

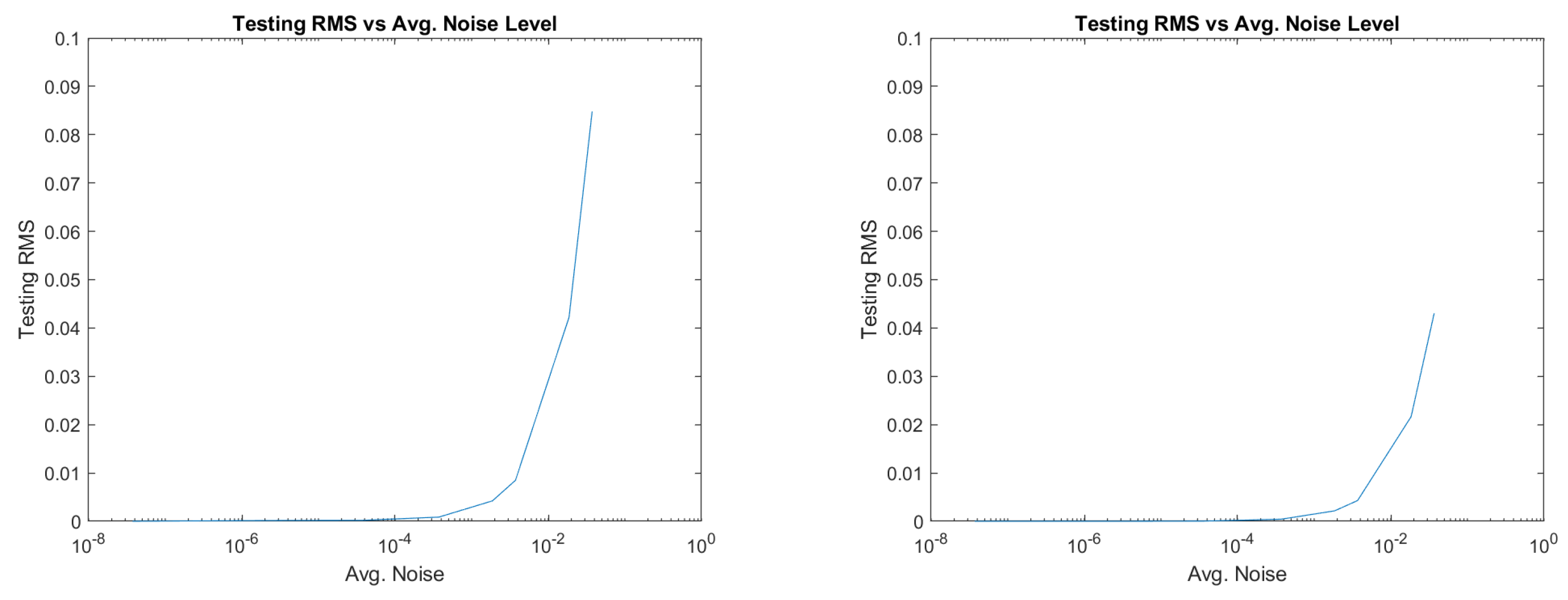
| Testing RMS | |
|---|---|
| 2 | |
| 4 | |
| 6 | |
| 8 |
| RNP | Pure Noise RMS | Decoherence RMS | Complex Noise RMS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0019 | 0.0047 | 0.0085 |
| RNP | Pure Noise RMS | Decoherence RMS | Complex Noise RMS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0012 | 0.0021 |
| RNP | Pure Noise RMS | Decoherence RMS | Complex Noise RMS |
|---|---|---|---|
| RNP | Pure Noise RMS | Decoherence RMS | Complex Noise RMS |
|---|---|---|---|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fuentealba, D.; Dahn, J.; Steck, J.; Behrman, E. Robust and Scalable Quantum Repeaters Using Machine Learning. Information 2025, 16, 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16070552
Fuentealba D, Dahn J, Steck J, Behrman E. Robust and Scalable Quantum Repeaters Using Machine Learning. Information. 2025; 16(7):552. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16070552
Chicago/Turabian StyleFuentealba, Diego, Jackson Dahn, James Steck, and Elizabeth Behrman. 2025. "Robust and Scalable Quantum Repeaters Using Machine Learning" Information 16, no. 7: 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16070552
APA StyleFuentealba, D., Dahn, J., Steck, J., & Behrman, E. (2025). Robust and Scalable Quantum Repeaters Using Machine Learning. Information, 16(7), 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16070552









