DDA-MSLD: A Multi-Feature Speech Lie Detection Algorithm Based on a Dual-Stream Deep Architecture
Abstract
1. Introduction
- 1.
- By simulating stressful situations in real environments, we constructed a single-person scenario lie speech dataset called “Local”. During the construction process, we fully considered the psychological pressure and real-world impacts faced when lying, which enhanced the ecological validity of the collected data. This dataset not only provides solid data support for the algorithm proposed in this paper but also offers high-quality training resources for future lie detection research, promoting the performance improvement and optimization of speech-based lie detection technology in practical applications.
- 2.
- The algorithm proposed in this paper integrates three network structures—the gated recurrent unit (GRU), attention mechanism, and transformer–to process the prosodic features, nonlinear dynamic features, and Mel spectrogram features of speech signals. It not only takes into account both static and dynamic characteristics but also combines manually extracted features with deep features adaptively learned by neural networks, capturing more comprehensive lie-related information and thereby improving the accuracy and generalization of lie detection.
- 3.
- Through experiments on the CSC dataset and the self-constructed Local dataset, the DDA-MSLD algorithm demonstrated better accuracy and generalization than existing methods, proving its potential and value in practical applications.
2. Related Work
2.1. Lie Detection Based on Handcrafted Feature Extraction
2.2. Lie Detection Based on Deep Learning
3. Datasets
3.1. CSC Dataset
3.2. Local Dataset
3.3. Local Dataset Evaluation
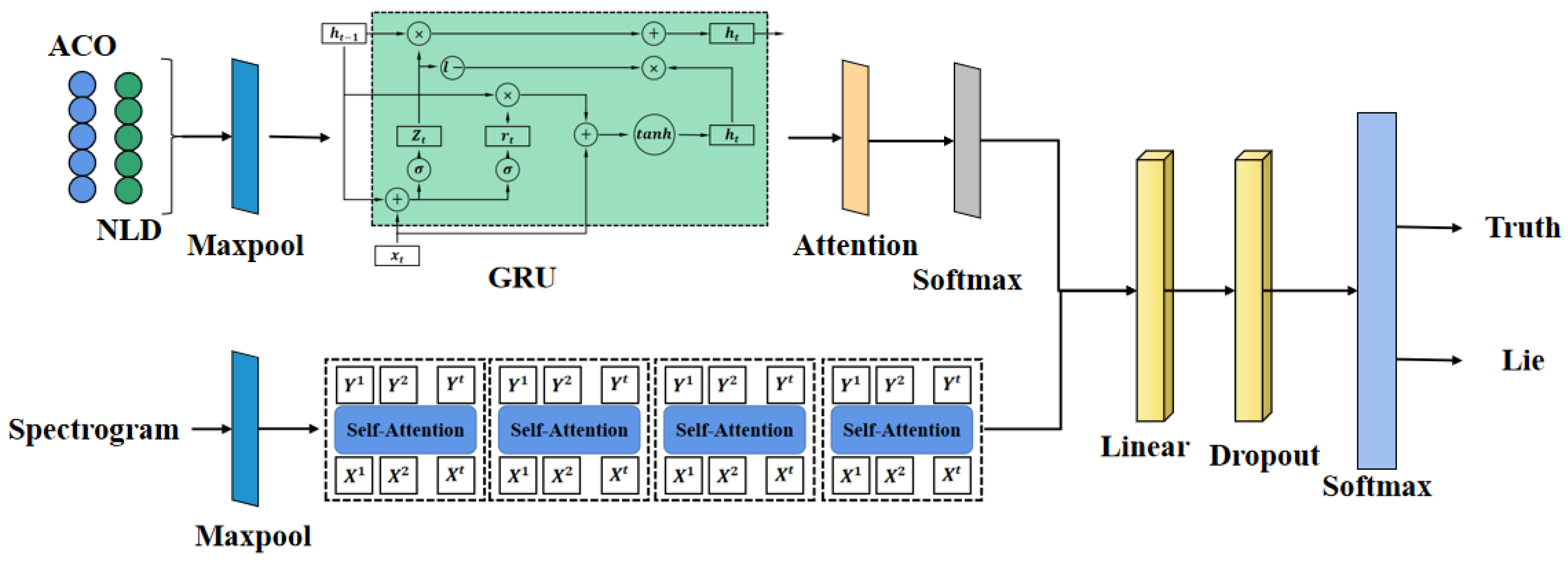
4. Methods
4.1. Feature Extraction
4.1.1. Acoustic Prosodic Features
4.1.2. Nonlinear Dynamic Features
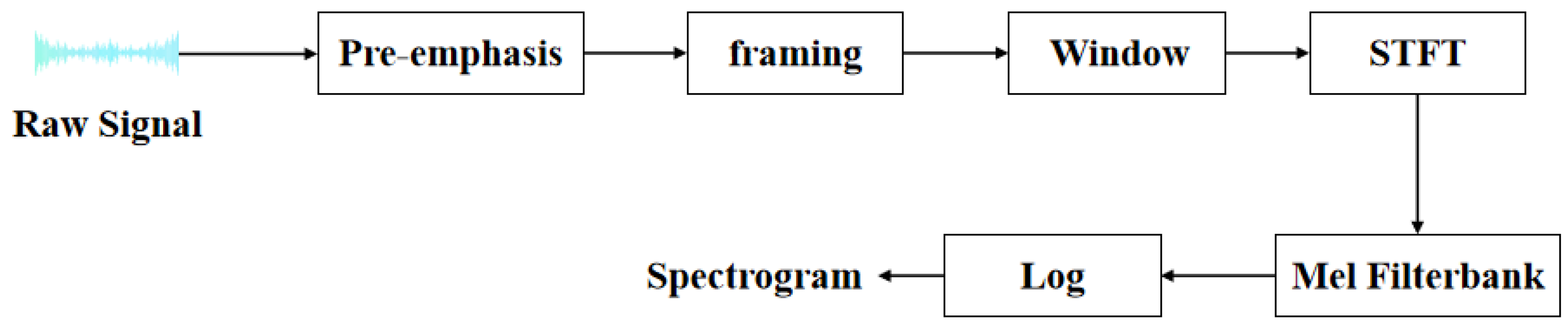
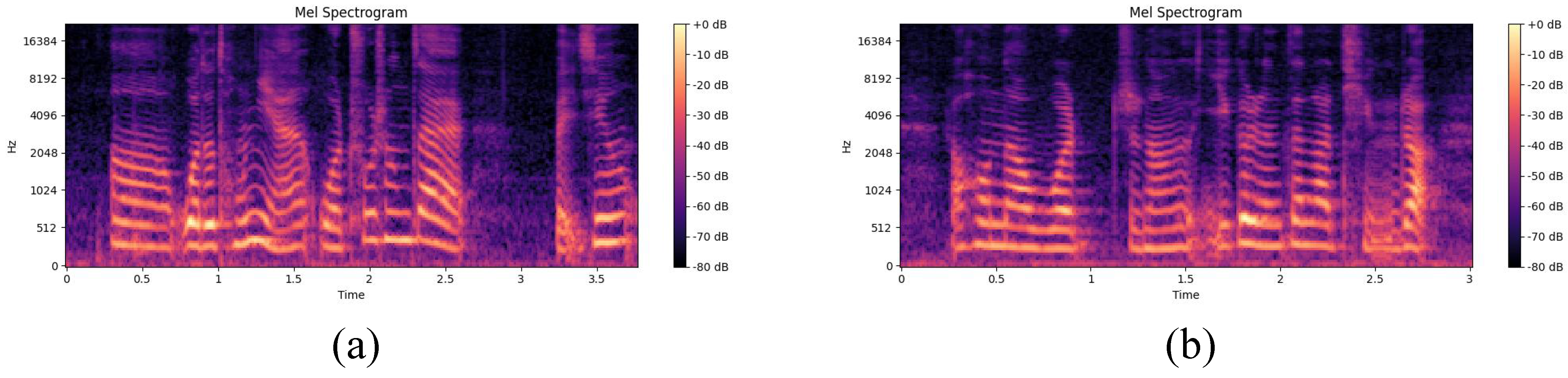
4.1.3. Mel Spectrograms
4.2. Network Structure
4.2.1. GRU-Attention
4.2.2. Transformer
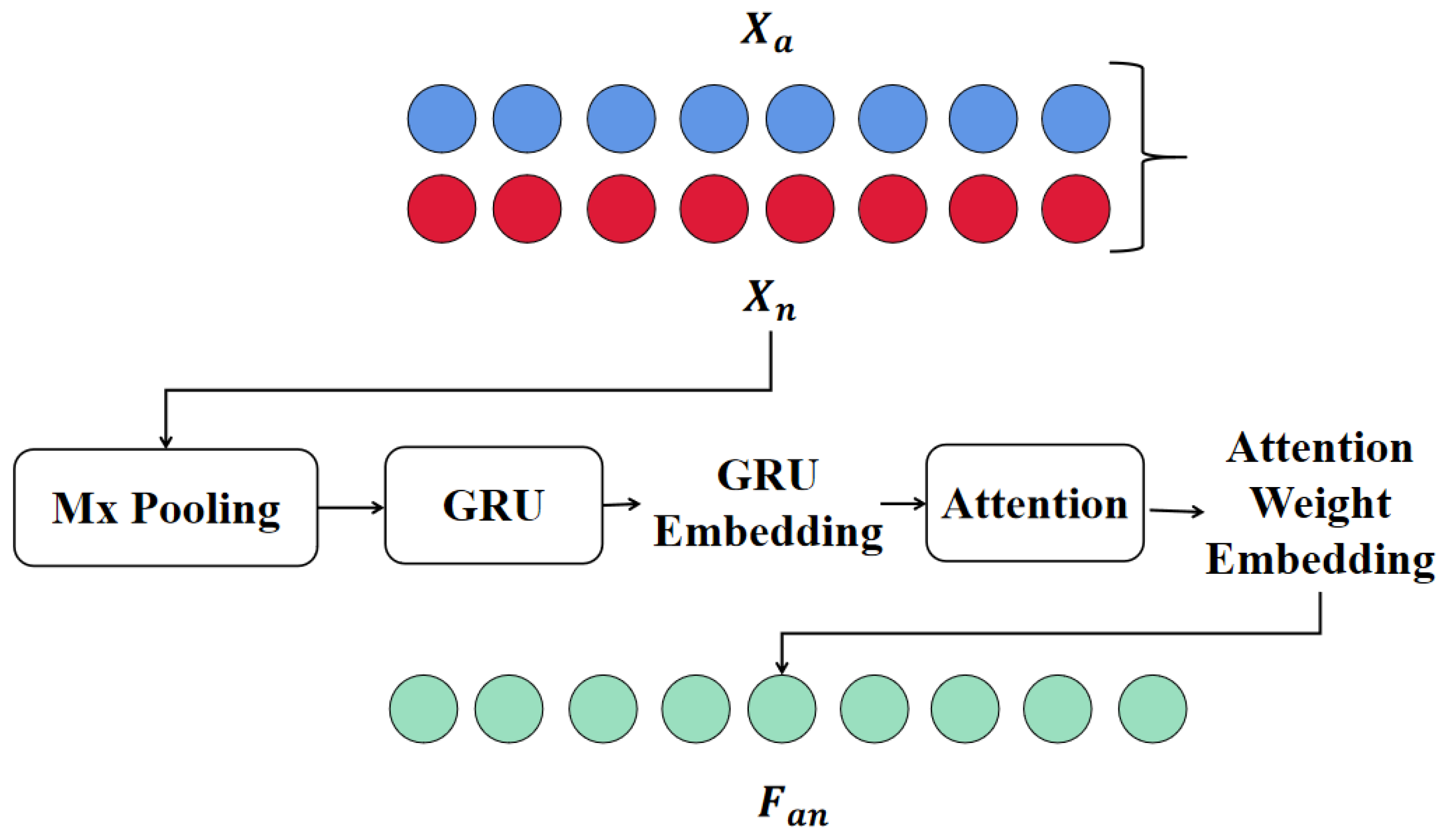
4.3. Multi-Feature Fusion
5. Experiment
5.1. Experimental Set-Up
5.2. Ablation Experiment
5.3. Experimental Comparison on the CSC Datasets
5.4. Experimental Comparison on the Local Datasets
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, H.; Pan, X.; Shang, L. Deception detecting from speech signal using relevance vector machine and non-linear dynamics features. Neurocomputing 2015, 151, 1042–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, C.; Wiley, L.E. Changes of blood pressure and respiration during deception. J. Comp. Psychol. 1926, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrij, A.; Granhag, P.A.; Porter, S. Pitfalls and opportunities in nonverbal and verbal lie detection. Psychol. Sci. Public Interest 2010, 11, 89–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graciarena, M.; Shriberg, E.; Stolcke, A.; Enos, F.; Hirschberg, J.; Kajarekar, S. Combining prosodic lexical and cepstral systems for deceptive speech detection. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing Proceedings, Toulouse, France, 14–19 May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ekman, P.; O’Sullivan, M.; Friesen, W.V.; Scherer, K.R. Invited article: Face, voice, and body in detecting deceit. J. Nonverbal Behav. 1991, 15, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePaulo, B.M.; Lindsay, J.J.; Malone, B.E.; Muhlenbruck, L.; Charlton, K.; Cooper, H. Cues to deception. Psychol. Bull. 2003, 129, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fradkov, A.L.; Evans, R.J. Control of chaos: Methods and applications in engineering. Annu. Rev. Control 2005, 29, 33–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewski, J.; Kröger, B.J. Using prosodic and spectral characteristics for sleepiness detection. In Proceedings of the INTERSPEECH, Antwerp, Belgium, 27–31 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, H.; Pan, X. Lie detection from speech analysis based on k–svd deep belief network model. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Computing Theories and Methodologies: 11th International Conference, ICIC 2015, Fuzhou, China, 20–23 August 2015; Volume 11, pp. 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, N.; Dubey, S. Deception detection using artificial neural network and support vector machine. In Proceedings of the 2018 Second International Conference on Electronics, Communication and Aerospace Technology (ICECA), Coimbatore, India, 29–31 March 2018; pp. 1205–1208. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.-T.; Wu, M.; Cao, W.-H.; Mao, J.-W.; Xu, J.-P.; Tan, G.-Z. Speech emotion recognition based on feature selection and extreme learning machine decision tree. Neurocomputing 2018, 273, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitan, S.I.; An, G.; Wang, M.; Mendels, G.; Hirschberg, J.; Levine, M.; Rosenberg, A. Cross-cultural production and detection of deception from speech. In Proceedings of the 2015 ACM on Workshop on Multimodal Deception Detection, Seattle, WA, USA, 13 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mannepalli, K.; Sastry, P.N.; Suman, M. Analysis of emotion recognition system for Telugu using prosodic and formant features. In Speech and Language Processing for Human-Machine Communications: Proceedings of CSI 2015; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.B.; Sun, L.X.; Shen, X.B. Research on speech spoofing detection based on big data and machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education (ICAIE), Dali, China, 18–20 June 2021; pp. 137–140. [Google Scholar]
- Nahari, G. ‘Language of lies’: Urgent issues and prospects in verbal lie detection research. Legal Criminol. Psychol. 2019, 24, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkx, D.; Frank, S.L.; Ernestus, M. Language learning using speech to image retrieval. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.03795. [Google Scholar]
- Gopalan, K.; Wenndt, S. Speech analysis using modulation-based features for detecting deception. In Proceedings of the 2007 15th International Conference on Digital Signal Processing, Cardiff, UK, 1–4 July 2007; pp. 619–622. [Google Scholar]
- Mathur, L.; Matarić, M.J. Affect–aware deep belief network representations for multimodal unsupervised deception detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 16th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG 2021), Jodhpur, India, 15–18 December 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, J.H.L.; Womack, B.D. Feature analysis and neural network-based classification of speech under stress. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 1996, 4, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitan, S.I.; Maredia, A.; Hirschberg, J. Linguistic cues to deception and perceived deception in interview dialogues. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long Papers); Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 1941–1950. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, T.; Bhattacharya, U.; Chandra, R.; Bera, A.; Manocha, D. Emotions don’t lie: An audio–visual deepfake detection method using affective cues. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 October 2020; pp. 2823–2832. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Ita Levitan, S.; Levine, M.; Mandic, M.; Hirschberg, J. Acoustic-prosodic and lexical cues to deception and trust: Deciphering how people detect lies. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2020, 8, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitan, S.I.; Maredia, A.; Hirschberg, J. Acoustic–Prosodic Indicators of Deception and Trust in Interview Dialogues. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2018, Hyderabad, India, 2–6 September 2018; pp. 416–420. [Google Scholar]
- Vrij, A.; Granhag, P. Anders; Mann, S.; Leal, S. Outsmarting the liars: Toward a cognitive lie detection approach. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2011, 20, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Fu, H.; Tao, H.; Liang, R.; Zhao, L. A novel hybrid network model based on attentional multi-feature fusion for deception detection. IEICE Trans. Fundam. Electron. Commun. Comput. Sci. 2021, 104, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Lei, P.; Tao, H.; Zhao, L.; Yang, J. Improved semi-supervised autoencoder for deception detection. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendels, G.; Levitan, S.I.; Lee, K.-Z.; Hirschberg, J. Hybrid Acoustic–Lexical Deep Learning Approach for Deception Detection. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2017, Stockholm, Sweden, 20–24 August 2017; pp. 1472–1476. [Google Scholar]
- Vrij, A. Baselining as a lie detection method. Appl. Cogn. Psychol. 2016, 30, 1112–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Liang, R.; Tao, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, L. Convolutional bidirectional long short-term memory for deception detection with acoustic features. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 76527–76534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Frühholz, S.; Schuller, B. Semisupervised autoencoders for speech emotion recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2017, 26, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, S.; Busso, C. Semi-supervised speech emotion recognition with ladder networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2020, 28, 2697–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.-G.; Han, C.-Z. Selection of embedding dimension and delay time in phase space reconstruction. Front. Electr. Electron. Eng. China 2006, 1, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrij, A.; Hartwig, M. Deception and lie detection in the courtroom: The effect of defendants wearing medical face masks. J. Appl. Res. Mem. Cogn. 2021, 10, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choromanski, K.; Likhosherstov, V.; Dohan, D.; Song, X.; Gane, A.; Sarlos, T.; Hawkins, P.; Davis, J.; Mohiuddin, A.; Kaiser, L.; et al. Rethinking attention with performers. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.14794v4. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Gao, M.; Kang, X.; Wang, S.; Du, J.; Yao, D.; Wang, S.-J. CDSD: Chinese Dysarthria Speech Database. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.15930. [Google Scholar]
- Nugroho, R.H.; Nasrun, M.; Setianingsih, C. Lie detector with pupil dilation and eye blinks using hough transform and frame difference method with fuzzy logic. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Control, Electronics, Renewable Energy and Communications (ICCREC), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 26–28 September 2017; pp. 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.-H.; Chou, H.-C.; Wu, Y.-T.; Lee, C.-C.; Liu, Y.-W. Acoustic Indicators of Deception in Mandarin Daily Conversations Recorded from an Interactive Game. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2019, Graz, Austria, 15–19 September 2019; pp. 1731–1735. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, H.-C. Automatic deception detection using multiple speech and language communicative descriptors in dialogs. APSIPA Trans. Signal Inf. Process. 2021, 10, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitan, S.I.; An, G.; Ma, M.; Levitan, R.; Rosenberg, A.; Hirschberg, J. Combining Acoustic–Prosodic, Lexical, and Phonotactic Features for Automatic Deception Detection. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2016, San Francisco, CA, USA, 8–12 September 2016; pp. 2006–2010. [Google Scholar]

| Speaker ID | Number of Truths/Lies | Speaker ID | Number of Truths/Lies |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1A | 45/12 | S17A | 94/113 |
| S2B | 57/31 | S18B | 85/70 |
| S3C | 51/8 | S19C | 25/77 |
| S4D | 65/34 | S20D | 220/32 |
| S5A | 87/8 | S21A | 117/33 |
| S6B | 62/28 | S22B | 126/111 |
| S7C | 89/82 | S23A | 66/63 |
| S8D | 124/70 | S24D | 47/90 |
| S9A | 82/45 | S25A | 49/78 |
| S10B | 58/50 | S26B | 73/82 |
| S11C | 63/52 | S27C | 84/41 |
| S12D | 21/47 | S28D | 92/21 |
| S13A | 70/24 | S29A | 60/32 |
| S14B | 150/73 | S30B | 63/63 |
| S15C | 99/26 | S31C | 83/41 |
| S16D | 61/99 | S32D | 94/25 |
| Collecting Scene | Truth/Lie | Speaker Num | Segments Num |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crime simulation | Lie | 32 | 392 |
| Deliberate lying | Lie | 32 | 792 |
| Recounting experiences | Truth | 32 | 1736 |
| Feature Category | Feature Meaning |
|---|---|
| 5 related to energy | The basic energy and frequency distribution of sound |
| 15 related to the frequency spectrum | Analyze and identify the characteristics of sound |
| 5 related to sound quality | Understand and quantify various physical and perceptual attributes of sound |
| 6 related to pitch | Gain a deeper understanding of the structure and function of sound |
| Feature | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACO | 63.22 | 62.19 | 63.54 | 62.78 |
| NLD | 62.20 | 61.35 | 62.56 | 60.08 |
| MEL | 65.19 | 65.43 | 66.21 | 65.78 |
| Features | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACO + NLD | 64.28 | 64.05 | 63.76 | 63.47 |
| ACO + Mel | 66.30 | 67.21 | 66.58 | 65.34 |
| NLD + Mel | 65.73 | 65.19 | 66.33 | 65.28 |
| All | 67.85 | 67.16 | 66.87 | 67.06 |
| Model | Features | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRU | ACO | 74.61 | 66.34 | 67.26 | 69.86 |
| GRU | ACO + NLD | 75.34 | 70.08 | 72.56 | 74.39 |
| GRU-Attention | ACO | 76.33 | 67.51 | 68.24 | 68.49 |
| GRU-Attention | ACO + NLD | 74.32 | 72.34 | 71.86 | 72.60 |
| Transformer | Mel | 78.77 | 74.65 | 75.24 | 76.33 |
| DDA-MSLD | All | 80.28 | 80.11 | 81.64 | 81.17 |
| Algorithm | Features | Fusion Type | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | ACO | * | 60.04 | 62.17 | 60.31 | 61.86 |
| DFNN | ACO | * | 63.25 | 64.28 | 63.19 | 62.88 |
| RVM | ACO | * | 67.21 | 66.31 | 66.45 | 66.21 |
| RVM | ACO + NLD | Hard Voting | 70.37 | 71.42 | 72.63 | 70.15 |
| RVM | ACO + NLD | Soft Voting | 69.56 | 70.25 | 70.98 | 70.24 |
| CovBiLSTM | ACO | * | 74.84 | 73.29 | 74.66 | 73.26 |
| HAN | ACO | * | 70.31 | 72.44 | 71.76 | 70.03 |
| HAN | ACO + NLD | Hard Voting | 74.71 | 73.28 | 75.36 | 74.39 |
| HAN | ACO + NLD | Soft Voting | 74.38 | 74.22 | 73.68 | 73.49 |
| DDA-MSLD | ACO + NLD | Hard Voting | 76.59 | 75.67 | 76.59 | 76.71 |
| DDA-MSLD | ACO + NLD | Soft Voting | 77.50 | 77.62 | 77.38 | 75.81 |
| DDA-MSLD | All | Hard Voting | 81.22 | 80.19 | 79.34 | 81.70 |
| DDA-MSLD | All | Soft Voting | 82.27 | 82.69 | 81.42 | 81.88 |
| Algorithm | Features | Fusion Type | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | ACO | * | 61.23 | 62.86 | 62.46 | 61.77 |
| DFNN | ACO | * | 65.49 | 64.33 | 64.27 | 64.92 |
| RVM | ACO | * | 67.52 | 65.26 | 66.33 | 66.91 |
| RVM | ACO + NLD | Hard Voting | 70.27 | 70.58 | 71.49 | 71.68 |
| RVM | ACO + NLD | Soft Voting | 70.21 | 69.59 | 71.24 | 70.81 |
| CovBiLSTM | ACO | * | 74.80 | 74.65 | 74.21 | 73.68 |
| HAN | ACO | * | 71.07 | 72.96 | 71.53 | 72.08 |
| HAN | ACO + NLD | Hard Voting | 73.36 | 73.44 | 73.49 | 75.25 |
| HAN | ACO + NLD | Soft Voting | 74.50 | 74.64 | 72.82 | 73.49 |
| DDA-MSLD | ACO + NLD | Hard Voting | 76.60 | 76.27 | 76.71 | 74.50 |
| DDA-MSLD | ACO + NLD | Soft Voting | 77.92 | 76.23 | 77.07 | 76.59 |
| DDA-MSLD | All | Hard Voting | 80.47 | 80.08 | 79.46 | 79.93 |
| DDA-MSLD | All | Soft Voting | 80.28 | 80.11 | 81.64 | 81.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, P.; Huang, S.; Li, M. DDA-MSLD: A Multi-Feature Speech Lie Detection Algorithm Based on a Dual-Stream Deep Architecture. Information 2025, 16, 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16050386
Guo P, Huang S, Li M. DDA-MSLD: A Multi-Feature Speech Lie Detection Algorithm Based on a Dual-Stream Deep Architecture. Information. 2025; 16(5):386. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16050386
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Pengfei, Shucheng Huang, and Mingxing Li. 2025. "DDA-MSLD: A Multi-Feature Speech Lie Detection Algorithm Based on a Dual-Stream Deep Architecture" Information 16, no. 5: 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16050386
APA StyleGuo, P., Huang, S., & Li, M. (2025). DDA-MSLD: A Multi-Feature Speech Lie Detection Algorithm Based on a Dual-Stream Deep Architecture. Information, 16(5), 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16050386






