Industrial Digitalization: Systematic Literature Review and Bibliometric Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Synthesize recent research on smart manufacturing ecosystems—state of the art, key challenges, and future directions for Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0, with emphasis on flexibility, adaptability, and scalability.
- Propose and validate a framework that reengineers core business processes across functional areas in industrial companies.
- A systematic literature review of manufacturing digitalization technologies and tools from the perspectives of evolutionary development and application needs;
- An integrated mechanism for implementation and for assessing capabilities and improvement potential across manufacturing processes;
- Actionable guidance for planning and evaluating investments in Industry 4.0 and related digital technologies, including applicability to SMEs.
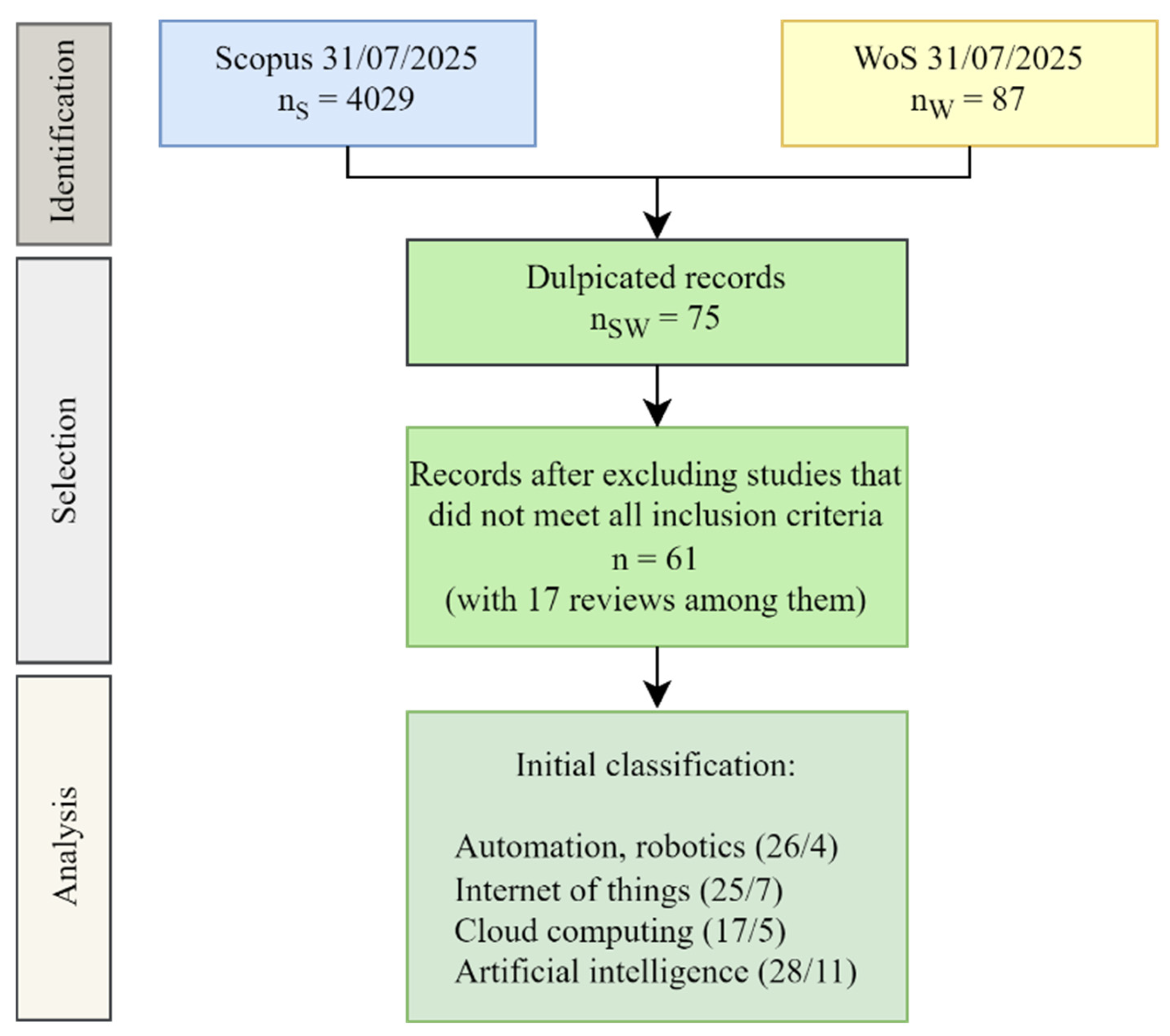
2. Research Methodology
3. Related Work: Review Articles on Industrial Transformation
- Strategic alignment frameworks—Serey et al. [27] emphasize that digital transformation in industrial firms must align technological investments with business models, workforce reskilling, and integrated digital ecosystems. Isoko et al. [30] complement this work by proposing an operational roadmap for Bioprocessing 4.0.
- Technical and architectural frameworks—Onaji et al. [22], Wang et al. [23], and Salierno et al. [29] describe layered DT architectures that combine physical systems, data infrastructure, and decision-making analytics. Wang and Jiao [34] propose a framework that merges smart in-process inspection with human–automation symbiosis to support real-time defect identification and adaptive task allocation. Kamble et al. [32] outline and validate a multidimensional smart-manufacturing performance-measurement system for SMEs that links Industry 4.0 investments to outcomes such as flexibility, real-time analytics, and sustainability.
4. Findings from the Literature Sample
4.1. Publication Trends, Keyword Dynamics, and Thematic Evolution
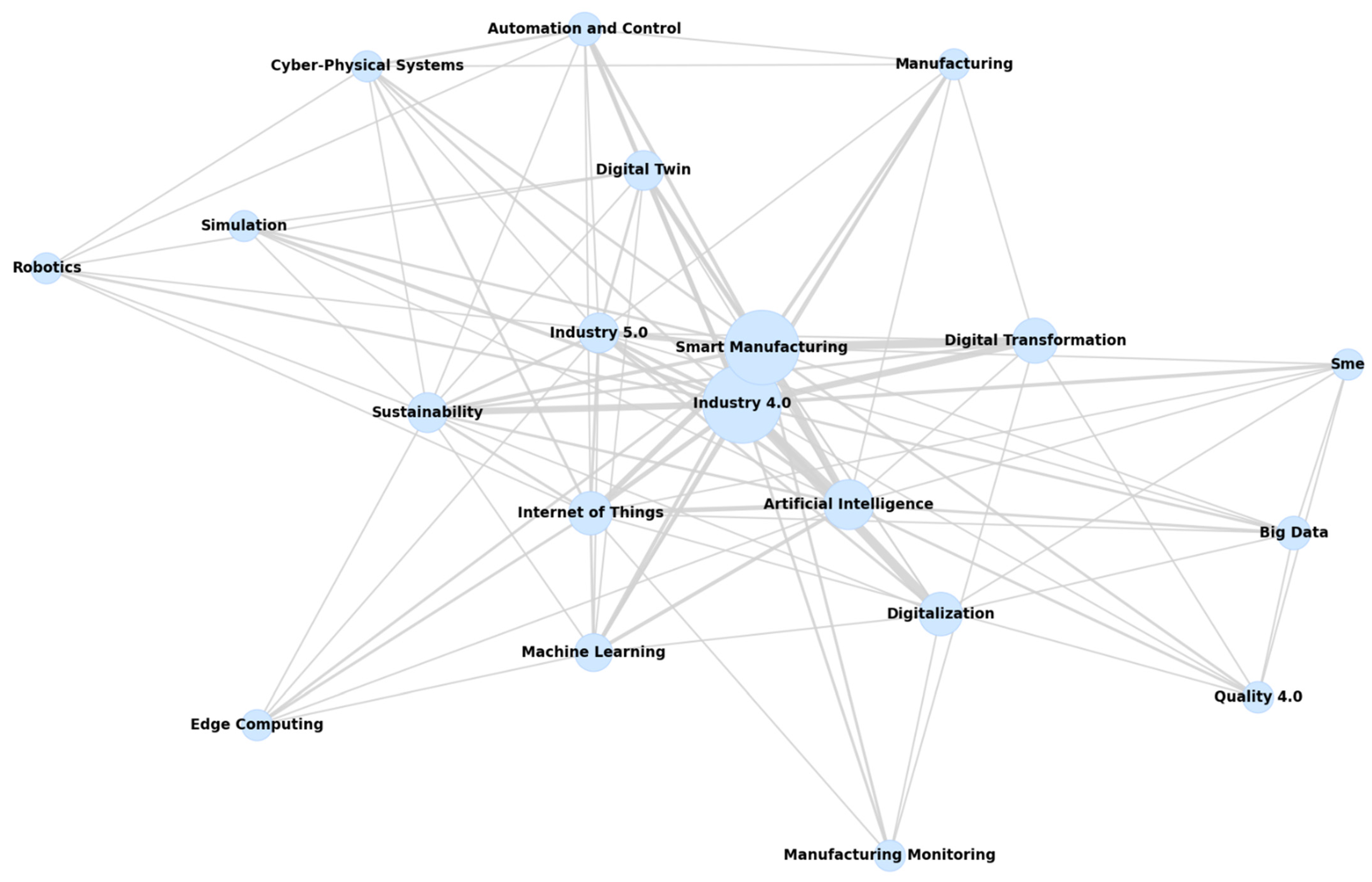
4.2. Keyword Co-Occurrence
4.3. Identification and Synthesizing of Key Research Topics
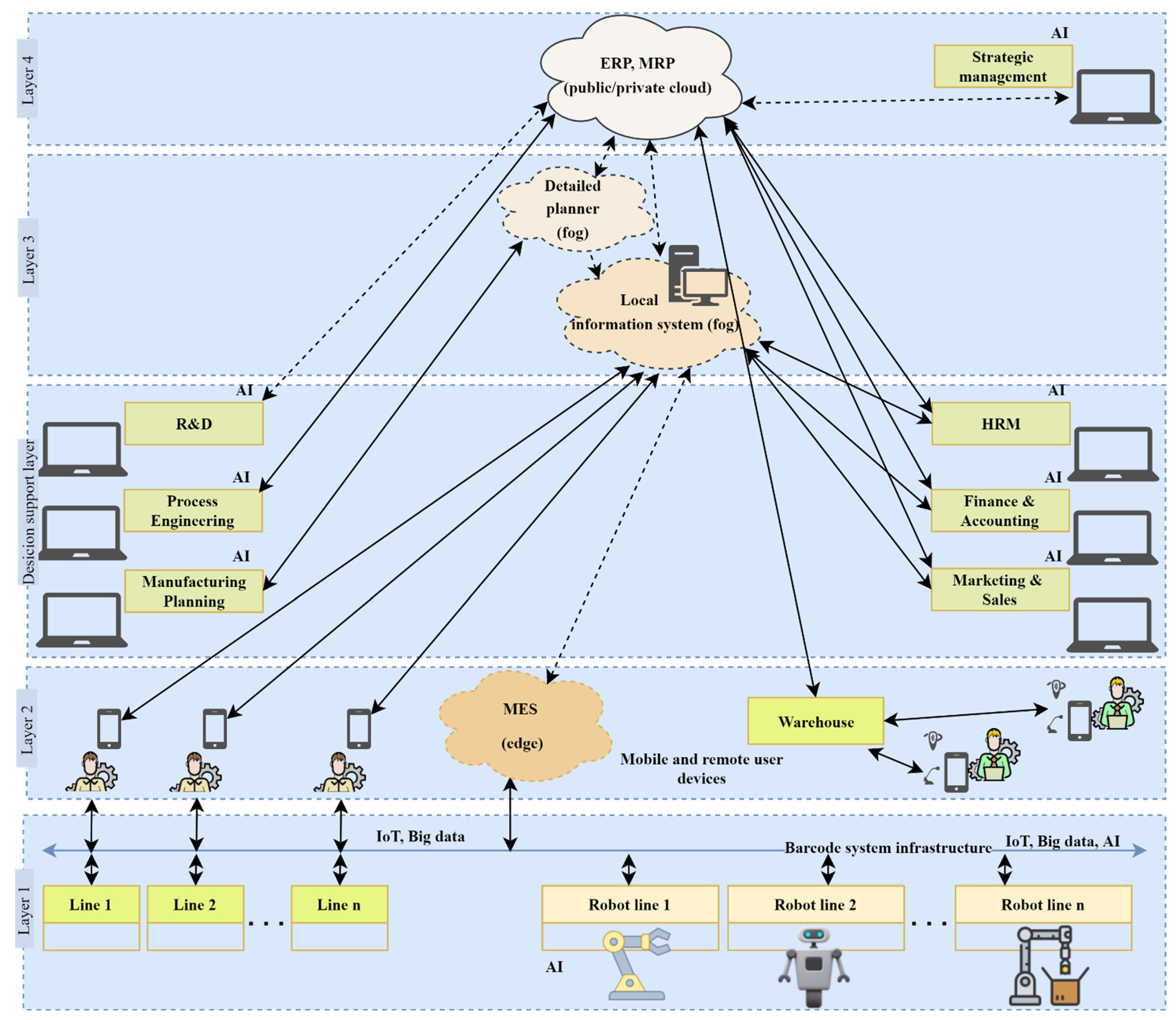
5. Proposed Conceptual Framework for Industrial Digitalization
5.1. Framework Architecture and Design
5.2. Framework Validation
- Short term—Develop detailed resource-utilization planning and achieve complete sensor coverage on bottleneck assets, with dynamic schedule adaptation to current conditions (e.g., operator availability, unexpected failures, material shortages). Scale edge AI for predictive maintenance. Extend MES to all lines and core operations, and link WMS–MES for closed-loop materials tracking.
- Medium term—Introduce lightweight station-level DT. Pilot cloud-based demand forecasting linked to S&OP. Formalize data governance and tiered KPIs. Deploy AI across all key control operations to cover 100% of processed modules and critical materials.
- Longer term—Integrate PLM with MES/ERP for end-to-end lifecycle visibility. Expand operator and planner training. Deploy XAI dashboards to provide explainable recommendations for scheduling, quality, and maintenance.
5.3. Recommendations for Framework Implementation
6. Challenges and Future Perspectives in Industrial Digitalization
6.1. Challenges
6.2. Future Perspectives
7. Conclusions
- Reveals interdependencies among technologies, resources, and organizational capabilities across time and layers (shop floor, MES/ERP, enterprise level).
- Enables dynamic orchestration of IT/OT by clarifying when and how to integrate automated systems, cloud computing, and AI so they reinforce one another rather than operate in isolation.
- Prevents fragmented initiatives in which isolated projects and siloed technology stacks create inefficiencies and duplicate costs.
- Supports SMEs through modular, phased adoption (low-cost sensorization–edge analytics–fog/MES coordination–cloud/AI), use of open standards to avoid vendor lock-in, and the option to leverage managed cloud services to reduce upfront investment and IT burden.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The Rise of Industry 4.0 in 5 Stats. Available online: https://iot-analytics.com/industry-4-0-in-5-stats/ (accessed on 31 July 2025).
- Culot, G.; Nassimbeni, G.; Orzes, G.; Sartor, M. Behind the definition of Industry 4.0: Analysis and open questions. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 226, 107617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrid-Guijarro, A.; Maldonado-Guzmán, G.; Rodríguez-González, R. Unlocking resilience: The impact of Industry 4.0 technologies on manufacturing firms’ response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Manag. Decis. 2025, 63, 126–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy. Industrie 4.0. Available online: https://www.bundeswirtschaftsministerium.de/Redaktion/EN/Dossier/industrie-40.html (accessed on 31 July 2025).
- People’s Republic of China State Council. Made in China 2025 (English Translation). Available online: http://english.www.gov.cn/policies/latest_releases/2015/05/19/content_281475110703534.htm (accessed on 31 July 2025).
- Basile, V.; Tregua, M.; Giacalone, M. A three-level view of readiness models: Statistical and managerial insights on Industry 4.0. Technol. Soc. 2024, 77, 102528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIST Industrial Automation. Available online: https://csrc.nist.gov/glossary/term/industrial_control_system (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- NIST IIoT. Available online: https://csrc.nist.gov/glossary/term/industrial_internet_of_things (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- NIST SP 800-145. The NIST Definition of Cloud Computing. Available online: https://csrc.nist.gov/pubs/sp/800/145/final (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- NIST Artificial Intelligence. Available online: https://csrc.nist.gov/glossary/term/artificial_intelligence (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- NIST Big Data. Available online: https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/SpecialPublications/NIST.SP.1500-1r2.pdf (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Industry 5.0 European Commission: Directorate-General for Research and Innovation; Breque, M.; De Nul, L.; Petridis, A. Industry 5.0—Towards a Sustainable, Human-Centric and Resilient European Industry; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2021; Available online: https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2777/308407 (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Zhou, K.; Liu, T.; Zhou, L. Industry 4.0: Towards future industrial opportunities and challenges. In Proceedings of the 2015 12th International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery (FSKD), Zhangjiajie, China, 15–17 August 2015; pp. 2147–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canavese, D.; Mannella, L.; Regano, L.; Basile, C. Security at the edge for resource-limited IoT devices. Sensors 2024, 24, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieste, M.; Orzes, G.; Culot, G.; Sartor, M.; Nassimbeni, G. The “dark side” of Industry 4.0: How can technology be made more sustainable? Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2024, 44, 900–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayem, A.; Biswas, P.K.; Khan, M.M.A.; Romoli, L.; Dalle Mura, M. Critical Barriers to Industry 4.0 Adoption in Manufacturing Organizations and Their Mitigation Strategies. J. Manuf. Mater. Process 2022, 6, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzla, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: Explanation and elaboration. BMJ 2009, 339, b2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çınar, Z.M.; Nuhu, A.A.; Zeeshan, Q.; Korhan, O.; Asmael, M.; Safaei, B. Machine learning in predictive maintenance towards sustainable smart manufacturing in Industry 4.0. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burzyńska, A. Review of data-driven decision support systems and methodologies for the diagnosis of casting defects. Arch. Foundry Eng. 2024, 24, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargalo, C.L.; Malanca, A.A.; Aouichaoui, A.R.N.; Huusom, J.K.; Gernaey, K.V. Navigating Industry 4.0 and 5.0: The role of hybrid modelling in (bio)chemical engineering’s digital transition. Front. Chem. Eng. 2024, 6, 1494244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Knoblauch, R.; El Mansori, M.; Corleto, C. Towards AI driven surface roughness evaluation in manufacturing: A prospective study. J. Intell. Manuf. 2024, 36, 4519–4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaji, I.; Tiwari, D.; Soulatiantork, P.; Song, B.; Tiwari, A. Digital twin in manufacturing: Conceptual framework and case studies. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2022, 35, 831–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kang, X.; Chen, Z. A survey of digital twin techniques in smart manufacturing and management of energy applications. Green Energy Intell. Transp. 2022, 1, 100014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, C.A.; McGovern, M.E.; Morales-Menendez, R. Quality 4.0: A review of big data challenges in manufacturing. J. Intell. Manuf. 2021, 32, 2319–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benslimane, T.; Benabbou, R.; Mouatassim, S.; Benhra, J. Understanding the relationship, trends, and integration challenges between lean manufacturing and Industry 4.0: A literature review. Int. J. Prod. Manag. Eng. 2024, 12, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suuronen, S.; Ukko, J.; Eskola, R.; Semken, R.S.; Rantanen, H. A systematic literature review for digital business ecosystems in the manufacturing industry: Prerequisites, challenges, and benefits. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2022, 37, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serey, J.; Alfaro, M.; Fuertes, G.; Vargas, M.; Ternero, R.; Duran, C.; Sabattin, J.; Gutierrez, S. Framework for the strategic adoption of Industry 4.0: A focus on intelligent systems. Processes 2023, 11, 2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voinea, G.D.; Girbacia, F.; Duguleană, M.; Boboc, R.G.; Gheorghe, C. Mapping the emergent trends in industrial augmented reality. Electronics 2023, 12, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salierno, G.; Leonardi, L.; Cabri, G. The future of factories: Different trends. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isoko, K.; Cordiner, J.L.; Kis, Z.; Moghadam, P.Z. Bioprocessing 4.0: A pragmatic review and future perspectives. Digit. Discov. 2024, 3, 1662–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Kumar, A.; Hu, J.; Sharma, P.; Tang, Y.B.; Xu Xiang, Y.; Hong, J. A review on integrating IoT, IIoT, and Industry 4.0: A pathway to smart manufacturing and digital transformation. IET Inf. Secur. 2025, 1, 9275962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, S.S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Ghadge, A.; Raut, R. A performance measurement system for Industry 4.0 enabled smart manufacturing system in SMMEs—A review and empirical investigation. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 229, 107853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes Domínguez, D.; Infante Abreu, M.B.; Parv, A.L. Main trend topics on Industry 4.0 in the manufacturing sector: A bibliometric review. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jiao, R.J. Smart in-process inspection in human–cyber–physical manufacturing systems: A research proposal on human–automation symbiosis and its prospects. Machines 2024, 12, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilieva, G.; Yankova, T.; Staribratov, P.; Ruseva, G. Industrial digitalization technologies and their applications (2020–2025). Mendeley Data 2025, V1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K.; Huo, Y.Z.; Zhang, S.Z.; Ng, K.K. Design of a smart manufacturing system with the application of multi-access edge computing and blockchain technology. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 28659–28667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Gutiérrez, A.; Díez-González, J.; Ferrero-Guillén, R.; Verde, P.; Álvarez, R.; Perez, H. Digital twin for automatic transportation in Industry 4.0. Sensors 2021, 21, 3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, Z.; Byun, Y.C. Improving transactional data system based on an edge computing–blockchain–machine learning integrated framework. Processes 2021, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga-Lamas, P.; Lopes, S.I.; Fernández-Caramés, T.M. Green IoT and edge AI as key technological enablers for a sustainable digital transition towards a smart circular economy: An Industry 5.0 use case. Sensors 2021, 21, 5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akundi, A.; Euresti, D.; Luna, S.; Ankobiah, W.; Lopes, A.; Edinbarough, I. State of Industry 5.0—Analysis and identification of current research trends. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2022, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellert, A.; Sorostinean, R.; Pirvu, B.-C. Robust assembly assistance using informed tree search with Markov chains. Sensors 2022, 22, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahveci, S.; Alkan, B.; Mus’ab, H.A.; Ahmad, B.; Harrison, R. An end-to-end big data analytics platform for IoT-enabled smart factories: A case study of battery module assembly system for electric vehicles. J. Manuf. Syst. 2022, 63, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofic, A.; Rakic, S.; Pezzotta, G.; Markoski, B.; Arioli, V.; Marjanovic, U. Smart and Resilient Transformation of Manufacturing Firms. Processes 2022, 10, 2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sverko, M.; Grbac, T.G.; Mikuc, M. SCADA systems with focus on continuous manufacturing and steel industry: A survey on architectures, standards, challenges and Industry 5.0. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 109395–109430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, F.M.; Al-Ahmari, A.M.; Anwar, S. A Hybrid Fuzzy Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Model for Evaluating the Influence of Industry 4.0 Technologies on Manufacturing Strategies. Machines 2023, 11, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Sampath, V.; May, M.C.; Shan, S.; Jorg, O.J.; Aguilar Martín, J.J.; Stamer, F.; Fantoni, G.; Tosello, G.; Calaon, M. Machine Learning in Manufacturing towards Industry 4.0: From ‘For Now’ to ‘Four-Know’. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, M.; Lăzăroiu, G.; Valaskova, K. Machine intelligence and autonomous robotic technologies in the corporate context of SMEs: Deep learning and virtual simulation algorithms, cyber-physical production networks, and Industry 4.0-based manufacturing systems. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnathai, M.K.; Alkan, B. A digital life-cycle management framework for sustainable smart manufacturing in energy intensive industries. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 419, 138259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyang, V.; Kanakana, G.M.; Laseinde, O.T. Application of sustainable smart manufacturing technologies and toolkits in the automotive industry. Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol. 2023, 18, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Gutiérrez, A.; Díez-González, J.; Verde, P.; Ferrero-Guillen, R.; Perez, H. Hyperconnectivity proposal for smart manufacturing. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 70947–70959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryalat, M.; ElMoaqet, H.; AlFaouri, M. Design of a smart factory based on cyber-physical systems and Internet of Things towards Industry 4.0. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hozdić, E.; Makovec, I. Evolution of the human role in manufacturing systems: On the route from digitalization and cybernation to cognitization. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2023, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, D.-J.; Jun, C.; Song, S.; Baek, J.-G. Production system maturity model (PSMM) for assessing manufacturing execution system. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 123459–123475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, A.; Savini, I.; Andreoni, A.; Morolli, M.; Solfrini, V. Manufacturing execution system application within manufacturing small–medium enterprises towards key performance indicators development and their implementation in the production line. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Salah, B.; Habib, T. Utilizing Industry 4.0-related technologies and modern techniques for manufacturing customized products—Smart yogurt filling system. J. Eng. Res. 2024, 12, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Gómez, A.M.; Agote-Garrido, A.; Lama-Ruiz, J.R. A Framework for Sustainable Manufacturing: Integrating Industry 4.0 Technologies with Industry 5.0 Values. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Albuquerque Bezerra, N.R.; Marchisotti, G.G.; Bezerra, M.J.S.; de Farias Filho, J.R. Digital transformation in naval industry. Braz. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2024, 21, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryalat, M.; Franco, E.; Elmoaqet, H.; Almtireen, N.; Al-Refai, G. The integration of advanced mechatronic systems into Industry 4.0 for smart manufacturing. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Kapukotuwa, J.; Gouveia, E.L.S.; Fuenmayor, E.; Qiao, Y.; Murry, N.; Devine, D. Unity and ROS as a digital and communication layer for digital twin application: Case study of robotic arm in a smart manufacturing cell. Sensors 2024, 24, 5680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; He, F.; Yuan, L.; Commins, P.; Ding, D.; Pan, Z. A digital shadow approach for enhancing process monitoring in wire arc additive manufacturing using sensor fusion. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2024, 40, 100609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Shin, M.; Hwang, S. Design and development of a precision defect detection system based on a line scan camera using deep learning. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 12054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, E.; Akter, M. Prediction of seam strength of cotton canvas fabric using fuzzy logic. Results Control Optim. 2024, 17, 100502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosak-Szyrocka, J.; Knop, K. Navigating the Fourth Industrial Revolution: Insights from a Comprehensive Bibliometric Study on Industry 4.0. Prod. Eng. Arch. 2024, 30, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Song, L.; Tao, F. Artificial intelligence-enhanced digital twin systems engineering towards the industrial metaverse in the era of Industry 5.0. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2025, 38, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singapore Economic Development Board. The Smart Industry Readiness Index. Available online: https://www.edb.gov.sg/content/dam/edb-en/about-edb/media-releases/news/the-smart-industry-readiness-index/the-sg-smart-industry-readiness-index-whitepaper%20(1).pdf (accessed on 15 October 2025).
- Alexopoulos, K.; Nikolakis, N.; Xanthakis, E. Digital transformation of production planning and control in manufacturing SMEs—The mold shop case. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanane, B.; Bentaha, M.-L.; Dafflon, B.; Moalla, N. Bridging the gap between Industry 4.0 and manufacturing SMEs: A framework for an end-to-end Total Manufacturing Quality 4.0’s implementation and adoption. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2025, 45, 100833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonazzo, L.; Stroud, D.; Weinel, M. Smart manufacturing and tasks automation in the steel industry: Reflecting on routine work and skills in Industry 4.0. Econ. Ind. Democr. 2024, 45, 914–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeter, K.; Szász, L.; Rácz, B.-G.; Györfy, L.-Z. Fourth industrial (r)evolution? Investigating the use of technology bundles and performance implications. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2024, 35, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakhnovich, A.D.; Moskvin, D.A.; Zegzhda, D.P. Approach for securing network communications modelling based on smart multipath routing. Nonlinear Phenom. Complex Syst. 2020, 23, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, A.H.; Trimi, S.; Kou, T.C. Critical factors for implementing smart manufacturing: A supply chain perspective. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popan, I.A.; Cosma, C.; Popan, A.I.; Bocăneț, V.I.; Bâlc, N. Monitoring Equipment Malfunctions in Composite Material Machining: Acoustic Emission-Based Approach for Abrasive Waterjet Cutting. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, M.Z.; Memon, S.A.; Hämäläinen, J. Evolution of wireless communication to 6G: Potential applications and research directions. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
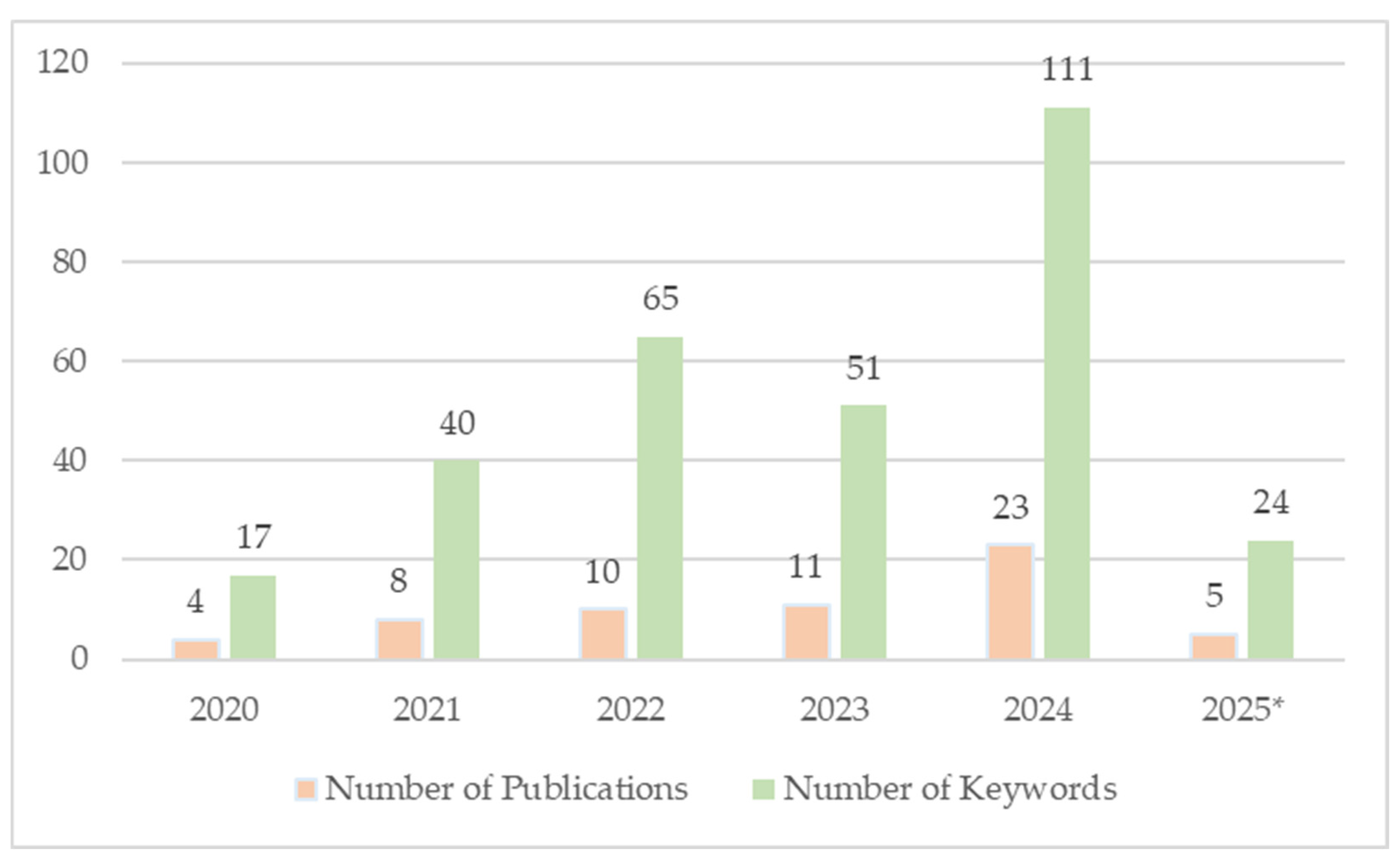
| Keywords | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 * | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smart Manufacturing | 4 | 4 | 9 | 8 | 14 | 3 | 42 |
| Industry 4.0 | 1 | 5 | 7 | 10 | 14 | 3 | 40 |
| Artificial Intelligence/AI | 1 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 14 |
| Machine Learning/ML | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 10 |
| Cyber-Physical Systems/CPS | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 9 |
| Digital Transformation | 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 9 |
| Digitalization | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 9 |
| IoT | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 9 |
| Industry 5.0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 8 |
| Digital Twins | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| IIoT | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 5 |
| Robotics | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 5 |
| Automation and Control | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 5 |
| Big Data | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 4 |
| Cloud Computing | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Blockchain | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Period | Concise Focus | Key Threads | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020–2021 | Foundations, then consolidation with quality and sustainability | IoT/IIoT, CPS, edge–cloud, blockchain, security, performance measurement/optimization, PdM; by 2021: Quality 4.0, Green IoT/I5.0 | [18,24,32,36,38,39] |
| 2022 | Human-centered turn and ecosystems/servitization; deeper data/operations layers | Industry 5.0, digital ecosystems/servitization, IoT + big-data pipelines, SCADA/ICS modernization | [22,40,42,43] |
| 2023 | AI/ML scale-up on the shop floor and governance | Defect detection, process optimization, digital-transformation governance, skills/HMI (human-centric I5.0) | [45,46,49,52] |
| 2024 | Application pivot and maturity | Real-time machine-vision QC, DT/robotic simulation (Unity/ROS), maturity models, bioprocessing 4.0, sensor-fusion (digital shadows, AE) | [25,53,55,63] |
| 2025 * | Synthesis and pragmatism | Reference architectures/reviews (IIoT, AI-enhanced DT/industrial metaverse), low-cost SME methods (current-sensor “fingerprints”), sectoral digitalization and sustainability (e.g., furniture) | [31,64] |
| Year | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 * | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industry 4.0 | 4 | 8 | 9 | 11 | 21 | 5 | 58 |
| Operations and process improvement | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 10 | 0 | 16 |
| Quality 4.0 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 14 | 0 | 32 |
| Simulation and modeling | 4 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 13 | 1 | 41 |
| Industry 5.0 | 3 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 12 | 3 | 35 |
| Conceptual frameworks | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 8 | 2 | 18 |
| Cybersecurity | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 11 | 1 | 22 |
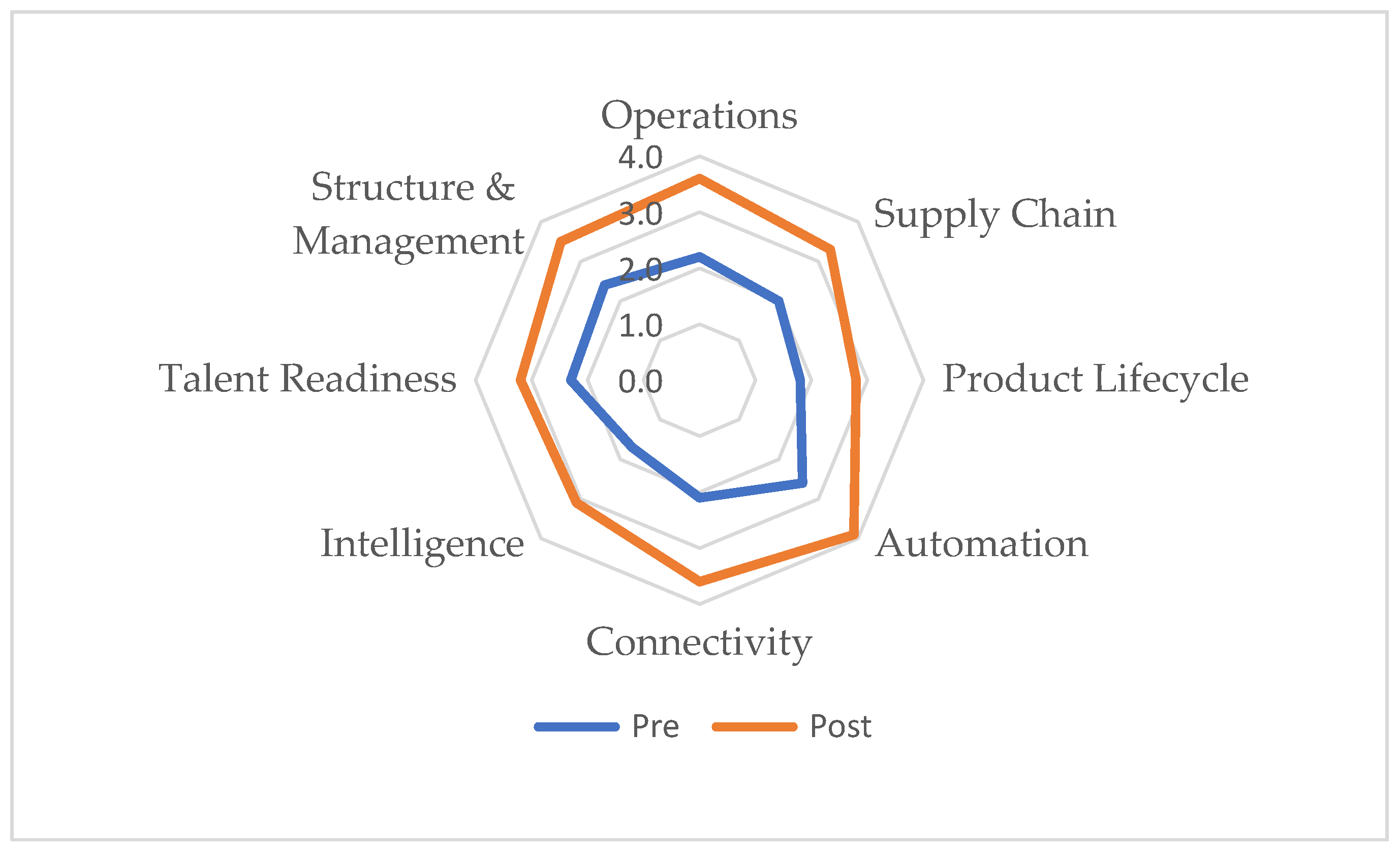
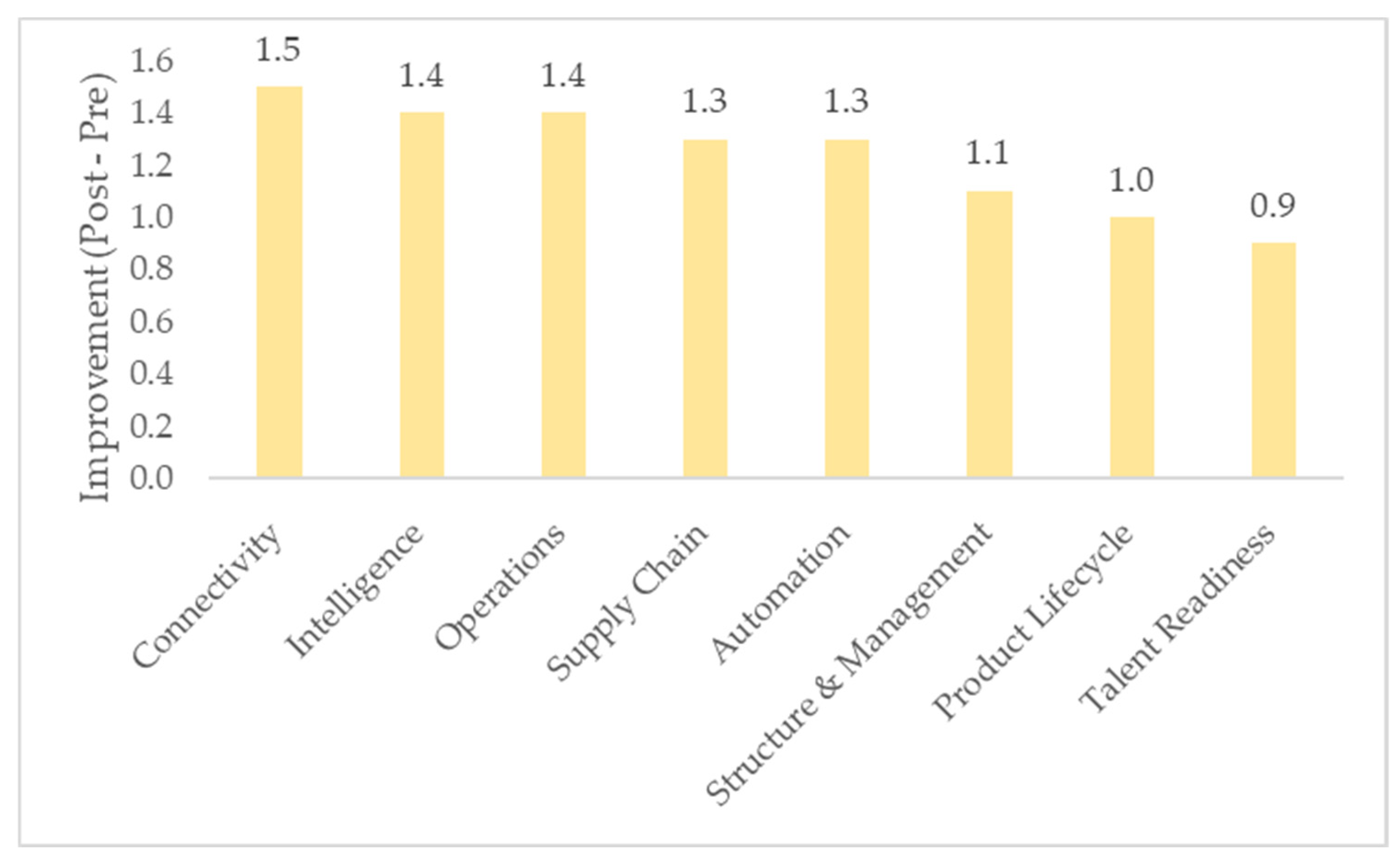
| Pillar | Dimension | Pre | Post | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Process | Operations | 2.2 | 3.6 | 1.4 |
| Process | Supply Chain | 2.0 | 3.3 | 1.3 |
| Process | Product Lifecycle | 1.8 | 2.8 | 1.0 |
| Technology | Automation | 2.6 | 3.9 | 1.3 |
| Technology | Connectivity | 2.1 | 3.6 | 1.5 |
| Technology | Intelligence | 1.7 | 3.1 | 1.4 |
| Organization | Talent Readiness | 2.3 | 3.2 | 0.9 |
| Organization | Structure and Management | 2.4 | 3.5 | 1.1 |
| Overall (mean) | – | 2.1 | 3.4 | 1.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ilieva, G.; Yankova, T.; Staribratov, P.; Ruseva, G.; Iliev, Y. Industrial Digitalization: Systematic Literature Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Information 2025, 16, 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16121080
Ilieva G, Yankova T, Staribratov P, Ruseva G, Iliev Y. Industrial Digitalization: Systematic Literature Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Information. 2025; 16(12):1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16121080
Chicago/Turabian StyleIlieva, Galina, Tania Yankova, Peyo Staribratov, Galina Ruseva, and Yuliy Iliev. 2025. "Industrial Digitalization: Systematic Literature Review and Bibliometric Analysis" Information 16, no. 12: 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16121080
APA StyleIlieva, G., Yankova, T., Staribratov, P., Ruseva, G., & Iliev, Y. (2025). Industrial Digitalization: Systematic Literature Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Information, 16(12), 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16121080








