Soil–Water–Air (SWA) Interface Channel Model for River Bridge Pillar Health Monitoring Using WSN
Abstract
1. Introduction
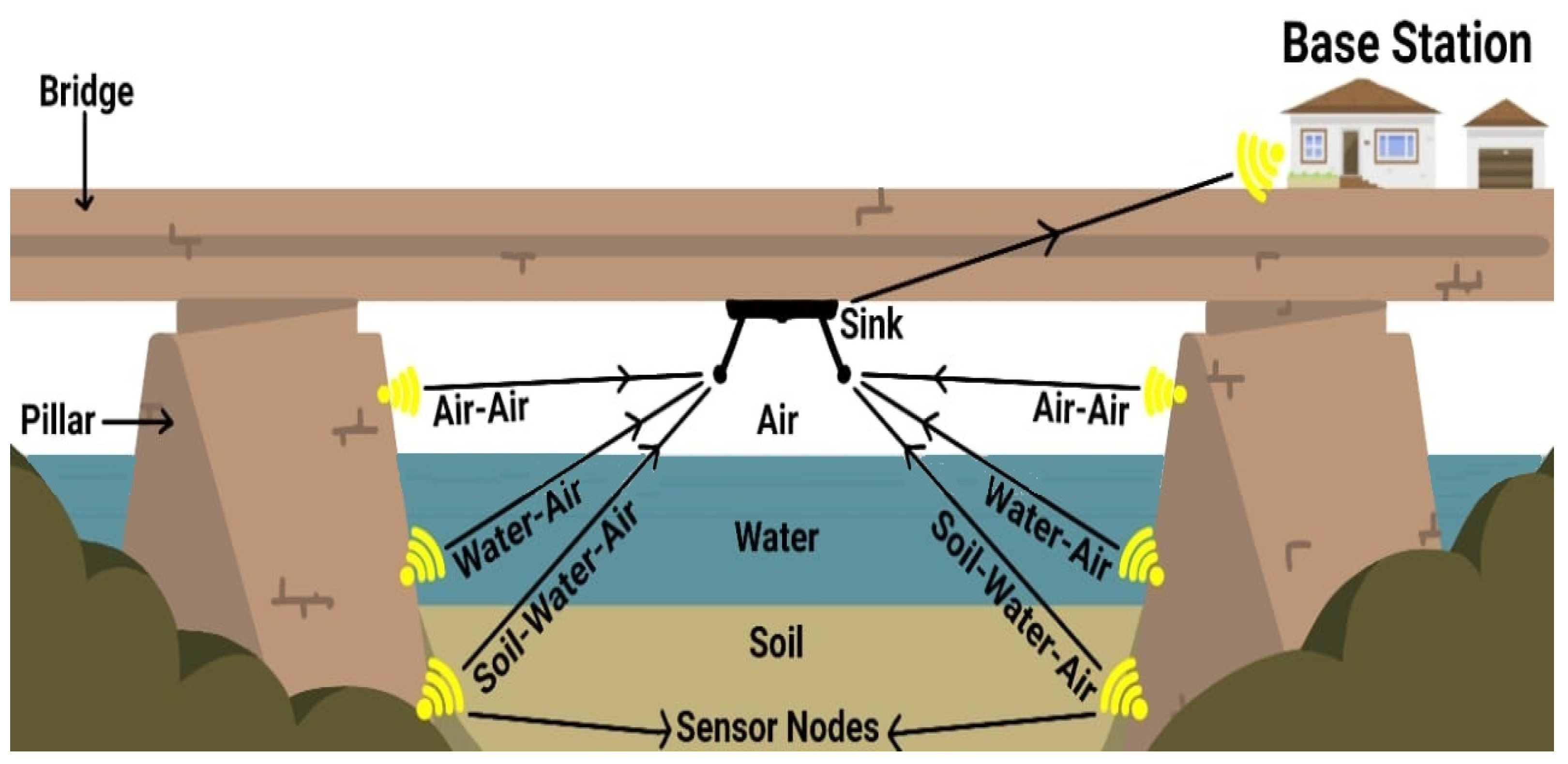
- Wireless communication schemes that are required to monitor the health of a bridge pillar completely were identified.
- Based on the wireless schemes identified, a wireless underground communication channel model for signals that transmit through the soil, water, and air was developed.
- An experimental setup using LoRa-based sensor nodes [13] was arranged to validate the performance of the SWA channel path–loss model.
- The impact of varying water levels, soil burial depths, frequencies, and inter-node separations (across both vertical and horizontal directions) on the path loss of the SWA channel was analysed.
- The different components of path loss in the SWA channel were identified, and their effect on net path loss was analysed.
2. Related Works
3. Proposed Path-Loss Model
3.1. Signal Attenuation Due to the Direct Route
- Attenuation due to air ().
- Attenuation due to water ().
- Attenuation due to soil ().
- Attenuation due to refraction ().
- Attenuation due to reflection ().
3.2. Signal Attenuation Due to the Reflected Route
- Attenuation occurring during reflection at the air–bridge interface ().
4. Experimental Setup
4.1. Framework
4.2. Communication Process
4.3. Experimental Procedure
5. Results and Discussion
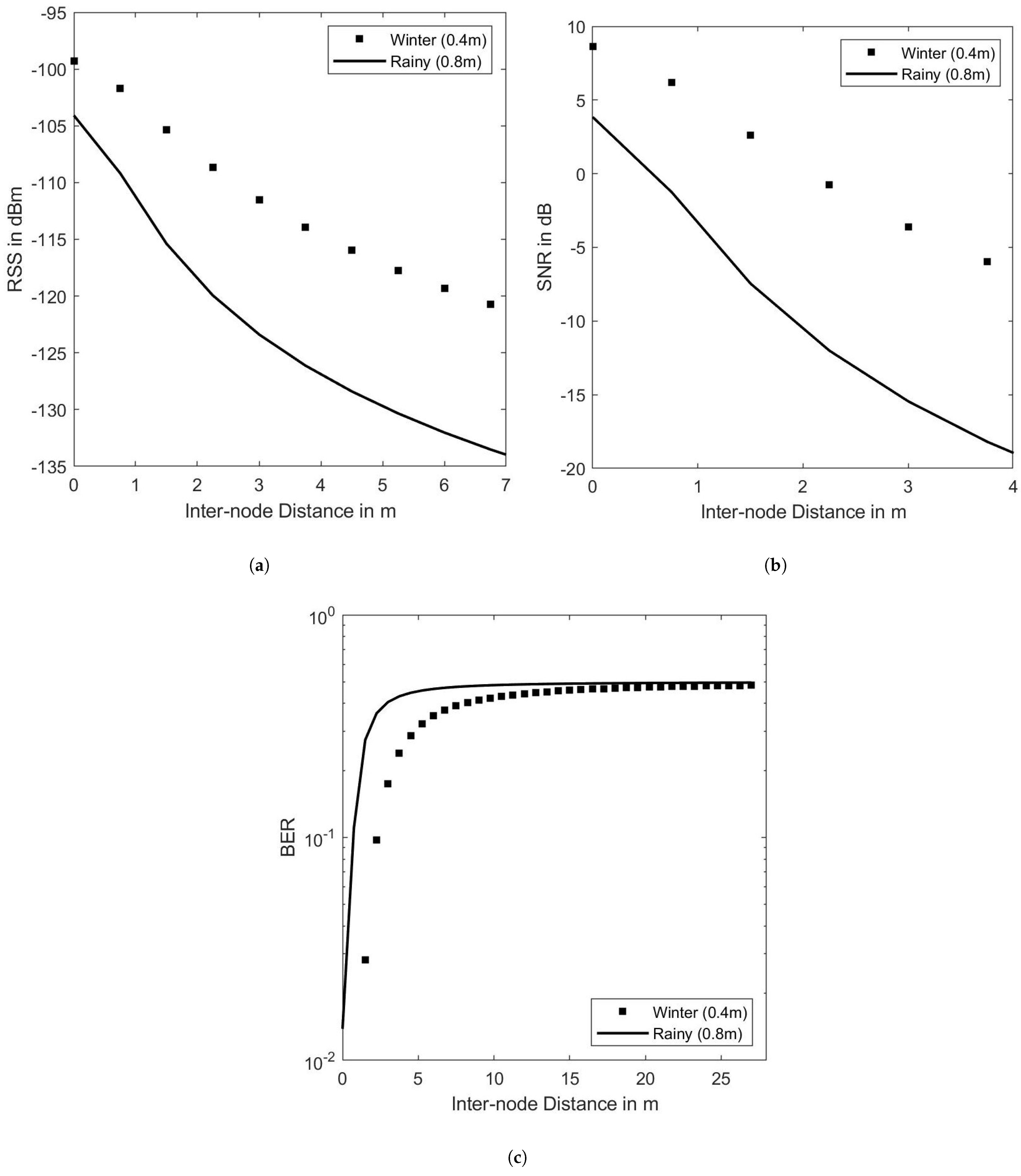
5.1. Effects of Horizontal Inter-Node Separation and Water Level Variation
5.2. Effects of Horizontal Inter-Node Separation and Soil Level Variation
5.3. Effects of Bridge Height Variation
5.4. Effects of Signal Frequency Variation
5.5. Effects of Seasonal Variation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akyildiz, I.F.; Stuntebeck, E.P. Wireless underground sensor network: Research challenges. Ad Hoc Netw. J. 2006, 4, 669–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, F.J.L.; de Castro Pinto Pedroza, A.; Costa, L.H.M.K. Underwater monitoring system for oil exploration using acoustic sensor networks. Telecommun. Syst. 2015, 58, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, A.B.; Abdaoui, A.; Elfouly, T.; Ahmed, M.H.; Badawy, A.; Shehata, M.S. Structural health monitoring using wireless sensor networks: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 1403–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, U.; Salam, A. Wireless Underground Communications in Sewer and Stormwater Overflow Monitoring: Radio Waves through Soil and Asphalt Medium. Information 2020, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, H.; Kolade, O.; Mahboob, M.A.; Cawood, F.T.; Kawamura, Y. Communication of Sensor Data in Underground Mining Environments: An Evaluation of Wireless Signal Quality over Distance. Mining 2021, 1, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, A.; Rejeb, K.; Rejeb, A.; Mostafa, M.M.; Zailani, S. Wireless Sensor Networks in Agriculture: Insights from Bibliometric Analysis. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R. Smart remote sensing network for disaster management: An overview. Telecommun. Syst. 2024, 87, 213–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonbul, O.S.; Rashid, M. Towards the Structural Health Monitoring of Bridges Using Wireless Sensor Networks: A Systematic Study. Sensors 2023, 23, 8468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ali, A.R.; Beheiry, S.; Alnabulsi, A.; Obaid, S.; Mansoor, N.; Odeh, N.; Mostafa, A. An IoT-Based Road Bridge Health Monitoring and Warning System. Sensors 2024, 24, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rappaport, T.S. Wireless Communications Principles and Practice; Prentice Hall PTR: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 69–138. [Google Scholar]
- Mekid, S.; Wu, D.; Hussain, R.; Youcef-Toumi, K. Channel modeling and testing of wireless transmission for underground in-pipe leak and material loss detection. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2017, 13, 155014771774471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, H.; Li, Y.; Sun, Q.; Wu, Y.; Jin, S.; Quek, T.Q.S.; Xu, C. Wireless Channel Models for Maritime Communications. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 68070–68088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piroddi, A.; Torregiani, M. Machine Learning Applied to LoRaWAN Network for Improving Fingerprint Localization Accuracy in Dense Urban Areas. Network 2023, 3, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyildiz, I.F.; Kasimoglu, I.H. Wireless sensor and actor networks: Research challenges. Ad Hoc Netw. 2004, 2, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohraby, K.; Minoli, D.; Znati, T. Wireless Sensor Networks: Technology, Protocols, and Applications; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith, A. Wireless Communications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005; pp. 27–63. [Google Scholar]
- Vuran, M.C.; Silva, A.R. Communication through soil in wireless underground sensor networks–theory and practice. In Sensor Networks-Where Theory Meets Practice; Ferrari, G., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 309–347. [Google Scholar]
- Panda, H.; Das, M.; Sahu, B. Multi-Hop Communication in Wireless Underground Sensor Network. In Proceedings of the International Conference in Advances in Power, Signal, and Information Technology (APSIT), Bhubaneswar, India, 8–10 October 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Trinchero, D.; Fiorelli, B.; Galardini, A.; Stefanelli, R. Underground Wireless Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE 10th Annual Wireless and Microwave Technology Conference, Clearwater, FL, USA, 20–21 April 2009; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaoya, H.; Chao, G.; Bingwen, W.; Wei, X. Channel modeling for wireless underground sensor networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE 35th Annual Computer Software & Applications Conference Workshops, Munich, Germany, 18–22 July 2011; pp. 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- Panda, H.; Das, M.; Sahu, B. Experimental analysis of Underground-Underground communication channel in WUSN. In Proceedings of the 2nd Odisha International Conference on Electrical Power Engineering, Communication and Computing Technology (ODICON), Bhubaneswar, India, 11–12 November 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Theocharidis, T.; Kavallieratou, E. Underwater communication technologies: A review. Telecommun. Syst. 2025, 88, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknami, N.; Srinivasan, A.; St. Germain, K.; Wu, J. Maritime Communications—Current State and the Future Potential with SDN and SDR. Network 2023, 3, 563–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Chen, W.; Kong, D.; Zuo, X.; Yu, Z. Design and implementation of SDN-based underwater acoustic sensor networks with multi-controllers. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 25698–25714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Huang, X.; Pan, Q.; Pace, P.; Aloi, G.; Fortino, G. Cooperative Data Collection for UAV-Assisted Maritime IoT Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 10333–10349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, L.M.; Gomes, J. River Water Quality Monitoring Using LoRa-Based IoT. Designs 2024, 8, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I. Underwater Sensor Networks for Communication, Navigation, and Localization. Sensors 2025, 25, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanov, A.; Stojanovic, M. Design and performance analysis of underwater acoustic networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2011, 29, 2012–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauni, S.; Manimegalai, C.T.; Krishnan, K.M.; Shreeram, V.; Arvind, V.V.; Srinivas, T.V.N. Design and Analysis of Co-operative Acoustic and Optical Hybrid Communication for Underwater Communication. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2021, 20, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, P.S.S.P.; Venkataraman, H. RF-based Wireless Communication for Shallow Water Networks: Survey and Analysis. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2021, 120, 3415–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, M.; Aamir, M.; Khan, A.M. A Prospect of Efficient radio-frequency based underwater Wireless Data Transfer. In Proceedings of the 2020 Global Conference on Wireless and Optical Technologies (GCWOT), Malaga, Spain, 6–8 October 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, U.M.; Shaikh, F.K.; Aziz, Z.; Shah, S.M.Z.S.; Sheikh, A.A.; Felemban, E.; Qaisar, S.B. RF Path and Absorption Loss Estimation for Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks in Different Water Environments. Sensors 2016, 16, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattab, G.; El-Tarhuni, M.; Al-Ali, M.; Joudeh, T.; Qaddoumi, N. An underwater wireless sensor network with realistic radio frequency path loss model. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2013, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, P.; Singh, P.R.; Sinha, A. Path loss analysis of RF waves for underwater wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference of Computer Communication Technologies Smart Nation (IC3TSN), Gurgaon, India, 12–14 October 2017; pp. 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Panda, H.; Das, M.; Sahu, B. Received signal strength prediction model for wireless underground sensor networks using machine learning algorithms. J. Inf. Optim. Sci. 2022, 43, 949–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, H.; Das, M.; Sahu, B. A Generalized Mixed Path Loss (MPL) Model for Wireless Underground Sensor Networks. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2023, 129, 2749–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambo, D.W.; Forster, A.; Yenke, B.O.; Sarr, I.; Gueye, B.; Dayang, P. Wireless underground sensor networks path loss model for precision agriculture (WUSN-PLM). IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 5298–5313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guru, B.S.; Hiziroglu, H.R. Electromagnetic Field Theory Fundamentals; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Akyildiz, I.F.; Hancke, G.P. Dynamic connectivity in wireless underground sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2011, 10, 4334–4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjadj-Aoul, Y.; Ait-Chellouche, S. Access Control in NB-IoT Networks: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Strategy. Information 2020, 11, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, M.; Pascale, F.; Santaniello, D. Internet of Things: A General Overview between Architectures, Protocols and Applications. Information 2021, 12, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bembe, M.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.; Masonta, M.; Ngqondi, T. A survey on low-power wide area networks for IoT applications. Telecommun. Syst. 2019, 79, 249–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greitans, M.; Gaigals, G.; Levinskis, A. Implementation of LoRa TDMA-Based Mobile Cell Broadcast Protocol for Vehicular Networks. Information 2025, 16, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Hao, T. Experimental Link Quality Analysis for LoRa-Based Wireless Underground Sensor Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 6565–6577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironov, V.L.; Kosolapova, L.G.; Fomin, S.V. Physically and mineralogically based spectroscopic dielectric model for moist soils. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 2059–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, A. An Underground Radio Wave Propagation Prediction Model for Digital Agriculture. Information 2019, 10, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peplinski, N.; Ulaby, F.; Dobson, M. Corrections to ‘dielectric properties of soils in the 0.3-1.3-GHz range. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironov, V.L.; Dobson, M.C.; Kaupp, V.H.; Komarov, S.A.; Kleshchenko, V.N. Generalized refractive mixing dielectric model for moist soils. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghioon, A.M.; Chapman, D.N.; Metje, N.; Anthony, C.J. A New Approach to Estimating the Path Loss in Underground Wireless Sensor Networks. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2017, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, P.K.; Xanthakis, E.; Jury, V.; Le-Bail, A. An Overview on Magnetic Field and Electric Field Interactions with Ice Crystallisation; Application in the Case of Frozen Food. Crystals 2017, 7, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, T.; Wentz, F.J. The complex dielectric constant of pure and sea water from microwave satellite observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1836–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro-Castillo, C.; Cervantes-Lozano, J.; Serrano-García, D.I.; González-Ochoa, H.O. Derivation of the Ray Equation from Snell’s Law. Physics 2025, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgouli, K.; Plati, C. Dielectric Response of Asphalt Mixtures and Relationship to Air Voids and Stiffness. Constr. Mater. 2024, 4, 566–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdi, T.; Rhazi, J.E.; Boone, F.; Ballivy, G. Modelling dielectric constant values of concrete: An aid to shielding effectiveness prediction and ground-penetrating radar wave technique interpretation. J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 405401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Temim, M.A.; Ferré, G.; Laporte-Fauret, B.; Dallet, D.; Minger, B.; Fuché, L. An enhanced receiver to decode superposed LoRa-like signals. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 7419–7431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomé, J.; del Río, I.; Martínez, A.; Aranguren, A.; Laña, I.; Alloza, S. Game On: Exploring the Potential for Soft Skill Development Through Video Games. Information 2025, 16, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adefemi Alimi, K.O.; Ouahada, K.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M.; Rimer, S. A Survey on the Security of Low Power Wide Area Networks: Threats, Challenges, and Potential Solutions. Sensors 2020, 20, 5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Jamil, H.M.M.; Pranto, S.A.; Das, R.K.; Amin, A.; Khan, A. Future Industrial Applications: Exploring LPWAN-Driven IoT Protocols. Sensors 2024, 24, 2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, L.J. Satellite Communications Systems Engineering-Atmospheric Effects Satellite Link Design and System Performance; Wiley: West Sussex, UK, 2008; pp. 363–365. [Google Scholar]
- Busacca, F.; Mangione, S.; Palazzo, S.; Restuccia, F.; Tinnirello, I. SDR-LoRa, an open-source, full-fledged implementation of LoRa on Software-Defined-Radios: Design and potential exploitation. Comput. Netw. 2024, 241, 110194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Soil Constituent Attribute | Value of the Attribute |
|---|---|
| Soil’s moisture content % | |
| Sand % | |
| Silt % | |
| Clay % |
| Physical Attribute | Value of the Attribute |
|---|---|
| Frequency | 433 MHz |
| Bridge height | 0.5–5 m |
| Transmission power | 20 dBm |
| Receiver antenna gain | 1.5 dBi |
| Soil’s bulk density | 1.5 g/cm3 |
| Horizontal inter-node distance | 0–28 m |
| Dielectric constant of bridge | 6.93–j0.93 (at 433 MHz and 5% moisture content) [54] |
| Receiver rode’s antenna height | 10 cm |
| Transmitter antenna gain | 1.5 dBi |
| Soil’s particle density | 2.66 g/cm3 |
| Height of Water Level | RMSE (dBm) | MAE (dBm) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.1 m | 1.43 | 1.806 |
| 0.2 m | 1.68 | 2.23 |
| Height of Soil Level | RMSE (dBm) | MAE (dBm) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.1 m | 1.49 | 1.87 |
| 0.2 m | 1.43 | 1.806 |
| Height of Water Level | RMSE (dBm) | MAE (dBm) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.1 m | 1.36 | 0.553 |
| 0.2 m | 1.56 | 0.942 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panda, H.; Ramesh, R.; Subbaiyan, S.; Nagendra, S.T.; Das, M.; Sahu, B. Soil–Water–Air (SWA) Interface Channel Model for River Bridge Pillar Health Monitoring Using WSN. Information 2025, 16, 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16121019
Panda H, Ramesh R, Subbaiyan S, Nagendra ST, Das M, Sahu B. Soil–Water–Air (SWA) Interface Channel Model for River Bridge Pillar Health Monitoring Using WSN. Information. 2025; 16(12):1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16121019
Chicago/Turabian StylePanda, Hitesh, Roopesh Ramesh, Saranya Subbaiyan, Swamy Thimmaiah Nagendra, Manoranjan Das, and Benudhar Sahu. 2025. "Soil–Water–Air (SWA) Interface Channel Model for River Bridge Pillar Health Monitoring Using WSN" Information 16, no. 12: 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16121019
APA StylePanda, H., Ramesh, R., Subbaiyan, S., Nagendra, S. T., Das, M., & Sahu, B. (2025). Soil–Water–Air (SWA) Interface Channel Model for River Bridge Pillar Health Monitoring Using WSN. Information, 16(12), 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16121019







