Abstract
Large Language Models (LLMs) represent a major step in AI development and are increasingly used in daily applications. However, they are prone to hallucinations, generating claims that contradict established facts, deviating from prompts, and producing inconsistent responses when the same prompt is presented multiple times. Addressing these issues is challenging due to the lack of comprehensive and easily assessable benchmark datasets. Most existing datasets are limited in scale and scope and rely on multiple-choice questions, which are insufficient for evaluating the generative capabilities of LLMs. To assess hallucination in LLMs, this paper introduces a comprehensive benchmark dataset consisting of over 20,000 unique prompts (more than 75,000 prompts in total) across eight domains. These prompts are designed to elicit definitive, concise, and informative answers. The dataset is divided into two segments: one publicly available for testing and assessing LLM performance, and a hidden segment for benchmarking various LLMs. In our experiments, we tested nine State-of-The-Art (SoTA) models, GPT-4o, GPT-3.5, LLama 2 7B, LLama 3 8B, Gemini 1.0 Pro, Mixtral 8x7B, Zephyr 7B, Deepseek-r1-7b, and Qwen2.5-14B, revealing that overall factual hallucination ranges from 48% to 82% on the public dataset and 31% to 76% on the hidden benchmark. Prompt Misalignment Hallucination ranges up to 95% in the public dataset and up to 94% in the hidden counterpart. Average consistency ranges from 21% to 61% and 44% to 63%, respectively. Domain-wise analysis reveals that LLM performance significantly deteriorates when asked for specific numeric information, whereas it performs moderately with queries involving persons, locations, and dates. Our dataset demonstrates its efficacy and serves as a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating LLM performance.
1. Introduction
The domain of generative artificial intelligence (AI) has witnessed a paradigm shift with the emergence of LLMs. These powerful AI models, capable of processing and generating human-like text, have become widespread across diverse applications. From facilitating seamless machine translation and engaging in chatbot interactions to composing creative content and generating code, LLMs have fundamentally revolutionized numerous fields [1]. However, their immense potential is overshadowed by a critical challenge—hallucinations [2,3,4,5].
Hallucination is defined as the LLM-generated response that lacks coherence or deviates from the original source material [6,7]. Hallucination results in a response that diverges from the user prompt or the previously generated context [8] or contradicts established facts [9]. These hallucinations manifest in various forms, including demonstrably false information as well as content that varies significantly from the context of the prompt [10]. The capacity of LLMs to generate such misleading information represents a substantial threat to their trustworthiness, particularly in contexts where factual accuracy and adherence to prompts are of utmost importance [5,11]. In simple words, hallucination is a model-generated response that is not supported by the prompt or verifiable facts.
Hallucinations can be grouped from different viewpoints. One such perspective broadly categorizes the hallucinations into two main types: contradiction to fact and prompt misalignment. Factual hallucinations address the truthfulness of the generated content. They can be further divided into factual inconsistency, where the information contradicts existing facts, and factual fabrication, where entirely new, unverified information is created, as shown in Figure 1a. Prompt misalignment, on the other hand, focuses on the deviation from the intent and context of the prompt. This includes instructional hallucinations, in which the LLM ignores specific instructions within the prompt, and contextual hallucinations, in which the generated response deviates from the prompt’s overall theme or style. Examples are provided in Figure 1b.
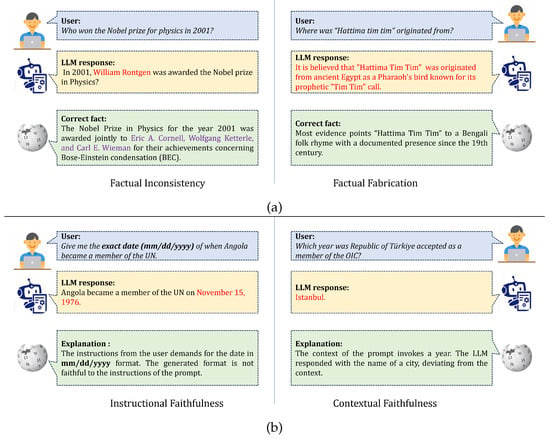
Figure 1.
Comparison between different types of hallucinations. (a) Fact Contradicting Hallucinations and (b) Prompt Misalignment Hallucinations. Best viewed on a zoomed-in screen.
Detecting and mitigating hallucinations presents a complex task in LLM research. Evaluation benchmarks play a significant role in assessing an LLM’s hallucination level. These benchmarks serve as essential tools for assessing the trustworthiness of LLMs by offering a structured framework for evaluating their vulnerability to the generation of hallucinations [12]. Despite commendable endeavors that have led to the development of benchmarks such as FELM [13], HaluEval [14], and HaluEval-Wild [15], the prevailing situation concerning LLM evaluation datasets remains inadequate. A critical limitation is that the majority of existing benchmarks exhibit a narrow focus. Many prioritize either factual hallucinations or prompt misalignment, thereby neglecting the complex nature of LLM hallucinations. Additionally, relying on metrics derived from LLM-judge, a performance assessment model, raises concerns regarding inherent biases and potential inaccuracies associated with these metrics [16]. Human evaluation, although preferable for attaining the highest degree of accuracy, swiftly becomes impractical when dealing with large datasets.
We present a novel approach to address the aforementioned limitations by introducing a large-scale benchmark dataset that is carefully designed to thoroughly evaluate three critical aspects of LLM performance:
- Factual Accuracy: This facet assesses the LLM’s ability to generate information grounded in verifiable reality.
- Faithfulness to the Prompt: Here, the focus shifts to evaluating how well the LLM adheres to the intent and style of the provided prompt.
- Consistency of Generated Responses: This dimension assesses the LLM’s ability to maintain consistency within its generated outputs, ensuring a logical and coherent flow of information.
Our proposed benchmark dataset overcomes the limitations of existing approaches by incorporating a feasible and straightforward automated evaluation method. This strategy represents a significant advancement in the effort to ensure the trustworthiness of LLMs, providing a robust and efficient means for detecting and mitigating hallucinations.
2. Related Works
Over the past year, several studies have explored the causes, effects, and detection of hallucinations in various LLMs. Most of the research has concentrated on hallucinations regarding the factuality of the responses and their faithfulness to the prompts. Additionally, some benchmark datasets have been proposed for hallucination detection as well [17,18,19,20,21].
The majority of datasets proposed for assessing hallucinations predominantly concentrate on the detection of hallucinated content within the generated output [13,14,15,22,23]. These datasets commonly employ LLMs, such as ChatGPT, to deliberately generate hallucinatory responses. Subsequently, these responses are annotated through additional phases with LLMs or human experts. The annotated data is then utilized to evaluate the effectiveness of LLMs in detecting hallucinations within these samples. These benchmark datasets primarily deal with large-scale generated responses, such as passages, requiring human annotators or LLMs to assess performance. However, LLM-based evaluations may be prone to biases, while human judgments can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, leading to the development of smaller datasets.
Several additional datasets have been proposed to evaluate the performance across various tasks and methodologies for assessing hallucinations within generated responses. Some of these datasets employ static prompts for question-answering tasks [24,25], while [26] introduces a method for dynamically generating questions based on real-time news events to assess the adaptability of LLM knowledge bases. These datasets typically adopt multiple-choice question (MCQ) formats for evaluation. However, the MCQ format may not adequately assess hallucination, as it fails to effectively evaluate the generative capabilities of LLMs. LLMs exhibit order sensitivity in MCQs, often favoring answers positioned at specific locations, such as the first option. Furthermore, the study reveals a low correlation between LLMs’ responses to MCQs and long-form generation questions (LFGQs) for identical queries, suggesting that MCQs may not accurately reflect the true capabilities of LLMs [27]. LLMs may not consistently select the distinctly correct answer but rather the option that is “least incorrect,“ indicating that models might perceive multiple choices as partially correct [28]. Models may merely guess answers or identify patterns within the provided options rather than genuinely generating responses.
Recent efforts have introduced more refined and comprehensive benchmarks for evaluating hallucination behavior in modern LLMs. For example, HalluLens [29] proposes a taxonomy that distinguishes between intrinsic and extrinsic hallucinations, employing dynamically generated test sets to mitigate potential data leakage and model memorization biases. Similarly, HALoGEN [30] introduces a large-scale benchmark comprising over 10,000 prompts across nine domains. The benchmark decomposes model outputs into atomic factual units and classifies hallucinations into categories such as fabrication, incorrect knowledge, and memory-based inconsistencies. Furthermore, FaithBench [31] presents a diverse and human-annotated hallucination benchmark for summarization tasks, covering multiple model families and including cases that are particularly challenging for both models and hallucination detectors.
There exists a trade-off among the widely utilized evaluation methods: MCQs, constrained answer formats that are assessed using regular expressions, and open-ended generative responses evaluated by judges based on LLMs. While none of these methods achieves perfect accuracy, evaluating constrained outputs using regular expressions provides a more balanced and consistent assessment framework [32]. Therefore, we adopt this particular approach for our evaluation benchmark. Our dataset is specifically designed to elicit the generative capabilities of LLMs while minimizing reliance on human judgment. In comparison to existing datasets, ours is at least twice the size, thereby offering a more robust benchmark for assessing LLM performance in hallucination detection. A summary of the existing works is presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
A summary of existing hallucination benchmarks. Evaluation aspect denotes the category of hallucination being assessed. Granularity of a dataset denotes the level of information being labeled. The symbol “✓” indicates that the corresponding evaluation aspect is addressed by the benchmark.
3. Proposed DefAn Dataset
The main objective of this paper is to develop a benchmark to evaluate the factual accuracy of the LLMs, as well as their faithfulness to the given prompt. Existing benchmarks focus primarily on detecting hallucinations in LLM responses. A specific question-answering benchmark is necessary to understand how LLMs hallucinate factual information. Considering this, we have created a dataset that requires precise responses and gathered the responses from the official documents available online. The LLM output provides insight into how it hallucinates over specific details and how much of the facts an LLM offers can be trusted.
3.1. Dataset Overview
The proposed dataset comprises approximately 75,000 samples from diverse domains of knowledge. The target information of these questions is a specific number, date, location, or person. The prompts also ask for specific information from the LLMs.
3.2. Design Basics
Factuality: The design of our dataset starts by defining Factuality. According to [34], factuality hallucination is defined by six fine-grained categories. In general, factuality refers to the degree of accuracy and truthfulness of the generated text about real-world facts or events. It covers how faithfully the generated text represents the information provided or the context in which it is generated. Text can vary in factuality, ranging from entirely factual and precise to speculative or fictional. In text generation tasks, ensuring high factuality is crucial, particularly in applications where accuracy and reliability are paramount, such as news reporting, academic writing, or legal documentation. However, factuality can sometimes be challenging, especially when the generated content involves complex reasoning, interpretation, or subjective perspectives. The existing benchmarks mainly focus on claims made in responses generated by LLMs. Even the QA datasets focus primarily on world knowledge. We have collected samples from diverse domains of world knowledge. We have also collected questions from the math domain that test the understanding of mathematical concepts and reasoning. These domains serve as tools to understand the characteristics of the hallucinated responses of LLMs.
Faithfulness: A primary objective of the dataset is to assess the faithfulness of responses generated by LLMs to the provided prompts. We carefully craft the prompts to elicit specific answers, thereby facilitating a focused evaluation process. Even if a generated response contains accurate information, a deviation from the prescribed format is considered unfaithful to the prompt. This emphasis on prompt fidelity ensures that the evaluation accurately reflects the LLMs’ ability to produce responses that align closely with the intended context and requirements.
Consistency: One crucial aspect of the dataset evaluation involved examining whether language models consistently generated responses for the same question over time and across paraphrased versions. To obtain this, each sample underwent rigorous testing through 15 paraphrased versions, allowing for a comprehensive assessment of response consistency, as shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Paraphrasing of questions. Each sample is paraphrased 15 times initially with the help of chatGPT. Human experts annotated later to maintain the accuracy of the prompts.
Granularity: The granularity of a dataset refers to the level of detail or specificity at which the data is organized and structured. In text generation tasks, granularity often pertains to the distinction between responses, claims, and segments within the dataset. We strategically design prompts to ensure that the generated response becomes the sole claim, thereby ensuring clarity and precision in the evaluation process. This approach enhances user friendliness and specificity, allowing for a more targeted assessment of the generated content against the provided prompts. By carefully considering the granularity of the dataset, we can streamline evaluation procedures and facilitate a more accurate analysis of text generation model performance.
Category: The dataset has been partitioned into public and hidden datasets. The public dataset will be accessible to evaluate the performance of various LLMs and their respective modifications. Conversely, the hidden dataset, which possesses a similar structure to the public dataset, will remain private and serve as a benchmark for assessing model performance. This deliberate division is done to prevent contamination [35]. One of the major challenges for evaluation benchmarks is that the newer models may be trained on the benchmark data. As a result, some scores may not accurately reflect the model’s overall performance. The models might start to overfit the benchmark data. The privacy of the hidden dataset is essential to maintaining the integrity and validity of benchmarking procedures.
3.3. Factuality Domains
The proposed dataset comprises questions from eight domains of word knowledge and mathematical problems that require logical reasoning. They are Sports, Census Australia, Nobel, Entertainment, World Organizations, QS Ranking, Conference Venue, and Math. Among these, the Sports domain contains information about FIFA World Cup finals (https://www.rsssf.org/tablesw/worldcup.html (accessed on 28 March 2025)). Census Australia (https://www.abs.gov.au/census/find-census-data/quickstats/2021/1 (accessed on 28 March 2025)) archives the statistical information from the Australian Bureau of Statistics census from 2001 to 2021. The Nobel domain contains information about all Nobel laureates (https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/lists/all-nobel-prizes/ (accessed on 28 March 2025)) for different categories. The entertainment domain comprises winners’ information and their birth dates for OSCAR winners (https://awardsdatabase.oscars.org/ (accessed on 28 March 2025)). The joining date for the member states of the United Nations (UN) (https://www.un.org/en/about-us/member-states (accessed on 28 March 2025)) and the Organization for Islamic Cooperation (OIC) (https://new.oic-oci.org/SitePages/MemberStates.aspx (accessed on 28 March 2025)) is archived in Word Organization. In QS ranking (https://www.qs.com/reports-whitepapers/qs-world-university-rankings-2024-results-table-excel/(accessed on 28 March 2025)), we accumulate the ranking information for educational institutions. The host location for the top conferences is gathered for the Conference Venue. In Math (https://github.com/google-deepmind/AQuA (accessed on 28 March 2025)), the domain includes problems comprising math-related questions designed to assess LLMs’ algebraic proficiency and reasoning abilities. Table 3 shows an overview of the domains, while Figure 2 depicts the distribution of the prompts.

Table 3.
Overview of the domains of the proposed dataset. Response type denotes the type of answers in the datasets. The column Paraphrased indicates whether the samples in that domain are paraphrased or not. For the size of each domain, the number in parentheses denotes the unique prompts. The ✓ symbol indicates that responses in the corresponding domain include that data type (Date, Numeric, Name, Location).
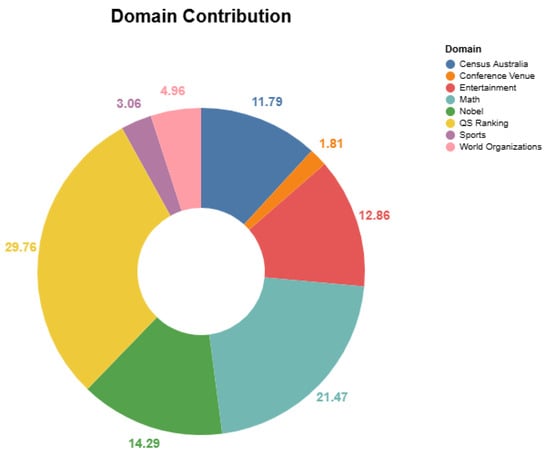
Figure 2.
Distribution of prompts by domain. Values indicate percentage of total number of prompts.
3.4. Question Generation
Generating samples for a QA dataset is a long process that involves several steps to ensure the data’s quality, reliability, and consistency. Initially, we gathered information from various official sources, such as government publications, academic papers, and official websites. This diverse pool of sources guarantees that the data collected is comprehensive, accurate, and up-to-date. Importantly, each piece of information is carefully examined to ensure its relevance and authenticity, with an emphasis on publicly available content to maintain transparency and accessibility.
Once the information is compiled, clear and specific questions and queries are formulated to extract targeted knowledge from the dataset. These questions are designed to be unambiguous, prompting for particular details or facts directly supported by the collected information. The goal is to create a set of questions that covers a wide range of topics and requires precise answers.
To further evaluate the LLMs, each question is paraphrased multiple times to assess the consistency of responses generated by language models. This iterative process helps identify potential inconsistencies or ambiguities in the dataset, ensuring that the LLMs produce coherent and accurate answers across variations of the same question. We use ChatGPT to generate initial samples to paraphrase the questions. The human experts checked these samples to ensure the prompt adhered to the original meaning and invoked the same response. A sample of question paraphrasing is shown in Table 2.
To assess the quality of paraphrased questions in our dataset, we computed the average semantic similarity within each question set. Specifically, for each set, the first question was treated as the reference question, and its semantic similarity was computed with every other question in the same set. The average of these pairwise similarity scores defined the semantic similarity score of the set. Finally, the overall paraphrasing quality was estimated by computing the mean semantic similarity across all question sets. This can be formally expressed as
where N is the total number of question sets, is the number of questions in the set, denotes the reference question of the set, and represents the semantic similarity between the reference and the question in that set. To ensure a comprehensive evaluation, we employed three complementary semantic similarity metrics:
Cosine Similarity: This measures similarity based on the angular distance between vector representations of the questions. It ranges from to 1, and is efficient for capturing structural similarity and lexical overlap. However, it is less sensitive to deeper semantic equivalence.
BERTScore: It utilizes contextual embeddings from BERT to evaluate semantic similarity. BERTScore reports precision, recall, and F1-score, with values ranging from 0 to 1. We have taken the average F1-score as a similarity score to incorporate both the precision and recall performance. It is more effective at identifying semantic equivalence despite surface-level differences, although it is computationally more intensive.
GPT-Judge (ChatGPT-4.5): We prompted ChatGPT-4.5 in a zero-shot setting to rate the semantic similarity between the reference and paraphrased questions. The model returned a similarity score between 0 (entirely dissimilar) and 1 (semantically identical). These scores are presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Semantic similarity scores for each question set using Cosine Similarity, BERTScore (F1), and GPT-Judge. All average similarity scores across metrics exceed 0.915, indicating a high degree of semantic alignment between the reference and paraphrased questions.
4. Experiment
Our experiment evaluates the hallucination of publicly available LLMs, analyzing their performance in terms of factual correctness, faithfulness to prompts, consistency of facts, and identifying potential use cases for our dataset.
Experimental Setup
LLMs under scrutiny: In our study, we utilized open-source and closed-source LLMs to evaluate their performance on our dataset. The models employed include zephyr [36], Mixtral-8x7B [37], GPT-3.5 [38], LLaMA 2 7B [39], LLaMA 3 8B [40], GPT- 4o [41], Gemini 1.0 Pro [42], Deepseek-r1-7B [43] and Qwen2.5-14B [44]. These models represent diverse architectures and capabilities, providing a comprehensive overview of LLM performance across different platforms.
GPT-3.5, developed by OpenAI, is a closed-source model known for its robust language understanding and generation capabilities. LLaMA 2 7B and LLaMA 3 8B are open-source models that offer transparency and the ability to fine-tune the models to specific tasks, which is advantageous for research and development purposes. Gemini Pro, a proprietary model, was also included to compare the performance of enterprise-level solutions. We accessed GPT-3.5 and LLaMA 2 using the OpenAI API, facilitating seamless integration and testing of the model within our workflow. For Gemini Pro, we leveraged Google Cloud Services to manage these models. We used Huggingface transformer to access the DeepSeek and Qwen models. Among the existing models, GPT-4o is considered one of the best based on its performance on several benchmarks. GPT-4o is estimated to have trillions of parameters, which enables it to perform better than other models. Details of these models are summarized in Table 5.

Table 5.
An overview of all the models used for evaluation. The parameters correspond to the model we used. The context window denotes the maximum allocated context window for the model used. Accessibility is the platform used to access these models. * indicates an estimation by tech experts, not from the official statements.
Metrics: We evaluate the performance of the models based on three perspectives: factual accuracy, faithfulness to prompts, and consistency with paraphrased prompts. Each of these requires a separate metric for evaluation. Let us assume that we have a total of n questions in the dataset, and among them, k is unique. Others include their paraphrased versions. The LLM generates a response for each question, .
For FCH evaluation, we propose using the FCH rate, which denotes the response percentage with the hallucinated fact. The FCH rate can be calculated as shown in Equations (2) and (3).
To measure the Prompt Misalignment Hallucination (PMH), we propose using the PMH rate, calculated as shown in Equations (4) and (5).
Consistency denotes the percentage of responses that have the same claim over the paraphrased prompts. For measuring consistency, we used response consistency (RC), calculated as Equation (6), where is 1 if all 15 paraphrased versions of the prompt generate the same claim.
Claim extraction. Upon recording responses from the language models, these responses undergo a rigorous evaluation process. Each response is compared to the reference answer to assess Fact Contradicting Hallucination (FCH) and to the original prompts to evaluate Prompt Misalignment Hallucination (PMH). This involves extracting factual claims from the responses. Initially, the responses are subjected to basic natural language processing (NLP) pre-processing steps, such as removing punctuation, stopping words, and formatting dates. Subsequently, depending on the target data type, the claims are extracted. For claim extraction, we adopted a hybrid approach that balances precision and robustness across different response types. When model outputs followed the prescribed answer format, simple string matching was sufficient to identify the factual claim. However, for unstructured or verbose responses, we relied on type-specific natural language processing (NLP) techniques. In particular, we used named entity recognition (NER) with spaCy to extract entities such as persons, organizations, and locations; regular expressions to normalize and capture structured data such as dates and numeric values; and fuzzy string matching (fuzzywuzzy) to account for minor lexical variations and approximate matches. Once the claims are extracted, they are matched against the reference answers for further detailed analysis.
Case study. Once the pre-processing is completed, the responses generated by the LLM undergo evaluation by FCH, PMH, and RC. Table 6 illustrates an example of this evaluation process.

Table 6.
Responses generated by LLMs under evaluation. The cell color denotes PMH, and the text color denotes the FCH.
In this example, 15 zero-shot prompts request a specific university’s QS ranking. The responses here are generated by Gemini 1.0 pro. Of 15 responses, 3 contain correct answers, making 12 factually incorrect claims. Hence, the FCH rate here is .
The prompts are designed to obtain only ranks from the LLMs. In total, 5 out of 15 responses deviate from the instructions provided. The PMH rate here is .
To assess response consistency, first, the claims from each paraphrased version of the prompts are assessed. If all the claims are the same, then the RC for is called to be 1. As all the claims in Table 6 are not the same, the RC value here is 0. The final RC value is the average RC for all sets of prompts like Table 6.
5. Result Analysis
The results from the experiment reveal the hallucination rates of nine language models across eight domains: Zephyr-7B, Mixtral 8x7B, Llama3-8B, Llama2-7B, GPT-3.5, GPT-4o, Gemini 1.0 Pro, Deepseek-r1-7b, and Qwen2.5-14B.
5.1. Performance Comparison for Specific Domains
This section presents the domain-wise performance of each LLM. For each domain, we have two sections—public and hidden.
FCH rate. Each model’s performance was assessed based on the correctness of the factual claim. A higher FCH value, which indicates more hallucinations, suggests that the model is less reliable for factual claims. The FCH rate in each domain is presented in Table 7.

Table 7.
FCH rates for specific domains. The best results are in bold and a higher value indicates worse performance.
Domains that require specific numeric information or dates, such as Census, QS Ranking, and Math, exhibit more severe hallucination rates in public and hidden datasets. This suggests that models struggle significantly with generating accurate numbers. For instance, all models display scores of 1 in the Census domain, indicating a high rate of generating incorrect numbers. High scores in QS Ranking and Math indicate significant challenges in maintaining accuracy with numeric data.
Conversely, domains such as Sports, Entertainment, and World Organizations, which typically require names and locations, face less severe hallucinations. Zephyr, for example, shows relatively lower hallucination rates in these domains, with scores improving from 0.50 to 0.29 in Sports and from 0.68 to 0.20 in Entertainment when transitioning from the public to the hidden dataset. This pattern suggests that LLMs perform better when generating non-numeric responses.
Among the models, performance varies considerably across domains and dataset types (hidden vs. public). Overall, GPT-4o demonstrates the best performance, consistently achieving lower hallucination rates, particularly in domains requiring names and locations. Conversely, Zephyr performs the worst across most domains, particularly those that require specific numeric responses. The other models, such as Llama3, Llama2, and GPT-3.5, exhibit moderate performance with significant variability depending on the domain and dataset type. Notably, while Llama2 and Llama3 perform better in some numeric-focused domains, they still struggle with maintaining accuracy in responses involving specific numbers.
PMH rate: Here, prompt misalignment refers to the degree to which a response accurately deviates from the prompt. It may deviate by generating lengthy passages of text instead of providing definitive answers, or it may offer totally out-of-context information or present information in an incorrect format.
The data in Table 8 reveals that prompt misalignment is predominantly model-specific rather than domain-specific. Most models exhibit misalignment issues across all domains, indicating a general challenge in generating responses that accurately align with the given prompts. However, certain models demonstrate a higher adherence to prompts compared to others.

Table 8.
PMH rates for specific domains. The best results are in bold and a higher value indicates worse performance.
Zephyr and Mixtral show the highest rates of prompt misalignment across all domains, with values close to or at 1.00 in most cases, indicating significant difficulty in producing responses that match the prompt. For instance, Zephyr’s misalignment rates in Sports and Census are exceptionally high, with public dataset values of 0.87 and 1.00, respectively.
In contrast, models like Gemini and Llama3 perform considerably better at maintaining prompt alignment. Gemini, for example, exhibits very low misalignment rates, with values of 0.01 in Census and 0.04 in Math for the public dataset, and similarly low rates in the hidden dataset. Llama3 also shows lower misalignment rates in several domains, such as a public dataset rate of 0.18 in Sports and 0.01 in Entertainment, although it struggles more in domains like Census. Among all the models, GPT-4o has the lowest PMH rate across all the domains. One possible reason could be the model’s size. GPT-4o has a large number of parameters that make it more effective at maintaining performance.
RC: RC measures the prowess to generate consistent responses over paraphrased versions of the same prompt. The bigger the value, the better the performance. RC is calculated for all the domains except the math domain, as the prompts in this domain are not paraphrased. The data is shown in Table 9.

Table 9.
RC scores for specific domains. The best results are in bold, and the higher value denotes better performance.
The data show that models generally exhibit more significant inconsistency when generating specific numbers, as seen in domains such as census. In contrast, other domains tend to elicit more consistent responses over paraphrased prompts. Models like Gemini, LLaMA 2, LLaMA 3, and GPT show more consistency for the domains other than census and QS ranking. Different models are inconsistent.
5.2. Overall Performance
Figure 3 illustrates the performance of the LLMs based on the three metrics we proposed. The model performance analysis reveals noteworthy trends across various evaluation metrics. First, focusing on FCH, it becomes evident that most models struggle to generate factually accurate responses. Both Llama 2 and GPT-3.5 exhibit a moderate level of performance across both public and hidden datasets, suggesting a better ability to produce factually correct responses. However, models such as Llama 3, Gemini, and Mixtral display fluctuating performance, indicating variability in their accuracy in generating factually correct responses across different datasets.
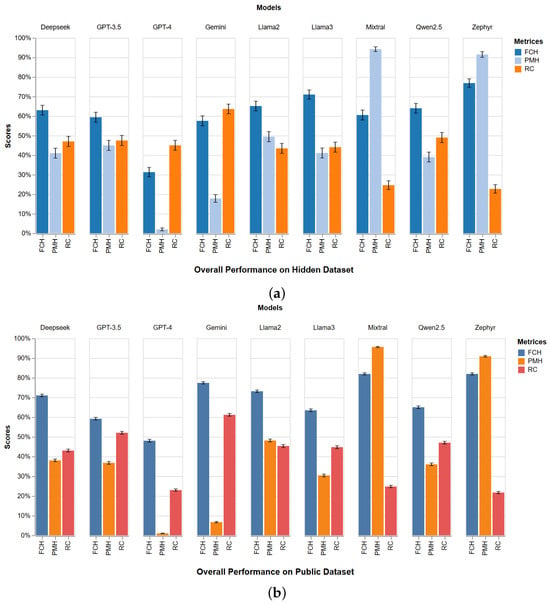
Figure 3.
Comparison of LLM performance on (a) hidden and (b) public datasets across three evaluation metrics. Bars show mean metric scores, and black whiskers denote variance corresponding to 95% confidence interval.
Considering PMH, specific models, notably Zephyr and Mixtral, demonstrate severe deviations from the provided prompts. This suggests significant challenges in accurately adhering to the provided prompts. Conversely, Gemini emerges as a standout performer in both datasets, showcasing its superior adherence capability. Other models exhibit moderate performance, with varying degrees of deviation from the provided prompts.
Lastly, in terms of response consistency, Gemini stands out as the most consistent model, demonstrating strong coherence across paraphrased prompt variations. Models like Mixtral and Zephyr demonstrate the worst performance, suggesting difficulties in producing coherent responses across paraphrased prompts. Other models exhibit moderate levels of performance in response consistency.
5.3. Closed-Source Large Models vs. Open-Source Small Models
A clear performance divide emerges between closed-source large models (e.g., GPT-4o, Gemini, GPT-3.5) and open-source smaller models (e.g., LLaMA, Mixtral, Zephyr, Qwen, DeepSeek). While all models struggled with raw numeric facts (e.g., census statistics, QS rankings), larger closed-source models handled numeric reasoning tasks such as mathematics more effectively, showing higher consistency and correctness. In contrast, smaller open-source models often produced severe hallucinations and exhibited greater prompt misalignment, particularly in structured domains.
Beyond numbers, closed-source models also showed stronger faithfulness to prompts and stability across paraphrased variations, whereas open-source models were less reliable, though occasionally competitive in simpler domains such as Sports or Entertainment. These differences likely stem from the scale of training data, parameter counts, and proprietary optimization pipelines available to closed-source systems, in contrast to the constraints of open-source models.
While these results suggest notable differences between model scale and accessibility, it is difficult to draw firm causal conclusions on the effect of size or open-/closed-source status from the present experimental design. A more meticulous experimental setup focused specifically on this comparison is required, which we leave for future work. This study can serve as a baseline for such investigations.
5.4. Ablation Study
The performance results indicate that LLMs consistently struggle with numeric data while performing moderately well with non-numeric facts such as locations and names. These observations raise important questions regarding the underlying reasons for these deficits, particularly with numeric information.
Training Data Coverage: Numeric information, especially domain-specific data such as census statistics, may not be adequately represented in the models’ training datasets.
Data Source Familiarity: If the model is asked for numeric data from sources likely present in its training data (e.g., Wikipedia), its performance may improve.
Temporal Effects: The cut-off period of the model’s training data may also affect performance, particularly with more recent data.
To investigate these possibilities, we conducted two ablation studies to test two hypotheses.
Hypothesis 1.
“Performance on numeric tasks decreases when the data postdates the model’s cut-off period.”
In this study, we analyzed GPT-4o’s responses to questions from the QS ranking domain, spanning three years: 2022, 2023, and 2024. The goal was to evaluate whether the model’s performance drops when asked about data beyond its training cut-off. The results showed that GPT-4o performed relatively well for 2022 and 2023 data, with an FCH rate of approximately 20%. However, for 2024 prompts, the model’s performance dropped significantly, with the FCH rate increasing to 65%. This contrast suggests that the knowledge cut-off indeed impacts the model’s ability to handle recent numeric facts.
Hypothesis 2.
“LLMs will perform reasonably well if asked for numeric facts from familiar sources, presumably part of their training data.”
For this study, we selected 125 questions from the SQuAD dataset, primarily sourced from Wikipedia, which invoke factual information. Given that Wikipedia data is a likely component of the training corpus for many LLMs, we expected a higher level of accuracy with this familiar content. To ensure that the prompts were suitable for LLM evaluation, we modified the questions to include specific contexts and response format instructions. When these prompts were fed to GPT-4o, the results showed that only 54% of the responses were accurate, leaving a factual consistency hallucination (FCH) rate of 46%. This suggests that even with familiar numeric data, LLMs struggle to generate accurate responses.
These findings confirm that LLMs face real challenges in handling numeric information, even when that information is part of their training data. Furthermore, the model’s knowledge cut-off substantially affects its performance on more recent data. These insights highlight the potential of using prompts like those in these studies as benchmarks for retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems. Models that outperform on these prompts can demonstrate their ability to mitigate the limitations caused by temporal data cut-offs.
5.5. Possible Use Cases of DefAn
The DefAn benchmark can serve multiple purposes in the evaluation and development of Large Language Models. First, it provides a standardized resource for benchmarking competitions, especially the hidden unpublished version of the dataset, enabling consistent comparison of models across diverse domains and hallucination dimensions. Second, DefAn can be used to stress-test retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems, where controlling hallucinations is particularly critical for ensuring factual reliability. Finally, the dataset can guide dataset curation practices by highlighting linguistic and domain-specific factors that influence hallucination rates, thereby informing the design of more robust training corpora and evaluation frameworks. These use cases underscore the broader utility of DefAn beyond static evaluation, supporting both research and applied deployment of LLMs.
6. Conclusions
This paper introduces a comprehensive benchmark dataset designed for evaluating hallucinations in LLMs. To facilitate the accurate assessment and evaluation of hallucinations in the generative capabilities of LLMs, the dataset ensures that target responses have definitive answers. The resulting dataset combines responses and claims, enhancing its granularity. Comprising over 75,000 prompts across nine distinct domains, the dataset features target answers in the form of names, places, dates, or specific numeric values. We have proposed three evaluation metrics: factual accuracy, faithfulness accuracy, and consistency accuracy. Utilizing our dataset, we tested several prominent public LLMs. Our findings reveal that most LLMs exhibit hallucinations, both factually and in terms of faithfulness to the prompt. For consistency, apart from specific numeric values, most LLMs were consistent in their responses to paraphrased prompts. Overall, performance in generating names, places, and dates was moderate, but significant hallucinations occurred when numeric values were required.
Looking forward, several practical extensions can enhance the value of DefAn. First, additional domains, such as science, medicine, law, economics, and ethics, would enable more comprehensive coverage, though this will require careful prompt design and expert annotation. Second, integrating further hallucination dimensions, including non-determinism [45] in inference and temporal drift, would capture variability that current metrics cannot. Third, extending the dataset to include multilingual prompts and domain-expert-validated subsets would improve both inclusivity and reliability. Finally, incorporating novel metrics such as sycophancy [46] could provide a more nuanced view of model behavior under uncertain or ambiguous conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.A., I.A. and A.M.; methodology, A.B.M.A.R., S.A. and M.U.; validation, A.B.M.A.R., S.A., M.U. and A.M.; formal analysis, A.B.M.A.R., S.A., I.A. and A.M.; investigation, A.B.M.A.R., S.A. and I.A.; resources, S.A. and M.U.; data curation, A.B.M.A.R.; writing—original draft preparation, A.B.M.A.R.; writing—review and editing, S.A., A.M., M.U., I.A. and A.M.; visualization, A.B.M.A.R.; supervision, S.A., M.U., I.A. and A.M.; project administration, M.U.; funding acquisition, S.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Not applicable.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset “DefAn” and all the LLM responses are available at https://github.com/ashikiut/DefAn (accessed on 5 September 2025).
Acknowledgments
The author/s would like to acknowledge the support received from the Saudi Data and AI Authority (SDAIA) and King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals (KFUPM) under SDAIA-KFUPM Joint Research Center for Artificial Intelligence Grant No. JRC-AI-RFP-11.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| BERT | Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers |
| DefAn | Definitive Answer based dataset |
| FCH | Fact Contradicting Hallucinations |
| FELM | Factuality Evaluation of Large Language Models |
| FIFA | Fédération Internationale de Football Association |
| LFPQ | Long-Form Generation Questions |
| LLM | Large Language Model |
| MCQ | Multiple-Choice Question |
| NLP | Natural Language Processing |
| NER | Named Entity Recognition |
| OIC | Organisation of Islamic Cooperation |
| PMH | Prompt Misalignment Hallucinations |
| QA | Question Answering |
| QS | Question Set |
| RAG | Retrieval-Augmented Generation |
| RC | Response Consistency |
| SoTA | State of the Art |
| UN | United Nations |
References
- Naveed, H.; Khan, A.U.; Qiu, S.; Saqib, M.; Anwar, S.; Usman, M.; Akhtar, N.; Barnes, N.; Mian, A. A Comprehensive Overview of Large Language Models. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2025, 16, 1–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawte, V.; Sheth, A.; Das, A. A survey of hallucination in large foundation models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.05922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perković, G.; Drobnjak, A.; Botički, I. Hallucinations in llms: Understanding and addressing challenges. In Proceedings of the 2024 47th MIPRO ICT and Electronics Convention (MIPRO), Opatija, Croatia, 20–24 May 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 2084–2088. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, W.; Chen, W.; Chen, Q.; Pan, S.; Zhou, H.; Pan, Y. A Survey of Hallucination in Large Visual Language Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.15359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, G.; Wu, J.; Pan, Q.; Morello, R. Quantifying the uncertainty of LLM hallucination spreading in complex adaptive social networks. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.; Lee, N.; Frieske, R.; Yu, T.; Su, D.; Xu, Y.; Ishii, E.; Bang, Y.J.; Madotto, A.; Fung, P. Survey of hallucination in natural language generation. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonmoy, S.; Zaman, S.; Jain, V.; Rani, A.; Rawte, V.; Chadha, A.; Das, A. A comprehensive survey of hallucination mitigation techniques in large language models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.01313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlakha, V.; BehnamGhader, P.; Lu, X.H.; Meade, N.; Reddy, S. Evaluating correctness and faithfulness of instruction-following models for question answering. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.16877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhlgay, D.; Ram, O.; Magar, I.; Levine, Y.; Ratner, N.; Belinkov, Y.; Abend, O.; Leyton-Brown, K.; Shashua, A.; Shoham, Y. Generating benchmarks for factuality evaluation of language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.06908. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Cui, L.; Cai, D.; Liu, L.; Fu, T.; Huang, X.; Zhao, E.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Siren’s song in the AI ocean: A survey on hallucination in large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.01219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Consul, S.; Zhou, E.; Wong, J.; Farooqui, N.; Ye, Y.; Manohar, N.; Wei, Z.; Wu, T.; Echols, B.; et al. Banishing LLM hallucinations requires rethinking generalization. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.17642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Yu, W.; Ma, W.; Zhong, W.; Feng, Z.; Wang, H.; Chen, Q.; Peng, W.; Feng, X.; Qin, B.; et al. A survey on hallucination in large language models: Principles, taxonomy, challenges, and open questions. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.05232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chern, I.; Gao, S.; Liu, P.; He, J. Felm: Benchmarking factuality evaluation of large language models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 36, 4502–44523. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, W.X.; Nie, J.Y.; Wen, J.R. Halueval: A large-scale hallucination evaluation benchmark for large language models. In Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Singapore, 6–10 December 2023; pp. 6449–6464. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Z. HaluEval-Wild: Evaluating Hallucinations of Language Models in the Wild. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.04307. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, A.S.; Choudhary, K.; Ramayapally, V.S.; Vaidyanathan, S.; Hupkes, D. Judging the judges: Evaluating alignment and vulnerabilities in llms-as-judges. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.12624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, N.; Yang, X.; Li, Q.; Shen, Y.; Liang, L.; Gu, J.; Chen, H. Unified hallucination detection for multimodal large language models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.03190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Li, T.; Wu, D.; Jenkin, M.; Liu, S.; Dudek, G. Hallucination detection and hallucination mitigation: An investigation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.08358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin, S.; Fu, J.; Detommaso, G.; Xu, S.; Zappella, G.; Wang, B. Cost-effective hallucination detection for llms. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.21424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Asai, A.; Balachandran, V.; Wang, Y.; Neubig, G.; Tsvetkov, Y.; Hajishirzi, H. Fine-grained hallucination detection and editing for language models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.06855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Ru, D.; Qiu, L.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, T.; Xu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z. RefChecker: Reference-based Fine-grained Hallucination Checker and Benchmark for Large Language Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.14486. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Sun, R.; Wan, X. A new benchmark and reverse validation method for passage-level hallucination detection. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.06498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Das, K.; Malin, B.A.; Kumar, S. SAC3: Reliable Hallucination Detection in Black-Box Language Models via Semantic-aware Cross-check Consistency. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.01740. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.; Hilton, J.; Evans, O. Truthfulqa: Measuring how models mimic human falsehoods. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.07958. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Q.; Sun, T.; Zhang, W.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; He, J.; Huang, M.; Yin, Z.; Chen, K.; et al. Evaluating hallucinations in chinese large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.03368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, J.; Sakaguchi, K.; Le Bras, R.; Asai, A.; Yu, X.; Radev, D.; Smith, N.A.; Choi, Y.; Inui, K. RealTime QA: What’s the Answer Right Now? Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 36, 49025–49043. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Li, L.; Xiang, T.; Liu, X.; Deng, W.; Garcia, N. Can multiple-choice questions really be useful in detecting the abilities of LLMs? arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.17752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, S.; Qiang, Z.; Xi, N.; Qin, B.; Liu, T. LLMs May Perform MCQA by Selecting the Least Incorrect Option. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.01349. [Google Scholar]
- Bang, S.; Kim, M.; Lee, H.; Choi, Y. HalluLens: A Fine-Grained Benchmark for Evaluating Intrinsic and Extrinsic Hallucinations in Large Language Models. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.17550. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Sun, R.; Li, T.; He, J.; Wan, X. HALoGEN: Fantastic LLM Hallucinations and Where to Find Them. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.08292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, T.; Li, Z. FaithBench: A Diverse Hallucination Benchmark for Summarization Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.13210. [Google Scholar]
- Molfese, F.M.; Moroni, L.; Gioffrè, L.; Scirè, A.; Conia, S.; Navigli, R. Right Answer, Wrong Score: Uncovering the Inconsistencies of LLM Evaluation in Multiple-Choice Question Answering. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.14996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shi, L.; Wang, K.; Wang, H. HalluVault: A Novel Logic Programming-aided Metamorphic Testing Framework for Detecting Fact-Conflicting Hallucinations in Large Language Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.00648. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.; Ren, R.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, W.X.; Nie, J.Y.; Wen, J.R. The dawn after the dark: An empirical study on factuality hallucination in large language models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.03205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourrier, C.; Habib, N.; Lozovskaya, A.; Szafer, K.; Wolf, T. Performances Are Plateauing, Let’s Make the Leaderboard Steep Again. 2024. Available online: https://huggingface.co/spaces/open-llm-leaderboard/blog (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Tunstall, L.; Beeching, E.; Lambert, N.; Rajani, N.; Huang, S.; Rasul, K.; Rush, A.M.; Wolf, T. The Alignment Handbook. 2023. Available online: https://github.com/huggingface/alignment-handbook (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- Jiang, A.Q.; Sablayrolles, A.; Roux, A.; Mensch, A.; Savary, B.; Bamford, C.; Chaplot, D.S.; Casas, D.d.l.; Hanna, E.B.; Bressand, F.; et al. Mixtral of experts. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.04088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenAI. ChatGPT. 2021. Available online: https://openai.com/ (accessed on 5 June 2024).
- Touvron, H.; Martin, L.; Stone, K.; Albert, P.; Almahairi, A.; Babaei, Y.; Bashlykov, N.; Batra, S.; Bhargava, P.; Bhosale, S.; et al. Llama 2: Open foundation and fine-tuned chat models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.09288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touvron, H.; Martin, L.; Stone, K.; Albert, P.; Almahairi, A.; Babaei, Y.; Bashlykov, N.; Batra, S.; Bhargava, P.; Bhosale, S.; et al. Meta Llama 3. 2024. Available online: https://github.com/meta-llama/llama3 (accessed on 5 June 2024).
- Achiam, J.; Adler, S.; Agarwal, S.; Ahmad, L.; Akkaya, I.; Aleman, F.L.; Almeida, D.; Altenschmidt, J.; Altman, S.; Anadkat, S.; et al. Gpt-4 technical report. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.08774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepmind, G. Google AI for Developers. 2023. Available online: https://ai.google.dev/gemini-api/docs/models/gemini (accessed on 5 June 2024).
- Guo, D.; Yang, D.; Zhang, H.; Song, J.; Zhang, R.; Xu, R.; Zhu, Q.; Ma, S.; Wang, P.; Bi, X.; et al. Deepseek-r1: Incentivizing reasoning capability in llms via reinforcement learning. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.12948. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, A.; Yang, B.; Zhang, B.; Hui, B.; Zheng, B.; Yu, B.; Li, C.; Liu, D.; Huang, F.; Wei, H.; et al. Qwen2. 5 Technical Report. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2409.12186. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Lab, T.M. Defeating Nondeterminism in LLM Inference. Thinking Machines Lab: Connectionism. 2025. Available online: https://thinkingmachines.ai/blog/defeating-nondeterminism-in-llm-inference/ (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Sharma, M.; Tong, M.; Korbak, T.; Duvenaud, D.; Askell, A.; Bowman, S.R.; Cheng, N.; Durmus, E.; Hatfield-Dodds, Z.; Johnston, S.R.; et al. Towards understanding sycophancy in language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.13548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).