Planning Future EV Charging Infrastructure by Forecasting Spatio-Temporal Adoption Trends Across Heterogeneous User Segments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
- Develop a three-stage planning framework that combines user segmentation, spatio-temporal adoption forecasting, and mixed-integer linear programming (MILP)–based charger placement optimization under budget constraints. This approach bridges behavioral modeling and infrastructure optimization, creating a reproducible workflow.
- Using K-Means clustering on detailed EV registration data, the framework derives segment-specific charging requirements. By classifying them based on vehicle attributes such as range, MSRP, and EV type, the framework captures behavioral and technical heterogeneity that has often been ignored in previous planning studies.
- The proposed framework includes an optimization model that incorporates minimum service coverage thresholds for each user segment, ensuring equitable access to charging infrastructure while maintaining efficiency.
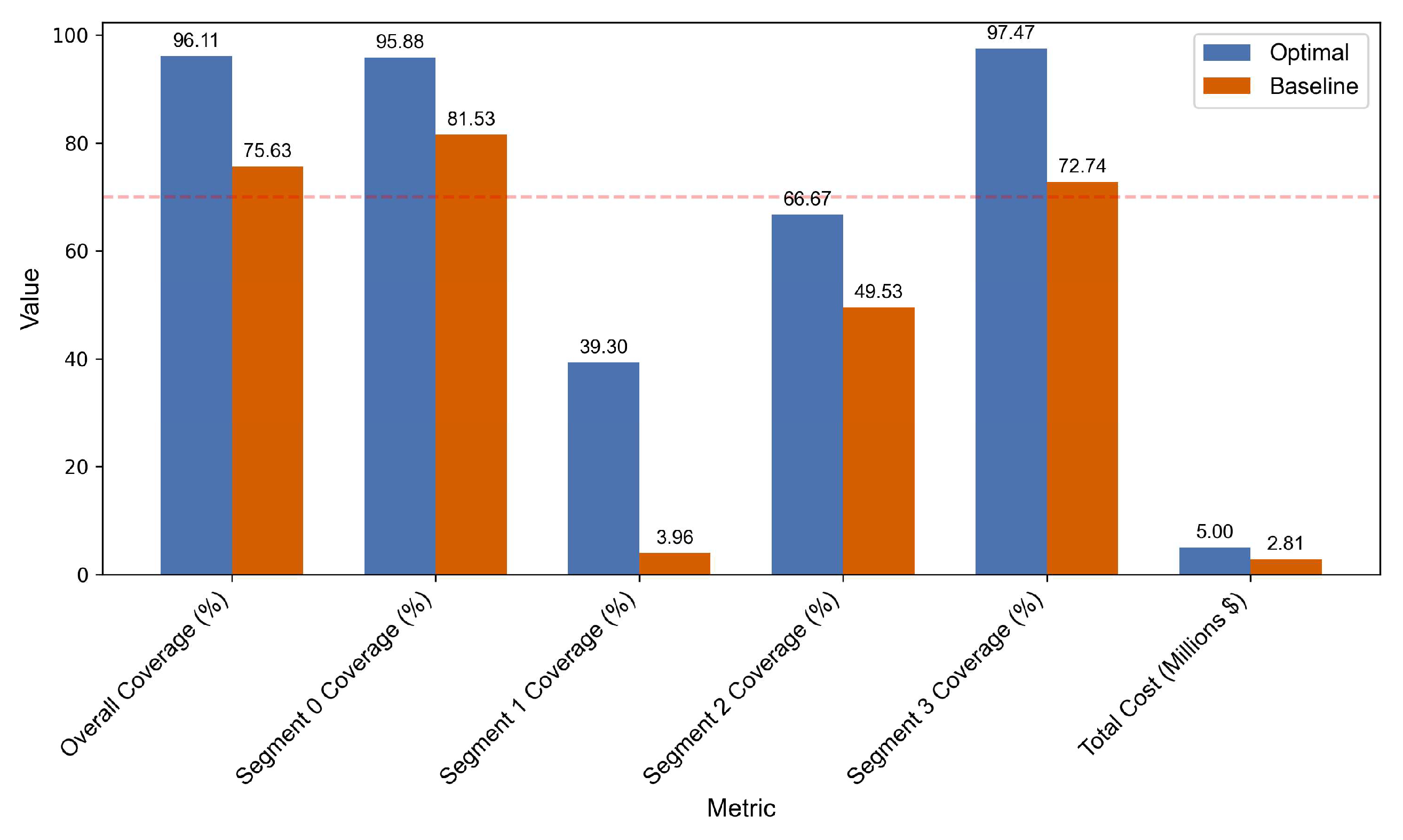
- The framework is validated using over a decade of EV registration data from Washington State (2010–2025), achieving 96% total demand coverage and at least 70% service accessibility across all user groups.
3. Data and Methodology
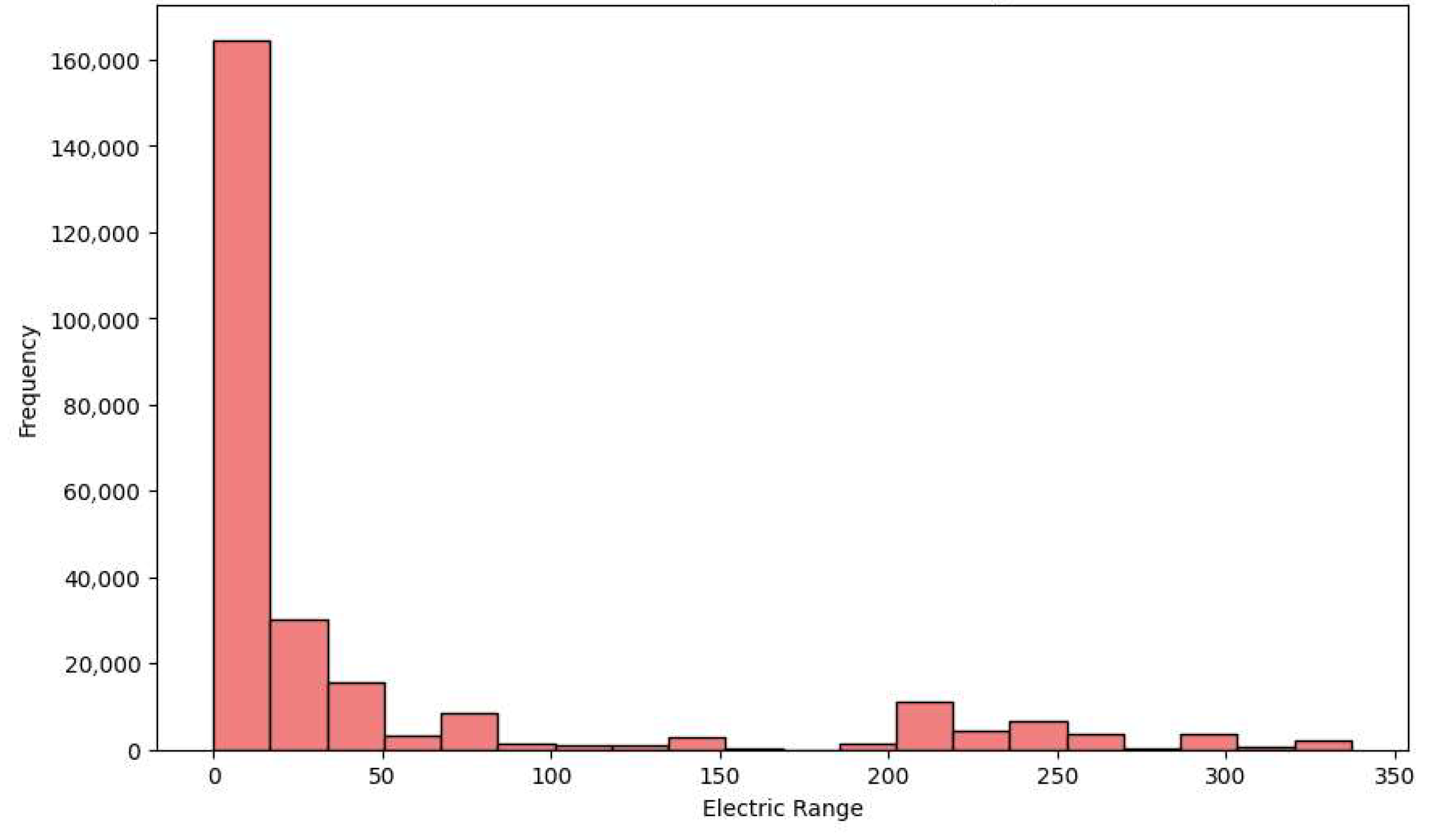
3.1. Electric Vehicle Population Dataset
3.2. User Segmentation
3.3. Spatio-Temporal Adoption Forecasting
3.4. Demand and Need Definition
3.5. Charger Placement Optimization
4. Experimental Setup
4.1. Implementation Details
4.2. Baseline Model
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
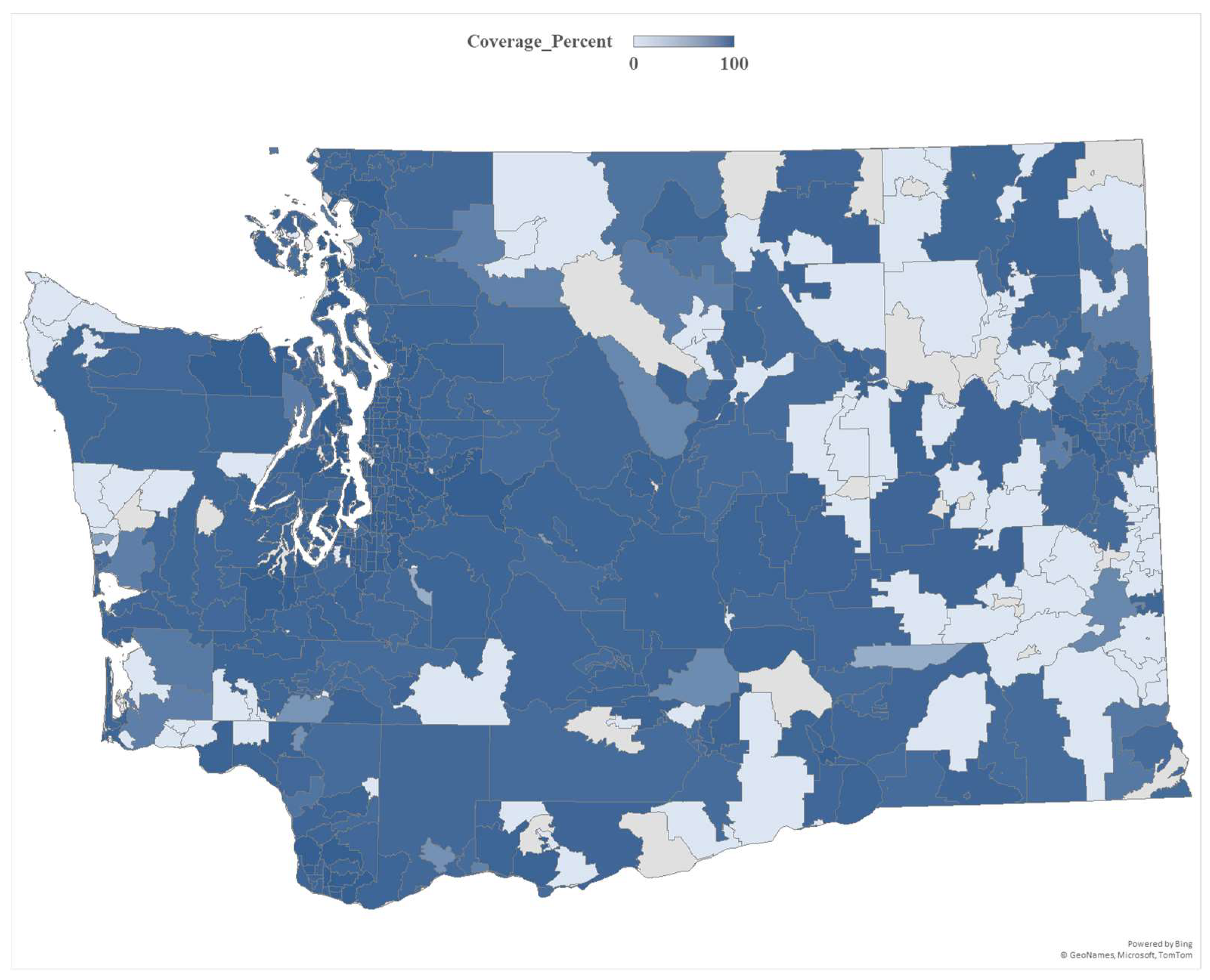
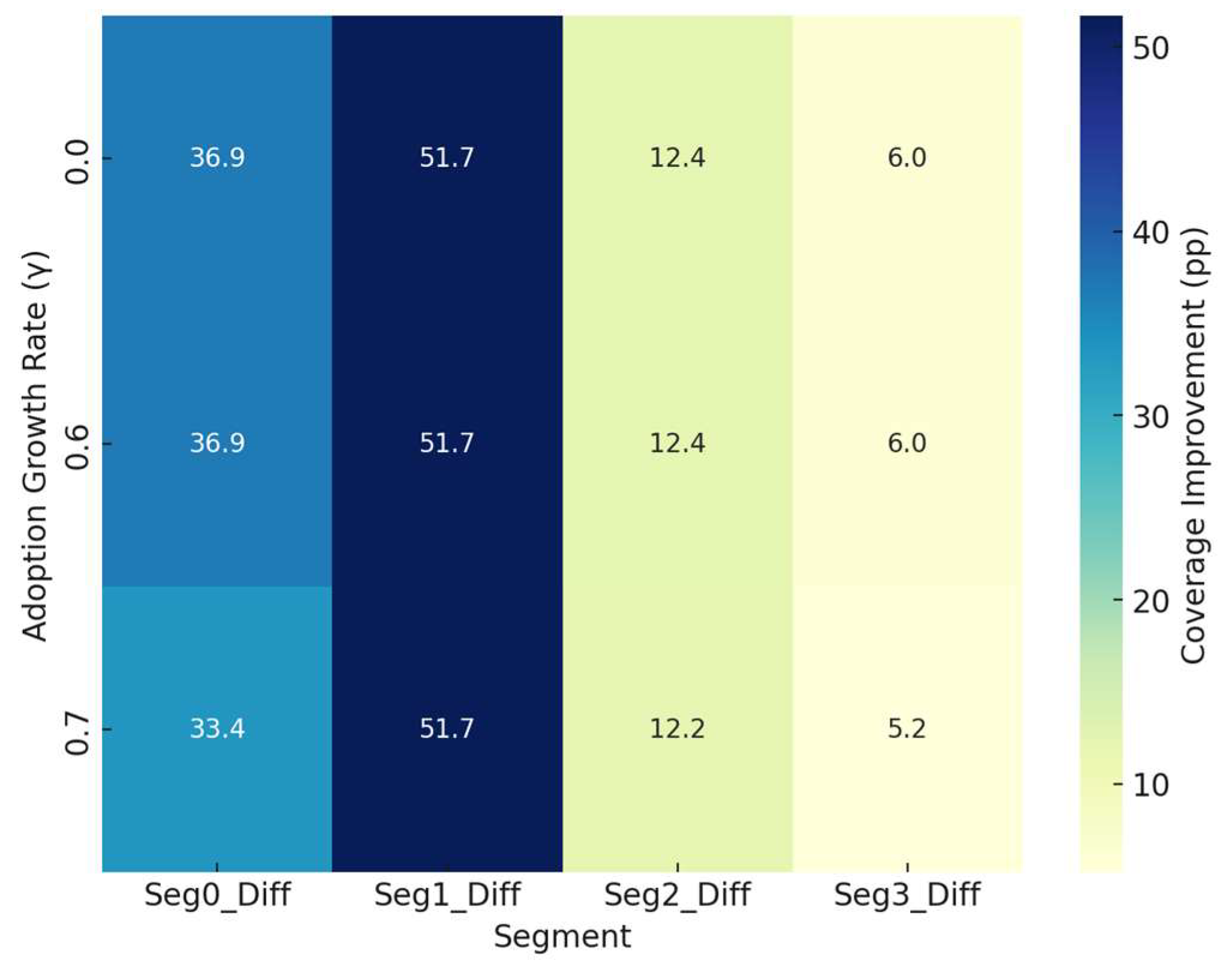
5. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EVs | Electric Vehicles |
| BEVs | Battery Electric Vehicles |
| PHEVs | Plug-in Hybrids |
| MSRP | Manufacturer’s Suggested Retail Price |
| DCFCs | DC Fast Chargers |
| MILP | Mixed-integer linear program |
| V2G | Vehicle-to-grid |
References
- Çelik, S.; Ok, Ş. Electric vehicle charging stations: Model, algorithm, simulation, location, and capacity planning. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkawsi, G.; Baashar, Y.; Abbas, U.D.; Alkahtani, A.A.; Tiong, S.K. Review of renewable energy-based charging infrastructure for electric vehicles. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyothi, P.; Saketh, P.; Vignesh, C.; Devi, V.K. Renewable energy powered DC charging system for electric vehicle. In Proceedings of the Journal of Physics: Conference Series, Coimbatore, India, 13–14 August 2020; p. 012085. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, F.; Shafaati Shemami, M.; Saad Alam, M.; Khateeb, S. A comprehensive review on solar powered electric vehicle charging system. Smart Sci. 2018, 6, 54–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manousakis, N.M.; Karagiannopoulos, P.S.; Tsekouras, G.J.; Kanellos, F.D. Integration of renewable energy and electric vehicles in power systems: A review. Processes 2023, 11, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Chauhan, P.; Singh, N.J. Feasibility of grid-connected solar-wind hybrid system with electric vehicle charging station. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2020, 9, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilsel, M.; Kilic, H.S.; Kalender, Z.T.; Tuzkaya, G. Multi-objective model for electric vehicle charging station location selection problem for a sustainable transportation infrastructure. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 198, 110695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, A.; Wang, P.; Zhuge, C. Predicting electric vehicle charging demand using a heterogeneous spatio-temporal graph convolutional network. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2023, 153, 104205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadoss, T.V.; Lee, J.H.; Davis, A.W.; Hardman, S.; Tal, G. Classifying electric vehicle adopters and forecasting progress to full adoption. npj Sustain. Mobil. Transp. 2025, 2, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crozier, C.; Apostolopoulou, D.; McCulloch, M. Clustering of usage profiles for electric vehicle behaviour analysis. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference Europe (ISGT-Europe), Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, 21–25 October 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Kim, G.; Yoo, J.; Heo, J.; Cho, J.; Ryu, S.; Kim, J. Data-Driven Clustering Analysis for Representative Electric Vehicle Charging Profile in South Korea. Sensors 2024, 24, 6800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magsino, E.; Espiritu, F.M.M.; Go, K.D. Discovering electric vehicle charging locations based on clustering techniques applied to vehicular mobility datasets. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2024, 13, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.J.; Jiao, J. Uncovering electric vehicle ownership disparities using K-means clustering analysis: A case study of Austin, Texas. J. Comput. Soc. Sci. 2024, 7, 2403–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małek, A.; Marciniak, A. Selection of the photovoltaic system power for the electric vehicle. Arch. Motoryz. 2023, 100, 44–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinchen, T.; Typaldos, P.; Malikopoulos, A.A. A United Framework for Planning Electric Vehicle Charging Accessibility. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2508.05827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousuf, A.; Wang, Z.; Paranjape, R.; Tang, Y. An in-depth exploration of electric vehicle charging station infrastructure: A comprehensive review of challenges, mitigation approaches, and optimization strategies. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 51570–51589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaraj, T.; Devabalaji, K.; Kumar, J.A.; Thanikanti, S.B.; Nwulu, N.I. A comprehensive review and analysis of the allocation of electric vehicle charging stations in distribution networks. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 5404–5461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, S. Forecasting charging demand of electric vehicles using time-series models. Energies 2021, 14, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akshay, K.; Grace, G.H.; Gunasekaran, K.; Samikannu, R. Power consumption prediction for electric vehicle charging stations and forecasting income. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Wu, B.; Chiang, Y.-Y.; Zhang, X. Efficient deployment of electric vehicle charging infrastructure: Simultaneous optimization of charging station placement and charging pile assignment. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 22, 6654–6659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Huang, K.; Jeub, J.; Qian, J.; Song, Y. Deploying electric vehicle charging stations considering time cost and existing infrastructure. Energies 2018, 11, 2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Tang, W.; Huang, P.; Li, X.; Xiao, Q. Electric Vehicle Charging Load Prediction Based on User Portrait. In Proceedings of the 2023 6th Asia Conference on Energy and Electrical Engineering (ACEEE), Chengdu, China, 21–23 July 2023; pp. 365–371. [Google Scholar]
- Eagon, M.; Fakhimi, S.; Lyu, G.; Yang, A.; Lin, B.; Northrop, W.F. Model-Based Framework to Optimize Charger Station Deployment for Battery Electric Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Aachen, Germany, 4–9 June 2022; pp. 1639–1648. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.; Wang, P.; Yao, Z.; Zheng, X.; Chen, Z. Enhancing Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Planning with Pre-Trained Language Models and Spatial Analysis: Insights from Beijing User Reviews. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2025, 14, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmaker, A.K.; Sturmberg, B.; Behrens, S.; Hossain, M.; Pota, H. Characterizing electric vehicle plug-in behaviors using customer classification approach. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Energy Technologies for Future Grids (ETFG), Wollongong, Australia, 3–6 December 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bose, P.; Sivraj, P. Smart charging infrastructure for electric vehicles in a charging station. In Proceedings of the 2020 4th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), Madurai, India, 13–15 May 2020; pp. 186–192. [Google Scholar]
- Firouzjah, K.G.; Ghasemi, J. A clustering-based approach to scenario-driven planning for EV charging with autonomous mobile chargers. Appl. Energy 2025, 379, 124925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipto, D.R.; Rahman, M.T.; Shib, S.K.; Shufian, A.; Islam, R. Dynamic Load Forecasting in EV Charging Systems Using Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2025 4th International Conference on Robotics, Electrical and Signal Processing Techniques (ICREST), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 11–12 January 2025; pp. 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, K.; Jia, X.; Fan, J. Electric Vehicle Charging Load Demand Forecasting Model based on Spatial and Temporal Characteristics. In Proceedings of the Journal of Physics: Conference Series, Chengdu, China, 18–20 November 2023; p. 012005. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhari, K.S. Agent-Based Modelling of Electric Vehicle Charging for Optimized Charging Station Operation. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Yun, J.; Zhou, S.; Lie, T.T.; Han, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, Q.; Ge, Z. A spatiotemporal distribution prediction model for electric vehicles charging load in transportation power coupled network. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostermann, A.; Haug, T. Probabilistic forecast of electric vehicle charging demand: Analysis of different aggregation levels and energy procurement. Energy Inform. 2024, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, P.K.A.G.; Farhan, M.A.; Subramanian, G.S.; Manivannan, G.; Reddy, R.R.P. Forecasting of energy demand for electric vehicles using machine learning techniques. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Energy Technologies for Future Grids (ETFG), Wollongong, Australia, 3–6 December 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Amezquita, H.; Guzman, C.P.; Morais, H. Forecasting Electric Vehicles’ Charging Behavior at Charging Stations: A Data Science-Based Approach. Energies 2024, 17, 3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orzechowski, A.; Lugosch, L.; Shu, H.; Yang, R.; Li, W.; Meyer, B.H. A data-driven framework for medium-term electric vehicle charging demand forecasting. Energy AI 2023, 14, 100267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington State Department of Licensing. Electric Vehicle Population Dataset. Available online: https://data.wa.gov/Transportation/Electric-Vehicle-Population-Data/f6w7-q2d2/about_data (accessed on 16 August 2025).
- Hartigan, J.A.; Wong, M.A. Algorithm AS 136: A k-means clustering algorithm. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C 1979, 28, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner Jr, E.S. Exponential smoothing: The state of the art. J. Forecast. 1985, 4, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S.; OSullivan, M.; Dunning, I. Pulp: A linear programming toolkit for python. Univ. Auckl. Auckl. N. Z. 2011, 65, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, A.; Cappellucci, J.; Gaus, M.; Buleje, H. Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Trends from the Alternative Fueling Station Locator: Second Quarter 2024; National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Szumska, E.M. Electric vehicle charging infrastructure along highways in the EU. Energies 2023, 16, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Silva, J.A.; Romero-Gelvez, J.I.; Aristizábal, A.J.; Zapata, S. Optimization and Trends in EV Charging Infrastructure: A PCA-Based Systematic Review. World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudziak, A.; Droździel, P.; Stoma, M.; Caban, J. Market Electrification for BEV and PHEV in Relation to the Level of Vehicle Autonomy. Energies 2022, 15, 3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Description | Overall Coverage (%) | Overall Utilization (%) | Seg 0 (Low Range) | Seg 1 (Long BEV) | Seg 2 (Mid BEV) | Seg 3 (PHEV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline (Proportional) | 100.00 | 48.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Proposed (No Constraints) | 95.88 | 51.91 | 95.88 | 39.30 | 66.67 | 97.47 |
| Proposed (With Constraints) | 96.05 | 52.15 | 95.10 | 70.24 | 70.88 | 97.25 |
| γ | L2 Mult. | DCFC Mult. | Optimal Demand | Optimal Coverage (%) | Optimal Utilization (%) | Baseline Demand | Baseline Coverage (%) | Baseline Utilization (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 24,340 | 82.83 | 45.75 | 15,122 | 51.46 | 24.83 |
| 0.6 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 24,340 | 82.83 | 45.75 | 15,122 | 51.46 | 24.83 |
| 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 19,623 | 83.47 | 38.29 | 12,097 | 51.46 | 19.86 |
| 0.7 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 22,682 | 84.98 | 42.64 | 15,122 | 56.66 | 24.83 |
| 0.7 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 24,340 | 82.83 | 45.75 | 15,122 | 51.46 | 24.83 |
| 0.7 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 25,726 | 80.19 | 51.50 | 15,122 | 47.13 | 24.83 |
| 0.7 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 28,771 | 81.59 | 54.75 | 18,146 | 51.46 | 29.80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Voinea, G.-D.; Gîrbacia, F.; Duguleană, M.; Postelnicu, C.-C. Planning Future EV Charging Infrastructure by Forecasting Spatio-Temporal Adoption Trends Across Heterogeneous User Segments. Information 2025, 16, 933. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16110933
Voinea G-D, Gîrbacia F, Duguleană M, Postelnicu C-C. Planning Future EV Charging Infrastructure by Forecasting Spatio-Temporal Adoption Trends Across Heterogeneous User Segments. Information. 2025; 16(11):933. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16110933
Chicago/Turabian StyleVoinea, Gheorghe-Daniel, Florin Gîrbacia, Mihai Duguleană, and Cristian-Cezar Postelnicu. 2025. "Planning Future EV Charging Infrastructure by Forecasting Spatio-Temporal Adoption Trends Across Heterogeneous User Segments" Information 16, no. 11: 933. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16110933
APA StyleVoinea, G.-D., Gîrbacia, F., Duguleană, M., & Postelnicu, C.-C. (2025). Planning Future EV Charging Infrastructure by Forecasting Spatio-Temporal Adoption Trends Across Heterogeneous User Segments. Information, 16(11), 933. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16110933










