An Optimization-Based Aggregation Approach with Triangular Intuitionistic Fuzzy Numbers in High-Dimensional Multi-Attribute Decision-Making
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Preliminaries
3.1. Concept of Triangular Intuitionistic Fuzzy Number and Its Basic Operation
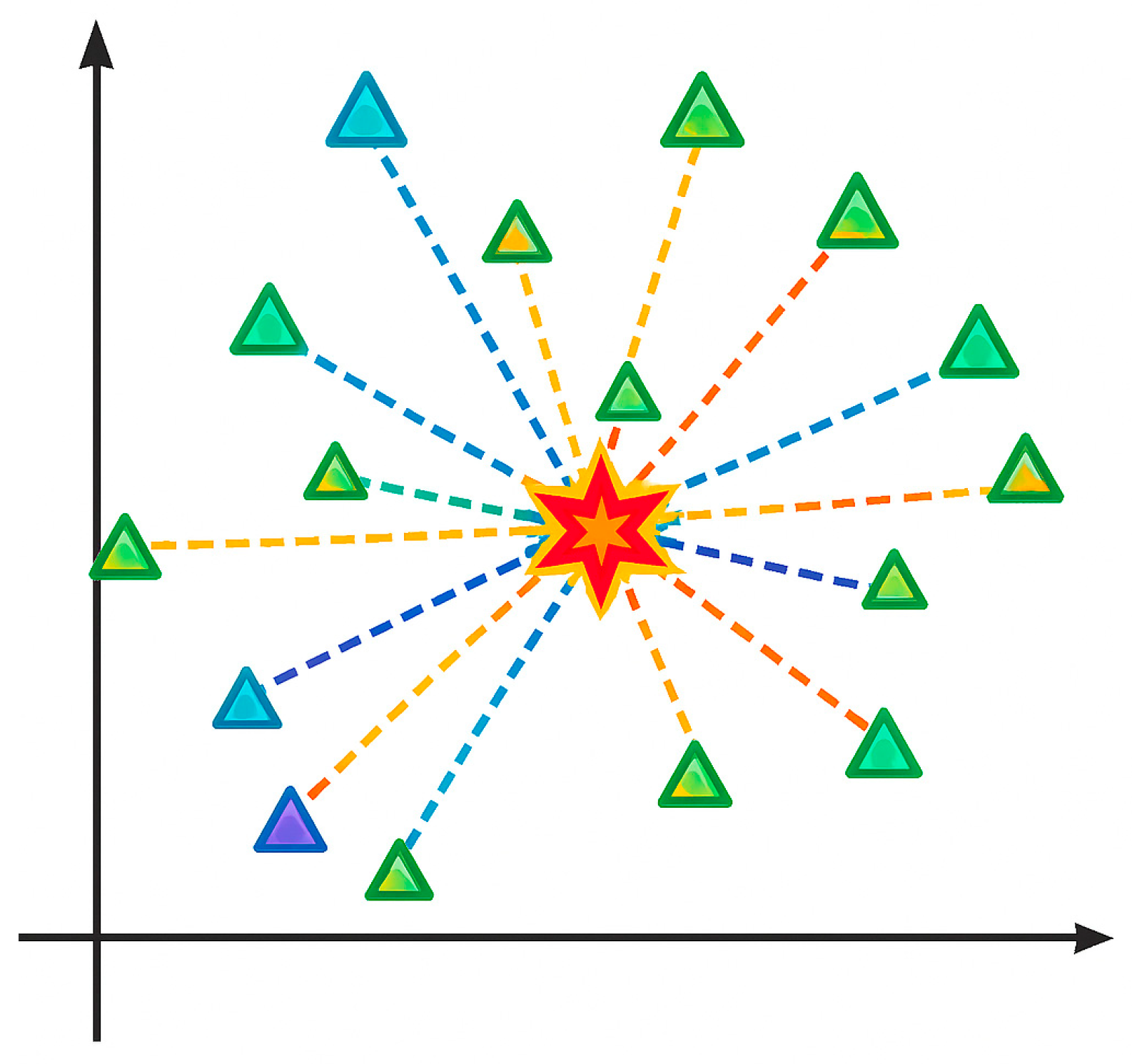
3.2. The Optimal Rally Point
3.3. Plant Growth Simulation Algorithm (PGSA)
4. Key Methods
4.1. The Process of Aggregation of Expert Preferences
4.1.1. Aggregation Idea
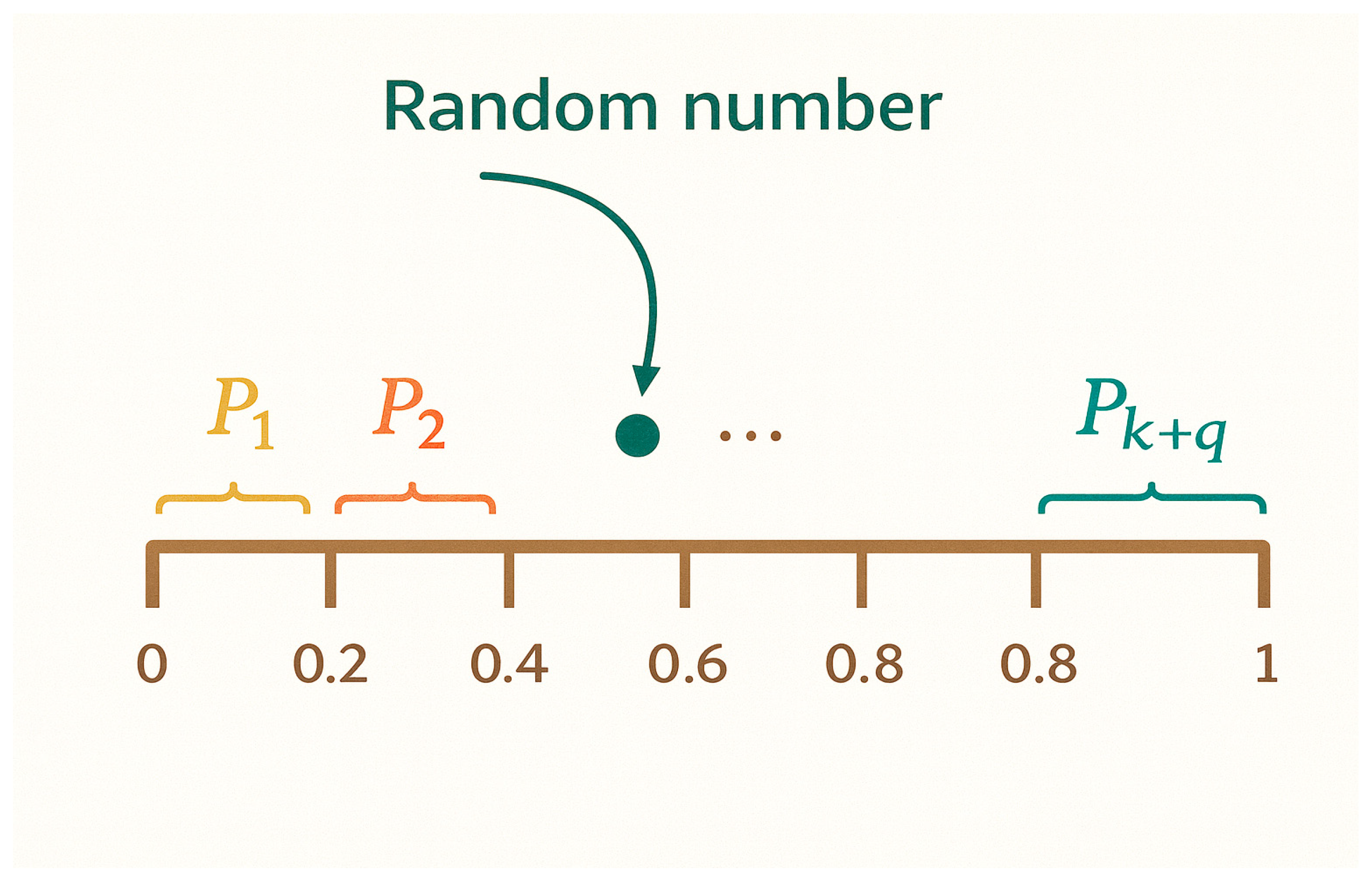
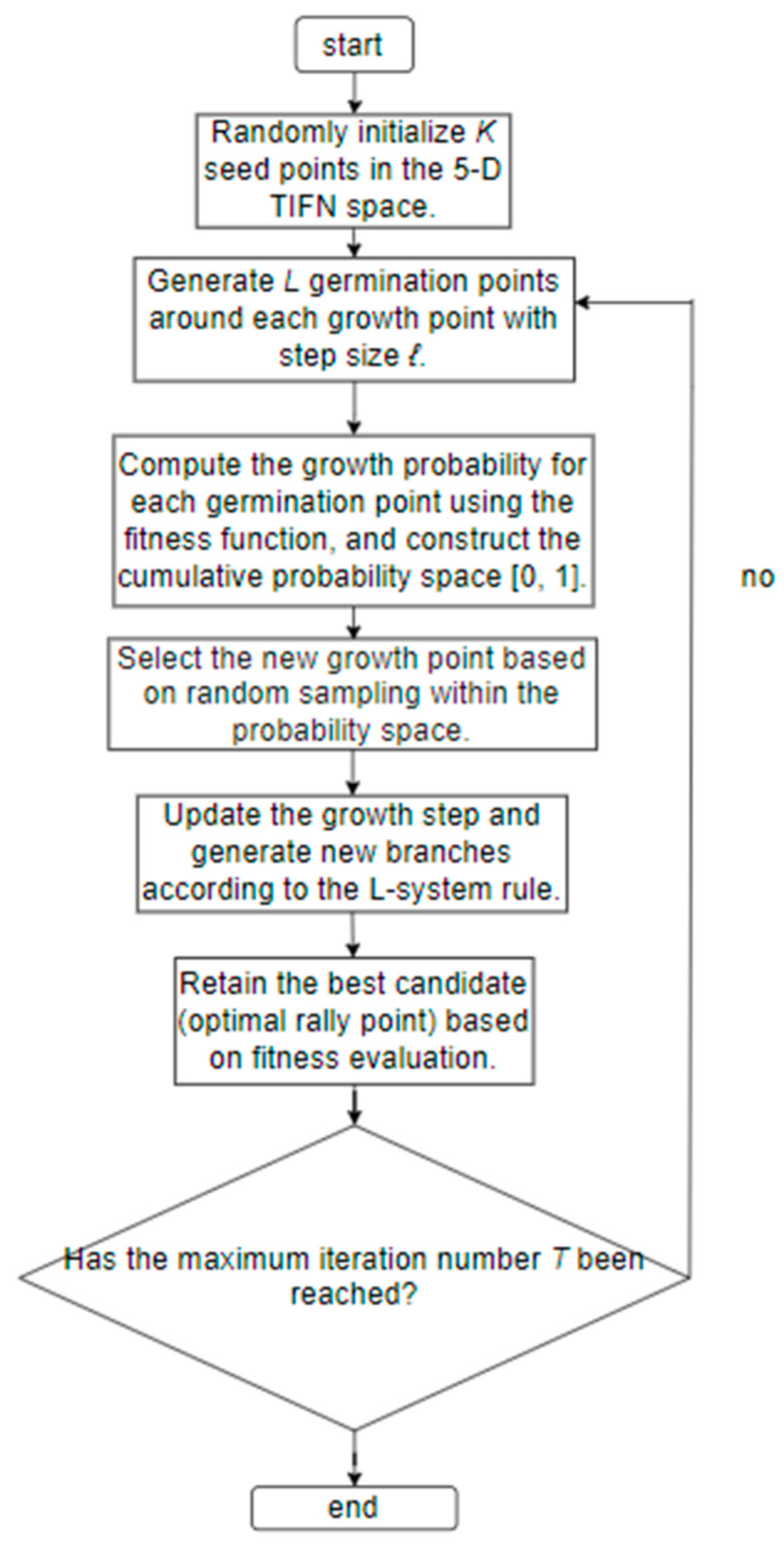
4.1.2. Core Steps for Selecting Optimal Rally Point Based on PGSA
4.2. Rankings of Alternatives
4.3. Hyperparameter Setting and Computational Complexity
| Algorithm 1. PGSA-Based Aggregation Procedure for Multi-Attributes TIFN Decisions |
| Input: Expert TIFN evaluations ; parameters (T, r, L, ℓ0, α, ε, δ, K) Output: Optimal rally point p* (* represents the best point) |
| 1: Initialize K seed points randomly in the 5-D TIFN space |
| 2: For each seed k = 1 to K do |
| 3: Generate L germination points within radius r |
| 4: Compute fitness for each germination point using Equations (9) and (10) |
| 5: Select the point with the maximum fitness improvement |
| 6: Update step size ℓ_t = α × ℓ_{t − 1} and apply random perturbation δ |
| 7: If , stop growth for this seed |
| 8: End for |
| 9: Return the rally point p* with the highest global fitness |
5. Illustrative Example and Comparative Study
5.1. Illustrative Example
5.2. Comparative Study
5.3. Sensitivity and Convergence Analysis
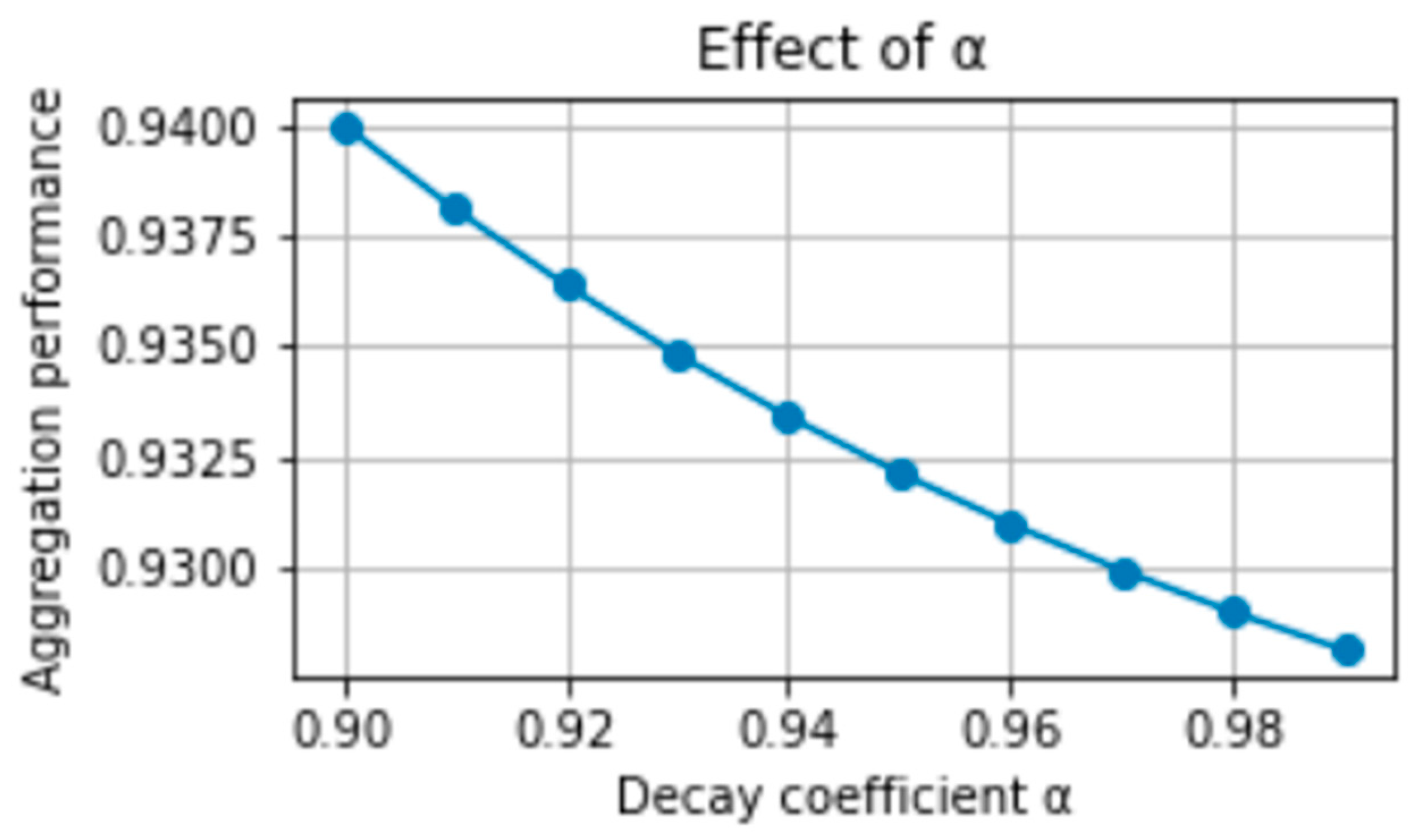
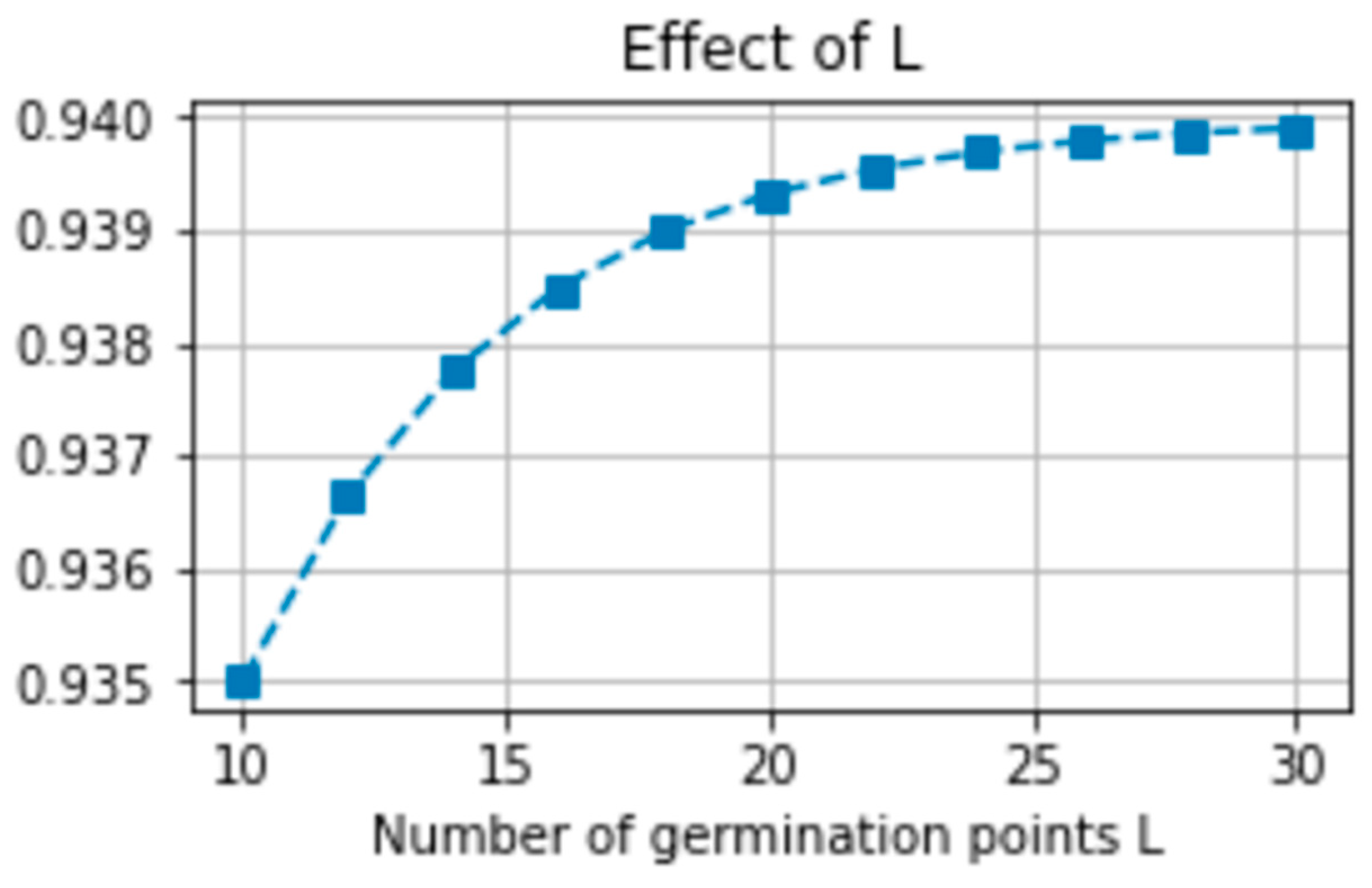
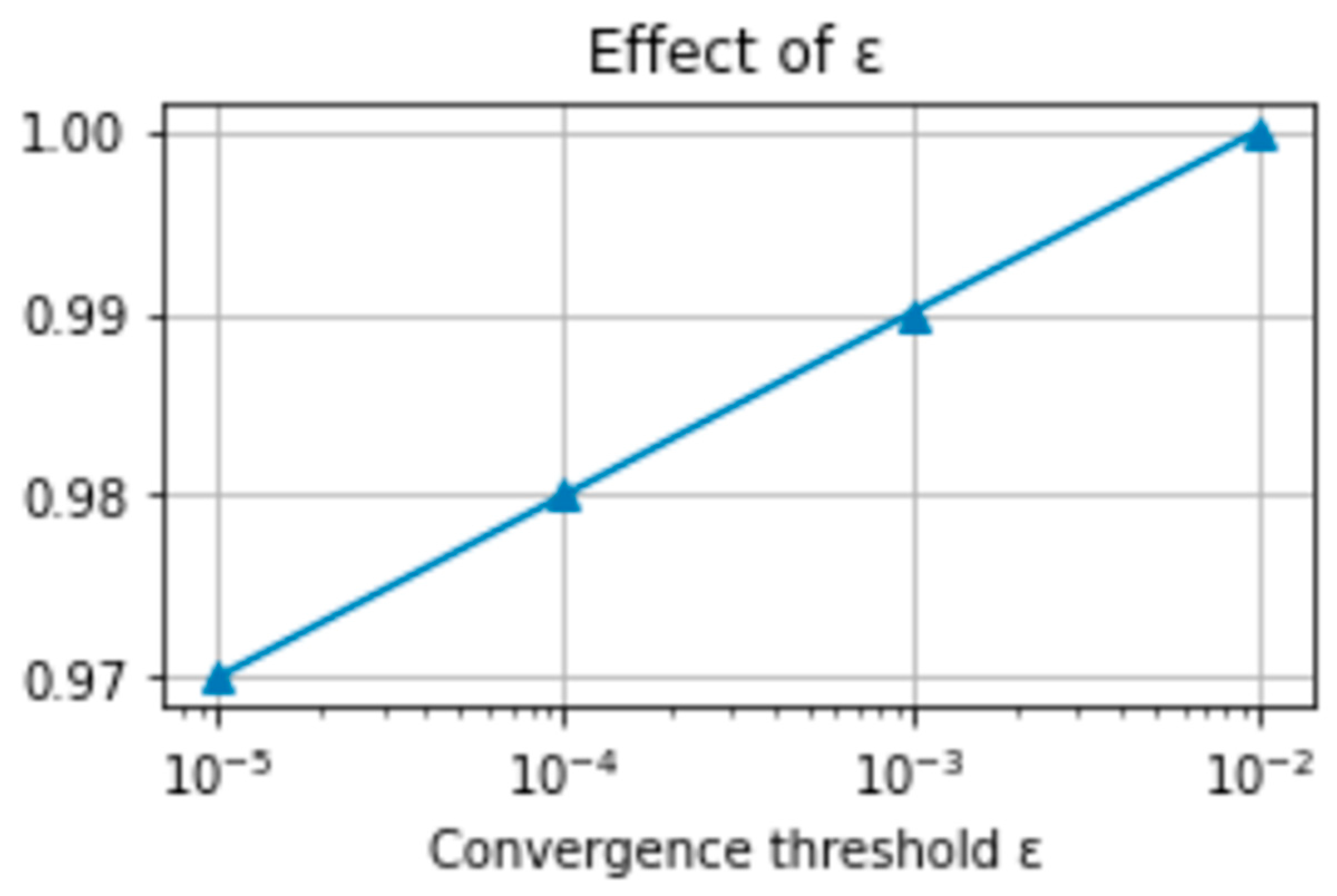
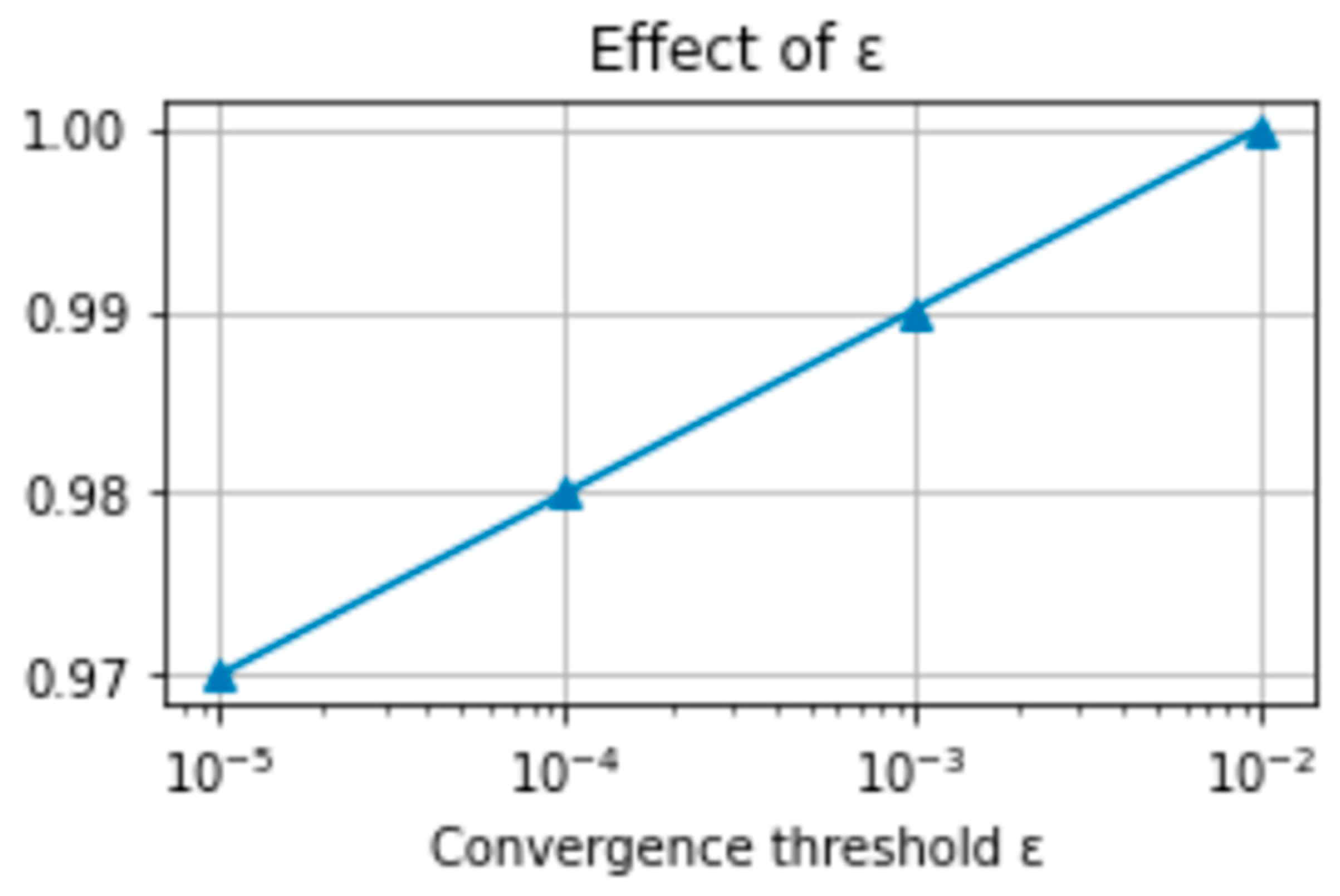
5.3.1. Parameter Sensitivity of PGSA
5.3.2. Convergence Characteristics
5.3.3. Runtime Scaling and Complexity
5.3.4. Trade-Off Between Information Energy and Aggregation Consistency
5.3.5. Comparative Computational Cost Analysis
5.4. Comparative Discussion of Distance and Weight Alternatives
6. Conclusions and Suggestions for Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zahedi Khameneh, A.; Kılıçman, A. Multi-attribute decision-making based on soft set theory: A systematic review. Soft Comput. 2019, 23, 6899–6920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talafha, M.; Alkouri, A.U.; Alqaraleh, S.; Zureigat, H.; Aljarrah, A. Complex hesitant fuzzy sets and its applications in multiple attributes decision-making problems. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 41, 7299–7327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amman, M.; Rashid, T.; Ali, A.; Albalawi, O.; Alharthi, A.M. Dual-hesitant fermatean fuzzy Hamacher aggregation operators and TOPSIS with their application to multi-criteria decision-making. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0311580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wu, M.; Tan, C.; Zhang, T. A random intuitionistic fuzzy factor analysis model for complex multi-attribute large group decision-making in dynamic environments. Fuzzy Optim. Decis. Mak. 2021, 20, 101–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Huang, H.; Cao, Q. Research on AHP with interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets and its application in multi-criteria decision making problems. Appl. Math. Model. 2013, 37, 9898–9906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Pei, Z. Interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy generalised Bonferroni mean operators for multi-attribute decision making. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 23, 1728–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhankhar, C.; Kumar, K. Multi-attribute decision making based on the q-rung orthopair fuzzy Yager power weighted geometric aggregation operator of q-rung orthopair fuzzy values. Granul. Comput. 2023, 8, 1013–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Qin, X. Power average operators of linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy numbers and their application to multiple-attribute decision making. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2017, 32, 1029–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.-H.; Zhu, C.-Y.; Chen, Z.-S.; Deveci, M.; Chiclana, F.; Skibniewski, M.J. On extended power geometric operator for proportional hesitant fuzzy linguistic large-scale group decision-making. Inf. Sci. 2023, 632, 637–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Y. A novel similarity-based consensus model for probabilistic linguistic sets and its application in multi-attribute large-scale group decision making. Comput. Appl. Math. 2022, 41, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafar, M.; Gharehpetian, G.B.; Niknam, T. Using modified fuzzy particle swarm optimization algorithm for parameter estimation of surge arresters models. Int. J. Innov. Comput. 2012, 8, 567–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Zhou, X.; Martinez, L. A hybrid group decision making framework for achieving agreed solutions based on stable opinions. Inf. Sci. 2019, 490, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sun, C. A fast clustering based evolutionary algorithm for super-large-scale sparse multi-objective optimization. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2022, 10, 1048–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Xiong, L.; Xu, Z.; Huang, G. A simulation-based optimization model for watershed multi-scale irrigation water use with considering impacts of climate changes. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debbagh, M.; Sun, S.; Lefsrud, M. Predictive Pattern Recognition Techniques Towards Spatiotemporal Representation of Plant Growth in Simulated and Controlled Environments: A Comprehensive Review. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.10538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-C.; Dong, Y.; Liang, H.; Pedrycz, W.; Herrera, F. Data-driven method to learning personalized individual semantics to support linguistic multi-attribute decision making. Omega 2022, 111, 102642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, R.M.A.; Meshram, S.G.; Hasan, M.A.; Cao, X.; Alvandi, E.; Meshram, C.; Islam, S. The application of multi-attribute decision making methods in integrated watershed management. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2024, 38, 297–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, G.; Pal, A.K. Three-way decisions based multi-attribute decision-making with utility and loss functions. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2024, 316, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Atef, M.; Yang, B. Fermatean fuzzy covering-based rough set and their applications in multi-attribute decision-making. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 127, 107181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Ma, X.; Zhan, J.; Yao, Y. A three-way multi-attribute decision making method based on regret theory and its application to medical data in fuzzy environments. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 123, 108975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, M.; Shahzadi, G.; Alcantud, J.C.R. Multi-attribute decision-making with q-rung picture fuzzy information. Granul. Comput. 2022, 7, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.; Shen, J.; Huang, X.; Gao, X.; Hu, P.; Sun, F. A new framework for eco-compensation funds allocation in China based on multi-attribute decision-making method. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2025, 114, 107891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Ullah, K.; Alshahrani, M.N.; Yang, M.-S.; Pamucar, D. Novel Aczel–Alsina operators for Pythagorean fuzzy sets with application in multi-attribute decision making. Symmetry 2022, 14, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, C.; Garg, H.; Pal, M. Multi-attribute decision making for power Dombi operators under Pythagorean fuzzy information with MABAC method. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2023, 14, 10761–10778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, P.; Chen, S.M.; Mishra, A.R. Multi-attribute decision-making based on similarity measure between picture fuzzy sets and the MARCOS method. Inf. Sci. 2024, 658, 119990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xia, P.; Zhang, X. Multi-attribute decision-making method of pumped storage capacity planning considering wind power uncertainty. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 449, 141655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yang, C.; Huang, T. A visual analytics approach for multi-attribute decision making based on intuitionistic fuzzy AHP and UMAP. Inf. Fusion 2023, 96, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, G.; Ying, L. Multi-attribute decision-making based on comprehensive hesitant fuzzy entropy. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 237, 121459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Ullah, K.; Yang, M.-S.; Pamucar, D. Aczel-Alsina aggregation operators on T-spherical fuzzy (TSF) information with application to TSF multi-attribute decision making. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 26011–26023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gireesha, O.; Kamalesh, A.; Krithivasan, K.; Sriram, V.S. A fuzzy-multi attribute decision making approach for efficient service selection in cloud environments. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 206, 117526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, D.; Kanchana, A.; Jacob, K.; Kausar, N.; Edalatpanah, S.A.; Shah, M.A. A novel approach based on neutrosophic Bonferroni mean operator of trapezoidal and triangular neutrosophic interval environments in multi-attribute group decision making. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Q.; Gao, Y.; Fan, J. An investment decision framework for offshore CCUS project under interval-valued fermatean fuzzy environment. Environ. Technol. 2025, 46, 1112–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xu, T.; Feng, L.; Mahmood, T.; Ullah, K. Aczel–Alsina Hamy mean aggregation operators in T-spherical fuzzy multi-criteria decision-making. Axioms 2023, 12, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, A.; Khan, K.A.; Rahman, A.U. Multi-Attribute Decision-Making Method for the Assessment of Research Productivity Using Entropy Measures of Complex Fermatean Fuzzy Soft Sets. Fuzzy Inf. Eng. 2024, 16, 314–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajwar, K.; Deep, K.; Das, S. An exhaustive review of the metaheuristic algorithms for search and optimization: Taxonomy, applications, and open challenges. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 13187–13257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, S.W.; Ali, K.W.H.; Askar, S.; Xoshaba, F.S.; Hawezi, R. Metaheuristic algorithms in optimization and its application: A review. JAREE (J. Adv. Res. Electr. Eng.) 2022, 6, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rishabh, R.; Das, K.N. A critical review on metaheuristic algorithms based multi-criteria decision-making approaches and applications. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2025, 32, 963–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.P.; Wang, Q.Y.; Dong, J.Y. The extended VIKOR method for multi-attribute group decision making with triangular intuitionistic fuzzy numbers. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2013, 52, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Li, L. A new approach for multiple attribute group decision-making based on interval neutrosophic sets. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 36, 5929–5942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Jiang, L.; Fan, H.; Li, P.; You, C. Dynamic nonlinear simplified neutrosophic sets for multiple-attribute group decision making. Heliyon 2024, 10, e27493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-B.; Li, R.-D.; Li, C.-H. A global optimization bionics algorithm for solving integer programming-plant growth simulation algorithm. Syst. Eng.-Theory Pract. 2005, 25, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, W.; Zhong, C.H. Optimization of network configuration in large distribution systems using plant growth simulation algorithm. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2008, 23, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Li, Y. A multi-criteria framework for sustainability evaluation of hydrogen-based multi-microgrid systems under triangular intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, T.; ur Rehman, U.; Ali, Z. Analysis and application of Aczel-Alsina aggregation operators based on bipolar complex fuzzy information in multiple attribute decision making. Inf. Sci. 2023, 619, 817–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Family | Search Mechanism | Typical Aggregation Objective | Representation | Distinction of This Work |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSO | Population; velocity–position update | Minimize consensus distance | Numeric/fuzzy vectors | Searches in parameter space; ours searches directly in 5-D TIFN space |
| DE | Differential mutation + crossover | Same | Numeric vectors | Defines explicit TIFN global set-point objective |
| GA | Selection–crossover–mutation | Same | Encoded chromosomes | Operator-driven recombination; ours uses phototropism growth |
| SA | Trajectory; probabilistic acceptance | Same | Numeric scores | Single-trajectory search; ours includes hyperparameter + complexity analysis |
| ABC/BA/WOA | Swarm-inspired foraging/echolocation/spiral | Same | Numeric/fuzzy | Heuristic exploration; ours is geometry-preserving in TIFN space |
| PGSA (this work) | Biologically inspired growth; phototropism | Global rally-point in 5-D TIFN space | 5-D TIFN point cloud | (i) 5-D embedding (ii) set-point objective (iii) explicit PGSA design |
| Parameter | Symbol | Description | Default | Range/Adjustment | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iteration number | T | Maximum number of growth iterations | 100 | 50–200 | Balances convergence and computational cost |
| Growth radius | r | Search radius controlling exploration region | 0.5 | 0.3–1.0 | Larger r enhances global search ability |
| Growth nodes | L | Number of germination points | 20 | 10–30 | Increases population diversity |
| Initial step size | ℓ0 | Starting value of growth step | 0.3 | 0.1–0.5 | Prevents premature convergence |
| Step decay coefficient | α | Step-size attenuation factor | 0.95 | 0.9–0.99 | Regulates convergence rate |
| Convergence threshold | ε | Termination tolerance for growth | 1 × 10−4 | 10−3–10−5 | Stops minor oscillations |
| Random perturbation | δ | Random bias factor during exploration | 0.05 | 0.01–0.1 | Enhances stochastic exploration |
| Number of seeds | K | Initial growth seeds | 10 | 5–15 | Improves solution diversity |
| A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C11 | ((5.6, 6, 7.5); 0.7, 0.1) | ((6.4, 7.5, 8.2); 0.8, 0.1) | ((8, 8.6, 9.4); 0.6, 0.2) | ((5.5, 6.5, 7.4); 0.8, 0.1) |
| C12 | ((5.2, 6.2, 7.6); 0.6, 0.3) | ((6.1, 7.3, 8.4); 0.6, 0.4) | ((5.6, 7.6, 8.5); 0.7, 0.2) | ((6.5, 7.6, 8.4); 0.5, 0.3) |
| C13 | ((5.6, 7.5, 8.3); 0.5, 0.4) | ((5.8, 6.8, 8.6); 0.5, 0.4) | ((6.8, 7.5, 8.5); 0.8, 0.1) | ((6.8, 7.5, 8.6); 0.6, 0.3) |
| C14 | ((5.4, 6.7, 7.8); 0.8, 0.1) | ((6, 7.8, 8.8); 0.7, 0.2) | ((8, 8.5, 9.2); 0.7, 0.1) | ((7.2, 8.3, 9.4); 0.7, 0.2) |
| C15 | ((6.5, 7.2, 8.5); 0.6, 0.3) | ((7, 8.2, 9); 0.7, 0.1) | ((8.2, 8.8, 9.6); 0.6, 0.3) | ((6.3, 7.7, 8.6); 0.6, 0.3) |
| C16 | ((7.3, 8.5, 9.6); 0.7, 0.2) | ((7.5, 8.4, 8.9); 0.8, 0.1) | ((7.5, 8.5, 9.3); 0.8, 0.2) | ((7.2, 8.6, 9.3); 0.8, 0.1) |
| C21 | ((6.8, 7.5, 8.6); 0.6, 0.2) | ((6.5, 7.6, 8.5); 0.6, 0.3) | ((6.8, 7.2, 8.8); 0.7, 0.2) | ((7.3, 8.5, 9.6); 0.7, 0.1) |
| C22 | ((7.2, 8.2, 9.5); 0.8, 0.1) | ((6.7, 7.8, 9.2); 0.7, 0.2) | ((6.8, 8.2, 9); 0.8, 0.1) | ((6.8, 7.4, 9.2); 0.7, 0.2) |
| C23 | ((6.9, 8.3, 8.8); 0.8, 0.2) | ((6.6, 7.5, 8.5); 0.8, 0.1) | ((7.1, 8.5, 9.2); 0.7, 0.3) | ((6.7, 7.6, 8.5); 0.5, 0.4) |
| C31 | ((5.8, 6.6, 7.8); 0.6, 0.3) | ((6.3, 7.5, 8.8); 0.8, 0.2) | ((7.2, 8.3, 9.2); 0.6, 0.2) | ((7, 8.2, 9.1); 0.6, 0.3) |
| C32 | ((6, 7.3, 8.4); 0.7, 0.1) | ((6.1, 7.8, 9.2); 0.8, 0.1) | ((6.5, 7.5, 8.6); 0.8, 0.1) | ((6.5, 7.3, 8.5); 0.6, 0.2) |
| C33 | ((5.6, 7.5, 8.5); 0.6, 0.2) | ((6.2, 7.5, 8.9); 0.6, 0.3) | ((7, 8.2, 9.1); 0.8, 0.2) | ((7.5, 8, 9.2); 0.7, 0.2) |
| C34 | ((5.3, 6.6, 7.6); 0.8, 0.1) | ((7.3, 8.5, 9.4); 0.6, 0.2) | ((7, 7.6, 8.5); 0.6, 0.4) | ((7.6, 8.6, 9.3); 0.8, 0.1) |
| C41 | ((6.8, 7.8, 8.9); 0.7, 0.3) | ((6.8, 7.6, 9.1); 0.7, 0.3) | ((6.8, 7.5, 8.4); 0.5, 0.4) | ((7.1, 7.7, 8.6); 0.8, 0.1) |
| C42 | ((7.3, 8.6, 9.5); 0.7, 0.1) | ((7.7, 8.6, 9.6); 0.8, 0.1) | ((7.3, 8.5, 9.2); 0.6, 0.3) | ((7.5, 8.4, 9.4); 0.5, 0.4) |
| C43 | ((7.9, 8.8, 9.4); 0.8, 0.1) | ((7.5, 8.6, 9.5); 0.7, 0.1) | ((6.5, 8, 9.2); 0.7, 0.2) | ((7.6, 8.2, 9); 0.7, 0.1) |
| C51 | ((8.2, 9, 9.6); 0.7, 0.2) | ((7.6, 8.6, 9.3); 0.8, 0.1) | ((6.6, 7.5, 8.5); 0.6, 0.3) | ((8, 8.6, 9.3); 0.7, 0.2) |
| C52 | ((8.5, 9.2, 9.8); 0.6, 0.3) | ((8.3, 8.8, 9.6); 0.7, 0.2) | ((6.7, 7.8, 8.6); 0.8, 0.1) | ((7.8, 8.4, 9.6); 0.8, 0.1) |
| C53 | ((7.8, 8.6, 9.5); 0.5, 0.4) | ((8.1, 8.9, 9.5); 0.6, 0.3) | ((7, 8.2, 9); 0.7, 0.2) | ((8.2, 8.8, 9.6); 0.8, 0.1 |
| A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 |
|---|---|---|---|
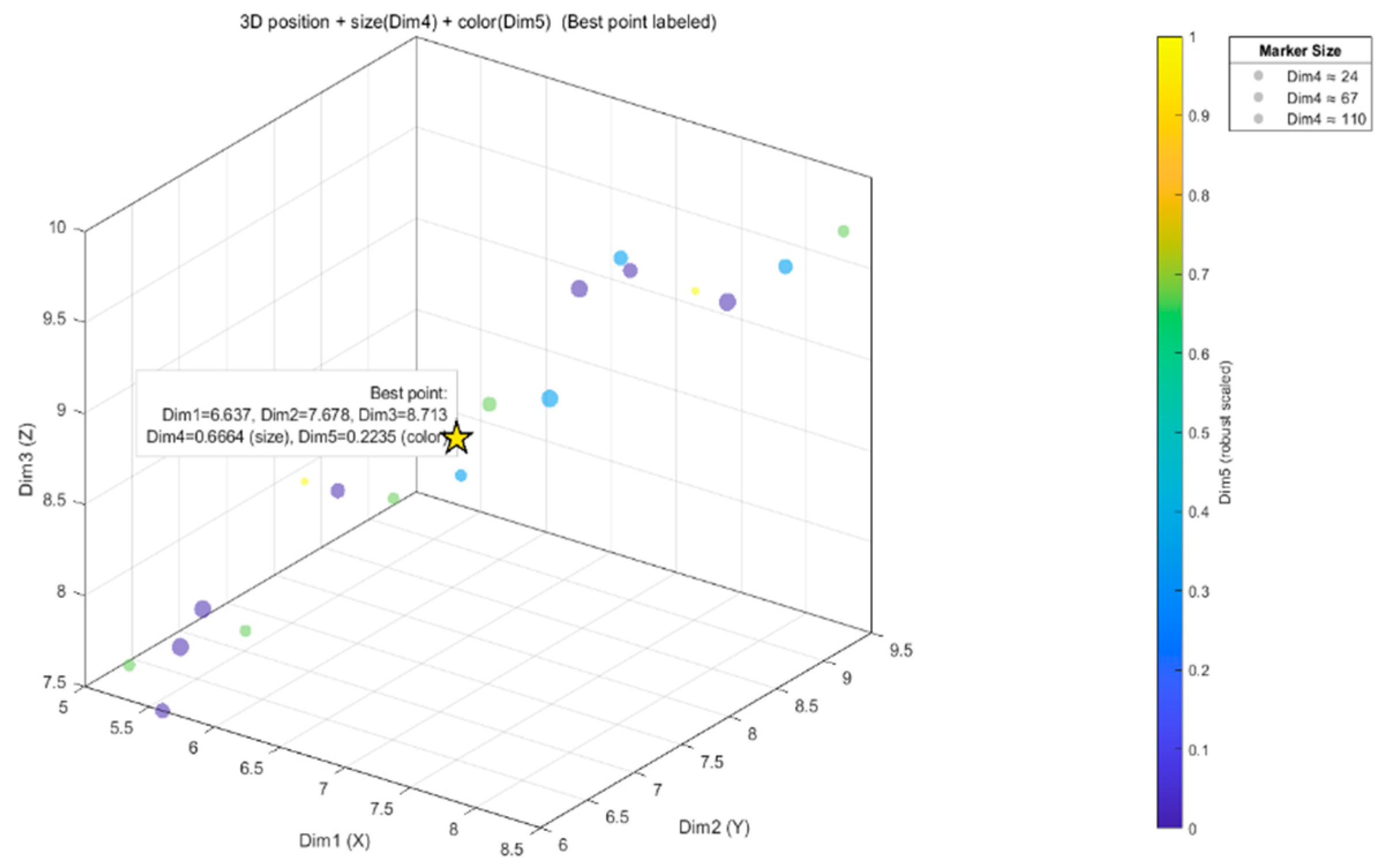
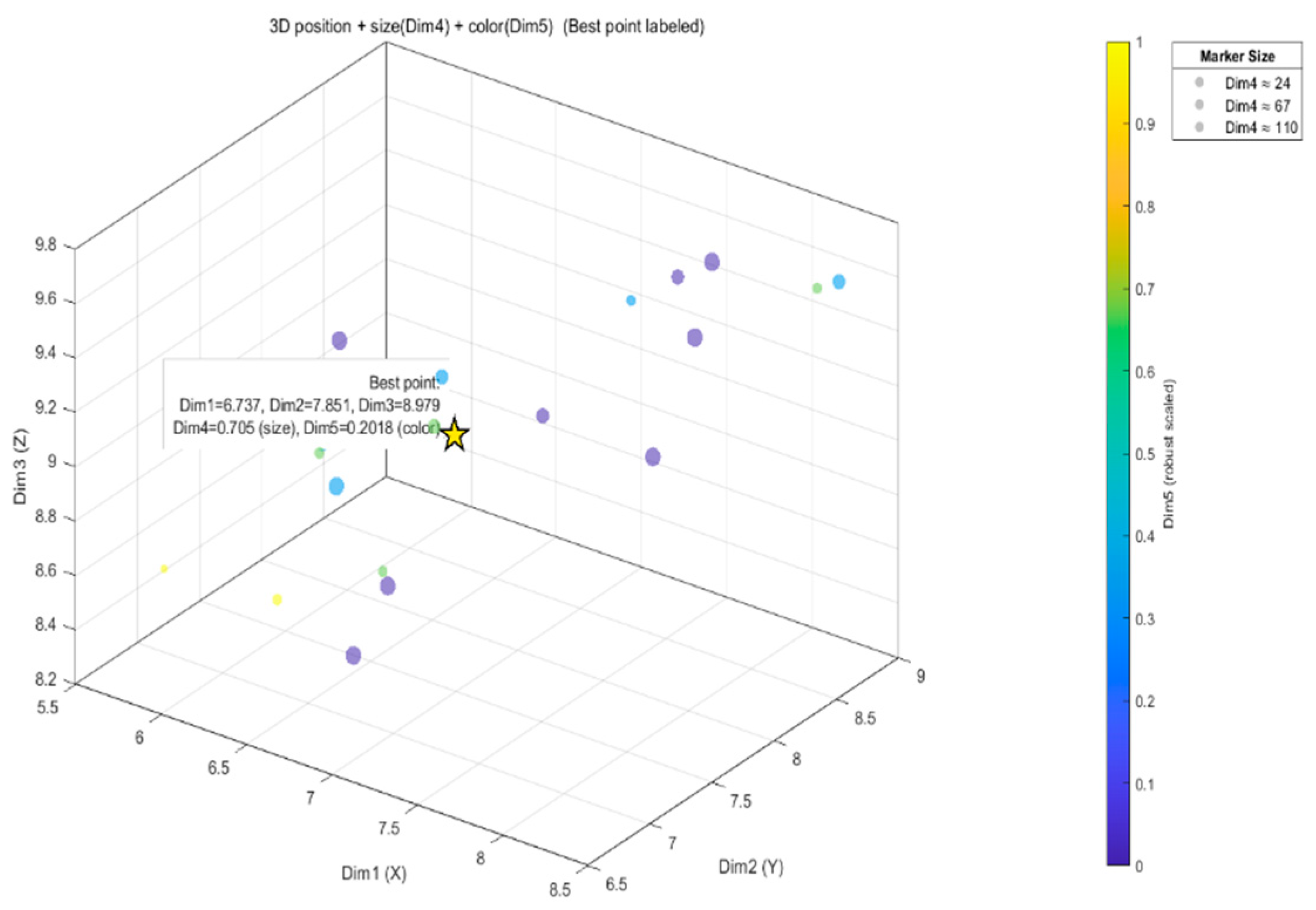
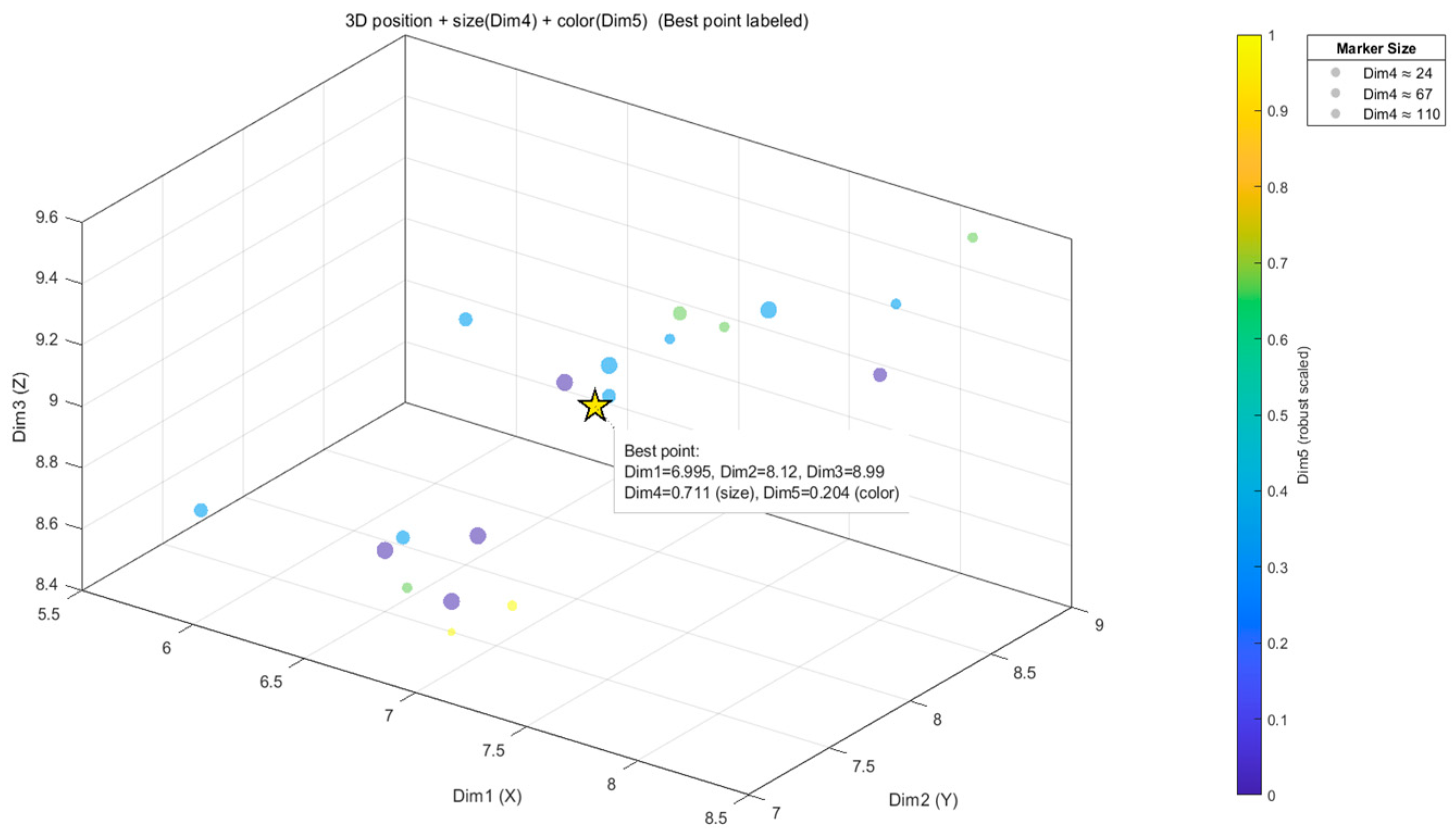
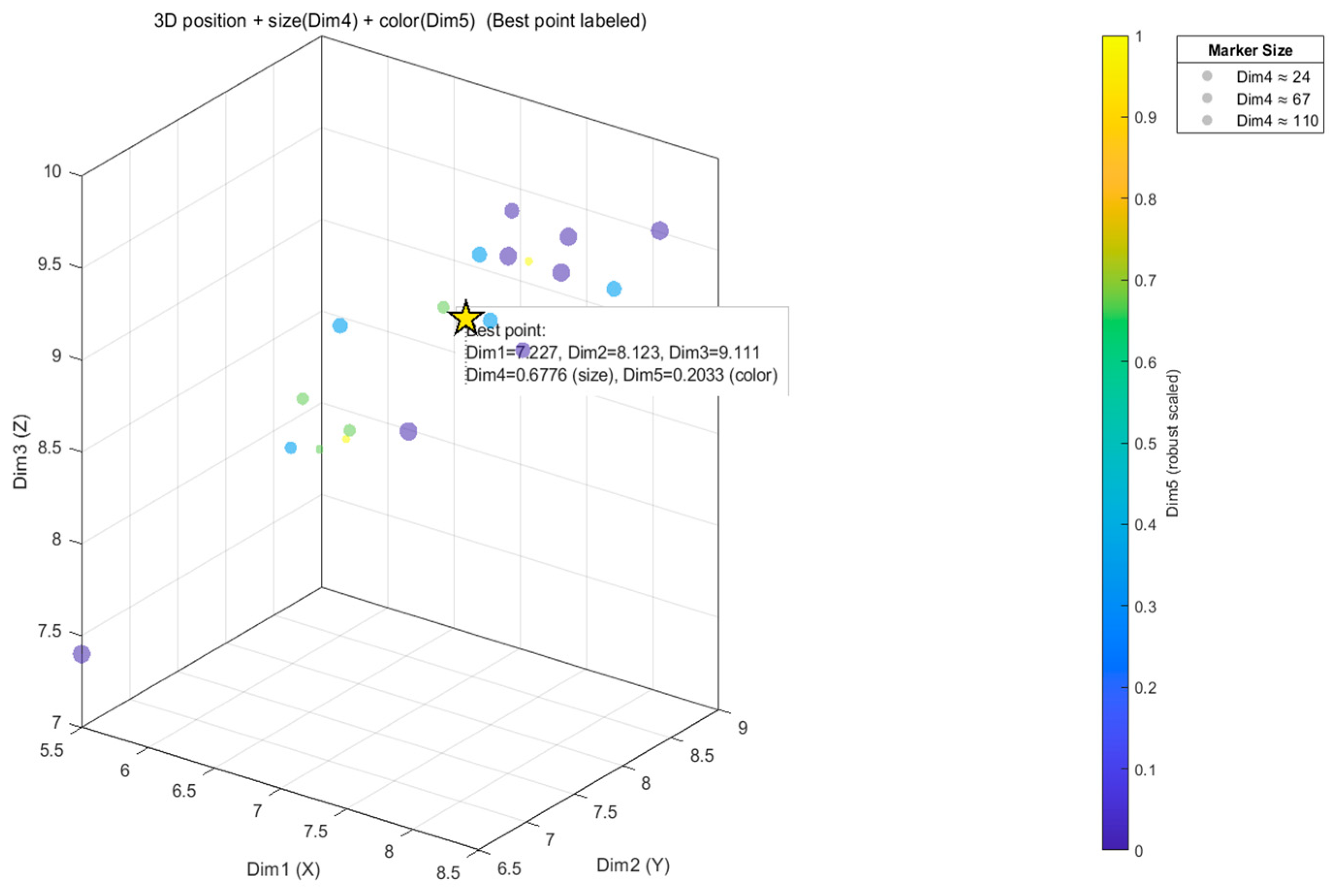
| ((6.6366, 7.6785, 8.7135); 0.6664, 0.2235) | ((6.7367, 7.8509, 8.9786); 0.7050, 0.2018) | ((6.9952, 8.1197, 8.9895); 0.7110, 0.2040) | ((7.2267, 8.1229, 9.1115); 0.6776, 0.2033) |
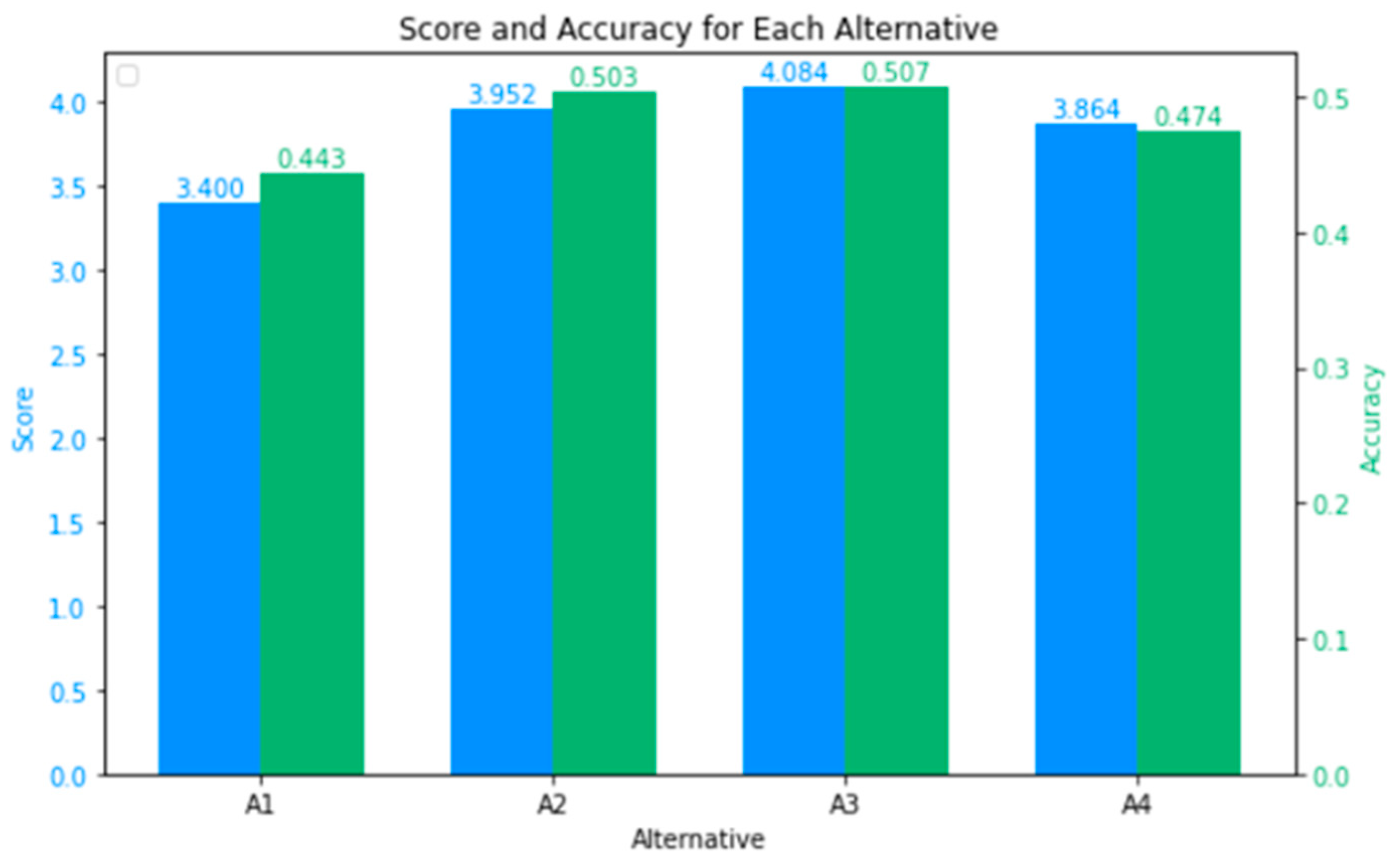
| Alternative | Score | Accuracy | Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 3.400 | 0.443 | 4 |
| A2 | 3.952 | 0.503 | 2 |
| A3 | 4.084 | 0.507 | 1 |
| A4 | 3.864 | 0.474 | 3 |
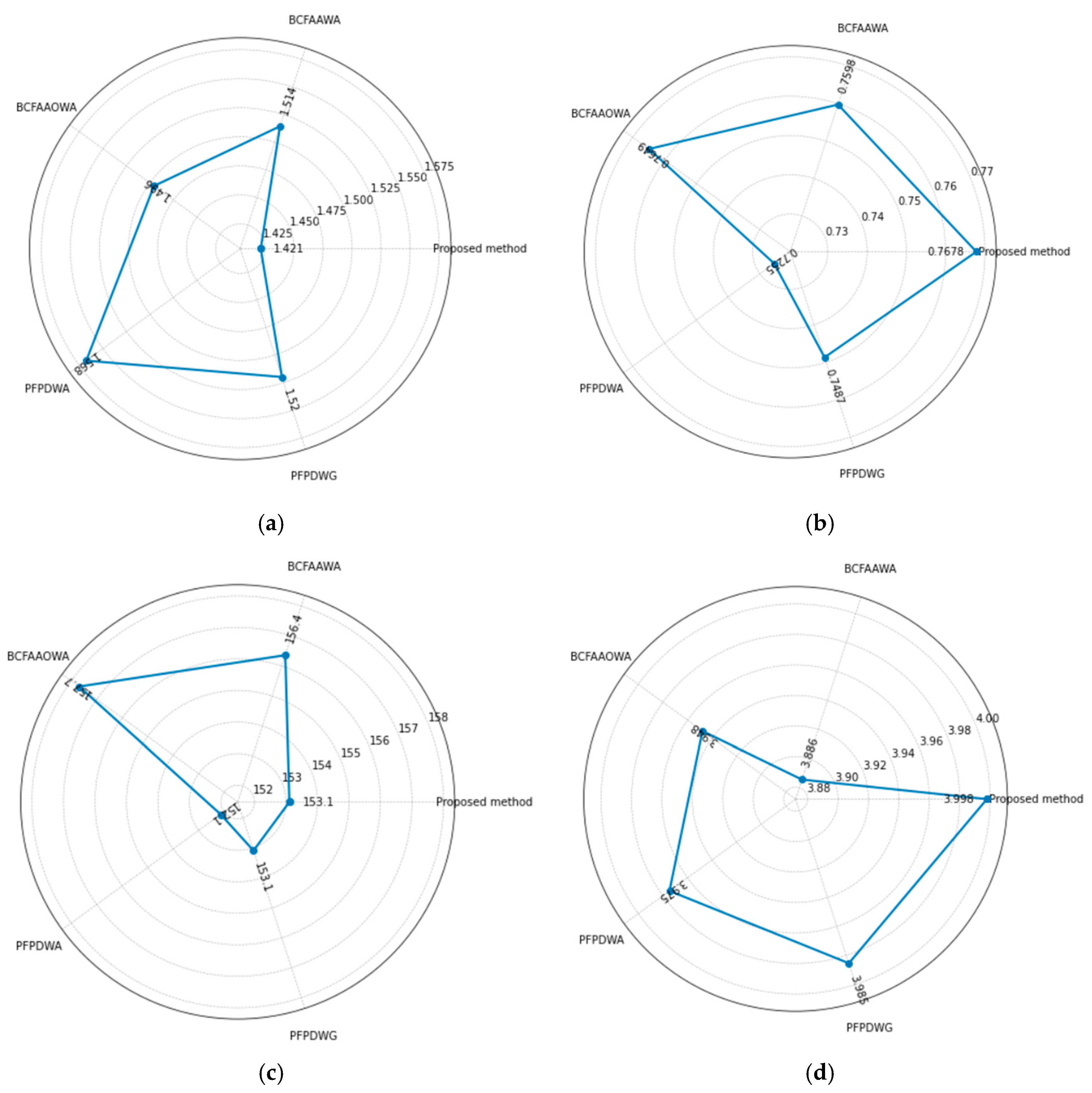
| proposed method | 1.4213 | 0.7678 | 153.1085 | 3.9979 |
| BCFAAWA | 1.5145 | 0.7598 | 156.3598 | 3.8856 |
| BCFAAOWA | 1.4956 | 0.7649 | 157.6897 | 3.9478 |
| PFPDWA | 1.5677 | 0.7255 | 152.1345 | 3.9746 |
| PFPDWG | 1.5199 | 0.7487 | 153.0896 | 3.9854 |
| Method | Average Runtime (s) | Iterations to Convergence | Relative Cost (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PFPDWA | 1.64 | —— | 69.2% |
| BCFAAWA | 1.82 | —— | 76.2% |
| PSO | 3.15 | 120 | 132.9% |
| GA | 3.78 | 140 | 159.5% |
| PGSA (proposed) | 2.37 | 95 | 100% (baseline) |
| Distance Metric/Weight Scheme | Runtime (s) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Euclidean + Equal weights | 1.4213 | 0.7678 | 153.1085 | 3.9979 | 0.96 |
| Manhattan + Equal weights | 1.5671 | 0.7425 | 132.6977 | 3.8765 | 1.07 |
| Mahalanobis + Equal weights | 1.4565 | 0.6987 | 145.8965 | 3.9654 | 1.12 |
| Euclidean + Entropy weights | 1.4789 | 0.7489 | 150.3645 | 3.5654 | 1.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, Y.; Qiu, J.; Tang, J.; Liu, Q.; Li, C.; Chen, S. An Optimization-Based Aggregation Approach with Triangular Intuitionistic Fuzzy Numbers in High-Dimensional Multi-Attribute Decision-Making. Information 2025, 16, 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16111010
Qian Y, Qiu J, Tang J, Liu Q, Li C, Chen S. An Optimization-Based Aggregation Approach with Triangular Intuitionistic Fuzzy Numbers in High-Dimensional Multi-Attribute Decision-Making. Information. 2025; 16(11):1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16111010
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Yanshan, Junda Qiu, Jiali Tang, Qi Liu, Chuanan Li, and Senyuan Chen. 2025. "An Optimization-Based Aggregation Approach with Triangular Intuitionistic Fuzzy Numbers in High-Dimensional Multi-Attribute Decision-Making" Information 16, no. 11: 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16111010
APA StyleQian, Y., Qiu, J., Tang, J., Liu, Q., Li, C., & Chen, S. (2025). An Optimization-Based Aggregation Approach with Triangular Intuitionistic Fuzzy Numbers in High-Dimensional Multi-Attribute Decision-Making. Information, 16(11), 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16111010








