Abstract
Micro-expressions are facial movements with extremely short duration and small amplitude, which can reveal an individual’s potential true emotions and have important application value in public safety, medical diagnosis, psychotherapy and business negotiations. Since micro-expressions change rapidly and are difficult to detect, manual recognition is a significant challenge, so the development of automatic recognition systems has become a research hotspot. This paper reviews the development history and research status of micro-expression recognition and systematically analyzes the two main branches of micro-expression analysis: micro-expression detection and micro-expression recognition. In terms of detection, the methods are divided into three categories based on time features, feature changes and deep features according to different feature extraction methods; in terms of recognition, traditional methods based on texture and optical flow features, as well as deep learning-based methods that have emerged in recent years, including motion unit, keyframe and transfer learning strategies, are summarized. This paper also summarizes commonly used micro-expression datasets and facial image preprocessing techniques and evaluates and compares mainstream methods through multiple experimental indicators. Although significant progress has been made in this field in recent years, it still faces challenges such as data scarcity, class imbalance and unstable recognition accuracy. Future research can further combine multimodal emotional information, enhance data generalization capabilities, and optimize deep network structures to promote the widespread application of micro-expression recognition in practical scenarios.
1. Introduction
In human non-verbal interaction, facial expressions, voice intonation and body language are important carriers of emotional expression. Among them, facial expressions are widely used in emotion recognition and behavior analysis research because they directly reflect the inner state of human beings. With the rapid development of computer vision and artificial intelligence technology, facial expression recognition technology has become an important research direction in many fields such as human–computer interaction, public safety, mental health, and educational assessment.
Compared with macro-expressions, which are long-lasting, large-amplitude and artificially controllable emotional expressions, micro-expressions are more valuable for research [1]. They are unconscious facial reactions with extremely short duration and extremely small movement amplitude, occurring in local areas of the face, and cannot be deliberately disguised. Micro-expressions are believed to reveal the true emotions that individuals try to hide and have important psychological significance and application prospects. They are widely used in scenarios such as lie detection, counterterrorism, psychological intervention, business negotiations and marriage assessment [2,3].
As early as the 1960s, Ekman [4] first proposed the concept of micro-expressions. Since then, Paul Ekman and other scholars have conducted systematic research on micro-expressions and developed the Micro-Expression Training Tool (METT) to assist manual training in identifying micro-expressions. However, studies have shown that even after professional training, the accuracy of manual micro-expression recognition is usually only about 47–50% [5], and it is time-consuming and subjective, which is not suitable for large-scale applications. Therefore, building an automated, efficient and stable micro-expression recognition system has become a research hot spot.
Micro-expression recognition systems usually include three main stages: image preprocessing, feature extraction and micro-expression classification. Image preprocessing involves operations such as face detection, alignment, registration, and cropping, aiming to minimize interference and improve the accuracy of subsequent feature extraction. Feature extraction is the core of the entire system. In the early days, traditional machine learning methods based on textures such as local binary patterns (LBP) [6] and histogram of oriented gradients (HOG) [7] or based on optical flow features such as multi-directional motion feature descriptor (MDMO) [8] were mainly used. For example, Zhao, Pietikainen [9] proposed a feature extraction method based on LBP-TOP, which can better extract spatiotemporal texture information; Liong, Phan [10] proposed the MDMO method, which improves the sensitivity of micro-expressions by capturing the movement direction information of the face. Ben, Zhang [11] proposes a more discriminative feature space expression from the perspective of high-dimensional tensor modeling.
In recent years, with the rise of deep learning, especially convolutional neural networks (CNN), researchers have begun to combine it with time series models such as LSTM to build an end-to-end spatiotemporal feature extraction and recognition framework. For example, Khor, See [12] designed a CNN-LSTM network structure to extract spatial features first and then model time series changes. Reddy, Karri [13] further used 3D-CNN to simultaneously process spatial and temporal dimensions to achieve dynamic modeling of micro-expressions. The more advanced Transformer structure has also been gradually introduced into this field due to its advantages in modeling global dependencies. For example, Wang, Zhang [14] built a global attention mechanism model between facial region movements based on Transformer, which further improved the recognition accuracy and generalization ability.
While the methods are constantly developing, the construction of datasets is also an important factor restricting the research of micro-expressions. At present, mainstream micro-expression datasets such as CASME II [15], SMIC [16] and SAMM [17] are all collected by high-frame rate cameras and annotated with rich emotion categories and action unit information. However, these datasets generally have problems such as small number of samples, unbalanced emotion categories, and poor cross-individual generalization ability, which limits the training effect of deep models. To address these problems, researchers are also trying to introduce strategies such as data enhancement [18], transfer learning [19], and multimodal fusion [20] to improve the robustness and practicality of the model.
Micro-expression recognition is not only a research challenge at the intersection of artificial intelligence and psychology but also a key component of affective computing and intelligent human–computer interaction. With the rapid advancement of deep learning techniques and increasing interdisciplinary integration, micro-expression recognition is expected to gain broader applications in emotional understanding and social security. Several prior surveys have provided valuable foundations for this field. Oh et al. [21] presented one of the earliest comprehensive reviews, summarizing available databases, methodologies, and challenges, which has since become a cornerstone reference. More recently, Goh et al. [22] further refined earlier categorizations and identified new research directions that were beginning to take shape at the time. While these works established an essential baseline, their scope primarily reflects the state of research before 2020. In contrast, the present review emphasizes developments between 2018 and 2025, with particular focus on the rapid adoption of deep learning, Transformer-based architecture, graph neural networks, and multimodal fusion strategies. In addition, we present updated comparative results on newly introduced benchmark datasets, thereby extending the coverage of earlier surveys and offering a timely perspective on the trajectory of this field. Overall, this paper provides a systematic review of algorithms, datasets, and future research directions in micro-expression recognition.
The paper is structured as follows: Section 2 introduces action unit (AU) modeling for micro-expression recognition, Section 3 describes commonly used micro-expression datasets, Section 4 reviews recognition and classification methods, Section 5 compares the performance of various methods on standard datasets, Section 6 outlines future research directions, and Section 7 summarizes the main findings and answers the research questions.
2. Action Unit Modeling for Micro-Expression Recognition
The current research system of micro-expression recognition can be summarized into two typical technical process frameworks. Figure 1 shows an idealized processing path. The system uses edited and calibrated micro-expression clips as input. The model task is mainly to determine whether there are micro-expressions and further perform emotion classification or AU recognition. This type of method is mostly used in laboratory control environments, with low modeling difficulty, but weak adaptability in practical applications.
Figure 1.
Standard micro-expression recognition pipeline.
In comparison, the integrated framework shown in Figure 2 is more aligned with practical application needs. Instead of relying on pre-edited clips, the system must handle continuous long-term facial video streams, automatically detecting and localizing candidate micro-expressions within unstructured sequences. This involves calibrating the three temporal landmarks, namely onset, apex, and offset, and then performing subsequent recognition tasks. Importantly, in this pipeline, AU-based modeling plays a central role, as it provides objective and physiologically grounded representations of subtle muscle activations, which are essential for distinguishing genuine micro-expressions from noise or overlapping macro-expressions. This process places higher requirements on the algorithm’s temporal modeling ability, robustness and cross-individual generalization ability, especially under the challenges of high difficulty inducing micro-expressions, short duration and small expression amplitude in natural scenes [23].
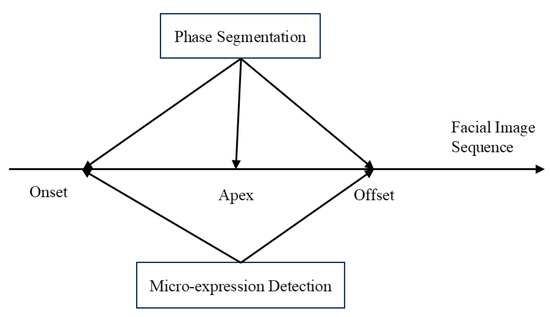
Figure 2.
Integrated detection and recognition framework for micro-expressions.
Micro-expression recognition is not just a one-time classification task. Its recognition process includes multiple stages. The first step is detection, that is, identifying whether there are micro-expressions in the image sequence. The two common scenarios are to identify implicit micro-expressions from a static expressionless state, or to distinguish micro-expression fragments from ordinary macro-expressions. Since micro-expressions often last only a few hundred milliseconds and the changes in facial muscles are extremely weak, high requirements are placed on the model’s temporal perception and differentiation capabilities [24].
After the detection is completed, the research usually enters the classification stage. Traditional methods are mostly based on emotional labels for classification, such as anger, fear or sadness, but this method has limitations in practical applications. Due to the influence of individual differences, cultural background and experimental conditions, the induction of natural micro-expressions is extremely difficult, making classification based on subjective labels susceptible to interference from human bias [25].
To improve objectivity and consistency of recognition, more studies have introduced the Facial Action Coding System (FACS) as the basis for recognition. FACS encodes facial muscle movements into a set of standardized action units, with each AU representing muscle activity in a specific area [26]. For example, AU1 represents raising the eyebrows, and AU12 represents raising the corners of the mouth. With these AUs, the model can bypass the ambiguity of subjective emotion labels and establish a more stable physical feature representation [27].
Existing studies have shown that micro-expression recognition methods based on AUs are generally superior to traditional emotion label classification methods in terms of accuracy, fairness, and cross-cultural adaptability. When facial muscle activity cannot correspond one-to-one to a specific emotional state, AUs as an intermediary can provide more discernible physical information, thereby improving the stability and interpretability of the recognition system [28]. In addition, the use of AUs can effectively avoid the subjective bias caused by manual emotion labeling and improve the fairness and generalization ability of the algorithm [17].
In recent years, research has further emphasized the division of micro-expression stages, that is, structurally annotating micro-expressions in the time dimension, usually including the starting point, the vertex, and the end point. This stage division helps to reveal the dynamic evolution of micro-expressions, while providing clear supervision signals for deep learning-based time series models, thereby improving the model’s ability to learn temporal features [29].
3. Micro-Expression Dataset
In the study of automatic micro-expression recognition, the quality, scale, and diversity of the dataset are important factors that determine the performance of the algorithm and the generalizability of the research results. Micro-expressions usually last for a very short time, generally between 1/25 s and 1/3 s, and are accompanied by very small facial muscle movements, which makes their collection in a natural environment extremely challenging. Compared with regular facial expressions, micro-expressions have higher requirements in terms of temporal and spatial resolution, requiring the use of high-frame rate cameras (such as 100 fps and above) for video collection, and high-precision facial movement analysis tools. Figure 3 is an example of SMIC [30], CASME [31], CASME II [15], SAMM [17], CAS(ME)2 [32] and MMEW [8] micro-expression datasets.
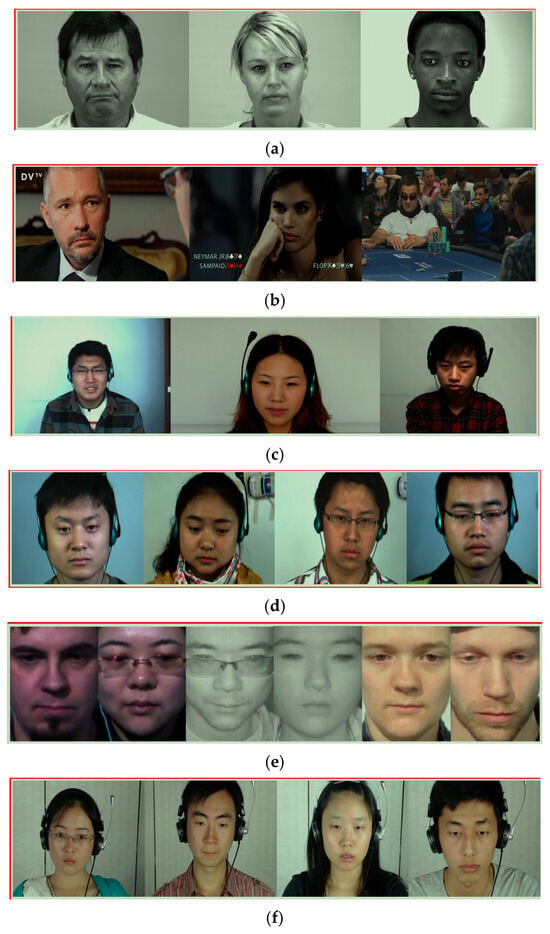


Figure 3.
Examples of the various datasets are listed as: (a) SMIC; (b) MEVIEW; (c) CASME; (d) CASME II; (e) SAMM; (f) CAS(ME)2; (g) MMEW.
3.1. SMIC
SMIC is one of the early spontaneous micro-expression datasets released by the University of Oulu Vision Research Group, OUVIS, in Finland in 2013 [25]. It aims to capture the micro-expression reactions of individuals while watching emotional videos. The dataset contains 164 video clips from 16 subjects, covering three basic emotion categories: positive, negative, and neutral, including surprise and other ambiguous emotions. Based on the imaging method and frame rate, SMIC is further divided into three subsets: SMIC-HS for high-speed imaging at 100 frames per second [33], SMIC-NIR for near-infrared imaging [34], and SMIC-VIS for visible light imaging [35].
One notable advantage of SMIC is its use of high-speed camera equipment, which enables the preservation of fine-grained temporal dynamics in micro-expressions. This makes the dataset particularly suitable for training time series modeling methods such as long short-term memory networks (LSTM) and three-dimensional convolutional neural networks (3DCNN) [12,30]. However, the emotion labels provided in the dataset are relatively coarse, and there is an imbalance in the number of samples across categories. These factors limit their effectiveness in multi-class recognition tasks. Furthermore, its emotional elicitation approach primarily relies on video stimulation, and the authenticity and naturalness of the resulting expressions remain subjects of debate [36].
3.2. MEVIEW
The MEVIEW dataset is one of the earliest publicly available micro-expression databases captured under real-world conditions, specifically designed to reflect spontaneous facial reactions in high-pressure scenarios such as poker games and interviews. Unlike traditional lab-controlled datasets such as CASME II or SMIC, MEVIEW focuses on in-the-wild settings, offering higher ecological validity that aligns more closely with practical micro-expression applications [37].
MEVIEW contains 31 short video clips extracted from real-life videos, involving 16 different subjects. Each video is recorded at 25 frames per second and has an average duration of around 3 s. The dataset includes annotations of seven emotion categories: happiness, contempt, disgust, surprise, fear, anger, and uncertain emotions. These labels were assigned by experts trained in the Micro-Expression Training Tool (METT) and the FACS, ensuring reliable onset, apex, and offset annotation [37].
Despite its high realism, MEVIEW has several limitations. The dataset size is relatively small compared to newer datasets such as CASME3 or MMEW, which may hinder its use in training deep learning models. Furthermore, camera angle variations, facial occlusions, and lighting inconsistencies pose challenges to automatic recognition systems. Nevertheless, MEVIEW remains a valuable resource for evaluating the generalizability and robustness of micro-expression recognition algorithms, especially in cross-dataset or real-world scenario evaluations [38].
3.3. CASME and CASME II
The CASME dataset and its improved version CASME II are representative small-sample spontaneous micro-expression datasets released by the Institute of Psychology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, focusing on spontaneous micro-expressions at high frame rates [15]. The original CASME dataset was collected by 19 subjects with a frame rate of 60 frames per second. CASME II has made significant optimizations in the accuracy of camera equipment and annotation methods. It uses a high-speed camera with a frame rate of 200 frames per second and an image resolution of 640 × 480.
It contains 247 micro-expression videos, covering 7 groups of AU combinations and corresponding to 5 emotion labels, including happiness, disgust, depression, surprise and others [15]. A highlight of CASME II is the introduction of the FACS for AU-level annotation. Compared with traditional emotion labels, AU expressions are more fine-grained and can simultaneously support emotion classification tasks and action unit recognition and joint modeling. In addition, the facial posture and lighting conditions were controlled during the acquisition process of the dataset, which improved the standardization of the data structure and the controllability of the experiment [28]. However, due to the limitations of the collection site and context, the shooting environment of CASME II is relatively ideal, and the diversity of facial expressions is still not enough to fully reflect the distribution characteristics of micro-expressions in real scenes [17].
3.4. SAMM
SAMM is a high-quality micro-expression dataset released by University College London in 2016 [17]. Its greatest features are ethnic diversity and sample standardization. The dataset contains 159 micro-expression samples from 32 subjects of different genders and ethnic backgrounds, covering 7 common emotions. It uses a high-speed camera with a speed of up to 200 fps for acquisition, supplemented by FACS annotation.
The SAMM dataset enhances the naturalness of micro-expressions through multiple emotion induction methods, and provides accurate onset, apex and offset time point annotations to support detailed time series analysis. In addition, SAMM places special emphasis on standardization between samples, such as unified facial alignment and occlusion control, which provides a good foundation for the training of deep learning models. However, due to the small overall sample size, there may be a risk of overfitting in training deep networks, and strategies such as transfer learning need to be used in conjunction [17].
3.5. CAS(ME)2
To further integrate the micro-expression and macro-expression recognition tasks, the Chinese Academy of Sciences released the CAS(ME)2 dataset in 2018 [39]. The dataset contains 57 macro-expression samples and more than 300 micro-expression samples from 22 subjects, all collected by a 200-fps high-speed camera. The main advantage of this dataset is that it provides complete facial video sequences and their emotion categories, action unit annotations, and time segmentation information, which can be used to train joint models to achieve complex tasks such as macro/micro mixed recognition and switch detection.
This dataset helps to improve the robustness and adaptability of the model in complex real-world scenarios. However, when the proportion of micro-expression samples is relatively low, the problem of class imbalance still exists, which needs to be alleviated by data augmentation or resampling techniques [39].
3.6. MMEW
The MMEW dataset collects the natural facial expressions of 68 subjects when watching emotion-inducing videos, covering spontaneous micro-expressions and macro-expressions. A major highlight of MMEW is the introduction of multimodal synchronous acquisition. In addition to visible light image sequences, it also collects audio, physiological signals, head posture and other information, providing a rich foundation for cross-modal emotion recognition research. The video resolution of this dataset is 640 × 480, the acquisition frame rate is 90 fps, and it contains a total of about 300 micro-expression samples and more than 1000 macro-expression clips [23].
In terms of emotion labeling, MMEW not only provides emotion classification labels, but also introduces a multi-level labeling system, including 6 basic emotions (anger, disgust, fear, happiness, sadness, surprise) and AU labeling information. In addition, each video is independently labeled by multiple experts using the FACS and reaches a consistent judgment, which effectively improves the accuracy and scientific of the label. Compared with earlier datasets, MMEW is closer to multimodal emotional expressions in real environments and has stronger generalization training capabilities [23].
The MMEW dataset has significantly improved sample size and data dimensions compared to SMIC, CASME II, but it still has the problem of sample category imbalance. For example, since sadness and fear are difficult to naturally stimulate in experimental induction, the corresponding micro-expression samples are relatively small. In addition, although its acquisition frame rate (90 fps) can cover micro-expression key frames, it is still lower than the 200-fps level of CASME II and SAMM, which may have certain limitations on the accurate modeling of extremely short transient expressions [17].
3.7. Comparative Analysis of Micro-Expression Datasets
Table 1 presents a comparison of commonly used micro-expression datasets, outlining differences in sample size, frame rate, resolution, emotional categories, annotation methods, and recording conditions. These characteristics directly affect how recognition systems are developed and evaluated.

Table 1.
Comparison of micro-expression datasets.
The number of subjects and samples varies greatly across datasets. For example, MMEW contains more than 3000 samples, offering a relatively large pool of data, whereas CASME and SAMM have fewer than 200 samples, which may restrict the generalizability of models. The number of participants also differs considerably, ranging from fewer than ten in SMIC to more than thirty in MMEW and SAMM, reflecting different levels of demographic diversity.
Frame rate and resolution are also critical factors for capturing the subtle and rapid facial changes that define micro-expressions. CASME II, recorded at 200 FPS, and SAMM, with its high spatial resolution (2040 × 1088), are particularly well suited for detailed temporal analysis. In contrast, datasets such as SMIC and MMEW, which adopt lower frame rates and standard resolutions, may fail to capture very brief or fine-grained movements.
Differences are also observed in terms of emotion categories and annotation methods. CASME II and SAMM cover seven emotion categories and rely on expert coding using FACS, ensuring higher labeling precision. By comparison, SMIC and MMEW include fewer categories and depend on self-reports or multiple annotators, which improves ecological validity but may reduce consistency. Thus, there is a trade-off between annotation accuracy and naturalistic expression capture.
Recording conditions further distinguish the datasets. Lab-controlled environments, such as those used in CASME and CASME II, provide standardized data collection but may limit the naturalness of expressions. MMEW, on the other hand, is collected in less constrained settings, which enhances ecological validity but introduces greater variability and potential noise.
4. Micro-Expression Recognition and Classification Methods
Facial micro-expressions are defined as brief, involuntary facial movements that reveal genuine emotions, typically lasting less than 0.5 s and involving subtle muscle activations [40]. As a subtask of facial expression recognition, micro-expression recognition includes not only detecting weak, short-lived, involuntary expressions, but also classifying the emotional categories of these expressions. This section introduces the main methods for micro-expression recognition and classification, including traditional methods and deep learning-based methods.
4.1. Micro-Expression Recognition Process
As shown in Figure 4, micro-expression recognition usually includes four key stages: image preprocessing, micro-expression detection, feature extraction, and micro-expression classification.
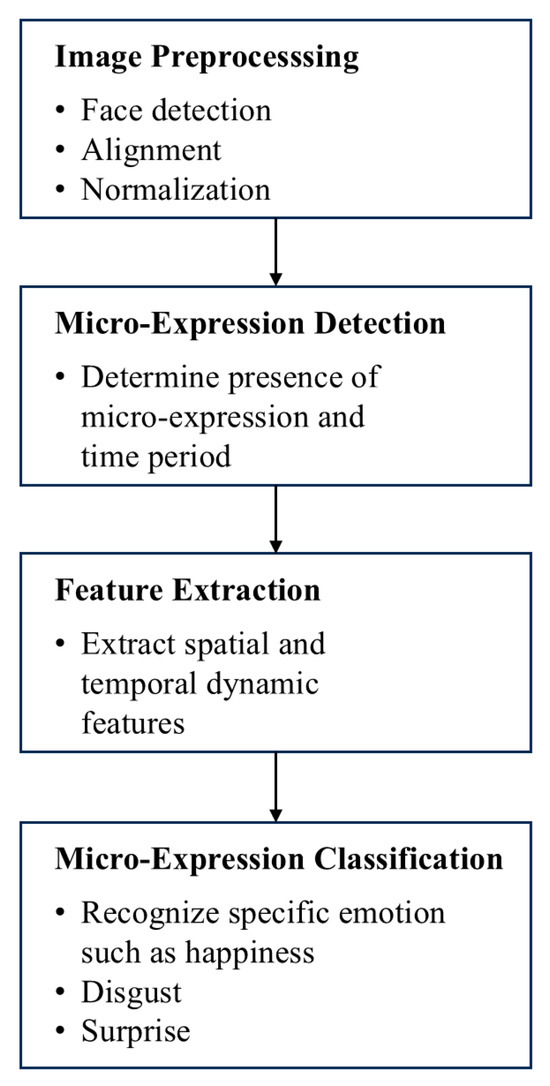
Figure 4.
Micro-expression recognition process.
First, image preprocessing is the basis of the entire process, which aims to detect, align, and normalize faces in original images or video sequences, thereby reducing interference caused by changes in posture, illumination, and scale, and laying a stable foundation for subsequent feature extraction and recognition tasks [28].
Next, in the micro-expression detection stage, the system needs to identify whether there are micro-expressions in the video sequence and determine their specific start and end time points. This step is particularly critical when dealing with short and imperceptible expression changes [31]. Subsequently, the feature extraction stage focuses on capturing the extremely subtle and rapidly changing muscle movement characteristics in micro-expressions. It often uses a combination of spatial texture features and temporal dynamic features to enhance the sensitivity to micro-dynamics of expressions [25].
Finally, in the micro-expression classification stage, the extracted features are input into the classifier to determine the corresponding emotion category, such as pleasure, disgust, surprise, etc. Currently, supervised learning methods such as Support Vector Machine (SVM) and CNN are mostly used to achieve efficient recognition [41]. This whole process provides a systematic technical path for the automatic recognition of micro-expressions and has been put into practical application in many fields such as psychological research and security monitoring.
4.2. Micro-Expression Detection Method
The core task of micro-expression detection is to automatically identify short and subtle facial muscle movements from video sequences [8]. These changes usually last for a very short time, generally less than 0.5 s, making them difficult to perceive by the human eye. Technical detection relies on precise modeling of small and transient facial dynamics. Current mainstream detection methods can be clearly categorized into four types: (1) optical flow-based methods, (2) dynamic area extraction methods, (3) temporal sliding window strategies, and (4) deep learning-based detection networks.
- (1)
- Optical flow-based methods represent one of the earliest approaches to micro-expression detection. They estimate facial motion by computing pixel displacements across frames. Among them, the Main Directional Mean Optical Flow (MDMO) method captures micro-motion features by extracting the average optical flow direction and amplitude in local facial regions [42]. This approach is effective for short-term motion capture but is vulnerable to illumination changes.
- (2)
- Dynamic area extraction methods, such as strain maps [43] and frame differences [44], identify regions of interest by highlighting local muscle deformation or intensity changes between consecutive frames [17]. These methods are simple and intuitive, offering clear visual interpretations. However, their sensitivity to noise and limited robustness under high-frequency interference reduce their reliability.
- (3)
- Temporal sliding window strategies focus on modeling dynamic patterns over time. By defining a fixed-length window within a video sequence and sliding it across frames, these methods analyze localized temporal information to determine whether micro-expressions occur. They are often integrated with classifiers such as SVMs or random forests [45]. Nonetheless, the performance of this approach heavily depends on the chosen window length, which involves a trade-off between temporal resolution and computational efficiency.
- (4)
- Deep learning-based detection networks have recently become a dominant research direction. By employing CNNs, LSTMs, or hybrid architectures, these methods enable end-to-end spatiotemporal feature extraction and automatic detection. For instance, the two-stream network by Yang and Sun [46] combines spatial appearance with temporal optical flow features, while LSTM models capture long-term temporal dependencies to reduce feature omission [12]. Although deep learning achieves superior accuracy, it requires large-scale annotated datasets and substantial computational resources.
In summary, micro-expression detection has evolved from traditional shallow feature analysis to advanced data-driven modeling, reflecting a clear transformation of research focus. With increasing computational power and the continuous development of benchmark datasets, end-to-end deep learning approaches are expected to play an even greater role in practical applications.
4.3. Feature Extraction
Feature extraction plays a vital role in micro-expression recognition, and its quality directly determines the upper limit of subsequent classifier performance. Since micro-expressions are short-lived and weak in amplitude, it is particularly important to extract significant features that can effectively distinguish emotion categories. Current feature extraction methods can be roughly divided into two categories: manual feature methods and deep feature methods.
4.3.1. Manual Feature Method
In the early stages of micro-expression recognition research, manual feature extraction methods were the main means. These methods rely on manually designed visual features to capture subtle changes in facial regions during micro-expression occurrence. Although deep learning has made significant progress in recent years, manual feature methods still have the advantages of high computational efficiency and strong interpretability in scenarios with limited sample size and are therefore still widely used in current systems or as auxiliary inputs to deep models.
LBP-TOP is one of the most representative three-dimensional texture descriptors in micro-expression analysis. It is based on the Local Binary Pattern (LBP) algorithm and extended to the spatiotemporal domain. It calculates LBP encoding on three orthogonal planes, XY (space), XT, and YT (time), to comprehensively model spatial structure and temporal changes [9]. This method can effectively capture texture variations caused by small facial movements, has rotation invariance and grayscale invariance, and is suitable for expressing short-term, local micro-movements. LBP-TOP has achieved good recognition performance on multiple public micro-expression datasets (such as CASME and SMIC), becoming one of the mainstream methods in early research.
The HOG feature was proposed by Dalal and Triggs [7] and was originally used for pedestrian detection. Its core idea is to divide the image into small cells and calculate the distribution histogram of the pixel gradient direction in each cell. Since facial micro-movements often involve subtle contour changes, HOG can effectively reflect the contour changes of local areas such as the corners of the eyes and the corners of the mouth under different expression states.
The Gabor filter is a multi-scale and multi-directional frequency analysis tool that can simulate the response of the human primary visual cortex to spatial frequency and direction [47]. In micro-expression recognition, Gabor filters are often used to extract texture change features in key facial areas, especially for identifying high-frequency micro-expression components such as subtle frowns and raised corners of the mouth.
Micro-expression recognition requires not only capturing static textures, but also effectively modeling dynamic changes. Optical flow is a motion estimation method based on pixel motion between consecutive frames, which can reflect the direction and intensity of facial motion. HOOF quantifies and counts the optical flow vectors by direction to form a histogram representation, which is suitable for capturing the movement trends of different facial regions [48]. HOOF has strong expressiveness in describing subtle movements of facial muscles and is particularly suitable for dynamic micro-expression recognition in continuous video sequences.
Strain maps are a method for describing the degree of deformation of local areas, which was first introduced by Shreve, Godavarthy [49] for micro-expression analysis. This method depicts the degree of stretching and compression of facial muscle tissue during expression changes by calculating the deformation tensor field between each frame in the video and the reference frame (such as the neutral frame). Unlike traditional optical flow, strain maps can capture non-rigid deformations more sensitively, so they are outstanding in identifying slight but emotionally meaningful movements.
4.3.2. Deep Feature Methods
Feature extraction methods based on neural networks have gradually replaced traditional manual feature methods in the field of micro-expression recognition and become the mainstream of research. Deep networks can automatically learn multi-level, high-abstract feature representations, which are particularly suitable for processing subtle and complex nonlinear spatiotemporal patterns in micro-expressions. The following introduces several typical deep feature extraction architectures and their applications in micro-expression recognition.
2D-CNN is the earliest deep model used in image analysis, which is suitable for processing single-frame images or a small number of key frames. Its basic structure includes convolutional layers, activation functions, pooling layers, and fully connected layers, which can extract spatial texture features in facial images. In micro-expression research, researchers usually select Apex frames (frames with the largest expression amplitude) as input and use 2D-CNN to extract their spatial structure information [50]. This method is computationally efficient and suitable for deployment in scenarios with limited data.
However, 2D-CNN cannot model dynamic changes between frames, so it has obvious shortcomings in temporal modeling, especially when processing complete micro-expression video sequences. To capture both spatial and temporal information, 3D-CNN introduces the time dimension based on 2D convolution and performs stereo convolution operations on continuous video frames. This method can extract dynamic change patterns within a local time window and is ideal for processing micro-expression video sequences [41]. By analyzing the continuous changes of facial muscles during micro-expressions, 3D-CNN can more accurately identify action features such as short frowns and twitching of the corners of the mouth. In addition, classic 3D models such as C3D [51] have also been successfully migrated to the micro-expression recognition task, achieving effective extraction of short-term dynamic features. However, 3D models usually have many parameters, require a high amount of training data, and have the risk of overfitting.
To better model long-term dependencies, researchers combined CNN with a recurrent neural network (RNN) structure. CNN is responsible for extracting spatial features of each frame, and LSTM or GRU further models the temporal dynamics between these frames [52]. This structure uses the memory mechanism of RNN to capture the evolution trajectory of expression development and is particularly suitable for continuous modeling of micro-expressions from Onset (start) to Offset (end). Compared with the pure CNN model, this combined architecture is better at modeling the dependencies between different expression stages and has advantages in temporal modeling capabilities and expression recognition accuracy.
In recent years, the Transformer structure has been widely used in the field of computer vision due to its powerful temporal modeling capabilities and self-attention mechanism. Among them, Vision Transformer (ViT) first used the Transformer architecture for image processing and captured global information by dividing the image into patches and performing sequence modeling [53]. In addition, Swin Transformer introduces a hierarchical structure and a sliding window mechanism based on ViT, which is more suitable for modeling local micro-motion features [54]. In the task of micro-expression recognition, the introduction of the Transformer structure not only improves the perception of long-distance inter-frame dependencies but also pays attention to the subtle changes in local facial areas at different stages. The attention mechanism can dynamically weight important feature areas, thereby enhancing the model’s sensitivity to key micro-movements.
Considering that the micro-expression process has obvious stage characteristics, researchers have proposed a method based on keyframe (Onset, Apex, Offset) modeling. This method extracts image differences or feature change vectors between keyframes to significantly enhance the model’s sensitivity to the moment of expression change. For example, by constructing a different map or feature fusion map between Apex and Onset frames, the area where micro-movements occur can be highlighted, thereby improving the accuracy of emotion classification. Keyframe modeling is also often used in combination with CNN, 3D-CNN or Transformer as an input or enhancement module to guide the recognition model, especially in data-scarce scenarios with good robustness [55,56].
4.4. Micro-Expression Classification Method
The goal of micro-expression classification is to classify the detected or segmented facial micro-expression sequences into specific emotion categories, including anger, disgust, happiness, sadness, surprise, and fear. Since micro-expressions are short-lived, small-amplitude, and easily confused with macro-expressions, the classification algorithm not only needs to extract highly recognizable features but also needs to be highly sensitive to spatiotemporal details and tiny movements. Currently commonly used classification methods can be roughly divided into traditional machine learning methods, deep learning methods, and AU-based methods.
4.4.1. Machine Learning-Based Methods
In the early research of micro-expression recognition, traditional machine learning methods were widely used for classification tasks because of their good adaptability to small sample data and low computational complexity. Such methods usually rely on a clear feature engineering process. Researchers need to manually extract texture, motion or frequency features from images or videos, such as local binary pattern three orthogonal planes (LBP-TOP) [57], Histogram of Oriented Optical Flow (HOOF) [58] or Gabor filter response [59] and then input the extracted feature vector into the classifier for training and prediction.
SVM is one of the most used traditional methods. Its core idea is to find a hyperplane that can maximize the inter-class interval in a high-dimensional space. SVM has good generalization ability and is particularly suitable for dealing with high-dimensional and small sample problems that are common in micro-expression recognition. Pfister, Li [25] used LBP-TOP features combined with multi-class SVM in their research to achieve effective classification of spontaneous micro-expressions, especially on the SMIC dataset, achieving high recognition accuracy. Another common method is the K-nearest neighbor (KNN), which is a non-parametric model based on sample distance. The principle is to find the most similar K neighbors in the training set for the test sample and determine the category by majority voting. Although the KNN model has a simple structure, is easy to implement, and performs stably on small-scale data sets, it is sensitive to feature dimensions and sample size and has problems such as high computational overhead and dimensionality disaster [60].
In addition to SVM and KNN, decision trees and random forests are also widely used classification methods. Decision trees construct classification rules by gradually dividing the feature space, and the model has good interpretability; meanwhile, random forests make voting decisions by integrating multiple decision trees, which significantly improves the stability and robustness of classification [61]. In micro-expression research, random forests are often used for classification tasks after multimodal feature fusion and can effectively handle complex interactions between features. For example, the recognition method based on facial salient area features proposed by Happy and Routray [62] uses random forests as a classifier and has achieved ideal results on multiple public data sets.
4.4.2. Deep Learning-Based Methods
With the development of deep learning, researchers have begun to try to replace the traditional process of separating feature engineering and classifiers with end-to-end models such as CNN to achieve automation and performance improvement of micro-expression recognition tasks. The biggest advantage of deep models lies in their powerful feature representation capabilities, especially when dealing with nonlinear, micro-amplitude, and complex temporal dynamic micro-expressions, which can automatically learn discriminative spatial and temporal features through multi-layer network structures. Currently, widely used models include static convolutional networks (such as CNNs), spatiotemporal convolutional networks (such as 3D-CNNs), hybrid models of convolutional and recurrent neural networks, Transformer structures based on attention mechanisms, and few-sample learning models proposed for data scarcity problems.
In terms of static models, the more typical representative is OFF-ApexNet, which takes the Apex frame at the key moment of micro-expressions as the core and combines the optical flow information of the previous and next frames to construct input, thereby focusing on the instantaneous changes in micro-expressions. This method makes full use of the sensitivity of optical flow differences to small facial movements and improves the model’s emotion discrimination ability [63]. STSTNet is another lightweight shallow convolutional network. Its design is based on the separation of spatiotemporal features and parallel structure. It is suitable for scenarios with limited training samples and can extract local dynamic changes in key areas while maintaining a low number of parameters [64].
To simultaneously model the spatial texture and temporal dynamics of facial expressions, researchers have introduced three-dimensional convolutional neural networks (3D-CNNs), such as C3D and I3D. 3D-CNN can capture the spatiotemporal features in video frame sequences through three-dimensional convolution kernels and is more suitable for processing complete micro-expression video clips, not just key frames. The I3D model introduces a deeper network structure and a larger dataset pre-training based on C3D, showing stronger feature capture capabilities [51,65]. In addition, the combination of CNN and RNN is also widely used. This type of structure usually uses CNN to extract the spatial features of each frame and then inputs the feature sequence into LSTM to capture the temporal dependency and dynamic evolution between frames. This method is particularly effective in micro-expressions, because micro-expressions are essentially short-term changes driven by time [66].
In recent years, Transformer-based methods have gradually been introduced into micro-expression recognition tasks due to their advantages in long-term temporal modeling and attention mechanisms. For example, models such as ViT and Swin Transformer can globally model the entire frame sequence through the self-attention mechanism, thereby more accurately locating and identifying the temporal key points involved in micro-expressions [54]. Unlike traditional RNNs, Transformers do not rely on sequential recurrence, can more efficiently model non-local dependencies, and show better performance and scalability when processing high-resolution, multi-frame inputs.
Considering the high cost of annotation and difficulty in obtaining micro-expression data, the number of samples is usually very limited, which limits the training effect of deep models. For this reason, few-shot learning has become a research hotspot in recent years. Metric learning methods such as Siamese networks and Prototypical Networks have been introduced into micro-expression recognition, which can quickly adapt to new categories by constructing similarity functions between samples. Zhu, Toisoul [67] proposed an attention learning framework based on prototype clustering, which achieved robust classification results under low-resource conditions. Such methods are usually combined with data enhancement strategies or transfer learning techniques to improve the usability and generalization ability of micro-expression recognition in real-world applications.
4.4.3. AU-Based Methods
AU-based methods have high interpretability and psychological basis in micro-expression recognition. This type of method is based on the FACS proposed by Ekman [4]. It breaks down facial expressions into a series of independent or combined muscle movement units, such as eyebrow raising (AU1) and mouth corner raising (AU12). The activation and combination of these AUs are analyzed to determine the emotional category expressed by the individual. Compared with deep models directly based on pixel or image features, the AU method is more in line with the physiological structure of human facial movements, so it is widely used in behavioral analysis, clinical psychology, lie detection and other fields.
The FACS coding method requires precise tracking and segmentation of the facial area in the video and then determines whether each AU is activated through feature extraction algorithms or training models and further combines these AUs to map to six basic emotions or more dimensional emotions. Early implementations of this type of method mostly use traditional machine learning, such as SVM to classify each AU and then perform combined recognition. With the development of deep learning, researchers have tried to introduce CNN to extract facial region features and then judge the existence and strength of AUs through fully connected layers or attention mechanisms. For example, Zhang and Vorobeychik [68] proposed an AU detection framework based on a multi-label convolutional model, which effectively improved the recognition ability in the case of weak expressions.
In recent years, to further model the spatial position and semantic dependency between AUs, graph neural networks (GNNs) have become a new research hotspot. In this type of method, each facial region or action unit is represented as a node of the graph, and the connection between nodes represents the coordinated movement or anatomical relationship between muscles. Feature aggregation and global modeling are performed through graph convolution operations. The AU-GCN model proposed by Li, Peng [69] is an example. By explicitly constructing AU semantic graphs and geometric graphs, structured learning and reasoning between AUs are realized, which significantly improves the performance in complex facial expression recognition. This method not only performs well in micro-expression recognition but also has good interpretability and generalization.
Although the AU method has physiological rationality and strong interpretability, it still faces several challenges in micro-expression recognition. On the one hand, the amplitude of micro-expressions is extremely small, making the AU activation signal very weak; on the other hand, accurate AU labeling requires expert manual coding, which has high labeling costs and subjective differences. In addition, most of the existing micro-expression databases have incomplete or inaccurate AU labeling, which limits the further development of this type of method. To alleviate these problems, researchers are trying to combine transfer learning, multimodal input, and data enhancement strategies to improve the robustness of AU recognition.
In addition, one important but often overlooked issue is the question of fusion and relation of micro-expressions. Most existing methods treat micro-expressions as isolated signals, without sufficiently exploring how different micro-expressions interact, co-occur, or transition across temporal segments. Fusion strategies, such as integrating micro-expressions with macro-expressions [1,19], physiological signals [2,24], or multimodal behavioral cues [20], may provide richer emotional representations. Moreover, examining the relational patterns among micro-expressions could help reveal underlying psychological states [3,5,23] and improve the accuracy of emotion recognition. Recent works, such as Xia et al. [1], have shown that learning from macro-expressions can enhance micro-expression recognition, highlighting the potential of cross-scale fusion. Zhao et al. [20] proposed a multimodal fusion-based Swin Transformer that effectively combines complementary cues.
4.5. Comparison of Micro-Expression Recognition Methods
As shown in Table 2, this section systematically summarizes the current mainstream technical routes from the perspectives of feature extraction methods, model structure, applicable scenarios and main advantages. For manual feature methods, such as LBP-TOP, HOG and Gabor filters, they rely on human prior knowledge for feature engineering, which has the advantages of low computational cost, simple implementation and strong interpretability, and are suitable for scenarios with small data volume or high real-time requirements. However, such methods have limited ability to model complex facial changes and are not robust enough under conditions such as illumination changes, occlusion and posture deviation [9,25].

Table 2.
Comparison of micro-expression recognition methods.
With the development of deep learning, models such as CNN, 3D-CNN and Transformer have been widely used in micro-expression recognition tasks, showing higher accuracy and stronger feature expression capabilities. These methods teach spatiotemporal features through large-scale data and achieve end-to-end modeling without manual feature design [28,70]. However, they are highly dependent on computing resources and data scale, take a long time to train, and face certain interpretability issues.
Traditional classifiers such as SVM, KNN, and random forest are often used in combination with artificial features and are still competitive when there are fewer samples or lower feature dimensions [23]. However, in the face of complex nonlinear temporal changes in micro-expressions, their expressive ability is relatively limited.
In recent years, more studies have focused on recognition methods based on AU modeling. FACS encodes facial expressions as a combination of actions in specific muscle areas, providing a stable foundation for the structured representation of micro-expressions. Structural modeling methods such as GNN can mine semantic and spatial dependencies between AUs and improve cross-cultural and cross-individual generalization capabilities [12,71]. This type of method is particularly suitable for scenarios with high interpretability requirements such as medical and psychological diagnosis, but because AU annotation relies on professionals, the cost of data acquisition is high.
In addition, keyframe modeling methods, such as using only Apex frames or constructing Onset–Apex differential features, reduce the computational burden while ensuring recognition efficiency, and are suitable for embedded environments with limited hardware resources. However, such methods often sacrifice some temporal information and have the risk of missed detection [41].
To solve problems such as sample scarcity and category imbalance, few sample learning methods such as twin networks and prototype networks have gradually been applied to micro-expression recognition in recent years. This type of method improves the generalization ability of the model through metric learning and still maintains a high recognition accuracy when only a small number of samples are provided [72]. At the same time, some studies have begun to introduce self-supervised learning and data enhancement strategies to alleviate label dependence.
5. Comparison and Analysis
Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5 present the comparative performance of representative algorithms on the CASME II, CAS(ME)3, and SMIC datasets, covering studies published between 2022 and 2024. These tables summarize the structural characteristics of the selected models together with their recognition accuracy and F1 scores on standard benchmark datasets.

Table 3.
Performance comparison on CASME II dataset.

Table 4.
Performance comparison on CAS(ME)3 dataset.

Table 5.
Performance comparison on SMIC dataset.
As shown in Table 3, OFF-ApexNet [63] employs optical flow differences between Onset and Apex frames combined with CNN architecture. On the CASME II dataset, it achieves an accuracy of 74.6% with an F1 score of 71.0%, representing a substantial improvement over earlier handcrafted feature methods such as LBP-TOP. The Two-Stream Difference Network (TSDN) [73], adopting a dual-stream spatiotemporal structure, achieves 71.5% accuracy and 70.2% F1, thereby outperforming conventional CNN-LSTM approaches. Furthermore, the Composite 3D-Fusion model [74], integrating STSTNet with three-dimensional convolutional features, improves recognition accuracy to 76.0% and F1 score to 73.5%, highlighting the effectiveness of 3D feature integration. With the growing adoption of Transformer-based frameworks, Micron-BERT [75] leverages a Tiny-BERT backbone with a self-attention mechanism and achieves 80.1% accuracy and 77.2% F1 on CASME II, demonstrating the potential of NLP-inspired architectures for micro-expression recognition.
According to Table 4, Transformer-based models also show superior performance on the CAS(ME)3 dataset. The Hierarchical Spatiotemporal Transformer (HSTA) [76] captures essential temporal dynamics of facial changes and achieves 83.7% accuracy and 81.0% F1. Building on graph-based modeling, ATM-GCN [77] incorporates action unit information within graph convolutional networks, attaining the best results so far with 85.0% accuracy and 82.4% F1. This model demonstrates particular advantages in representing structured facial dynamics across different subjects.
On the SMIC dataset (Table 5), models designed for small-sample and real-time scenarios have been proposed. The TSG-MER-ELL method [78], which employs graph attention with edge label learning, yields 77.9% accuracy and 76.5% F1, making it a suitable solution for online or interactive applications. Similarly, the MMM-Transformer [79], a multimodal and multi-scale Transformer framework, reports comparable performance (77.9% accuracy and 76.5% F1), indicating strong robustness under multimodal fusion.
6. Future Research Directions
As an important research direction in the field of affective computing, micro-expression recognition needs to rely on a richer data foundation for future development. Although the current mainstream data sets such as CASME II, SAMM and MMEW are representative, they still have shortcomings in terms of sample quantity, annotation consistency, emotion types and cultural diversity. In particular, the scarcity of spontaneous micro-expression samples collected in natural environments seriously restricts the generalization ability of the model. Therefore, future research can expand the data source through cross-cultural, multi-scene, and multi-ethnic methods, and introduce high-frame rate shooting and more advanced AU automatic annotation tools to reduce the burden of manual annotation [17].
Faced with the natural small sample characteristics of micro-expression data, deep learning methods urgently need to turn into a few-sample and self-supervised learning paths. In recent years, methods based on contrastive learning, meta-learning and generative adversarial networks (GANs) have received increasing attention. These technologies can mine the potential structure between images in the absence of labels and improve the quality of representation learning. In addition, combining micro-expression tasks with large-scale facial recognition or expression recognition pre-training tasks through transfer learning has also become an effective means to improve accuracy [80].
Single-modal visual information is often difficult to fully portray complex emotions, and future research should pay more attention to multimodal fusion. Multimodal emotion recognition that combines voice, intonation, language text, and physiological signals (such as electrocardiogram, electroencephalogram, and skin galvanic response) is gradually becoming a trend. For example, some studies have tried to synchronize micro-expressions with electroencephalogram signals to identify subjects’ hidden anxiety, depression, and other states, effectively enhancing the robustness of the model and the ability to interpret emotions [81]. The integration of multimodal technologies is expected to promote the transition from “recognition” to “understanding” emotions.
In addition, future research should strengthen the connection between micro-expression recognition and downstream emotion inference. Detecting and recognizing micro-expressions is not equivalent to emotion recognition but rather provides critical cues that can be mapped to higher-level affective states. For example, Malik et al. [82] proposed an action unit-based micro-expression recognition framework, which demonstrates how localized facial activations can serve as intermediaries for emotion classification. This highlights the necessity of integrating micro-expression detection with emotion modeling to achieve a more complete understanding of human affective behavior, especially in practical applications such as psychological research, lie detection, and security monitoring.
Most micro-expression recognition methods remain under laboratory control conditions and lack the robustness of actual deployment. Light changes, head posture deflection, occlusion, and background interference in natural scenes can significantly weaken the recognition effect. Therefore, the design of micro-expression recognition systems for “wild environments” needs to be strengthened, such as introducing multi-scale face tracking mechanisms, attention masking techniques, and robust feature alignment strategies. The Adaptive Attention mechanism proposed in the latest research can effectively filter environmental noise and focus on key areas, improving performance in natural scenes [83].
The deep model structure needs to strike a balance between accuracy and computational efficiency while enhancing interpretability. For instance, although Transformer-based models demonstrate superior capabilities in modeling long-range dependencies, their high computational cost limits their applicability in real-time systems and edge devices. As a result, lightweight architectures such as MobileViT and TinyFormer have attracted increasing attention in recent research [84]. Moreover, interpretability has become a vital consideration in domains like security and psychological analysis. Recent efforts have explored visual attention mechanisms and causal inference frameworks to improve model transparency and explainability [85].
Establishing standardized evaluation protocols is essential for ensuring comparability and reproducibility in micro-expression recognition research. A major challenge in the current literature is the inconsistency in dataset partitioning strategies and evaluation metrics, which hampers cross-study benchmarking. Drawing inspiration from the action recognition community, future work could adopt cross-subject and cross-dataset validation schemes to comprehensively assess model generalizability and robustness. Some researchers have advocated for the creation of a unified evaluation framework and publicly maintained leaderboards to support long-term innovation and benchmarking in this field [41].
7. Conclusions
Micro-expression recognition technology has made significant progress, especially in AU modeling, key frame modeling, and few-shot learning. The AU method based on the FACS improves cross-cultural and individual generalization capabilities by structurally representing facial muscle movements and mining semantic and spatial dependencies with the help of graph neural networks. It is especially suitable for medical and psychological diagnosis fields with high interpretability requirements, but the high cost of professional annotation limits its large-scale application. The key frame method reduces computational overhead while ensuring recognition efficiency. It is suitable for embedded environments with limited hardware resources, but there is a risk of partial temporal information loss. In response to data scarcity and category imbalance, few-shot learning methods based on metric learning have gradually become a hot topic, effectively enhancing the generalization ability of the model. At the same time, self-supervised learning and data enhancement strategies also play a role in alleviating annotation dependence.
Comparative analysis shows that deep learning models, especially 3D-CNN, hybrid convolutional loop structures, and Transformer models that integrate spatiotemporal information, have become the mainstream of micro-expression recognition, showing better accuracy and cross-dataset generalization capabilities than traditional optical flow or manual feature methods. Transformer architecture has driven performance improvements in this field with its powerful long-distance dependency modeling and attention mechanism. Graph neural networks have also made important breakthroughs in structured dynamic modeling, further enhancing the model’s ability to express complex facial movements. In addition, for real-time and small sample scenarios, graph attention mechanisms and multimodal contrastive learning methods have shown strong robustness and recognition capabilities.
Future micro-expression recognition research urgently needs rich and diverse data sets, especially high-quality spontaneous micro-expression samples covering cross-cultural, multi-scenario, and natural environments, combined with high-frame rate shooting and automated AU annotation technology to reduce labor costs. Faced with the natural small sample characteristics of micro-expression data, it is imperative to develop technologies such as a few samples, self-supervision, contrastive learning, and generative adversarial networks. The integration of multimodal information, including physiological signals such as speech, language, and EEG, facilitates the shift from mere emotion recognition to a deeper understanding of emotional states. System design needs to strengthen its adaptability to complex outdoor environments and improve practicality through technologies such as multi-scale face tracking, attention masking, and robust feature alignment.
In addition, the model architecture needs to strike a balance between accuracy, computational efficiency, and interpretability, and lightweight Transformer structures and interpretability mechanisms have become research focuses. Finally, a unified and standardized evaluation protocol and public rankings are of great significance for promoting continuous innovation and fair comparison in the field of micro-expression recognition.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.S. and S.B.; methodology, T.S.; software, T.S.; validation, T.S., S.B. and F.B.K.; formal analysis, T.S.; investigation, T.S.; resources, T.S.; data curation, T.S.; writing—original draft preparation, T.S.; writing—review and editing, T.S.; visualization, T.S.; supervision, R.W.B.O.K.R.; project administration, R.W.B.O.K.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data is available in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| METT | Micro-Expression Training Tool |
| LBP | Local Binary Patterns |
| MDMO | Multi-directional motion feature descriptor |
| CNN | Convolutional neural networks |
| AU | Action Unit |
| FACS | Facial Action Coding System |
| LSTM | long short-term memory networks |
| 3DCNN | Three-dimensional convolutional neural networks |
| RNN | Recurrent neural network |
| ViT | Vision Transformer |
| LBP-TOP | Local binary pattern three orthogonal planes |
| HOOF | Histogram of Oriented Optical Flow |
| KNN | K-nearest neighbor |
| GNNs | Graph neural networks |
| LOSO | Leave-one-subject-out |
| TSDN | Two-Stream Difference Network |
| HSTA | Hierarchical Space-Time Attention |
| GANs | Generative adversarial networks |
References
- Xia, B.; Wang, W.; Wang, S.; Chen, E. Learning from macro-expression: A micro-expression recognition framework. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Online, 12–16 October 2020; pp. 2936–2944. [Google Scholar]
- Ekman, P.; Friesen, W.V. Nonverbal leakage and clues to deception. Psychiatry 1969, 32, 88–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, S.; Ten Brinke, L. Reading between the lies: Identifying concealed and falsified emotions in universal facial expressions. Psychol. Sci. 2008, 19, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekman, P. Micro Expressions Training Tool. Available online: https://www.paulekman.com/micro-expressions-training-tools/ (accessed on 18 June 2025).
- Frank, M.G.; Ekman, P.; Friesen, W.V. Behavioral markers and recognizability of the smile of enjoyment. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1993, 64, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, M.A.; Hossain, M.N.; Wahid, T.; Azam, M.S. Face recognition using local binary patterns (LBP). Int. Res. J. 2013, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Dalal, N.; Triggs, B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 886–893. [Google Scholar]
- Ben, X.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.-J.; Kpalma, K.; Meng, W.; Liu, Y.-J. Video-based facial micro-expression analysis: A survey of datasets, features and algorithms. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 5826–5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Pietikainen, M. Dynamic texture recognition using local binary patterns with an application to facial expressions. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2007, 29, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liong, S.-T.; Phan, R.C.-W.; See, J.; Oh, Y.-H.; Wong, K. Optical strain based recognition of subtle emotions. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Symposium on Intelligent Signal Processing and Communication Systems (ISPACS), Kuching, Malaysia, 1–4 December 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 180–184. [Google Scholar]
- Ben, X.; Zhang, P.; Yan, R.; Yang, M.; Ge, G. Gait recognition and micro-expression recognition based on maximum margin projection with tensor representation. Neural Comput. Appl. 2016, 27, 2629–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khor, H.-Q.; See, J.; Phan, R.C.W.; Lin, W. Enriched long-term recurrent convolutional network for facial micro-expression recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), Xi’an, China, 22–26 May 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 667–674. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, S.P.T.; Karri, S.T.; Dubey, S.R.; Mukherjee, S. Spontaneous facial micro-expression recognition using 3D spatiotemporal convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Budapest, Hungary, 14–19 July 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Luo, W.; Sankaranarayana, R. Htnet for micro-expression recognition. Neurocomputing 2024, 602, 128196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.-J.; Li, X.; Wang, S.-J.; Zhao, G.; Liu, Y.-J.; Chen, Y.-H.; Fu, X. CASME II: An improved spontaneous micro-expression database and the baseline evaluation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hong, X.; Moilanen, A.; Huang, X.; Pfister, T.; Zhao, G.; Pietikainen, M. Reading hidden emotions: Spontaneous micro-expression spotting and recognition. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2015, 2, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Davison, A.K.; Lansley, C.; Costen, N.; Tan, K.; Yap, M.H. Samm: A spontaneous micro-facial movement dataset. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2016, 9, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Ling, M.; Tang, J.; Hu, J.J.V.R. A micro-expression recognition algorithm based on feature enhancement and attention mechanisms. Virtual Real. 2023, 27, 2405–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, T. From macro to micro expression recognition: Deep learning on small datasets using transfer learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), Xi’an, China, 15–19 May 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 657–661. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Lv, Y.; Huang, Z. Multimodal fusion-based swin transformer for facial recognition micro-expression recognition. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Guilin, China, 7–10 August 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 780–785. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, Y.-H.; See, J.; Le Ngo, A.C.; Phan, R.C.-W.; Baskaran, V.M. A survey of automatic facial micro-expression analysis: Databases, methods, and challenges. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, K.M.; Ng, C.H.; Lim, L.L.; Sheikh, U.U. Micro-expression recognition: An updated review of current trends, challenges and solutions. Vis. Comput. 2020, 36, 445–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.-J.; Wu, Q.; Liang, J.; Chen, Y.-H.; Fu, X. How fast are the leaked facial expressions: The duration of micro-expressions. J. Nonverbal Behav. 2013, 37, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekman, P. Telling Lies: Clues to Deceit in the Marketplace, Politics, and Marriage; Revised Edition; WW Norton & Company: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pfister, T.; Li, X.; Zhao, G.; Pietikäinen, M. Recognising spontaneous facial micro-expressions. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 1449–1456. [Google Scholar]
- Ekman, P.; Friesen, W.V. Facial Action Coding System; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Lucey, P.; Cohn, J.F.; Kanade, T.; Saragih, J.; Ambadar, Z.; Matthews, I. The extended cohn-kanade dataset (ck+): A complete dataset for action unit and emotion-specified expression. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition-Workshops, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Hong, X.; Moilanen, A.; Huang, X.; Pfister, T.; Zhao, G.; Pietikainen, M. Towards reading hidden emotions: A comparative study of spontaneous micro-expression spotting and recognition methods. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2017, 9, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hong, X.; Arandjelović, O.; Zhao, G. Short and long range relation based spatio-temporal transformer for micro-expression recognition. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2022, 13, 1973–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pfister, T.; Huang, X.; Zhao, G.; Pietikäinen, M. A spontaneous micro-expression database: Inducement, collection and baseline. In Proceedings of the 2013 10th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG), Shanghai, China, 22–26 April 2013; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, W.-J.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Y.-J.; Wang, S.-J.; Fu, X. CASME database: A dataset of spontaneous micro-expressions collected from neutralized faces. In Proceedings of the 2013 10th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG), Shanghai, China, 22–26 April 2013; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, F.; Wang, S.-J.; Yan, W.-J.; Fu, X. CAS (ME) 2: A Database of Spontaneous Macro-expressions and Micro-expressions. In Proceedings of the Human-Computer Interaction Novel User Experiences: 18th International Conference, HCI International 2016, Toronto, ON, Canada, 17–22 July 2016; Proceedings, Part III 18. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 48–59. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, T.-K.; Vo, Q.-N.; Hong, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, G. Micro-expression spotting: A new benchmark. Neurocomputing 2021, 443, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yap, M.H.; Cheng, W.-H.; See, J.; Hong, X.; Li, X.; Hong, X.; Wang, S.-J. MEGC2022: ACM multimedia 2022 micro-expression grand challenge. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisbon, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; pp. 7170–7174. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, D.; Zhao, G.; Pietikäinen, M. Spatiotemporal integration of optical flow vectors for micro-expression detection. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems, Catania, Italy, 26–29 October 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 369–380. [Google Scholar]
- Takalkar, M.; Xu, M.; Wu, Q.; Chaczko, Z. A survey: Facial micro-expression recognition. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 19301–19325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, Z.; Dong, Y.; Guo, S.; Leung, V.; Deen, M.J.; Hu, X. Facial Expression Analysis and Its Potentials in IoT Systems: A Contemporary Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2024, 58, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.; Vipparthi, S.K.; Singh, G. Deep insights of learning-based micro expression recognition: A perspective on promises, challenges, and research needs. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2022, 15, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Wang, S.-J.; Yan, W.-J.; Li, H.; Wu, S.; Fu, X. CAS (ME)2: A database for spontaneous macro-expression and micro-expression spotting and recognition. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2017, 9, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Pietikäinen, M. Facial micro-expressions: An overview. Proc. IEEE 2023, 111, 1215–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liong, S.-T.; See, J.; Wong, K.; Phan, R.C.-W. Less is more: Micro-expression recognition from video using apex frame. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2018, 62, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-J.; Zhang, J.-K.; Yan, W.-J.; Wang, S.-J.; Zhao, G.; Fu, X. A main directional mean optical flow feature for spontaneous micro-expression recognition. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2015, 7, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clocksin, W.F.; da Fonseca, J.Q.; Withers, P.; Torr, P.H. Image processing issues in digital strain mapping. In Proceedings of the Applications of Digital Image Processing XXV, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–11 July 2002; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2002; pp. 384–395. [Google Scholar]
- Singla, N. Motion detection based on frame difference method. Int. J. Inf. Comput. Technol. 2014, 4, 1559–1565. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, T.-K.; Hong, X.; Zhao, G. Sliding window based micro-expression spotting: A benchmark. In Proceedings of the Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems: 18th International Conference, ACIVS 2017, Antwerp, Belgium, 18–21 September 2017; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 542–553. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Sun, S.; Chen, J. Deep Learning-Based Micro-Expression Recognition Algorithm Research. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. 2024, 2, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lades, M.; Vorbruggen, J.C.; Buhmann, J.; Lange, J.; Von Der Malsburg, C.; Wurtz, R.P.; Konen, W. Distortion invariant object recognition in the dynamic link architecture. IEEE Trans. Comput. 1993, 42, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polikovsky, S.; Kameda, Y.; Ohta, Y. Facial micro-expressions recognition using high speed camera and 3D-gradient descriptor. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Imaging for Crime Detection and Prevention (ICDP 2009), London, UK, 1–2 September 2009; IET: Stevenage, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Shreve, M.; Godavarthy, S.; Goldgof, D.; Sarkar, S. Macro-and micro-expression spotting in long videos using spatio-temporal strain. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG), Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 21–25 March 2011; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Jia, J.; Mao, N. Micro-expression recognition based on 2D-3D CNN. In Proceedings of the 2020 39th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Shenyang, China, 27–29 July 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 3152–3157. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, D.; Bourdev, L.; Fergus, R.; Torresani, L.; Paluri, M. Learning spatiotemporal features with 3d convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 4489–4497. [Google Scholar]
- Donahue, J.; Anne Hendricks, L.; Guadarrama, S.; Rohrbach, M.; Venugopalan, S.; Saenko, K.; Darrell, T. Long-term recurrent convolutional networks for visual recognition and description. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 2625–2634. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Liong, S.-T.; See, J.; Wong, K.; Le Ngo, A.C.; Oh, Y.-H.; Phan, R. Automatic apex frame spotting in micro-expression database. In Proceedings of the 2015 3rd IAPR Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition (ACPR), Lille, France, 14–18 May 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 665–669. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Z.; Hong, X.; Gao, X.; Feng, X.; Zhao, G. Corrections to “spatiotemporal recurrent convolutional networks for recognizing spontaneous micro-expressions”. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 2020, 22, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Tian, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhang, X. Micro-expression recognition based on local binary patterns from three orthogonal planes and nearest neighbor method. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Beijing, China, 6–11 July 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 3473–3479. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Yu, J.; Kurihara, T.; Zhang, H.; Zhan, S. Deep convolutional neural network with optical flow for facial micro-expression recognition. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 2020, 29, 2050006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Long, F.; Huang, J.; Li, J. Micro-expression recognition based on spatiotemporal Gabor filters. In Proceedings of the 2018 Eighth International Conference on Information Science and Technology (ICIST), Kaifeng, China, 24–26 March 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 487–491. [Google Scholar]
- Cover, T.; Hart, P. Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1967, 13, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happy, S.; Routray, A. Automatic facial expression recognition using features of salient facial patches. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2014, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.S.; Liong, S.-T.; Yau, W.-C.; Huang, Y.-C.; Tan, L.-K. OFF-ApexNet on micro-expression recognition system. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2019, 74, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liong, S.-T.; Gan, Y.S.; See, J.; Khor, H.-Q.; Huang, Y.-C. Shallow triple stream three-dimensional cnn (ststnet) for micro-expression recognition. In Proceedings of the 2019 14th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2019), Lille, France, 14–18 May 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Carreira, J.; Zisserman, A. Quo vadis, action recognition? A new model and the kinetics dataset. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6299–6308. [Google Scholar]
- Qingqing, W. Micro-expression recognition method based on CNN-LSTM hybrid network. Int. J. Wirel. Mob. Comput. 2022, 23, 67–77. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Toisoul, A.; Perez-Rua, J.-M.; Zhang, L.; Martinez, B.; Xiang, T. Few-shot action recognition with prototype-centered attentive learning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.08085. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Vorobeychik, Y. Proceedings of the 30th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. In Proceedings of the AAAI Palo Alto, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 12–17 February 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Peng, W.; Zhao, G. Micro-expression action unit detection with dual-view attentive similarity-preserving knowledge distillation. In Proceedings of the 2021 16th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG 2021), Jodhpur, India, 15–19 December 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, H.; Provost, E.M. Deep learning for robust feature generation in audiovisual emotion recognition. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–31 May 2013; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 3687–3691. [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett, M.S.; Littlewort, G.; Frank, M.G.; Lainscsek, C.; Fasel, I.R.; Movellan, J.R. Automatic recognition of facial actions in spontaneous expressions. J. Multimed. 2006, 1, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopalidis, T.; Solachidis, V.; Vretos, N.; Daras, P. Advances in facial expression recognition: A survey of methods, benchmarks, models, and datasets. Information 2024, 15, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Xie, L.; Li, J.; Lv, Z.; Wang, Z. Micro-expression recognition by two-stream difference network. IET Comput. Vis. 2021, 15, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomathi, R.; Logeswari, S.; Jothimani, S.N.; Sangeethaa, S.; Sangeetha, A.; LathaJothi, V. MEFNet-Micro Expression Fusion Network Based on Micro-Attention Mechanism and 3D-CNN Fusion Algorithms. Int. J. Intell. Eng. Syst. 2023, 16, 113. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, X.-B.; Duong, C.N.; Li, X.; Gauch, S.; Seo, H.-S.; Luu, K. Micron-bert: Bert-based facial micro-expression recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 1482–1492. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, F.; Wang, Y.-G.; Tang, W.; Zhu, G.; Kwong, S. Starvqa+: Co-training space-time attention for video quality assessment. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.12298. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, W.; Nielsen, T.D.; Zhao, Y.; Larsen, K.G.; Yu, J. Uncertainty-aware temporal graph convolutional network for traffic speed forecasting. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 8578–8590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Kim, B.-G.; Slowik, A.; Pan, D. Temporal–spatial correlation and graph attention-guided network for micro-expression recognition in English learning livestreams. Discov. Comput. 2024, 27, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, J.; Qi, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, P. Multi-scale multi-modal micro-expression recognition algorithm based on transformer. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.02969. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J.; Genovese, A.; Piuri, V.; Scotti, F. Few-Shot Steel Surface Defect Recognition via Self-Supervised Teacher–Student Model with Min–Max Instances Similarity. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 5026016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; Leng, Q.; Zhao, X. Deep learning-based multimodal emotion recognition from audio, visual, and text modalities: A systematic review of recent advancements and future prospects. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 237, 121692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, P.; Singh, J.; Ali, F.; Sehra, S.S.; Kwak, D. Action unit based micro-expression recognition framework for driver emotional state detection. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 27824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- bin Talib, H.K.; Xu, K.; Cao, Y.; Xu, Y.P.; Xu, Z.; Zaman, M.; Akhunzada, A. Micro-Expression Recognition using Convolutional Variational Attention Transformer (ConVAT) with Multihead Attention Mechanism. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 20054–20070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chefer, H.; Gur, S.; Wolf, L. Transformer interpretability beyond attention visualization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 782–791. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, S.; Rastegari, M. Mobilevit: Lightweight, general-purpose, and mobile-friendly vision transformer. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.02178. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).