TFI-Fusion: Hierarchical Triple-Stream Feature Interaction Network for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
Our Contribution
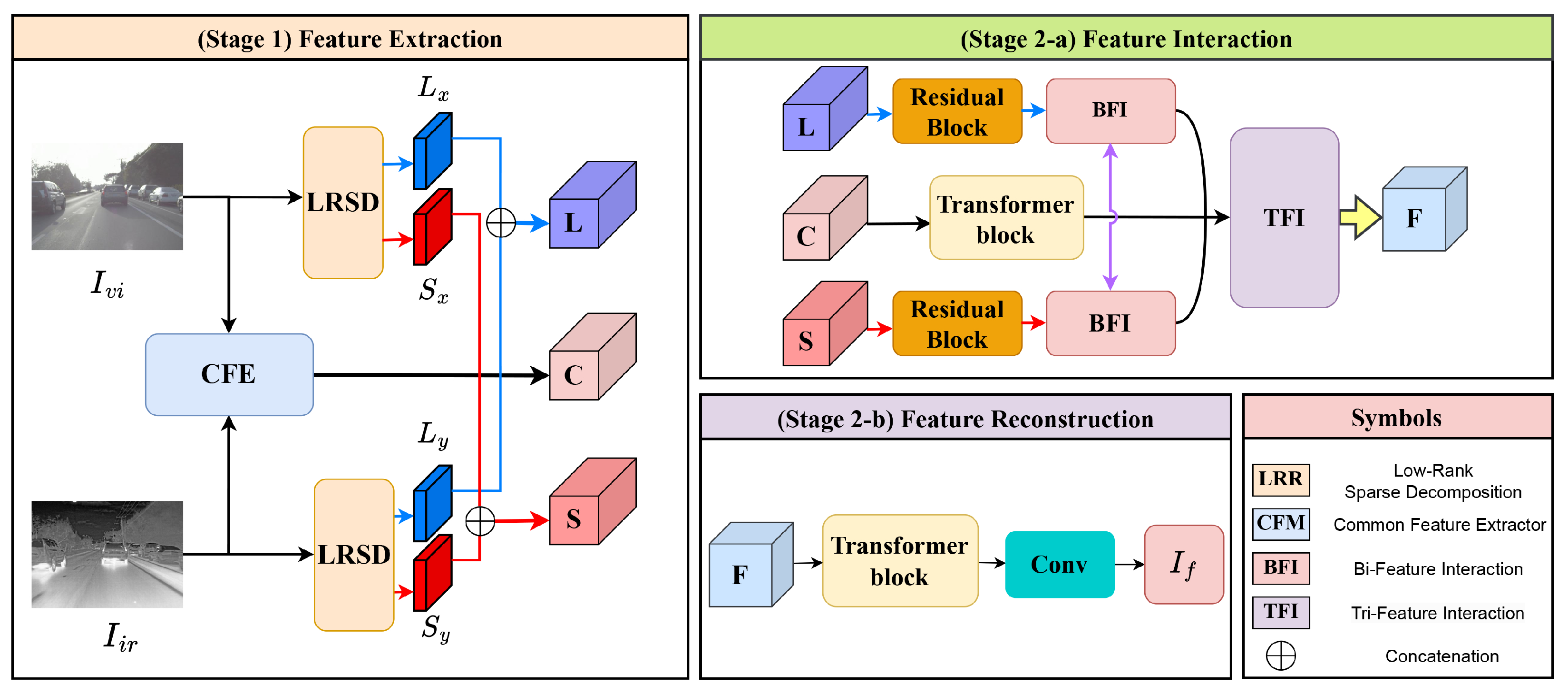
- This study proposes a Hierarchical Triple-Feature Interaction Fusion Network (TFI-Fusion) with a three-stage architecture for high-quality infrared-visible image fusion.
- This study employs Low-Rank Sparse Decomposition (LRSD) and a Shared Feature Extractor (SFE) to decouple and extract structural, detailed, and cross-modal features.
- This study designs Bi-Feature Interaction (BFI) and Triple-Feature Interaction (TFI) modules to achieve dynamic multi-level feature fusion via cross-attention mechanisms.
- This study builds a Swin Transformer-based reconstruction module, combining global attention and local convolution for detail preservation.
- This study introduces a multi-objective loss (structural/Charbonnier/cosine similarity) to enhance fusion performance through end-to-end training.
2. Related Work
2.1. Sparse Representation Methods
2.2. CNN-Based Methods
2.3. Transformer-Based Methods
3. Method
3.1. Overall Architecture
3.2. Phase 1 Feature Extraction
3.2.1. Low-Rank Sparse Decomposition Module
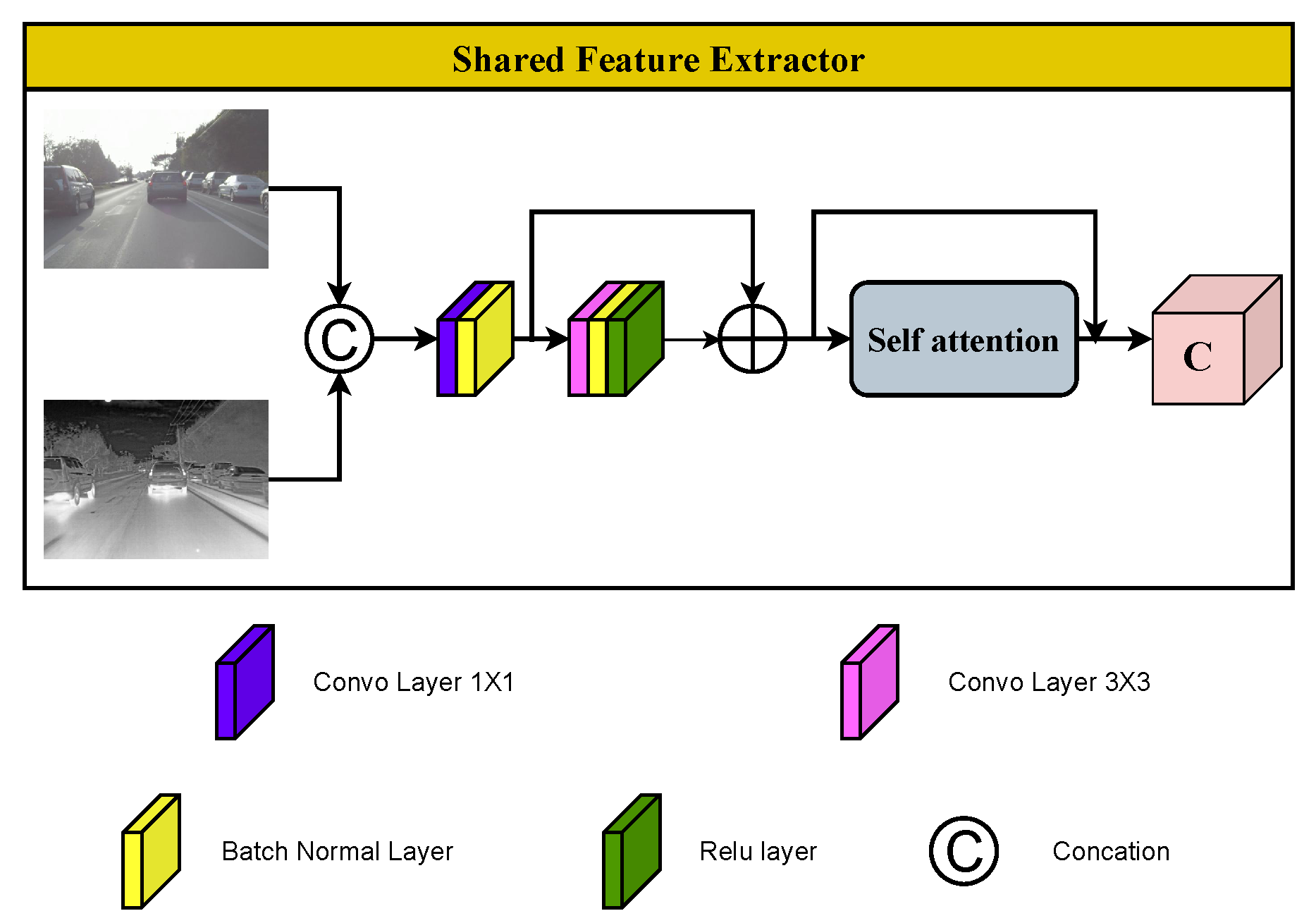
3.2.2. Shared Feature Extractor (SFE) Module
3.3. Phase 2(a) Feature Interaction
3.3.1. Bi-Feature Interaction
3.3.2. Tri-Feature Interaction
3.4. Phase 2(b) Feature Reconstruction
3.5. The Loss Function
4. Experiments
4.1. Training Dataset and Settings
4.2. Testing Datasets
- KAIST Test Set: Two hundred pairs of images not used in training were randomly selected from the KAIST dataset for testing. These image pairs have a resolution of 640 × 512 and cover various complex scenes, effectively validating the model’s performance within the training data distribution.
- TNO Dataset: This dataset contains aligned multispectral nighttime images of different military-related scenes, with resolutions ranging from 280 × 280 to 768 × 576. The test set used in this study includes 20 image pairs, which are employed to evaluate the model’s performance under low-light and complex environmental conditions.
- RoadScene Dataset: This dataset consists of 221 aligned image pairs with resolutions as high as 563 × 459, captured using real-world cameras. These images were selected from the FLIR dataset provided by Xu et al. [48], enabling the validation of the model’s generalization capability in practical application scenarios.
4.3. Quantitative Experiments
4.4. Qualitive Experiments
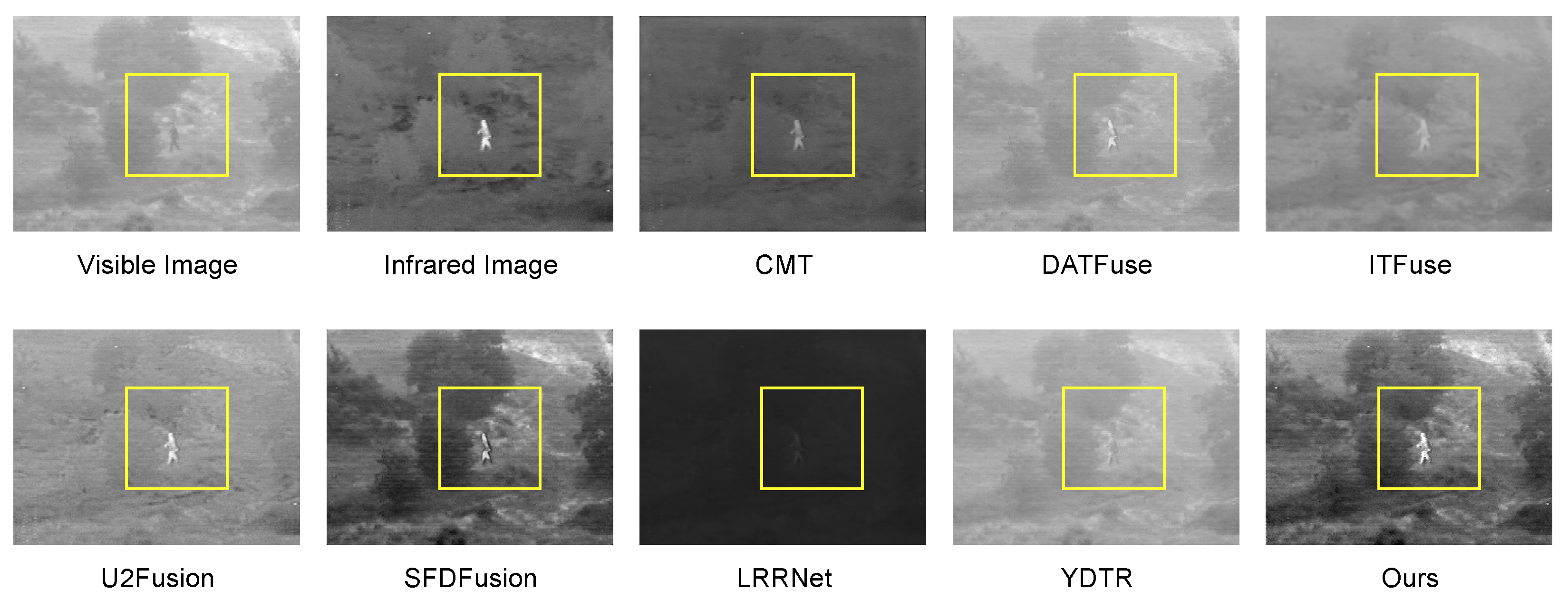



4.5. Efficiency Experiments
4.6. Ablation Study
5. Discussion
6. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meher, B.; Agrawal, S.; Panda, R.; Abraham, A. A survey on region based image fusion methods. Inf. Fusion 2019, 48, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Xiao, Z.; Yao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, Z. Stereo video super-resolution via exploiting view-temporal correlations. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Virtual, 20–24 October 2021; pp. 460–468. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Vien, A.G.; Lee, C. Cross-modal transformers for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 770–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Tian, X.; Jiang, J.; Ma, J. Image fusion meets deep learning: A survey and perspective. Inf. Fusion 2021, 76, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Bai, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Lin, Z.; Timofte, R.; Van Gool, L. Cddfuse: Correlation-driven dual-branch feature decomposition for multi-modality image fusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 5906–5916. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, C. Infrared and visible image fusion methods and applications: A survey. Inf. Fusion 2019, 45, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, H. CAIF: Cross-Attention Framework in Unaligned Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. In Proceedings of the 2024 4th International Conference on Computer Science and Blockchain (CCSB), Shenzhen, China, 6–8 September 2024; pp. 266–270. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Li, X.; Luo, L.; Mei, X.; Ma, J. Infrared and visible image fusion based on target-enhanced multiscale transform decomposition. Inf. Sci. 2020, 508, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, B.; Hu, J. Performance comparison of different multi-resolution transforms for image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2011, 12, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Yin, H.; Chai, Y.; Li, Y.; Qi, G. A novel multi-modality image fusion method based on image decomposition and sparse representation. Inf. Sci. 2018, 432, 516–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Xu, S.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Li, P.; Zhang, J. DIDFuse: Deep image decomposition for infrared and visible image fusion. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.09210. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Lian, Y.; Wang, K.; Ma, C.; Xu, X. Unsupervised hybrid network of transformer and CNN for blind hyperspectral and multispectral image fusion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5507615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ma, J.; Jiang, J.; Guo, X.; Ling, H. U2Fusion: A unified unsupervised image fusion network. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 44, 502–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wu, S.; Ma, L. Adversarial attacks on GAN-based image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2024, 108, 102389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fan, X.; Huang, Z.; Wu, G.; Liu, R.; Zhong, W.; Luo, Z. Target-aware dual adversarial learning and a multi-scenario multi-modality benchmark to fuse infrared and visible for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5802–5811. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, C.; Yang, G.; Hong, D.; Wang, H.; Yao, J.; Atkinson, P.M.; Ghamisi, P. IG-GAN: Interactive guided generative adversarial networks for multimodal image fusion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5634719. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.; He, F.; Liu, Y. ITFuse: An interactive transformer for infrared and visible image fusion. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 156, 110822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; He, F. FATFusion: A functional–anatomical transformer for medical image fusion. Inf. Process. Manag. 2024, 61, 103687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Li, S. Multifocus image fusion and restoration with sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2009, 59, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Yang, F.; Huang, J. Deep sparse representation for robust image registration. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 4894–4901. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Peng, H.; Wang, Z. Multi-focus image fusion with a deep convolutional neural network. Inf. Fusion 2017, 36, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.J. DenseFuse: A fusion approach to infrared and visible images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 2614–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, R.; Zhou, D.; Nie, R.; Liu, D.; Xiong, L.; Guo, Y.; Yu, C. VIF-Net: An unsupervised framework for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2020, 6, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, Z.; Jeon, G.; Gao, M.; Chisholm, D. SEDRFuse: A symmetric encoder–decoder with residual block network for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 70, 5002215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, X.; Ma, J. DRF: Disentangled representation for visible and infrared image fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 5006713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Ma, J. Classification saliency-based rule for visible and infrared image fusion. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2021, 7, 824–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.J.; Kittler, J. RFN-Nest: An end-to-end residual fusion network for infrared and visible images. Inf. Fusion 2021, 73, 72–86. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Liu, J.; Fan, X.; Liu, R. Unsupervised misaligned infrared and visible image fusion via cross-modality image generation and registration. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.11876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, J.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Q.; Kasabov, N.K. Infrared and visible image fusion based on residual dense network and gradient loss. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2023, 128, 104486. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the NIPS’17: 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Tang, L.; Fan, F.; Huang, J.; Mei, X.; Ma, Y. SwinFusion: Cross-domain long-range learning for general image fusion via swin transformer. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2022, 9, 1200–1217. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Chen, W.; Qiu, Q.; Chen, L.; Wu, B.; Lin, B.; He, X.; Liu, W. Crossformer++: A versatile vision transformer hinging on cross-scale attention. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 46, 3123–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Yang, K.; Hu, X.; Liu, R.; Stiefelhagen, R. CMX: Cross-modal fusion for RGB-X semantic segmentation with transformers. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 14679–14694. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Shao, F.; Chen, G.; Chen, H.; Jiang, Q.; Meng, X.; Ho, Y.S. Cross-modality double bidirectional interaction and fusion network for RGB-T salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 4149–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Liu, Z.; Tan, Y.; He, Q. HRTransNet: HRFormer-driven two-modality salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 33, 728–742. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Liu, T.; Wang, X.; Tao, D. On compressing deep models by low rank and sparse decomposition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7370–7379. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Zhao, E.; Zheng, W.; Peng, X.; Niu, W.; Yang, Z. Infrared small target detection via two-stage feature complementary improved tensor low-rank sparse decomposition. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 17690–17709. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Cheng, D.; Wang, N.; Gao, X. Exploring homogeneous and heterogeneous consistent label associations for unsupervised visible-infrared person reid. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2025, 133, 3129–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, D. Scene classification based on the sparse homogeneous–heterogeneous topic feature model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 2689–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, T.; Wu, X.J.; Lu, J.; Kittler, J. Lrrnet: A novel representation learning guided fusion network for infrared and visible images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 11040–11052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Draganov, A.; Vadgama, S.; Bekkers, E.J. The hidden pitfalls of the cosine similarity loss. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.16468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourbakhsh Kaashki, N.; Hu, P.; Munteanu, A. ANet: A Deep Neural Network for Automatic 3D Anthropometric Measurement Extraction. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 24, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y. The Level Weighted Structural Similarity Loss: A Step Away from MSE. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.13362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Metaxas, D.N. Multispectral pedestrian detection: Benchmark dataset and baseline. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2016; pp. 1037–1045. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.; Ma, J. PIA-Fusion: A Progressive Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Network Based on Illumination Aware. Inf. Fusion 2022, 83–84, 79–91. [Google Scholar]
- Toet, A. The TNO Multiband Image Data Collection. Data Brief 2017, 15, 249–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Ma, J.; Le, Z.l.; Jiang, J.; Guo, X. Fusion-DN: A Unified Densely Connected Network for Image Fusion. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Fourth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.; He, F.; Liu, Y.; Duan, Y.; Si, T. DATFuse: Infrared and Visible Image Fusion via Dual Attention Transformer. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 3159–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; He, F.; Liu, Y. YDTR: Infrared and Visible Image Fusion via Y-Shaped Dynamic Transformer. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 25, 5413–5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, Y. SFDFusion: An efficient spatial-frequency domain fusion network for infrared and visible image fusion. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.22837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studholme, C.; Hawkes, D.J.; Hill, D.L. Normalized entropy measure for multimodality image alignment. In Proceedings of the SPIE Medical Imaging, San Diego, CA, USA, 21–26 February 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Simoncelli, E.P.; Bovik, A.C. Multiscale structural similarity for image quality assessment. In Proceedings of the Thrity-Seventh Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems & Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 9–12 November 2003. [Google Scholar]


| Method | NMI ↑ | MS_SSIM ↑ | EN ↑ | Qabf ↑ | SD ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMT | 0.306 | 0.890 | 6.035 | 0.476 | 30.090 |
| DATFuse | 0.512 | 0.923 | 6.581 | 0.501 | 39.846 |
| ITFuse | 0.334 | 0.896 | 6.188 | 0.452 | 23.508 |
| LRRNet | 0.337 | 0.709 | 4.436 | 0.344 | 21.444 |
| U2Fusion | 0.299 | 0.946 | 6.652 | 0.389 | 29.523 |
| YDTR | 0.374 | 0.681 | 6.439 | 0.451 | 28.784 |
| SFDFusion | 0.651 | 0.934 | 7.146 | 0.547 | 45.843 |
| Ours | 0.586 | 0.951 | 7.241 | 0.562 | 46.021 |
| Method | NMI ↑ | MS_SSIM ↑ | EN ↑ | Qabf ↑ | SD ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMT | 0.396 | 0.878 | 6.395 | 0.398 | 32.638 |
| DATFuse | 0.531 | 0.883 | 6.726 | 0.502 | 39.570 |
| ITFuse | 0.386 | 0.903 | 6.322 | 0.225 | 30.715 |
| LRRNet | 0.340 | 0.753 | 4.595 | 0.228 | 26.963 |
| U2Fusion | 0.374 | 0.892 | 6.862 | 0.464 | 36.579 |
| YDTR | 0.441 | 0.691 | 6.777 | 0.452 | 33.326 |
| SFDFusion | 0.654 | 0.950 | 7.376 | 0.457 | 55.892 |
| Ours | 0.593 | 0.972 | 7.430 | 0.517 | 56.661 |
| Method | NMI ↑ | MS_SSIM ↑ | EN ↑ | Qabf ↑ | SD ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMT | 0.340 | 0.884 | 5.561 | 0.311 | 26.133 |
| DATFuse | 0.643 | 0.911 | 6.384 | 0.627 | 35.562 |
| ITFuse | 0.456 | 0.909 | 5.805 | 0.232 | 24.668 |
| LRRNet | 0.433 | 0.732 | 3.805 | 0.217 | 20.597 |
| U2Fusion | 0.331 | 0.900 | 5.151 | 0.452 | 23.897 |
| YDTR | 0.450 | 0.884 | 5.521 | 0.348 | 24.072 |
| SFDFusion | 0.813 | 0.943 | 6.570 | 0.680 | 42.891 |
| Ours | 0.817 | 0.962 | 6.601 | 0.677 | 43.385 |
| Method | Time (ms) | Params (M) | FLOPs (G) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CMT | 37.24 | 1.27 | 5.67 |
| DATFuse | 10.3 | 0.01 | 5.04 |
| ITFuse | 11.08 | 0.02 | 4.43 |
| LRRNet | 11.18 | 0.05 | 4.86 |
| U2Fusion | 60.23 | 0.66 | 79.21 |
| YDTR | 9.19 | 0.11 | 17.4 |
| SFDFusion | 1.26 | 0.14 | 6.99 |
| Ours | 7.80 | 0.33 | 26.98 |
| Method | NMI ↑ | MS_SSIM ↑ | EN ↑ | Qabf ↑ | SD ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| One-stream input | 0.551 | 0.739 | 6.328 | 0.342 | 34.847 |
| Two-stream input | 0.671 | 0.758 | 6.411 | 0.417 | 35.412 |
| w/o LRSD | 0.772 | 0.879 | 6.883 | 0.539 | 41.286 |
| w/o BFI | 0.710 | 0.789 | 6.731 | 0.548 | 40.216 |
| w/o TFI | 0.768 | 0.863 | 6.831 | 0.552 | 41.490 |
| TotalNet | 0.817 | 0.962 | 7.130 | 0.617 | 43.315 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, M.; Su, S.; Li, H. TFI-Fusion: Hierarchical Triple-Stream Feature Interaction Network for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. Information 2025, 16, 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16100844
Zhao M, Su S, Li H. TFI-Fusion: Hierarchical Triple-Stream Feature Interaction Network for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. Information. 2025; 16(10):844. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16100844
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Mingyang, Shaochen Su, and Hao Li. 2025. "TFI-Fusion: Hierarchical Triple-Stream Feature Interaction Network for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion" Information 16, no. 10: 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16100844
APA StyleZhao, M., Su, S., & Li, H. (2025). TFI-Fusion: Hierarchical Triple-Stream Feature Interaction Network for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. Information, 16(10), 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16100844






