Abstract
Brain tumour disease develops due to abnormal cell proliferation. The early identification of brain tumours is vital for their effective treatment. Most currently available examination methods are laborious, require extensive manual instructions, and produce subpar findings. The EfficientNet-B0 architecture was used to diagnose brain tumours using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The fine-tuned EffeceintNet B0 model was proposed for the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) environment. The fine-tuned EfficientNet-B0 architecture was employed to classify four different stages of brain tumours from the MRI images. The fine-tuned model showed 99% accuracy in the detection of four different classes of brain tumour detection (glioma, no tumour, meningioma, and pituitary). The proposed model performed very well in the detection of the pituitary class with a precision of 0.95, recall of 0.98, and F1 score of 0.96. The proposed model also performed very well in the detection of the no-tumour class with values of 0.99, 0.90, and 0.94 for precision, recall, and the F1 score, respectively. The precision, recall, and F1 scores for Glioma and Meningioma classes were also high. The proposed solution has several implications for enhancing clinical investigations of brain tumours.
1. Introduction
The brain is the most complex and complicated part of the human body. Its structure is not easy to understand, as more than one hundred nerves communicate with each other to enable brain function [1]. Brain-related diseases are spreading day by day [2]. Some disorders can be detected at early stages, but some need proper diagnosis, like brain tumours, a type of brain-related disease that may lead to death. It has two major types: malignant or high-grade tumours and benign or low-level tumours [3]. High-level tumours are cancerous and may be metastatic and may affect other organs, while low-grade tumours are non-cancerous and non-metastatic. High-level-grade tumours are one of the most life-threatening tumour types. They may lead to death instantly due to their metastatic property. Furthermore, malignant and benign tumours are categorized as glioma, meningioma, and pituitary tumours [4]. According to statistics and research, in 2023, almost 1.4 million people struggled with brain tumours. Around 18,990 people in the world have died due to brain tumours [5]. This number is expected to increase to 24 million by 2035. According to Cancer Net, there is a 36% five-year survival rate and over 30% ten-year survival rate of brain tumours [5]. Figure 1 shows the difference between the average normal brain and tumour brain.
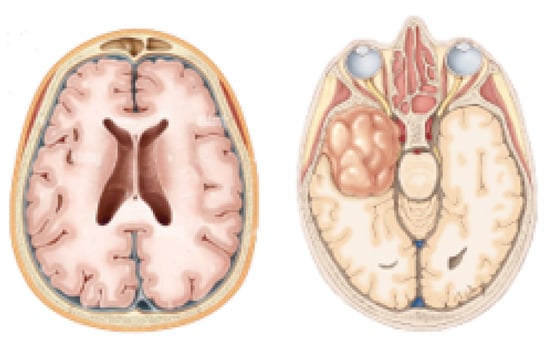
Figure 1.
Normal brain and brain with tumour.
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) is the interconnected system of software applications, medical devices, and health products and services [6]. IoMT refers to the system of medical devices and applications connected to healthcare IT systems through computer networks [7]. These devices collect, analyse, and transmit health data to healthcare providers [8]. IoMT enables real-time monitoring and improved healthcare outcomes to a large extent. IoMT includes smart medical equipment and mobile health applications that help in effective patient management [9]. Brain tumour requires special treatment and patient care. Therefore, IoMT offers efficient services in the healthcare department to effectively manage patients suffering from brain tumours [8]. IoMT has combined several automated disease identification models for appropriate disease diagnosis [9].
Image processing has become an essential part of the field of computer vision. It is used in several medical fields to diagnose disease and abnormality of any body part. This terminology is used in different fields like medicine, geography, and multimedia. Medical experts like radiologists and doctors interpret medical images in the medical field. Still, due to the chances of human error and fatigue, they use computer-aided systems to obtain better results [10]. A biopsy is one of the techniques used for diagnosis with the help of a needle, which may lead to infections. The second technique that is used widely is X-ray. The excess use of this technique may lead to skin cancer or brain cancer. The third technique used for detection is positron emission tomography (PET). In this technique, images of the brain are captured using a radioactive tracer. These images help doctors detect the disease, but it may lead to unpleasant pain and conditions. A CT scan uses the different views and angles of the brain, or any area for which images are captured, and the sections are known as slices. However, the images received using this technique could be more transparent for detecting a high-level medical disease.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is used to scan the brain to detect brain tumours. MRI images provide better and more precise results than CT (computed tomography) scans. X-ray radiation is not used in MRI scanning, and there is no pain throughout the procedure. Several scholars and researchers used this scanning technique in their research as it is easy to scan an image and then transfer it to the computer system for calculating the results. MRI scans are of several types, including T1- and T2-weighted, and Flair images [11]. These images are quite different from each other. T1-weighted images show cerebrospinal fluid (CFS) as dark, while T2-weighted images show cerebrospinal fluid as bright. Flair images are like T2-weighted images, while abnormalities are brightly visible in these images. Three-dimensional views of the brain are used in scanning. Coronal, horizontal, and sagittal views are included for scanning the brain from all sides to detect the abnormality properly. Experts are needed to make a good decision. In recent studies, many techniques have been used for detecting brain tumours using MRI as the manual detection of cancer may involve human error, which can be life-threatening.
Machine learning (ML) techniques have shown a significant impact on medical image processing. ML can help doctors in different medical fields. It assists doctors in the radiology, cardiology, and neurology fields. In the past few years, the ML field has shown state-of-the-art results in image recognition with a high accuracy rate. ML can extract prominent features not adequately visible to the human eye. ML techniques often depend upon voxel intensities and textural features. Individual vectors are classified based on feature vectors. The error rate and computational cost are less in the image recognition field using ML techniques. MLT was chosen due to its high examination accuracy with less complex datasets [12]. In the past few years, two techniques have been used in the ML approach: (1) the supervised method and (2) the unsupervised method. The supervised method includes input classes. This method comprises an artificial neural network (ANN) and a support vector machine (SVM).
Meanwhile, the unsupervised method consists of no input classes. This method includes K-mean clustering and ISODATA techniques. Along with ML, the Internet of Things (IoT) also has shown benefits in the healthcare sector. It has exhibited state-of-the-art results by connecting different medical devices to provide better medical services. The network created by these devices is also known as the IoMT. IoMT has shown beneficial outcomes in real-time settings [13].
In this area, ML has been demonstrated as one of the most appropriate computational models with the embedded intelligence of IoMT for the prediction and contemporary diagnosis of diseases, especially brain tumours. Many efforts have been made to accurately identify brain tumours from different types of brain images. The existing solutions are limited to a few classes that are unable to classify the stage of brain tumours. Multi-class brain tumour identification solutions are limited and suffer from low accuracy. Existing techniques and methods have limitations in using small datasets, poor texture and resolution of MRI scans, and low accuracy in prediction. The multi-class identification of brain tumours is still challenging in the fields of radiology and neurology as compared to a binary classification of brain tumours. The multi-class identification of brain tumours in the IoMT environment is even more important. It has a significant advantage in the efficient diagnosis of patients suffering from brain tumours, given the limitations of other detection methods in the existing literature.
To address the limitations of existing methods, a new solution is proposed, and the major contributions of the proposed solution are as follows:
- To design and implement a neural network model based on the EfficientNet architecture for the accurate classification of brain tumours;
- To optimize and fine-tune the EfficientNet model to achieve the highest possible accuracy and efficiency in brain tumour identification;
- To explore and apply various data augmentation and preprocessing techniques to increase the generalization capability of the EfficientNet model for accurate brain tumour classification;
- To evaluate the performance of the EfficientNet model using various metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score in classifying four brain tumour classes.
This study is organized into different sections: Literature Review, Materials and Methods, Results, and Discussion. Conclusions are drawn in the final section.
2. Literature Review
This section reviews the major advancements related to brain tumour identification using machine learning (ML) capabilities.
Francisco Javier Díaz-Pernas et al. [14] used CNNs for the classification and segmentation of three classes of brain tumours. The accuracy results achieved by this method was 97.3% P Gokila Brindha et al. [15] recommended a binary classification of brain tumours using an artificial neural network (ANN) and a convolutional neural network (CNN). The ANN yielded an accuracy of 65.21%, while the CNN had an accuracy of 89%. Jagadeesh Kakarla et al. [16] presented a method based on a three-class average pooling convolutional neural network. The accuracy achieved by this model was 97.42% M. Ganesan et al. [17] proposed IoMT and a CNN framework for the binary classification of brain tumours. The proposed solution yielded an accuracy of 98.07% for binary classification of brain tumour.
Hareem Kibriya et al. [18] proposed multi-class brain tumour classification using GoogleNet and ResNet to classify three tumour classes. The GoogleNet model had an accuracy of 97.6%, and ResNet achieved an accuracy of 98.0%.
Hareem Kibriya et al. [19] used a novel CNN-based architecture for the classification of three major classes of tumours. The proposed methodology achieved 97.2% accuracy. Prasun Chandra Tripathi et al. [20] recommended a deep residual network for the identification of two grades of glioma. The accuracy achieved by this method was 95.87%. Isunuri B.V et al. [21] proposed a separable CNN-based method. Three classes of brain tumours were used for classification purposes. The accuracy result achieved by classification was 97%. S. Deepak et al. [22] presented a model based on support vector machine (SVM) and CNNs for the identification of three classes of brain tumours. The proposed solution achieved 0.95% accuracy in brain tumour classification.
Ramdas Vankdothu et al. [23] presented a model based on IoMT with a support value and CNN for the binary classification of brain tumours. The accuracy result achieved by this technique was 94% Omar Adil Kamil et al. [24] presented a model incorporating IoT concepts. CNN-MRFO was applied to three classes of brain tumours. The accuracy result reported with this architecture was 98% G. Ignisha Rajathi et al. [25] presented a method incorporating IoMT and a cloud-enabled diagnosis model. This technique was applied to binary brain tumour classes. The accuracy reported using this model was 98%.
Sarah Zuhair Kurdi et al. [26] used CNNs for binary brain tumour classification on a small dataset. The accuracy result achieved with this methodology was 98%. The results of the analysis of existing techniques for brain tumour classification are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Results of the analysis of existing techniques.
3. Methodology
IoMT significantly enhances human well-being and life quality while concurrently reducing healthcare costs. This section elaborates on the proposed IoMT architecture and flowchart of machine learning model training and evaluates the classification of brain tumours. The proposed IoMT architecture consists of three layers, as shown in Figure 2. The proposed IoMT architecture aims to provide optimal healthcare services, thus efficiently contributing to the overall improvement in healthcare delivery for patients suffering from brain tumours.
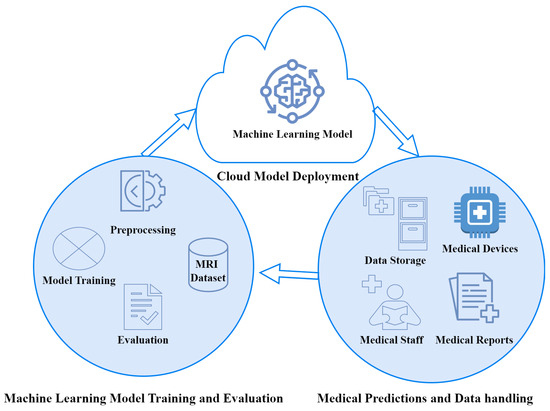
Figure 2.
Proposed IoMT architecture for the MRI-based classification of brain tumours.
The proposed IoMT architecture consists of three layers, with descriptions as follows:
- Cloud model deployment: The trained ML model is stored on the cloud for universal access by all he stakes holders.
- Machine learning model training and evaluation: This layer is responsible for data preprocessing, ML model training, and evaluation. The process of ML model training and evaluation is further explored in subsequent subsections.
- Medical predictions and data handling: This layer is responsible for providing an interface to the medical staff and medical equipment to use the deployed ML model for brain tumour classification. This layer also stores data regarding predictions made. The dataset in this layer is further used to train and improve the performance of the ML model.
3.1. Machine Learning Model’s Training and Evaluation
This section describes the training and evaluation of the ML model. This process is depicted with the help of a flowchart, as shown in Figure 3.
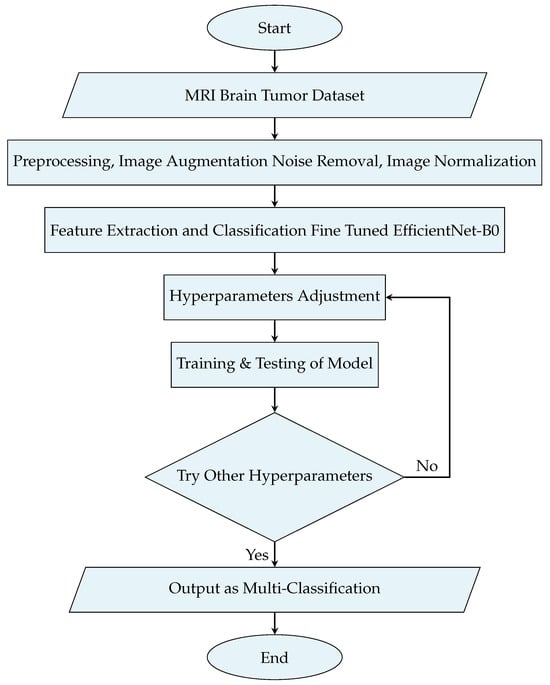
Figure 3.
Flowchart of the proposed methodology for model training and evaluation.
3.2. Dataset
The dataset for implementing the proposed system is the Brain Tumour MRI dataset, comprising 7023 brain MRI scans. We used Br35H in this study [28]. Br35H contains 804 MRI scans of four different classes of brain tumours, namely no tumour, benign tumour, malignant tumour, and pituitary tumour. These four tumour classes are important to accurately classify brain tumour stages. Sample images from the dataset are depicted in Figure 4. The dataset was divided into three categories training, validation, and testing. The distribution of images in the dataset for each category is presented in Table 2.
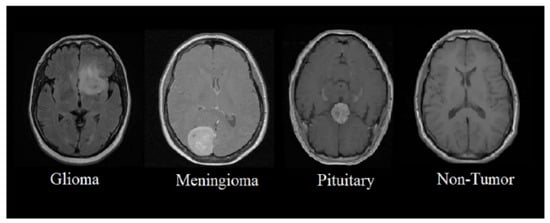
Figure 4.
MRI scans of brain tumour.

Table 2.
Dataset description.
3.3. Preprocessing
Data cleaning and organization are important steps in preprocessing, especially for the classification of brain tumours using MRI scans. Image preprocessing was used to improve the visual representation of the images. The primary goal of the preprocessing step was to enhance the quality of the images. All MRI scans were resized to 224 × 224 × 3 to reduce computational time and increase the efficiency of model training. Image augmentation was applied to increase the diversity of the data, which helped in training the model more effectively. Augmentation techniques included setting the rotation range to 15 degrees, the width shift range to 0.1, the height shift range to 0.1, the shear range to 0.1, the zoom range to 0.1, enabling horizontal flipping, and using the ‘Nearest’ fill mode. The description of each image augmentation technique is given in Table 3. Data preprocessing was performed on the MRI scans to enhance the quality and generalization ability of the model. Median and contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE) filters were also used to remove noise from images. The augmentation techniques applied are given in Table 3.

Table 3.
Image augmentation techniques.
3.4. Machine Learning Model (EfficientNet-B0)
The proposed solution used EffecientNet-B0 for the classification of brain tumours from MRI scans. EfficientNet belongs to the family of CNNs and is designed for superior and efficient image classification. EfficientNet-B0 is the baseline model of the EfficientNet family. EffecientNet-B0 has shown significant success in image classification tasks. Its framework includes a scaling method for consistent dimension scaling and resolution scaling for state-of-the-art performance. This model can be fine-tuned for image classification tasks. The architecture of EffecientNet-B0 is shown in Figure 5.

Figure 5.
EfficientNet-B0 architecture.
The EfficientNet-B0 architecture is based on Mobile Inverted Bottleneck Convolution (MBConv) components with the addition of squeeze-and-excitation (SE) blocks. This design is effective in maximizing accuracy while minimizing the number of parameters. It incorporates depth-separable convolution to reduce computational complexity by a factor of , where k is the kernel size. The architecture also includes inverted residual blocks to decrease the number of trainable parameters. Depth, width, and resolution are scaled for proper model scaling by the EffecientNet-B0 model. In compound scaling, a compound coefficient is used that is expressed by Equation (1).
where , , and are scaling factors. These values are determined through grid search, and depends on model scaling.
The Swiss function is defined by Equation (2) as follows:
The final layer of the EfficientNet-B0 architecture, known as the head, is responsible for predicting the final classification output based on the features extracted from the preceding layers.
3.5. Fine-Tuned EfficientNet-B0 Model
This section presents the fine-tuned EffeceintNet-B0 model. The Keras library was imported for the pretrained EfficientNet-B0. A total of 241 layers were utilized to train the network. Features were extracted using the multiple layers included in the architecture. The last three layers of EfficientNet-B0 were modified for transfer learning to achieve better results than the original EfficientNet-B0 model. A 2D convolutional window was utilized. A global average pooling (GAP) 2D layer, a dropout layer with a rate of 0.5, and a dense layer with Softmax activation were applied in the fine-tuned EffecientNet-B0 architecture.
3.6. Evaluation Metrics
For the EfficientNet-B0-based multi-class prediction of brain tumours from MRI scans, the accuracy, precision, recall, confusion matrix and ROC curve were used to evaluate the model’s performance.
3.6.1. Accuracy
Accuracy is the proportion of correctly classified images of brain tumours to the total predictions of brain tumours from MRI scans, which is defined by Equation (3).
Precision
Precision is the proportion of true-positive predictions to the positive predictions and is expressed by Equation (4).
3.6.2. Recall (Sensitivity)
Recall, or sensitivity, measures the proportion of true-positive instances to the actual positive instances and is expressed by Equation (5).
3.6.3. F1 Score
The F1 Score is the harmonic mean of precision and recall, which balances both precision and recall. The F1 score is expressed by Equation (6).
Apart from these metrics, the model’s performance was also evaluated using the confusion matrix and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve.
4. Results
The performance of EffecientNet-B0 for brain tumour classification was assessed using the test dataset. The performance of the proposed fine-tuned EffecientNet-B0 was compared against the normal EffecientNet-B0 model. This section presents the results of the comparison of EffceintNet-B0 and fine-tuned EffeceintNet-BO for the classification of brain tumour from MRI scans.
4.1. Performance of Simple EfficientNet-B0
The EfficientNet-B0 model without any tuning was applied on the same dataset with four classes. The training accuracy range reached 93%, and the validation accuracy was up to 90% with the simple EffeceintNet-B0 model. The training and validation accuracy over epochs is shown in Figure 6a. The training and validation loss of the simple EffecientNet-B0 model is shown in Figure 6b. The precision–recall and F1 score of EffecientNet-B0 are presented in Table 4. Table 4 shows the testing results of brain tumour multi-classification using the simple EfficientNet-B0 model in terms of accuracy, precision, recall, F1 score, and support vector machine values.
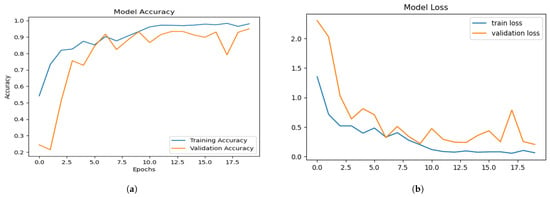
Figure 6.
Training and validation: (a) accuracy (b) loss of simple EfficientNet-B0.

Table 4.
Performance of trained EfficientNet-B0.
The confusion matrix reveals each class’s impact more clearly and broadly. Figure 7 shows the confusion matrix generated by applying the simple EfficientNet-B0. The row of the confusion matrix represents true labels, while the column represents predicted labels.
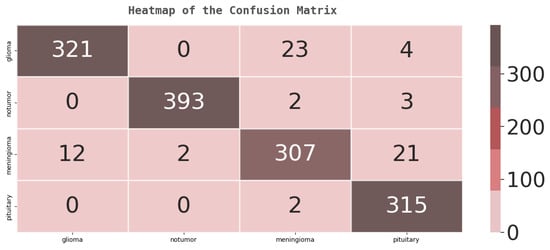
Figure 7.
Testing confusion matrix for EfficientNet-B0.
The ROC curve is essential for the detection of brain tumours. The ratio between TPR and FPR of each brain tumour class is illustrated by the ROC curve shown in Figure 8.
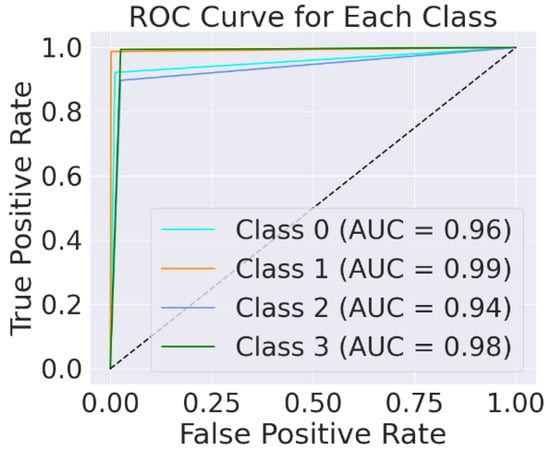
Figure 8.
Testing ROC for EfficientNet-B0.
4.2. Performance of Fine-Tuned EfficientNet-B0
The performance of the fine-tuned EffeceintNet-B0 was also assessed using the test dataset. The training and validation accuracy of the fine-tuned EffecientNet-BO model over all epochs is shown in Figure 9a. The training accuracy ranges from 98% to 99% with an epoch value of 40, and as the epoch value increases, the model loss decreases. The training and validation loss of the fine-tuned EffecientNet-B0 model is shown in Figure 9b. The precision–recall and F1 score of the EffecientNet-B0 model are presented in Table 5. Table 5 shows the testing results of brain tumour multi-classification with fine-tuned EfficientNet-B0 in terms of accuracy, precision, recall, F1 score, and support vector machine values. Figure 9b shows the model loss; the blue line shows the training loss, and the brown line shows the validation loss. Table 5 shows the testing results of brain tumour multi-classification with the fine-tuned EffeceintNet-B0 in terms of accuracy, precision, recall, F1 score, and support vector machine values.
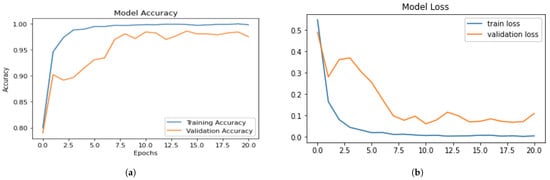
Figure 9.
Training and validation: (a) accuracy; (b) loss of proposed EfficientNet-B0.

Table 5.
Testing results of fine-tuned EfficientNet-B0.
The confusion matrix reveals each class’s impact more clearly and broadly. Figure 10 shows the confusion matrix generated by applying fine-tuned EfficientNet-B0. The rows represent the data’s true label, while the column represents the output’s predicted labels.
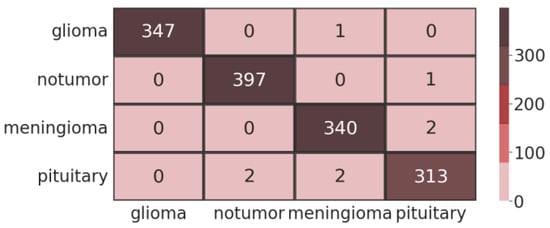
Figure 10.
Testing confusion matrix for proposed EfficientNet-B0.
The model achieved 99% accuracy in predicting the no-tumour class, meningioma class, and pituitary class as compared to the simple EfficientNet-B0 model implemented without fine-tuning. This value represents the efficacy of the EfficientNet-B0 architecture for extracting features and classifying different types of brain tumours. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve is important for the detection of brain tumours. The ratio between the TPR and FPR of each brain tumour class is illustrated by ROC. Figure 11 shows the ROC curve plotted using fine-tuned EfficientNet-B0.
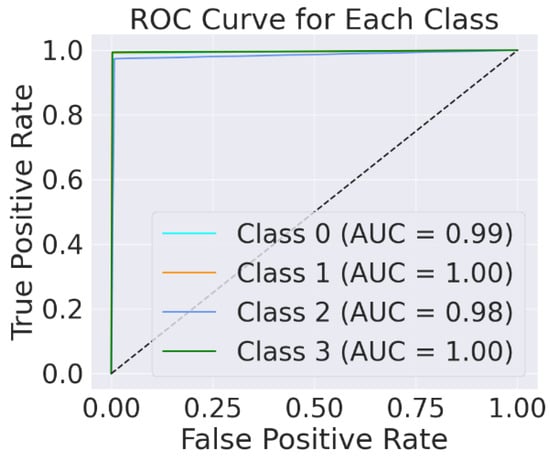
Figure 11.
Testing ROC for proposed EfficientNet-B0.
4.3. Comparative Analysis with Existing Methods
The results of the fine-tuned method were compared with those of other existing methods for brain tumour detection and classification. This section presents a comparative analysis based on effectiveness and significance with other methods. Table 6 shows that the accuracy obtained with the fine-tuned EfficientNet-B0 multi-classification is quite acceptable and higher than the state-of-the-art approach.

Table 6.
Comparative analysis with existing methods.
The fine-tuned EffeceintNet B0 outperformed the simple EffeceintNet-B0 model and state-of-the-art approaches in the classification of multi-class brain tumours from MRI images.
5. Discussion
The results of this study demonstrate the effectiveness of the fine-tuned EffeceintNet-B0 model for the multi-class classification of brain tumours using MRI scans. The architecture of EffeceintNet-B0 integrates Mobile Inverted Bottleneck Convolution (MBConv) components with squeeze-and-excitation (SE) blocks, which allow for maximizing accuracy while minimizing computational complexity. The fine-tuning process, which included the use of a GAP 2D layer, a dropout layer with a rate of 0.5, and a dense layer with Softmax activation, proved to be highly effective in increasing the model’s performance.
The fine-tuned EfficientNet-B0 model achieved an accuracy of 99% in classifying four brain tumour classes (glioma, no tumour, meningioma, and pituitary). This high accuracy demonstrates the model’s potential in clinical applications where accurate diagnosis is critical. The model performed well in detecting the pituitary class, with a precision of 0.95, a recall of 0.98, and an F1 score of 0.96. It also showed high precision, recall, and F1 scores for the glioma, meningioma, and no-tumour classes. The ROC curve and the area under the curve (AUC) further validate the performance of the model in brain tumour classification. An AUC of 0.92 indicates that the model has a high true-positive rate while maintaining a low false-positive rate, which is significant for medical diagnoses.
The fine-tuned EffeceintNet-B0 model significantly outperformed other state-of-the-art approaches. The accuracy achieved by our model was higher than those reported in recent studies, highlighting the advantage of using the EfficientNet-B0 architecture combined with fine-tuning techniques. For instance, methods using pretrained CNNs like ResNet50 and EfficientNet variants achieved up to 97.12% accuracy, whereas our approach reached 99%.
The integration of the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) with the EfficientNet-B0 model opens new avenues for remote and real-time medical diagnostics. The proposed model can be deployed in cloud-based systems, making it accessible to healthcare providers worldwide. This can significantly improve the efficiency and accuracy of brain tumour diagnosis.
This study is limited to a specific dataset, and the model’s performance needs to be validated on larger and more diverse datasets to validate model performance. The computational cost of training and making predictions was not determined in this work but would be an important area for future research. Future studies should also explore optimizing the model further to reduce computational overhead without compromising performance.
6. Conclusions
The early identification of brain tumours using MRI is very important for reducing global fatality rates. This study introduces an IoMT-based EfficientNet-B0 model for the multi-class classification of brain tumours. The fine-tuned EffeceintNet-BO achieved 99% accuracy and outperformed the simple EffeceintNet-B0 and state-of-the-art approaches for multi-class brain tumour classification. By outperforming traditional classifiers, the proposed approach demonstrates the potential of integrating IoMT with deep learning for accurate tumour detection. This advancement supports radiologists and neurologists in making precise diagnostic decisions, which lead to improving patient outcomes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.I. and R.J.; methodology, A.I. and R.J.; software, A.I.; validation, A.I., M.A.J. and R.J.; formal analysis, A.I.; investigation, R.J.; resources, M.A.J.; data curation, A.I.; writing—original draft preparation, A.I.; writing—review and editing, R.J. and M.A.J.; visualization, R.J.; supervision, M.A.J. and R.J.; project administration, M.A.J.; funding acquisition, A.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available on request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, Y.Q.; Chiu, K.S.; Liu, X.R.; Hsiao, T.Y.; Zhao, G.; Li, S.J.; Lin, C.P.; Sun, C.W. Polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography for brain tumor characterization. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2019, 25, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graber, J.J.; Cobbs, C.S.; Olson, J.J. Congress of neurological surgeons systematic review and evidence-based guidelines on the use of stereotactic radiosurgery in the treatment of adults with metastatic brain tumors. Neurosurgery 2019, 84, E168–E170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swati, Z.N.K.; Zhao, Q.; Kabir, M.; Ali, F.; Ali, Z.; Ahmed, S.; Lu, J. Brain tumor classification for MR images using transfer learning and fine-tuning. Comput. Med Imaging Graph. 2019, 75, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodapati, J.D.; Shaik, N.S.; Naralasetti, V.; Mundukur, N.B. Joint training of two-channel deep neural network for brain tumor classification. Signal Image Video Process. 2021, 15, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Society, A.C. 2023. Available online: http://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/brain-tumor/statistics/ (accessed on 23 May 2024).
- Elhoseny, M.; Bian, G.B.; Lakshmanaprabu, S.; Shankar, K.; Singh, A.K.; Wu, W. Effective features to classify ovarian cancer data in internet of medical things. Comput. Networks 2019, 159, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, I.U.; Guizani, M.; Kim, B.S.; Hassan, S.; Khan, M.K. Trust management techniques for the Internet of Things: A survey. IEEE Access 2018, 7, 29763–29787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.H.; Zhang, Y.D. Applicable artificial intelligence for brain disease: A survey. Neurocomputing 2022, 504, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, M.; ElAffendi, M.; Ateya, A.A.; Abd El-Latif, A.A. Efficient brain tumor detection with lightweight end-to-end deep learning model. Cancers 2023, 15, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meera, R.; Anandhan, P. A review on automatic detection of brain tumor using computer aided diagnosis system through MRI. EAI Endorsed Trans. Energy Web 2018, 5, e17. [Google Scholar]
- Zulfiqar, F.; Bajwa, U.I.; Mehmood, Y. Multi-class classification of brain tumor types from MR images using EfficientNets. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 84, 104777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiri, A.A.; Iqbal, A.; Ferzund, J.; Ali, T.; Aamir, M.; Alshamrani, K.A.; Alshamrani, H.A.; Alqahtani, F.F.; Irfan, M.; Alshehri, A.H. A Novel Hybrid Machine Learning Approach for Classification of Brain Tumor Images. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Khosravi, M.R.; Wan, S. Class consistent and joint group sparse representation model for image classification in internet of medical things. Comput. Commun. 2021, 166, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Pernas, F.J.; Martínez-Zarzuela, M.; Antón-Rodríguez, M.; González-Ortega, D. A deep learning approach for brain tumor classification and segmentation using a multiscale convolutional neural network. Healthcare 2021, 9, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brindha, P.G.; Kavinraj, M.; Manivasakam, P.; Prasanth, P. Brain tumor detection from MRI images using deep learning techniques. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Sanya, China, 12–14 November 2021; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 1055, p. 012115. [Google Scholar]
- Kakarla, J.; Isunuri, B.V.; Doppalapudi, K.S.; Bylapudi, K.S.R. Three-class classification of brain magnetic resonance images using average-pooling convolutional neural network. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2021, 31, 1731–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, M.; Sivakumar, N.; Thirumaran, M. Internet of medical things with cloud-based e-health services for brain tumour detection model using deep convolution neural network. Electron. Gov. Int. J. 2020, 16, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibriya, H.; Masood, M.; Nawaz, M.; Rafique, R.; Rehman, S. Multiclass brain tumor classification using convolutional neural network and support vector machine. In Proceedings of the 2021 Mohammad Ali Jinnah University International Conference on Computing (MAJICC), Karachi, Pakistan, 15–17 July 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kibriya, H.; Masood, M.; Nawaz, M.; Nazir, T. Multiclass classification of brain tumors using a novel CNN architecture. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 29847–29863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, P.C.; Bag, S. A computer-aided grading of glioma tumor using deep residual networks fusion. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 215, 106597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isunuri, B.V.; Kakarla, J. Three-class brain tumor classification from magnetic resonance images using separable convolution based neural network. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2022, 34, e6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepak, S.; Ameer, P. Automated categorization of brain tumor from mri using cnn features and svm. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021, 12, 8357–8369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vankdothu, R.; Hameed, M.A.; Ameen, A.; Unnisa, R. Brain image identification and classification on Internet of Medical Things in healthcare system using support value based deep neural network. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 102, 108196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamil, O.A.; Al-Shammari, S.W. IoT framework for brain tumor classification using optimized CNN-MRFO model. Am. J. Bioinform. Res. 2021, 11, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Rajathi, G.I.; Kumar, R.R.; Ravikumar, D.; Joel, T.; Kadry, S.; Jeong, C.W.; Nam, Y. Brain Tumor Diagnosis Using Sparrow Search Algorithm Based Deep Learning Model. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2023, 44, 1793–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdi, S.Z.; Ali, M.H.; Jaber, M.M.; Saba, T.; Rehman, A.; Damaševičius, R. Brain tumor classification using meta-heuristic optimized convolutional neural networks. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, A.; Islam, M.S. A Hybrid Deep CNN-SVM Approach for Brain Tumor Classification. J. Inf. Syst. Eng. Bus. Intell. 2023, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, A. Br35H :: Brain Tumor Detection 2020. 2020. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/ahmedhamada0/brain-tumor-detection (accessed on 12 July 2024).
- Filatov, D.; Ahmad Hassan Yar, G.N. Brain tumor diagnosis and classification via pre-trained convolutional neural networks. medRxiv 2022, arXiv:2208.00768. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Guzmán, M.A.; Jiménez-Beristaín, L.; García-Guerrero, E.E.; López-Bonilla, O.R.; Tamayo-Perez, U.J.; Esqueda-Elizondo, J.J.; Palomino-Vizcaino, K.; Inzunza-González, E. Classifying brain tumors on magnetic resonance imaging by using convolutional neural networks. Electronics 2023, 12, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, S.; Karthick, K.; Selvanathan, N.; Saravanan, U.B.; Murali, M.; Dhiyanesh, B. Brain Tumor Detection Using Deep Learning Neural Network for Medical Internet of Things Applications. In Proceedings of the 2021 6th International Conference on Communication and Electronics Systems (ICCES), Coimbatore, India, 8–10 July 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).