Object Tracking Based on Optical Flow Reconstruction of Motion-Group Parameters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Optic Flow Reconstruction Problem
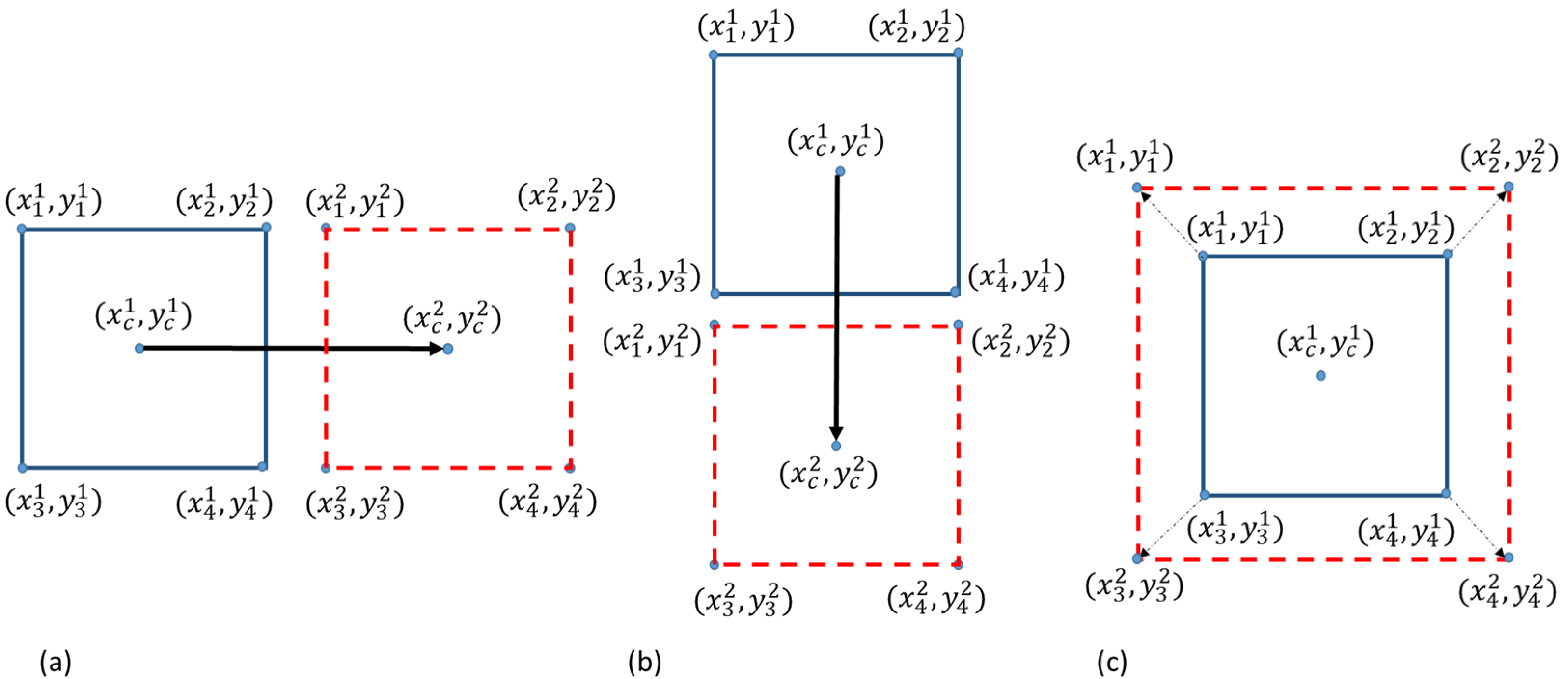
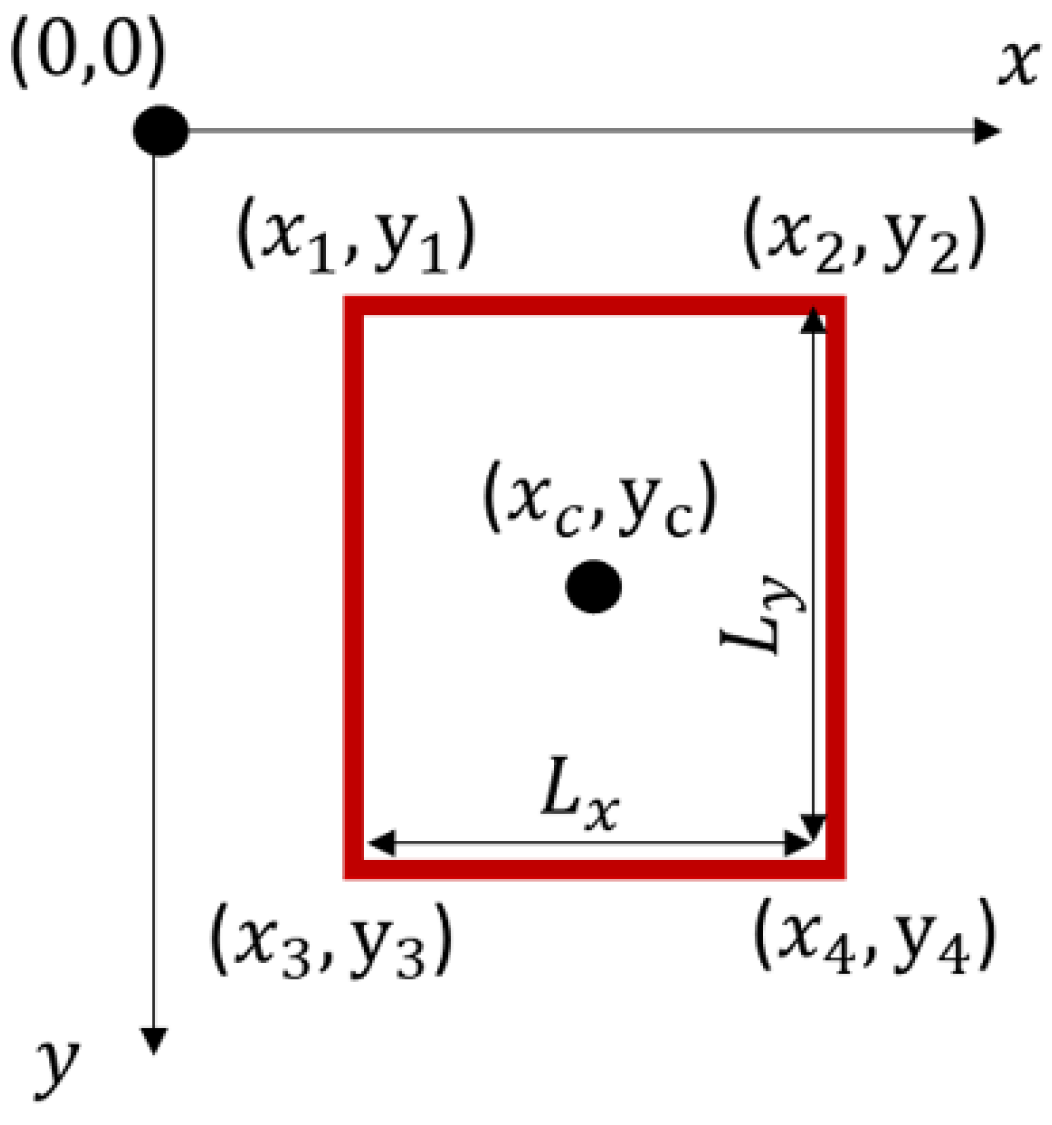
2.2. Region of Interest (ROI) Transformations
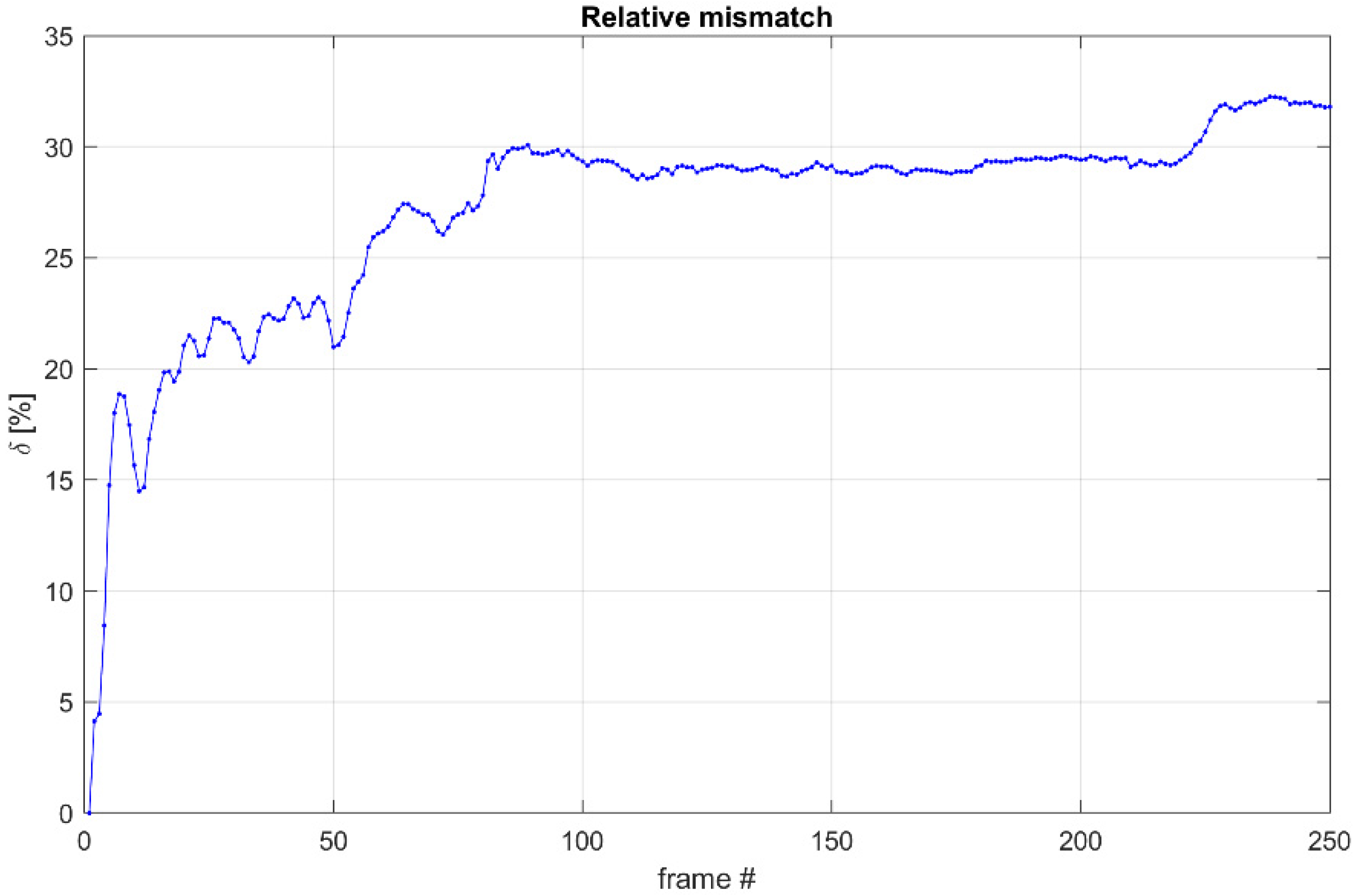
2.3. Evaluation of the ROI Tracking Performance
3. Results
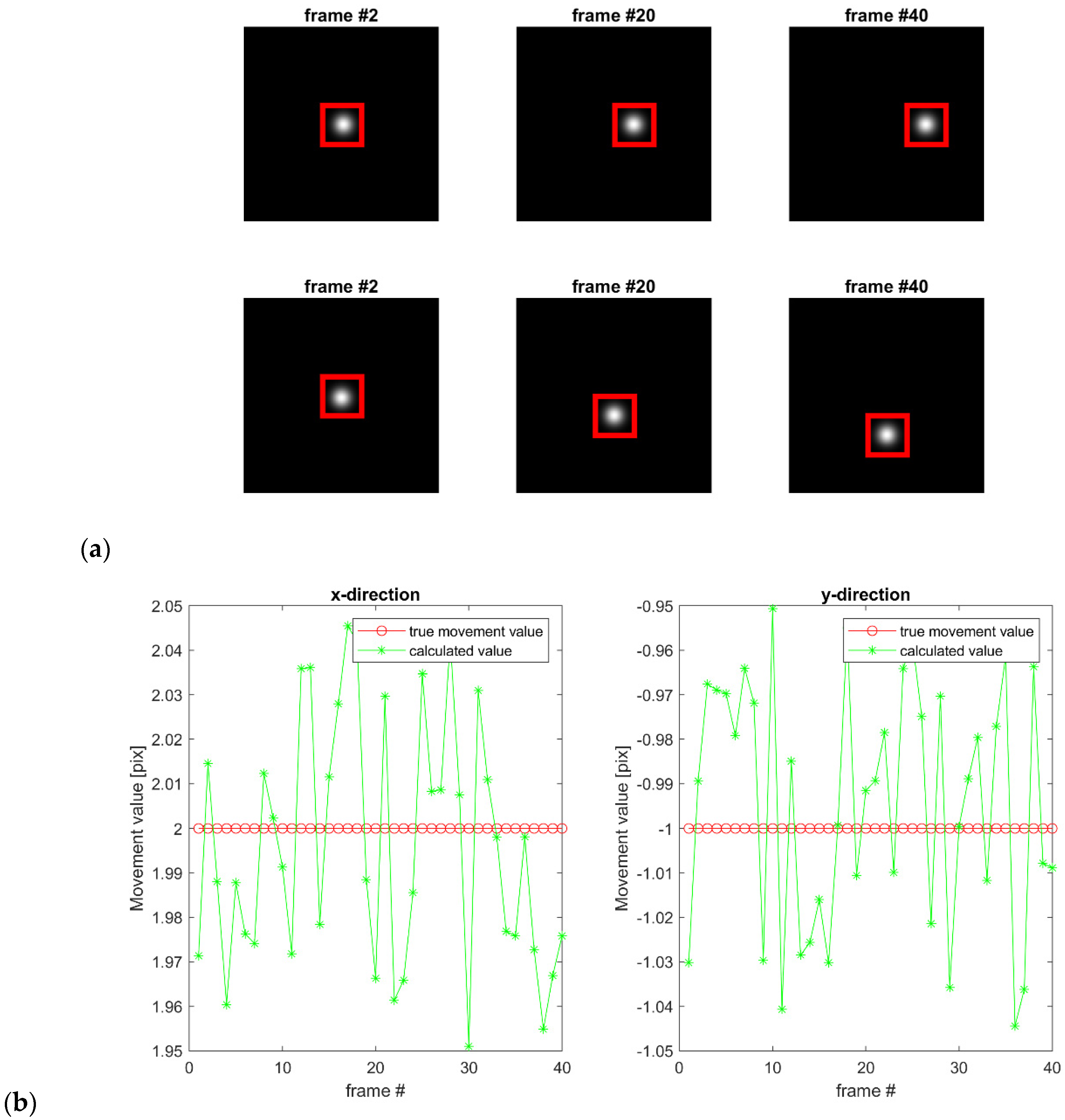
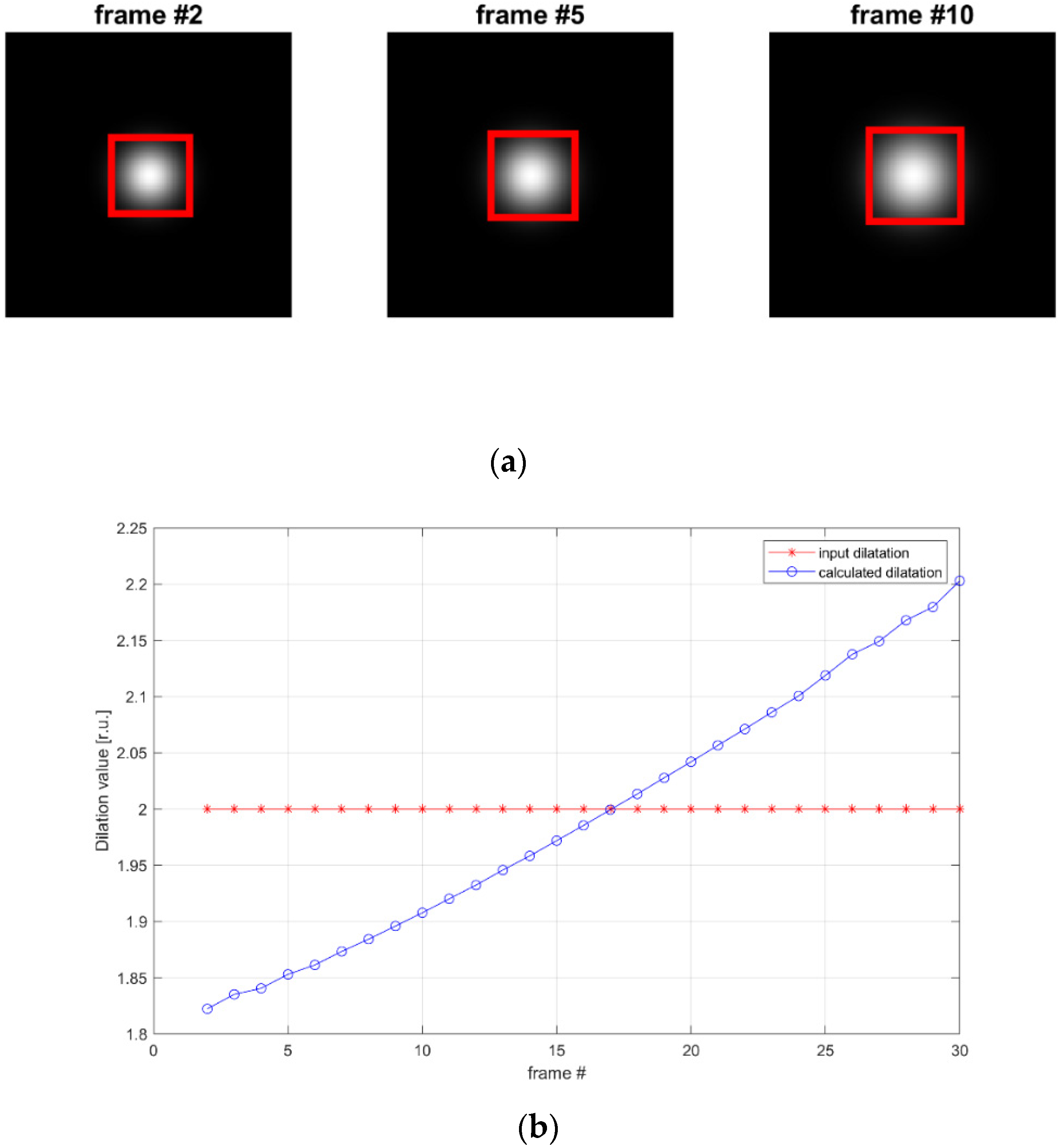
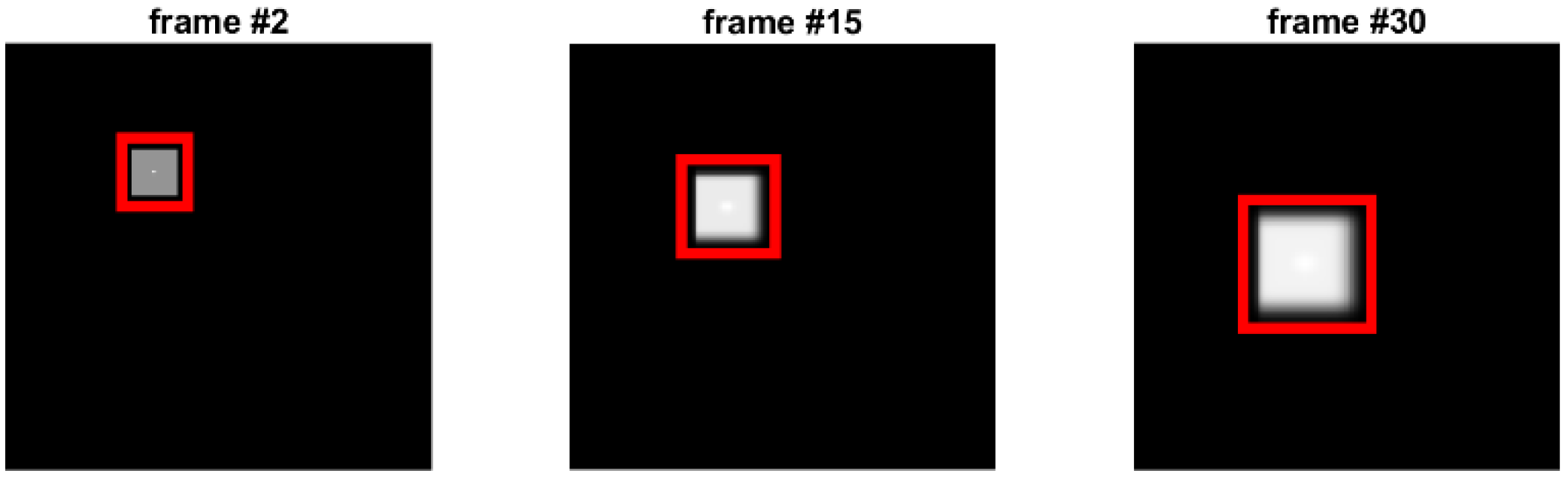
3.1. Tracking Capabilities
- Generate an initial image, in our case, a Gaussian spot with a starting size and coordinates on a homogenous background;
- Specify the coordinates and size of the first region of interest, R1;
- Transform the initial image with any number of basic movement generators, as described in Figure 1, to arrive at an image sequence;
- Using the GLORIA algorithm, calculate the transformation parameters;
- Update the ROI according to Equation (7);
- Compare properties of regions of interest—coordinates and size.
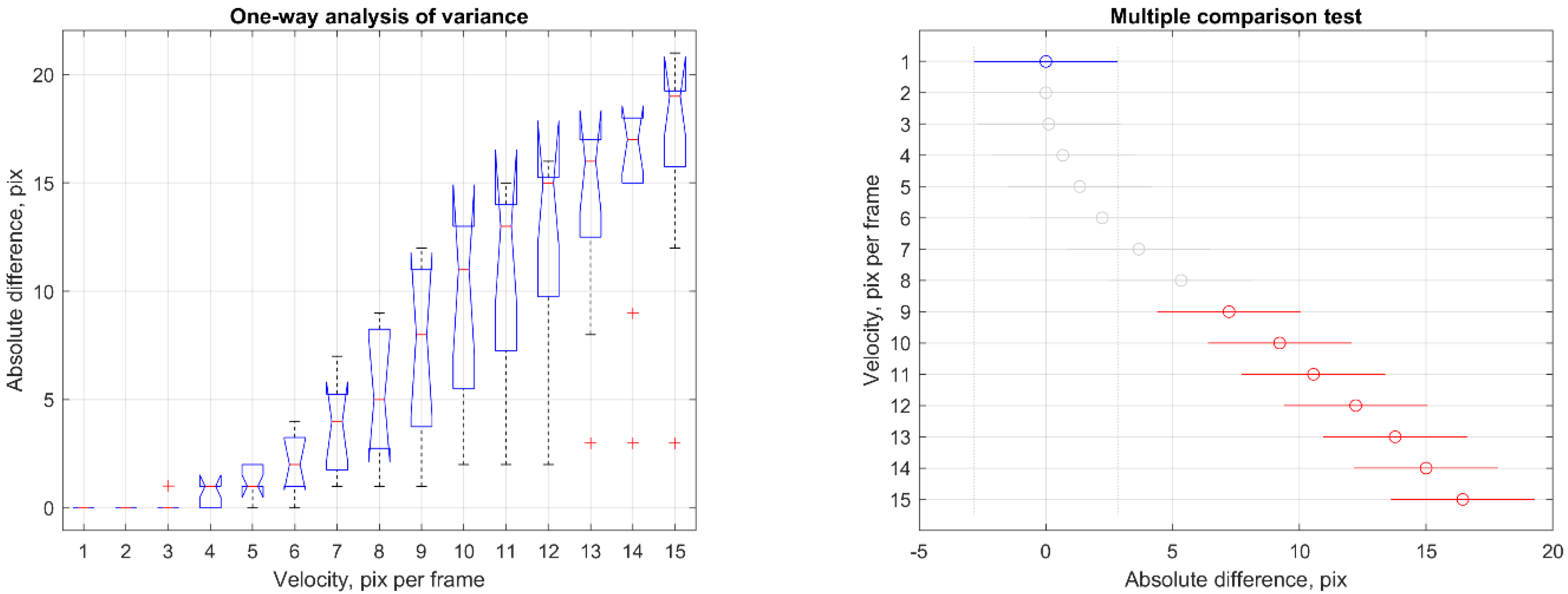
3.2. Tests with Simulated Data
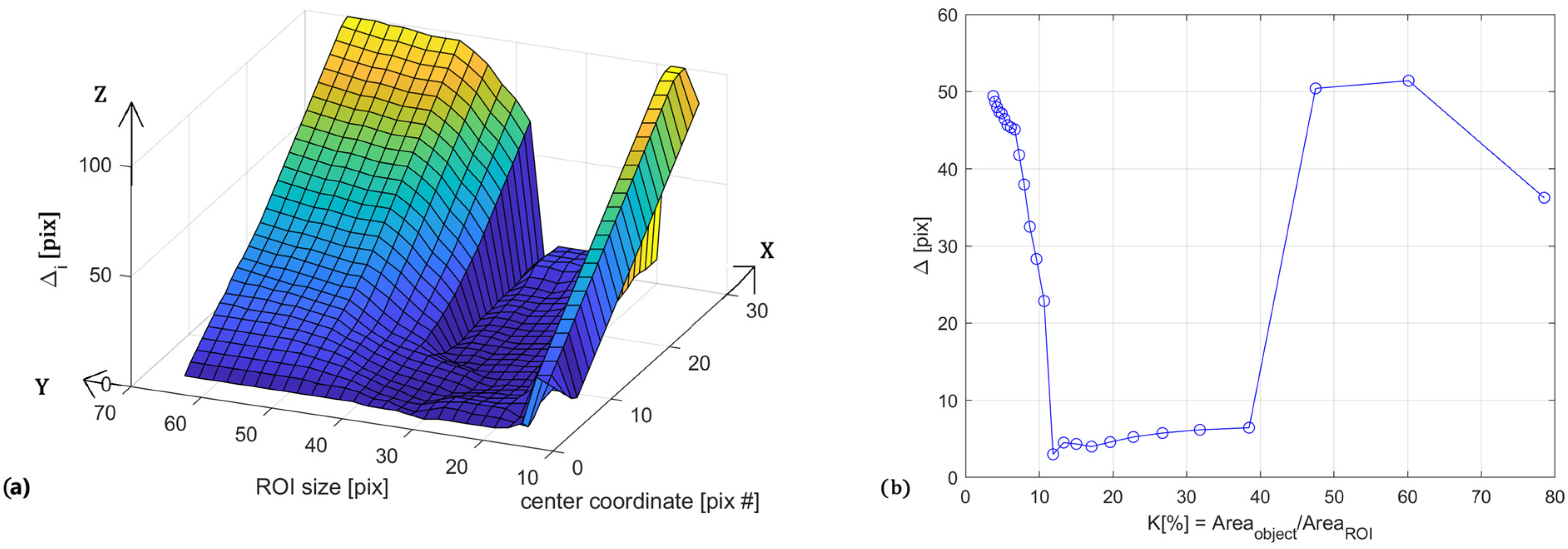
3.3. Influence of the Background
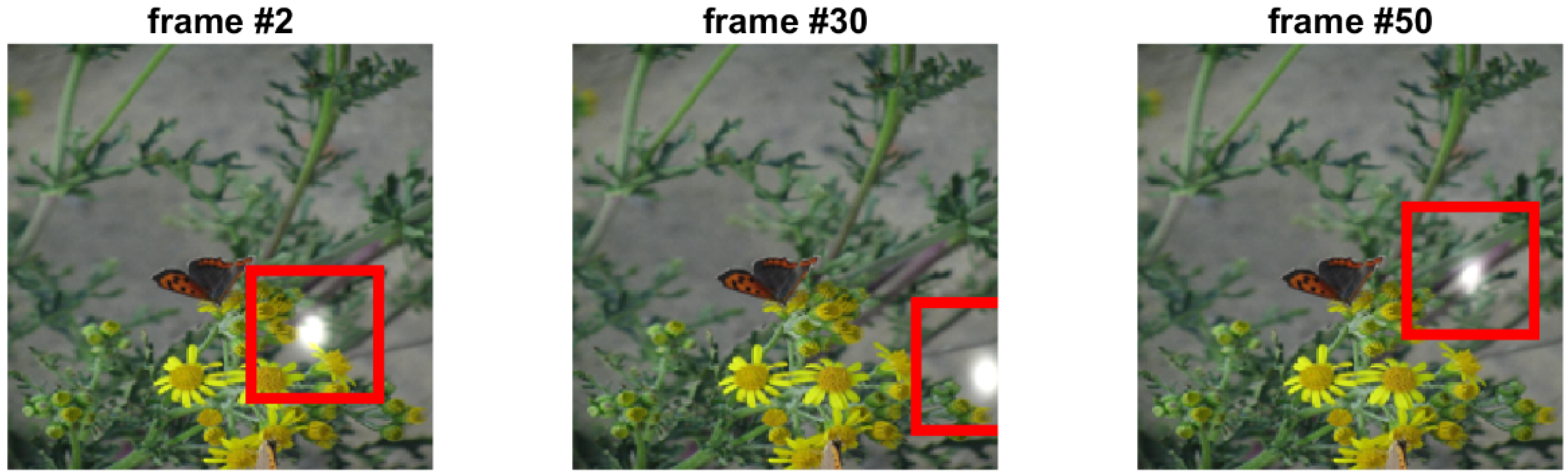
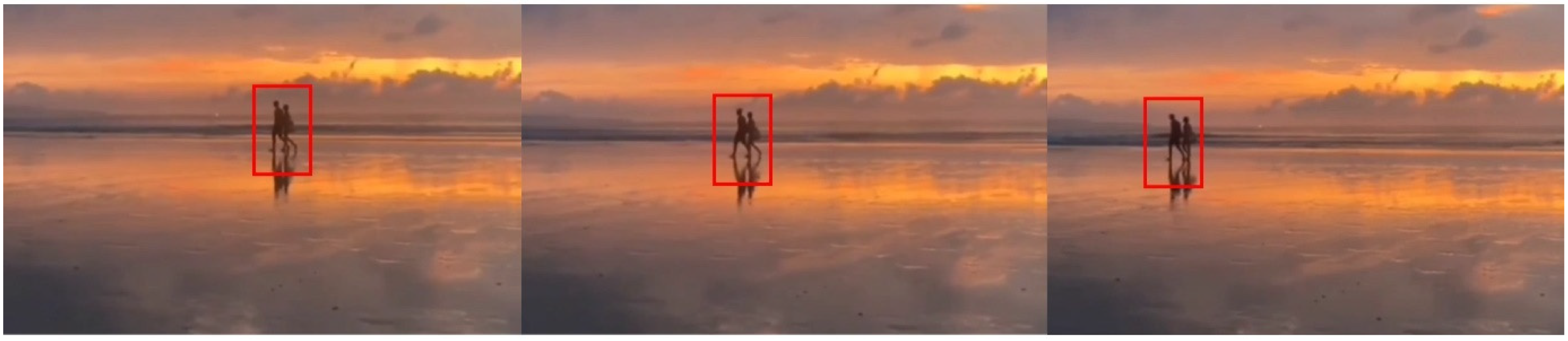
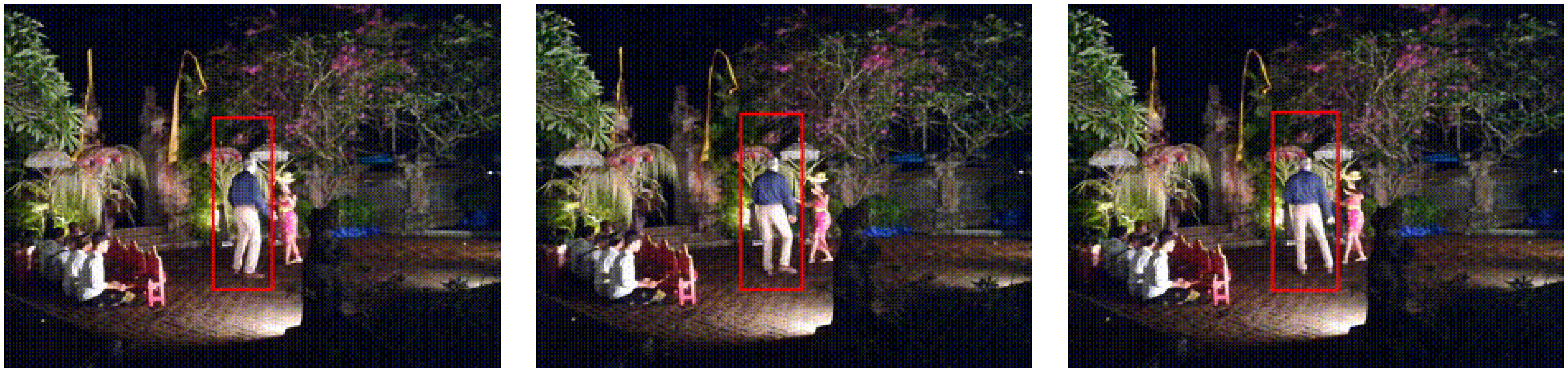
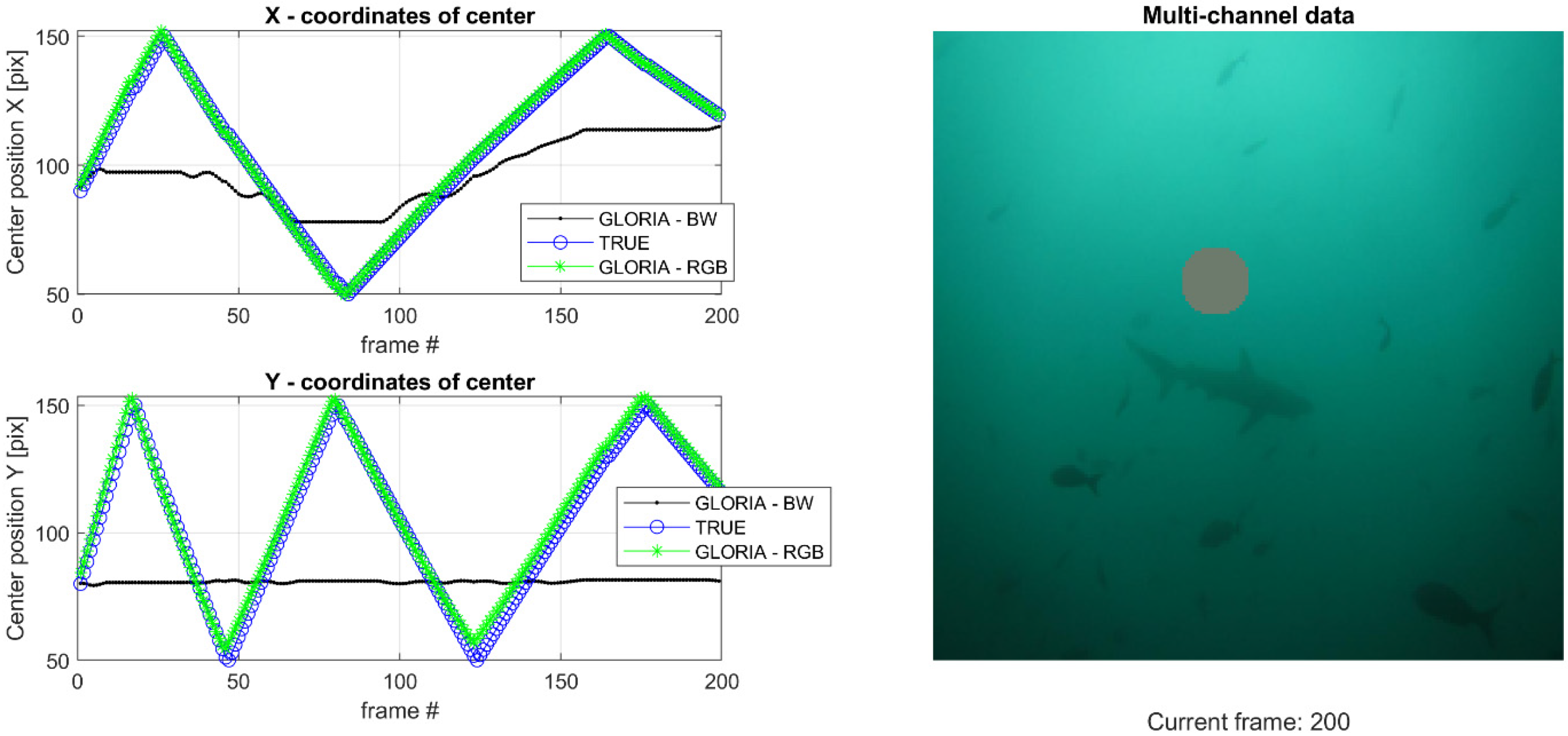
3.4. Tests with Real-World Data
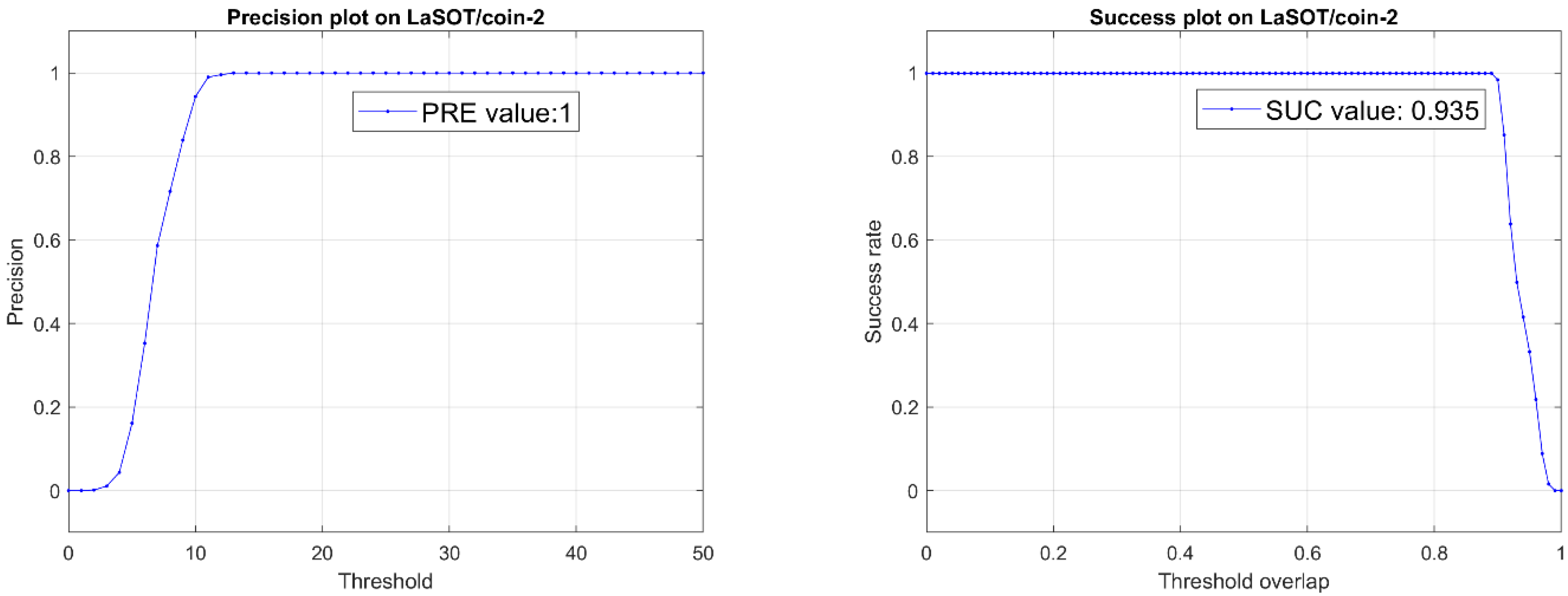
3.5. Tests on the Public Database LaSOT
3.6. Multi-Spectral vs. Mono-Spectral Results
3.7. Tracking Limitations
4. Summary and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalitzin, S.; Petkov, G.; Velis, D.; Vledder, B.; da Silva, F.L. Automatic segmentation of episodes containing epileptic clonic seizures in video sequences. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 3379–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geertsema, E.E.; Visser, G.H.; Sander, J.W.; Kalitzin, S.N. Automated non-contact detection of central apneas using video. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 55, 101658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geertsema, E.E.; Visser, G.H.; Viergever, M.A.; Kalitzin, S.N. Automated remote fall detection using impact features from video and audio. J. Biomech. 2019, 88, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.; Kang, B.; Kim, D. Moving object tracking based on sparse optical flow with moving window and target estimator. Sensors 2022, 22, 2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farag, W.; Saleh, Z. An advanced vehicle detection and tracking scheme for self-driving cars. In Proceedings of the 2nd Smart Cities Symposium (SCS 2019), Bahrain, 24–26 March 2019; IET: Stevenage, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.; Anpalagan, A.; Guan, L.; Khwaja, A.S. Deep learning for object detection and scene perception in self-driving cars: Survey, challenges, and open issues. Array 2021, 10, 100057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, A.J.; Reartwell, C.; Haering, N.; Madden, D. Automated video protection, monitoring & detection. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2003, 18, 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Gee, T.; Price, J.; Qi, H. Real time multi-vehicle tracking and counting at intersections from a fisheye camera. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 5–9 January 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H. Multiple vehicle tracking and classification system with a convolutional neural network. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2022, 13, 1603–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, H.-S.; Lee, B.-G.; Lim, H. Hand tracking and gesture recognition system for human-computer interaction using low-cost hardware. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2015, 74, 2687–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagiani, C.; Betke, M.; Gips, J. Evaluation of Tracking Methods for Human-Computer Interaction. In Proceedings of the WACV, Orlando, FL, USA, 3–4 December 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hunke, M.; Waibel, A. Face locating and tracking for human-computer interaction. In Proceedings of the 1994 28th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 31 October–2 November 1994; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Salinsky, M. A practical analysis of computer based seizure detection during continuous video-EEG monitoring. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1997, 103, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.; Javed, O.; Shah, M. Object tracking: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2006, 38, 13-es. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deori, B.; Thounaojam, D.M. A survey on moving object tracking in video. Int. J. Inf. Theory 2014, 3, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangawati, A.; Leesan, M.; Aradhya, H.R. Object Tracking Algorithms for video surveillance applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing (ICCSP), Melmaruvathur, India, 3–5 April 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Hu, W.; Shen, C.; Zhang, Z.; Dick, A.; Hengel, A.V.D. A survey of appearance models in visual object tracking. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2013, 4, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccardi, M. Background subtraction techniques: A review. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (IEEE Cat. No. 04CH37583), The Hague, The Netherlands, 10–13 October 2004; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Benezeth, Y.; Jodoin, P.-M.; Emile, B.; Laurent, H.; Rosenberger, C. Comparative study of background subtraction algorithms. J. Electron. Imaging 2010, 19, 033003. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Lv, S.; Niu, X. Visual object tracking: A survey. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2022, 222, 103508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondrašovič, M.; Tarábek, P. Siamese visual object tracking: A survey. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 110149–110172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, D.D.; Jennings, A.L.; Black, J.T. Optical flow background estimation for real-time pan/tilt camera object tracking. Measurement 2014, 48, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husseini, S. A Survey of Optical Flow Techniques for Object Tracking. Bachelor’s Thesis, Tampere University, Tampere, Finland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kalitzin, S.; Geertsema, E.E.; Petkov, G. Optical Flow Group-Parameter Reconstruction from Multi-Channel Image Sequences. In Proceedings of the APPIS, Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain, 8–12 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Horn, B.K.; Schunck, B.G. Determining optical flow. Artif. Intell. 1981, 17, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, B.D.; Kanade, T. An iterative image registration technique with an application to stereo vision. In Proceedings of the IJCAI’81: 7th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 August 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Koenderink, J.J. Optic flow. Vis. Res. 1986, 26, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchemin, S.S.; Barron, J.L. The computation of optical flow. ACM Comput. Surv. 1995, 27, 433–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florack, L.; Niessen, W.; Nielsen, M. The intrinsic structure of optic flow incorporating measurement duality. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1998, 27, 263–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niessen, W.; Maas, R. Multiscale optic flow and stereo. In Gaussian Scale-Space Theory, Computational Imaging and Vision; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, R.; ter Haar Romeny, B.M.; Viergever, M.A. A Multiscale Taylor Series Approaches to Optic Flow and Stereo: A Generalization of Optic Flow under the Aperture. In Proceedings of the Scale-Space Theories in Computer Vision: Second International Conference, Scale-Space’99 Proceedings 2, Corfu, Greece, 26–27 September 1999; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Aires, K.R.; Santana, A.M.; Medeiros, A.A. Optical flow using color information: Preliminary results. In Proceedings of the 2008 ACM Symposium on Applied Computing, Fortaleza, Brazi, 16–20 March 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Niessen, W.; Duncan, J.; Florack, L.; Viergever, M. Spatiotemporal operators and optic flow. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Physics-Based Modeling in Computer Vision, Cambridge, MA, USA, 18–19 June 1995; IEEE Computer Society: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Pavel, M.; Sperling, G.; Riedl, T.; Vanderbeek, A. Limits of visual communication: The effect of signal-to-noise ratio on the intelligibility of American Sign Language. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1987, 4, 2355–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalitzin, S.N.; Parra, J.; Velis, D.N.; Da Silva, F.L. Quantification of unidirectional nonlinear associations between multidimensional signals. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 54, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Bai, H.; Lin, L.; Yang, F.; Chu, P.; Deng, G.; Yu, S.; Harshit; Huang, M.; Liu, J. Lasot: A high-quality large-scale single object tracking benchmark. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 439–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pediaditis, M.; Tsiknakis, M.; Leitgeb, N. Vision-based motion detection, analysis and recognition of epileptic seizures—A systematic review. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2012, 108, 1133–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuppens, K.; Vanrumste, B.; Ceulemans, B.; Lagae, L.; Van Huffel, S. Detection of epileptic seizures using video data. In Proceedings of the 2010 Sixth International Conference on Intelligent Environments, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 19–21 July 2010; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, X.; Liu, B. Video object tracking based on YOLOv7 and DeepSORT. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.12202. [Google Scholar]
- Jana, D.; Nagarajaiah, S. Computer vision-based real-time cable tension estimation in Dubrovnik cable-stayed bridge using moving handheld video camera. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2021, 28, e2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karpuzov, S.; Petkov, G.; Ilieva, S.; Petkov, A.; Kalitzin, S. Object Tracking Based on Optical Flow Reconstruction of Motion-Group Parameters. Information 2024, 15, 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15060296
Karpuzov S, Petkov G, Ilieva S, Petkov A, Kalitzin S. Object Tracking Based on Optical Flow Reconstruction of Motion-Group Parameters. Information. 2024; 15(6):296. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15060296
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarpuzov, Simeon, George Petkov, Sylvia Ilieva, Alexander Petkov, and Stiliyan Kalitzin. 2024. "Object Tracking Based on Optical Flow Reconstruction of Motion-Group Parameters" Information 15, no. 6: 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15060296
APA StyleKarpuzov, S., Petkov, G., Ilieva, S., Petkov, A., & Kalitzin, S. (2024). Object Tracking Based on Optical Flow Reconstruction of Motion-Group Parameters. Information, 15(6), 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15060296










