Abstract
AliAmvra is a project developed to explore and promote high-quality catches of the Amvrakikos Gulf (GP) to Artas’ wider regions. In addition, this project aimed to implement an integrated plan of action to form a business identity with high added value and achieve integrated business services adapted to the special characteristics of the area. The action plan for this project was to actively search for new markets, create a collective identity for the products, promote their quality and added value, engage in gastronomes and tasting exhibitions, dissemination and publicity actions, as well as enhance the quality of the products and markets based on the customer needs. The primary focus of this study is to observe and analyze the data retrieved from various tasting exhibitions of the AliAmvra project, with a target goal of improving customer experience and product quality. An extensive analysis was conducted for this study by collecting data through surveys that took place in the gastronomes of the AliAmvra project. Our objective was to conduct two types of reviews, one focused in data analysis and the other on evaluating model-driven algorithms. Each review utilized a survey with an individual structure, with each one serving a different purpose. In addition, our model review focused its attention on developing a robust recommendation system with said data. The algorithms we evaluated were MLP (multi-layered perceptron), RBF (radial basis function), GenClass, NNC (neural network construction), and FC (feature construction), which were used for the implementation of the recommendation system. As our final verdict, we determined that FC (feature construction) performed best, presenting the lowest classification rate of 24.87%, whilst the algorithm that performed the worst on average was RBF (radial basis function). Our final objective was to showcase and expand the work put into the AliAmvra project through this analysis.
1. Introduction
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on sustainable and high-quality catches from regional areas. The goal of such efforts is twofold: on the one hand, there is a focus on preserving the existing ecosystems as well as the biodiversity; on the other hand, this leads to the creation of investment opportunities for businesses in this market.
The AliAmvra project (Figure 1) stands as a noteworthy initiative, specifically focusing on the exploration and promotion of premium catches from the Amvrakikos Gulf, extending its reach to the broader regions of Arta. The core objective of the project is to establish an integrated plan of action, fostering a business identity characterized by high added value and tailored services that align with the unique features of the area.

Figure 1.
AliAmvra project logo.
This paper centers its attention on scrutinizing and interpreting data obtained from various tasting exhibitions associated with the AliAmvra project. The overarching goal is to enhance product quality, contribute to the ongoing action plan of AliAmvra on improving the quality of the products [1], and ultimately elevate the customer experience [2,3]. The methodology employed involves a comprehensive analysis of survey data collected during gastronomic events facilitated by the project, utilizing Google Forms to gather insights into both demographic information and product evaluations.
Furthermore, the publication extends its inquiry into the development of a robust recommendation system based on the acquired data. A pivotal aspect of this research is the incorporation of data-driven and model-driven algorithms to optimize the recommendation system’s efficacy. The model-driven analysis utilized in this study focused on the application of several ML/DL algorithms. A series of machine learning algorithms were utilized in the current work, such as MLP [4], RBF [5], GenClass [6], NNC [7], and FC [8]. Through this multifaceted approach, the paper seeks not only to contribute valuable insights to the AliAmvra project, but also to advance and broaden the understanding of the application of diverse algorithms in optimizing recommendation systems for projects of similar nature and scope.
Similar studies on the improvement or assessment of the quality of food products using machine learning or deep learning techniques have shown promising results. Computer Vision is also one of many ways to determine or help improve the quality of food products. One study applied convolutional neural networks [9] in food reviews to classify the quality of products using images as inputs; this task was achieved by segmenting the contents of the plate into multiple sections. Another similar study [10] used Computer Vision to analyze the color of coffee beans and classify their quality. In addition, machine learning is capable of assessing the quality of products through large-scale reviews with the assistance of demographic data or food product data. Two studies mention the use of ML algorithms, one focused on the association of demographic data and food choice motives [11] and the other focused on food quality assessment [12].
Moreover, machine learning techniques have also been applied to food safety models [13,14], food sales prediction [15,16], the evaluation of food quality [17,18], food security [19,20], etc.
The latter sections thoroughly convey the process of each analysis. Materials and Methods (Section 2) discusses the methodologies, tools, and techniques used in each analysis. Section 3 clarifies the data we retrieved from the exhibitions, including the development of our dataset. The Results Section (Section 4) expands the study even further by analyzing and visualizing the results of the models, as well as features a thorough visualization using data analysis. Finally, we provide a conclusion to the experiments applied in this study and determine the best-fitting model for the problem in question.
2. Materials and Methods
This section will begin with the basic principles of Grammatical Evolution, accompanied by a full example of producing valid expressions, and continue with a full description of the methods used to effectively evaluate the data collected during the execution of the project. Furthermore, this section covers information about the tools applied in the analysis of this project, including the methodologies applied to the model and data-driven analysis.
2.1. Grammatical Evolution
Grammatical Evolution [21] is a genetic algorithm with integer chromosomes. The concept of genetic algorithms was proposed by John Holland [22] and they are considered as biologically inspired algorithms. The algorithm produces potential solutions of an optimization problem randomly and these solutions are gradually altered in a series of iterations through the application of the genetic operators of selection, crossover, and mutation [23,24]. Genetic algorithms have been used in a series of real-world problems, such as electromagnetic problems [25], combinatorial problems [26], water distribution problems [27], neural network training [28,29], etc. The main advantage of genetic algorithms is that they can be easily parallelized [30,31] using programming techniques such as MPI [32] or OpenMP [33]. The chromosomes in Grammatical Evolution represent production rules of the provided BNF (Backus–Naur form) grammar [34]. Any BNF grammar G can be defined as the set with the following definitions:
- 1.
- N denotes the set of non terminal symbols of the underlying grammar.
- 2.
- T stands for the set of terminal symbols, where .
- 3.
- The terminal symbol S is named the start symbol of the grammar.
- 4.
- P is a finite set of production rules in the form or .
The Grammatical Evolution starts from the symbol S and produces valid programs, expressed only with terminal symbols, selecting production rules from the grammar. The production rules are selected using the following procedure:
- Read the next element V from the chromosome that is being processed.
- Obtain the rule: Rule = V mod R, where R is the total number of production rules for the current non-terminal symbol.
As an example, consider the grammar of Figure 2, which was used to produce valid expressions in C-like programming language. This grammar can be used to produce valid expressions in a language similar to the programming language C. On the right, each production rule is the sequential rule number for the corresponding non-terminal symbol. This number will be used by Grammar Evolution to select the next rule during expression generation.

Figure 2.
An example grammar to produce expressions in a C-like programming language.
Also, consider the chromosome and . The steps to produce the final string are outlined in Table 1.

Table 1.
An example for the production of a valid expression.
The Grammatical Evolution has been used in a variety of problems such as function approximation [35,36], in solving trigonometric equations [37], the automatic composition of music [38], neural network construction [39,40], creating numeric constraints [41], video games [42,43], estimation of energy demand [44], combinatorial optimization [45], cryptography [46], etc. Recent extensions of the Grammatical Evolution procedure include the Structured Grammatical Evolution [47,48], parallel implementations [49,50], the Probabilistic Grammatical Evolution variant [51], the Multi-Objective Grammatical Evolution approach [52], etc.
2.2. Construction of Classification Rules
A basic technique that will be used in conducting the experiments is that of constructing classification rules using Grammatical Evolution. This method was initially proposed in [6] and the corresponding software was described in [53]. This technique constructs classification rules with the assistance of Grammatical Evolution. The main steps of the used method are provided below.
- 1.
- Initialization Step:
- (a)
- Set as the number of chromosomes that will participate.
- (b)
- Set the total number of allowed generations as .
- (c)
- Produce (randomly) chromosomes. Each chromosome is considered as a set of integer values representing production rules of the underlying BNF grammar.
- (d)
- Define as the used selection rate, with .
- (e)
- Define as the used mutation rate, with .
- (f)
- Read the train set for the corresponding dataset.
- (g)
- Set iter = 0.
- 2.
- Fitness calculation Step:
- (a)
- For do
- i.
- Create a classification program . As an example of a classification program, consider the following expression:
- ii.
- Compute the fitness value as
- (b)
- Select EndFor.
- 3.
- Genetic Operations Step:
- (a)
- Selection procedure. The chromosomes are sorted initially according to their fitness values. The first chromosomes with the lowest fitness values are copied to the next generation. The rest of the chromosomes are replaced by offsprings produced during the crossover procedure.
- (b)
- Crossover procedure. For every pair of produced offsprings, two chromosomes are selected from the current population using the tournament selection. The process of tournament selection is as follows: Firstly, create a group of randomly selected chromosomes from the current population and the individual with the best fitness in the group is selected. These chromosomes will produce the offsprings and using one-point crossover. An example of one-point crossover is shown in Figure 3.
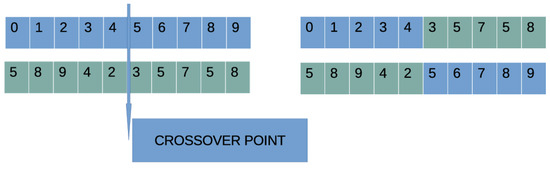 Figure 3. An example of the one-point crossover procedure.
Figure 3. An example of the one-point crossover procedure. - (c)
- Perform the mutation procedure. In this process, a random number is drawn for every element of each chromosome and it is altered randomly if .
- 4.
- Termination Check Step:
- (a)
- Set ;
- (b)
- If , terminate; or else, return to the Fitness Calculation Step.
2.3. Neural Network Construction
Another technique that maximizes the potential of Grammatical Evolution is the production of artificial neural networks that use it [7]. This technique can simultaneously construct the optimal structure of an artificial neural network as well as estimate the values of the network weights, minimizing the training error. The steps used in NNC are listed below.
- 1.
- Initialization Step:
- (a)
- Set as the number of chromosomes.
- (b)
- Set as the total number of generations allowed.
- (c)
- Produce (randomly) chromosomes as a series of production rules expressed in integer format.
- (d)
- Set the selection rate to and the mutation rate to .
- (e)
- Read the associated train set .
- (f)
- Set iter = 0.
- 2.
- Fitness Calculation Step:
- (a)
- For do
- i.
- Construct an artificial neural network . The neural networks constructed by this procedure are in the form:where d stands for the dimension of the input dataset and H denotes the number of processing nodes in the neural network. The function stands for the sigmoid function:
- ii.
- Compute the corresponding fitness value as
- (b)
- Select EndFor.
- 3.
- Genetic Operations Step:
- (a)
- Selection procedure. Initially, the chromosomes are sorted according to their associated fitness values. The first chromosomes with the lowest fitness values are transferred to the next generation without changes. The rest of the chromosomes are replaced by offsprings produced during the crossover procedure.
- (b)
- Crossover procedure. For each pair of newly added chromosomes, two parents are selected using tournament selection. The new chromosomes are created using one-point crossover.
- (c)
- Perform the mutation procedure. In this process, a random number is drawn for every element of each chromosome and it is altered randomly if .
- 4.
- Termination Check Step:
- (a)
- Set ;
- (b)
- If , terminate; or else, return to the Fitness Calculation Step.
2.4. Feature Construction with Grammatical Evolution
The Grammatical Evolution was also used as the base to construct artificial features from the original one for classification and regression problems [8]. The artificial features that create this procedure will be evaluated using a radial basis function (RBF) network [5]. The RBF network has an extremely fast and efficient training procedure with the incorporation of the K-means [54] method; additionally, RBF networks have been used with success in a variety of problems, such as physics problems [55,56], estimation of solutions for differential equations [57,58], robotics [59], chemistry [60], etc. The procedure of creating artificial features is divided in a series of steps listed below.
- 1.
- Initialization Step:
- (a)
- Set the number of chromosomes to .
- (b)
- Set the total number of allowed generations to .
- (c)
- Produce (randomly) chromosomes as random sets of integer.
- (d)
- Set the selection rate to and the mutation rate to .
- (e)
- Set F as the number of artificial features that will be constructed by the procedure.
- (f)
- Read the train set .
- (g)
- Set iter = 0.
- 2.
- Fitness Calculation Step:
- (a)
- For do
- i.
- Produce F artificial features from the original ones of the dataset.
- ii.
- The original training set TR is mapped to a new one using the artificial features produced. Denote this new training set as .
- iii.
- Train an RBF network using the set .
- iv.
- Compute the fitness value as
- (b)
- Select EndFor
- 3.
- Genetic Operations Step:
- (a)
- Selection procedure. Chromosomes are sorted based on the fitness of each one. The first will be transferred without changes to the next generation, while the rest will be replaced by chromosomes created in the crossover process.
- (b)
- Crossover procedure. For every pair of produced offsprings, two chromosomes are selected using tournament selection. These chromosomes will be the parents for two new offsprings and created with one-point crossover.
- (c)
- Mutation procedure. A random number is drawn for every element of each chromosome. The corresponding element is altered randomly if .
- 4.
- Termination Check Step:
- (a)
- Set ;
- (b)
- If , terminate; or else return to the Fitness Calculation Step.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis was to calculate the frequency of occurrences of all entries. Data visualization was achieved using Python libraries that are capable of generating interactable pie charts as a web application.
The frequency calculation for each entry was achieved by counting each occurrence of an entry for each question. The following formula was used to calculate the frequencies of every answer separately:
In Equation (5), n is the total number of answers; references the index and value of a given answer to a question; x represents the given answer we want to count; evaluates as 1 if is equal to x, otherwise as 0.
Once every frequency for each answer and each question is calculated, the data are prepared to be visualized with the help of graphing libraries.
2.6. Plotting Libraries
Streamlit is a highly capable open-source framework that allows users to deploy web applications exceedingly fast and easily in Python. It is compatible with many modern third-party frameworks and was created for data scientists, as well as ML, DL, and Computer Vision engineers. Furthermore, Streamlit has been a perfect use case for our analysis, not only for data visualization, but also due to its interactiveness. data charts. Streamlit’s impact on our analysis was the ease of use in embedding multiple interactive charts into a web application, allowing us to display the results as we desired.
Plotly is a high-level low-code graphing library [61] that allows users to create interactive graphs from their data. Plotly is fully supported by Streamlit, allowing users to build professional dashboards under the influence of their data. Seaborn [62] is a high-level Python data visualization library based on Matplotlib. We used Seaborn to visualize the prediction result experiments produced by the models we evaluated.
3. Datasets and Data Retrieval
The development of our dataset was instigated once we had completed a large portion of the data retrieval. We retrieved data from a total of eight different exhibitions/locations.
As previously mentioned, we received data by interacting with each customer in the tasting exhibitions. The information retrieved included demographic data, alongside graded products and general questions involving the experience customers had and their preferences.
The data retrieval was achieved with the assistance of the members of the AliAmvra project. Google Forms allowed us to build a very simple and fast survey to use. Our members approached each individual once they had tasted each or some of the samples and were provided with several questions about the experience they had with the products.
Prior to the processing of the dataset by the models, we made sure to clean and process any dormant values to remove possible casualties and improve the model’s performance. Any sample that was not tasted by the customers was attributed as a null value (0). Finally, we made sure to convert the data to numerical values so that the models could detect them successfully.
Survey Structures
There were two types of surveys used in the exhibitions. The first survey included mostly data for a thorough visualization and statistical analysis. We retrieved a total of 366 entries. The second survey included data appropriate for prediction and recommendation systems. Both surveys included timestamps which allowed us to differentiate the locations of each exhibition that every entry was retrieved from. The structure of the first survey included general questions involving the experience customers had with the products, as well as questions referring to each product, how much they enjoyed it, and what they enjoyed the most about it. The names of the samples introduced in the exhibitions with the first survey are “Beetroot risotto with smoked eel”, “Fried Sardine”, “Fish croquettes with mullet”, and “Sea bream Ceviche with lemon cream and pickled fennel”.
Data retrieval locations described in Table 2 include: Neoxori Arta 06/11/2023 https://maps.app.goo.gl/QurQhbfQxLFbUsAF9 (GP); (accessed on 1 February 2024). Kommeno Arta 08/04 https://maps.app.goo.gl/E4sBgJeki66qqD3p9 (GP); (accessed on 1 February 2024). Koronisia Arta 08/18 https://maps.app.goo.gl/rqdRxdmWrxSdybtg7 (GP); (accessed on 1 February 2024). Bigla Artas 08/19 https://maps.app.goo.gl/Agh4zGWXkG29db2n7 GP); (accessed on 1 February 2024). Skoufa Plazza Artas 09/21 https://maps.app.goo.gl/9wSJ9hrCRXFxms8K7 (GP); (accessed on 1 February 2024). Saint Dimitris Plazza Arta 09/22 https://maps.app.goo.gl/CLgkrQTuvBucYwPL9 (GP); (accessed on 1 February 2024). Zerva Plazza Arta 09/23 https://maps.app.goo.gl/tmWa7Eu1UPqZoFP38 (GP); (accessed on 1 February 2024).

Table 2.
The first survey structure which includes two grading questions repeated for each sample and two general questions.
The structure of the second survey included three demographic questions and five questions involving the grading of the products within the exhibitions. The names of the samples introduced in the exhibition with the second survey are “Grilled Eel”, “Baked Eel”, “Grilled Sea Bream”, “Grilled Chub”, and “Sardine”.
Data retrieval locations described in Table 3 include: Psathotopi Artas 10/15 https://maps.app.goo.gl/RA1TSZz7ApVit81a7 (GP). (accessed on 1 February 2024).

Table 3.
The second survey structure which includes three demographic questions and five sample grading questions.
The second survey, Figure 3 has an equivalent structure to the first; however, the described products in the exhibition with the second survey were different compared to the exhibitions of the first survey. Furthermore, the second survey did not include questions regarding the reason why a sample was endorsed, which is included in the first survey. The general questions of the second survey focused primarily on retrieving demographic data. Finally, the goal was to observe a correlation between the demographic data and the sample endorsement results.
The total count of entries for the first survey is a total of 366 entries. For the second survey, we retrieved data only from one location and it contains a total of 39 entries. Due to the reduced number of information provided in the second survey, there can be a significant difficulty in training neural networks.
4. Results
The experiments we conducted utilized data retrieved from both surveys. However, for our data analysis, we aimed our focus primarily on the first survey, due to its larger dataset and a wider range of provided questions. For our model review, we directed our attention to the second survey. This decision was driven based on the characteristics of the dataset, as outlined in Table 2, which includes demographic data essential to observing correlations.
4.1. Experimental Results
We conducted a thorough experiment by breaking down the structure of the second survey into two different phases. For the first phase, we used the models mentioned previously to predict customer preferences using only demographic data. For the second phase, we made the models to predict customer preferences using the demographic data, including the rest of the products as class features for each entry.
The experiments were executed 30 times for all used methods, and in each experiment, a different seed was used each time for the random number. To execute the experiments, the freely available QFc software [63] was used, and it is available from https://github.com/itsoulos/QFc/(accessed on 7 December 2023). The results were validated using the 10-fold cross-validation method. The execution machine was an AMD Ryzen 5950X with 128GB of RAM, running on Debian Linux, and the programs were compiled using the GNU C++ compiler. The values for the parameters of the used methods are shown in Table 4 and the results for the first phase of the experiments are outlined in Table 5 and for the second phase in Table 6, respectively.

Table 4.
The values of the experimental parameters.

Table 5.
Experiments for the first phase: demographic data-based dataset preferences.

Table 6.
Experiments for the second phase: dataset with the demographic data counting the rest of the product preferences.
Table 5 and Table 6 represent various information such as the dataset and the algorithms used to extract the evaluation results:
- 1.
- The column DATASET denotes the tested preference.
- 2.
- The column MLP stands for the application of an artificial neural network [64] with H hidden nodes to the dataset. The network is trained using the BFGS variant of Powell [65].
- 3.
- The column RBF represents the application of an RBF network with H hidden nodes to the dataset.
- 4.
- The column PCA represents the application of an artificial neural network to two new features constructed by the Principal Component Analysis (PCA) method [66].
- 5.
- The column GENCLASS refers to the application of the GenClass method, used to construct classification rules using a Grammatical Evolution-guided procedure.
- 6.
- The column NNC stands for the application of the neural network construction method analyzed previously.
- 7.
- The column FC refers to the application of the feature construction method of Section 2.4 to the dataset, where two artificial features are created.
- 8.
- In the experimental tables, an additional row was added with the title AVERAGE. This row contains the average classification error for all datasets.
4.2. Data Visualization
This section includes visualizations of the analysis applied to the exhibition data, using Streamlit [67], Plotly [61], and Seaborn [62]. Both surveys were included; however, as mentioned previously, we focused our attention onto the first survey, which was the largest dataset and which contained the most amount of information for our analysis.
4.2.1. Prediction Results
In this section, we describe the experimental findings derived from the analysis of both datasets showcased under Table 5 and Table 6. In the current section, we utilized box plots to visualize and better understand the prediction results of both experiments.
Figure 4 describes the results retrieved from the first experiment. We can observe a significant imbalance of the overall classification error between each model. FC displays a smaller overall gap and a lower classification error compared to the other model results, meaning that FC performed best for the first phase using only the demographic data. On the other hand, the radial basis function (RBF) displays the highest classification error and gap with two visible outliers compared to the other models. In other words, it displays the least favorable performance in terms of two visible outliers.
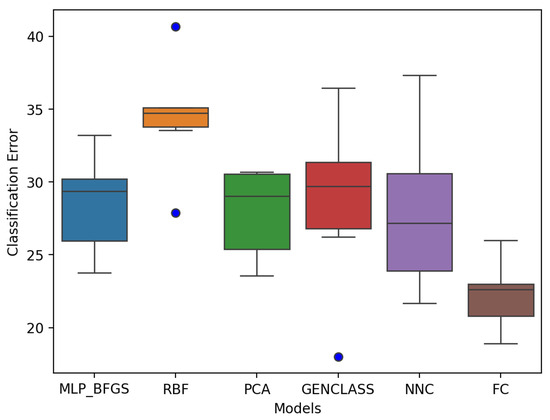
Figure 4.
First experiment model review results.
In the second experiment (Figure 5), the results display a better distribution among the models compared to the first phase. FC demonstrates superior performance, displaying a more favorable overall range and median classification error than the other models. MLP, RBF, and PCA present a rather suboptimal performance, with the overall range and median classification error much higher compared to the other models; however, NNC appears to perform well in terms of the distribution between each product.
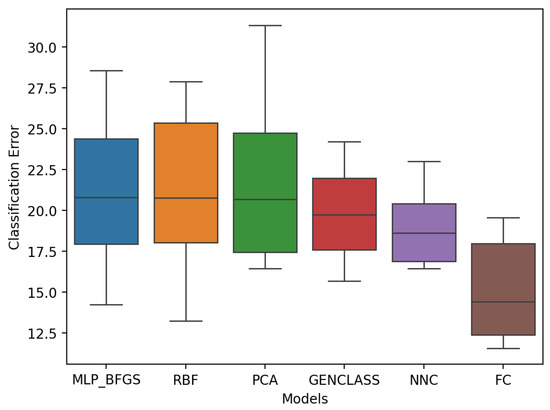
Figure 5.
Second experiment model review results.
4.2.2. Data Analysis
As mentioned previously, the first survey contained general questions regarding the overall experience the customers had with the samples. This information for the first survey is displayed in Figure 6 and Figure 7.
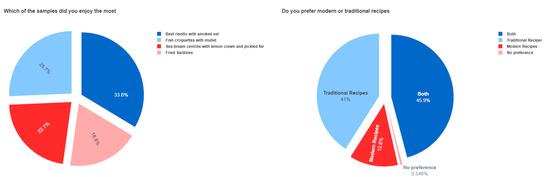
Figure 6.
General question results of the first survey.
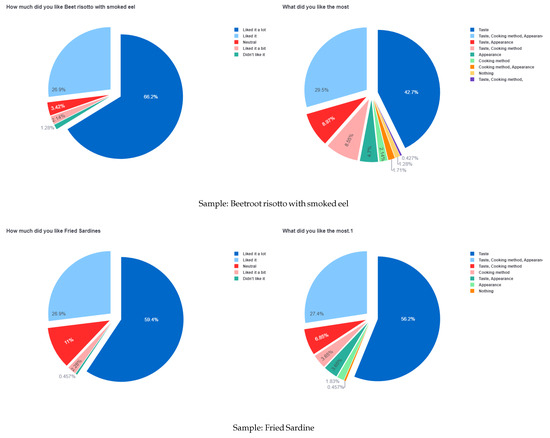
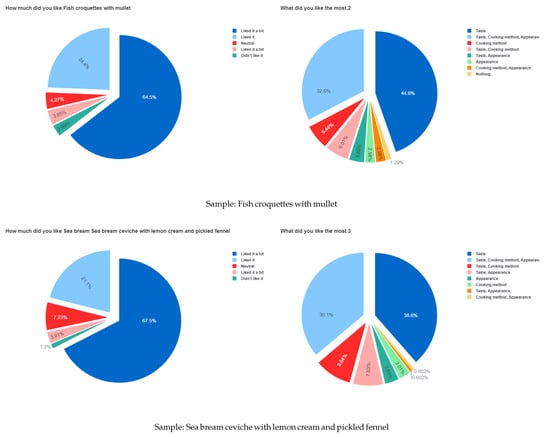
Figure 7.
Sample question results of the first survey.
Figure 6 describes the most endorsed sample and the type of cooking method. Figure 7 is a collection of results containing information regarding the individual preferences for each sample. The left pie charts describe the overall satisfaction of the customer with the sample. The right pie chart describes the reason for their satisfaction with the sample described on the left chart.
The data analysis results of the second survey, as shown in Figure 8 and Figure 9, are similar in terms of visualization to the previous pie chart except for the introduction to the satisfaction of the sample.
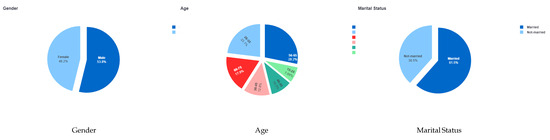
Figure 8.
Demographic question results of the second survey.
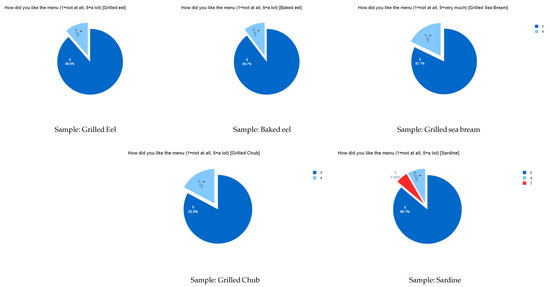
Figure 9.
Second survey sample question results.
Figure 8 describes the analysis of all the demographic data (gender, age, and marital Status) for every customer. Figure 9 describes the overall satisfaction of each sample for every customer.
In our final observation of the first survey results, the information collected and displayed in Table 7 describes that the most liked sample with the highest endorsement percentage was beet risotto with smoked eel; however, the least endorsed sample was fried sardines. Based on the observed results, the customers focused their attention onto the taste and looks and not significantly to the nutritional value of the sample. Whilst both samples are high in nutritional value, sardines contain a high amount of omega-3 fatty acids, which are considered to be healthy fats. On the other hand, the sample beet risotto with smoked eel contains a variety of vitamins such as minerals or antioxidants; however, it might also contain increased fat or calorie content based on the preparation of the sample (added butter, oil contents).

Table 7.
The overall endorsement percentage of each sample visualized based on Figure 6.
Under the circumstances of Table 7, there is a visible selection bias toward the entries referring to the sample beet risotto with smoked eel. The selection bias refers to the higher total number of entries compared to the other samples.
Table 8 describes the averaged grading of each plate without any constraints. The analysis applied to the second survey does not have enough entries for us to estimate an overall grade to determine which sample was enjoyed the most.

Table 8.
The averaged grading of each sample visualized in Figure 9.
5. Conclusions
AliAmvra focused on the promotion of the products produced by high-quality catches of the Amvrakikos Gulf. As a research team, we focused on a thorough analysis of the data retrieved from each exhibition. In addition, we developed a recommendation system to determine a person’s preferences for the products displayed in the exhibitions, based on their demographic data.
Each experiment focused on the production of different results. In our model-driven analysis, we found a strong correlation between each customer with their demographic data and preferences for each product, as we can observe in the previous plotted results (Figure 4 and Figure 5). We determined that FC performed the best compared to the rest of the models. In our data-driven analysis, we were able to observe the preferences of the mass for each individual question. We found that each analysis contributed to a different conclusion, in demand for the project.
Based on the analysis that was executed, it can be concluded that the best-fitting algorithm for the development of the project AliAmvra is FC [8]. FC performed best in both phases, where only the demographic data, or all of the data, were used to recommend a customer a product they would consider.
6. Future Work
To obtain more accurate results from our model-driven analysis, more data will need to be retrieved using the second survey with the demographic data. This can be achieved with future exhibitions that can take place with the AliAmvra project.
After our analysis, we have acknowledged that in order to improve the accuracy of our model-driven analysis, it is vital that we proceed to retrieve more data through the second survey. This can be accomplished by conducting future exhibitions as part of the AliAmvra project.
Author Contributions
I.G.T., D.M. and J.B. conceived the idea and methodology and supervised the technical part regarding the software. I.G.T. and D.M. conducted the experiments, employing several datasets, and provided the comparative experiments. J.B. and all other authors prepared the manuscript. I.G.T. organized the research team. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This research has been financed by the European Union: European Fund for Regional Development, under the call RESEARCH INNOVATION PLAN (2014–2020) of Central Macedonia Region, project name “Research and development IoT application for collecting and exploiting big data and create smart hotel” (project code: KMP6-0222906).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Misztal, A. Product improvement on the basis of data analysis concerning customer satisfaction. In Knowledge Base for Management—Theory and Practice; University of Žilina: Žilina, Slovakia, 2010; pp. 287–291. [Google Scholar]
- Alkerwi, A.; Vernier, C.; Sauvageot, N.; Crichton, G.E.; Elias, M.F. Demographic and socioeconomic disparity in nutrition: Application of a novel Correlated Component Regression approach. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e006814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishan, M.; Amir, A.L.; Supir, M.; Kushan, A.; Zulkifli, N.; Rahmat, M. Integrating Business Intelligence and Recommendation Marketplace System for Hawker Using Content Based Filtering. In Proceedings of the 2023 4th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Data Sciences (AiDAS), Ipoh, Malaysia, 6–7 September 2023; pp. 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawi, N.M.; Ransing, M.R.; Ransing, R.S. An Improved Learning Algorithm Based on The Broyden-Fletcher-Goldfarb-Shanno (BFGS) Method For Back Propagation Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Intelligent Systems Design and Applications, Jian, China, 16–18 October 2006; pp. 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpa, C.N.; Patil, A.; Thriveni, J.; Venugopal, K.R.; Patnaik, L.M. Web page recommendations using Radial Basis Neural Network technique. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 8th International Conference on Industrial and Information Systems, Peradeniya, Sri Lanka, 17–20 December 2013; pp. 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoulos, I.G. Creating classification rules using grammatical evolution. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Stud. 2020, 9, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoulos, I.; Gavrilis, D.; Glavas, E. Neural network construction and training using grammatical evolution. Neurocomputing 2008, 72, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilis, D.; Tsoulos, I.G.; Dermatas, E. Selecting and constructing features using grammatical evolution. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2008, 29, 1358–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, F.; Qiu, Z.; He, Y. Application of Deep Learning in Food: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1793–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybył, K.; Gawrysiak-Witulska, M.; Bielska, P.; Rusinek, R.; Gancarz, M.; Dobrzański, B.; Siger, A. Application of Machine Learning to Assess the Quality of Food Products. Case Study: Coffee Bean. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorage, L.; Wiseman, N.; Graca, J.; Harris, N. The Association of Demographic Characteristics and Food Choice Motives with the Consumption of Functional Foods in Emerging Adults. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, H.; Anwar, T.; Murtaza, S. Review on food quality assessment using machine learning and electronic nose system. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2023, 14, 100365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IZSTO; Ru, G.; Crescio, M.; Ingravalle, F.; Maurella, C.; UBESP; Gregori, D.; Lanera, C.; Azzolina, D.; Lorenzoni, G.; et al. Machine Learning Techniques applied in risk assessment related to food safety. EFSA Support. Publ. 2017, 14, 1254E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Cao, S.; Horn, A.L. Emerging Applications of Machine Learning in Food Safety. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 12, 513–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ichise, R. Food Sales Prediction with Meteorological Data—A Case Study of a Japanese Chain Supermarket. In Data Mining and Big Data, Proceedings of the Second International Conference, DMBD 2017, Fukuoka, Japan, 27 July–1 August 2017; Tan, Y., Takagi, H., Shi, Y., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- Tsoumakas, G. A survey of machine learning techniques for food sales prediction. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2019, 52, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Carvelo, A.M.; González-Casado, A.; Bagur-González, M.G.; Cuadros-Rodríguez, L. Alternative data mining/machine learning methods for the analytical evaluation of food quality and authenticity—A review. Food Res. Int. 2019, 122, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Li, T.; He, Y.; Gao, Q. Using Machine Learning Approaches for Food Quality Detection. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 6852022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, S.; Singh, H. Computer vision and machine learning based approaches for food security: A review. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 27973–27999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lentz, E.; Michelson, H.; Kim, C.; Baylis, K. Machine learning for food security: Principles for transparency and usability. Appl. Econ. Perspect. Policy 2022, 44, 893–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, M.; Ryan, C. Grammatical Evolution. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2001, 5, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.H. Genetic algorithms. Sci. Am. 1992, 267, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, D.E. Cenetic Algorithms in Search. In Optimization, Machine Learning; Addison-Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Michalewicz, Z. Genetic Algorithms + Data Structures = Evolution Programs; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Haupt, R.L. An introduction to genetic algorithms for electromagnetics. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 1995, 37, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grefenstette, J.; Gopal, R.; Rosmaita, B.; Van Gucht, D. Genetic algorithms for the traveling salesman problem. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Genetic Algorithms and Their Applications; Psychology Press: London, UK, 2014; pp. 160–168. [Google Scholar]
- Savic, D.A.; Walters, G.A. Genetic algorithms for least-cost design of water distribution networks. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 1997, 123, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, F.H.F.; Lam, H.K.; Ling, S.H.; Tam, P.K.S. Tuning of the structure and parameters of a neural network using an improved genetic algorithm. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2003, 14, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedki, A.; Ouazar, D.; El Mazoudi, E. Evolving neural network using real coded genetic algorithm for daily rainfall–runoff forecasting. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 4523–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantú-Paz, E.; Goldberg, D.E. Efficient parallel genetic algorithms: Theory and practice. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2000, 186, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Wang, S. A scalable parallel genetic algorithm for the generalized assignment problem. Parallel Comput. 2015, 46, 98–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, R.L.; Shipman, G.M.; Barrett, B.W.; Castain, R.H.; Bosilca, G.; Lumsdaine, A. Open MPI: A high-performance, heterogeneous MPI. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Cluster Computing, Barcelona, Spain, 28 September 2006; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Dagum, L.; Menon, R. OpenMP: An industry standard API for shared-memory programming. IEEE Comput. Sci. Eng. 1998, 5, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backus, J.W. The syntax and semantics of the proposed international algebraic language of the Zurich ACM-GAMM Conference. In Proceedings of the IFIP Congress, Paris, France, 15–20 June 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, C.; Collins, J.; Neill, M.O. Grammatical evolution: Evolving programs for an arbitrary language. In Proceedings of the Genetic Programming, Paris, France, 1 January 2006; Banzhaf, W., Poli, R., Schoenauer, M., Fogarty, T.C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 83–96. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, M.; Ryan, C. Evolving Multi-line Compilable C Programs. In Proceedings of the Genetic Programming, Paris, France, 26–27 May 1999; Poli, R., Nordin, P., Langdon, W.B., Fogarty, T.C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, C.; O’Neill, M.; Collins, J.J. Grammatical Evolution: Solving Trigonometric Identities. In Proceedings of the Mendel 1998: 4th International Mendel Conference on Genetic Algorithms, Optimisation Problems, Fuzzy Logic, Neural Networks, Rough Sets, Brno, Czech Republic, 24–26 June 1998; pp. 111–119. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega, A.; Alfonso, R.S.; Alfonseca, M. Automatic composition of music by means of grammatical evolution. In Proceedings of the APL Conference, Madrid, Spain, 25 July 2002. [Google Scholar]
- de Campos, L.M.L.; de Oliveira, R.C.L.; Roisenberg, M. Optimization of neural networks through grammatical evolution and a genetic algorithm. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 56, 368–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltanian, K.; Ebnenasir, A.; Afsharchi, M. Modular Grammatical Evolution for the Generation of Artificial Neural Networks. Evol. Comput. 2022, 30, 291–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, I.; O’Neill, M.; Brabazon, A. Constant Creation in Grammatical Evolution. Int. J. Innov. Comput. Appl. 2007, 1, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galván-López, E.; Swafford, J.M.; O’Neill, M.; Brabazon, A. Evolving a Ms. PacMan Controller Using Grammatical Evolution. In Proceedings of the Applications of Evolutionary Computation, Brno, Czech Republic, 12–14 April 2010; Di Chio, C., Cagnoni, S., Cotta, C., Ebner, M., Ekárt, A., Esparcia-Alcazar, A.I., Goh, C.K., Merelo, J.J., Neri, F., Preuß, M., et al., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 161–170. [Google Scholar]
- Shaker, N.; Nicolau, M.; Yannakakis, G.N.; Togelius, J.; O’Neill, M. Evolving levels for Super Mario Bros using grammatical evolution. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computational Intelligence and Games (CIG), Granada, Spain, 14 September 2012; pp. 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Rodríguez, D.; Colmenar, J.M.; Hidalgo, J.I.; Villanueva Micó, R.J.; Salcedo-Sanz, S. Particle swarm grammatical evolution for energy demand estimation. Energy Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 1068–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabar, N.R.; Ayob, M.; Kendall, G.; Qu, R. Grammatical Evolution Hyper-Heuristic for Combinatorial Optimization Problems. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2013, 17, 840–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, C.; Kshirsagar, M.; Vaidya, G.; Cunningham, A.; Sivaraman, R. Design of a cryptographically secure pseudo-random number generator with grammatical evolution. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, N.; Pereira, F.B.; Costa, E. Unveiling the properties of structured grammatical evolution. Genet. Program. Evolvable Mach. 2016, 17, 251–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, N.; Assunção, F.; Pereira, F.B.; Costa, E.; Machado, P. Structured Grammatical Evolution: A Dynamic Approach. In Handbook of Grammatical Evolution; Ryan, C., O’Neill, M., Collins, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerladn, 2018; pp. 137–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, I.L.; Bernardino, H.S.; Barbosa, H.J. A massively parallel Grammatical Evolution technique with OpenCL. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2017, 109, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufek, A.S.; Augusto, D.A.; Barbosa, H.J.C.; da Silva Dias, P.L. Multi- and Many-Threaded Heterogeneous Parallel Grammatical Evolution. In Handbook of Grammatical Evolution; Ryan, C., O’Neill, M., Collins, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 219–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mégane, J.; Lourenço, N.; Machado, P. Probabilistic Grammatical Evolution. In Genetic Programming, Proceedings of the 224th European Conference, EuroGP 2021, Held as Part of EvoStar 2021, Virtual Event, 7–9 April 2021; Hu, T., Lourenço, N., Medvet, E., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 198–213. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, P.J.; Cortez, P.; Mendes, R. Multi-objective Grammatical Evolution of Decision Trees for Mobile Marketing user conversion prediction. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 168, 114287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasopoulos, N.; Tsoulos, I.G.; Tzallas, A. GenClass: A parallel tool for data classification based on Grammatical Evolution. SoftwareX 2021, 16, 100830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacQueen, J. Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations. In Proceedings of the Fifth Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, Oakland, CA, USA, 21 June 1967; Volume 1, pp. 281–297. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, P. Machine-learning quantum mechanics: Solving quantum mechanics problems using radial basis function networks. Phys. Rev. E 2018, 98, 033305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, R.Ž.; Sretenović, A.A. Ensemble of radial basis neural networks with k-means clustering for heating energy consumption prediction. FME Trans. 2017, 45, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai-Duy, N. Solving high order ordinary differential equations with radial basis function networks. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2005, 62, 824–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarra, S.A. Adaptive radial basis function methods for time dependent partial differential equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 2005, 54, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, M.; Jena, D. Backstepping terminal sliding mode control of robot manipulator using radial basis functional neural networks. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2018, 67, 690–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, V.; Wright, G.B.; Fogelson, A.L.; Kirby, R.M. A radial basis function (RBF) finite difference method for the simulation of reaction–diffusion equations on stationary platelets within the augmented forcing method. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2014, 75, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotly. Collaborative Data Science 2013–2015. 5555 Av. de Gaspé 118, Montreal, Quebec H2T 2A3, Canada. Available online: https://plotly.com/ (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Waskom, M.L. Seaborn: Statistical data visualization. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoulos, I.G. QFC: A Parallel Software Tool for Feature Construction, Based on Grammatical Evolution. Algorithms 2022, 15, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtagh, F. Multilayer perceptrons for classification and regression. Neurocomputing 1991, 2, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, M. A tolerant algorithm for linearly constrained optimization calculations. Math. Program. 1989, 45, 547–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkmen, B.; Yıldırım, T. Improving classification performance of sonar targets by applying general regression neural network with PCA. Expert Syst. Appl. 2008, 35, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streamlit • A Faster Way to Build and Share Data Apps. Available online: https://streamlit.io/ (accessed on 1 February 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).