Clustering Visual Similar Objects for Enhanced Synthetic Image Data for Object Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Industrial Object Detection
2.2. Synthetic Data for Object Detection
2.3. Object Similarity Analysis
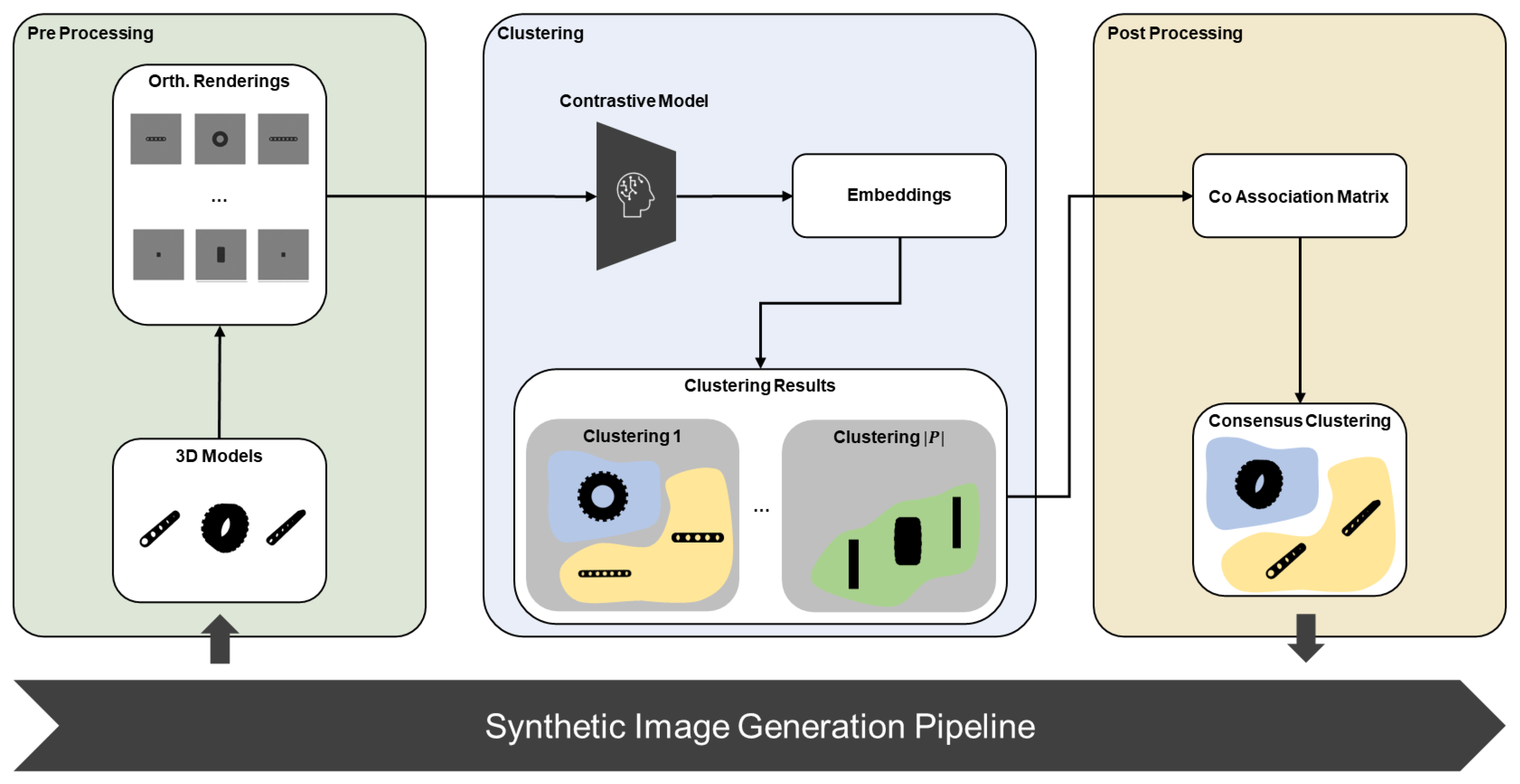
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Similarity Analysis
3.1.1. Pre-Processing
3.1.2. Clustering
3.1.3. Post-Processing
3.2. Fine-Tuning
3.3. Experimental Procedure
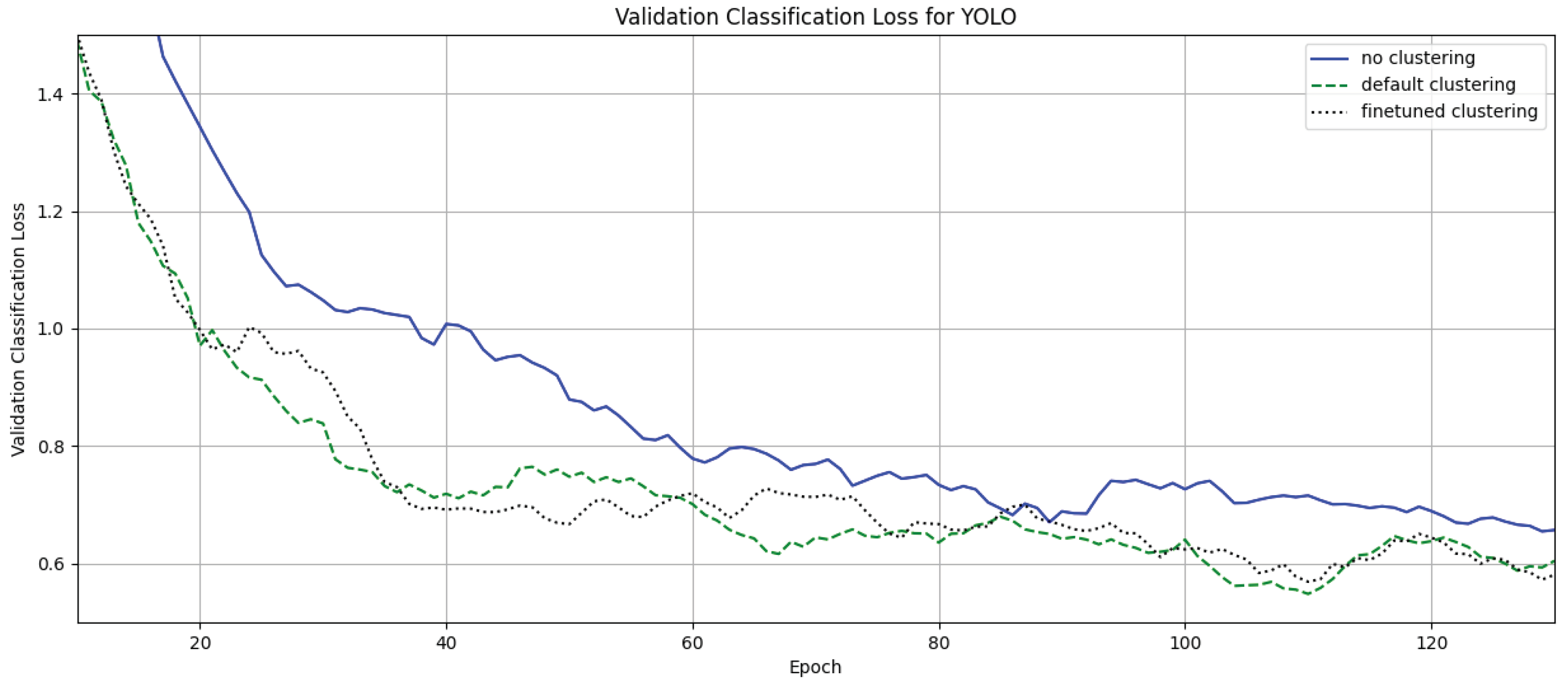
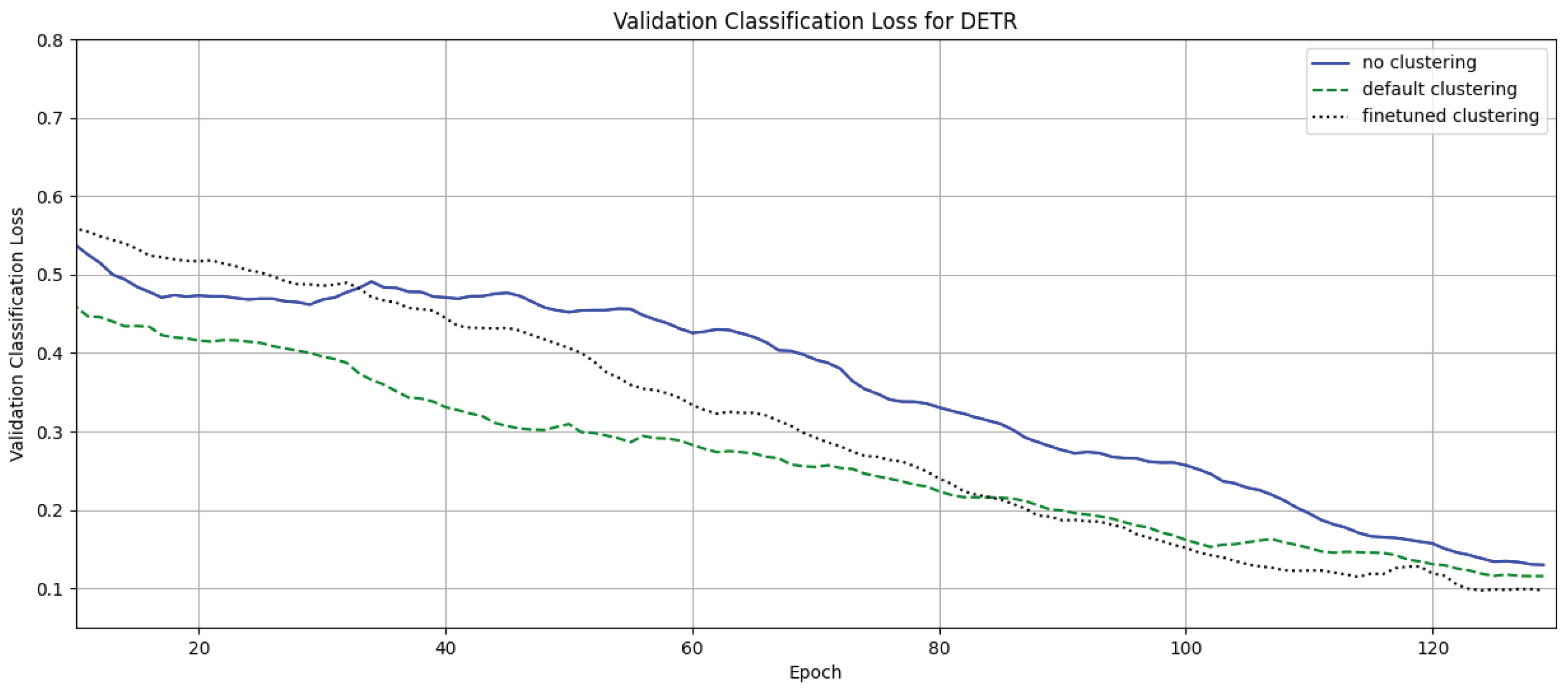
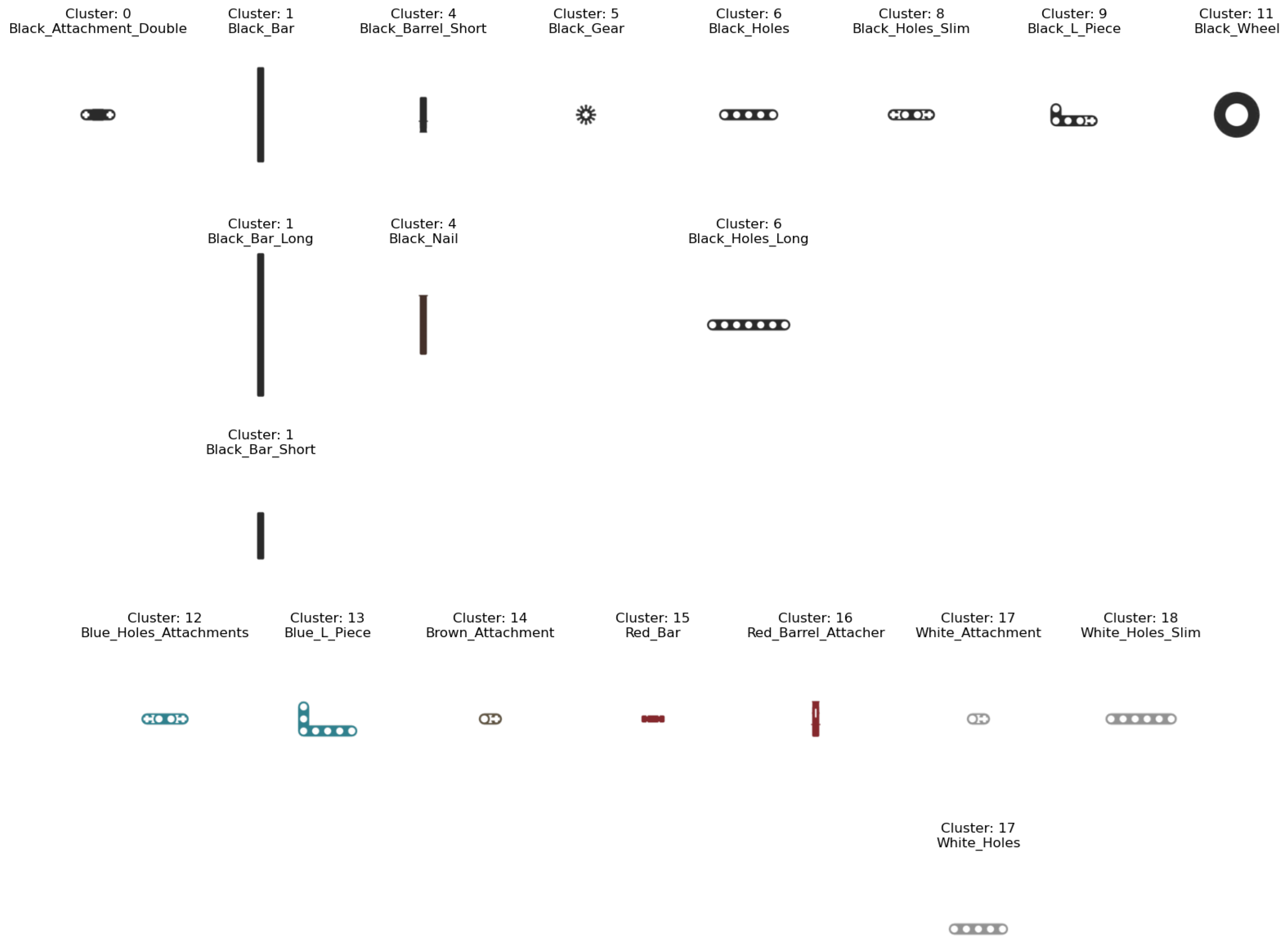
4. Results
4.1. Clustering Without Fine Tuning
4.2. Clustering with Fine-Tuning
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hussain, M. YOLO-v1 to YOLO-v8, the Rise of YOLO and Its Complementary Nature toward Digital Manufacturing and Industrial Defect Detection. Machines 2023, 11, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, H.; Kim, E.; Kim, D.M.; Park, H.W.; Jun, M.B.G. Machine Learning for Object Recognition in Manufacturing Applications. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2023, 24, 683–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.M.; Rahimi, A. Deep learning methods for object detection in smart manufacturing: A survey. J. Manuf. Syst. 2022, 64, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, A.; Gerlach, J.; Dietsch, M.; Herbst, S.; Engelmann, F.; Brehm, N.; Pfeifroth, T. A deep learning-based worker assistance system for error prevention: Case study in a real-world manual assembly. Adv. Prod. Eng. Manag. 2021, 16, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Song, L.; Ge, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Shan, Y. YOLO-World: Real-Time Open-Vocabulary Object Detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.17270. [Google Scholar]
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; Xiao, T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.C.; Wan-Yen, L.; et al. Segment Anything. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgart, N.; Lange-Hegermann, M.; Mücke, M. Investigation of the Impact of Synthetic Training Data in the Industrial Application of Terminal Strip Object Detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.04809. [Google Scholar]
- Trentsios, P.; Wolf, M.; Gerhard, D. Overcoming the Sim-to-Real Gap in Autonomous Robots. Procedia CIRP 2022, 109, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangold, S.; Steiner, C.; Friedmann, M.; Fleischer, J. Vision-Based Screw Head Detection for Automated Disassembly for Remanufacturing. Procedia CIRP 2022, 105, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogan, D.P.; DiFilippo, N.M.; Jouaneh, M.K. Deep learning computer vision for robotic disassembly and servicing applications. Array 2021, 12, 100094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, E.; Brinker, T.; Renaudo, E.; Hollenstein, J.; Haller-Seeber, S.; Piater, J.; Wörgötter, F. A Visual Intelligence Scheme for Hard Drive Disassembly in Automated Recycling Routines. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics, Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems, Online, 4–6 November 2020; SCITEPRESS—Science and Technology Publications. pp. 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basamakis, F.P.; Bavelos, A.C.; Dimosthenopoulos, D.; Papavasileiou, A.; Makris, S. Deep object detection framework for automated quality inspection in assembly operations. Procedia CIRP 2022, 115, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, R.J.; Nursyahid, F.F. Foreign objects detection using deep learning techniques for graphic card assembly line. J. Intell. Manuf. 2023, 34, 2989–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Židek, K.; Lazorík, P.; Piteľ, J.; Pavlenko, I.; Hošovský, A. Automated Training of Convolutional Networks by Virtual 3D Models for Parts Recognition in Assembly Process. In Advances in Manufacturing II; Trojanowska, J., Ciszak, O., Machado, J.M., Pavlenko, I., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 287–297. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, W.; Lai, Z.H.; Leu, M.C.; Yin, Z.; Qin, R. A self-aware and active-guiding training & assistant system for worker-centered intelligent manufacturing. Manuf. Lett. 2019, 21, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.H.; Tao, W.; Leu, M.C.; Yin, Z. Smart augmented reality instructional system for mechanical assembly towards worker-centered intelligent manufacturing. J. Manuf. Syst. 2020, 55, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greff, K.; Belletti, F.; Beyer, L.; Doersch, C.; Du, Y.; Duckworth, D.; Fleet, D.J.; Gnanapragasam, D.; Golemo, F.; Herrmann, C.; et al. Kubric: A scalable dataset generator. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rolf, J.; Wolf, M.; Gerhard, D. Investigation of an Integrated Synthetic Dataset Generation Workflow for Computer Vision Applications. In Product Lifecycle Management. Leveraging Digital Twins, Circular Economy, and Knowledge Management for Sustainable Innovation; IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology; Danjou, C., Harik, R., Nyffenegger, F., Rivest, L., Bouras, A., Eds.; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; Volume 702, pp. 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohbuchi, R.; Nakazawa, M.; Takei, T. Retrieving 3D shapes based on their appearance. In Proceedings of the 5th ACM SIGMM International Workshop on Multimedia Information Retrieval—MIR ’03, Berkeley, CA, USA, 7 November 2003; Sebe, N., Lew, M.S., Djeraba, C., Eds.; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2003; p. 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaku, K.; Okada, Y.; Niijima, K. Similarity measure based on OBBTree for 3D model search. In Proceedings of the Proceedings. International Conference on Computer Graphics, Imaging and Visualization, Penang, Malaysia, 26–29 July 2004; pp. 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehtaban, L.; Elazhary, O.; Roller, D. A framework for similarity recognition of CAD models. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2016, 3, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, G.; Sun, X.; Yan, M.; Zhang, J.; Ji, R. X-CLIP: End-to-End Multi-grained Contrastive Learning for Video-Text Retrieval. In MM ’22: Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisboa, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; Magalhães, J., Del Bimbo, A., Satoh, S., Sebe, N.T., Alameda-Pineda, X., Jin, Q., Oria, V., Toni, L., Eds.; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oquab, M.; Darcet, T.; Moutakanni, T.; Vo, H.; Szafraniec, M.; Khalidov, V.; Fernandez, P.; Haziza, D.; Massa, F.; El-Nouby, A.; et al. DINOv2: Learning Robust Visual Features without Supervision. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2304.07193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.N.; Groueix, T.; Ponimatkin, G.; Lepetit, V.; Hodan, T. CNOS: A Strong Baseline for CAD-based Novel Object Segmentation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.11067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wen, C.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, N. RS-CLIP: Zero shot remote sensing scene classification via contrastive vision-language supervision. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 124, 103497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. Unsupervised Deep Embedding for Clustering Analysis. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, NY, USA, 19–24 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Arutiunian, A.; Vidhani, D.; Venkatesh, G.; Bhaskar, M.; Ghosh, R.; Pal, S. Fine Tuning CLIP with Remote Sensing (Satellite) Images and Captions. 2021. Available online: https://huggingface.co/blog/fine-tune-clip-rsicd (accessed on 22 August 2024).
- Becht, E.; McInnes, L.; Healy, J.; Dutertre, C.A.; Kwok, I.W.H.; Ng, L.G.; Ginhoux, F.; Newell, E.W. Dimensionality reduction for visualizing single-cell data using UMAP. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 37, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Maaten, L.; Hinton, G. Visualizing Data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 2579–2605. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chechik, G.; Sharma, V.; Shalit, U.; Bengio, S. Large Scale Online Learning of Image Similarity Through Ranking. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2010, 11, 1109–1135. [Google Scholar]
- Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Usunier, N.; Kirillov, A.; Zagoruyko, S. End-to-End Object Detection with Transformers. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.12872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekhtiar, J.; Durupt, A.; Bricogne, M.; Eynard, B.; Rowson, H.; Kiritsis, D. Deep learning for big data applications in CAD and PLM—Research review, opportunities and case study. Comput. Ind. 2018, 100, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tresson, P.; Carval, D.; Tixier, P.; Puech, W. Hierarchical Classification of Very Small Objects: Application to the Detection of Arthropod Species. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 63925–63932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Kalhagen, E.S.; Olsen, Ø.L.; Goodwin, M. Hierarchical Object Detection applied to Fish Species. Nord. Mach. Intell. 2022, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwemer, M.H.; Wijnhoven, R.G.J.; de With, P.H.N. Hierarchical Object Detection and Classification Using SSD Multi-Loss. In Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications; Communications in Computer and Information Science; Bouatouch, K., de Sousa, A.A., Chessa, M., Paljic, A., Kerren, A., Hurter, C., Farinella, G.M., Radeva, P., Braz, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing and Imprint Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; Volume 1474, pp. 268–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, Faster, Stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, S.; Matveev, A.; Jiang, Z.; Williams, F.; Artemov, A.; Burnaev, E.; Alexa, M.; Zorin, D.; Panozzo, D. ABC: A Big CAD Model Dataset For Geometric Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]


| Contr. Model | avg. loss | avg. loss impr. | min. loss | min. loss impr. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | 0.944 | - | 0.546 | - |
| DINOv2 | 0.735 | 22.15% | 0.426 | 22.03% |
| Finetuned DINOv2 | 0.729 | 22.82% | 0.437 | 20.44% |
| Contr. Model | avg. loss | avg. loss impr. | min. loss | min. loss impr. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | 0.377 | - | 0.123 | - |
| DINOv2 | 0.285 | 24.54% | 0.108 | 12.95% |
| Finetuned DINOv2 | 0.332 | 11.94% | 0.090 | 26.93% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rolf, J.; Gerhard, D.; Kosic, P. Clustering Visual Similar Objects for Enhanced Synthetic Image Data for Object Detection. Information 2024, 15, 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15120761
Rolf J, Gerhard D, Kosic P. Clustering Visual Similar Objects for Enhanced Synthetic Image Data for Object Detection. Information. 2024; 15(12):761. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15120761
Chicago/Turabian StyleRolf, Julian, Detlef Gerhard, and Pero Kosic. 2024. "Clustering Visual Similar Objects for Enhanced Synthetic Image Data for Object Detection" Information 15, no. 12: 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15120761
APA StyleRolf, J., Gerhard, D., & Kosic, P. (2024). Clustering Visual Similar Objects for Enhanced Synthetic Image Data for Object Detection. Information, 15(12), 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15120761









