Abstract
Implementing single-channel speech enhancement under unknown noise conditions is a challenging problem. Most existing time-frequency domain methods are based on the amplitude spectrogram, and these methods often ignore the phase mismatch between noisy speech and clean speech, which largely limits the performance of speech enhancement. To solve the phase mismatch problem and further improve enhancement performance, this paper proposes a dual-stream Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) with phase awareness, named DPGAN. Our generator uses a dual-stream structure to predict amplitude and phase separately and adds an information communication module between the two streams to fully apply the phase information. To make the prediction more efficient, we apply Transformer to build the generator, which can learn the sound’s structural properties more easily. Finally, we designed a perceptually guided discriminator that quantitatively evaluates the quality of speech, optimising the generator for specific evaluation metrics. We conducted experiments on the most widely used Voicebank-DEMAND dataset and DPGAN achieved state-of-the-art on most metrics.
1. Introduction
Speech plays a critical role in both human communication and human-machine interaction. However, speech captured in natural space using consumer-grade devices often contains a variety of noise, reverberation, etc. It must be enhanced before it can be used in research. Nowadays, a large number of denoising methods have been proposed and applied in related fields [1,2,3,4,5]. Despite this, denoising in real environments still needs to be solved and speech enhancement performance needs to be improved. The goal of this paper is to enhance noisy speech to improve its recognisability and intelligibility.
Existing single-channel speech enhancement methods can be divided into two categories: time domain methods and time-frequency (T-F) domain methods [6,7]. The former deals directly with the speech waveform, while the latter is done with a two-dimensional spectrogram. T-F methods have now been applied in many speech enhancement algorithms, and the most widely used of them is the T-F masking method. This method minimizes noise by predicting the T-F mask of the input speech spectrogram. However, most of them recover only the amplitude, combining it with the noise phase in order to recover the waveform. This can create phase mismatch problems and lead to artifacts. The complex ideal ratio mask (CIRM) [8] although adds phase information to the enhancement process by means of complex arithmetic, the author of [9] demonstrated that simply changing the training target to CIRM does not achieve the desired effect, while complex arithmetic does not provide significant recovery of phase while greatly increasing the computational effort. To address these issues, we were inspired by [10] and proposed a dual-stream structure with phase awareness that uses a dual-stream network to recover amplitude and phase separately. Since CIRM pointed out that there is no clearly identifiable structure for phase in polar coordinates, this suggests that it is difficult for us to perform phase estimation independently. Therefore, we designed an information communication module between the dual streams to enhance the recovery results through the interaction between the two predictions.
Traditional deep neural networks are often sensitive to training data and difficult to generalise to unknown noise. In contrast, the properties of generative adversarial networks (GAN) dictate that they can improve the authenticity of the recovered audio by adversarial loss [11,12]. When applying GAN to a speech enhancement task, enhancement is done through the generator (G), and the discriminator (D) is used to discriminate between clean and noisy speech. However, many experiments such as [13,14,15,16,17] have demonstrated that the method used by the discriminator in most GANs to determine whether each sample is true or not is not perfectly correlated with the metric considered for testing performance. Thus, the discriminator should be designed to guide the generator towards the right goal. Inspired by MetricGAN [18], we propose a discriminative model for this problem by converting the discriminator’s target space from discrete (true 1 and false 0) to continuous (evaluation metrics). The goal of optimisation is to give a perceptual evaluation score of the input spectrogram. When selecting the generator, the convolutional neural networks (CNN) used in traditional image processing often do not adequately capture the harmonic information in the spectrogram (correlations in images are mostly local, while correlations along the frequency axis in the speech spectrogram are mostly non-local [10]). While networks such as recurrent neural networks (RNN) and long-short-term memory (LSTM), which are more commonly used in speech enhancement, can better capture the features of speech sequences, their structures are often homogeneous. This makes it challenging to learn long-term and short-term dependencies at the same time. The emergence of Transformers has addressed this problem to some extent [19].Unlike traditional deep neural networks, the entire network structure of Transformer is composed entirely of the attention mechanism. This mechanism helps us focus comprehensively on the input information in relevance. Specifically, the Transformer consists of Self-Attenion and Feed Forward Neural Networks. This multi-headed attention mechanism is able to better capture the relationships between distant sequence elements. At the same time, the attention mechanism also determines that it can focus on all elements in the sequence, which also makes it easier to achieve Inter-contextual prediction to some extent. Compared with the familiar neural network architectures (CNN, RNN, etc.), it greatly improves the efficiency and accuracy of machine learning tasks. It also provides an alternative way of thinking about speech enhancement. Considering that in our task we only need to extract features from the spectrogram of noisy speech to obtain the corresponding mask, we decided to eliminate the decoder. Instead, we used only the encoder to process the spectrogram.
In brief, we design a dual-stream GAN with phase awareness for speech enhancement, called DPGAN. We summarize our contributions as follows:
- In the generator stage, we propose a novel dual-stream structure that incorporates phase into the enhancement process, effectively solving the phase mismatch problem while being able to further improve enhancement performance.
- In this dual stream structure, information communication (IC) between the two prediction streams is added to improve the respective enhancement effects.
- We propose Mask Estimated Blocks (MEB) based on Transformer, which can better extract sound features to accomplish mask estimation.
- In the discriminator stage, inspired by MetricGAN [18], we designed a perceptually guided discriminator to accomplish targeted optimisation by modelling specific evaluation metrics.
- We conducted more comprehensive experiments to justify the design structure. As shown by the experimental results, DPGAN is capable of improving the performance of speech enhancement to a certain extent compared with the current method.
The remainder of the paper is structured as follows. Section 2 presents related work, Section 3 describes the implementation of our work, Section 4 lists experimental details and analyses of experimental results. Section 5 summarises the content of the paper, discussing limitations and future research directions.
2. Related Work
2.1. T-F Domain Methods
Speech enhancement based on the T-F domain can be divided into two types: masking and mapping, and we focus here on the widely used and more effective T-F domain-based masking method. This method can be traced back to the spectral subtraction method proposed by Boll in 1979 [20], which treats the spectrogram of noise as a special linear mask. We first need to convert the waveform into amplitude and phase by short-time Fourier transform (STFT). Then, the mask is inferred by learning from the noisy amplitude spectrogram and applied to it to obtain the predicted amplitude. Finally, combined with the phase of noisy speech, the predicted spectrogram is transformed back into the time domain by the inverse short-time Fourier transform (ISTFT). The same steps are followed for preprocessing deep learning tasks.
The choice of mask is closely related to the performance of speech enhancement. Most of the current work only deals with the amplitude, using mostly ideal binary masking (IBM) [21], ideal ratio masking (IRM) or ideal amplitude masking (IAM) [22,23], often using the phase of noisy speech to complete the transformation of the speech waveform. However, subsequent studies have demonstrated that phase plays a significant role in improving speech quality and intelligibility [24]. As a result of this, phase sensitive masking (PSM) [25] was proposed to improve IAM by simply adding phase information, which is still essentially real-valued masking. CIRM has influenced most current speech enhancement methods to some extent. As a complex-valued mask, CIRM takes the amplitude and phase of speech as the real and imaginary parts respectively in the computation, and is theoretically optimal under the assumption of additive noise. Since then, based on the principle of plural arithmetic [26], Choi designed a complex convolution layer and constructed a complex-valued U-Net [27]. Later Hu added complex-valued LSTM to further improve the composition of complex networks [28]. In spite of this, experiments have also shown that complex masking does not significantly improve speech enhancement as we had hoped [10,29]; the problem of phase mismatch remains unresolved.
2.2. Time Domain Methods
Traditional time-domain speech enhancement methods include Wiener filtering [30], Kalman filtering [31], etc. Similar to many traditional methods, these methods require complex mathematical computation to complete, and are ineffective when dealing with non-smooth noise. Time-domain-based deep learning uses waveforms as inputs, which eliminates the need for waveform synthesis, as well as the challenge of phase prediction. We can simply understand this process as waveform mapping. In contrast, RNNs and LSTMs, which are widely used, are often unsuited to long sequences, and the gradient disappearance problem occurs when speech signals are ultra-long. As a solution to this problem, WaveNet was developed to learn mappings of sampled value sequences directly and more efficiently [32]. Rethage improved WaveNet by using non-causal expansion convolution to predict the target domain [33]. Later Stoller used the construction of a one-dimensional convolution combined with U-Net to accomplish enhancement by means of phonetic source separation [34]. The same idea was also proposed by [35], which mainly consists of a U-Net structure and a bidirectional LSTM. Luo et al., on the other hand, partitioned the long sequence input into smaller chunk chunks and iteratively applied intra-chunk and inter-chunk RNNs, while the dependencies between the spectrum of a single frame and consecutive frames were modeled, which leads to a large modeling overhead while improving the enhancement effect [36]. The excellent performance of Transformer [37] in the field of natural language processing has also led many researchers to experiment with its introduction into the speech domain. The attempts in [38,39] have demonstrated that the Transformer structure is comprehensively ahead of all previously used network structures in the field of speech separation and speech recognition. The research on speech enhancement further proves the effectiveness of multi-head attention mechanisms in modeling global context information [40,41]. However, although these time-domain approaches address the estimation of phase to some extent, they also ignore sound features that are more easily distinguishable in the T-F domain. As a result, there is still room for further research into time-domain methods. Meanwhile, in order to further explore the performance of speech enhancement, researchers have started to try to introduce GAN into this field.
2.3. GAN-Based Method
SEGAN first imports GAN into the SE problem by minimizing the loss function and training G to map noisy speech x to clean speech y [42]. As an end-to-end network structure, its input and output are both time-domain signals. As its main operations are performed by convolution, it consumes relatively little memory and time. On this basis, SERGAN modified the discriminator to improve the enhancement by determining the probability of the input data being true or false [43]. This also demonstrates the importance of a well-performing discriminator for GAN. To improve the performance of the discriminator, HiFi-GAN proposed a multi-scale discriminator, and constructed discriminators in the frequency and time domains separately for joint training [44]. In order to improve the performance of optimization even further. Researchers have attempted to combine evaluation metrics with optimization directions. Kolbaek tries to construct an objective function similar to STOI to optimize for this evaluation metric [45]. Fu, on the other hand, constructs a loss function by combining STOI with MSE, which is able to further improve speech intelligibility [46]. These methods also provide novel ideas for the design of discriminators. However, since a part of the evaluation functions are not fully differentiable (e.g., PESQ, ESTOI, etc.), their computation tends to be more complicated compared with STOI, so we cannot directly use them as the objective function (in most cases researchers manually produce simple differentiable functions to approximate the evaluation metrics). MetricGAN, on the other hand, proposes a new solution idea, using a black box approach, where the evaluation metric is used as a reward and a discriminator is used to model the behavior of an objective metric that can predict the PESQ score of the input speech in order to motivate the generator to further improve its performance on this metric [18]. Additionally, the choice of generator model is also critical. On the one hand, Longer data can significantly increase the computational effort of RNNs and LSTMs. On the other hand, it is becoming increasingly common for CNNs and transformers to be used as generators. We set up a comprehensive speech enhancement framework by combining the Transformer, which is more suitable for extracting acoustic features, and the perceptually guided discriminator in MetricGAN. Our discriminator can quantitatively evaluate speech quality metrics that are closely related to human hearing. To further enhance the enhancement effect, we blend phase information to complete the network construction. Compared to other current GAN methods, we are able to exploit the phase information more fully and still be adaptive to unfamiliar noise.
3. Methods
3.1. Overview
The overall architecture of our system is shown in Figure 1, with Training D and Training G representing the training stages of the discriminator and generator, respectively. The main body of the system consists of a generator G and an audio quality discriminator D. During the discriminator stage, we design a perceptually guided discriminator inspired by MetricGAN, which guides the optimisation of the generator by simulating a specific evaluation metric function, such as Perceptual evaluation of speech quality (PESQ) [47] or Short-Time Objective Intelligibility (STOI) [48]. We use the Q Function to represent the evaluation metrics of speech, and D needs to simulate its behavior. So similarly, D requires pairs of spectrograms as input (speech to be evaluated and clean target speech), and optimisation of the discriminator is accomplished by continuously reducing the loss between the predicted score given by D and the true score given by the Q Function.
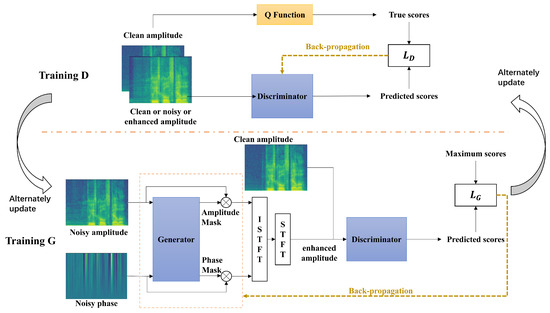
Figure 1.
The overall framework of our system is shown here, with Training G and Training D representing the training process for the generator and discriminator respectively. They are updated alternately. Where Q Function is our target score, which we can choose to set as PESQ or STOI. STFT and ISTFT refer to Short Time Fourier Transform and Inverse Short Time Fourier Transform respectively. and denote the loss functions of the discriminator and the generator respectively.
In the training stage of the generator, we need to take both the amplitude spectrogram and phase spectrogram as input. G can perform feature extraction on them respectively to derive the most suitable amplitude and phase mask. This mask can be applied to the input signal to obtain preliminary estimates of amplitude and phase. Then we can recover them to the enhanced speech waveform by ISTFT. Finally, the final enhanced speech amplitude spectrogram can be obtained by STFT. The amplitude spectrogram of the enhanced speech is used as input together with the corresponding amplitude spectrogram of the target speech. The optimisation of the generator is done by the loss between the predicted score given by D and the target score. In practical experiments, the target score can generally be set to the maximum score. To address the problem that static surrogates can easily be deceived by adversarial examples [49] (estimated mass fraction increases but true fraction decreases [50]), We update these two training stages alternately.
3.2. Dual Stream Generator with Phase Awareness
In our system, the main task of the generator is to estimate the mask for the spectrogram of noisy speech. We can apply it to perform the main task of speech enhancement. In order to solve the phase mismatch problem that exists in most current work, as well as to improve enhancement performance at the same time. We propose a dual-stream generator with phase awareness. The basic structure is shown in Figure 2.
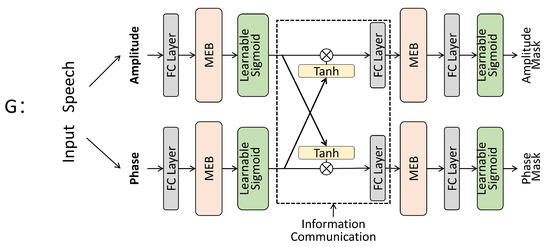
Figure 2.
This is a dual stream generator structure with phase awareness. Stream A represents the amplitude stream, while stream P represents the phase stream. Streams A and P provide amplitude masks and phase masks, respectively. Each stream consists of two MEB modules.
Our basic idea is to distinguish between the prediction of amplitude and phase, and perform enhancement through two parallel streams. These two streams can be denoted by and respectively, and their main structure is similar. We first complete the integration of the input data by means of a fully connected (FC) layer of 256 channels. Afterwards the Mask Estimated Blocks (MEB) module is connected to perform the initial feature extraction operation. We need two such feature extraction operations to complete the final mask estimation. In order to avoid oversize values affecting the training process, we introduced the Learnable Sigmoid layer to complete the truncation of the data [51]. The mathematical representation is shown in Equation (1).
where is a learnable parameter, it will vary depending on the frequency band of the training data. On the other hand, can be configured with a variety of truncation intervals, which is the range of values for our Mask. In most of the experiments, masks are typically truncated between 0 and 1, but in the superposition of speech and noise, the problem of inverse phase extinction can easily arise. Therefore, the amplitude and phase of the noise may not necessarily be much higher than that of pure speech (i.e., it is possible that the value of pure speech is higher than that of the noisy signal). Meanwhile, for the phase, most of the phase mask does not produce many variations, and the phase wrapping problem created by a certain degree of phase amplification just compensates for the lack of negative values of our Mask. It is able to meet the needs of a small portion of the phase that needs to change significantly. In order to determine the value of , we randomly selected 1200 sets of speech data from the train set and the test set, each containing the noisy speech and the corresponding clean speech. We divided them to obtain the standard replication and phase Mask, and plotted the distribution histograms separately, as shown in the following Figure 3. Accordingly, we chose to set to 1.2, the interval of 0–1.2 can contain the vast majority of the data in it. In addition, inspired by [52], we pre-set the lower limit of mask to 0.05 before applying it to the spectrogram to avoid musical noise.
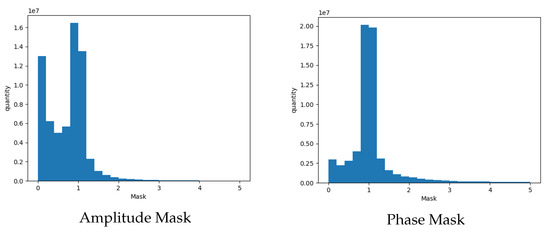
Figure 3.
We randomly selected 1200 groups of speech and calculated the standard mask values of amplitude and phase. It is intuitively apparent that some mask values are outside the range of 0 to 1.
3.3. Information Communication
Information communication plays a crucial role in the dual-stream structure. Numerous experiments have demonstrated that it is very difficult to recover phase information singularly [8,10]. In order to make more complete use of the information in the phase spectrogram, we set up an Information Interaction (IC) module between the dual streams. We expect that the mask estimates of the dual streams can communicate with each other. The phase prediction can be better guided by the amplitude stream. Likewise, the phase prediction results can also be applied back to the amplitude streams, and the combination of the two can further improve the enhancement performance. The implementation of this module is shown in Equation (2).
where ⊙ denotes element-wise multiplication and and denote the amplitude and phase stream respectively. The and represent the amplitude and phase stream of the next stage. After that, we need to complete all the information communication operations through a fully connected layer. As shown in Figure 2, in the generator our IC module is located between the two feature extraction operations.
3.4. Mask Estimated Blocks
In both Stream A and Stream P, the main operation is handled by Mask Estimated Blocks, whose main function is to extract features from the amplitude or phase spectrogram. We have chosen to use the Transformer to perform this function, as its unique multi-head attention mechanism is better able to capture the dependencies in the speech information. The basic Transformer is a codec structure, but we only need to perform feature extraction on the spectrogram to get the estimated mask. Instead of improving the results, the decoder module would make the consumption of computational resources increase significantly. Therefore, we decided to use only Encoder to complete the construction of the MEB module. As shown in Figure 4, the left side shows the basic structure of a MEB module, which consists of eight Transformer encoders and a fully connected layer of 257 nodes. We set a Dropout of 0.1 for each encoder in our experiments and set the residual connectivity and normalization layers before Multi-Head Attention and Feed Forward, an operation that improves the performance and stability of the training. The structure of multi-head attention is shown on the right, which is also consistent with the structure of the base Transformer. We set n to 16 in the figure, indicating the number of heads. The Feed Forward layer is composed of a linear layer and a LeakyReLU layer, each with 512 nodes.
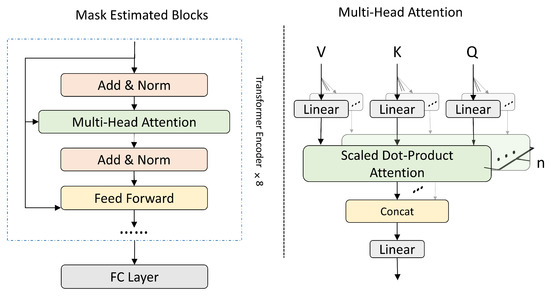
Figure 4.
Structure of the MEB. Its main body is an 8-layer Transformer encoder with a fully connected layer. In the experiment, we set the n to 16.
3.5. Perception Guided Discriminator
Our discriminator guides the generator by giving a quality-aware score for the input speech, and it only needs to model an evaluation metric that can be implemented by simple feature extraction. The structure is shown in Figure 5. Usually, the discriminator requires two inputs, namely the amplitude spectrogram of the speech being scored and the amplitude spectrogram of the target speech. We need to concatenate them together first, and standardize the data through the BatchNorm layer. Here we set the momentum parameter to 0.01. The body of the discriminator is a CNN with four two-dimensional convolutional layers. The number of channels in each layer is 15, and the kernel size is 5 × 5. A global averaging pooling layer was added to handle different lengths of speech input. This resulted in a fixed dimensionality of 15 for the features (i.e., the number of feature mappings in the previous layer). Three FC layers were added. The first two layers had 50 and 10 linear nodes respectively, and a LeakyReLu layer was applied after each layer for activation (the of LeakyReLu was set to 0.3). The final layer has only one linear node for outputting the final prediction score. We applied spectral normalization with 1-Lipschitz continuity [53] to all layers used in the discriminator to stabilize the training process, and we trained D as a smooth functional model that estimates the amplitude spectrogram to derive the corresponding scores. Our discriminator can be set up with different evaluation metrics to accomplish different optimisation goals. Here, we tried two main evaluation metrics, PESQ and STOI, which take full account of human auditory perception and are closer to subjective test results in most cases.
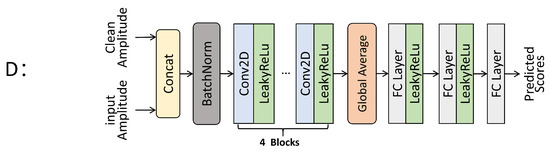
Figure 5.
The proposed structure of the perceptually guided discriminator, whose body is four two-dimensional CNNs, ultimately outputs a normalised prediction score through feature extraction.
3.6. Loss Function
We will present our loss function in two parts, the generator and the discriminator. Similarly to MetricGAN [18], we abandon the traditional binary labeling strategy in the design of the discriminator and simulate evaluation metrics instead. We can refer to Q(I) as the normalised evaluation metric, where I represents the input to the metric. Since PESQ takes values in the range of (−0.5, 4.5). In order to complete the experiment more conveniently, we add it to 0.5 and divide by 5 to ensure that the final number finger can be maintained between (0, 1). It is necessary to train the discriminator so that its behavior conforms to Q(I). Following [51], we incorporate noisy speech into the training of the discriminator, optimising it based on the loss between the true scores and the predicted scores given by D. The final discriminator loss of DPGAN can be described as the Equation (3):
where x and y denote noisy speech and clean speech, and represents enhanced speech processed by the generator. Q refers to the optimisation evaluation metric we set. and denote the prediction score of the discriminator and the true objective evaluation metric. The three terms in the equation represent the discriminator applied to clean speech, enhanced speech and noisy speech, respectively. Similarly, we take the amplitude spectrogram of the augmented speech and the amplitude spectrogram of the clean speech as input and use the discriminator to give a prediction score, using the loss between this score and the target score to optimise the generator, as shown in Equation (4).
where s represents the desired optimisation score, which we can simply assign a value of 1 to generate the enhanced speech.
4. Results
4.1. Implementation Details
Voicebank+DEMAND: In order to provide a more meaningful comparison with other existing methods, we used the publicly available VoiceBank-DEMAND dataset [54], which is widely used in almost all speech enhancement (SE) systems. A predefined training set and a test set are included. Clean speech was provided by 30 speakers from the VoiceBank corpus. Of these, 28 were included in the training set and two were included in the test set. Alternatively, noisy speech consists of clean speech mixed with noise from DEMAND [55]. In the training set, there are 40 different types of noise, with a total of 11,572 samples and signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs) of 15, 10, 5 and 0 dB. 20 different kinds of noise are included in the test set, with a total of 824 samples and signal to noise ratios of 17.5, 12.5, 7.5, and 2.5 (The noise and speakers in the test set are not visible in the training set). Detailed parameters of the data can be found in the original literature.
Our full experiments were constructed in Pytorch, based on the Speechbrain toolkit [56]. All speech samples in the experiments were resampled to 16 kHz. The amplitude spectrogram and phase spectrogram were obtained by STFT, which was computed using Hamming windows with a window length of 32 ms, a hop length of 16 ms, and FFT points set to 512. The network models were all optimised using Adam [57]. We set as 0.9 and as 0.999, the learning rates of G and D are set to 0.0001 and 0.0005. There are four phases of training in each of our epochs. Of these, the first three training phases are for D. The following is a brief description of the training process for D and G.
G: 100 data are randomly drawn from the training set to train.
D: Our G undergoes through three training phases. First, we also extract 100 sets of real data from the training set to complete the initial training. According to the study in [58], we also believe that the training of the discriminator can be improved by adding data generated in previous epochs. Without this mechanism, the discriminator is likely to forget the target behaviour, i.e., only optimise D, rather than bringing it closer to the pattern of the evaluation metric. For this reason, A second stage of training has been added to D. In each epoch, a random portion of the generated data is incorporated into the historical dataset, and D is optimized with this portion of data. Our tests have shown that the most effective results are obtained when the extraction ratio is set at 20%. Thus, the historical dataset is increased by 20 data points per epoch. Following this, we will randomly select 100 sets of data from the training set for optimization. This will further improve the performance of D. To complete the training process, we set 850 epochs. The experiment shows that the best convergence occurs around the 800th epoch.
LibriSpeech+PNL: To further test the performance and scalability of the network, we constructed the corresponding training set, validation set and test set using the LibriSpeech dataset [59]. In our experiments, we randomly selected 5000 clean discourses from the train_clean100 subset of the LibriSpeech dataset. We mixed these discourses based on 10 noise types from [60] (two crowd noises, two machine noises, alarms and siren, traffic and car noises, animal sound, wind, cough, and laugh) according to different levels of SNR (0 dB, 5 dB, 10 dB and 15 dB). To form the final 20,000 training utterances. As a validation set, we chose to incorporate another 1000 clean utterances and another 10 noisy samples with 4 different SNRs (1 dB, 6 dB, 11 dB, and 16 dB), which totals 4000 examples. Finally, we randomly selected the LibriSpeech dataset test_clean with 2000 speech as our test set, and these discourses are mixed with five invisible noise types (bell, clap, cry, tooth brushing, and footsteps), with SNRs of The SNRs were 2.5 dB, 7.5 dB, 12.5 dB and 17.5 dB, respectively. The training parameters on this dataset are the same as those mentioned above.
4.2. Quantitative Evaluation
In order to evaluate the performance of speech enhancement and to compare it with other systems, the following five objective metrics were used: PESQ [47], STOI [48], CSIG, CBAK and COVL [61].
PESQ: Perceptual evaluation of speech quality.which is the major optimisation objectives for our proposed DPGAN. The wide-band version recommended in ITU-T P.862.2 is used (from −0.5 to 4.5).
STOI: Short-time objective intelligibility, which indicates the intelligibility of speech (from 0 to 1).
CSIG: Mean opinion score (MOS) prediction of signal distortion attending only to speech signals (from 1 to 5).
CBAK: MOS prediction of the intrusiveness of background noise (from 1 to 5).
COVL: MOS prediction of the overall effect (from 1 to 5).
All the above metrics are the higher the better.
To analyze the performance of the system, we tried to reproduce some of the classical speech enhancement algorithms, including SEGAN [42], iSEGAN, DSEGAN [62], MetricGAN [18], HiFiGAN [44], MetricGAN+ [51], and PHASEN [10]. iSEGAN and DSEGAN are extensions of SEGAN training, which connect multiple generators in order to enhance the enhancement effect. While HiFiGAN and MetricGAN+ are the networks with better performance among different repair methods. Meanwhile, since Voicebank+DEMAND has been limited to a training set, a validation set, and a test set, we cite some papers based on this dataset (including SERGAN [43],CP-GAN [63],MMSE-GAN [64] and the recently published PGGAN [65] and DCCRGAN [66]). Furthermore, we have selected some of the better performing and classical non-GAN methods for comparison, including DC-U-Net [27] and Wave-U-Net [67], both of which are built on the U-Net architecture, and S-DCCRN [68] using the plural domain. (For the purpose of fair and representative comparisons, all of these papers use training data from the original Voicebank+DEMAND dataset for training). Table 1 shows the comparison results with the above baseline, where DPGAN(S) and DPGAN(P) are the results of our discriminator’s fits to the STOI and PESQ, respectively. As can be seen, compared to most GANs, our method has a breakthrough performance lead in both the main evaluation metric PESQ, improving to 3.32, and some degree of improvement in other metrics, which demonstrates the effectiveness of dual-stream GAN with phase awareness in the field of speech enhancement, and the feasibility of using only the Transformer encoder to build the generator. At the same time, we note that the CSIG and CBAK scores in some of the models are slightly higher than ours, because we set the lower limit of Mask to 0.05, which makes the speech more natural-sounding [51]. However, our repair for phase also introduces new noise to some extent, so it may cause a decrease in these two metrics. We also show multiple sets of restoration effects in the subsequent qualitative analysis, from which we can see that our restoration effect is improved compared to some other methods. As for the decrease in these two indicators. We also made the following attempts. We also experimented with truncating Mask to 0-1, which proved to improve both metrics to some extent, but at the same time reduced the performance of the main optimization metric, PESQ. Moreover, the analysis of the actual enhanced audio shows that the slight reduction of these two metrics has an acceptable impact on the final restoration results. We have also tried to use CBAK, CSIG, and COVL to be the main optimization metrics, but more experiments show that the improvement of these data tends to cause a large decrease in the remaining metrics and affects the the final enhancement effect. In addition, our discriminator is currently trained to fit only PESQ and STOI. In general, DPGAN is able to provide some enhancements to the current SOTA system.

Table 1.
Comparison of DPGAN with the other top methods on Voicebank+DEMAND datasets, - indicates that the corresponding results are not given in the text.
The following Table 2 illustrates the effects of our restoration on the self-built LibriSpeech+PNL dataset. We show here the comparative results of SEGAN, MetricGAN, HiFiGAN, PHASEN, and MetricGAN+ with DPGAN. In the table, it can be seen that DPGAN is able to improve the performance of PESQ more significantly while the difference in STOI is relatively small. In addition, this study proves that phase information can be incorporated into speech enhancement using DPGAN. As a result of combining the above two parts of experiments, DPGAN can perform the enhancement task more effectively when trained for PESQ. At the same time, it can also provide us with an idea for speech enhancement task. We can target some more suitable evaluation metrics to train for a comprehensive improvement of speech enhancement.

Table 2.
Comparison of DPGAN with the other classical methods on LibriSpeech+PNL datasets.
4.3. Acoustic Analysis
In Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9 we show the enhancement effect for different kinds of noise. From left to right and from top to bottom in the figures are clean speech, noisy speech, and the enhanced effects of SERGAN, MetricGAN, PHASEN and DPGAN, respectively. We visualise using waveforms and Mel spectrograms. For display purposes, we set the NFFT to 512 and the hop width to 16 when obtaining the Mel spectrogram, using the hamming window for the transformation. It can be seen that our method is able to remove most of the high frequency noise or low frequency noise very well, without causing excessive damage to the original sound information of the session.
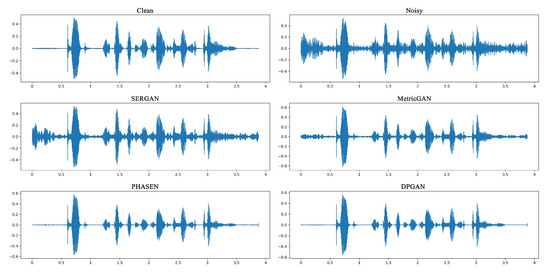
Figure 6.
A comparative waveform plot of the enhancement effect of low-frequency noise at higher signal-to-noise ratios is shown. From left to right and top to bottom are pure speech, noisy speech, and the enhanced effects of SERGAN, MetricGAN, PHASEN and DPGAN, respectively.
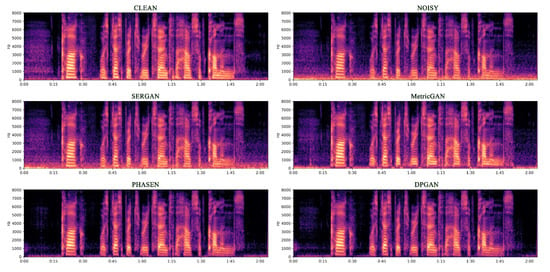
Figure 7.
A comparative spectrogram of the enhancement effect of low frequency noise at higher signal-to-noise ratios is shown. The noise is shown in the plot as the cluttered highlighted blocks at the bottom.
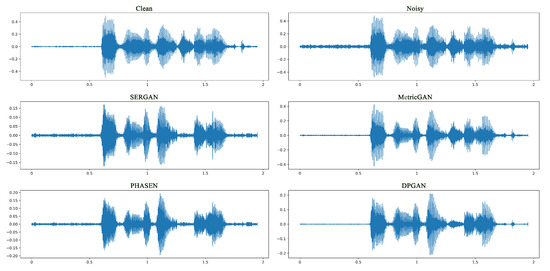
Figure 8.
A comparison of the waveforms of the enhancement effect for full-band noise at lower signal-to-noise ratios is shown. Noise appears as cluttered pulses in waveform.
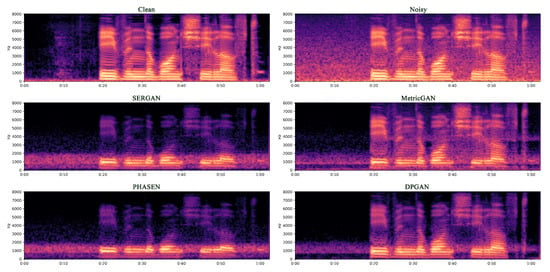
Figure 9.
A comparative spectrogram of the enhancement effect of full-band noise at lower signal-to-noise ratios is shown. This contains most of the low frequency noise, which is shown as lighter coloured blurred noise in the plot.
4.4. Image Analysis
To show our restoration results even further. We show a portion of the generated image in the following Figure 10 and Figure 11. It includes a comparison of the Mel spectrogram and waveform plot of the noisy speech with the enhanced speech. It can be seen from the images that DPGAN is able to perform the speech enhancement task better. However, some distortion may also occur in the face of higher SNR. Overall, DPGAN is able to remove most of the noise signal, while the phase change further improves the enhancement performance.
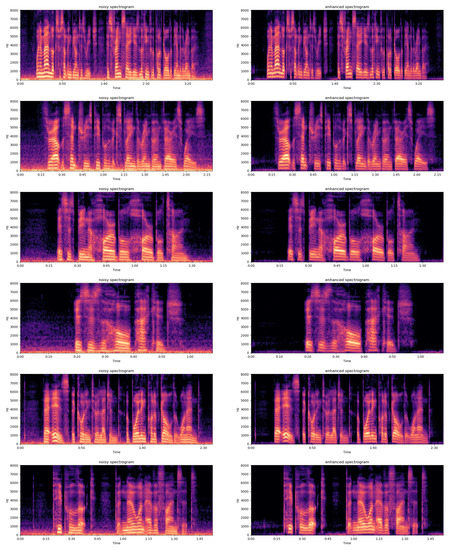
Figure 10.
A comparison of the Mel spectrograms of the noisy speech and the enhanced speech, where the left is the noisy speech and the right image is the enhanced speech.
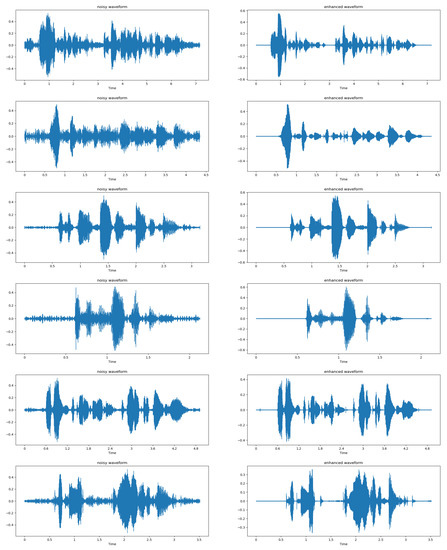
Figure 11.
A comparison of the waveform plot of the noisy speech and the enhanced speech, where the left is the noisy speech and the right image is the enhanced speech.
And we also show a part of the restoration process with amplitude mask and phase mask. As shown in Figure 12 and Figure 13. We can see that the amplitude has a large variation, and extending the value of mask to 1.2 can enhance the action ability of mask more effectively. At the same time, for most of the phases, The mask values are kept around 1, there is actually not much variation, which also avoids the appearance of phase wrapping to some extent, and also avoids generating more noise information.
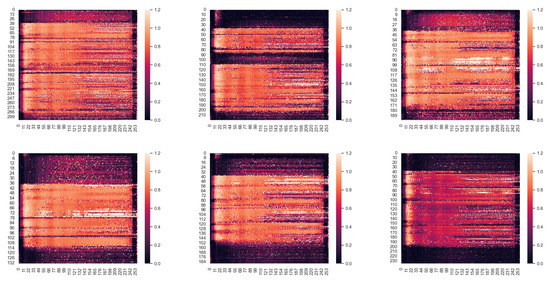
Figure 12.
Amplitude enhancement masks for different noise speech. Lighter colors represent larger values.
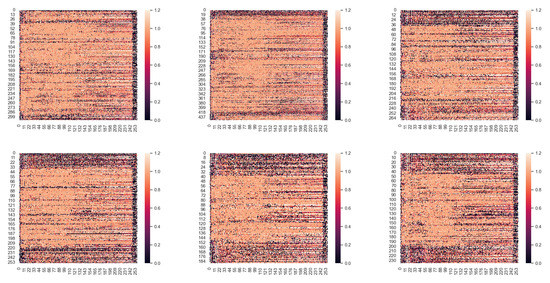
Figure 13.
Phase enhancement masks for different noise speech. Lighter colors represent larger values.
4.5. Ablation Study
To demonstrate the effectiveness of the structure, we conducted an ablation study on networks with different settings. In Table 3 we show in detail the effect of the different training techniques introduced in Section 3 using a split SNR. The results in each row are obtained by adding the settings of the previous row to the current technique. It can be seen that most algorithms process best at SNRs of 12.5 dB and 7.5 dB, while the results tend to decrease when faced with low SNR situations. In this case, our base uses two bi-directional LSTM (BLSTM) designed generators, using noise phase to restore the speech waveform and discriminators for PESQ simulation. Using the MEB instead of the BLSTM (MEB is the replacement of BLSTM with Transformer Encoder), a substantial improvement in the results was obtained, indicating the soundness of the design. Furthermore, as can be seen from the table, the scores even show a degree of decrease after the inclusion of the phase. This also confirms that it is not feasible to estimate the phase singularly without going through the information communication. As we mentioned in Section 2, it is due to the specificity of the phase structure itself that relatively scant work has been done to optimise for phase. Therefore, we need some additional information to help predict the phase. Experimental results also support this idea, and the effect is further improved by adding a dual-stream information communication (IC), where communication between the two predicted streams is necessary. Where P and S denote the simulation of PESQ and STOI respectively. Combining the information in the table we can see that the use of PESQ to construct the discriminator has a much better restoration effect. The main reason for this is the design of the STOI scores themselves. Training on this metric does not fully exploit the potential of the network; STOI only discriminates intelligibility and is not comprehensive in its ability to assess the quality of speech. For example, speech that contains noise and reverberation is just as likely to be more intelligible as speech with less noise. On the other hand, our approach can also provide some indication of the comprehensiveness and generalisability of the evaluation metrics. On balance, the choice to optimise for the PESQ metric is more convincing.

Table 3.
Ablation experiments.
5. Limitations
According to the above experimental results, our system is able to make better improvements to the optimization objectives in most cases. The PESQ scores have been significantly improved. It should be noted, however, that some of the non-major optimization metrics are degrading as well. As a result, we evaluate the limitations of the current experiments and reflect on the future.
1. The analysis in Section 4 showed that, since the phase is more abstract information, a small change will have a significant effect on the final enhanced result. However, there have not been many attempts to recover the phase in speech enhancement. We recover the phase spectrogram separately and use the similar mask as the amplitude spectrogram when choosing the recovery method, without fully considering the phase information itself. We should take it further and think about a more suitable mask for phase characteristics to improve dual-stream path optimization. On the other hand, as shown in Figure 3, although we expanded the mask range to (0,1.2), some standard mask values still fell outside this interval, and we tried to further expand the mask range, but the experimental results were not satisfactory. This also requires us to readjust parameters to solve this problem.
2. In our experiments, we did not adequately address the phase wrapping problem. We tried to use the more widely used complex domain to complete the recovery instead of the phase spectrum. However, the experimental results were disappointing. Furthermore, phase mismatch, which occurs frequently in speech enhancement, continues to exist. The results of this study indicate that there is still room to improve the recovery of the phase spectrogram. DPGAN provides an innovative solution for this purpose and also demonstrates the need to add information communication between the recovery of phase and the recovery of amplitude, but the experimental results also show that there is still room for further exploration of this problem.
3. We present our experimental results using PESQ and STOI as optimization targets (Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3). Moreover, we also used CSIG, CBAK, and COVL as optimization targets during our experiments, but the final scores were much lower than the first two. To some extent, we believe that this reflects the performance of the sound quality evaluation metrics. Li [69] attempted to evaluate many new metrics, such as Speech intelligibility in bits (SIIB) [70], Hearing-aid speech perception index (HASPI) [71], Extended short-time objective intelligibility (ESTOI) [72], etc. It is also proposed to train jointly with several metrics. In the future, we can try similar approaches to improve the performance.
4. Furthermore, we have only tested the network on single-channel speech with different SNRs against common natural noise, and have not explored its performance on de-reverberation or multi-channel speech. In order to improve the content of future experiments, we are currently working on developing a more comprehensive noise dataset. In addition, the English data does not adequately reflect the generalization abilities of the network, and it is necessary to expand to data in other languages as well.
In summary, our method proposes a novel way of speech enhancement and provides an innovative idea for phase recovery. However, given the decline in CSIG and CBAK scores, further studies of phase characteristics and the selection of the main optimization metrics are required.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we design a dual-stream GAN with phase awareness for single-channel speech enhancement tasks. To achieve better enhancement performance, our generator uses a dual-stream network to recover amplitude and phase separately, and adds a bi-directional information communication module to guide the two prediction streams to each other. We also propose to use a more advanced Transformer structure to extract speech features for mask estimation. The full-scale experiments also justify the design we have adopted in DPGAN. Compared with the current SOTA system, DPGAN is able to improve its performance to a certain extent. At the same time, however, the introduction of phase into speech enhancement is still in its infancy and there is still room for further improvement in our experimental results. In the future, we will attempt to try other networks that are more suitable for phase features to further enhance the usefulness of the network. We will also explore the potential of DPGAN in low-latency environments and mobile applications, which often require faster response times, and we can also extend this architecture to other speech-related tasks such as speech separation and multi-channel speech enhancement.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.L. (Xintao Liang); Data curation, X.L. (Xintao Liang); Formal analysis, X.L. (Xintao Liang); Investigation, X.L. (Xintao Liang); Methodology, X.L. (Xintao Liang) and X.L. (Xiaomin Li); Resources, X.L. (Xintao Liang) and Y.Z.; Software, X.L. (Xintao Liang) and Y.D.; Supervision, Y.D.; Validation, X.L. (Xintao Liang), Y.L. and Y.D.; Visualization, X.L. (Xintao Liang); Writing—original draft, X.L. (Xintao Liang); Writing—review and editing, Y.L. and Y.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61303093, 61402278) and the Shanghai Natural Science Foundation (19ZR1419100).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The Voicebank-DEMAND dataset used in this article is publicly available. This public dataset can be found here: https://datashare.ed.ac.uk/handle/10283/3443 (accessed on 1 March 2022).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yang, L.P.; Fu, Q.J. Spectral subtraction-based speech enhancement for cochlear implant patients in background noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2005, 117, 1001–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R. Speech enhancement using MMSE short time spectral estimation with gamma distributed speech priors. In Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Orlando, FL, USA, 13–17 May 2002; Volume 1, pp. 1–253. [Google Scholar]
- Habets, E.A.P. Single- and multi-microphone speech dereverberation using spectral enhancement. Diss. Abstr. Int. 2007, 68. [Google Scholar]
- Nakatani, T.; Yoshioka, T.; Kinoshita, K.; Miyoshi, M.; Juang, B.H. Speech dereverberation based on variance-normalized delayed linear prediction. IEEE Trans. Audio, Speech Lang. Process. 2010, 18, 1717–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, F.G.; Mysore, G.J.; Fujioka, T. Equalization matching of speech recordings in real-world environments. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Shanghai, China, 20–25 March 2016; pp. 609–613. [Google Scholar]
- Defossez, A.; Synnaeve, G.; Adi, Y. Real time speech enhancement in the waveform domain. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.12847. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.L.; Fu, S.W.; Li, Y.J.; Huang, J.W.; Wang, H.M.; Tsao, Y. Multichannel speech enhancement by raw waveform-mapping using fully convolutional networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2020, 28, 1888–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, D.S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D. Complex ratio masking for monaural speech separation. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2015, 24, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ephrat, A.; Mosseri, I.; Lang, O.; Dekel, T.; Wilson, K.; Hassidim, A.; Freeman, W.T.; Rubinstein, M. Looking to listen at the cocktail party: A speaker-independent audio-visual model for speech separation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Luo, C.; Xiong, Z.; Zeng, W. Phasen: A phase-and-harmonics-aware speech enhancement network. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 9458–9465. [Google Scholar]
- Binkowski, M.; Donahue, J.; Dieleman, S.; Clark, A.; Elsen, E.; Casagrande, N.; Cobo, L.C.; Simonyan, K. High Fidelity Speech Synthesis with Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.11646. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.; Kumar, R.; de Boissiere, T.; Gestin, L.; Teoh, W.Z.; Sotelo, J.; de Brébisson, A.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A.C. MelGAN: Generative Adversarial Networks for Conditional Waveform Synthesis. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Ledig, C.; Theis, L.; Huszár, F.; Caballero, J.; Cunningham, A.; Acosta, A.; Aitken, A.; Tejani, A.; Totz, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4681–4690. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yu, K.; Wu, S.; Gu, J.; Liu, Y.; Dong, C.; Qiao, Y.; Change Loy, C. Esrgan: Enhanced super-resolution generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) Workshops, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, A.; Wang, D. On adversarial training and loss functions for speech enhancement. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 5414–5418. [Google Scholar]
- Michelsanti, D.; Tan, Z.H. Conditional generative adversarial networks for speech enhancement and noise-robust speaker verification. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1709.01703. [Google Scholar]
- Donahue, C.; Li, B.; Prabhavalkar, R. Exploring speech enhancement with generative adversarial networks for robust speech recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 5024–5028. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.W.; Liao, C.F.; Tsao, Y.; Lin, S.D. Metricgan: Generative adversarial networks based black-box metric scores optimization for speech enhancement. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 10–15 June 2019; pp. 2031–2041. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.u.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All you Need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Boll, S. Suppression of acoustic noise in speech using spectral subtraction. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1979, 27, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Wang, D. Speech segregation based on pitch tracking and amplitude modulation. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Workshop on the Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics (Cat. No. 01TH8575), New Platz, NY, USA, 24 October 2001; pp. 79–82. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, S.; Roman, N.; Wang, D. Binary and ratio time-frequency masks for robust speech recognition. Speech Commun. 2006, 48, 1486–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Narayanan, A.; Wang, D. On training targets for supervised speech separation. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2014, 22, 1849–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paliwal, K.; Wójcicki, K.; Shannon, B. The importance of phase in speech enhancement. Speech Commun. 2011, 53, 465–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, H.; Hershey, J.R.; Watanabe, S.; Le Roux, J. Phase-sensitive and recognition-boosted speech separation using deep recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), South Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 19–24 April 2015; pp. 708–712. [Google Scholar]
- Trabelsi, C.; Bilaniuk, O.; Serdyuk, D.; Subramanian, S.; Santos, J.F.; Mehri, S.; Rostamzadeh, N.; Bengio, Y.; Pal, C.J. Deep Complex Networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.09792. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Huh, J.; Kim, A.; Ha, J.W.; Lee, K. Phase-aware speech enhancement with deep complex u-net. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lv, S.; Xing, M.; Zhang, S.; Fu, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, B.; Xie, L. DCCRN: Deep complex convolution recurrent network for phase-aware speech enhancement. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.00264. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, N.; Agrawal, P.; Goswami, N.; Mitsufuji, Y. PhaseNet: Discretized Phase Modeling with Deep Neural Networks for Audio Source Separation. In Proceedings of the Interspeech, Hyderabad, India, 2–6 September 2018; pp. 2713–2717. [Google Scholar]
- Sreenivas, T.; Kirnapure, P. Codebook constrained Wiener filtering for speech enhancement. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 1996, 4, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliwal, K.; Basu, A. A speech enhancement method based on Kalman filtering. In Proceedings of the ICASSP’87. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Dallas, TX, USA, 6–9 April 1987; Volume 12, pp. 177–180. [Google Scholar]
- Oord, A.v.d.; Dieleman, S.; Zen, H.; Simonyan, K.; Vinyals, O.; Graves, A.; Kalchbrenner, N.; Senior, A.; Kavukcuoglu, K. Wavenet: A generative model for raw audio. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.03499. [Google Scholar]
- Rethage, D.; Pons, J.; Serra, X. A wavenet for speech denoising. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 5069–5073. [Google Scholar]
- Stoller, D.; Ewert, S.; Dixon, S. Wave-u-net: A multi-scale neural network for end-to-end audio source separation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.03185. [Google Scholar]
- Défossez, A.; Usunier, N.; Bottou, L.; Bach, F. Music source separation in the waveform domain. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.13254. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yoshioka, T. Dual-path rnn: Efficient long sequence modeling for time-domain single-channel speech separation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- Beltagy, I.; Peters, M.E.; Cohan, A. Longformer: The long-document transformer. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.05150. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.; Xu, S.; Xu, B. Speech-transformer: A no-recurrence sequence-to-sequence model for speech recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 5884–5888. [Google Scholar]
- Subakan, C.; Ravanelli, M.; Cornell, S.; Bronzi, M.; Zhong, J. Attention is all you need in speech separation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021—2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; He, B.; Zhu, W.P. TSTNN: Two-stage transformer based neural network for speech enhancement in the time domain. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021-2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 7098–7102. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, E.; Seo, H. SE-Conformer: Time-Domain Speech Enhancement Using Conformer. In Proceedings of the Interspeech, Brno, Czechia, 30 August–3 September 2021; pp. 2736–2740. [Google Scholar]
- Pascual, S.; Bonafonte, A.; Serra, J. SEGAN: Speech enhancement generative adversarial network. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.09452. [Google Scholar]
- Baby, D.; Verhulst, S. Sergan: Speech enhancement using relativistic generative adversarial networks with gradient penalty. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019-2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 106–110. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.; Jin, Z.; Finkelstein, A. HiFi-GAN: High-Fidelity Denoising and Dereverberation Based on Speech Deep Features in Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the Interspeech, Shanghai, China, 25–29 October 2020; pp. 4506–4510. [Google Scholar]
- Kolbæk, M.; Tan, Z.H.; Jensen, J. Monaural speech enhancement using deep neural networks by maximizing a short-time objective intelligibility measure. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 5059–5063. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.W.; Wang, T.W.; Tsao, Y.; Lu, X.; Kawai, H. End-to-end waveform utterance enhancement for direct evaluation metrics optimization by fully convolutional neural networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2018, 26, 1570–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rix, A.W.; Beerends, J.G.; Hollier, M.P.; Hekstra, A.P. Perceptual evaluation of speech quality (PESQ)-a new method for speech quality assessment of telephone networks and codecs. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Proceedings (Cat. No. 01CH37221), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 7–11 May 2001; Volume 2, pp. 749–752. [Google Scholar]
- Taal, C.H.; Hendriks, R.C.; Heusdens, R.; Jensen, J. An algorithm for intelligibility prediction of time–frequency weighted noisy speech. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2011, 19, 2125–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Zaremba, W.; Sutskever, I.; Bruna, J.; Erhan, D.; Goodfellow, I.; Fergus, R. Intriguing properties of neural networks. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.6199. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.W.; Liao, C.F.; Tsao, Y. Learning with learned loss function: Speech enhancement with quality-net to improve perceptual evaluation of speech quality. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2019, 27, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.W.; Yu, C.; Hsieh, T.A.; Plantinga, P.; Ravanelli, M.; Lu, X.; Tsao, Y. Metricgan+: An improved version of metricgan for speech enhancement. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.03538. [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi, Y.; Niwa, K.; Hioka, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Haneda, Y. DNN-based source enhancement to increase objective sound quality assessment score. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2018, 26, 1780–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyato, T.; Kataoka, T.; Koyama, M.; Yoshida, Y. Spectral normalization for generative adversarial networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.05957. [Google Scholar]
- Valentini-Botinhao, C.; Wang, X.; Takaki, S.; Yamagishi, J. Investigating RNN-based speech enhancement methods for noise-robust Text-to-Speech. In Proceedings of the SSW, Sunnyvale, CA, USA, 13–15 September 2016; pp. 146–152. [Google Scholar]
- Thiemann, J.; Ito, N.; Vincent, E. The diverse environments multi-channel acoustic noise database (demand): A database of multichannel environmental noise recordings. In Proceedings of the Meetings on Acoustics ICA2013, Montreal, QU, Canada, 2–7 June 2013; Volume 19, p. 035081. [Google Scholar]
- Ravanelli, M.; Parcollet, T.; Plantinga, P.; Rouhe, A.; Cornell, S.; Lugosch, L.; Subakan, C.; Dawalatabad, N.; Heba, A.; Zhong, J.; et al. SpeechBrain: A General-Purpose Speech Toolkit. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.04624. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Silver, D.; Rusu, A.A.; Veness, J.; Bellemare, M.G.; Graves, A.; Riedmiller, M.; Fidjeland, A.K.; Ostrovski, G.; et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 2015, 518, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panayotov, V.; Chen, G.; Povey, D.; Khudanpur, S. Librispeech: An asr corpus based on public domain audio books. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), South Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 19–24 April 2015; pp. 5206–5210. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.; Wang, D. A tandem algorithm for pitch estimation and voiced speech segregation. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2010, 18, 2067–2079. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Loizou, P.C. Evaluation of objective quality measures for speech enhancement. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2007, 16, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.; McLoughlin, I.V.; Pham, L.; Chén, O.Y.; Koch, P.; De Vos, M.; Mertins, A. Improving GANs for speech enhancement. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2020, 27, 1700–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Gong, K.; Liang, X.; Chen, Z. Cp-gan: Context pyramid generative adversarial network for speech enhancement. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 6624–6628. [Google Scholar]
- Soni, M.H.; Shah, N.; Patil, H.A. Time-frequency masking-based speech enhancement using generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 5039–5043. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Sun, M.; Zhang, X. Perception-guided generative adversarial network for end-to-end speech enhancement. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 128, 109446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wu, R.; Huang, J.; Lin, J.; Yin, J. DCCRGAN: Deep Complex Convolution Recurrent Generator Adversarial Network for Speech Enhancement. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Symposium on Electrical, Electronics and Information Engineering (ISEEIE), Chiang Mai, Thailand, 25–27 February 2022; pp. 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Giri, R.; Isik, U.; Krishnaswamy, A. Attention wave-u-net for speech enhancement. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Workshop on Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics (WASPAA), New Paltz, NY, USA, 20–23 October 2019; pp. 249–253. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, S.; Fu, Y.; Xing, M.; Sun, J.; Xie, L.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, T. S-dccrn: Super wide band dccrn with learnable complex feature for speech enhancement. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 7767–7771. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Yamagishi, J. Multi-metric optimization using generative adversarial networks for near-end speech intelligibility enhancement. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2021, 29, 3000–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kuyk, S.; Kleijn, W.B.; Hendriks, R.C. An instrumental intelligibility metric based on information theory. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2017, 25, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kates, J.M.; Arehart, K.H. The hearing-aid speech perception index (HASPI). Speech Commun. 2014, 65, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.; Taal, C.H. An algorithm for predicting the intelligibility of speech masked by modulated noise maskers. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2016, 24, 2009–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).