Analysis of Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) Based on the Deep Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
The Major Contributions Are as Follow
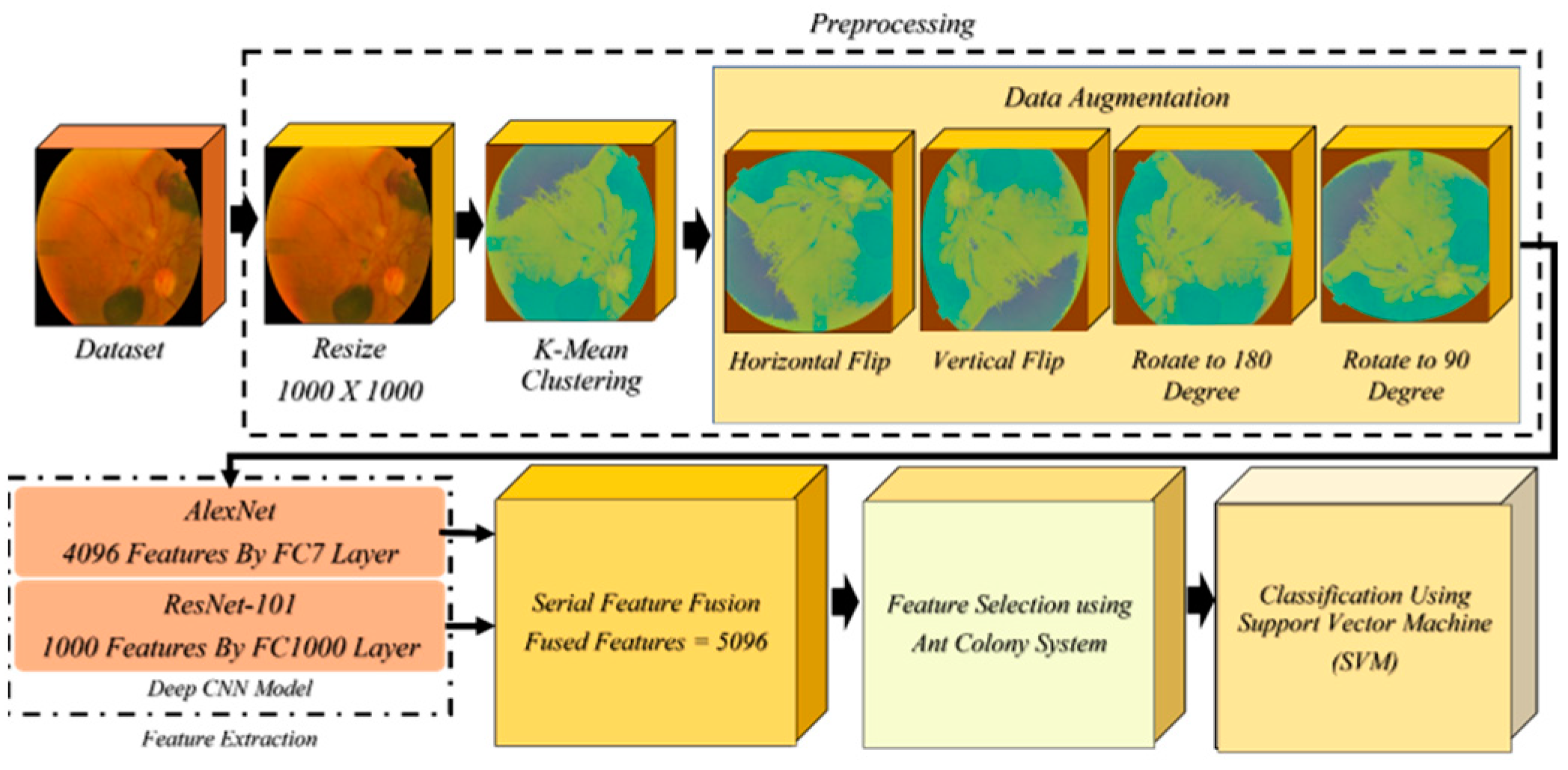
- In preprocessing, the resize function is used to scale all the images to 1000 × 1000 pixels since the images’ dimensions vary. After resizing, k-mean clustering is used to enhance the image. We used a variety of data augmentation techniques to boost the quantity of low-volume data while dealing with the original dataset. These strategies included vertical and horizontal flips as well as 90-degree and 180-degree rotations.
- To achieve features, AlexNet and Resnet101 are utilized. The characteristics are extracted from the fully connected layers.
- Serial feature fusion is used to fuse these extracted features.
- Several of these features are insignificant for successful classification; hence, we used an efficient feature selection method known as Ant Colony system to choose the most beneficial features to include in our classification. Afterwards, these selected attributes are sent to SVM with several kernels for final classification.
2. Related Work
3. Proposed Methodology
3.1. Resizing and Data Augmentation
3.2. Feature Extraction
3.2.1. AlexNet Deep CNN Model
3.2.2. ResNet-101 Deep CNN Model
3.2.3. Feature Selection Using Ant Colony System (ACS)
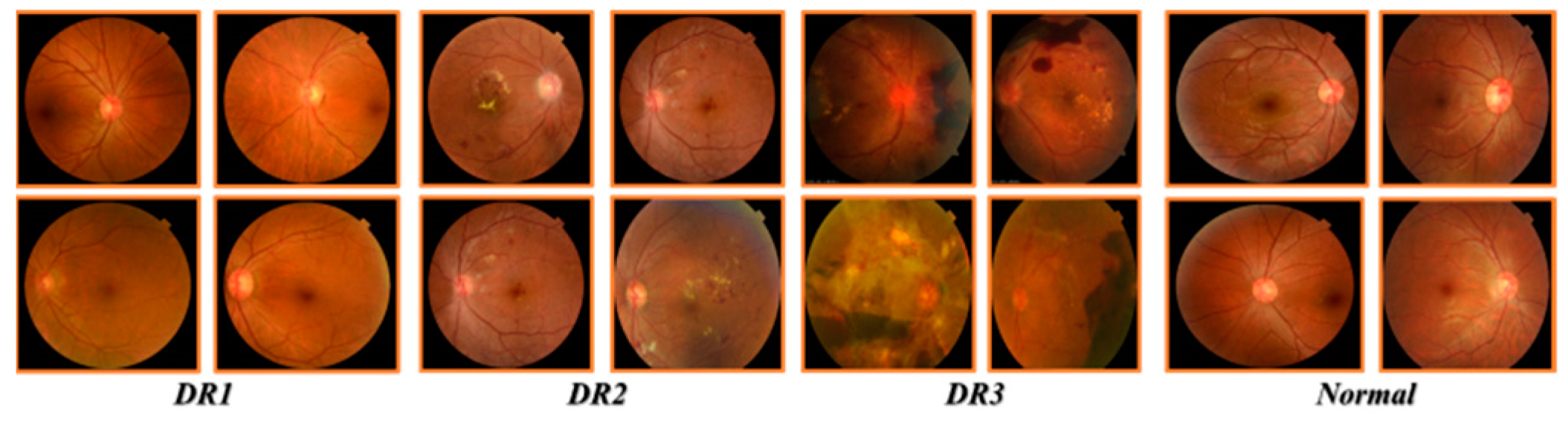
4. Results and Discussion
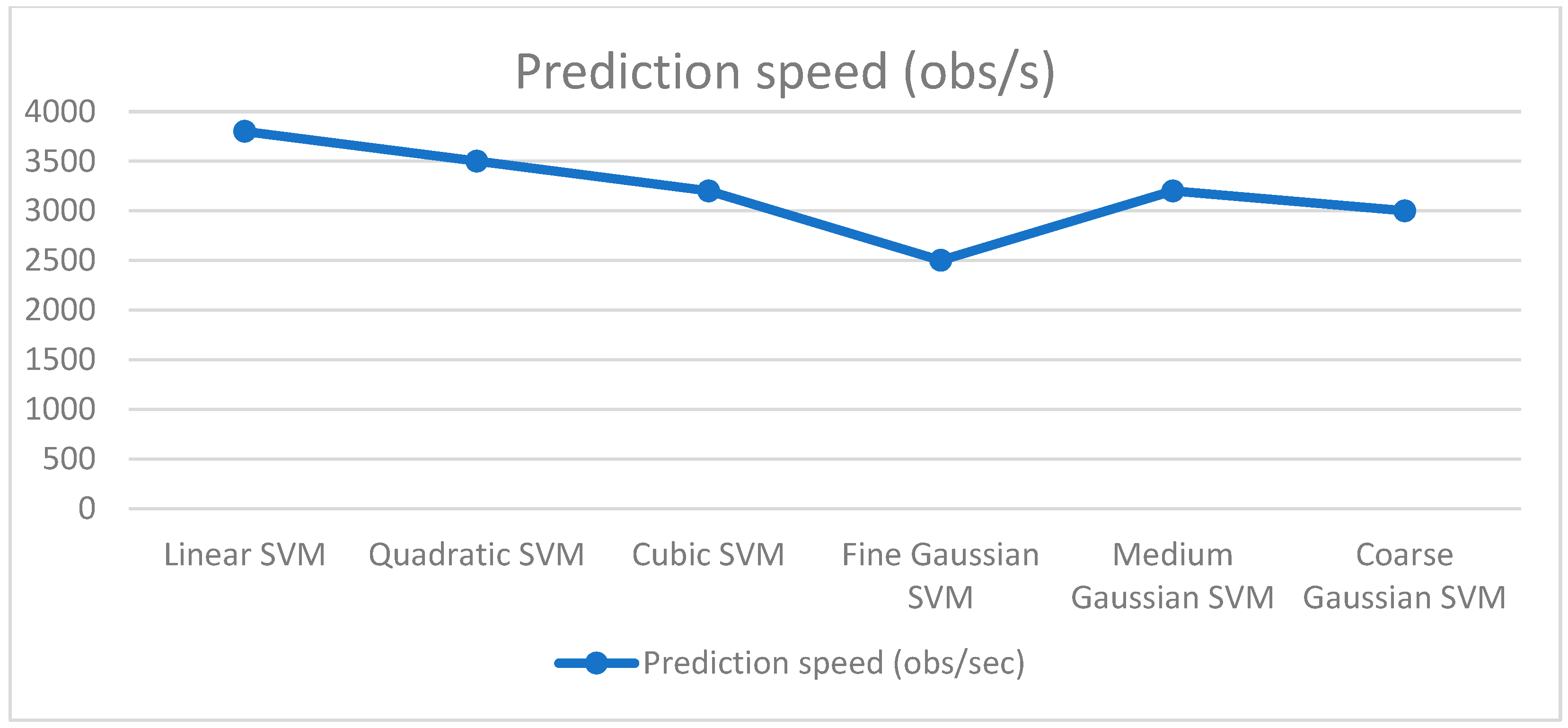
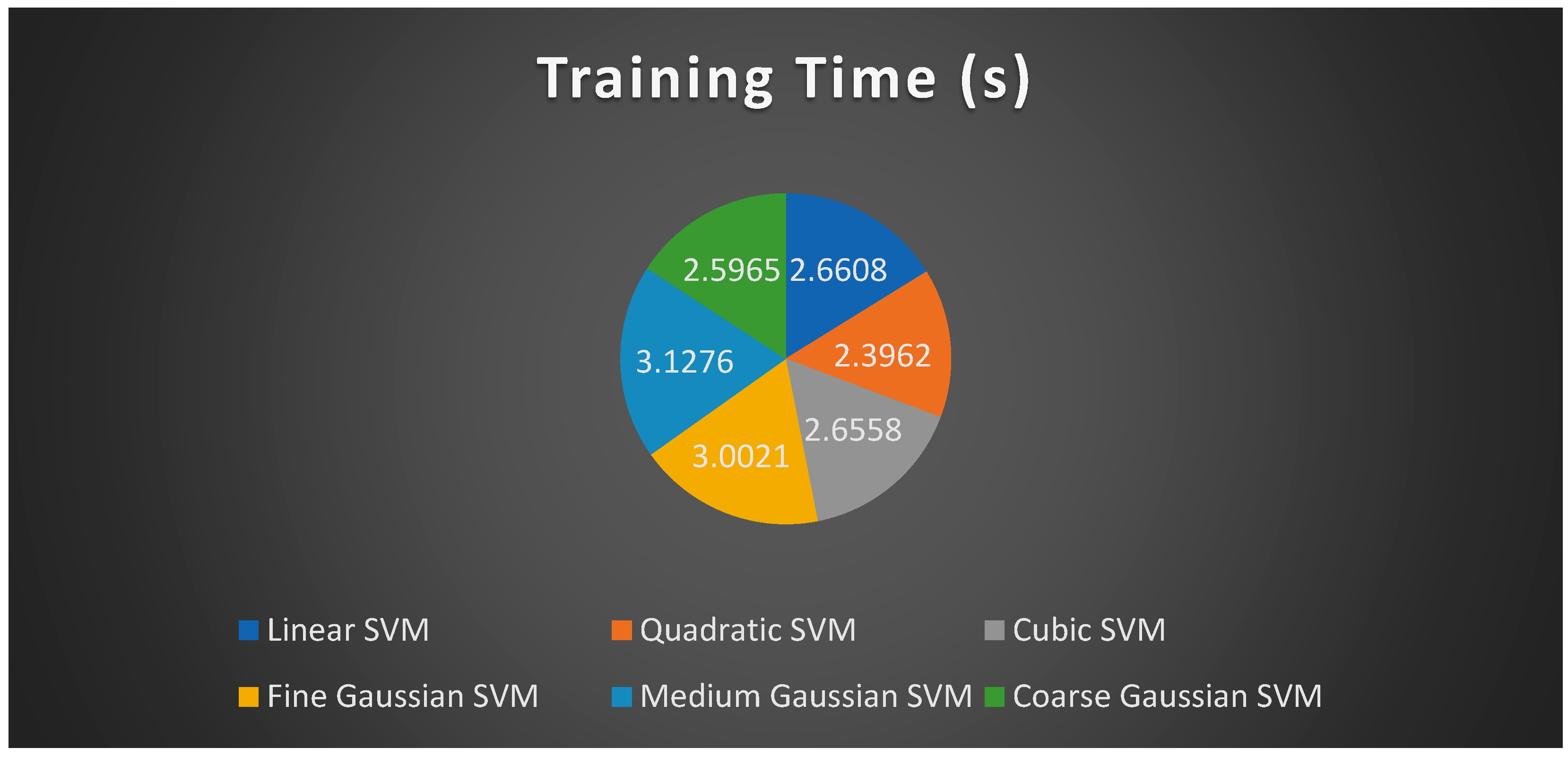
4.1. Experiment Setup 1 (250 Features)
4.2. Experiment Setup 2 (550 Features)
4.3. Experiment Setup 3 (750 Features)
4.4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, A.; Tewari, A.S.; Singh, J.P. Classification of diabetic macular edema severity using deep learning technique. Res. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 38, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, A.; Jafari Navimipour, N.; Unal, M.; Toumaj, S. Machine learning applications for COVID-19 outbreak management. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 15313–15348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, A.; Dias, M.; Bhuyan, B.P.; Tomar, R. Human Activity Recognition for Elderly People Using Machine and Deep Learning Approaches. Information 2022, 13, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateen, M.; Wen, J.; Song, S.; Huang, Z. Fundus image classification using VGG-19 architecture with PCA and SVD. Symmetry 2018, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, H.S. Towards Explainable Deep Neural Networks for the Automatic Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, K.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, L.; Chen, C.-H. Hyperparameter tuning deep learning for diabetic retinopathy fundus image classification. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 118164–118173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, U.; Sattar, N.Y. Improved automatic localization of optic disc in retinal fundus using image enhancement techniques and SVM. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Control System, Computing and Engineering (ICCSCE), Penang, Malaysia, 27–29 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Boreiko, V.; Ilanchezian, I.; Ayhan, M.S.; Müller, S.; Koch, L.M.; Faber, H.; Berens, P.; Hein, M. Visual explanations for the detection of diabetic retinopathy from retinal fundus images. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 539–549. [Google Scholar]
- Bala, R.; Sharma, A.; Goel, N. Classification of Fundus Images for Diabetic Retinopathy Using Machine Learning: A Brief Review. In Proceedings of the Academia-Industry Consortium for Data Science, Wenzhou, China, 19–20 December 2020; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Selvachandran, G.; Quek, S.G.; Paramesran, R.; Ding, W.; Son, L.H. Developments in the detection of diabetic retinopathy: A state-of-the-art review of computer-aided diagnosis and machine learning methods. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2022, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Felfeli, T.; Merritt, R.; Brent, M.H. Sociodemographics associated with risk of diabetic retinopathy detected by tele-ophthalmology: 5-year results of the Toronto tele-retinal screening program. Can. J. Diabetes 2022, 46, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Bhat, A. A survey on recent developments in diabetic retinopathy detection through integration of deep learning. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Bo, W.; Hu, C.; Kang, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, K.; Fu, H. Applications of deep learning in fundus images: A review. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 69, 101971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Feng, D.; Mi, H. Deep convolutional neural network-based early automated detection of diabetic retinopathy using fundus image. Molecules 2017, 22, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahlsten, J.; Jaskari, J.; Kivinen, J.; Turunen, L.; Jaanio, E.; Hietala, K.; Kaski, K. Deep learning fundus image analysis for diabetic retinopathy and macular edema grading. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, L.K.; Garg, H.; Khanna, M. Deep learning system applicability for rapid glaucoma prediction from fundus images across various data sets. Evol. Syst. 2022, 13, 807–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, S.; Kim, J.; Noh, K.J.; Park, S.J.; Lee, S. Combined Deep Learning of Fundus Images and Fluorescein Angiography for Retinal Artery/Vein Classification. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 70688–70698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Kharbanda, K.; Suchetha, M.; Raman, R.; Dhas, E. Deep learning architecture based on segmented fundus image features for classification of diabetic retinopathy. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 68, 102600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.S.; Radhika, Y. Optimized maximum principal curvatures based segmentation of blood vessels from retinal images. Biomed. Res. 2019, 30, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, R.R.; Stevens, G.A.; White, R.A.; Smith, J.L.; Flaxman, S.R.; Price, H.; Jonas, J.B.; Keeffe, J.; Leasher, J.; Naidoo, K. Causes of vision loss worldwide, 1990–2010: A systematic analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2013, 1, e339–e349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.; Batey, D. Handbook of Retinal Screening in Diabetes: Diagnosis and Management; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M.; Hou, B.; Liu, L.; Gordon, M.; Kass, M.; Wang, F.; Van Tassel, S.H.; Peng, Y. Automated diagnosing primary open-angle glaucoma from fundus image by simulating human’s grading with deep learning. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guo, C.; Nie, D.; Lin, D.; Cui, T.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Dongye, M. Automated detection of retinal exudates and drusen in ultra-widefield fundus images based on deep learning. Eye 2022, 36, 1681–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Karale, V.; Ghorai, G.; Sarkar, G.; Ghosh, S.; Dhara, A.K. Nested U-Net for Segmentation of Red Lesions in Retinal Fundus Images and Sub-image Classification for Removal of False Positives. J. Digit. Imaging 2022, 35, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, A.; Zhu, L.; Deng, A.; Lu, H.; Wu, N. AI-Based Automatic Detection and Classification of Diabetic Retinopathy Using U-Net and Deep Learning. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canayaz, M. Classification of diabetic retinopathy with feature selection over deep features using nature-inspired wrapper methods. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 128, 109462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Abdulrazak, L.F.; Nahiduzzaman, M.; Goni, M.O.F.; Anower, M.S.; Ahsan, M.; Haider, J.; Kowalski, M. Applying supervised contrastive learning for the detection of diabetic retinopathy and its severity levels from fundus images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 146, 105602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Xu, M.; Yang, X.; Han, Y. Multi-Label Fundus Image Classification Using Attention Mechanisms and Feature Fusion. Micromachines 2022, 13, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwany, M.Z.; Sahyoun, A.H.; Yaqub, M. Deep learning techniques for diabetic retinopathy classification: A survey. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 28642–28655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, R.; Kulkarni, S.; Walambe, R.; Deshpande, M.; Kotecha, K. Deep dive in retinal fundus image segmentation using deep learning for retinopathy of prematurity. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 11441–11460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Xu, T.; Dong, L.; Yan, L.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, H.; Wu, Z.; Zou, H. Deep learning-based automated detection for diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular oedema in retinal fundus photographs. Eye 2022, 36, 1433–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saranya, P.; Prabakaran, S.; Kumar, R.; Das, E. Blood vessel segmentation in retinal fundus images for proliferative diabetic retinopathy screening using deep learning. Vis. Comput. 2022, 38, 977–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.S.; Arooj, A.; Alroobaea, R.; Baqasah, A.M.; Jabarulla, M.Y.; Singh, D.; Sardar, R. Untangling computer-aided diagnostic system for screening diabetic retinopathy based on deep learning techniques. Sensors 2022, 22, 1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalithadevi, B.; Krishnaveni, S. Detection of diabetic retinopathy and related retinal disorders using fundus images based on deep learning and image processing techniques: A comprehensive review. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2022, 34, e7032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.; Iskandar, D.; Abdelhamid, S.; Latif, G.; Alghazo, R. Diabetic Retinopathy Detection from Fundus Images of the Eye Using Hybrid Deep Learning Features. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-S.; Tai, C.-L.; Sorkine, O.; Lee, T.-Y. Optimized scale-and-stretch for image resizing. In ACM SIGGRAPH Asia 2008 Papers; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Vassilvitskii, S.; Arthur, D. k-means++: The advantages of careful seeding. In Proceedings of the Eighteenth Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, New Orleans, LA, USA, 7–9 January 2007; pp. 1027–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Safdar, M.F.; Alkobaisi, S.S.; Zahra, F.T. A comparative analysis of data augmentation approaches for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan images of brain tumor. Acta Inform. Med. 2020, 28, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamp, A. Vertical Flip. Tex. Wesley. L. Rev. 2006, 13, 729. [Google Scholar]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; IEEE: Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Cen, L.-P.; Ji, J.; Lin, J.-W.; Ju, S.-T.; Lin, H.-J.; Li, T.-P.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.-F.; Liu, Y.-F.; Tan, S. Automatic detection of 39 fundus diseases and conditions in retinal photographs using deep neural networks. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamrat, F.M.J.M.; Azam, S.; Karim, A.; Islam, R.; Tasnim, Z.; Ghosh, P.; De Boer, F. LungNet22: A Fine-Tuned Model for Multiclass Classification and Prediction of Lung Disease Using X-ray Images. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, A.; Mansotra, V. Transfer Learning-based One versus Rest Classifier for Multiclass Multi-Label Ophthalmological Disease Prediction. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2021, 12, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


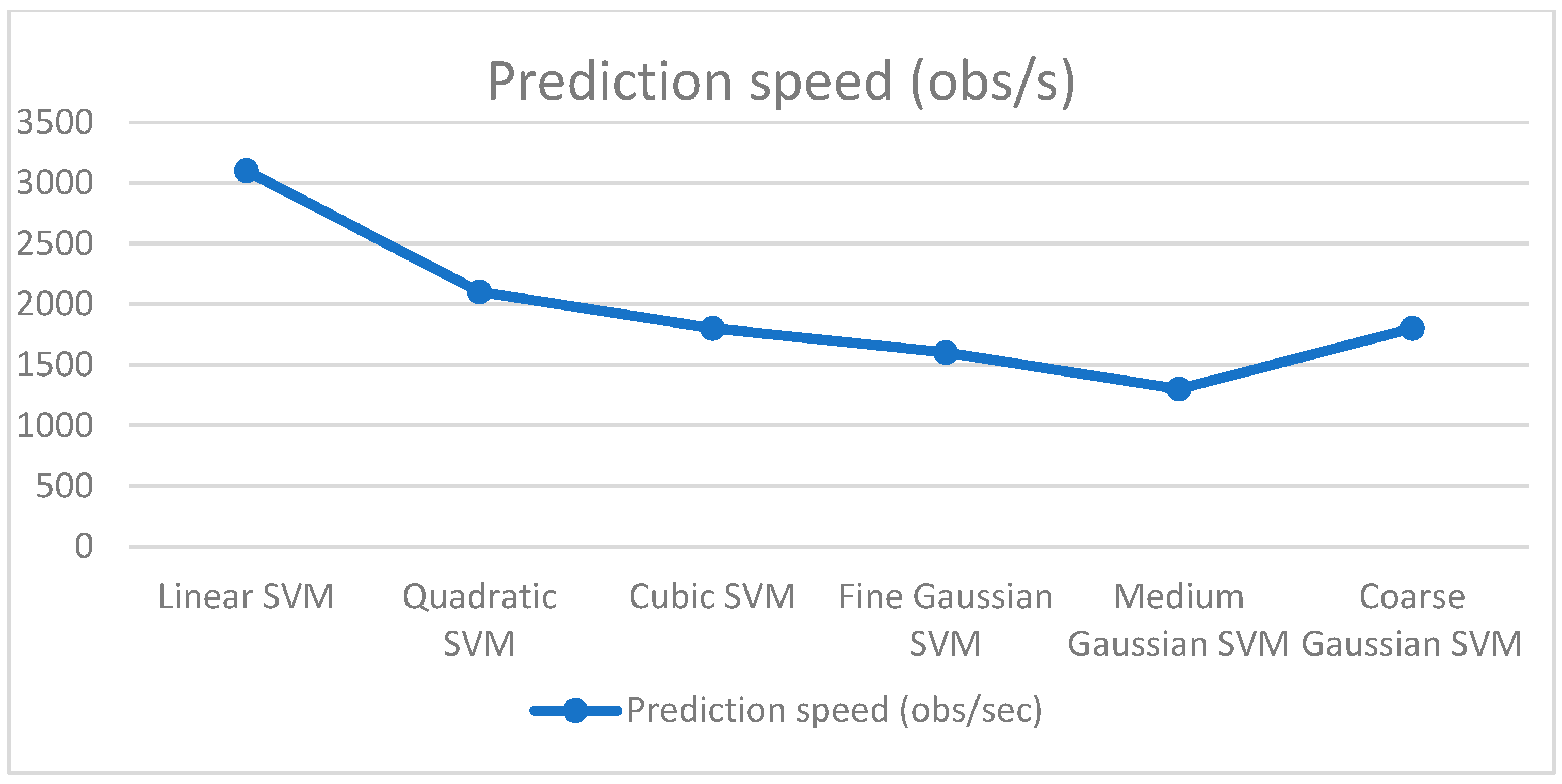
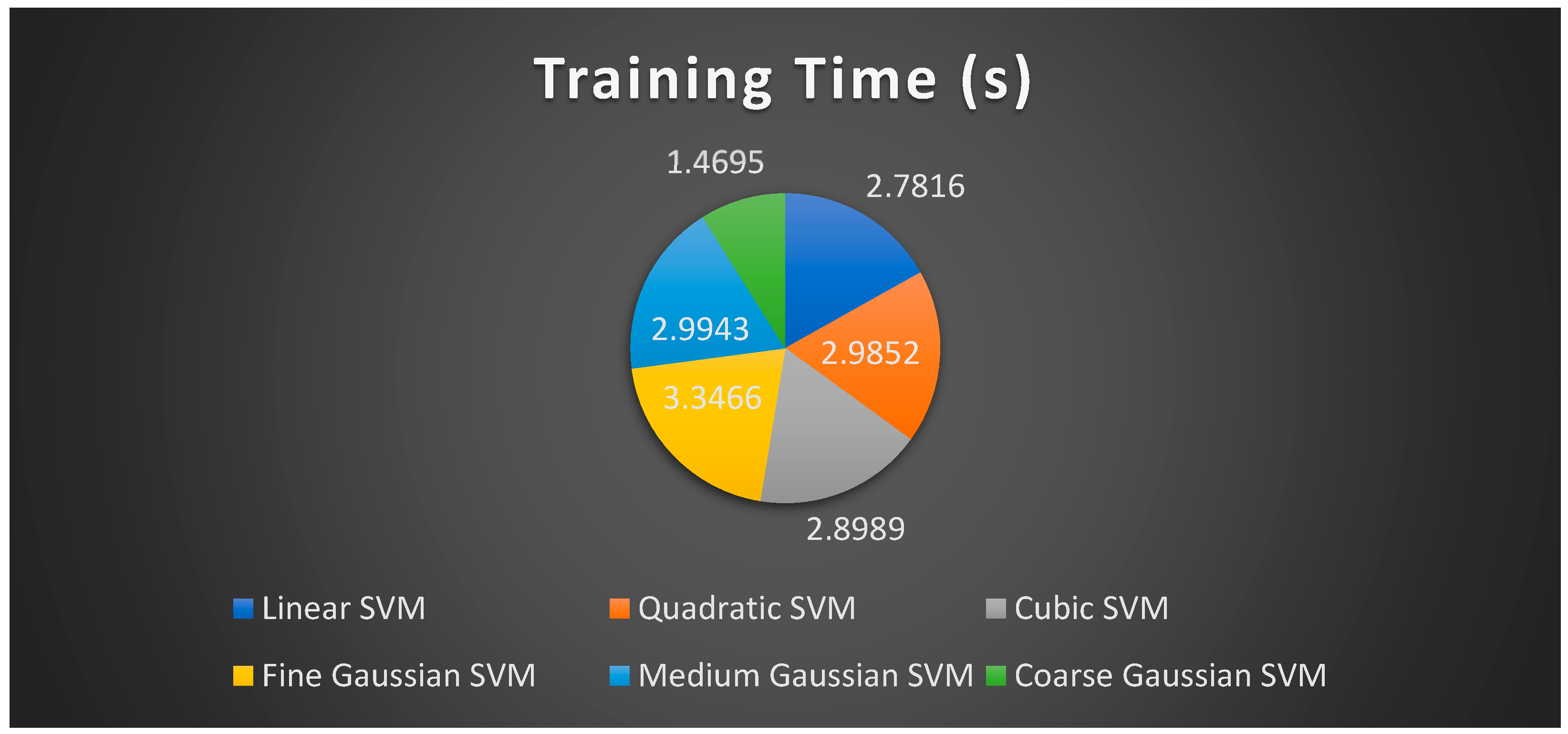
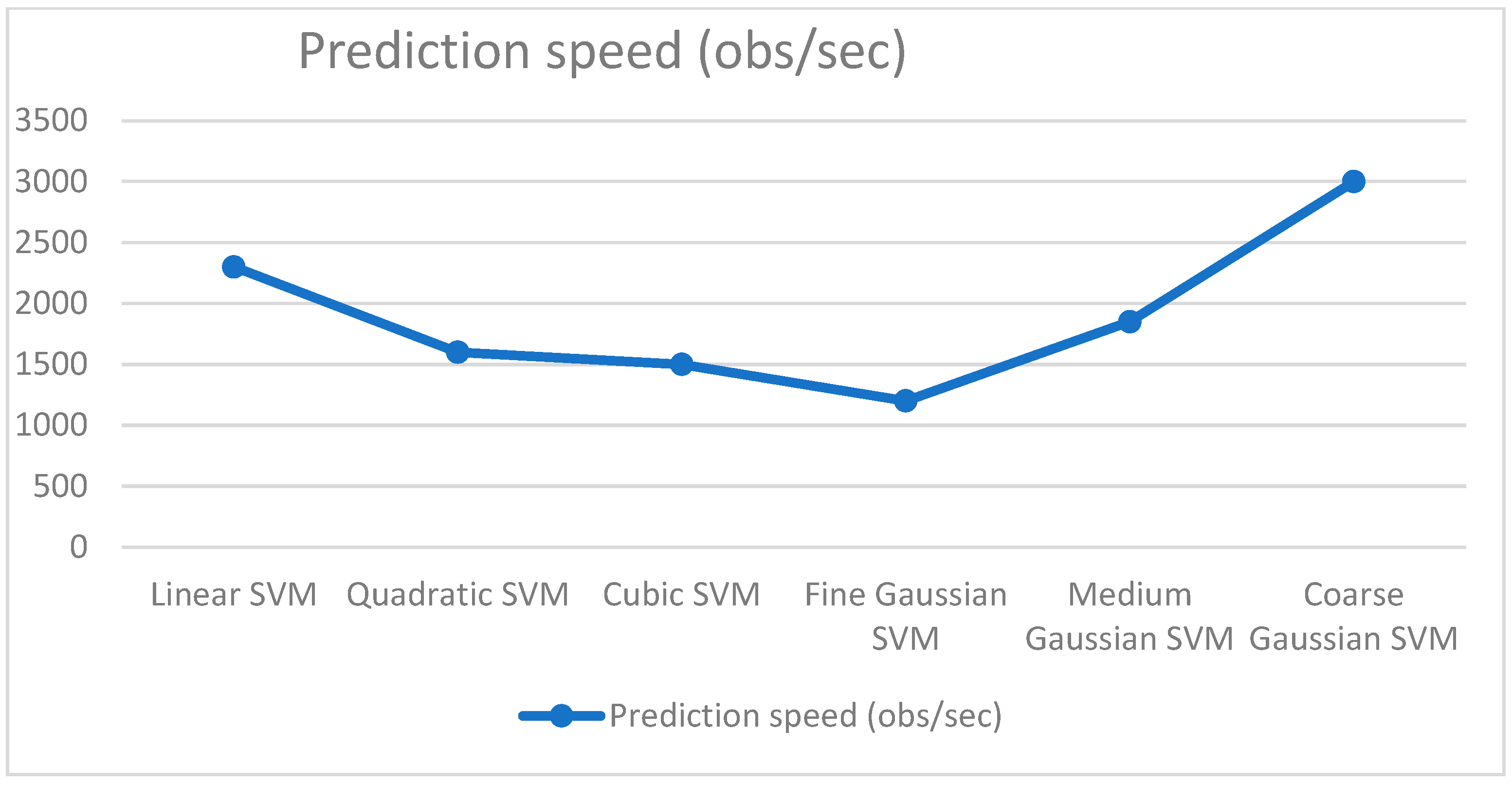
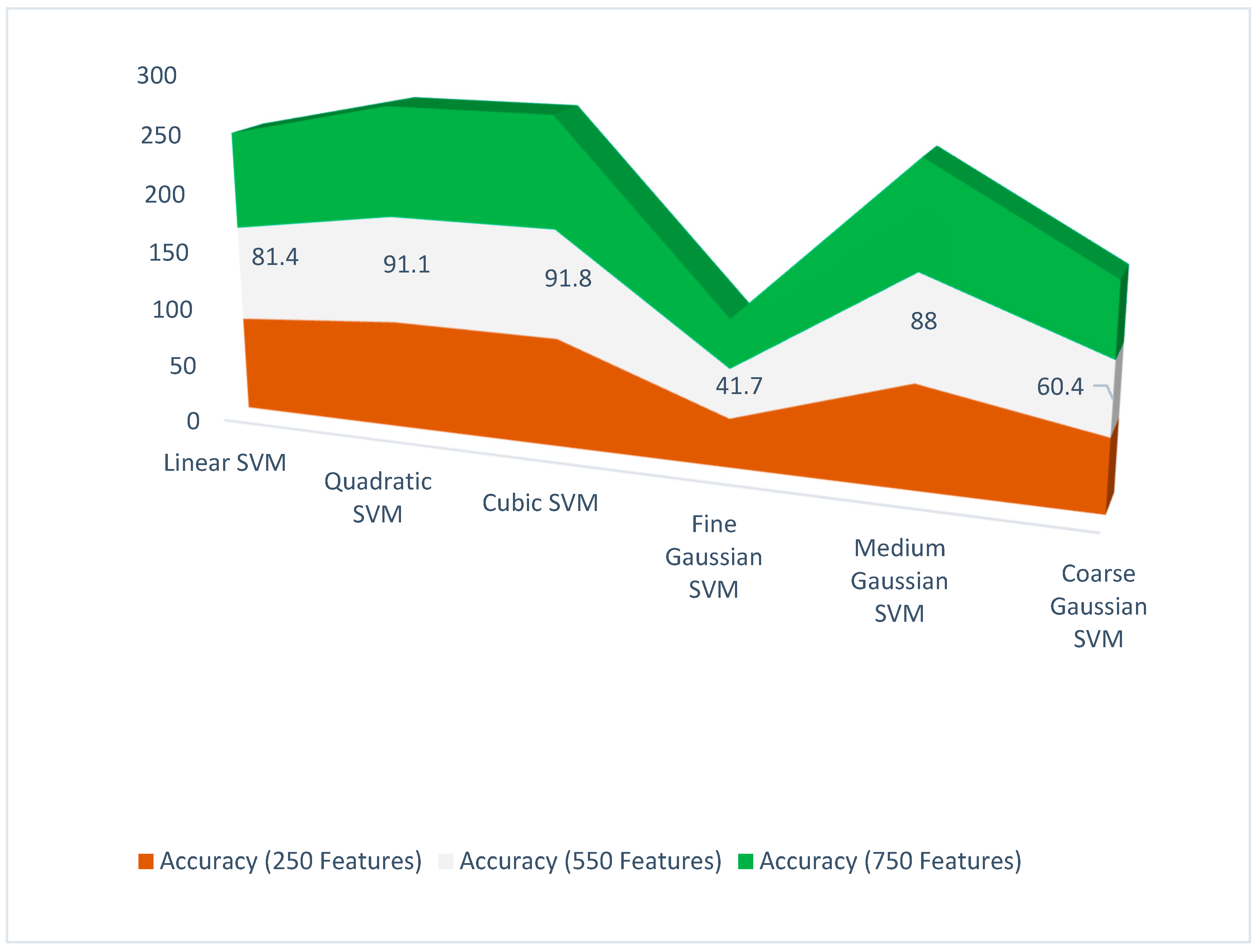
| Classifier | Features | Accuracy (%) | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liner SVM | 250 | 81.1 | 0.597 | 0.52 | 0.540 |
| Quadratic SVM | 250 | 92.3 | 0.957 | 0.955 | 0.955 |
| Cubic SVM | 250 | 92.6 | 0.922 | 0.937 | 0.927 |
| Fine Gaussian SVM | 250 | 41.3 | 0.33 | 0.592 | 0.282 |
| Medium Gaussian SVM | 250 | 87 | 0.852 | 0.882 | 0.862 |
| Coarse Gaussian SVM | 250 | 61.1 | 0.508 | 0.525 | 0.427 |
| Classifier | Features | Accuracy (%) | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liner SVM | 550 | 81.4 | 0.632 | 0.832 | 0.815 |
| Quadratic SVM | 550 | 91.1 | 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.912 |
| Cubic SVM | 550 | 91.8 | 0.915 | 0.93 | 0.917 |
| Fine Gaussian SVM | 550 | 41.7 | 0.345 | 0.842 | 0.422 |
| Medium Gaussian SVM | 550 | 88 | 0.655 | 0.83 | 0.647 |
| Coarse Gaussian SVM | 550 | 60.4 | 0.504 | 0.512 | 0.422 |
| Classifier | Features | Accuracy (%) | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liner SVM | 750 | 82.3 | 0.815 | 0.832 | 0.804 |
| Quadratic SVM | 750 | 92.6 | 0.93 | 0.932 | 0.93 |
| Cubic SVM | 750 | 93.0 | 0.93 | 0.935 | 0.932 |
| Fine Gaussian SVM | 750 | 40.8 | 0.64 | 0.842 | 0.286 |
| Medium Gaussian SVM | 750 | 87.9 | 0.857 | 0.897 | 0.872 |
| Coarse Gaussian SVM | 750 | 60.6 | 0.505 | 0.54 | 0.419 |
| Model | Results (%) | Dataset [43] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| [45] | Transfer learning using VGG-16 No fusion (considered left and right images as separate images) | Validation Accuracy: 90.85 and F1-score: 91.0 | Used all classes |
| Proposed | Fused features from fully connected layers of AlexNet and Resnet-101, after fusion used using ACS for core features selection for classification. | Accuracy = 93.0, Precision = 93.0, Recall = 93.5, F1-score = 93.2 | Used Normal vs. DR1, DR2, and DR3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fayyaz, A.M.; Sharif, M.I.; Azam, S.; Karim, A.; El-Den, J. Analysis of Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) Based on the Deep Learning. Information 2023, 14, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14010030
Fayyaz AM, Sharif MI, Azam S, Karim A, El-Den J. Analysis of Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) Based on the Deep Learning. Information. 2023; 14(1):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14010030
Chicago/Turabian StyleFayyaz, Abdul Muiz, Muhammad Imran Sharif, Sami Azam, Asif Karim, and Jamal El-Den. 2023. "Analysis of Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) Based on the Deep Learning" Information 14, no. 1: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14010030
APA StyleFayyaz, A. M., Sharif, M. I., Azam, S., Karim, A., & El-Den, J. (2023). Analysis of Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) Based on the Deep Learning. Information, 14(1), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14010030







