Abstract
There are more than 962 million people aged 60 and up globally. Physical activity declines as people get older, as does their capacity to undertake everyday tasks, effecting both physical and mental health. Many researchers use machine learning and deep learning methods to recognize human activities, but very few studies have been focused on human activity recognition of elderly people. This paper focuses on providing assistance to elderly people by monitoring their activities in different indoor and outdoor environments using gyroscope and accelerometer data collected from a smart phone. Smart phones have been routinely used to monitor the activities of persons with impairments; routine activities such as sitting, walking, going upstairs, going downstairs, standing, and lying are included in the dataset. Conventional Machine Learning and Deep Learning algorithms such as k-Nearest Neighbors, Random Forest, Support Vector Machine, Artificial Neural Network, and Long Short-Term Memory Network are used for human activity recognition. Long Short-Term Memory is a recurrent neural network variation that is best suited to handling temporal sequences. Two-fold and ten-fold cross-validation methods were performed to show the effect of changing the data in the training and testing dataset. Among all the classification techniques, the proposed Long Short-Term Memory Network gave the best accuracy of 95.04%. However, Support Vector Machine gave 89.07% accuracy with a very low computational time of 0.42 min using 10-fold cross-validation.
1. Introduction
In recent years, the subject of Human Activity Recognition (HAR) has become one of the most popular study fields. Due to the availability of sensors and accelerometers, minimal cost and low energy consumption, and advancements in computer vision, machine learning, artificial intelligence, and IoT, many applications have been built using human-centered design monitoring to recognize, detect, and categorize human behavior, and researchers have presented many methods around this topic. Human activity identification is an essential tool for monitoring a person’s dynamism, and it can be accomplished using machine learning algorithms. HAR is a method of automatically recognizing and analyzing human actions based on information acquired from various smartphone sensors and wearable devices, such as accelerometer sensors, gyroscope sensors, time, location, and a variety of other environmental sensors [1]. When integrated with other technologies, such as the Internet of Things, it can be used in a wide range of application areas such as healthcare, sports, and industry.
According to a 2011 World Health Organization (WHO) survey, over 650 million people of working age in the world are disabled [2]. Meanwhile, according to a study conducted by Survei Sosial Ekonomi Nasional (Susenas) in 2012, there were over six million people in Indonesia [3]. There are currently insufficient facilities to meet the requirements of people with disabilities [4,5]. One of them is the requirement for a companion to monitor their activities. To safeguard people with disabilities from injury, danger, or accidents, they must be protected and supervised 24 h per day [6]. Mobile phones, on the other hand, have been frequently used to monitor people’s activities [7,8]. In 2017, the global population of people aged 60 and above totaled 962 million, more than doubling the 382 million people aged 60 and up in 1980. By 2050, the number of elderly people is estimated to more than double, reaching over 2.1 billion. Two-thirds of the world’s elderly reside in developing countries, where their numbers are increasing at a quicker rate than in industrialized countries. Nearly 8 out of 10 of the world’s elderly people are anticipated to live in underdeveloped countries by 2050. The proportion of people aged 60 and over who live “independently”—alone or with a spouse exclusively—varied substantially among the 143 nations or territories with accessible data, ranging from 2.3 percent in Afghanistan to 93.4 percent in The Netherlands.
Artificial intelligence becomes more popular for HAR because of its self-learning nature and robust classification models [9]. In recent years, several studies have been conducted for HAR using machine learning and deep learning [10,11,12], but only a few focus on developing a framework for the HAR system for elderly people. Kaixuan Chen et al. [13] in their study gave an overview of challenges and opportunities in the area of human activity recognition using deep learning techniques. Due to the diversity of sensor data, it is really important to have multimodal features, which could help in maximizing the performance of the system [14]. The attention-based mechanism could be used in HAR to highlight the most important and differentiable modalities (Zeng et al. [15] and Chen et al. [16]). Chen et al. [16] used multiple agents to focus on modalities that are related to sub-motions. Although they have outperformed all the state-of-the-art methods, still, they have not been validated on a dataset of the elderly. This study mainly focuses on finding out the most effective approach for developing the HAR framework for elderly people. Both machine learning and deep learning approaches such as k-Nearest Neighbors (k-NN), Random Forest (RF), Support Vector Machine (SVM), Artificial Neural Network (ANN), and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) are used in this study to see which approach is more suitable.
HAR algorithms that give a high accuracy, precision, and recall of activity classification are required for this human-activity-monitoring application for elderly people. Machine learning approaches for classifying human activities have previously been mentioned in a few prior studies [17]. Classification or supervised learning is a data mining (machine learning) system used for the prediction of the group to which a particular set of information belongs [18]. Data analysis can be performed using classification and prediction; it helps in the division of data into classes making the prediction of future trends easier. Grouping helps put labels on the data, and prediction helps in determining the data value [19]. There are different algorithms of characterization that have been utilized for HAR: Naive Bayes, RF, k-NN, SVM, ANNs, and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) are among the most well-known approaches investigated. Among all, the RF algorithm is designed to deliver high accuracy and consistent speed for data mining, particularly classification with advanced features [20,21,22,23]. Unfortunately, all of these state-of-the-art algorithms are not compared very effectively in terms of performance, such as precision, accuracy, F1-score, and computation speed. In this work, all of the algorithms are evaluated with the above criteria for better understanding.
Figure 1 shows the basic building blocks for human activity recognition. Raw data will be collected from the smartphone, and various preprocessing steps will be performed on the dataset such as Principal Component Analysis (PCA), etc. After that, features will be extracted from the dataset, and the model will be trained on those features. In the final steps, user activity will be detected.
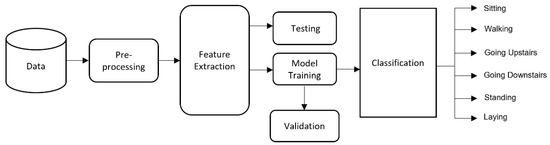
Figure 1.
Conventional machine learning architecture for human activity recognition.
2. Literature Review
Several studies on human activity recognition have been conducted in the past few years. Some of the significant literature works in this area that concentrate on real-time processing, as well as offline processing are listed below.
Activity recognition using smartphones has its own advantages because smartphones are very easy to establish and are robust in nature. Usharani J et al. [24] came up with an idea for a human activity recognition system based on the Android platform. They created an application using the accelerometer data for classification, which supported on-line training and classification. They used the clustered k-NN approach to enhance the performance, accuracy, and execution time of the k-NN classifier with limited resources on the Android platform. They also concluded that the classification times were also dependent on the device models and capabilities. Similarly, Meysam, Vakili et al. [25] proposed a real-time HAR model for online prediction of human physical movements based on the smartphone inertial sensors. A total of 20 different activities were selected, and six incremental learning algorithms were used to check the performance of the system, then all of them were also compared with the state-of-the-art HAR algorithms such as Decision Trees (DTs), AdaBoost, etc. Incremental k-NN and Incremental Naive Bayesian have given the best accuracy of 95%.
In Jirapond Muangprathub et al.’s [26] paper, they introduced a novel elderly person tracking system using a machine learning algorithm. In this work, they used the k-NN model with a k value of 5, which was able to achieve the best accuracy of 96.40% in detecting the real-time activity of elderly people. Furthermore, they created a system that displays information in a spatial format for an elderly person, and in case of an emergency, they can use a messaging device to request any help.
In Davide Anguita et al.’s paper [27], they introduced the improvised Support Vector Machine algorithm, which works with fixed point arithmetic to produce an energy-efficient model for the classification of human activities using a smartphone. They aimed to use the presented novel technology for various intelligence applications and smart environments for faster processing with the least possible use of system resources to save the consumption of energy along with maintaining comparable results with other generally used classification techniques.
To understand people’s behavior in different places such as homes, clinics, etc., Md Zia Uddin et al. [28] proposed a body-sensor-based activity recognition system using deep Neural Stretchered Learning based on Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM). For better clustering of features from all the activities, Kernel-based Discriminant Analysis (KDA) was applied, which will maximize inter-class scattering and minimize intra-class scattering of the samples. The proposed model successfully achieved a recall of 99%, which was further compared to the existing deep learning models such as the RNN, Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), and Deep Belief Network (DBN). None of the existing deep learning models would be able to achieve the recall rate of the proposed method. Similarly, Abdulmajid Murad et al. [29] proposed a deep LSTM network for recognizing six different activities based on smartphone data. The network was able to achieve an accuracy of 96.70% on the UCI-HAD dataset.
Baoding Zhou et al. [30] proposed a CNN for indoor human activity recognition. A total of nine different activities were recognized based on accelerometers, magnetometers, gyroscopes, and barometers collected by smartphones. The proposed method was able to achieve an excellent accuracy of 98%. Yashi Nan et al. [31] used combinations of CNN with LSTM to recognize the activity of older people. Out of all the combinations, a multichannel CNN-LSTM model was able to achieve the best accuracy of 81.1%.
In conclusion, most of the research focused on recognizing overall human activities is not specific to elderly people, and they are not evaluated on extensive evaluation parameters. This study focused on the overall activity recognition of elderly people, and more complex evaluation parameters were used for checking the performance of the models.
3. Methodology
3.1. Dataset Description
A dataset from the University of California Irvine (UCI) was used for this study. Data were collected from a variety of participants aged between 19 and 48 who had a smartphone [32]. The phone’s accelerometer and gyroscope may be utilized to capture the acceleration and angular velocity of the data at a sample rate of 50 Hz. To process the signals, a median filter and a notch filter with a drop frequency of 20 Hz were utilized. There were 561 features obtained from the dataset, and 10,299 sample were present in the dataset. The distribution of the dataset is shown in Figure 2. The data were split into two sections, with 80 percent being training data and 20 percent being testing data. In other words, there were 8240 training data and 2059 testing data. This dataset has six different categories of user activity: sitting, walking, going upstairs, going downstairs, standing, lying.
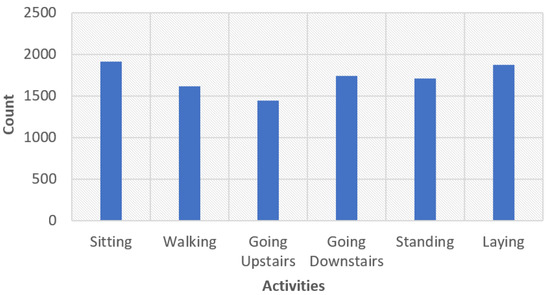
Figure 2.
Representation of the distribution of activities such as standing, sitting, laying, walking, going upstairs, and going downstairs with respect to the total data of 10,299 samples. From the data, it can be seen that the most-performed activity is sitting, and the least is going downstairs.
Furthermore, for the validation of the existing system, it was cross-validated on one more dataset “Activity recognition with healthy older people using a batteryless wearable sensor dataset” [33]. This dataset was collected from 14 participant aged between 66 and 86 in two clinical rooms. This dataset 75,128 samples and categories into 4 different user activities: sitting on the bed (16,406 instances), sitting on the chair (4911 instances), lying on the bed (51,520 instances), and ambulating (walking or standing within the room) (2291 instances).
3.2. Data Pre-Processing
This study did not perform extensive pre-processing to increase the generalization of the models. Only PCA was used for the dimensionality reduction for optimal processing [34]. PCA will compress the dataset into a lower-dimensional feature space with the idea of maintaining significant information.
3.3. Classification
3.3.1. Random Forest
RF classification consists of a multitude of decision trees. All these trees work together to give the result. A simple concept of voting is utilized where the class with the highest number of votes is the class prediction [35]. The bagging method was used in this study to improve the classification performance of a single tree. Different numbers of decision trees of RF were used in the training process {5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50} to see how many decision trees were required to achieve the best results. After comparing all the results from all the activities, an RF with a 30-decision-tree classifier gave the best accuracy among all. However, in order to achieve the best result, the RF requires a large number of labeled data. For impurity reduction, the Gini impurity index was calculated. When all the elements in the node are unique, it is called a pure node and its value will be 0. That means this node cannot be split after. The Gini index value will be maximum when the probability of two classes is the same [36].
3.3.2. k-NN
A simple, easy-to-implement method for supervised learning, k-NN, can be used for HAR [37]. It finds the most similar data points in training data to classify and makes an educated guess about the classification. The Euclidean distance was used to calculate the distance between two points. “k” is a user-defined constant, which is generally an odd number, which helps with the classification by querying the nearest point [38].
In this study, the value of “k” for training was taken from 2 to 50, and it was observed that when value of the “k” increases, the accuracy of the model also increases till a certain point, and then, it starts decreasing because the model becomes too generalized. k-NN with 20 as the “k” value gave the best accuracy among all.
3.3.3. Multi-Class SVM
SVM is generally used for binary problems, but it can be extended for multi-class problems such as HAR. In this study, the one vs. one method was used to create multi-class SVM. The one vs. one method breaks down our multiclass problem into a multiple binary problem. The one vs. one method needs (N(N − 1))/2 classifiers, where N is the total number of output classed; in our case, the value of N was 6. Here, the dataset is nonlinear in nature, and for the prediction, it should be linearly separable. In order to transform nonlinear data into a linear form, a kernel trick was applied, which transforms the data into a higher dimension with a lower computational cost [39]. The main idea behind the kernel trick is to allow the inner product of the mapping function instead of actual data points. The grid search method was employed to find the best kernel and parameters for SVM [40]. SVM with the Gaussian Radial Basis Function (RBF) kernel, the Cost parameter (C) as 1, and the gamma () value as 0.1 was chosen. Here, C is a hyperplane in the SVM space used to control error, and the gamma value is only used in the RBF kernel, which decides how much curvature is required in a decision boundary.
where and are data points. represents the Euclidean distance between and . is the variance, which is inversely proportional to .
3.4. Artificial Neural Network
In this study, Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) was used as the ANN. MLP is one of the most widely used neural networks. It consists of three major layers, an input layer that takes the input from the dataset, a hidden layer that contains the main logic, and an output layer for the predicted value [41]. Figure 3 shows the ANN model used in this study; all the features present in the HAR dataset after applying PCA are given to the input layer, and 3 hidden layers are used for more complex feature extraction.
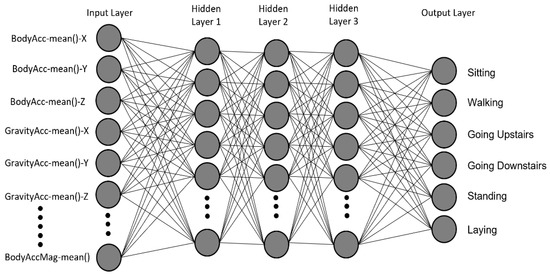
Figure 3.
Architecture of the proposed artificial feed-forward neural network with 3 hidden layers.
The output layer contains 6 nodes and uses the softmax activation function described in Equation (8) [8]. The Rectified Linear Unit (ReLu) activation function was used in the hidden layers [42,43]. The Adam optimizer was used for training the neural network with categorical cross-entropy as the loss function [44]. The proposed MLP’s mathematical computation can be described as follows:
Input layer: The first layer has “N” linear combinations of the d-dimensional inputs.
Here, is called the activation, which is further used by the activation function. i = 1, 2, …, N. are the weights; represents the input; is a biased value. Superscript (1) indicates that this is the first layer of the neural network.
Hidden layer: In each hidden layer, the weights and output vector of the previous layer are the input of the new layer.
For some kth layer,
Here, is the ReLu activation function, which is described as follows.
Output layer:
Here, represents the activation function. The output layer’s activation function specifies how the weighted sum of the input is converted. The softmax function was used as the activation function for the output layer.
Long Short-Term Memory
HAR is a classical time-series problem, and the RNN can be used to capture temporal information from sequential data; however, it faces the problem of the vanishing gradient in the feedback neural network, which will hinder the ability of the network to model between raw sensor data and human activities in a long context window [45,46]. LSTM is special kind of RNN, which has the capability to learn long-term dependencies and is used to solve the issue of the vanishing gradient in feedback neural networks [47]. LSTM’s main component is the memory cell, which helps in remembering values for a long or short time. An LSTM block usually contains three gates: input, output, and forget gate. The input and output gates represent the incoming and outgoing values of the memory cell, and the forget gate decides whether to ignore the previous state of the memory cell or not.
The LSTM network for the activity recognition of the elderly problem was used in this study, which was built by assembling multiple layers of LSTM in a fully connected manner. This fully connected architecture enables the network to fully exploit the correlations among the cells, which will result in achieving more complex features for prediction. Figure 4 shows the proposed LSTM architecture used in this study. This model is composed of three LSTM layers, and each layer consists of 64 memory cells. The activation of each LSTM is calculated by Equation (9) [18].
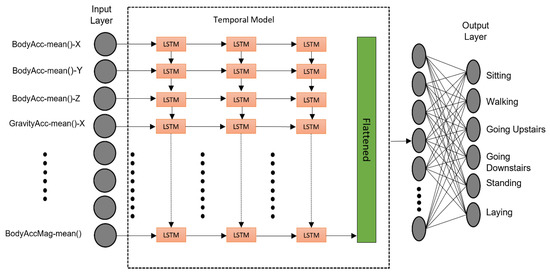
Figure 4.
Architecture of the proposed LSTM model for human activity recognition.
Here, and represent the activation at time t and t− 1. is the activation function; and are the input–hidden and hidden–hidden weights; respectively; is the bias value.
The output of LSTM was flattened and fed to the fully connected layer with the ReLu activation function, and at the output layer, the softmax activation function was used for the activity recognition. The Adam optimizer was used for network optimization, and the categorical cross-entropy function was used to calculate the loss.
3.5. Evaluation Criteria
In this study, besides the basic parameters: True Positive (TP), True Negative (TN), False Positive (FP), and False Negative (FN), dependent parameters such as the precision, recall, accuracy, and F1-score were obtained by the mathematical processing of the above-mentioned parameters for the result evaluation [48]. In this context, TP represents the number of correct predictions of the right activity, TN represents the number of correct predictions of the wrong activity, FP represents the number of incorrect predictions of the right activity, and FN represents the number of incorrect predictions of the wrong activity. The precision, recall, accuracy, and F1-score values were calculated using the above parameters defined in Equations (10)–(13).
Processing time was also considered as an evaluation criterion in this study because of the complex nature of the dataset, so it is important to measure the processing time of the algorithms. Two-fold cross-validation and 10-fold cross-validation were performed as the train–test processes in order to observe the effect of the change in the train–test dataset balance on the output. Furthermore, the “activity recognition with healthy older people dataset” was used as a validation dataset to check the generalization capabilities of the proposed methods.
4. Result and Discussion
In this section, the experimental results of all the conventional machine learning and deep learning methods for the activity detection of the elderly are presented and discussed. Each experiment was repeated 10 times in order to obtain stable results because of the random assignment of initial weights and parameters. The average results are shown in the study for consistency.
Figure 5 shows the standardized confusion matrix of each algorithm; it represents the performance of the classification algorithms. Every row in this matrix is used to depict the instances in a predicted class, and the columns are used to depict the instances in an actual class. By seeing all of the confusion matrix, it is possible to say that LSTM gave the best results when compared with the actual values.
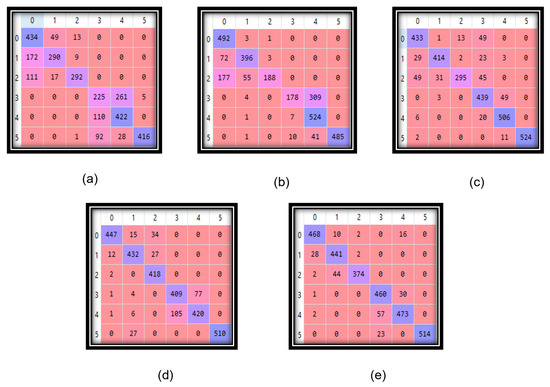
Figure 5.
Confusion matrix of the (a) RF, (b) k-NN (c) SVM (d) ANN, and (e) LSTM.
From Table 1 and Table 2, it is clearly visible that the LSTM approach outperformed all the other methods in most of the cases; the ANN gave the best accuracy in classifying “sitting” for both 2-fold and 10-fold cross-validation. If we compare deep learning methods (ANN and LSTM) with all the other methods, it is clearly depicted that deep learning methods outperformed other conventional machine learning methods in terms of accuracy. The overall accuracy of LSTM (95.05%) was the highest.

Table 1.
Accuracy table of all the algorithms for each activity using 2-fold cross-validation.

Table 2.
Accuracy table of all the algorithms for each activity using 10-fold cross-validation.
Additionally, from Figure 5 and Table 1 and Table 2, it is observed that most of the misclassified records came from “going upstairs” and “going downstairs”, as both activities are somewhat similar, and the model had problems separating these two activities. Now, it is possible to verify the performance of the system in terms of the other parameters as well.
Table 3 and Table 4 show that the best precision, recall, accuracy, and F1-score values were 92.87%, 85.32%, 95.05%, and 88.94%, respectively, and were achieved by the LSTM classifier using 10-fold cross-validation. However, SVM showed the best processing time of 0.08 and 0.42 min in both 2-fold and 10-fold cross-validation. Considering the overall performance of the methods, it is clearly visible that the proposed LSTM’s overall performance was better than other machine learning or deep learning models.

Table 3.
Overall performance assessment using 2-fold cross-validation.

Table 4.
Overall performance assessment using 10-fold cross-validation.
Figure 6 shows the training and loss curve versus epochs using 10-fold cross-validation for both deep learning models. It was observed that the ANN gave a training loss as low as 0.24 and a validation loss of 0.23, and LSTM gave a training loss of 0.16 and a validation loss of 0.15. In both, the model training and validation losses were higher initially, but at the end of the epoch cycle, the loss drastically decreased, while training and validation curves became almost equal. Training was stopped in both models because of the stopping criteria (complete continuous 10-epoch cycle without change in the loss). As it was already discussed above that at the end of the epoch cycle, both losses became almost equal for both deep leaning models, this implies that both models were working perfectly. It was also observed that in LSTM, the model training loss and validation loss difference was higher in the beginning, but this drastically decreased in between 20 and 40 epoch cycles.
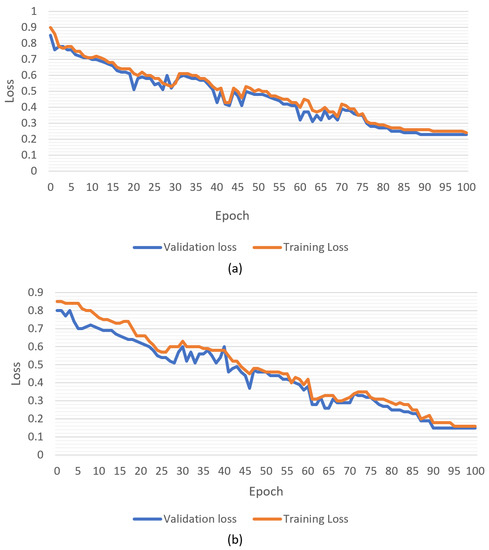
Figure 6.
Training and validation curve for loss using 10-fold cross-validation: (a) ANN model, (b) LSTM model.
Furthermore, to check the robustness and validity of the proposed methods, they were also validated on the “activity recognition with healthy older people using a batteryless wearable sensor dataset” [33]. Table 5 shows the performance assessment on this dataset using 10-fold cross-validation.

Table 5.
Performance assessment using 10-fold cross-validation on activity recognition with the healthy older people dataset [33].
From Table 5, it is possible to say that the proposed LSTM method gave satisfying results of 94.84%, 85.32%, 95.05%, and 88.94% for the precision, recall, accuracy, and F1-score, respectively. Although the dataset was highly imbalanced, still, the proposed system was able to achieve good performance. Therefore, it is possible to say that the proposed method can be used for detecting the activity of elderly people.
From this study, it was observed that deep learning methods are more suitable for the HAR of elderly people as compared to conventional machine learning methods. However, if the processing time is a constraint, machine learning methods are much faster than deep learning methods, especially SVM.
5. Conclusions
This research aimed to monitor the everyday activities of elderly people which will safeguard the elderly people’s health as elderly people usually follow the same routine day. Therefore, if a sudden change is seen in everyday activities, the right action can be taken. Automatic activity identification might assist older individuals in operating independently in their own homes in an aging society. In the proposed study, various conventional machine learning and deep learning methods were used to recognize the activity of elderly people.
The proposed work aimed to develop an automatic activity monitoring system that will automatically detect the activity of elderly people using different machine and deep learning methods such as RF, k-NN, SVM, ANN, and LSTM. Out of all the methods, the LSTM method gave the best accuracy of 95.05%, which is significant, as building an accurate HAR system is very challenging due to the large diversity of activities, and sometimes, these are very similar in nature. However, there is still a need for improvement of the proposed models by validating with larger datasets and with more activities. Our proposed models can also be used in various other fields where the constant supervision of activities is required.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.H. and B.P.B.; methodology, F.M.-D.; software, A.H.; validation, R.T., B.P.B. and A.H.; formal analysis, A.H.; investigation, F.M.-D.; resources, R.T.; data curation, F.M.-D.; writing—original draft preparation, A.H.; writing—review and editing, A.H., F.M.-D. and B.P.B.; visualization, A.H.; supervision, R.T.; project administration, R.T.; funding acquisition, F.M.-D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was also funded by LARSyS (Projeto—UIDB/50009/2020).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the support receive from the Bolsa de Investigação (BI) in Project BASE: BAnana Sensing (PRODERAM20-16.2.2-FEADER-1810).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Paul, P.; George, T. An Effective Approach for Human Activity Recognition on Smartphone. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Engineering and Technology (ICETECH), Coimbatore, India, 20–20 March 2015; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization; The World Bank. World Report on Disability 2011; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; Volume 91, p. 549. [Google Scholar]
- Kementrian Kesehatan Republic Indonesia. Situasi Penyandang Disabilitas. 2014. Available online: https://pusdatin.kemkes.go.id/article/view/15033100002/situasi-penyandang-disabilitas.html (accessed on 3 March 2022).
- Du, Y.; Lim, Y.; Tan, Y. A Novel Human Activity Recognition and Prediction in Smart Home Based on Interaction. Sensors 2019, 19, 4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustoni, I.A.; Hidayatulloh, I.; Azhari, S.N.; Augoestin, N.G. Multidimensional Earcon Interaction Design for The Blind: A Proposal and Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Seminar on Research of Information Technology and Intelligent Systems (ISRITI), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 21–22 November 2018; pp. 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernbumroong, S.; Cang, S.; Atkins, A.; Yu, H. Elderly activities recognition and classification for applications in assisted living, Expert Systems with Applications. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 1662–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulbul, E.; Cetin, A.; Dogru, I.A. Human Activity Recognition Using Smartphones. In Proceedings of the 2018 2nd International Symposium on Multidisciplinary Studies and Innovative Technologies (ISMSIT), Ankara, Turkey, 19–21 October 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, A.; Pomplun, M.; Tran, D.A. A Study on Human Activity Recognition Using Accelerometer Data from Smartphones. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2014, 34, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.C.; Nebel, J.C.; Florez-Revuelta, F. Recognition of activities of daily living with egocentric vision: A review. Sensors 2016, 16, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, C.; Vishwakarma, D.K. Review of state-of-the-art techniques for abnormal human activity recognition. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2019, 77, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Wan, Y.; Saudagar, A.N.; Namuduri, K.; Buckles, B.P. Advances in human action recognition: A survey. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1501.05964. [Google Scholar]
- Saraswathi, D.; Srinivasan, E. Performance analysis of mammogram CAD system using SVM and KNN classifier. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Inventive Systems and Control (ICISC), Coimbatore, India, 19–20 January 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Zhang, D.; Yao, L.; Guo, B.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Y. Deep Learning for Sensor-based Human Activity Recognition: Overview, Challenges, and Opportunities. ACM Comput. Surv. 2021, 54, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Yao, L.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Chang, X.; Nie, F. A semisupervised recurrent convolutional attention model for human activity recognition. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 31, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Gao, H.; Yu, T.; Mengshoel, O.J.; Langseth, H.; Lane, I.; Liu, X. Understanding and improving recurrent networks for human activity recognition by continuous attention. In Proceedings of the 2018 ACM International Symposium on Wearable Computers, Singapore, 8–12 October 2018; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 56–63. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Yao, L.; Zhang, D.; Guo, B.; Yu, Z. Multi-agent Attentional Activity Recognition. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI, Macao, China, 10–16 August 2019; pp. 1344–1350. [Google Scholar]
- Bustoni, I.A.; Hidayatulloh, I.; Ningtyas, A.M.; Purwaningsih, A.; Azhari, S.N. Classification methods performance on human activity recognition. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. ICTVT 2019, 1456, 012027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.; Huang, J.; Wang, H. LSTM-CNN Architecture for Human Activity Recognition. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 56855–56866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wei, Z.; Nie, J.; Huang, L.; Wang, S.; Li, Z. A review on human activity recognition using vision-based method. J. Healthc. Eng. 2017. Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/jhe/2017/3090343/ (accessed on 10 July 2019).
- Ougiaroglou, S.; Nanopoulos, A.; Papadopoulos, A.N.; Manolopoulos, Y.; Welzer-Druzovec, T. Adaptive k-Nearest-Neighbor Classification Using a Dynamic Number of Nearest Neighbors. In Proceedings of the 11th East European Conference, ADBIS 2007, Varna, Bulgaria, 29 September–3 October 2007; pp. 66–82. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes-Ortiz, J.; Ghio, A.; Anguita, D.; Parra-Llanas, X.; Cabestany, J.; Catalá, A. Human activity and motion disorder recognition: Towards smarter interactive cognitive environments. In Proceedings of the European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks, Computational Intelligence and Machine Learning, Bruges, Belgium, 24–26 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Madarshahian, R.; Caicedo, J.M. Human Activity Recognition Using Multinomial Logistic Regression. Model Valid. Uncertain. Quantif. 2015, 3, 363–372. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, T.; Billah, M.; Hossain, F. Random forests based recognition of human activities and postural transitions on smartphone. In Proceedings of the 2016 5th International Conference on Informatics, Electronics and Vision (ICIEV), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 13–14 May 2016; pp. 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usharani, J.; Saktivel, U. Human Activity Recognition using Android Smartphone. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Innovations in Computing & Networking ICICN16, Bengaluru, Karnataka, 12–13 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vakili, M.; Rezaei, M. Incremental Learning Techniques for Online Human Activity Recognition. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.09435. [Google Scholar]
- Muangprathub, J.; Sriwichian, A.; Wanichsombat, A.; Kajornkasirat, S.; Nillaor, P.; Boonjing, V. A Novel Elderly Tracking System Using Machine Learning to Classify Signals from Mobile and Wearable Sensors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anguita, D.; Ghio, A.; Oneto, L.; Parra-Llanas, X.; Reyes-Ortiz, J. Energy Efficient Smartphone-Based Activity Recognition using Fixed-Point Arithmetic. J. Univers. Comput. Sci. 2013, 19, 1295–1314. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, Z.; Soylu, A. Human activity recognition using wearable sensors, discriminant analysis, and long short-term memory-based neural structured learning. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murad, A.; Pyun, J.-Y. Deep Recurrent Neural Networks for Human Activity Recognition. Sensors 2017, 17, 2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Yang, J.; Li, Q. Smartphone-Based Activity Recognition for Indoor Localization Using a Convolutional Neural Network. Sensors 2019, 19, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Y.; Lovell, N.H.; Redmond, S.J.; Wang, K.; Delbaere, K.; van Schooten, K.S. Deep Learning for Activity Recognition in Older People Using a Pocket-Worn Smartphone. Sensors 2020, 20, 7195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguita, D.; Ghio, A.; Oneto, L.; Parra Perez, X.; Reyes Ortiz, J.L. A Public Domain Dataset for Human Activity Recognition Using Smartphones. In Proceedings of the 21th European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks, Computational Intelligence and Machine Learning, ESANN 2013, Bruges, Belgium, 24–26 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, R.L.S.; Ranasinghe, D.C.; Shi, Q.; Sample, A.P. Sensor enabled wearable RFID technology for mitigating the risk of falls near beds. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on RFID, Orlando, FL, USA, 30 April–2 May 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 191–198. [Google Scholar]
- Alrazzak, U.; Alhalabi, B. A survey on human activity recognition using accelerometer sensor. In Proceedings of the Joint 8th International Conference on Informatics, Electronics & Vision (ICIEV) and 2019 3rd International Conference on Imaging, Vision & Pattern Recognition (icIVPR), Spokane, WA, USA, 30 May–2 June 2019; pp. 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobark, M.; Chuprat, S. Recognition of complex human activity using mobile phones: A systematic literature review. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2018, 96, 3756–3779. [Google Scholar]
- Strobl, C.; Boulesteix, A.-L.; Augustin, T. Unbiased split selection for classification trees based on the gini index. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2006, 52, 483–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthick, G.; Harikumar, R. Comparative Performance Analysis of Naive Bayes and SVM classifier for Oral X-ray images. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Electronics and Communcation Systems (ICECS), Coimbatore, India, 24–25 February 2017; Volume 17, pp. 88–92. [Google Scholar]
- Taunk, K.; De, S.; Verma, S.; Swetapadma, A. A Brief Review of Nearest Neighbor Algorithm for Learning and Classification. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICCS), Madurai, India, 15–17 May 2019; pp. 1255–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patle, A.; Chouhan, D.S. SVM kernel functions for classification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Technology and Engineering (ICATE), Mumbai, India, 23–25 January 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahatsham; Singh, A.; Shahare, V.; Arora, N. An Efficient System for Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancer using Support Vector Machine. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. (IJEAT) 2019, 9, 7029–7035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-P.; Yang, J.-Y.; Liou, S.-N.; Lee, G.-Y.; Wang, J.-S. Online classifier construction algorithm for human activity detection using a tri-axial accelerometer. Appl. Math. Comput. 2008, 205, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.T.; Li, W.; Ogunbona, P.O. Human detection from images and videos: A survey. Pattern Recognit. 2016, 51, 148–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.M.; Lee, Y.-K.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, T.-S. Human Activity Recognition via an Accelerometer-Enabled-Smartphone Using Kernel Discriminant Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2010 5th International Conference on Future Information Technology, Busan, Korea, 21–23 May 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ahatsham; Jain, S.; Shahare, V.; Arora, N.; Rab, S. Real Time Human Activity Recognition using Smart Phone. Adv. Sci. Eng. Med. 2020, 12, 1200–1203. [Google Scholar]
- Maurer, U.; Smailagic, A.; Siewiorek, D.P.; Deisher, M. Activity recognition and monitoring using multiple sensors on different body positions. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks (BSN’06), Cambridge, MA, USA, 3–5 April 2006; pp. 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhong, K.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, X. LSTM Networks for Mobile Human Activity Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence: Technologies and Applications, Bangkok, Thailand, 24–25 January 2016; pp. 50–53. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmani, H.; Mian, A.; Shah, M. Learning a deep model for human action recognition from novel viewpoints. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goutte, C.; Gaussier, E. A Probabilistic Interpretation of Precision, Recall and F-Score, with Implication for Evaluation. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2005, 3408, 345–359. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).