Abstract
A graph is a tool for designing a system’s required interconnection network. The topology of such networks determines their compatibility. For the first time, in this work we construct subdivided network and discussed their topology. In graph theory, there are a variety of invariants to study the topology of a network, but topological indices are designed in such a way that these may transform the graph into a numeric value. In this work, we study via Zagreb connection indices. Due to their predictive potential for enthalpy, entropy, and acentric factor, these indices gain value in the field of chemical graph theory in a very short time. formed by time repeated process which consists copies of graph along with edges which used to join these copies of . The free hand to choose the initial graph for desired network and its relation with chemical networks along with the repute of Zagreb connection indices enhance the worth of this study. These computations are theoretically innovative and aid topological characterization of .
1. Introduction
Graph theory may use to design desired interconnection networks and provides its topology. Furthermore, interlink computer science, chemistry and mathematics for practical usage. This area of study has their worth as a separate field named Chem-informatics, a combination of chemistry, information science, and mathematics. In this discipline QSAR/QSPR relationship, bioactivity, and classification of chemical compounds are examined.
It is a new area of research that has captivated the interest of researchers. It creates a relationship between the structure of organic compounds and their physio-chemical properties using several helpful graph invariants and chemical graph of underlying compound. A chemical graph is a representation of a chemical compound’s structural formula using graph theory, consists vertices in place of atoms and edges for chemical bonds.
The theoretical analysis of underlying substance molecular graphs via graph invariants might assist in the QSPR/QSAR investigations. The use of topological descriptors of chemical structure in the study of structure-property interactions is common now a days, particularly in QSPR/QSAR investigations. There are many graph invariants which used to characterize interconnection networks for desired investigations in computer science and chemistry. However, in the QSPR/QSAR analysis, topological indices play an important role as they depict chemical substances’ physio-chemical properties. Topological indices are the graph invariants which may used to reduce the practical work at some extent through prediction of desired property of related structure via topology of the graph [1,2]. Harry Winner was the first who used the topology of chemical graph for prediction of bolling point in 1947 [3]. Later on, in 1972 and 1975, Gutman with their collaborator introduces
indices in there work of electron energy of hydrocarbons [4,5]. In [6], another version of Zagreb indices named Hyper Zagreb index introduced as
Recently, Ali and Trinajstic [7] used modified version of Zagreb indices named first Zagreb connection index which based on connection numbers associated with the vertices of graph as
The connection numbers is the total of distinct vertices which are at distance two from the fixed vertex . In [8], modified first Zagreb connection index studied which is defined as
The second Zagreb connection index is
Refs. [7,9,10,11,12] justify the applicability of these indices through correlation with entropy and acentric factor. For the first time in this work we construct subdivided network as and discussed its topology. One can extend applications of these networks by using fuzzy graphs techniques as used in [13,14,15]. Furthermore, We determined closed form formulas for and of when generated by the single vertex graph and extend our finding up to a large class generated by any graph . As applications, we computed and when represents a specific family of graphs. The research work [16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24] on Zagreb connection indices and the correlation of these indices with acentric factor, enthalpy and entropy along with the formation of with chemical networks by assure applicability of this work.
2. Material and Method
We adopted techniques as used in [25,26,27,28,29,30] for edges and vertex partition. We admits subdivision technique for the desired network . We used notation for graph, edge set, vetex set, order, size and degree of vertex as , and , respectively.
Network
network formed by time repeated process using Cartesian product. It consists copies of graph along with edges which used to join these copies of as . The new edges which join these copies joined corresponding vertices of all the copies. The total vertices and edges are and , respectively. The for and when is a single vertex graph shown in Figure 1.
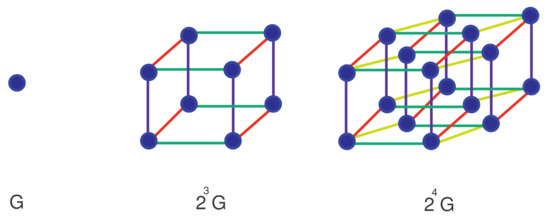
Figure 1.
for and when is a single vertex graph.
3. Molecular Networks Identical with
The importance of may estimates by its relation with chemical networks as shown in Figure 2.
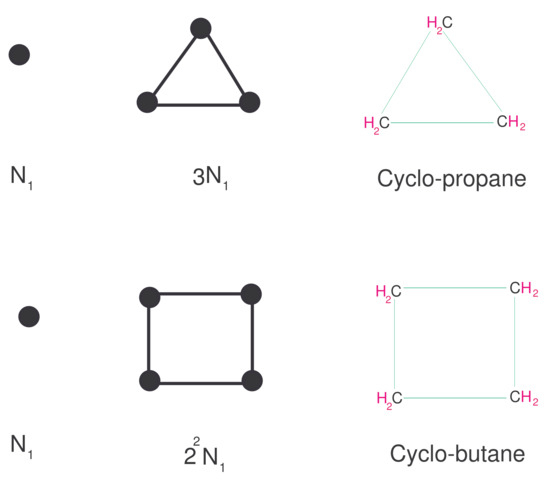
Figure 2.
as organic compounds.
Carbon Nanotube as
Carbon nanotube is identical with the graph formed by as , shown in Figure 3.
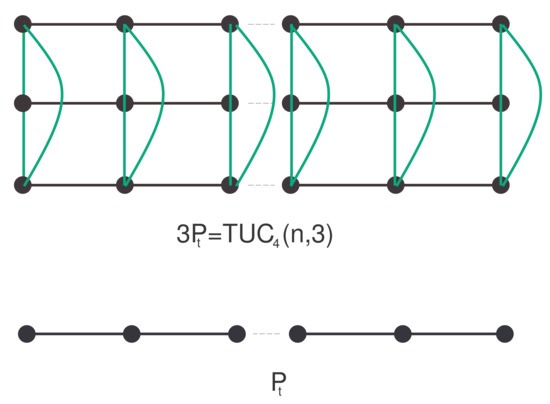
Figure 3.
as carbon nanotube .
Cyclo-butane is also identical with .
4. Subdivided Network When Consist Only One Vertex
Subdivided graph obtained by inserting new vertex at each edge, i.e., let and x be the new vertex and replace each edge with two edges and to form subdivided graph . In a similar way, we obtain shown in Figure 4 for and when is a single vertex graph. There are and vertices and edges of , respectively.
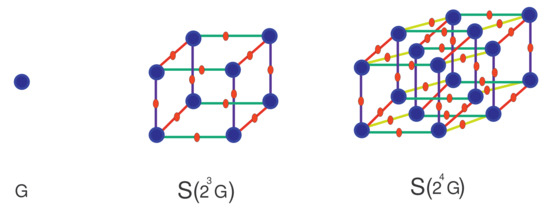
Figure 4.
for when is a single vertex graph.
Theorem 1.
Let Γ be the graph with . Then and of are
Proof.
Let , and . The construction of implies and connection numbers of . These findings enabled us to find
In case the total number of vertices of are , i.e., and .
Now for ,
For each edge the end vertex connection number is and . So,
Now for ,
Now again, for each edge the end vertex connection number and . So,
Equation (1) completes the proof. □
5. When Is Any -Vertex Simple Connected Graph
There are vertices and edges of for any graph . The degree of each vertex is [31]. In this section we defined subdivided graph and computed and of . The for , and shown in Figure 5.
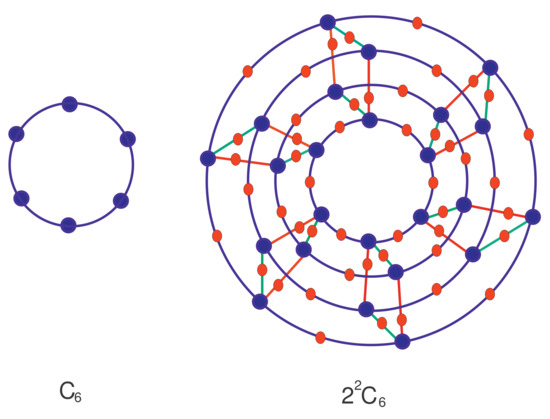
Figure 5.
for , and .
Theorem 2.
The for any graph Γ is
Proof.
The connection number of vertices is , and . The is
□
Theorem 3.
Let Γ be the simple connected graph with . Then
Proof.
Let be the sub divided graph of for any graph . The and .
□
Theorem 4.
For any graph Γ
Proof.
Let be the sub divided graph of for any graph . The and .
□
6. Applications of Computed Results as Zagreb Connection Indices of and
Corollary 1.
The is
Proof.
Let of order n and size m, . Replacing and in Theorem 2 we get,
□
Corollary 2.
The is
Proof.
Replacing and in Theorem 3 we get,
□
Corollary 3.
The is
Proof.
Replacing in Theorem 3 we get,
□
Corollary 4.
Let a complete graph of order m. Then
7. Future Work
In future, the study of can be done via the following methods:
- Study of via degree based topological indices.
- Study of via eccentricity based topological indices.
- Study of via distance based topological indices.
- One can compute the energies of .
8. Conclusions
For the first time in this work we construct subdivided graph of network as . We also discussed its topology and find closed form formulas for total number of edges and vertices. In Theorem 1, we determined and for single vertex graph . In Theorems 2–4 we extend our work for when is any graph. In Corollaries 1–4 we compute result for uni-cyclic graph and complete graph as an application of our computed results. Finally, we proposed some open problems for future work on .
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.H., A.u.R., A.S., M.A. and W.S.; methodology, M.H., A.u.R., A.S., M.A. and W.S.; software, M.H., A.u.R., A.S., M.A. and W.S.; validation, M.H., A.u.R., A.S., M.A. and W.S.; formal analysis, M.H., A.u.R., A.S., M.A. and W.S.; investigation, M.H., A.u.R., A.S., M.A. and W.S.; resources, M.H., A.u.R., A.S., M.A. and W.S.; data curation, M.H., A.u.R., A.S., M.A. and W.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.H., A.u.R., A.S., M.A. and W.S.; writing—review and editing, M.H., A.u.R., A.S., M.A. and W.S.; visualization, M.H., A.u.R., A.S., M.A. and W.S.; supervision, A.u.R.; project administration, W.S.; funding acquisition, W.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was supported by the National Science Centre, Decision number UMO-2018/29/ B/HS4/02725 (A.S., B.K. and W.S.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the editor and the anonymous reviewers, whose insightful comments and constructive suggestions helped us to significantly improve the quality of this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Trinajstic, N. Chemical Graph Theory; Routledge: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.-B.; Shaker, H.; Nadeem, I.; Hussain, M. Topological aspects of Boron nanotubes. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiener, H. Structural determination of paraffin boiling points. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1947, 69, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutman, I.; Trinajstić, N. Graph theory and molecular orbitals. Total ζ-electron energy of alternant hydrocarbons. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1972, 17, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoya, H.; Hosoi, K.; Gutman, I. A topological index for the total Π-electron energy. Theor. Chim. Acta 1975, 38, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirdel, G.; Rezapour, H.; Sayadi, A. The hyper-Zagreb index of graph operations. Iran. J. Math. Chem. 2013, 4, 213–220. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.; Trinajstic, N. A Novel/Old Modification of the First Zagreb Index. Mol. Inform. 2018, 37, 1800008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Ali, A.; Trinajstić, N. Alkanes with the first three maximal/minimal modified first Zagreb connection indices. Mol. Inform. 2019, 38, 1800116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, U.; Javaid, M.; Alanazi, A.M. Computing Analysis of Connection-Based Indices and Coindices for Product of Molecular Networks. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, U.; Javaid, M.; Kashif, A. Modified Zagreb connection indices of the T-sum graphs. Main Group Met. Chem. 2020, 43, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Ali, U.; Javaid, M.; Huang, C. Zagreb connection indices of molecular graphs based on operations. Complexity 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.-H.; Ali, U.; Javaid, M.; Shabbir, K. Zagreb connection indices of subdivision and semi-total point operations on graphs. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 9846913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akram, M. Single-Valued Neutrosophic Graphs, Infosys Science Foundation Series in Mathematical Sciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Akram, M. m-Polar Fuzzy Graphs, Studies in Fuzziness and Soft Computing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Akram, M.; Zafar, F. Hybrid Soft Computing Models Applied to Graph Theory, Studies in Fuzziness and Soft Computing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Javaid, M.; Ali, U.; Liu, J.-B. Computing analysis for first zagreb connection index and coindex of resultant graphs. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 6019517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureen, S.; Bhatti, A.A.; Ali, A. Extremal trees for the modified first Zagreb connection index with fixed number of segments or vertices of degree 2. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2020, 14, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.-B.; Raza, Z.; Javaid, M. Zagreb Connection Numbers for Cellular Neural Networks. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataineh, M.S.; Raza, Z.; Sukaiti, M.E. On the zagreb connection indices of hex and honeycomb networks. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 40, 4107–4114. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, Z. Zagreb Connection Indices for Some Benzenoid Systems. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducoffe, G.; Marinescu-Ghemeci, R.; Obreja, C.; Popa, A.; Tache, R. Extremal graphs with respect to the modified first Zagreb connection index. In Proceedings of the 2018 20th International Symposium on Symbolic and Numeric Algorithms for Scientific Computing (SYNASC), Timisoara, Romania, 20–23 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sahin, B.; Sahin, A. The Hosoya Polynomial of the Schreier Graphs of the Group and the Basilica Group. Turk. J. Sci. 2020, 5, 262–267. [Google Scholar]
- Ulker, A.; Gursoy, A.; Gursoy, N.K.; Gutman, I. Relating graph energy and Sombor index. Discret. Math. Lett. 2021, 8, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ulker, A.; Gürsoy, A.; Gürsoy, K.N. The energy and Sombor index of graphs. MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem. 2022, 87, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, N.F.; Naeem, M.; Chaudhry, F.; Afzal, D. Study of some topological invariants of subdivided mk graphs. Eurasian Chem. Commun. 2020, 2, 731–738. [Google Scholar]
- De, N.N.; Cancan, M.; Alaeiyan, M.; Farahani, M.R. On some degree based topological indices of mk-graph. J. Discret. Math. Sci. Cryptogr. 2020, 23, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancan, N.M.; Afzal, F.; Mahsud, M.; Naeem, M.; Afzal, D. Study of some connectivity index of subdivided mk graphs of ladder and triangular ladder graph. J. Discret. Math. Sci. Cryptogr. 2020, 23, 1279–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Hussain, M.; Almohamedh, H.; Alhamed, K.M.; Alabdan, R.; Almutairi, A.A.; Almotairi, S. Study of Carbon Nanocones via Connection Zagreb Indices. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5539904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Hussain, M.; Almohamedh, H.; Alhamed, K.M.; Almotairi, S. An Approach to the Extremal Inverse Degree Index for Families of Graphs with Transformation Effect. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 6657039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Kizielewicz, B.; Rehman, A.U.; Hussain, M.; Sałabun, W. Study of θϕ Networks via Zagreb Connection Indices. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayache, N.A.; Alameri, A. Topological indices of the mk-graph. J. Assoc. Arab. Univ. Basic Appl. Sci. 2017, 24, 283–291. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).