Goal-Driven Visual Question Generation from Radiology Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To the best of our knowledge, this work is the first attempt to generate visual questions about medical images that will result in a specific type of answer when provided with an initial indication of the question category/type.
- To overcome the data limitation of VQG in closed domains, we propose a new data augmentation method for natural language questions.
- VQGRaD is designed to work with or without an image caption and only requires the image and the question category as minimal inputs.
- We study the impact of domain knowledge incorporation, such as named entities and semantic types, in the proposed VQGRaD approach.
- VQGRaD is evaluated using the VQA-RAD dataset of clinical questions and radiology images. Experimental results show that VQGRaD performs better than strong baselines, with a BLEU-1 score of 61.86%. We also report the VQG models’ results in our participation at the VQA-Med 2020 challenge.
- We perform a manual evaluation to study the grammaticality, fluency, and relevance of the generated question from radiology images.
2. Related Work
3. Methods
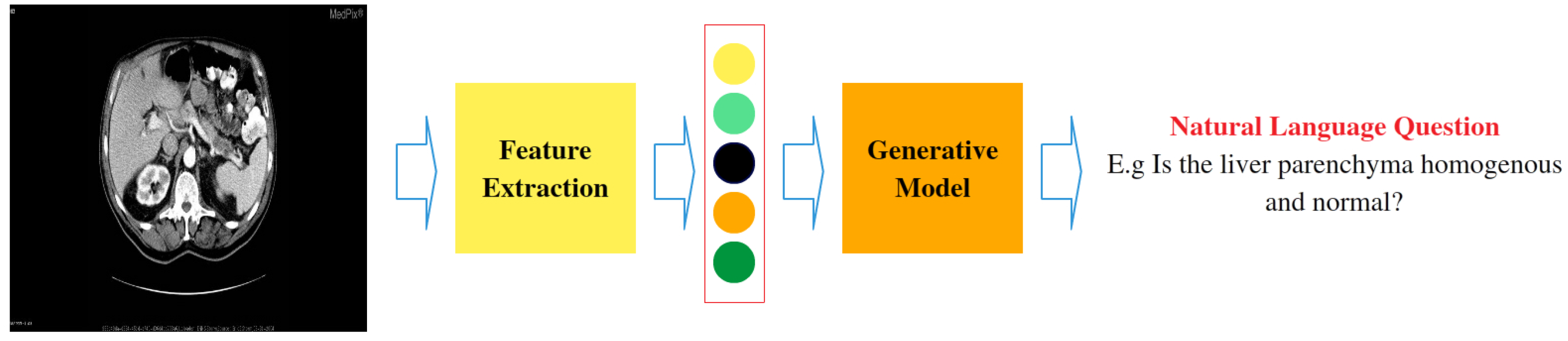
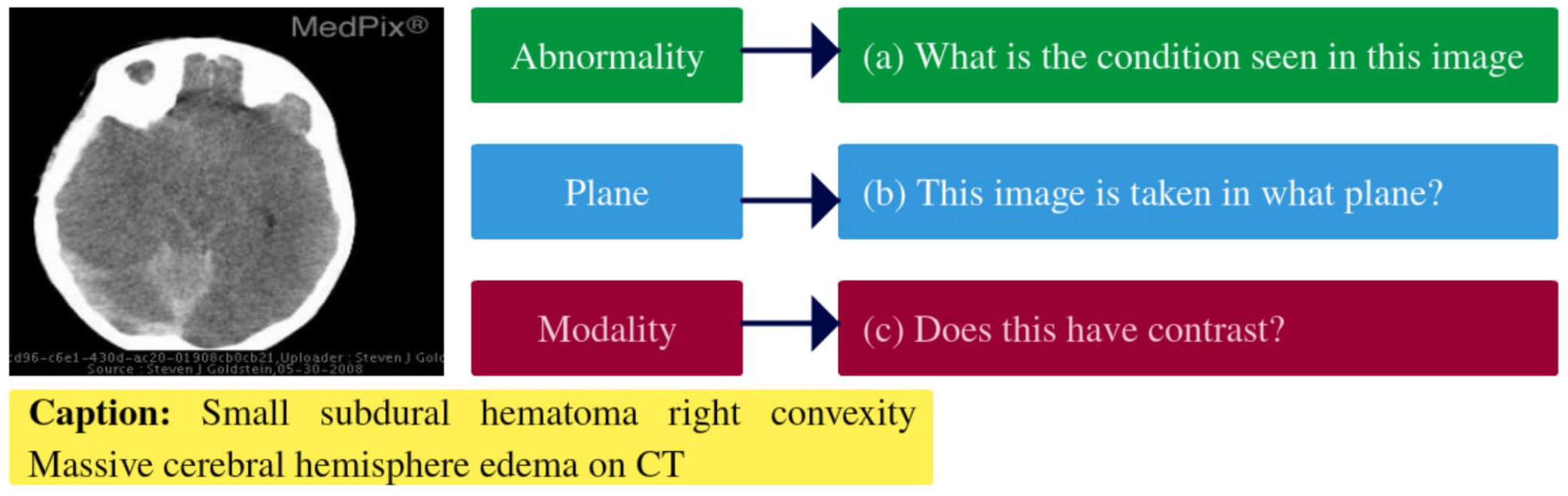
3.1. Problem Modeling
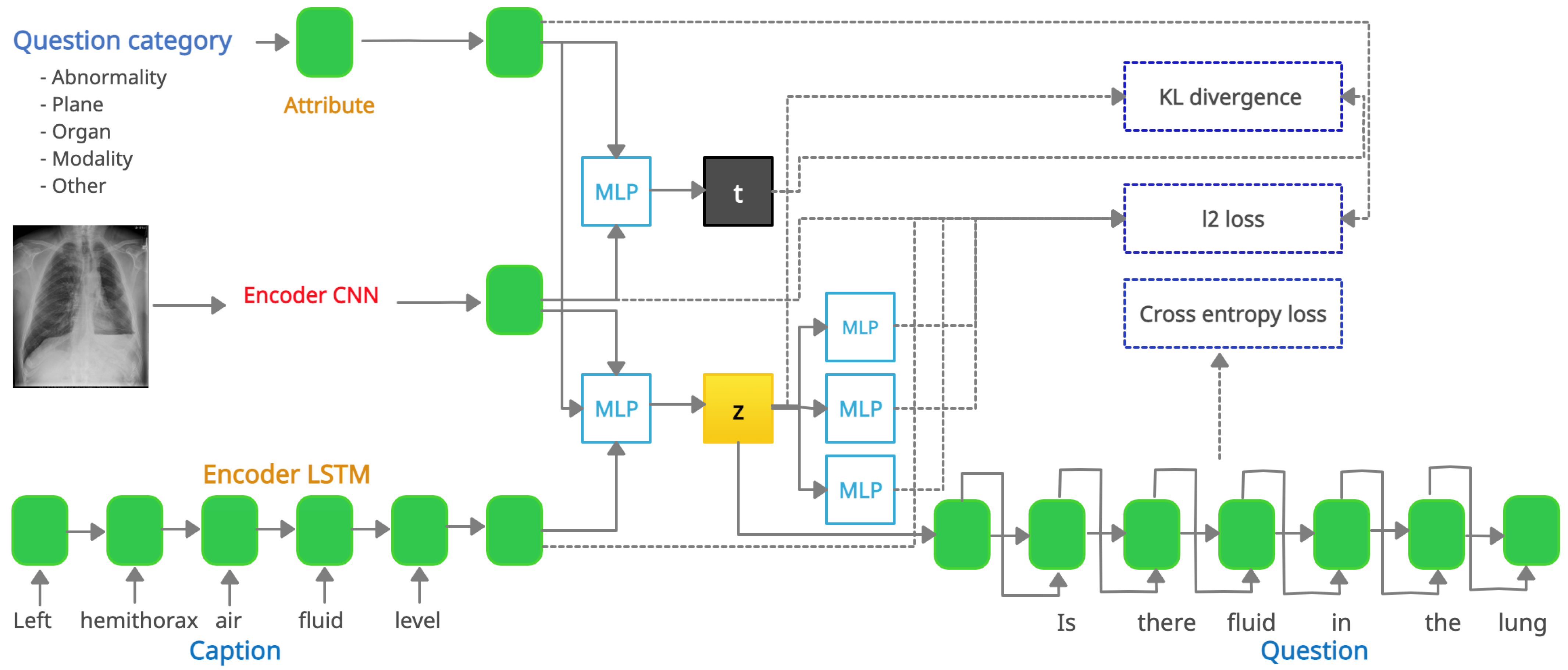
3.2. VQGRaD
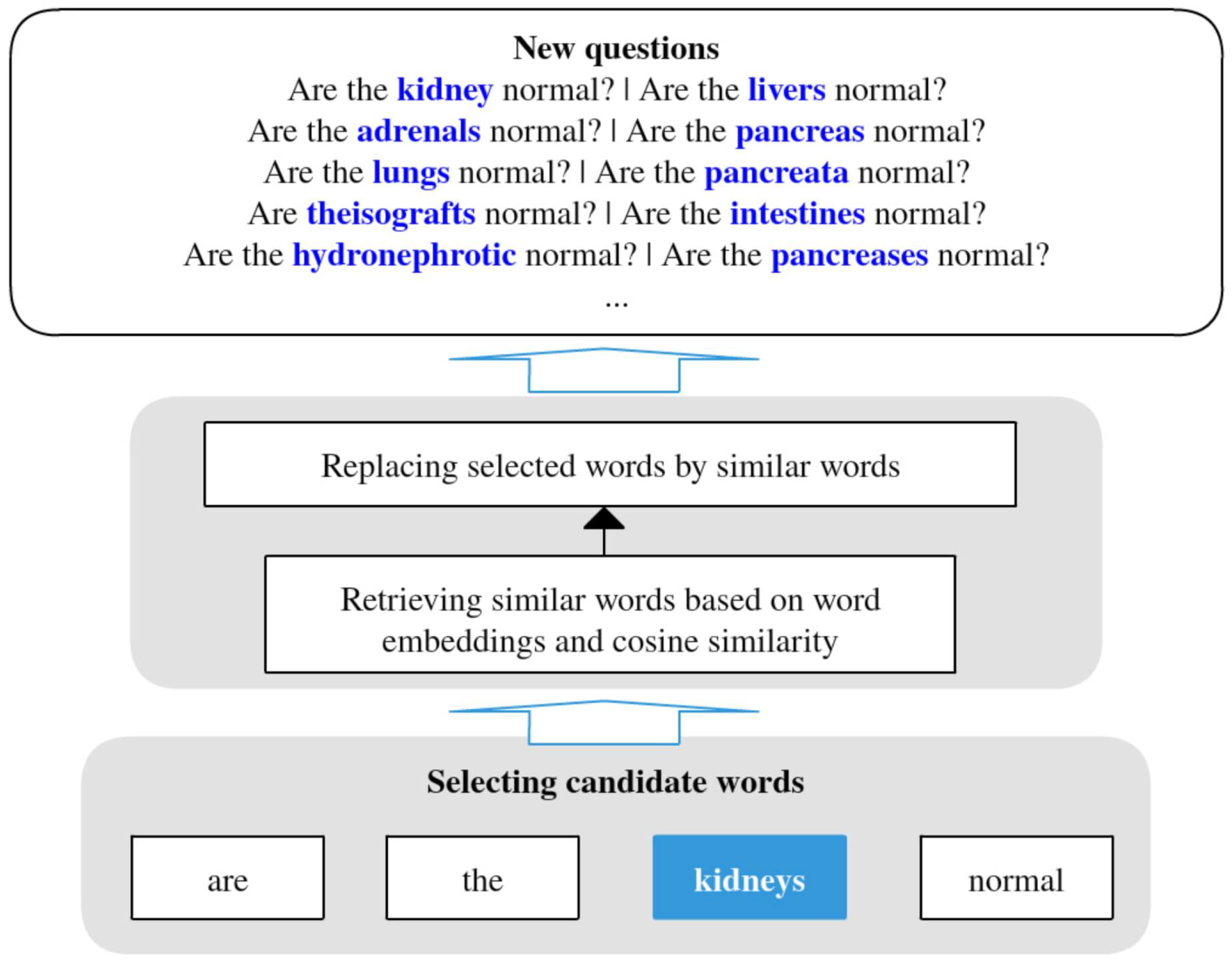
3.3. Data Augmentation
- NN: Noun, singular or mass.
- NNS: Noun, plural.
- NNP: Proper noun, singular.
- NNPS: Proper noun, plural.
- VBD: Verb, past tense.
- VBP: Verb, non-3rd person singular present.
- VBN: Verb, past participle.
- VBG: Verb, gerund or present participle.
- VBZ: Verb, 3rd person singular present.
- VB: Verb, base form.
4. Experimental Settings and Results
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.2.1. Automatic Evaluation
4.2.2. Human Evaluation
4.3. Implementation Details
4.4. Experiments and Results
- VQGRaD is our full model that can generate questions from either the caption latent space z (image, caption, and category) or the category latent space t (image and category).
- VQGRaD includes another LSTM encoder to encode the image titles.
- VQGRaD includes another LSTM encoder to encode the UMLS semantic types extracted from the image captions.
- VQGRaD uses only UMLS entities instead of using all words in captions. PyMetamap (https://github.com/AnthonyMRios/pymetamap, accessed on 15 August 2021), a python wrapper for MetaMap [59], has been used for extracting UMLS entities and semantic types.
- In VQGRaD, the -space contains only image and caption features.
- The VQGR baseline system is trained on the VQA-RAD dataset without data augmentation.
- VQGR is trained on the dataset generated by augmenting the images.
- VQGR is trained on the dataset generated by our data augmentation technique.
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Grandvalet, Y.; Davoine, F.; Cheng, J.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, H.; Belongie, S.; Tsai, Y.H.; Yang, M.H. Transfer learning in computer vision tasks: Remember where you come from. Image Vis. Comput. 2020, 93, 103853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; He, H.; He, T.; Lausen, L.; Li, M.; Lin, H.; Shi, X.; Wang, C.; Xie, J.; Zha, S.; et al. GluonCV and GluonNLP: Deep Learning in Computer Vision and Natural Language Processing. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2020, 21, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Pelka, O.; Friedrich, C.M.; Garcıa Seco de Herrera, A.; Müller, H. Overview of the ImageCLEFmed 2020 concept prediction task: Medical image understanding. In Proceedings of the CLEF 2020—Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum, Thessaloniki, Greece, 22–25 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Elharrouss, O.; Almaadeed, N.; Al-Maadeed, S.; Bouridane, A. Gait recognition for person re-identification. J. Supercomput. 2021, 77, 3653–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elharrouss, O.; Almaadeed, N.; Al-Maadeed, S. Mhad: Multi-human action dataset. In Fourth International Congress on Information and Communication Technology; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 333–341. [Google Scholar]
- Sarrouti, M.; Alaoui, S.O.E. SemBioNLQA: A semantic biomedical question answering system for retrieving exact and ideal answers to natural language questions. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 102, 101767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruder, S.; Peters, M.E.; Swayamdipta, S.; Wolf, T. Transfer Learning in Natural Language Processing. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Tutorials, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-allaly, E.-d.; Sarrouti, M.; En-Nahnahi, N.; Alaoui, S.O.E. An adverse drug effect mentions extraction method based on weighted online recurrent extreme learning machine. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2019, 176, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrouti, M.; Alaoui, S.O.E. A Yes/No Answer Generator Based on Sentiment-Word Scores in Biomedical Question Answering. Int. J. Healthc. Inf. Syst. Inform. 2017, 12, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sarrouti, M.; Lachkar, A. A new and efficient method based on syntactic dependency relations features for ad hoc clinical question classification. Int. J. Bioinform. Res. Appl. 2017, 13, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Yang, N.; Wang, W.; Wei, F.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhou, M.; Hon, H.W. Unified Language Model Pre-training for Natural Language Understanding and Generation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.03197. [Google Scholar]
- Moen, E.; Bannon, D.; Kudo, T.; Graf, W.; Covert, M.; Van Valen, D. Deep learning for cellular image analysis. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-allaly, E.-d.; Sarrouti, M.; En-Nahnahi, N.; Alaoui, S.O.E. DeepCADRME: A deep neural model for complex adverse drug reaction mentions extraction. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2021, 143, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-allaly, E.-d.; Sarrouti, M.; En-Nahnahi, N.; Alaoui, S.O.E. MTTLADE: A multi-task transfer learning-based method for adverse drug events extraction. Inf. Process. Manag. 2021, 58, 102473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Sarrouti, M.; Ben Abacha, A.; Demner-Fushman, D. Multi-task transfer learning with data augmentation for recognizing question entailment in the medical domain. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Healthcare Informatics (ICHI), Victoria, BC, Canada, 9–12 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ionescu, B.; Müller, H.; Villegas, M.; de Herrera, A.G.S.; Eickhoff, C.; Andrearczyk, V.; Cid, Y.D.; Liauchuk, V.; Kovalev, V.; Hasan, S.A.; et al. Overview of ImageCLEF 2018: Challenges, datasets and evaluation. In Proceedings of the International Conference of the Cross-Language Evaluation Forum for European Languages, Avignon, France, 10–14 September 2018; pp. 309–334. [Google Scholar]
- Pelka, O.; Friedrich, C.M.; Seco De Herrera, A.; Müller, H. Overview of the ImageCLEFmed 2019 concept detection task. In Proceedings of the CLEF 2019—Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum, Lugano, Switzerland, 9–12 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Abacha, A.; Datla, V.V.; Hasan, S.A.; Demner-Fushman, D.; Müller, H. Overview of the VQA-Med Task at ImageCLEF 2020: Visual Question Answering and Generation in the Medical Domain. In Proceedings of the CLEF 2020—Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum, Thessaloniki, Greece, 22–25 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, D.; Suman, S.; Ekbal, A. Hierarchical deep multi-modal network for medical visual question answering. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 164, 113993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafazadeh, N.; Misra, I.; Devlin, J.; Mitchell, M.; He, X.; Vanderwende, L. Generating Natural Questions about an Image. In Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers); Association for Computational Linguistics: Berlin, Germany, 2016; pp. 1802–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Qu, L.; You, S.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, J. Automatic Generation of Grounded Visual Questions. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Sixth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI-17), Melbourne, Australia, 19–25 August 2016; pp. 4235–4243. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Duan, N.; Zhou, B.; Chu, X.; Ouyang, W.; Wang, X. Visual Question Generation as Dual Task of Visual Question Answering. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6116–6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, R.; Bernstein, M.; Fei-Fei, L. Information Maximizing Visual Question Generation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 2008–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patro, B.N.; Kurmi, V.K.; Kumar, S.; Namboodiri, V.P. Deep Bayesian Network for Visual Question Generation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Snowmass Village, CO, USA, 1–5 March 2020; pp. 1555–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, C.; Patwardhan, M. Visual Question Generation: The State of the Art. ACM Comput. Surv. 2020, 53, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, J.J.; Gayen, S.; Ben Abacha, A.; Demner-Fushman, D. A dataset of clinically generated visual questions and answers about radiology images. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, L.; Wang, J. The Effectiveness of Data Augmentation in Image Classification using Deep Learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1712.04621. [Google Scholar]
- Inés, A.; Domínguez, C.; Heras, J.; Mata, E.; Pascual, V. Biomedical image classification made easier thanks to transfer and semi-supervised learning. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 198, 105782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrouti, M.; Ben Abacha, A.; Demner-Fushman, D. Visual Question Generation from Radiology Images. In Proceedings of the First Workshop on Advances in Language and Vision Research, Online, 6–8 July 2020; pp. 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Kalady, S.; Elikkottil, A.; Das, R. Natural language question generation using syntax and keywords. In Proceedings of the QG2010: The Third Workshop on Question Generation, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 14–18 June 2010; Volume 2, pp. 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, H.; Shin, J.; Jung, K. Improving neural question generation using answer separation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Volume 33, pp. 6602–6609. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Bing, L.; King, I.; Lyu, M.R. Improving Question Generation With to the Point Context. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, Hong Kong, China, 3–7 November 2019; Volume 33, pp. 3216–3226. [Google Scholar]
- Serban, I.V.; García-Durán, A.; Gulcehre, C.; Ahn, S.; Chandar, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generating Factoid Questions With Recurrent Neural Networks: The 30M Factoid Question-Answer Corpus. In Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Berlin, Germany, 7–12 August 2016; pp. 588–598. [Google Scholar]
- Kafle, K.; Kanan, C. Visual Question Answering: Datasets, Algorithms, and Future Challenges. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2017, 163, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.; He, X.; Buehler, C.; Teney, D.; Johnson, M.; Gould, S.; Zhang, L. Bottom-Up and Top-Down Attention for Image Captioning and Visual Question Answering. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6077–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Lu, J.; Antol, S.; Mitchell, M.; Zitnick, C.L.; Batra, D.; Parikh, D. VQA: Visual Question Answering. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 2425–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, Y.; Khot, T.; Agrawal, A.; Summers-Stay, D.; Batra, D.; Parikh, D. Making the V in VQA Matter: Elevating the Role of Image Understanding in Visual Question Answering. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2019, 127, 398–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.; Hariharan, B.; van der Maaten, L.; Fei-Fei, L.; Zitnick, C.L.; Girshick, R. CLEVR: A Diagnostic Dataset for Compositional Language and Elementary Visual Reasoning. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1988–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda-Mora, I.; Pascual-deLaPuente, S.; Giro-i-Nieto, X. Towards Automatic Generation of Question Answer Pairs from Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPR 2016), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, Q.; Shen, C.; Zhang, J.; Lu, J.; van den Hengel, A. Goal-Oriented Visual Question Generation via Intermediate Rewards. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lu, J.; Lee, S.; Batra, D.; Parikh, D. Visual Curiosity: Learning to Ask Questions to Learn Visual Recognition. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.00912. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, U.; Zhang, Z.; Schwing, A. Creativity: Generating diverse questions using variational autoencoders. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5415–5424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Welling, M. Auto-encoding variational bayes. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.6114. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, S.A.; Ling, Y.; Farri, O.; Liu, J.; Müller, H.; Lungren, M.P. Overview of ImageCLEF 2018 Medical Domain Visual Question Answering Task. In Working Notes of CLEF 2018, Proceedings of the Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum, Avignon, France, 10–14 September 2018; Cappellato, L., Ferro, N., Nie, J., Soulier, L., Eds.; CEUR-WS: Aachen, Germany, 2018; Volume 2125. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Abacha, A.; Gayen, S.; Lau, J.J.; Rajaraman, S.; Demner-Fushman, D. NLM at ImageCLEF 2018 Visual Question Answering in the Medical Domain. In Working Notes of CLEF 2018, Proceedings of the Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum, Avignon, France, 10–14 September 2018; Cappellato, L., Ferro, N., Nie, J., Soulier, L., Eds.; CEUR-WS: Aachen, Germany, 2018; Volume 2125. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Abacha, A.; Hasan, S.A.; Datla, V.V.; Liu, J.; Demner-Fushman, D.; Müller, H. VQA-Med: Overview of the Medical Visual Question Answering Task at ImageCLEF 2019. In Working Notes of CLEF 2019, Proceedings of the Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum, Lugano, Switzerland, 9–12 September 2019; Cappellato, L., Ferro, N., Losada, D.E., Müller, H., Eds.; CEUR-WS: Aachen, Germany, 2019; Volume 2380. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Sadi, A.; Al-Theiabat, H.; Al-Ayyoub, M. The Inception Team at VQA-Med 2020: Pretrained VGG with Data Augmentation for Medical VQA and VQG. In Working Notes of CLEF 2020, Proceedings of the Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum, Thessaloniki, Greece, 22–25 September 2020; Cappellato, L., Eickhoff, C., Ferro, N., Névéol, A., Eds.; CEUR-WS: Aachen, Germany, 2020; Volume 2696. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, S. Contextual Augmentation: Data Augmentation by Words with Paradigmatic Relations. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter ofthe Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 2 (Short Papers), New Orleans, LA, USA, 1–6 June 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, G.G.; Steedman, M. Data Augmentation via Dependency Tree Morphing for Low-Resource Languages. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 31 October–4 November 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidhuber, J.; Hochreiter, S. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar]
- Bird, S.; Klein, E.; Loper, E. Natural Language Processing with Python: Analyzing Text with the Natural Language Toolkit; O’Reilly Media, Inc.: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Fang, H.; Lin, T.Y.; Vedantam, R.; Gupta, S.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft COCO Captions: Data Collection and Evaluation Server. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1504.00325. [Google Scholar]
- Koehn, P.; Monz, C. Manual and automatic evaluation of machine translation between European languages. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Statistical Machine Translation—StatMT’06, New York, NY, USA, 8–9 June 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Cardie, C. Harvesting Paragraph-level Question-Answer Pairs from Wikipedia. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Melbourne, Australia, 15–20 July 2018; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 1907–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosking, T.; Riedel, S. Evaluating Rewards for Question Generation Models. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North. Association for Computational Linguistics, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Aronson, A.R. Effective mapping of biomedical text to the UMLS Metathesaurus: The MetaMap program. In Proceedings of the AMIA Symposium, Washington, DC, USA, 3–7 November 2001; p. 17. [Google Scholar]
- Sarrouti, M. NLM at VQA-Med 2020: Visual Question Answering and Generation in the Medical Domain. In Working Notes of CLEF 2020, Proceedings of the Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum, Thessaloniki, Greece, 22–25 September 2020; Cappellato, L., Eickhoff, C., Ferro, N., Névéol, A., Eds.; CEUR-WS: Aachen, Germany, 2020; Volume 2696. [Google Scholar]
- Viera, A.J.; Garrett, J.M. Understanding interobserver agreement: The kappa statistic. Fam. Med. 2005, 37, 360–363. [Google Scholar]
- Hripcsak, G. Agreement, the F-Measure, and Reliability in Information Retrieval. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2005, 12, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
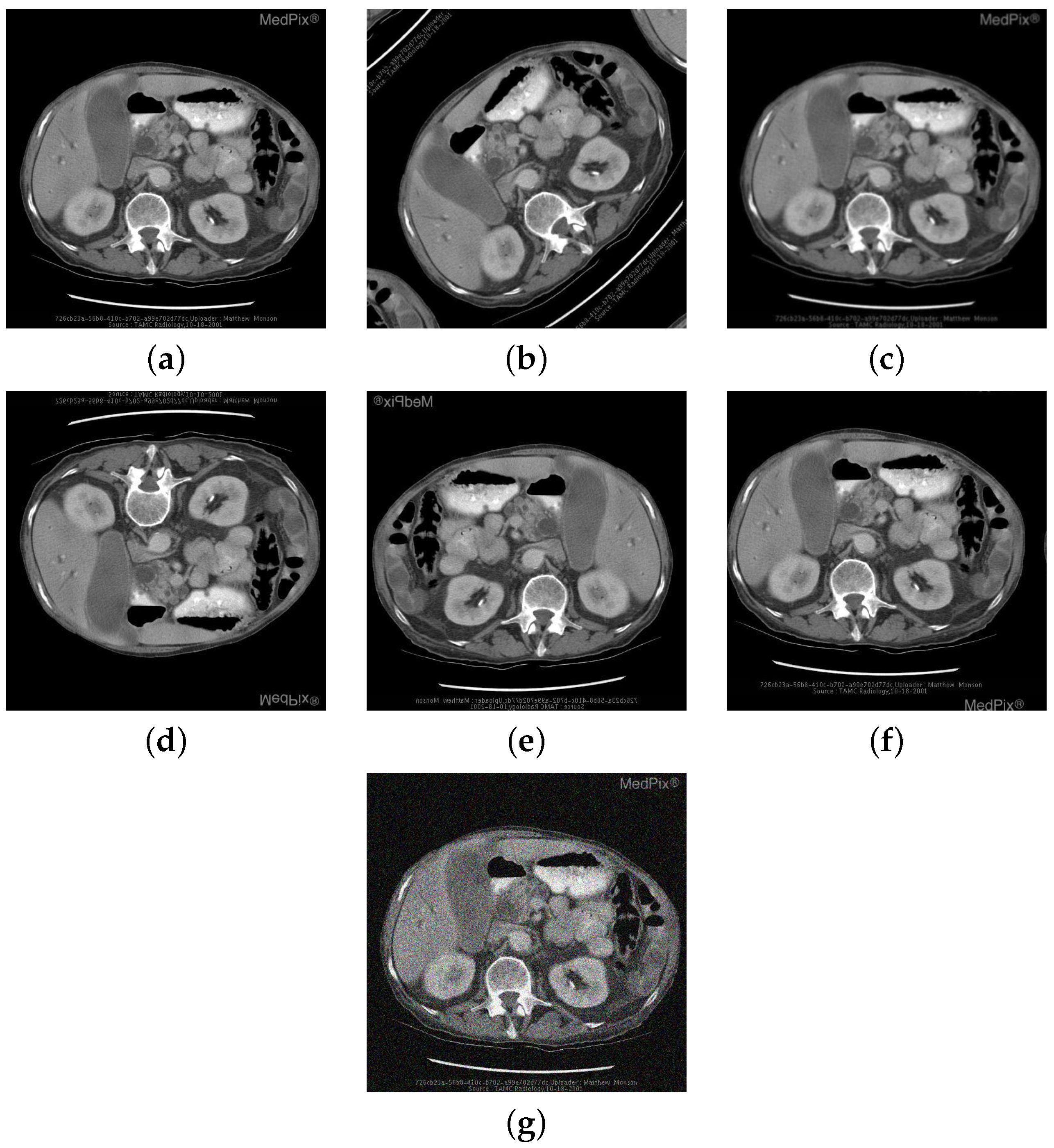
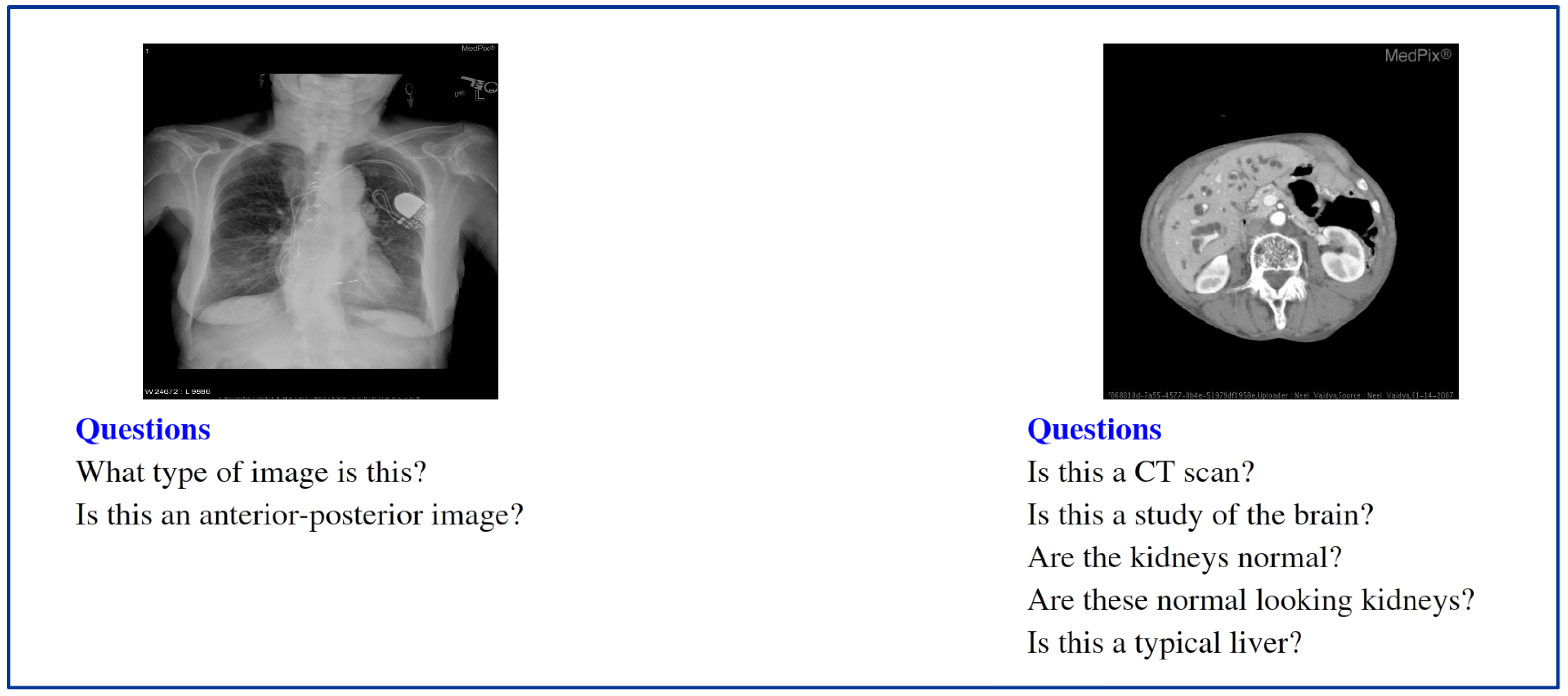
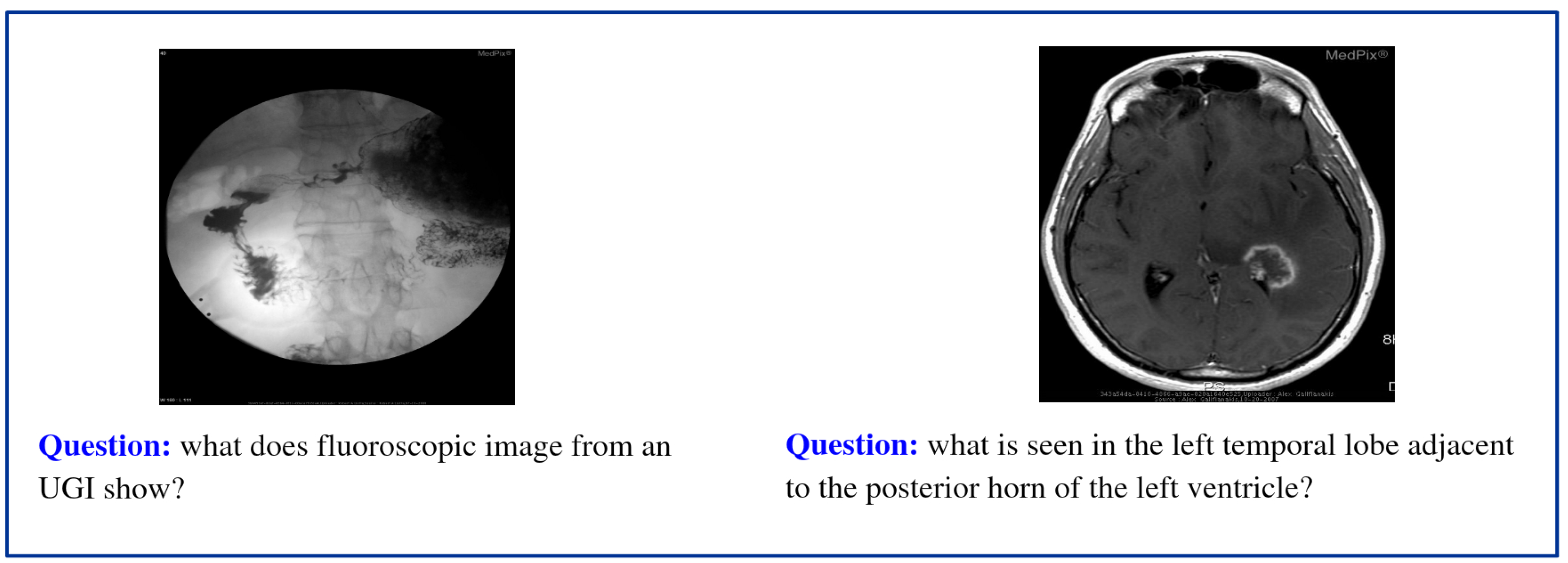
| Category | #Questions | #Images |
|---|---|---|
| Abnormality | 397/18,642 | 112/784 |
| Modality | 288/5534 | 54/378 |
| Organ | 73/16,408 | 135/945 |
| Plane | 163/9216 | 99/693 |
| Other | 348/19,798 | 81/567 |
| Total | 1269/69,598 | 239/1673 |
| Model | BLEU-1 | BLEU-2 | BLEU-3 | BLEU-4 | METEOR | ROUGE-L | CIDEr | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VQGR | 31.45 | 14.60 | 7.82 | 3.27 | 10.43 | 38.80 | 21.19 | |
| VQGR | 44.83 | 30.10 | 23.62 | 19.81 | 18.98 | 24.30 | 23.43 | |
| VQGR | 55.05 | 43.39 | 37.98 | 34.54 | 29.35 | 56.34 | 31.18 | |
| VQGRaD | 58.69 | 48.82 | 44.08 | 40.92 | 31.71 | 59.70 | 35.74 | |
| VQGRaD | 57.12 | 46.62 | 41.49 | 37.96 | 29.61 | 58.93 | 34.99 | |
| t-space | VQGRaD | 56.86 | 45.73 | 40.58 | 37.25 | 29.99 | 58.42 | 36.21 |
| VQGRaD | 61.81 | 51.69 | 46.69 | 43.35 | 33.94 | 63.62 | 40.33 | |
| VQGRaD | 61.86 | 51.65 | 46.70 | 43.40 | 33.88 | 63.75 | 41.13 | |
| VQGRaD | 59.31 | 49.31 | 44.73 | 41.75 | 32.54 | 60.90 | 36.38 | |
| VQGRaD | 58.49 | 48.26 | 43.87 | 41.21 | 31.79 | 58.81 | 36.03 | |
| z-space | VQGRaD | 60.74 | 50.06 | 45.00 | 41.90 | 32.81 | 61.36 | 36.89 |
| VQGRaD | 60.52 | 50.61 | 46.31 | 43.68 | 33.07 | 61.29 | 37.86 | |
| VQGRaD | 59.11 | 47.44 | 41.78 | 37.85 | 31.00 | 60.39 | 36.79 |
| Model | BLEU-1 | BLEU-2 | BLEU-3 | BLEU-4 | METEOR | ROUGE-L | CIDEr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VQGR | 33.32 | 23.18 | 5.86 | 2.64 | 11.59 | 35.38 | 20.69 |
| VQGR | 39.74 | 23.18 | 14.91 | 11.52 | 16.56 | 41.23 | 50.03 |
| Model | Relevancy | Grammaticality | Fluency | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VQGR | 78.3 | 93.3 | 80.0 | 83.3 |
| VQGRaD | 83.3 | 92.5 | 91.6 | 89.16 |
| VQGRaD | 81.6 | 92.5 | 93.3 | 89.16 |
| VQGRaD | 96.6 | 96.6 | 97.5 | 96.9 |
| VQGRaD | 86.6 | 96.6 | 92.5 | 91.9 |
| Model | Relevancy | Grammaticality | Fluency |
|---|---|---|---|
| VQG | 0.42 | 0.27 | 0.51 |
| VQGRaD | 0.32 | 0.64 | 0.40 |
| VQGRaD | 0.40 | 0.64 | 0.48 |
| VQGRaD | 0.32 | 0.72 | 0.33 |
| VQGRaD | 0.35 | 0.72 | 0.43 |
| Image | Category | Generated and Ground Truth Questions |
|---|---|---|
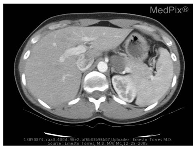 | Abnormality | is a ring enhancing lesion present in the right lobe of the liver? is a ring enhancing lesion present in the right lobe of the liver? is the liver normal? |
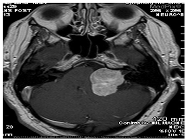 | Modality | was this mri taken with or without contrast? which ventricle is compressed by the t2-hyperintense? was this mri taken with or without contrast? |
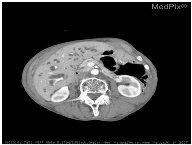 | Organ | is this a typical liver? are these normal laughed kidneys? Is this a study of the brain? |
 | Plane | what plane is this image obtained? what plane is this image blood-samples? Is this image of a saggital plane? |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sarrouti, M.; Ben Abacha, A.; Demner-Fushman, D. Goal-Driven Visual Question Generation from Radiology Images. Information 2021, 12, 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12080334
Sarrouti M, Ben Abacha A, Demner-Fushman D. Goal-Driven Visual Question Generation from Radiology Images. Information. 2021; 12(8):334. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12080334
Chicago/Turabian StyleSarrouti, Mourad, Asma Ben Abacha, and Dina Demner-Fushman. 2021. "Goal-Driven Visual Question Generation from Radiology Images" Information 12, no. 8: 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12080334
APA StyleSarrouti, M., Ben Abacha, A., & Demner-Fushman, D. (2021). Goal-Driven Visual Question Generation from Radiology Images. Information, 12(8), 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12080334






