An Imbalanced Image Classification Method for the Cell Cycle Phase
Abstract
1. Introduction
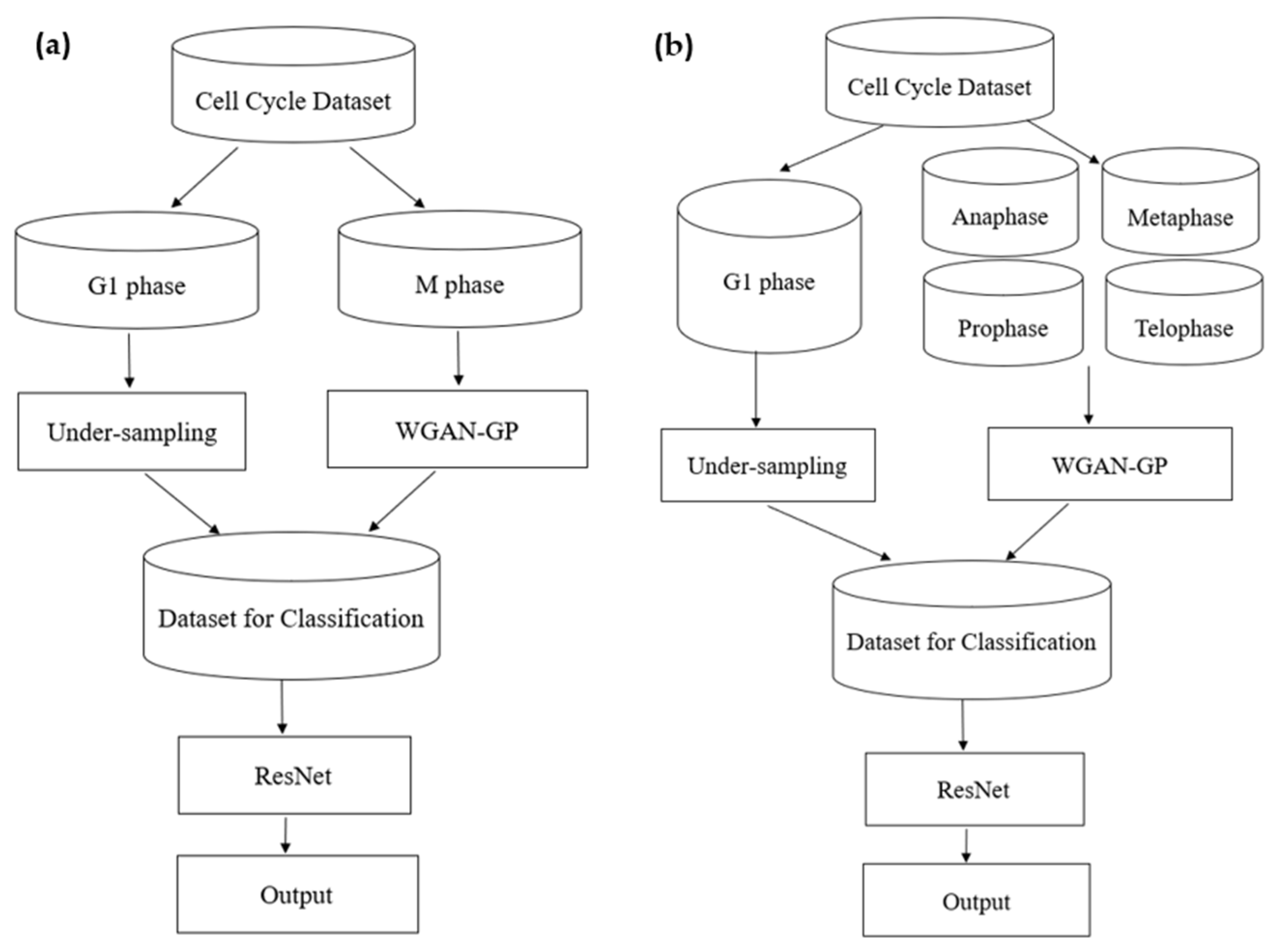
2. Method
2.1. WGAN-GP
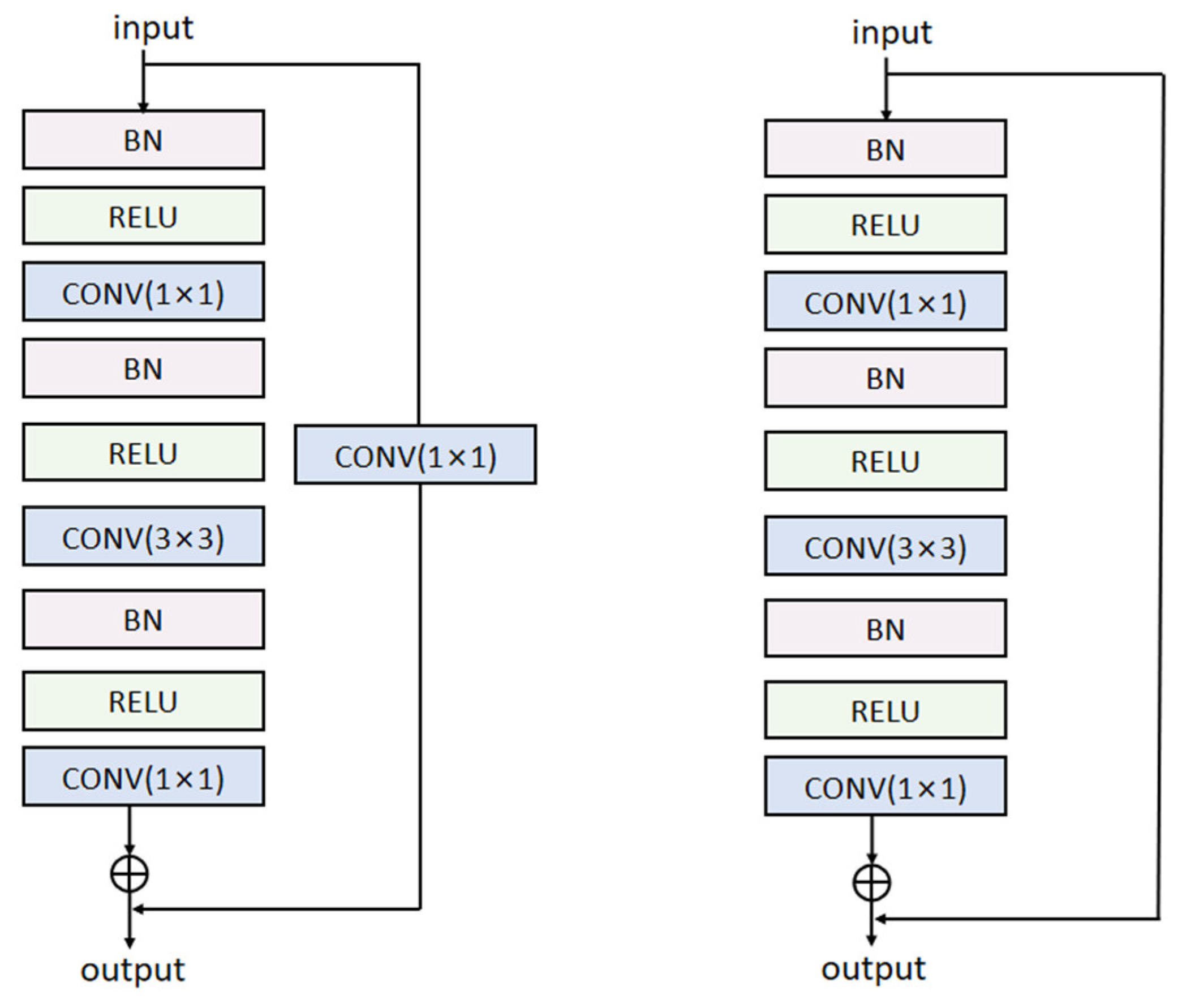
2.2. ResNet
3. Experiment
3.1. Dataset
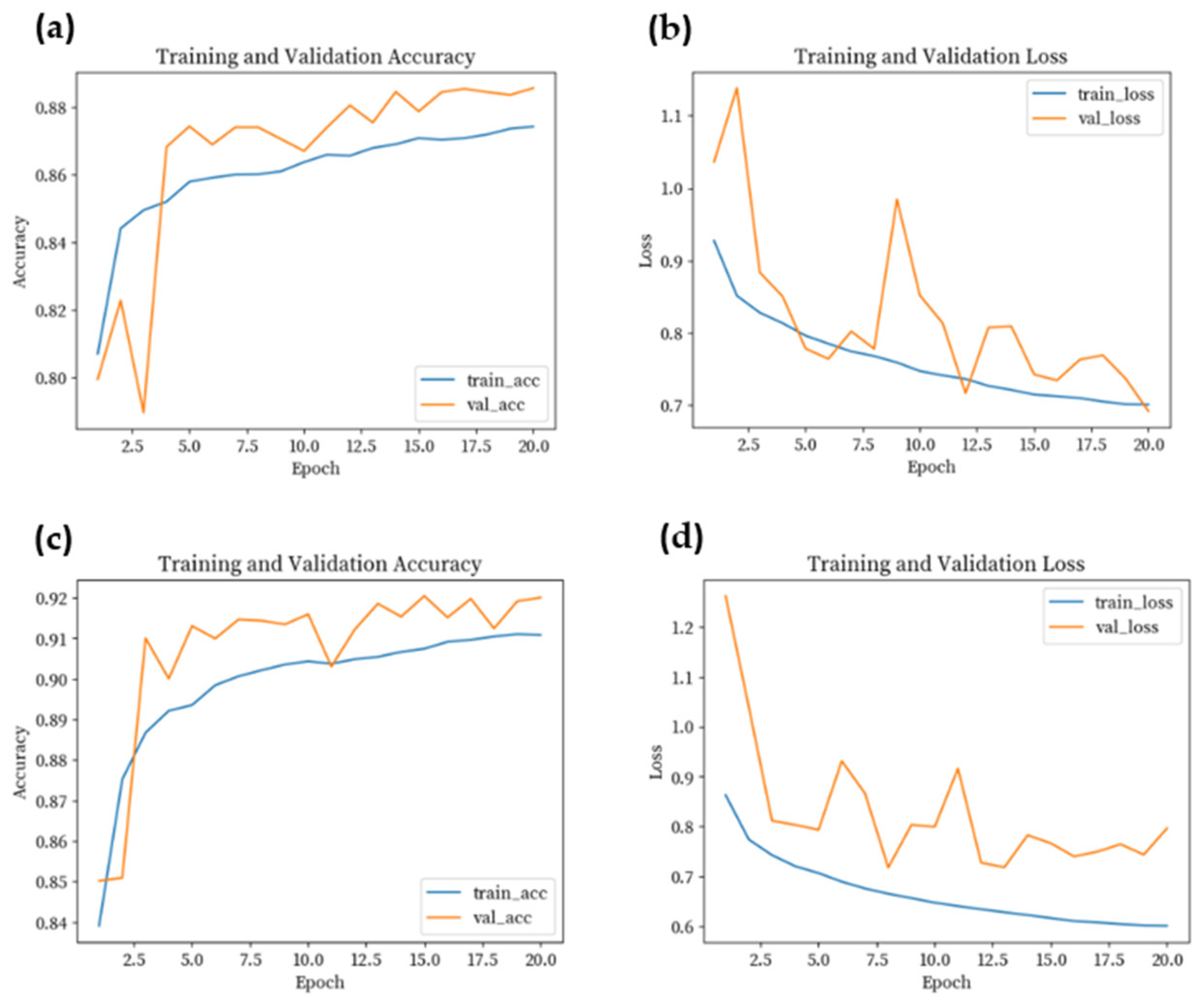
3.2. Model Training
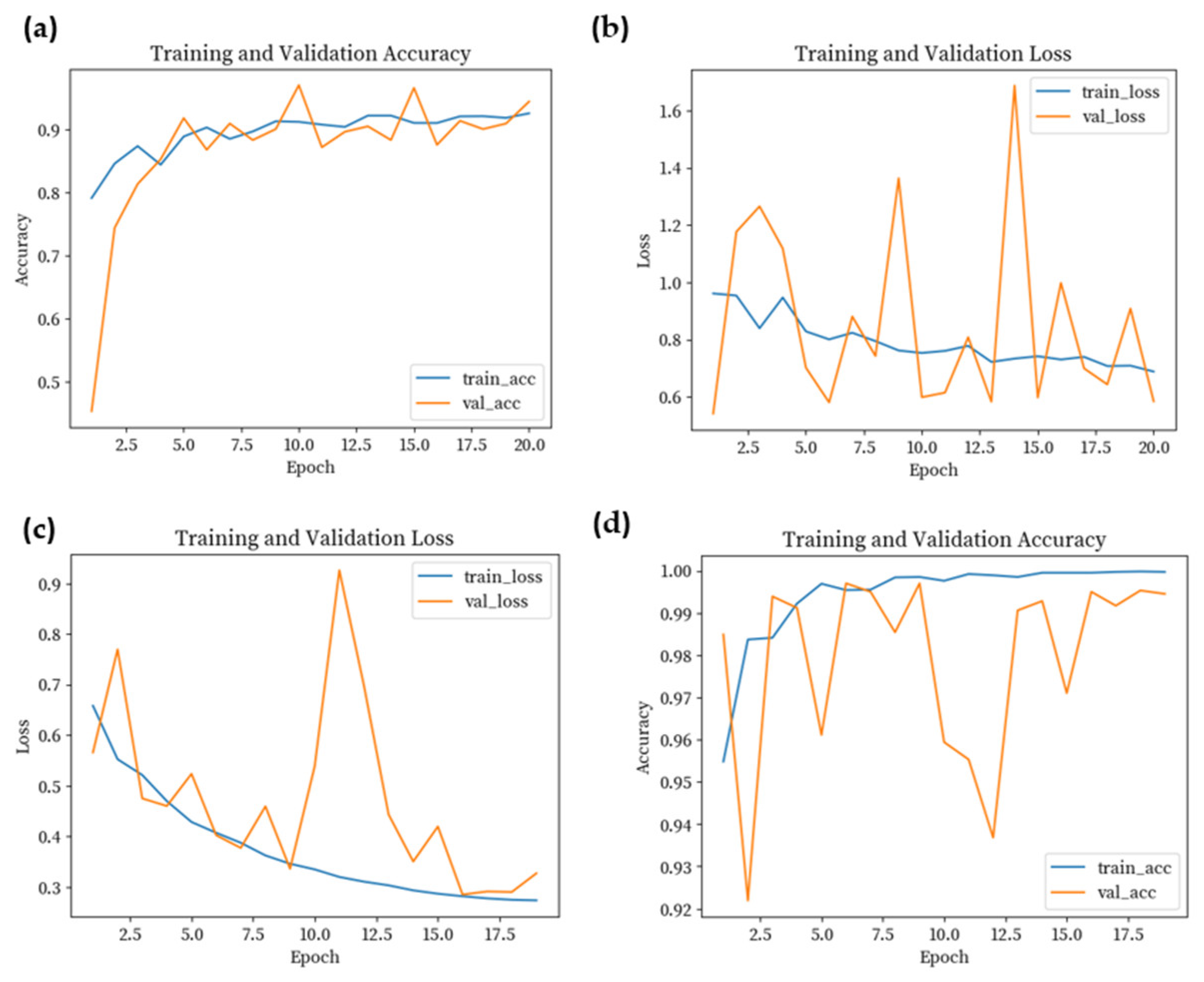
4. Results
4.1. Results of Generated Images by WGAN-GP
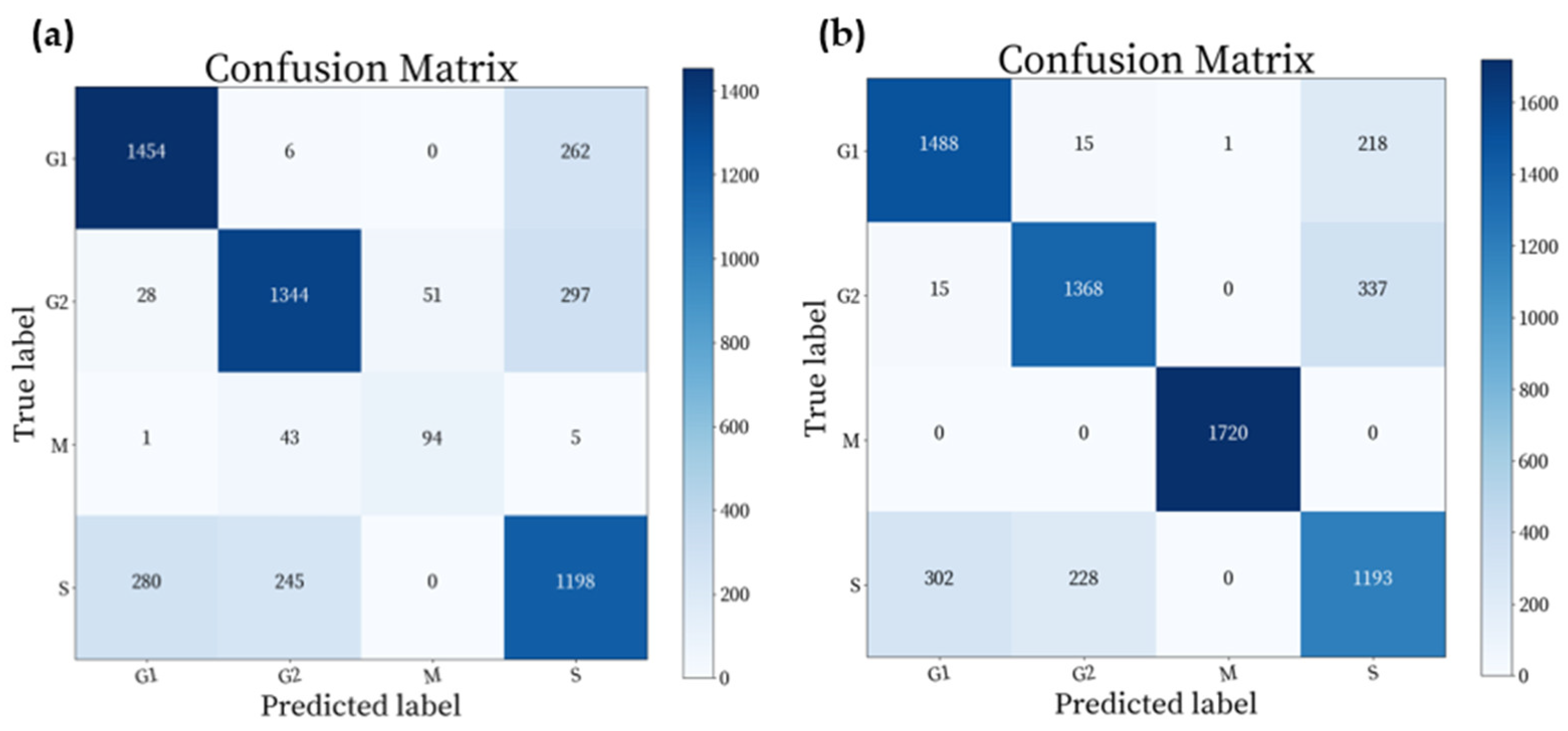
4.2. Results of Classification
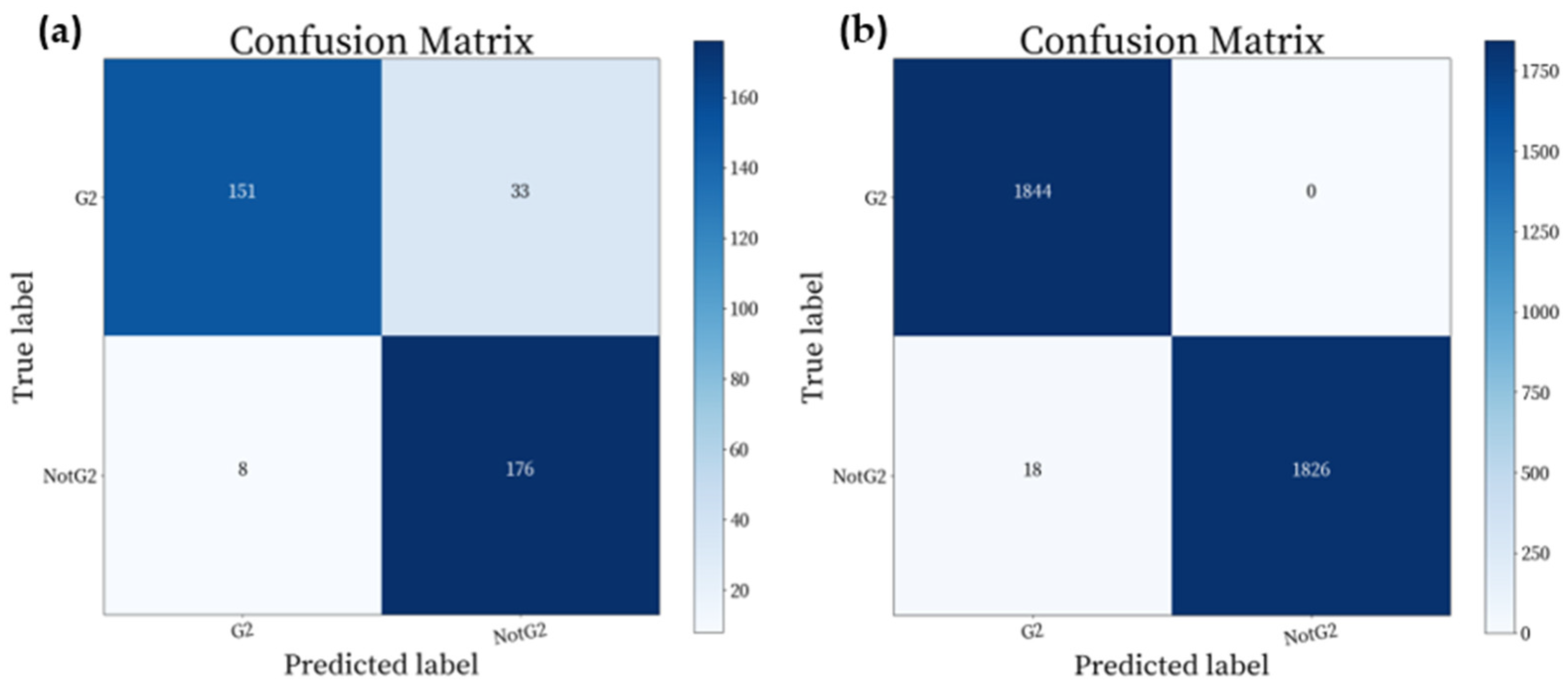
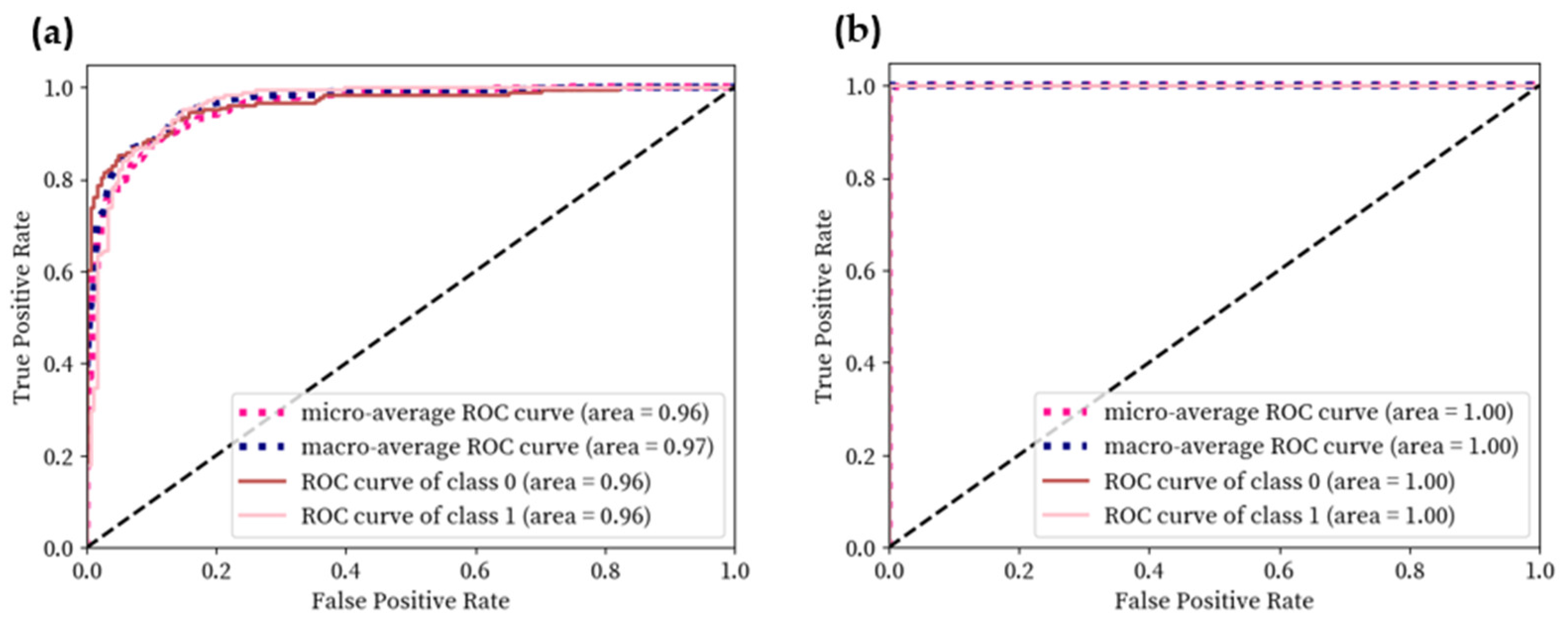
4.3. Verification of Results with New Dataset
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, H.-S.; Lang, M.-F.; Sun, J. New Methods for Cell Cycle Analysis. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2019, 47, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roukos, V.; Pegoraro, G.; Voss, T.C.; Misteli, T. Cell cycle staging of individual cells by fluorescence microscopy. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 334–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matuszewski, D.J.; Sintorn, I.-M.; Puigvert, J.C.; Wählby, C. Comparison of Flow Cytometry and Image-Based Screening for Cell Cycle Analysis. Nat. Comput. Ser. 2016, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönenberger, F.; Deutzmann, A.; Ferrando-May, E.; Merhof, D. Discrimination of cell cycle phases in PCNA-immunolabeled cells. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaue-Sawano, A.; Kurokawa, H.; Morimura, T.; Hanyu, A.; Hama, H.; Osawa, H.; Kashiwagi, S.; Fukami, K.; Miyata, T.; Miyoshi, H.; et al. Visualizing Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Multicellular Cell-Cycle Progression. Cell 2008, 132, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajar, B.T.; Lam, A.J.; Badiee, R.; Oh, Y.-H.; Chu, J.; Zhou, X.X.; Kim, N.; Kim, B.B.; Chung, M.; Yablonovitch, A.L.; et al. Fluorescent indicators for simultaneous reporting of all four cell cycle phases. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 993–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, A.; Mestre, T.; Carneiro, P.; Sahumbaiev, I.; Seruca, R.; Sanches, J.M. Blue intensity matters for cell cycle profiling in fluorescence DAPI-stained images. Lab. Investig. 2017, 97, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasi, T.; Hennig, H.; Summers, H.D.; Theis, F.J.; Cerveira, J.; Patterson, J.O.; Davies, D.; Filby, A.; Carpenter, A.E.; Rees, P. Label-free cell cycle analysis for high-throughput imaging flow cytometry. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10256–10264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Islam, N.; Jan, Z.; Din, I.U.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C. A novel deep learning based framework for the detection and classification of breast cancer using transfer learning. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2019, 125, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, F.H.; Silva, R.R.; Ushizima, D.M.; Rezende, M.T.; Carneiro, C.M.; Bianchi, A.G.C.; Medeiros, F.N. Deep learning for cell image segmentation and ranking. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2019, 72, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurnianingsih; Allehaibi, K.H.S.; Nugroho, L.E.; Widyawan; Lazuardi, L.; Prabuwono, A.S.; Mantoro, T. Segmentation and Classification of Cervical Cells Using Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 116925–116941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dürr, O.; Sick, B. Single-Cell Phenotype Classification Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. J. Biomol. Screen. 2016, 21, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagao, Y.; Sakamoto, M.; Chinen, T.; Okada, Y.; Takao, D. Robust classification of cell cycle phase and biological feature extraction by image-based deep learning. Mol. Biol. Cell 2020, 31, 1346–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eulenberg, P.; Köhler, N.; Blasi, T.; Filby, A.; Carpenter, A.E.; Rees, P.; Theis, F.J.; Wolf, F.A. Reconstructing cell cycle and disease progression using deep learning. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susan, S.; Kumar, A. SSO Maj -SMOTE- SSO Min: Three-step intelligent pruning of majority and minority samples for learning from imbalanced datasets. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 78, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susan, S.; Kumar, A. Learning Data Space Transformation Matrix from Pruned Imbalanced Datasets for Nearest Neighbor Classification. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 21st International Conference on High Performance Computing and Communications; IEEE 17th International Conference on Smart City; IEEE 5th International Conference on Data Science and Systems (HPCC/SmartCity/DSS), Zhangjiajie, China, 10–12 August 2019; pp. 2831–2838. [Google Scholar]
- Frid-Adar, M.; Diamant, I.; Klang, E.; Amitai, M.; Goldberger, J.; Greenspan, H. GAN-based synthetic medical image augmentation for increased CNN performance in liver lesion classification. Neurocomputing 2018, 321, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, M.; Susan, S. Deep transfer with minority data augmentation for imbalanced breast cancer dataset. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 97, 106759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, M.; Stein, O.; Turko, N.A.; Nygate, Y.; Roitshtain, D.; Karako, L.; Barnea, I.; Giryes, R.; Shaked, N.T. TOP-GAN: Stain-free cancer cell classification using deep learning with a small training set. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 57, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Li, T.; Zhu, R.; Tang, Y.; Tang, M.; Lin, L.; Ma, Z. Conditional Wasserstein generative adversarial network-gradient penalty-based approach to alleviating imbalanced data classification. Inf. Sci. 2020, 512, 1009–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjovsky, M.; Chintala, S.; Bottou, L. Wasserstein generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the Thirty-fourth International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 214–223. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Gulrajani, I.; Ahmed, F.; Arjovsky, M.; Dumoulin, V.; Courville, A. Generative Adversarial Nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 31, 5767–5777. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Shuai, R.; Ran, X.; Liu, W.; Ye, C. Combining DC-GAN with ResNet for blood cell image classification. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2020, 58, 1251–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrakopoulos, P.; Sfikas, G.; Nikou, C. ISING-GAN: Annotated Data Augmentation with a Spatially Constrained Generative Adversarial Network. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 17th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Iowa City, IA, USA, 3–7 April 2020; pp. 1600–1603. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Shi, D.; Sadiq, M.; Cheng, X. Image Denoising With Generative Adversarial Networks and its Application to Cell Image Enhancement. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 82819–82831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Hu, Y.; Chen, S.; Yao, J.; Zhang, L. Fine-Grained Classification of Cervical Cells Using Morphological and Appearance Based Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 71541–71549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Han, T.; Zhou, F.; Yu, Z.; Qin, J.; Elazab, A.; Lei, B. A deeply supervised residual network for HEp-2 cell classification via cross-modal transfer learning. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 79, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baykal, E.; Dogan, H.; Ercin, M.E.; Ersoz, S.; Ekinci, M. Modern convolutional object detectors for nuclei detection on pleural effusion cytology images. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangeline, I.K.; Precious, J.G.; Pazhanivel, N.; Kirubha, S.P.A. Automatic Detection and Counting of Lymphocytes from Immunohistochemistry Cancer Images Using Deep Learning. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2020, 40, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouda, N.; Amudha, J. Skin Cancer Classification using ResNet. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 5th International Conference on Computing Communication and Automation (ICCCA), Greater Noida, India, 30–31 October 2020; pp. 536–541. [Google Scholar]
- Shemona, J.S.; Kumar, A. Novel segmentation techniques for early cancer detection in red blood cells with deep learning based classifier-a comparative approach. IET Image Process. 2020, 14, 1726–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Identity Mappings in Deep Residual Networks. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 630–645. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos-López, D.; Maldonado, A.D. Cost-Sensitive Variable Selection for Multi-Class Imbalanced Datasets Using Bayesian Networks. Mathematics 2021, 9, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tan, K.C.; Li, H.; Hong, G.S. A Cost-Sensitive Deep Belief Network for Imbalanced Classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 30, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




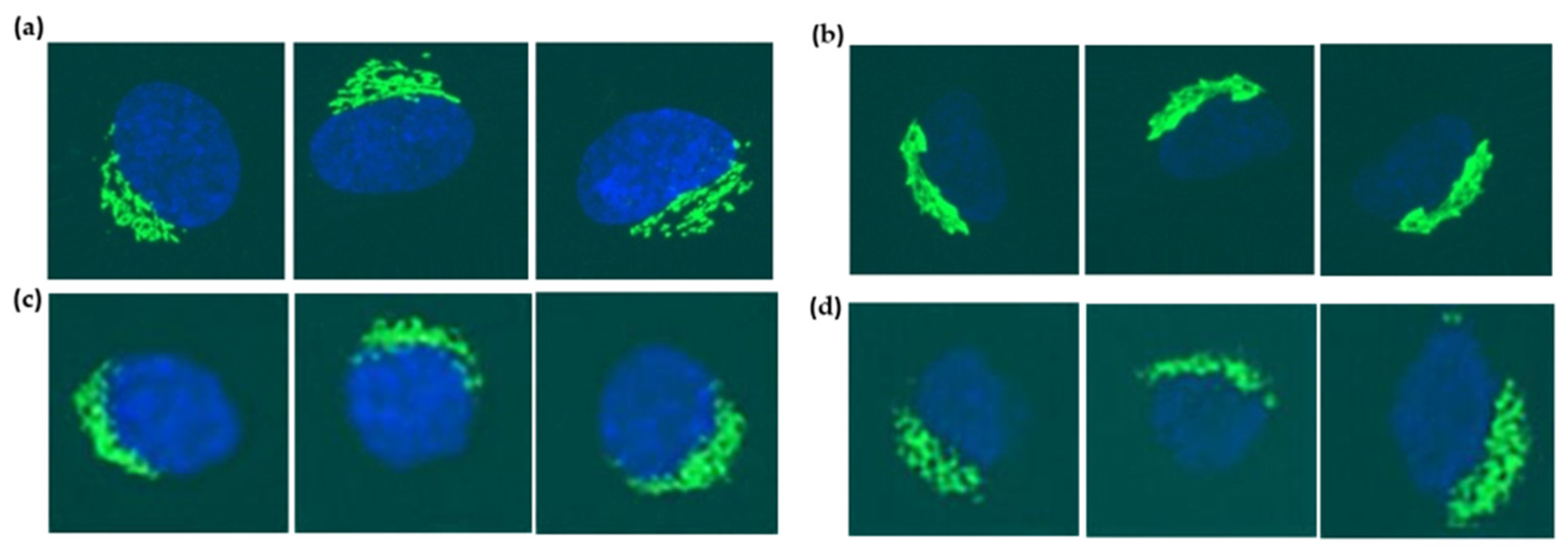
| Cell Cycle Stages | The Number of Original Images | The Number of Generated Images by WGAN-GP | The Number of Images Used for Classification | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classification 1 | Classification 2 | Classification 3 | Classification 4 | |||
| Anaphase | 15 | 150 | 15 | 15 | 150 | 150 |
| G1 | 14,333 | - | 14,333 | 8610 | 14,333 | 8610 |
| G2 | 8601 | - | 8601 | 8601 | 8601 | 8601 |
| Metaphase | 68 | 680 | 68 | 68 | 680 | 680 |
| Prophase | 606 | 6060 | 606 | 606 | 6060 | 6060 |
| S | 8616 | - | 8616 | 8616 | 8616 | 8616 |
| Telophase | 27 | 270 | 27 | 27 | 270 | 270 |
| Cell Cycle Stages | The Number of Original Images | The Number of Generated Images by WGAN-GP | The Number of Images Used for Classification | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classification 1 | Classification 2 | Classification 3 | Classification 4 | |||
| G1 | 14,333 | - | 14,333 | 8610 | 14,333 | 8610 |
| G2 | 8601 | - | 8601 | 8601 | 8601 | 8601 |
| M | 716 | 7160 | 716 | 716 | 7160 | 7160 |
| S | 8616 | - | 8616 | 8616 | 8616 | 8616 |
| Cell Cycle Stages | The Number of Original Images | The Number of Images Generated by WGAN-GP | The Number of Original Images after Under-Sampling | The Number of Images Generated by WGAN-GP after Under-Sampling |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anaphase | 15 | 150 | 15 | 150 |
| G1 | 14,333 | 14,333 | 8610 | 8610 |
| G2 | 8601 | 8601 | 8601 | 8601 |
| Metaphase | 68 | 680 | 68 | 680 |
| Prophase | 606 | 6060 | 606 | 6060 |
| S | 8616 | 8616 | 8616 | 8616 |
| Telophase | 27 | 270 | 27 | 270 |
| Weighted_Avg | 0.7837 | 0.8225 | 0.7835 | 0.8210 |
| Cell Cycle Stages | The Number of Original Images | The Number of Images Generated by WGAN-GP | The Number of Original Images after Under-Sampling | The Number of Images Generated by WGAN-GP after Under-Sampling |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 14,333 | 14,333 | 8610 | 8610 |
| G2 | 8601 | 8601 | 8601 | 8601 |
| M | 716 | 7160 | 716 | 7160 |
| S | 8616 | 8616 | 8616 | 8616 |
| Weighted_Avg | 0.7832 | 0.8360 | 0.7716 | 0.8388 |
| Cell Cycle Stages | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anaphase | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 3 |
| G1 | 0.8316 | 0.8403 | 0.8359 | 1722 |
| G2 | 0.8453 | 0.8012 | 0.8241 | 1720 |
| Metaphase | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 13 |
| Prophase | 0.8521 | 1.0000 | 0.9202 | 121 |
| S | 0.6765 | 0.7052 | 0.6905 | 1723 |
| Telophase | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 5 |
| Weight_Avg | 0.7835 | 0.7844 | 0.7835 | 5307 |
| Cell Cycle Stages | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anaphase | 1.0000 | 0.0667 | 0.1250 | 30 |
| G1 | 0.8181 | 0.8490 | 0.8333 | 1722 |
| G2 | 0.8456 | 0.7895 | 0.8166 | 1720 |
| Metaphase | 0.8125 | 0.9559 | 0.8784 | 136 |
| Prophase | 0.9934 | 0.9909 | 0.9922 | 1212 |
| S | 0.6700 | 0.6918 | 0.6808 | 1723 |
| Telophase | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 54 |
| Weight_Avg | 0.8210 | 0.8184 | 0.8174 | 6597 |
| Cell Cycle Stages | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 0.8247 | 0.8444 | 0.8344 | 1722 |
| G2 | 0.8205 | 0.7814 | 0.8005 | 1720 |
| M | 0.6483 | 0.6573 | 0.6528 | 143 |
| S | 0.6799 | 0.6953 | 0.6875 | 1723 |
| Weighted_Avg | 0.7716 | 0.7705 | 0.7708 | 5308 |
| Cell Cycle Stages | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 0.8244 | 0.8641 | 0.8438 | 1722 |
| G2 | 0.8492 | 0.7953 | 0.8214 | 1720 |
| M | 0.9994 | 1.0000 | 0.9997 | 1720 |
| S | 0.6825 | 0.6924 | 0.6874 | 1723 |
| Weighted_Avg | 0.8388 | 0.8379 | 0.8380 | 6885 |
| The Result of the Classification for Original Images | The Result of the Classification for Generated Images | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Support | Class | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Support |
| G2 | 0.9497 | 0.8207 | 0.8805 | 184 | G2 | 0.9903 | 1.0000 | 0.9951 | 1844 |
| Not-G2 | 0.8421 | 0.9565 | 0.8957 | 184 | Not-G2 | 1.0000 | 0.9902 | 0.9951 | 1844 |
| Avg | 0.8959 | 0.8886 | 0.8881 | 368 | Avg | 0.9952 | 0.9951 | 0.9951 | 3688 |
| Model | Method | Images | Accuracy | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | G2 | S | Ana | Meta | Pro | Telo | Weighted_Avg | |||
| Eulenber [14] | Deep learning (ResNet) | Dataset1 | 86.47% | 64.86% | 84.16% | 20% | 11.76% | 60.72% | 96.29% | / |
| Model1 | ResNet | Dataset1 + WGAN-GP (Ana, Meta, Pro, Telo) | 81.81% | 84.56% | 67.00% | 100% | 81.25% | 99.34% | 100% | 82.10% |
| Model | Method | Images | Accuracy | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | G2 | M | S | Weighted_Avg | |||
| Blasi [8] | feature extraction Boosting algorithm | Dataset1 Random under-sampling | 70.24% | 96.78% | 44.04% | 90.13% | / |
| Model2 | ResNet WGAN-GP | Dataset1 | 82.47% | 82.05% | 64.83% | 67.99% | 77.16% |
| Model3 | ResNet WGAN-GP | Dataset1 + WGAN-GP (M) | 82.44% | 84.92% | 99.94% | 68.25% | 83.88% |
| Model | Method | Images | Accuracy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G2 | NotG2 | Weighted_Avg | |||
| Nagao [13] | CNN | Dataset2 | / | / | 87% |
| Model2 | ResNet WGAN-GP | Dataset2 + WGAN-GP | 99.03% | 100% | 99.52% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, X.; Zou, Y.; Huang, Z. An Imbalanced Image Classification Method for the Cell Cycle Phase. Information 2021, 12, 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12060249
Jin X, Zou Y, Huang Z. An Imbalanced Image Classification Method for the Cell Cycle Phase. Information. 2021; 12(6):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12060249
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Xin, Yuanwen Zou, and Zhongbing Huang. 2021. "An Imbalanced Image Classification Method for the Cell Cycle Phase" Information 12, no. 6: 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12060249
APA StyleJin, X., Zou, Y., & Huang, Z. (2021). An Imbalanced Image Classification Method for the Cell Cycle Phase. Information, 12(6), 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12060249






