A Hybrid Model for Air Quality Prediction Based on Data Decomposition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Foundations
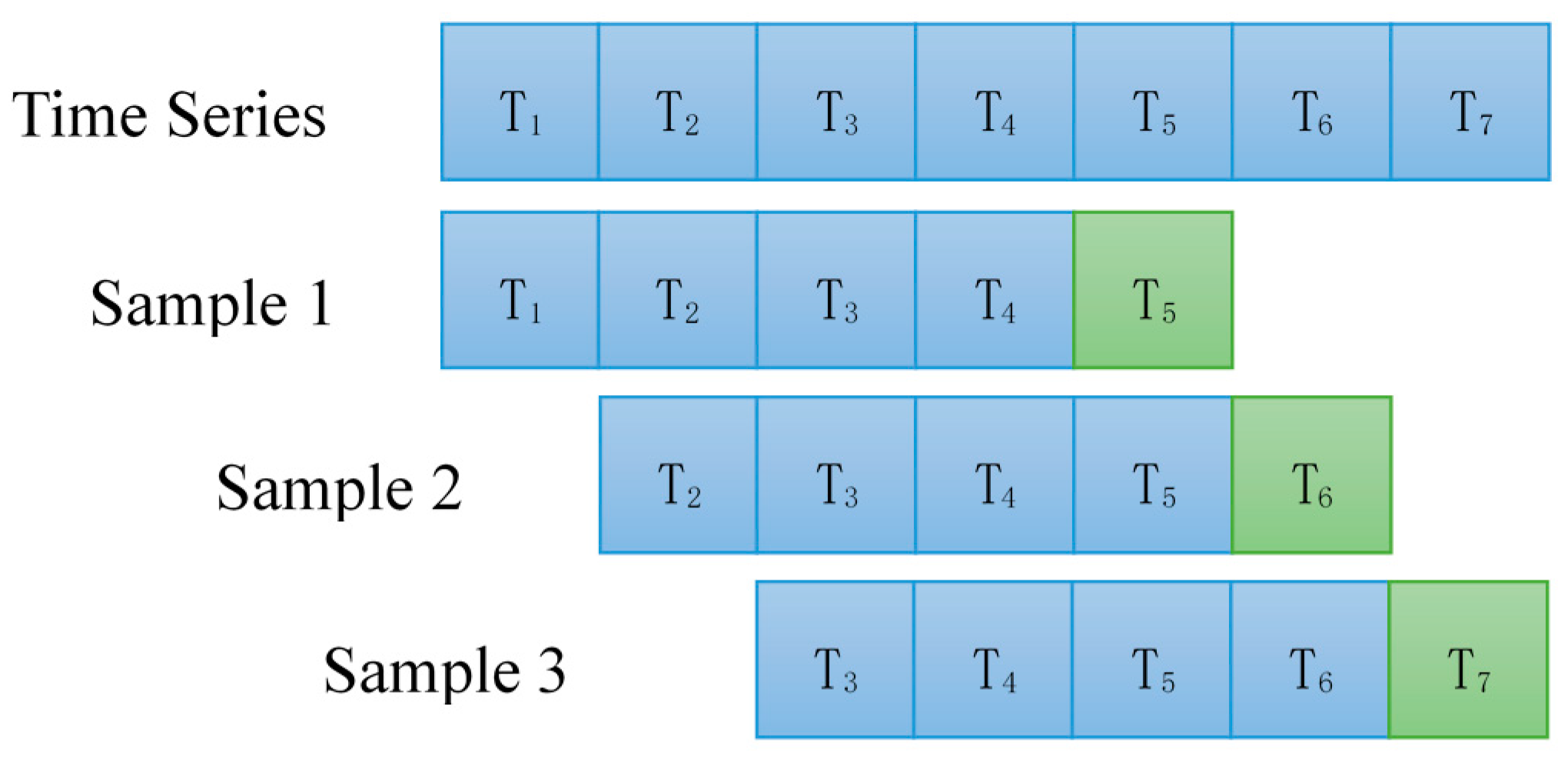
2.1. Sliding Window
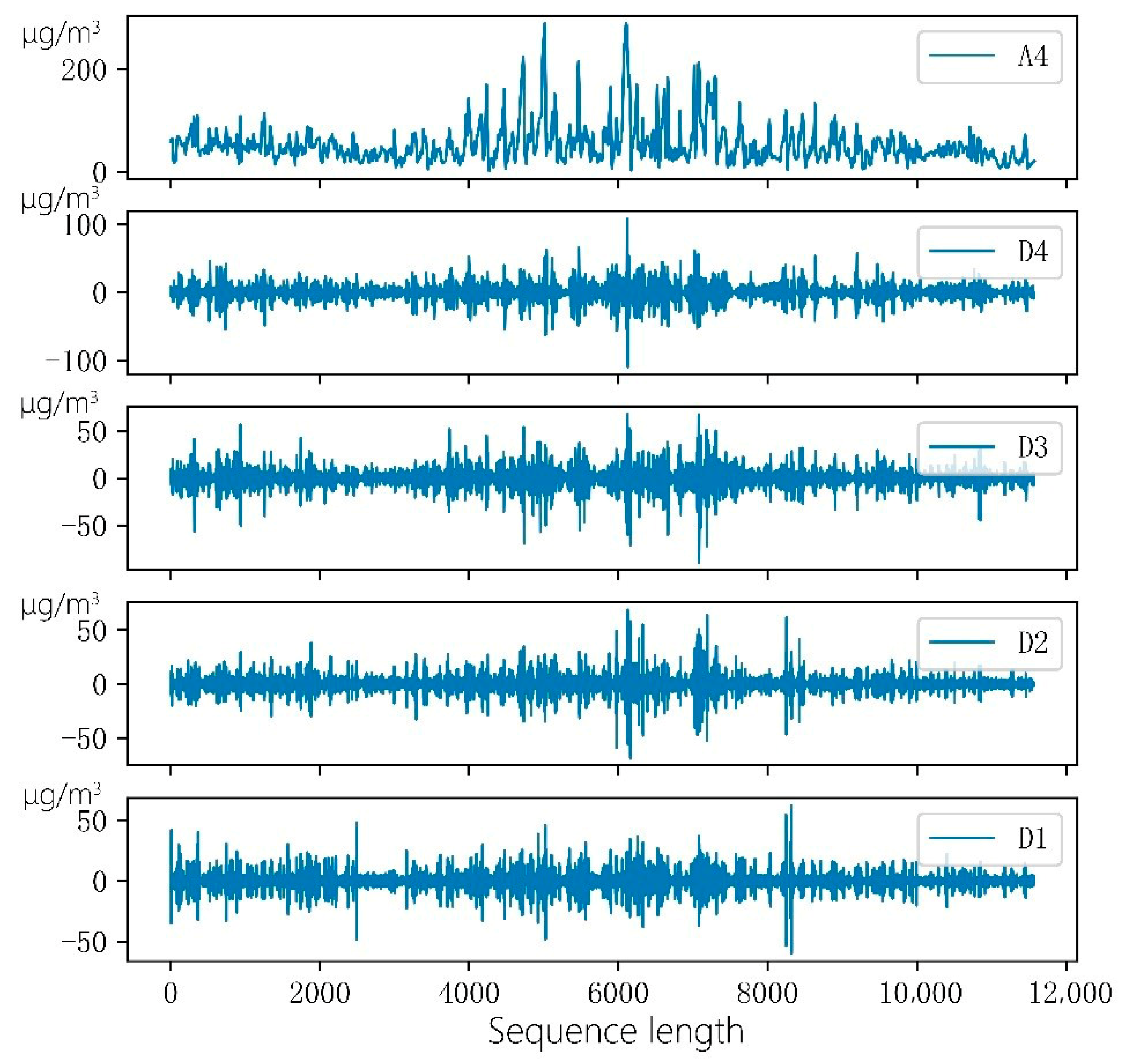
2.2. Wavelet Decomposition
2.3. Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise (CEEMDAN)
2.4. Autoregressive Moving Average Model
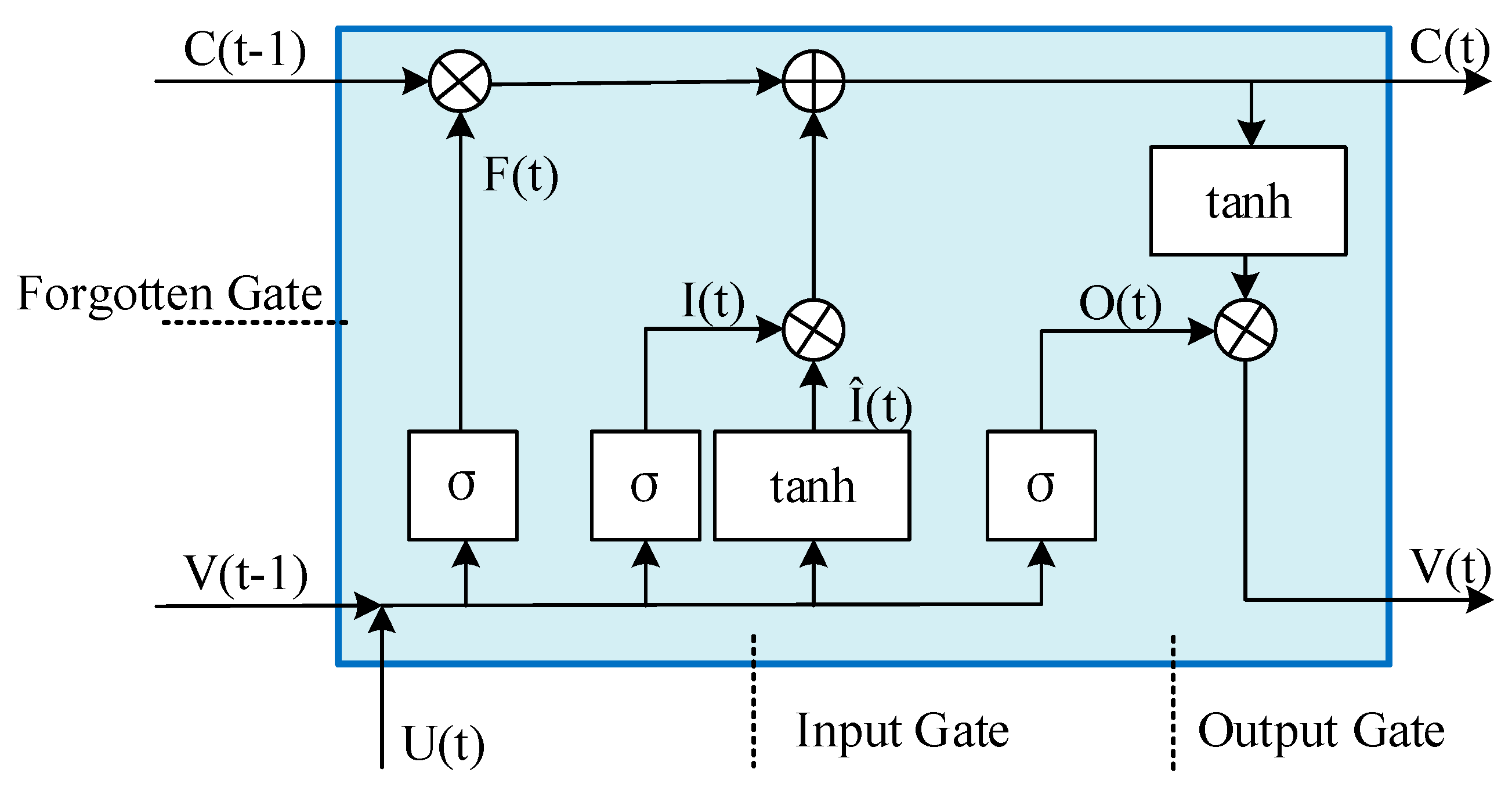
2.5. Long Short-Term Memory
2.6. Predictive Effect Evaluation Index
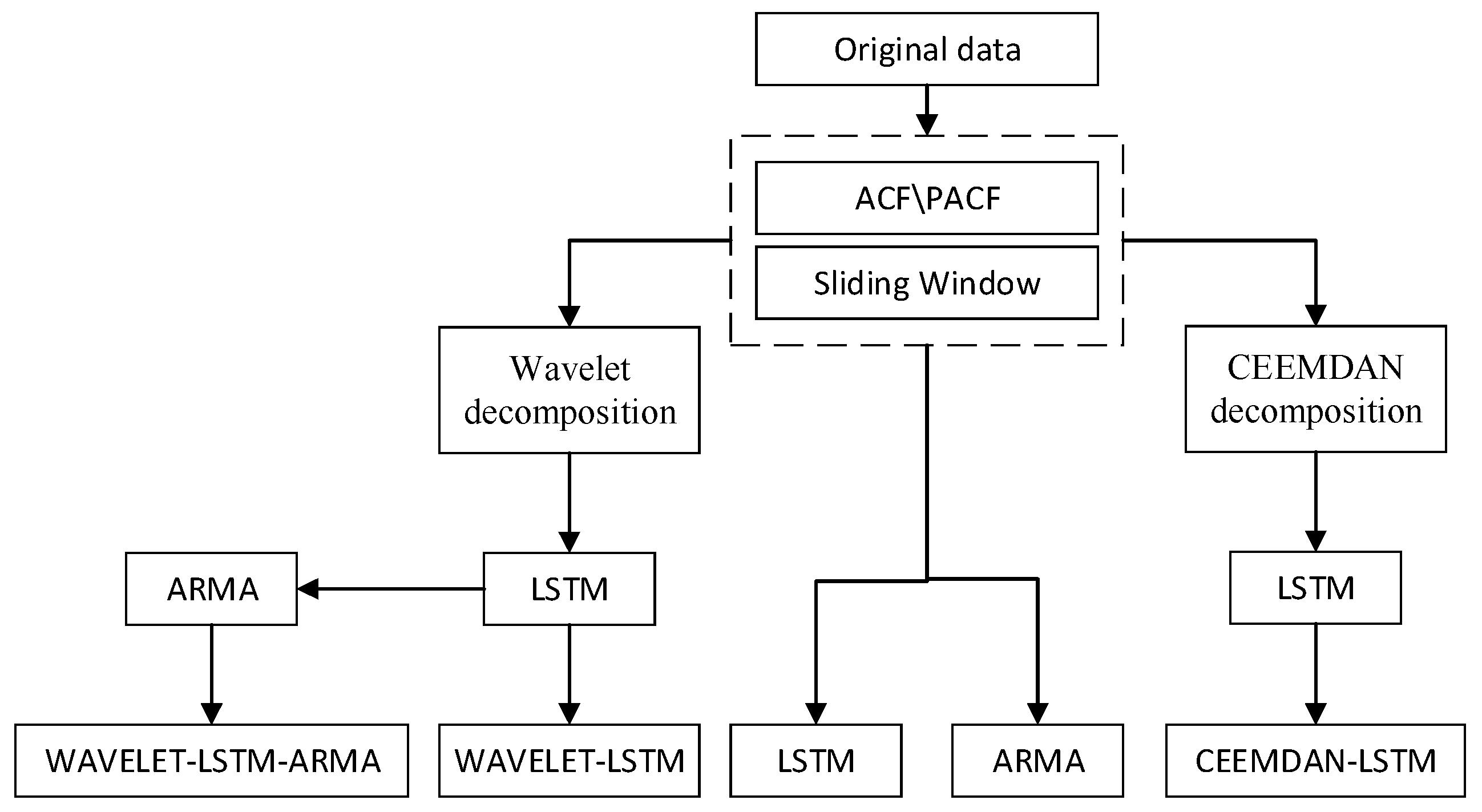
3. Model Construction
3.1. Experimental Environment
3.2. Experimental Data
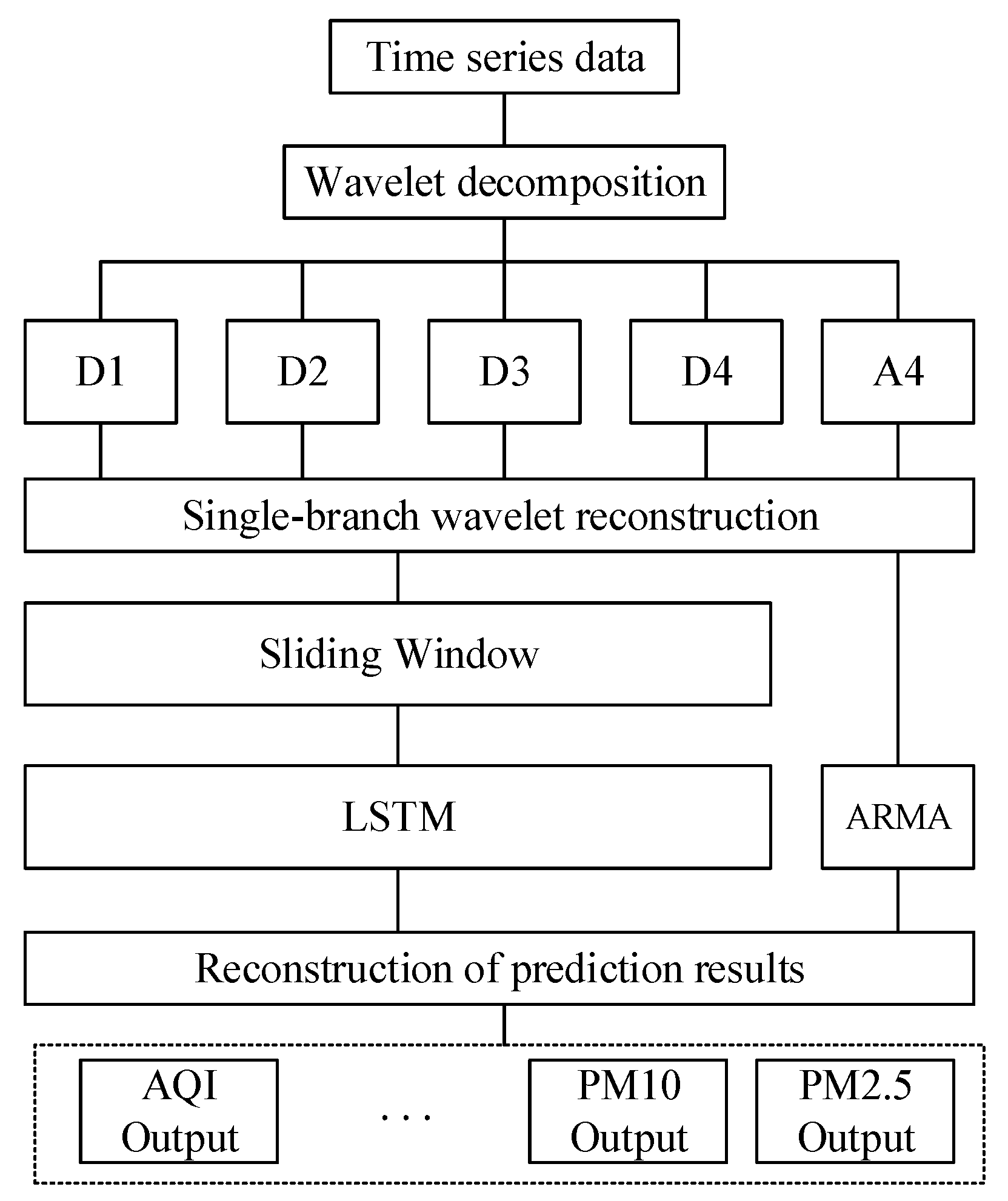
3.3. Wavelet Decomposition-Long Short Term Memory-Autoregressive Moving Average Prediction Model
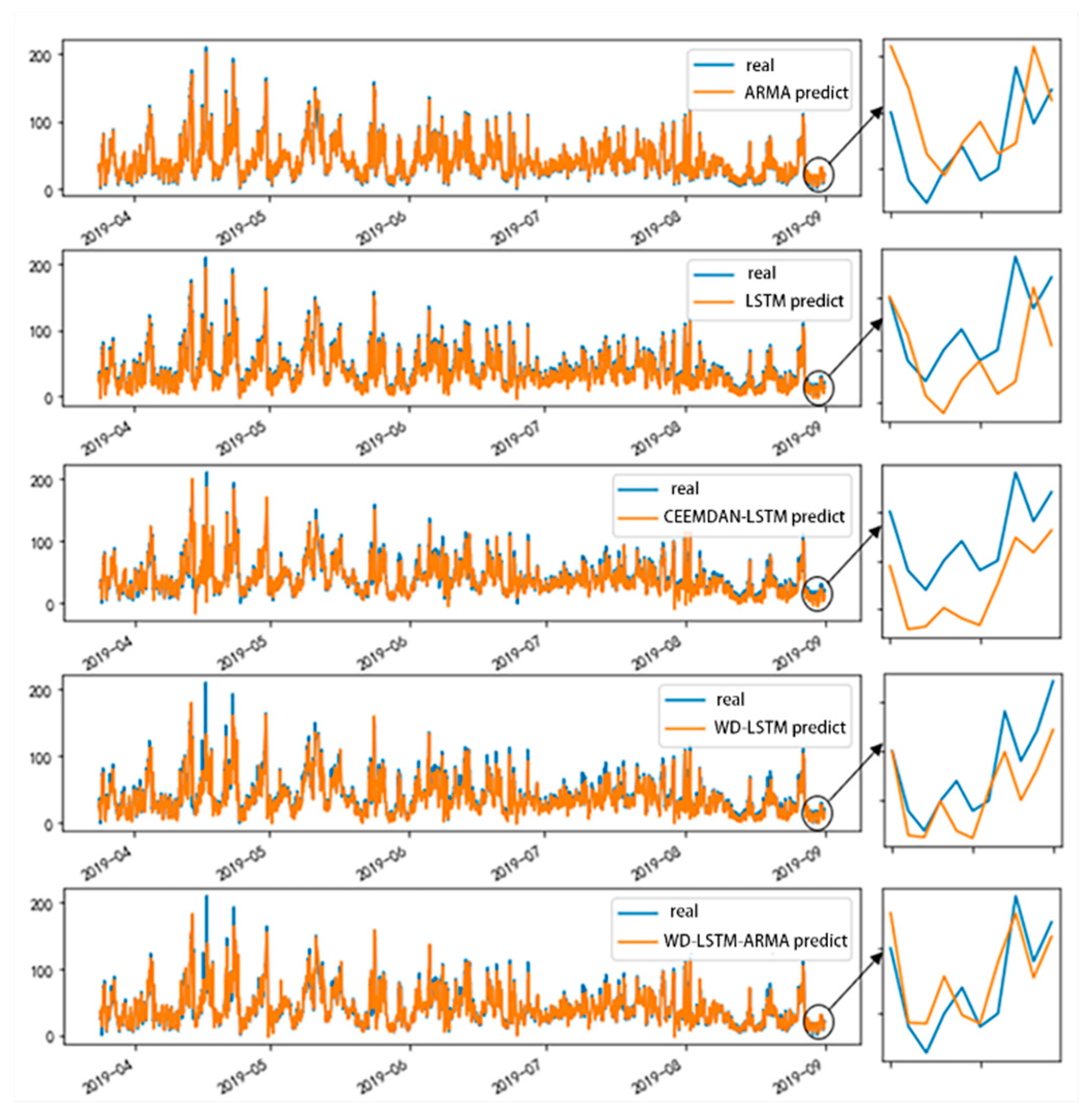
3.4. Predicted Results
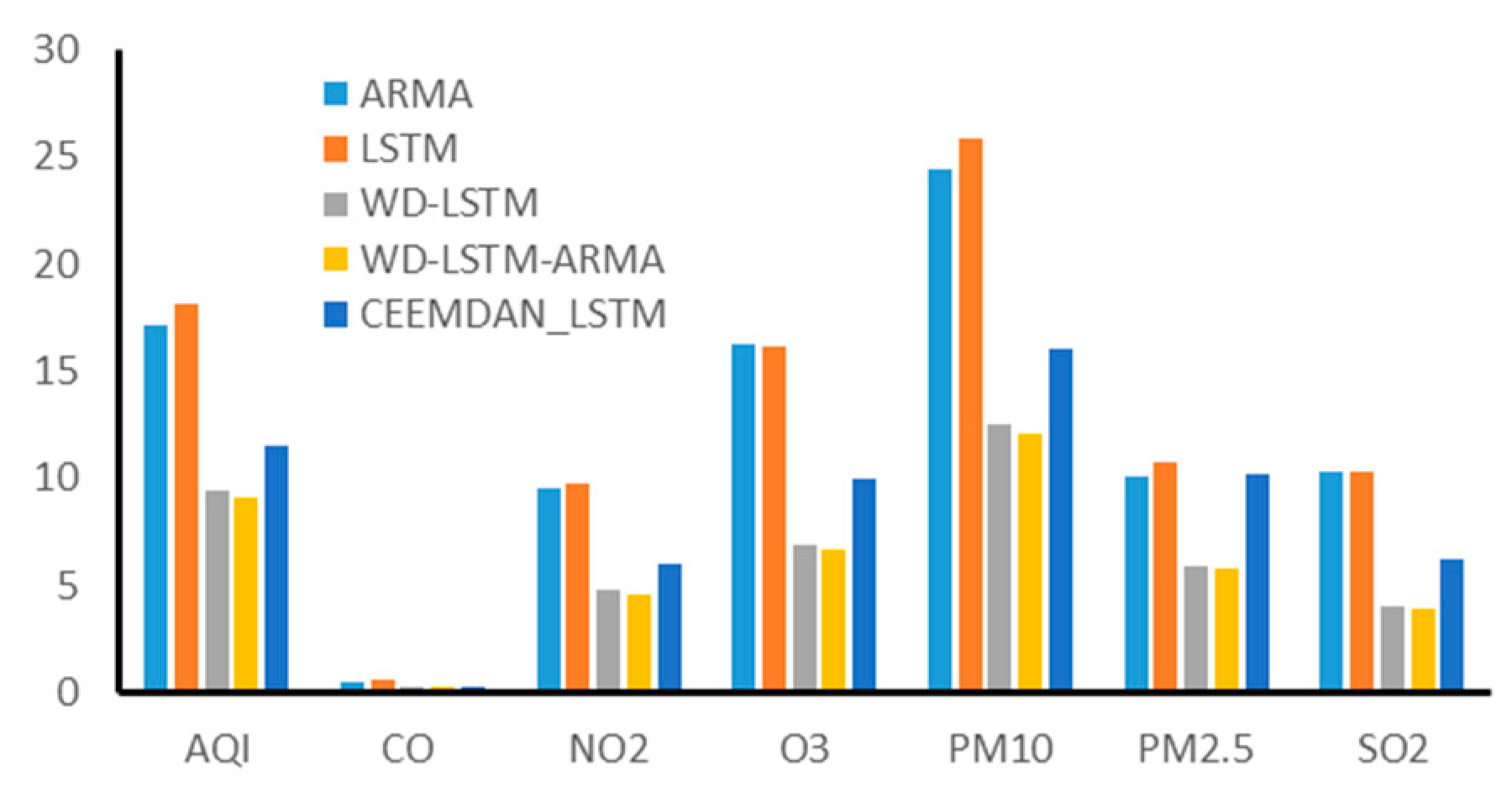
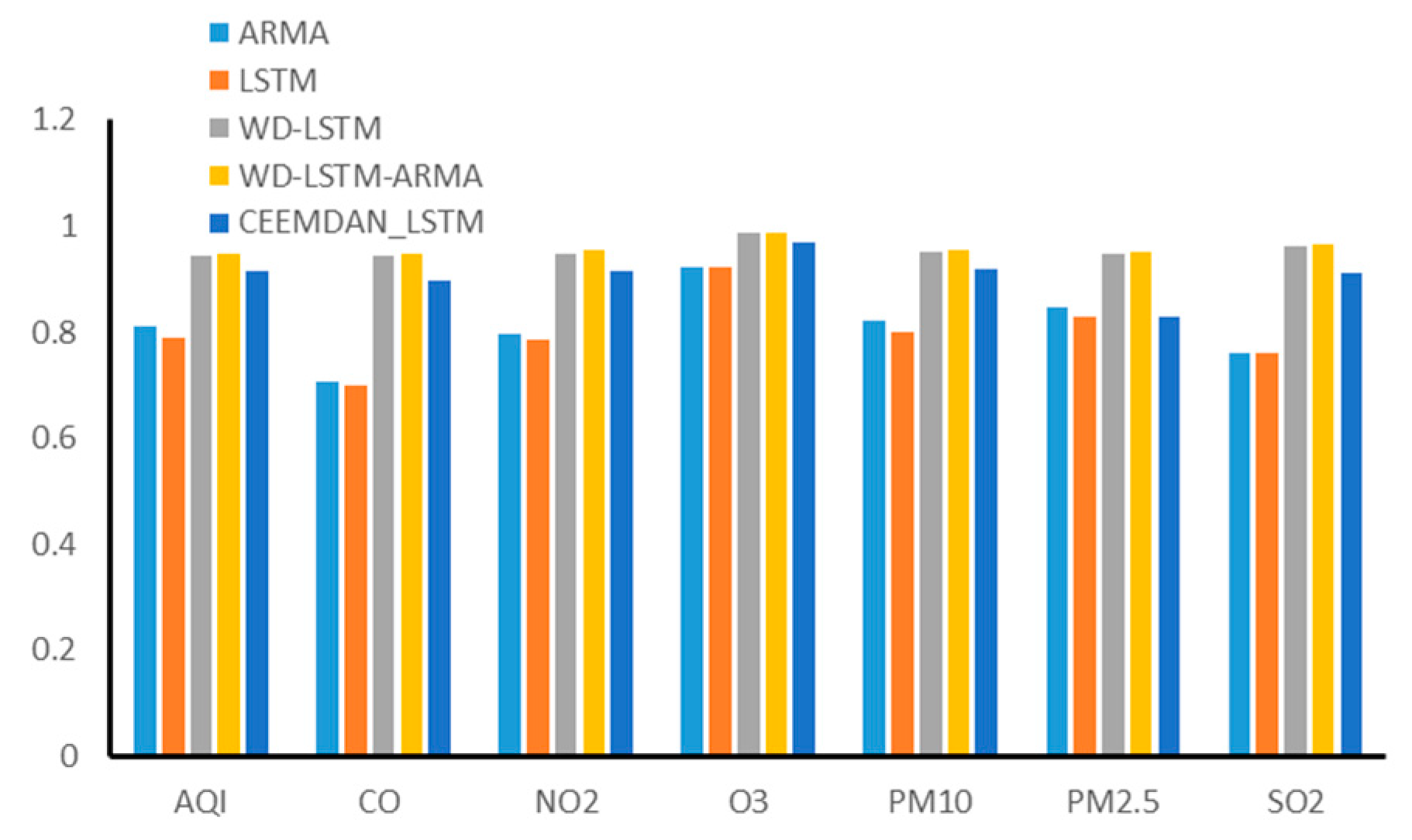
4. Comparison and Analysis
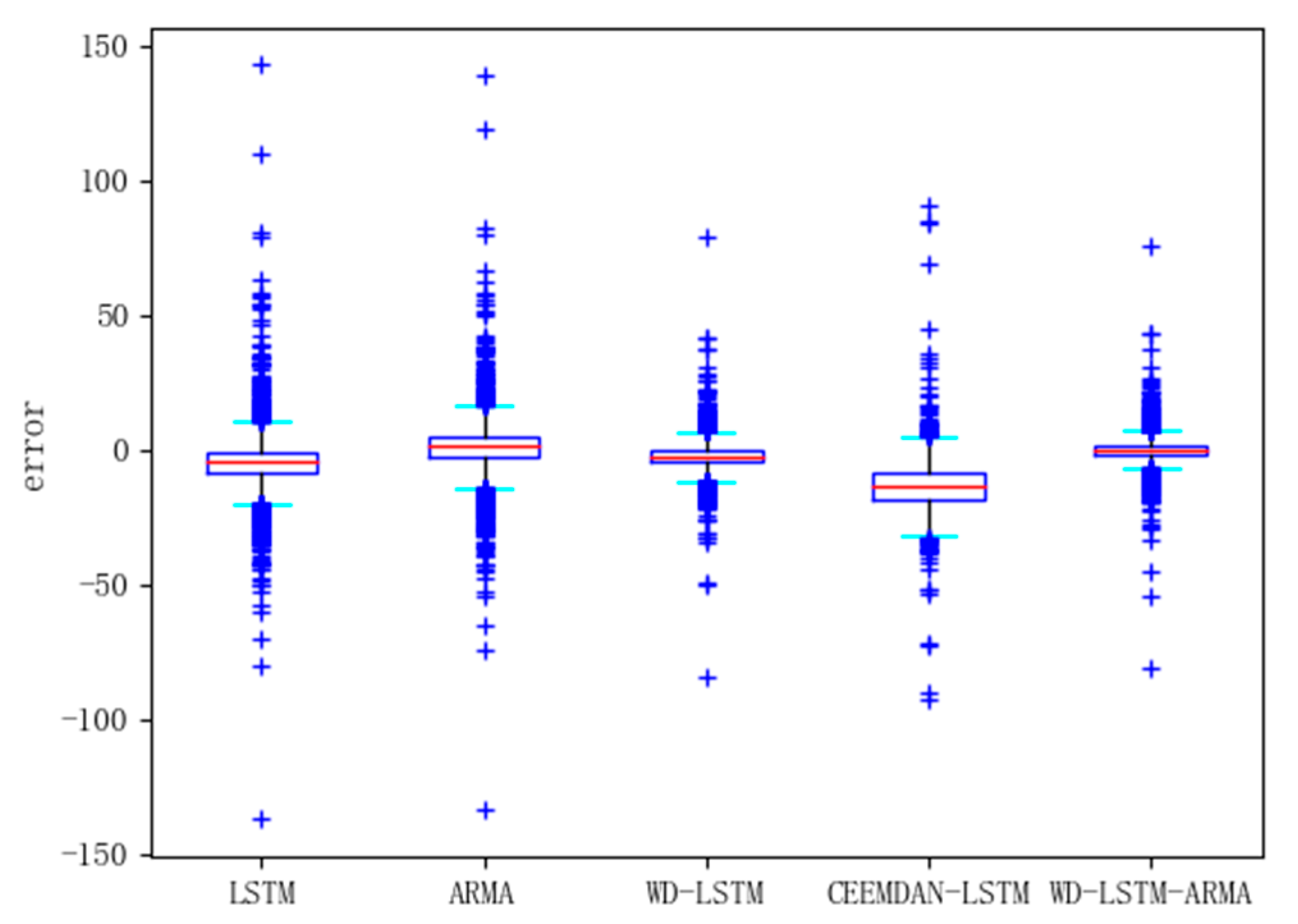
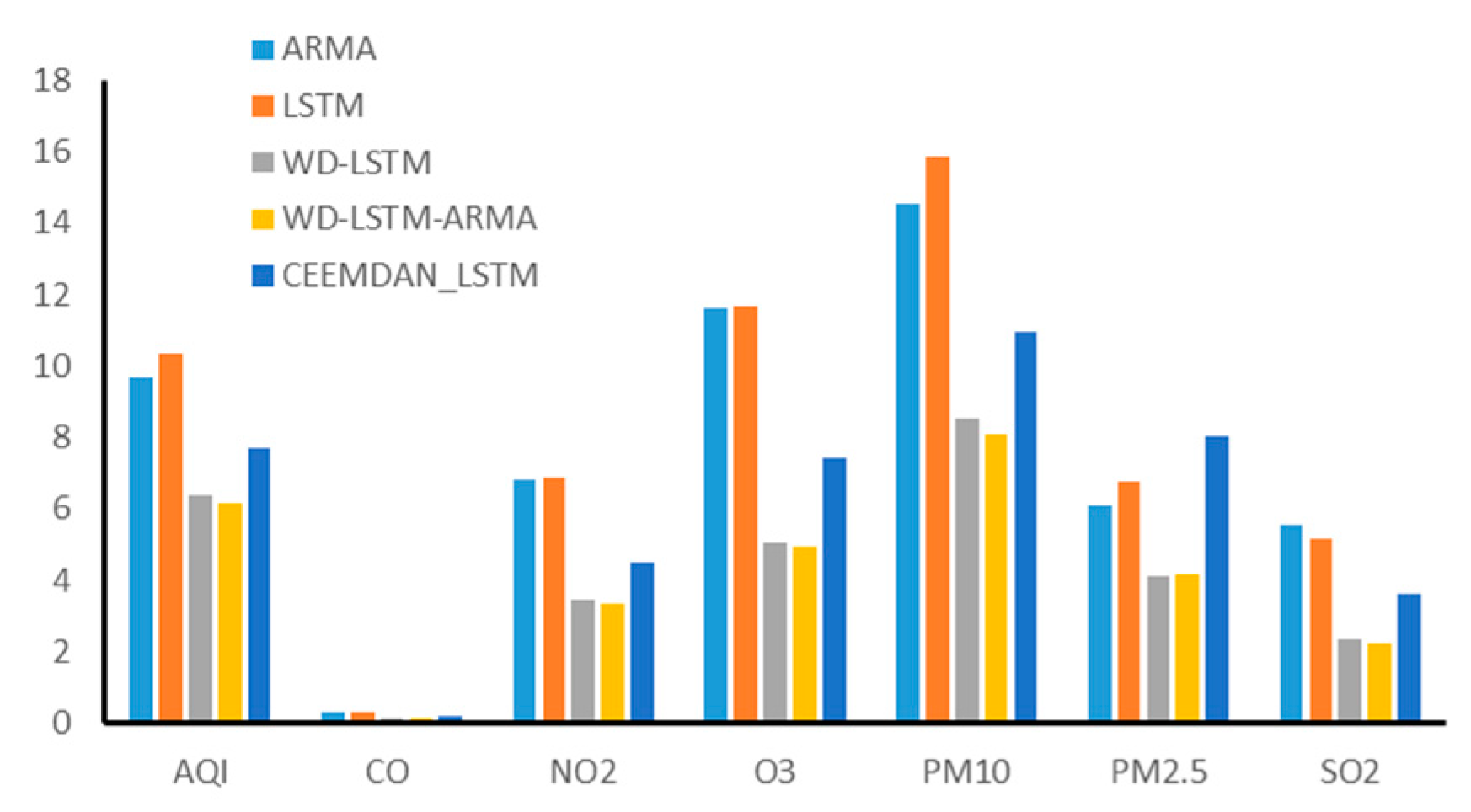
4.1. Model Comparison
4.2. Case Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, G.; Huang, G.; He, H.; He, H.; Ren, J. Regional Spatiotemporal Collaborative Prediction Model for Air Quality. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 134903–134919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Cheng, Y.; Li, H. Investigation of Model Ensemble for Fine-Grained Air Quality Prediction. China Commun. 2020, 17, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lu, C.; Ding, Y. A Systematic Simulating Assessment WithinReach Greenhouse Gas Target by Reducing PM2.5Concentrations in China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2017, 26, 683–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipiak-Florkiewicz, A.; Topolska, K.; Florkiewicz, A.; Cieślik, E. Are Environmental Contaminants Responsiblefor ‘Globesity’? Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2017, 26, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, S.; Ali, S.; Qamar, M.A.; Ashraf, M.R.; Atif, M.; Iqbal, M.; Hussain, T. Hard Water and Dyeing Properties:Effect of Pre- and Post-Mordanting on DyeingUsing Eucalyptus Globulus AndCurcuma Longa Extracts. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2017, 26, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Q.; Yu, D.; Gu, Y. Air Quality Index and Air Pollutant Concentration Prediction Based on Machine Learning Algorithms. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, K.W.; Pouliot, G.A.; Simon, H.; Sarwar, G.; Pye, H.O.T.; Napelenok, S.L.; Akhtar, F.; Roselle, S.J. Evaluation of Dust and Trace Metal Estimates from the Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) Model Version 5.0; Atmospheric Sciences: Leeds, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Woody, M.C.; Wong, H.-W.; West, J.J.; Arunachalam, S. Multiscale Predictions of Aviation-Attributable PM2.5 for U.S. Airports Modeled Using CMAQ with Plume-in-Grid and an Aircraft-Specific 1-D Emission Model. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 147, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, A.; Misstear, B.; Broderick, B. Real Time Air Quality Forecasting Using Integrated Parametric and Non-Parametric Regression Techniques. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 103, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.-B.; Yang, N.-X.; Wang, X.-Y.; Bai, Y.-T.; Su, T.-L.; Kong, J.-L. Deep Hybrid Model Based on EMD with Classification by Frequency Characteristics for Long-Term Air Quality Prediction. Mathematics 2020, 8, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Lin, H. A Novel Optimal-Hybrid Model for Daily Air Quality Index Prediction Considering Air Pollutant Factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 683, 808–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, L.; Nicolis, O.; Ruggeri, F.; Kisel’ák, J.; Stehlík, M. Predicting Hourly Ozone Concentrations Using Wavelets and ARIMA Models. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019, 31, 4331–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallat, S.G. Multifrequency Channel Decompositions of Images and Wavelet Models. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1989, 37, 2091–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; He, J.; Tian, T. A Clustering-Based Ensemble Approach with Improved Pigeon-Inspired Optimization and Extreme Learning Machine for Air Quality Prediction. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 85, 105827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabaneros, S.M.; Calautit, J.K.; Hughes, B. Spatial Estimation of Outdoor NO2 Levels in Central London Using Deep Neural Networks and a Wavelet Decomposition Technique. Ecol. Modell. 2020, 424, 109017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, C. Spatial Air Quality Index Prediction Model Based on Decomposition, Adaptive Boosting, and Three-Stage Feature Selection: A Case Study in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 265, 121777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wei, S.; Luo, H.; Yue, C.; Grunder, O. A Novel Hybrid Model for Air Quality Index Forecasting Based on Two-Phase Decomposition Technique and Modified Extreme Learning Machine. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 719–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Yan, K. A Hybrid Deep Learning Technology for PM2.5 Air Quality Forecasting. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-H.; Lu, C.-C.; Ma, Y.-F.; Lu, R.-S. A New Forecasting Framework for Bitcoin Price with LSTM. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshops (ICDMW), Singapore, 17–20 November 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 168–175. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Ding, Y.; Gan, V.J.L.; Lin, C.; Wan, Z. Spatiotemporal Prediction of PM2.5 Concentrations at Different Time Granularities Using IDW-BLSTM. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 107897–107907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L. Drought Prediction Method Based on an Improved CEEMDAN-QR-BL Model. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 6050–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, C.; Lobato, I.N. Frequency Domain Minimum Distance Inference for Possibly Noninvertible and Noncausal ARMA Models. Ann. Statist. 2018, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennon, H.; Yuan, J. Estimation of a Digitised Gaussian ARMA Model by Monte Carlo Expectation Maximisation. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2019, 133, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, A. Long Short-Term Memory. In Supervised Sequence Labelling with Recurrent Neural Networks; Studies in Computational Intelligence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 385, pp. 37–45. ISBN 978-3-642-24796-5. [Google Scholar]
| Stations | Longitude | Latitude |
|---|---|---|
| Gongxiaoshe | 118.1662 | 39.6308 |
| Shierzhong | 118.1838 | 39.65782 |
| Xiaoshan | 118.1997 | 39.6295 |
| Wuziju | 118.1853 | 39.6407 |
| Taocigongsi | 118.2185 | 39.6679 |
| Leidazhan | 118.144 | 39.643 |
| Stations | Index | AQI | SO2 | NO2 | CO | O3 | PM10 | PM2.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gongxiaoshe | RMSE | 8.9325 | 3.4657 | 4.7523 | 0.2258 | 8.5855 | 11.5951 | 5.9676 |
| MAE | 6.0555 | 1.9987 | 3.5679 | 0.1591 | 6.3389 | 7.7954 | 4.1122 | |
| R2 | 0.9456 | 0.9728 | 0.9501 | 0.9467 | 0.9802 | 0.9525 | 0.9441 | |
| Shierzhong | RMSE | 9.28 | 4.4069 | 5.1125 | 0.2962 | 6.5316 | 12.4035 | 6.069 |
| MAE | 6.5033 | 2.5241 | 3.7711 | 0.185 | 4.8603 | 8.3986 | 4.3578 | |
| R2 | 0.9478 | 0.9687 | 0.961 | 0.9322 | 0.9872 | 0.9528 | 0.9495 | |
| Xiaoshan | RMSE | 8.7925 | 4.3061 | 4.2181 | 0.2541 | 6.554 | 12.9483 | 5.6387 |
| MAE | 5.911 | 2.4288 | 3.1313 | 0.1516 | 4.9478 | 9.1704 | 4.1039 | |
| R2 | 0.9506 | 0.9619 | 0.9558 | 0.9285 | 0.9885 | 0.9447 | 0.9523 | |
| Wuziju | RMSE | 10.4078 | 4.2532 | 5.1094 | 0.2312 | 5.901 | 12.7252 | 5.9236 |
| MAE | 6.8036 | 2.4893 | 3.8179 | 0.1381 | 4.2853 | 8.209 | 4.305 | |
| R2 | 0.9332 | 0.9574 | 0.9508 | 0.9513 | 0.9886 | 0.9578 | 0.9516 | |
| Taocigongsi | RMSE | 8.6066 | 3.1685 | 4.6597 | 0.2251 | 5.9224 | 12.9119 | 5.9849 |
| MAE | 5.6633 | 1.9634 | 3.4786 | 0.146 | 4.4979 | 8.602 | 4.2579 | |
| R2 | 0.9615 | 0.9735 | 0.9576 | 0.9463 | 0.9886 | 0.9646 | 0.9508 | |
| Leidazhan | RMSE | 8.4232 | 3.5518 | 3.4449 | 0.1732 | 6.3126 | 9.7748 | 5.3129 |
| MAE | 6.0255 | 2.0302 | 2.4858 | 0.1128 | 4.7903 | 6.2446 | 3.8336 | |
| R2 | 0.9438 | 0.9666 | 0.956 | 0.9712 | 0.9885 | 0.9616 | 0.9498 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, S.; Hao, D.; Feng, Y.; Xia, K.; Yang, W. A Hybrid Model for Air Quality Prediction Based on Data Decomposition. Information 2021, 12, 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12050210
Fan S, Hao D, Feng Y, Xia K, Yang W. A Hybrid Model for Air Quality Prediction Based on Data Decomposition. Information. 2021; 12(5):210. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12050210
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Shurui, Dongxia Hao, Yu Feng, Kewen Xia, and Wenbiao Yang. 2021. "A Hybrid Model for Air Quality Prediction Based on Data Decomposition" Information 12, no. 5: 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12050210
APA StyleFan, S., Hao, D., Feng, Y., Xia, K., & Yang, W. (2021). A Hybrid Model for Air Quality Prediction Based on Data Decomposition. Information, 12(5), 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12050210








