Abstract
This research evaluates the effects of normative beliefs toward citizen engagement on eParticipation. Normative beliefs herein were assessed from the perspectives of citizenship norms, which include engaged-citizenship norms and duty-based norms, as well as the perspective of subjective norms, namely civic norms. A questionnaire was devised as the research instrument, and a survey was conducted as a means for data collection. The respondents were citizens who reside in the Greater Jakarta Region, in Indonesia, whom have had previous experiences with eParticipation. A total of 172 valid responses were collected in this study. Data were analyzed using Partial Least Squares Structural Equational Modeling (PLS-SEM), aided with SmartPLS 3 as a tool. The research results confirmed that perceived public value and perceived public satisfaction both concertedly shape citizens’ engagement in eParticipation. Furthermore, perceived public value as a pre-transactional norm also served as an antecedent to the post-transactional norm of perceived public satisfaction. The results also revealed that perceived public value was affected by a sole citizenship norm, namely, duty-based norm. Additionally, perceived public satisfaction was not affected by neither engaged-citizenship norm nor duty-based norm. Conversely, civic norms showed significant effects on both perceived public value and perceived public satisfaction.
1. Introduction
In modern society, technology has had an increasing role in political debates and democratic processes. Such development has led to a novel concept called eParticipation, which enables citizen engagement in democratic processes by utilizing information and communication technologies [1]. eParticipation is understood as employing technology to support democratic decision making, by enabling interactivity between government and citizens by making use of various technological tools [2].
Providing a technologically sound eParticipation platform is merely enough as a driver of successful electronic-aided democracy. Citizen adoption of eParticipation technologies is contingent to more than just technological factors. Against the reason of the eminently increasing role that intertwine technology and democratic processes, the analysis of the factors that drive citizen engagement in eParticipation technologies has attracted numerous researchers [3]. Some researchers have specifically highlighted the antecedents of eParticipation from various technological perspectives [4]. However, analyzing citizen engagement in eParticipation would be considered fragmentary if solely based on technology adoption theories. The existence of ambiguity when it comes to technological factors influencing eParticipation adoption has been acknowledged [5]. To encourage and increase citizen engagement in eParticipation calls for a much more intricate analysis, due to its inherent nature, which sometimes is considered more political and is aspired to influence public policy [6]. Conversely, eParticipation can potentially be examined deeper by making use of social perspectives [7]. However, research that specifically emphasizes on understanding the antecedents of citizen engagement in eParticipation is scarce, and those that look outside of technological factors are gravely lacking. In previous research pertaining this topic, most precursors understood toward eParticipation are geared more on the technological aspects, whereas the user or citizen aspects, which can be argued as equally important, tend to be overlooked.
It is interesting to note that the proliferation of eParticipation initiatives is not uniformly adopted. Moreover, citizen engagement within different eParticipation platforms is greatly varied. For example, previous research has noted that citizen engagement is higher when implemented in a smaller communal scale when compared to that of a larger national scale [2]. One logical explanation for such a difference can be viewed from a normative belief perspective. Normative belief is defined as a group’s beliefs and values, which are shaped by their previous experiences. Societal groups tend to form a set of normative beliefs, which reflect their daily experiences and in turns shape up their political attitudes [8]. Hence, this research aims to contribute to fill this knowledge gap by putting forward an analysis of the factors that drive citizen engagement in eParticipation, which is made cognizant through theories of social influence, specifically pertaining to normative beliefs.
This research argues that societal normative belief is an important antecedent of citizen engagement in eParticipation. The goal of this research is to understand citizens’ antecedents of engagement in eParticipation, more specifically from a normative belief perspective, and thereby, it provides empirical understanding of the social–psychological factors that affects citizen engagement in eParticipation. This research’s underlying assumption argues that normative beliefs can predict citizens’ engagement in eParticipation. Hence, the main research question herein is to identify the social psychological factors of normative beliefs that serve as antecedents of citizen engagement in eParticipation. The approach herein observed normative beliefs from the perspectives of citizenship norms, which include duty-based norms and engaged-citizenship norms, as well as the perspective of subjective norms, namely civic norms.
2. Theoretical Background and Hypotheses Development
2.1. Citizen Engagement on eParticipation
eParticipation can be understood as a technology-mediated interaction between civil society and formal politics, and between civil society and the administrative sphere. The focal point of eParticipation is the citizens, that is, to increase the ability of citizens to participate in digital governance, including participation in the political process and the transformation of digital government information and services. In this study, eParticipation is defined as the utilization of information and communication technologies (ICT) to support democratic decision making, where eParticipation is related to the problems of opportunity that allow for consultation and dialogue between government and citizens by using various ICT tools [1]. Moreover, the recent development of eParticipation has given birth to many new variants, which are referred to as eParticipation activities. These activities illustrate the various types of eParticipation that are commonly found today. The details of these activities can be exemplified as eVoting, Online Political Discourse, Online Decision Making, eActivism, eConsultation, eCampaigning, and ePetitioning [2].
Citizen engagement in eParticipation can be understood as the numerous ways in which a citizen can contribute to and shape their communities’ future [9]. Prior to recent technological advancements, citizen engagement in political participation is often limited to select individuals who have access to the political system. Technological advancements such as Web 2.0 and social media allow citizens to engage in civic issues more proactively. Engagement in eParticipation can take many forms, such as being digitally informed, or providing two-way communication to the government, or even actively taking part in the decision-making process. Such engagement in eParticipation has previously been described by the United Nations (UN) as eInformation, eConsultation, and eDecisionmaking [10].
2.2. eParticipation in Greater Jakarta
The Jakarta Provincial Government has launched a smart city initiative as one of the flagship programs in the Regional Medium-Term Development Plan. This is realized by forming a special unit, called the Jakarta Smart City Management Unit. This smart city initiative is expected to contribute positively in accelerating solutions to Jakarta’s community problems, such as handling congestion, floods, waste management, repairing damaged roads, trimming, and other public services bureaucracy. Innovations such as smart cities are expected to provide solutions to urban problems [11].
Jakarta Smart City manifests eParticipation, among others, through an application named Qlue. Qlue is an application that allows residents of Greater Jakarta to report various complaints or give appreciation for public services. The Jakarta Provincial Government hopes that Qlue can increase public participation and create transparency in government services. As arguments developed by other researchers, community involvement coupled with good data management are two keys to the success of smart city initiatives [12].
The Qlue platform enables citizens to communicate with the government, by reporting civic matters by means of text, images, and videos. Citizens can track their report and receive timely follow-ups from relevant government agencies [13]. Qlue ensures anonymity of the citizens and enables geo-tagging features in reported photos or videos to aid in tracking specific locations of the reports. Every citizen report is first validated by Qlue admin and then forwarded to the pertinent bureau/department to follow up. Then, citizens can track their reports, which will be marked as completed after a follow-up has been conducted. Through the Qlue platform, citizens are enabled to report complaints concerning public issues, such as garbage, flood, congestion, road damages, fires, and other environmental conditions. To ensure transparency, all reports can be monitored and tracked for progress [14].
Furthermore, one indicator of smart city initiative readiness is the existence of adequate infrastructure, in which Jakarta Province scores highly, and it can support the implementation of the eParticipation program launched [15,16,17]. Additionally, by law, civic engagement ought to play an active role in the political process and government management, which is regulated by Law No. 25 of 2009 concerning public services. The regulation states, in article 19 letter c, that the community has an obligation to actively participate in the implementation of public services [18]. The participation referred to herein can be realized digitally through eParticipation enabled by Qlue. The increasing number of public complaints directed to the government indicates a good mutualism and shows the existence of community involvement in public services [17].
However, the use of the Qlue application in Jakarta has not been optimal. The data show that Qlue users in Jakarta are limited to 600,000 individuals, and only half of them are active users. This small figure, around 8% of the total adult population of Jakarta, indicates a low level of participation [13]. The low level of community participation hinders the achievement of the goal of eParticipation, namely to be able to involve the widest possible community in their political process [1,19]. This indicates that the criteria for successful smart city implementation have not been achieved, more specifically those related to broad community participation [12].
2.3. Perceived Public Value and Perceived Public Satisfaction
Perceived value is considered as one of the most important factors in gaining a competitive advantage [20]. Relevant studies have highlighted the relationship of an individual’s perception of value toward satisfaction. The two constructs are distinct from one another. Perceived value occurs during pre-transactional and transactional processes, whereas satisfaction is typically understood as a post-use evaluation. Therefore, perceived value may be formed prior to using a product or service; however, satisfaction is more deemed as a conceptualization of outcome. Perceived value not only affects perceived satisfaction but also plays a key role in determining engagement. In this research, perceived value is measured specifically in the context of citizens’ perceived value upon taking part in public issues; hence, it is called perceived public value. By that, we mean citizens’ perceptions toward the values derived from their action pertaining to public issues. Several basic eParticipation benefits, such as maximizing knowledge and innovation from the community, avoiding conflicts, increasing social inclusion (involvement), mobilizing new resources, and generating higher public trust [21], are examples of potential perceived public value from eParticipation.
Satisfaction with eParticipation can lead to continuous citizen engagement with the eParticipation platform and reduce the likelihood of future disengagement [22]. New technologies such as those conducted in a mobile platform can generate user satisfaction as they are perceived as exciting and enjoyable [23]. Furthermore, [24] argues that perceived value and satisfaction as critical factors in determining whether one will engage in a chosen activity. Overall, satisfaction is deemed important for successful engagement, as it shapes citizens’ intention to engage in eParticipation. Previous work has argued that perceived value and satisfaction act as complement to one another; therefore, they both concurrently affect engagement [25]. Therefore, this research set forth the following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 1 (H1).
Perceived public value positively affects citizen engagement in eParticipation.
Hypothesis 2 (H2).
Perceived public satisfaction positively affects citizen engagement in eParticipation.
Hypothesis 3 (H3).
Perceived public value positively affects perceived public satisfaction.
2.4. Normative Beliefs
Normative belief can be understood as a group’s beliefs and values, which are shaped by their previous experiences. It relates to individuals’ beliefs that their close family and friends expect them to perform an act [26]. The defining element of democratic citizenship lies in public participation in political processes. Therefore, unless citizens are empowered to take part in the deliberation of public policies, then democratic processes are deemed as meaningless. Hence, the norm of political participation should be acknowledged as an essential element of democratic citizenship [27].
In this research, normative belief is first differentiated as citizenship norms, which consists of engaged-citizenship norms and duty-based norms, as defined by [27]. Furthermore, to ensure the inclusivity of other traditional norms as suggested by [28], this research includes civic norms to measure societal effects toward citizen engagement in eParticipation.
As an effort to understand citizen participation patterns, numerous previous works have highlighted the importance of citizenship norms’ transformation as its main precursor. For example, the idea that younger citizens prefer individualized forms of participation through loose or informal networks when compared to those through formal political institutions shows that the way political engagement is performed has been reshaped [29]. This notion highlights the importance of differentiating the traditional duty-based norms against the novel engaged-citizenship norms. This is highly relevant to the context of this research, which evaluates citizen engagement through a new form of electronically mediated communication platform of eParticipation.
Research that explores how normative beliefs shape political participation is scarce [30]. Despite the theoretical progression of understanding the changes in citizenship norms, empirical research in the field is atypical [28]. Hence, in order to answer the research question herein, a novel model that incorporates normative belief variables and those related to value and satisfaction was formulated.
Classical theories such as the theory of reasoned action and the theory of planned behaviors have been widely used as a model for predicting behavioral intentions [26]. Such theories corroborated the importance of normative beliefs as an antecedent of action. In this research, action was defined as citizens’ engagement through eParticipation. Such engagement can be mediated through the ways citizens perceive value and satisfaction [24]. Additionally, perceptions of a behavior are related to group norms; the behaviors of those around us act as cues to what our behaviors should be [31]. Hence, it is logical to recognize that perceptions of value and satisfaction are dependent on normative beliefs.
2.4.1. Citizenship Norms: Engaged-Citizenship Norms and Duty-Based Norms
A general understanding of citizenship norms can be defined as a shared set of expectations about the citizen’s role in politics. However, such norms can be delineated through different motivations. Civic engagement, persuaded through extrinsic motivation, is merely seen as the duty of a citizen to engage, due to external pressures. However, such notion has evolved and is keener toward intrinsic motivational factors for engagement, which is labeled as engaged-citizenship norm [28].
Despite the various potentials of defining norms pertaining to citizenship, two broad models that are contrasting can serve as a simple framework. Democratic societies can broadly be dichotomized into two contrasting perspectives of citizenship norms, which will affect their political attitudes and behaviors, namely engaged-citizenship norms and duty-based norms [27]. The two norms are interrelated and are the result of changes in modern citizen participation patterns and political behaviors. The prior is derived more from a sense of civic and moral duty serving as the guiding principle, while the latter emphasizes on what citizens themselves can do for their local community and is valued for its own sake. Political participation has shifted toward a new direction, in which citizens tend to pursue a novel approach of more participative acts of citizenship [27].
The more traditional duty-based norm is more strongly correlated with issues pertaining to the achievement of social orders. Duty-based norms persuade citizens to participate as a civic duty: for example, inducing individuals to come out to vote in an election, reporting a crime, or other institutionalized forms of actions. eParticipation technologies can act as a medium to enable citizens to fulfill duty-based norms. eParticipation can be treated as an institutionalized method for citizens to digitally communicate with the government.
On the other hand, engaged-citizenship norm is typically marked by citizens being active in civil society groups and political activities in general. The engaged citizen is willing to act on his or her principles, be politically independent, and address social needs. eParticipation technologies enable engaged citizens to fulfill their desire and willingness of being active in political activities, for example by facilitating them to participate directly in public decision-making processes, which are mediated by ICTs.
Hence, this research argues that both engaged-citizenship norms and duty-based norms affect citizens’ perceived public value and perceived public satisfaction toward eParticipation. Then, this research explores the following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 4 (H4).
Duty-based norms positively affect perceived public value.
Hypothesis 5 (H5).
Engaged-citizenship norms positively affect perceived public value.
Hypothesis 6 (H6).
Duty-based norms positively affect perceived public satisfaction.
Hypothesis 7 (H7).
Engaged-citizenship norms positively affect perceived public satisfaction.
2.4.2. Civic Norms
Previous research has shown that through the past two decades, a large proportion of citizens are indifferent to citizenship norms. Despite the heavy focus to highlight the roles of duty-based and engaged-citizenship norms, it is important to remember that many citizens adhere to other norms, including traditional ones [28]. This research accommodates those traditional norms as civic norms. Civic norms can be understood as a citizen’s habit of cooperation, which they learn from associational life and applied in wider polity [32].
The decision to participate in politics is highly influenced by what others do or are likely to do, which shape a specific civic norm within the group [33]. Civic norms vary across different societal groups and are correlated with the issues the group considers important. Civic norms allow individuals within the group to have a common understanding of actions within the group. This group understanding is parallel to subjective norms of the theory of planned behaviors [34], which refers to an individual’s perception about a behavior that is influenced by other individuals they deem important. Within the realms of political participation, civic norm is also similar to that of social norms [35] and mobilization [36,37], which refers to the extent that an individual is influenced by those around them.
Hypothesis 8 (H8).
Civic norms positively affect perceived public value.
Hypothesis 9 (H9).
Civic norms positively affect perceived public satisfaction.
A visual summary of the hypotheses proposed in this research is presented in Figure 1.
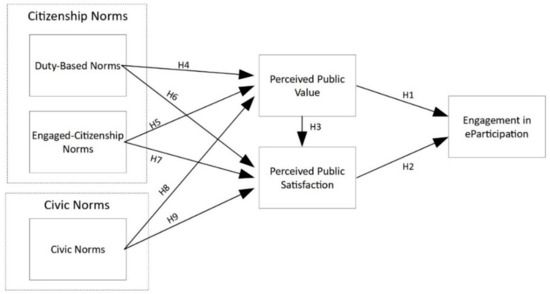
Figure 1.
Underlying research model.
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Research Method
This research conducted an empirical study to measure the relationships of the aforementioned constructs. First, this research devised a questionnaire as a research instrument and conducted a survey as a means for data collection. The details of each step are elaborated in the sections that follows.
3.2. Research Instrument Development
The underlying research model became the basis to formulate the research instrument. A questionnaire was first developed to measure every indicator by using a Likert scale with values of 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree) [38]. All measurement items were adapted from previous research and were adjusted to fit the context of this research. The questionnaires distributed were in Bahasa Indonesia language to fit the research’s locality and have been translated to English as presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Measurement question item list.
3.3. Readability Test
A readability test was conducted prior to distributing the questionnaire to the sample. The purpose of this step is to ensure that all statements in the research instrument can correctly be understood by the respondents. A readability test was conducted to eight graduate students in the field of Information Systems, and linguistic improvements were made to ensure accurate readability.
3.4. Data Collection and Sample
Then, the questionnaire was digitally devised and distributed by making use of social media promotions. The target respondents were those who reside in the Greater Jakarta Region, whom have had previous experience with eParticipation. The questionnaire was distributed in May 2019 for a four-week period. Ethical considerations were adhered to during data collection, as suggested by [40]. All participants in this research were voluntary and permissive of the data collection. Additionally, the questionnaire was purposely made anonymous to ensure respondents’ privacy and confidentiality.
3.5. Method of Analysis
Data in this research were analyzed using Partial Least Squares Structural Equational Modelling (PLS-SEM), which was aided with SmartPLS 3 as a tool. There are many advantages of using PLS-SEM compared to other methods, mainly its robustness and ease of use for analyzing reflective and formative constructs [41,42]. In addition, PLS-SEM is known for its capabilities in analyzing small and large amounts of data and does not require normal data distribution. PLS-SEM is desirable in analysis due to its ability to achieve acceptable statistical power with small sample sizes. An a priori power analysis was first conducted to define the minimum sample size for statistical analysis, which was 10 times the largest number of structural paths directed at a particular construct in the structural model [43]. This method is the most widely used in PLS-SEM, in the field of IS as well as in other fields [44]. Each construct in this research had at most three structural paths, which indicate that the minimum sample size for statistical analysis is thirty.
4. Analysis and Results
4.1. Respondents Demography
A total of 287 respondents participated in this study and filled out the questionnaire. However, this research had to eliminate 115 responses due to a variety of reasons, such as those from respondents who have no prior experience with eParticipation or those who reside outside of the Greater Jakarta Region. This high number of invalid responses is perhaps caused by the non-probabilistic sampling method, by means of online promotion through social media, hence not allowing the researchers to pre-select those individuals with the right credentials to participate. After eliminating those invalid responses, this research was left with 172 responses to be included in further analysis. A summary of the respondents’ demography is presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Respondents’ demography summary.
All of the samples in this study are residents of the Greater Jakarta Region, of which half (52.9%) of them reside in Jakarta, while the rest (47.1%) reside in the nearby suburbs. In terms of age, the respondents were mostly between 21 and 30 (43.0%) years old and 31 to 40 (44.2%) years old. The sample was represented more by male (57.6%) respondents than female (42.4%) ones, whom were mostly educated with at least an undergraduate degree (93.1%). A dominant portion of the sample was employed (72.1%), with middle-class economic status (75.6%). Almost all of the samples have had more than 5 years of mobile phone usage (93.6%) and have had previous experiences with mobile applications (98.8%), making them proficient in terms of technology. They also show high interest in following the government (82%) as well as politics (83.1%). All the samples have had experience with eParticipation with a variety of levels. Most of them use eParticipation to simply gather information (86.6%), while a lesser portion uses it to contribute (23.3%) or conduct interactive two-way communication to follow up public issues (27.3%).
4.2. Data Analysis
This research consists of six reflective variables, of which three of them are exogenous variables and the other three are endogenous ones. Duty norms, engagement norms, and civic norms were defined as exogenous reflective variables. Additionally, perceived public value, perceived public satisfaction, and engagement in eParticipation were defined as endogenous reflective variables. All variables were treated as reflective variables, and since the paths had their respective presumptive positive relationships, the model will be evaluated using one-tailed examination [41].
To evaluate the measurement model, this research conducted a validity and reliability test. The validity test is aimed to measure each indicator’s reliability level relative to its respective variable. In PLS, convergent validity as well as discriminant validity are both measured.
Convergent validity is measured by evaluating every indicator’s outer loading value and every variable’s average variance extracted (AVE) value. An outer loading value should be greater than 0.70 and can be accepted for exploratory research at a value of greater than 0.60 [41,45,46]. This research found two indicators that did not meet outer loading requirements: one indicator belonging to variable Duty Norm, and the other belonging to the variable Engagement Norm. The two indicators were consequently removed, and convergent validity was re-examined. The data showed that all the loading factor values were greater than 0.60 and all AVE values were greater than 0.50, ensuring that this research’s data were convergently valid. A summary of the measurement model evaluation is presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Measurement model summary.
Discriminant validity was measured two ways; the first was by evaluating all indicators’ cross-loading values and by means of Fornell–Larcker criterion. All indicators’ loading values should be higher in their belonging variable when compared to the values on other variables’ indicators [46]. A summary of discriminant validity in Fornell–Larcker criterion measurement is presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Discriminant validity evaluation using Fornell–Larcker criterion results.
Reliability measures the level of all indicators’ consistency. In PLS-SEM, a measure of critical ratio (CR) is deemed as more appropriate than that of Cronbach’s alpha, which is considered more conservative [41]. The value of CR should be greater than 0.70 [41]. The data in this research were considered reliable as it surpassed the aforementioned requirements, as depicted in Table 3.
Prior to testing the hypotheses, the structural model is evaluated by measuring the values of the coefficient of determination (R2), as well as its effect size (f2) [41]. The results show that the R2 values of all endogenous variables varied greatly from 0.24, 0.40, and 0.75 for perceived public value, engagement, and perceived public satisfaction, respectively. According to [45], R2 values of greater than 0.19 are considered weak, those greater than 0.33 are considered moderate, and those greater than 0.67 are considered substantial.
Then, this research went deeper by evaluating the model’s predictive relevance by measuring Cohen’s F2. The effects size of the predictive construct is calculated as the increase in R2 relative to the unexplained variance of the endogenous variable. Cohen defines F2 values of greater than 0.02, 0.15, and 0.35, as weak, moderate, and substantial effect sizes [47,48]. This research yielded two endogenous variables having no effect: five with weak relevance and two variables having medium predictive relevance. A summary of R2 values is presented in Table 5, and the F2 values are presented in Table 6.

Table 5.
Coefficient of determination (R2) values.

Table 6.
Hypotheses test results.
The hypotheses in this research were tested using a one-tailed examination, of which the arguments of the relationships were previously defined. The significance level was determined at 95%, with alpha at 0.05. Therefore, the T-Value referenced is at 1.65 [41]. Additionally, the path coefficient value is considered insignificant if it is within the range of −0.1 to 0.1, while values of greater than 0.1 are considered significant and proportional, and values less than −0.1 are considered significant inversely proportional [49]. Therefore, upon examining the hypotheses, each path was deemed to be significant having a coefficient value of greater than 0.1 and a t-value greater than 1.65. Finally, to be concluded as a supported hypothesis, each path p-value should not exceed 0.05 (p < 0.05) [50]. As can be seen in Table 6, this research showed that six hypotheses were supported, while the remaining three were not supported. A visual summary of the resulting model is presented in Figure 2.
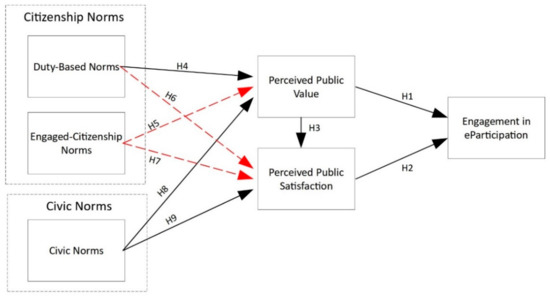
Figure 2.
Resulting Model. The red dotted arrows represent non-supported hypotheses. The black solid arrows represent supported hypotheses.
5. Discussion
The research results showed that perceived public value was affected by two factors, namely duty-based norm and civic norm. Engaged-citizenship norm was deemed as an insignificant contributor toward perceived public value. The effects of duty-based norm toward perceived public value is in line with previous research, such as those set forth by [27]; however, the insignificance of the engaged-citizenship norm is contradictive.
This research finding shows that citizens who have a stronger duty-based norm or inner sense to contribute tend to realize more value from eParticipation. This shows that generating public value on eParticipation should not only be focused on the technological or governmental perspectives, but additional efforts should also be considered to ensure a sound duty-based norm from the citizens themselves. On the other hand, citizens with stronger engaged-citizenship norm, which is identified by being more actively engaged in political agendas, do not realize more public value through eParticipation. A logical explanation is perhaps that they are already active in their respective political groups and existing political outlets, and the addition of a novel digital channel to voice out their opinion does not increase their sense of perceived public value. Furthermore, civic norm was shown to significantly shape the perceived public value of eParticipation; this finding is similar to other technologies and is also in line with the arguments of [33,51]. Citizens realize a greater sense of public value from eParticipation such as a more enjoyable experience, having the support of their friends and family.
Perceived public satisfaction of eParticipation in this research was affected by perceived public value and civic norm. In contrast, citizenship norms, which consist of the duty norm and engaged-citizenship norm, were considered as insignificant contributors. The way perceived public value affected perceived public satisfaction is similar in numerous technological applications and has been previously argued by [20]. The findings in this research corroborated those previously argued and exposed pre-transactional perceptions such as perceived public value as a significant influencer of post-transactional perceptions such as perceived satisfaction. Therefore, it is safe to assume that efforts toward shaping perceived satisfaction in eParticipation should not leave out pre-transactional phases, such as those that relate to shaping perceived public value. Additionally, civic norm plays a key role in determining perceived public satisfaction of eParticipation. This finding substantiated previous works such as those related to social norms [35] and mobilization [37], all of which argued that an individual is influenced by those around them. Two variables related to citizenship norms, which include duty norm and engaged-citizenship norm, did not have a significant effect toward public satisfaction. Perhaps, citizenship norms relate more toward pre-transactional perceptions such as perceived public value when compared to post-transactional perceptions.
Finally, engagement in eParticipation was affected concertedly by both perceived public value as well as perceived public satisfaction. Citizens tend to engage more in eParticipation having positive experiences in both pre-transactional as well as post-transactional phases. This finding validated previous works, such as [24], and [25]; hence, this research reasoned that successful engagement in eParticipation is achieved through a collaborative balance of perceived public value and perceived satisfaction.
When compared, perceived public satisfaction yielded as the stronger precursor of engagement in eParticipation, for its greater path coefficient value than perceived public value. However, the two variables showed a similar category of weak effect size. The result only showed one path with substantial effect, namely, the path from perceived public value to perceived public satisfaction, which is quite logical, as this relationship was derived from conventional understanding, and the results herein just substantiated the arguments of previous research [24,25]. Moreover, only one path, originating from civic norm to perceived public value, showed moderate effect size. Peculiarly, the moderate effect size toward perceived public value was not derived from either citizenship norm (duty-based/engaged-citizenship) but it was more pertinent to the universal concept of civic norms. Therefore, despite efforts to distinguish citizenship norms, citizens tend to adhere further to other norms in shaping their perceptions of public value and satisfaction, which in turn leads to engagement in eParticipation [28].
6. Implications
The result in this research offers both theoretical as well as practical implications. First, we now have empirical evidence of the roles of normative beliefs in shaping citizens’ engagement in eParticipation. Additionally, this research has demonstrated that citizenship norms [27] should carefully be assessed, as their sub-constructs play different roles as antecedents of perceived public value and satisfaction. The significance of duty-based norms and civic norms as normative beliefs’ precursors toward citizen engagement in eParticipation can now be established. Additionally, this research corroborated a normative belief as a significant antecedent of citizen engagement in eParticipation. Albeit, it is important to note that this research only includes citizens with prior experience of using eParticipation and therefore cannot be sure of the effects of normative beliefs toward citizen engagement for non-participants.
On a more practical note, efforts to achieve higher citizen engagement in eParticipation should be a universal endeavor and one that that embodies normative beliefs. Government organizations should strive to accentuate in building citizens’ duty-based and civic norms, for it will aid in shaping citizen engagement in eParticipation. This can be achieved by institutionalizing eParticipation as a formal means of citizen to government communication. Such will aid in cultivating citizens’ duty-based norms, and it in turns triggers citizen engagement in eParticipation. Moreover, building positive civic norms around eParticipation should also be envisioned, for example by advertising and promoting successful cases of civic engagement through eParticipation, because it will motivate other citizens to engage in eParticipation.
7. Conclusions
This research was intended to evaluate the effects of normative beliefs toward citizen engagement in eParticipation technologies. The research results confirmed that pre-transactional norms and post-transactional norms, namely perceived public value and perceived public satisfaction, both concertedly shape citizen engagement in eParticipation. Furthermore, perceived public value as a pre-transactional norm also served as an antecedent to the post-transactional norm of perceived public satisfaction. The results also revealed that perceived public value was affected by a sole citizenship norm, namely, duty-based norm, whereas engaged-citizen norm yielded an insignificant effect. Additionally, perceived public satisfaction was affected by neither duty-based norm nor engaged-citizen norm. Conversely, civic norms showed significant effects on both perceived public value and perceived public satisfaction.
8. Limitations and Future Works
As with any research, this research also has several limitations worth noting. First, the conclusion offered may be challenged in terms of its generalizability. The data collection process was conducted in a non-probabilistic manner, and the sample was limited to those who reside in the Greater Jakarta Region. Therefore, in order to achieve a more generalized result, the conclusion reached herein can benefit from further validation from different regions, which may use different eParticipation technologies, with a more varied cultural background, etc. Additionally, this research only examined three normative beliefs, which conceivably may lead to the absence of other substantial variables or important confounders such as channels of communications, digital divide, or citizens characteristics such as demographic status, digital literacy, or political attitudes. Finally, this research excluded responses from citizens who do not take part in eParticipation. Further works related to this research could include additional normative beliefs, test for important confounders, include a wider range of research participants, and allow for a comparative study of the norms across those who use eParticipation and those who do not.
Author Contributions
Formal analysis, M.R.S.; Investigation, M.R.S.; Methodology, A.N.H.; Supervision, A.N.H.; Validation, P.H.P.; Writing—original draft, M.R.S.; Writing—review & editing, A.N.H. and P.H.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Hibah Publikasi Terindeks Internasional (PUTI) Q2 2020 at Universitas Indonesia, grant number NKB-4071/UN2.RST/HKP.05.00/2020.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not Applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not Applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Macintosh, A. Characterizing e-participation in policy-making. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Big Island, HI, USA, 5–8 January 2004; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Medaglia, R. eParticipation research: Moving characterization forward (2006–2011). Gov. Inf. Q. 2012, 29, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susha, I.; Grönlund, Å. eParticipation research: Systematizing the field. Gov. Inf. Q. 2012, 29, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo Zolotov, M.; Oliveira, T.; Casteleyn, S. E-participation adoption models research in the last 17 years: A weight and meta-analytical review. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 81, 350–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly Garrett, R. Protest in an Information Society: A review of literature on social movements and new ICTs. Inf. Commun. Soc. 2006, 9, 202–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollmann, T.; Kayser, I. A Comprehensive Approach to Citizen Engagement in e-Democracy. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on e-Government-ICEG, Guangzhou, China, 7–9 May 2010; pp. 54–62. [Google Scholar]
- Manoharan, A.; Holzer, M. E-Governance and Civic Engagement: Factors and Determinants of E-Democracy; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2011; pp. 1–655. [Google Scholar]
- Staerklé, C. Political Psychology. In International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; ISBN 9780080970875. [Google Scholar]
- Adler, R.P.; Goggin, J. What Do We Mean By “Civic Engagement”? J. Transform. Educ. 2005, 3, 236–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. United Nations e-Government Survey 2016; United Nations: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 9211231744. [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Bergh, J.; Viaene, S. Key challenges for the smart city: Turning ambition into reality. In Proceedings of the Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Kauai, HI, USA, 5–8 January 2015; Volume 2015, pp. 2385–2394. [Google Scholar]
- Kogan, N.; Lee, K.J. Exploratory Research on the Success Factors and Challenges of Smart City Projects. Asia Pac. J. Inf. Syst. 2014, 24, 141–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robby, M.F. Partisipasi Masyarakat Dalam Penggunaan Aplikasi Qlue. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universitas Islam Negri Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta, Kota Tangerang Selatan, Indonesia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nurhidayati, D. Does Digital Public Service Complaint Promote Accountability? A Comparative Analysis of Upik Yogyakarta and Qlue Jakarta. Policy Gov. Rev. 2019, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampubolon, L.P.D. Pemeringkatan E-Government Indonesia (PEGI) dan Pemanfaatan Teknologi Informasi di DKI Jakarta. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2016, 8, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar]
- Reza, I.F.; Azmi, I.F. COMPARISON OF TECHNOLOGY, HUMAN RESOURCES, AND INSTITUTIONAL RESOURCES PERSPECTIVES: CASES OF JAKARTA SMART CITY. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Eviron. Sci. 2021, 717, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Didik Madyatmadja, E.; Abdurachman, E.; Gaol, F.L.; Pudjianto, B.W.; Hapsara, M. Potential Impact of Social Media to Support Government Services in Jakarta Smart City. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Information Management and Technology, Jakarta, Indonesia, 3–5 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yanuaria, T.; Katjong, K. Public Services in Health through Hospitals. Papua Law J. 2019, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, J.; Sæbø, Ø. Establishing political deliberation systems: Key problems. In Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Information Systems, ECIS 2008, Galway, Ireland, 9–11 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Parasuraman, A.; Zeithaml, V.A.; Malhotra, A. E-S-QUAL: A Multiple-Item Scale for Assessing Electronic Service Quality. J. Serv. Res. 2005, 7, 213–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S. Local issues discussion forums in comparative perspective: Whose voices are heard? Innov. Eur. J. Soc. Sci. 2008, 21, 371–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harter, J.; Asplund, J.; Flemming, J.H. HumanSigma: A Meta-Analysis the Relationship between Employee Engagement, Customer Engagement, and Financial Performance. Gall. Bus. J. 2004, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Pura, M. Linking perceived value and loyalty in location-based mobile services. Manag. Serv. Qual. 2005, 15, 509–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kim, D.J.; Wachter, K. A study of mobile user engagement (MoEN): Engagement motivations, perceived value, satisfaction, and continued engagement intention. Decis. Support Syst. 2013, 56, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggert, A.; Ulaga, W. Customer perceived value: A substitute for satisfaction in business markets? J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2002, 17, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishbein, M.; Ajzen, I. Belief, Attitude, Intention and Behaviour: An Introduction to Theory and Research; Addison-Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Dalton, R.J. Citizenship norms and the expansion of political participation. Polit. Stud. 2008, 56, 76–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooghe, M.; Oser, J. The rise of engaged citizenship: The evolution of citizenship norms among adolescents in 21 countries between 1999 and 2009. Int. J. Comp. Sociol. 2015, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglehart, R.; Welzel, C. Modernization, Cultural Change, and Democracy: The Human Development Sequence; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Scheidegger, R.; Staerklé, C. Political trust and distrust in Switzerland: A normative analysis. Swiss Polit. Sci. Rev. 2011, 17, 164–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, H.R. The Structure of Perception: How Networks Shape Ideas of Norms. Sociol. Forum 2017, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.K. Associations, civic norms, and democracy: Revisiting the Italian case. Theory Soc. 2004, 33, 135–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattie, C.; Johnston, R. Personal mobilisation, civic norms and political participation. Geoforum 2013, 45, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajzen, I. The theory of planned behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 1991, 50, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phang, C.W.E.I.; Kankanhalli, A. A Framework of ICT Exploitation for E-Participation Initiatives. Commun. ACM 2008, 51, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verba, S.; Schlozman, K.L.; Brady, H.E. Rational action and political activity. J. Polit. 2000, 12, 243–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verba, S.; Schlozman, K.L.; Brady, H.E.; Shapiro, R.Y.; Verba, S.; Schlozman, K.L.; Brady, H.E. Voice and Equality: Civic Voluntarism in American Politics; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Boone, H.N.J.; Boone, D.A. Analyzing Likert Data Likert-Type Versus Likert Scales. J. Ext. 2012, 50, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- De Oliveira, M.J.; Huertas, M.K.Z.; Lin, Z. Factors driving young users’ engagement with Facebook: Evidence from Brazil. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 54, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, E.; Bryman, A. The ethics of management research: An exploratory content analysis. Br. J. Manag. 2007, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Hult, G.T.M.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling; SAGE Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-1-4522-1744-4. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, D.X.; Lai, F. Using partial least squares in operations management research: A practical guideline and summary of past research. J. Oper. Manag. 2012, 30, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. PLS-SEM: Indeed a Silver Bullet. J. Mark. Theory Pract. 2011, 19, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kock, N.; Hadaya, P. Minimum sample size estimation in PLS-SEM: The inverse square root and gamma-exponential methods. Inf. Syst. J. 2018, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, W.W. The partial least squares approach to structural equation modeling. Mod. Methods Bus. Res. 1998, 295, 295–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, W.W. How to Write Up and Report PLS Analyses. In Handbook of Partial Least Squares; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power for the Social Sciences; Laurence Erlbaum and Associates: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.M.; Sinkovics, R.R. The use of partial least squares path modeling in international marketing. In New Challenges to International Marketing; Emerald Group Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2009; pp. 277–319. [Google Scholar]
- Lehner, F.; Haas, N. Knowledge Management Success Factors–Proposal of an Empirical Research. Electron. J. Knowl. Manag. 2010, 8, 79–90. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F.; Risher, J.J.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M. When to use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2019, 31, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, R.J.; Pattie, C.J. Towards an Understanding of Turnout at British General Elections: Voluntary and Involuntary Abstention in 1992. Parliam. Aff. 2012, 50, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).