The Role of Social Media in Generation Y Travel Decision-Making Process (Case Study in Poland)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Generation Typology
- the Silent Generation—born in 1922–1944,
- Baby Boomers—born in 1945–1964,
- Generation X—born in 1965–1980,
- Generation Y (the so-called millennials)—born in 1981–1994,
- Generation Z—born after 1995. It also often appears under the name C, meaning “connect, communicate, change”.
- Veterans (Radio Babies, The Silent Generations)—born in 1930–1945,
- Baby Boomers—born in 1946–1969,
- Generations X (Baby Busters)—born in 1970–1979,
- Generation Y (Millennials)—born after 1980.
2.2. Generation Y Characteristics
2.3. Defining the Concept of a Tourist Destination
2.4. SM in Search for Information in the Process of Making Decision on a Tourist Destination
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
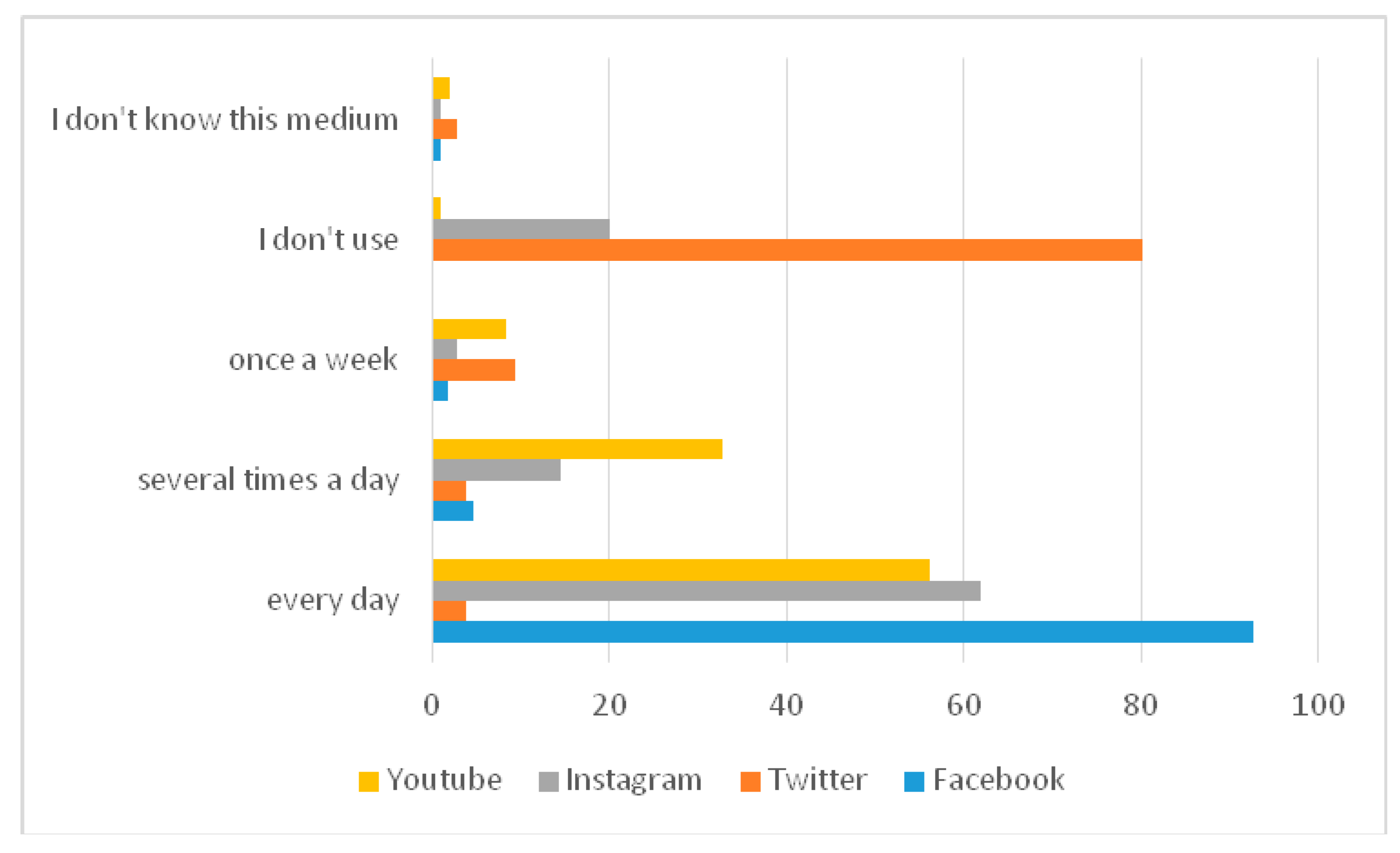
4.1. Popularity of SM among Representatives of Generation Y
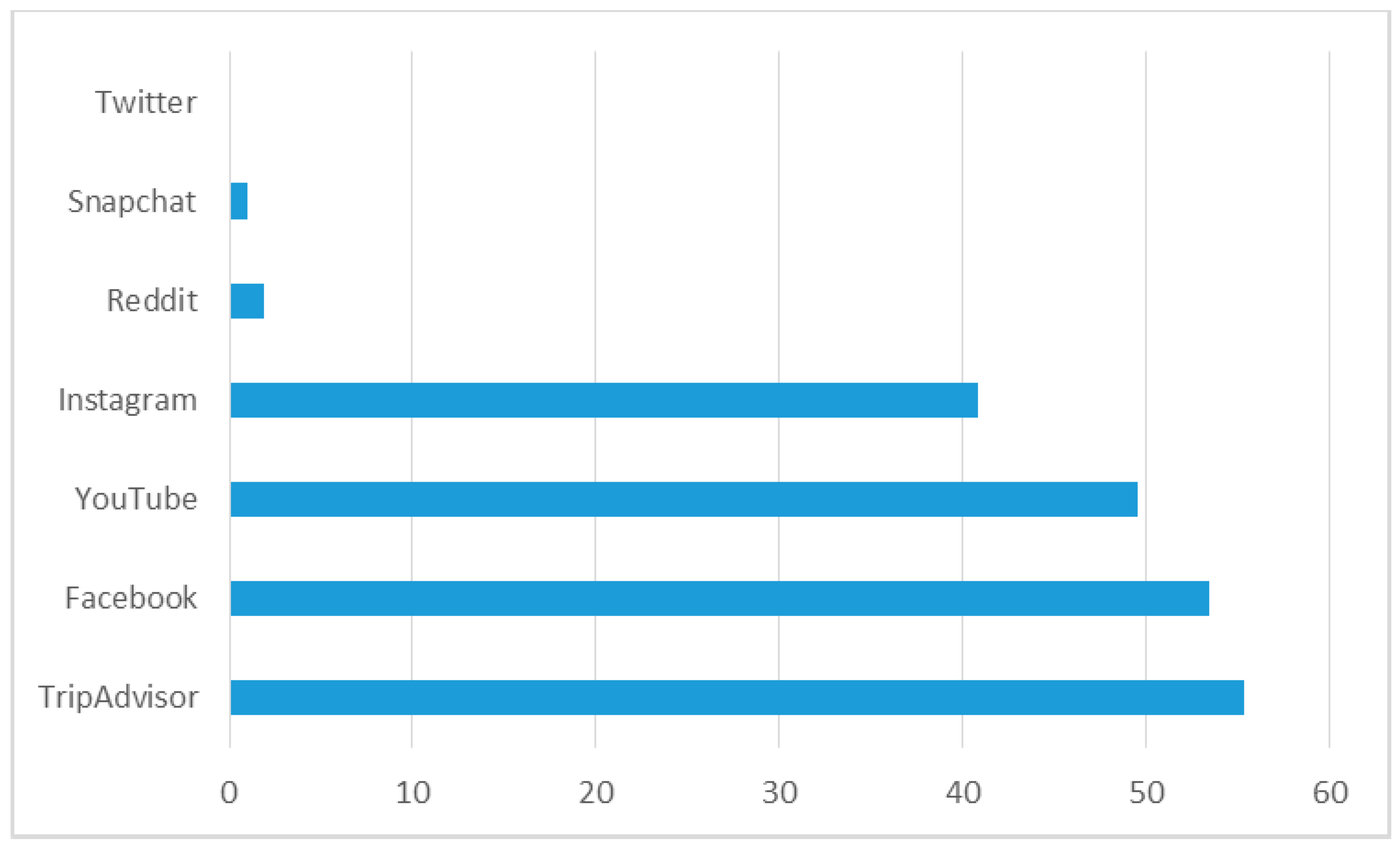
4.2. Use of SM in Obtaining Information on Tourist Destination Selection
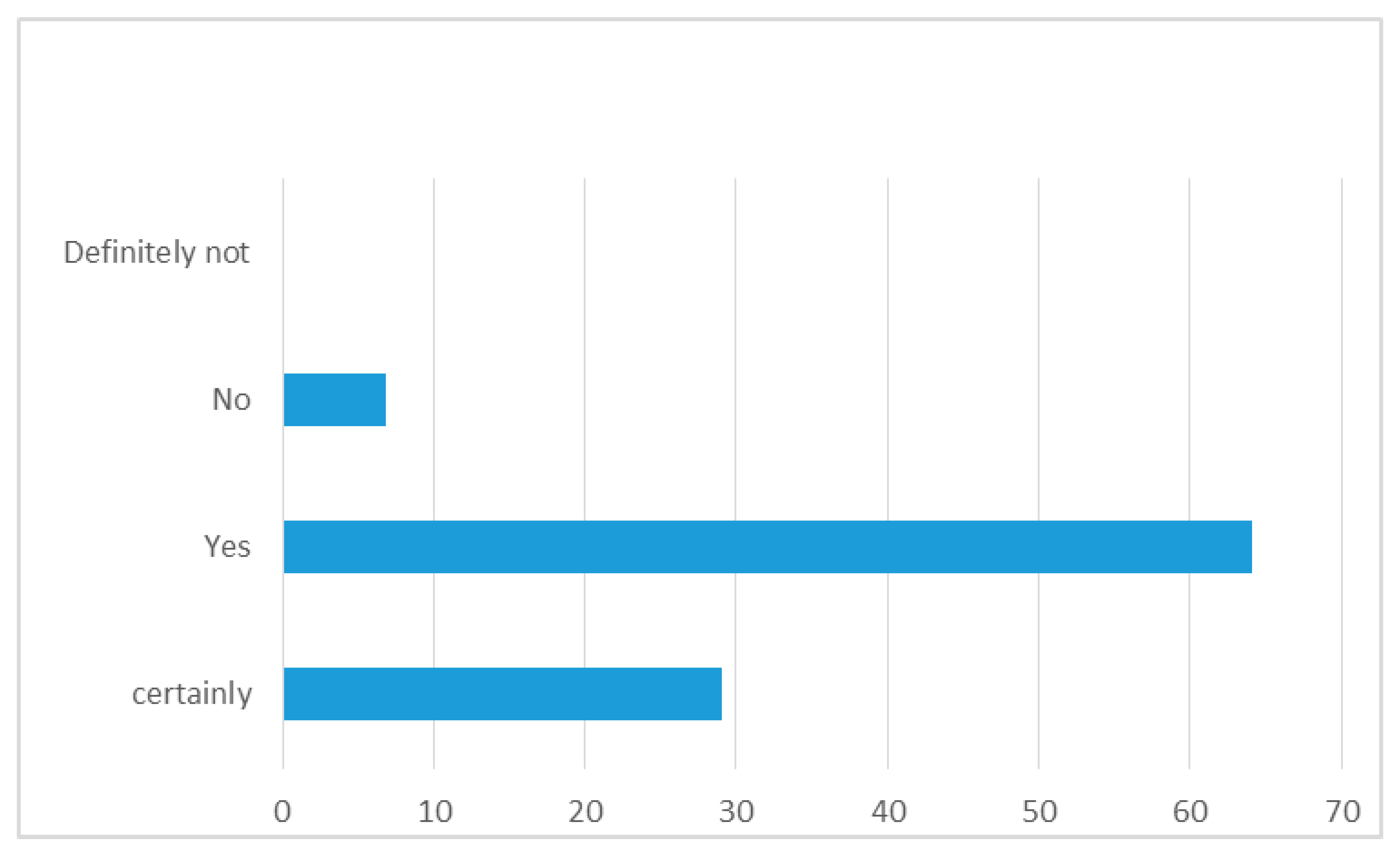
4.3. Factors Influencing the Assessment of the Attractiveness of a Tourist Destination in SM
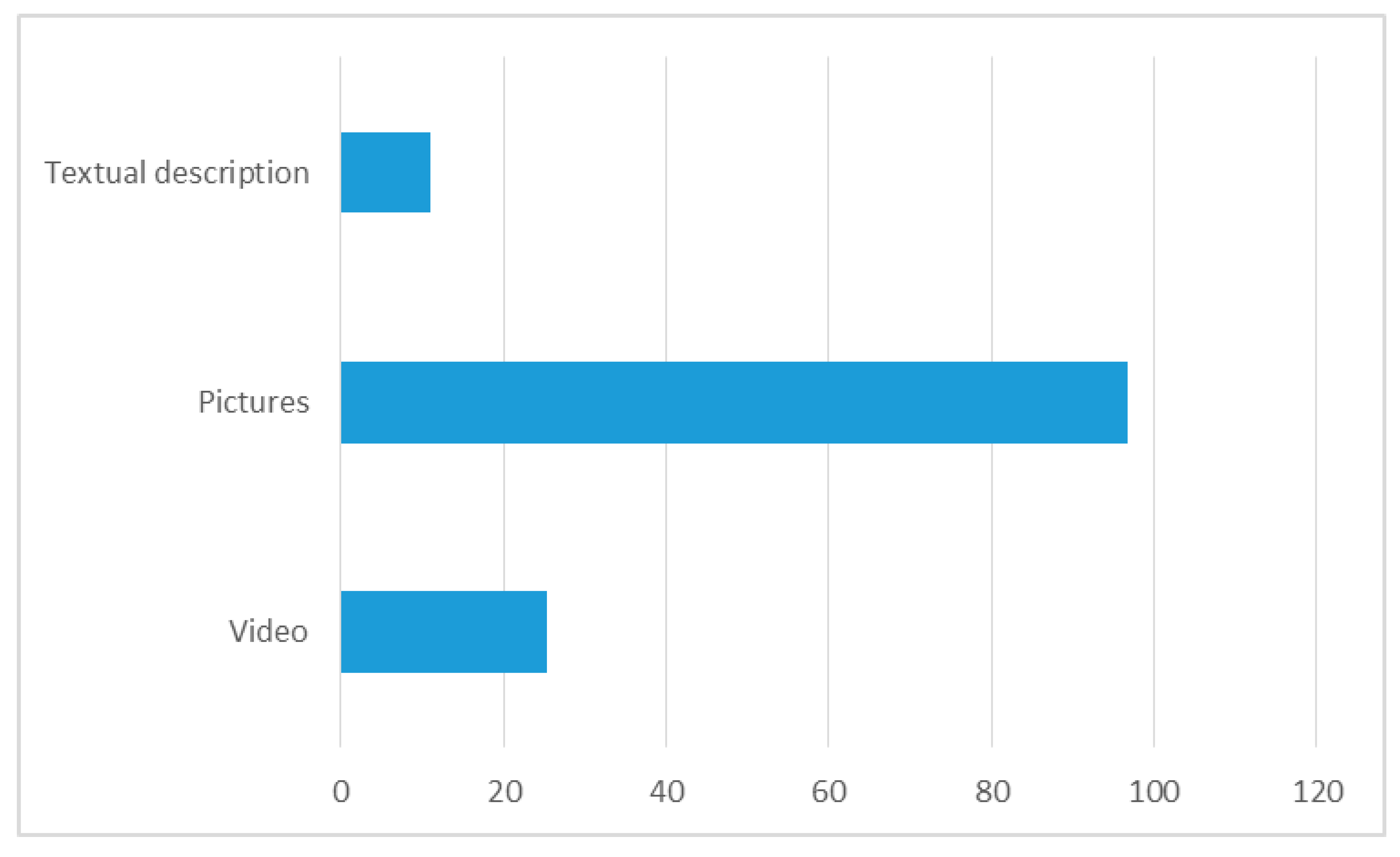
4.4. Reasons for Sharing Content in SM
5. Discussion
- The most popular social medium for acquiring information on travel destinations is Facebook.
- Generation Y assesses the attractiveness of a given destination based on opinions in social media.
- One of the main goals of the trip is to report and share travel content on social media.
- Content shared on social media affects the choice of travel destination.
6. Conclusions
- -
- The representatives of Generation Y seek information about tourist destinations using TripAdvisor or Facebook,
- -
- Generation Y indicates YouTube and Instagram as platforms that have quick and easy access to the content that is interesting for them,
- -
- Information obtained from social media was one of the factors in the selection of tourist destination,
- -
- Visual content, such as photographs, is very popular among the Millennials,
- -
- More than half of the respondents share the photographs in which they look the most attractive,
- -
- One of the reasons for sharing pictures from trips is to make friends and family jealous,
- -
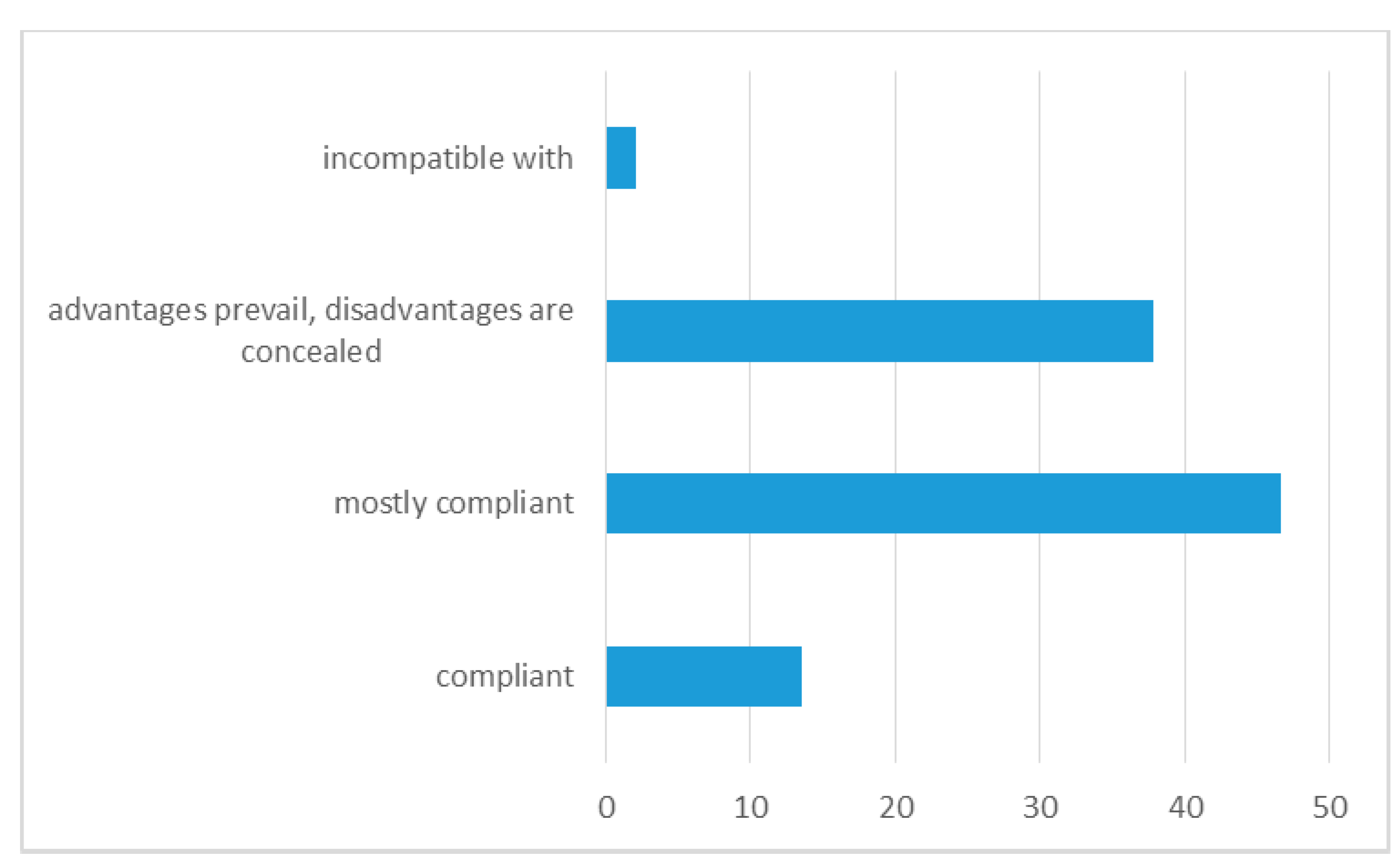
- Generation Y mostly trusts social media materials but is aware of the purposeful coloring of reality,
- -
- Sharing the experience of a tourist destination is an end in itself,
- -
- The content generated by the Millennials in social media is very effective advertisement, or anti-advertisement for a given destination,
- -
- Facebook, YouTube, and Instagram are the most widely used social media by Generation Y.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aboujaoude, E. The virtual personality of our time. The dark side of e-personalities. In Wirtualna Osobowość Naszych Czasów. Mroczna Strona E-Osobowości; Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Jagiellońskiego: Kraków, Poland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Iglesias, C.A.; Patti, V. Editorial for the Special Issue on “Love & Hate in the Time of Social Media and Social Networks”. Information 2018, 9, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Social Media Users in Poland. Available online: https://napoleoncat.com/stats/social-media-users-in-poland/2019/12 (accessed on 25 February 2020).
- Number of Monthly Active Facebook Users Worldwide as of 1st Quarter 2019. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/264810/number-of-monthly-active-facebook-users-worldwide/ (accessed on 25 February 2020).
- Management Encyclopedia. Available online: https://mfiles.pl/pl/index.php/Generacja_Y (accessed on 5 May 2020).
- Balińska, A. Agritourism as a form of recreation for students. In Link Cultural Tourism in a Digital Era: First International Conference IACuDiT, Athens; Vicky, K., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Magnini, V.P.; Fesenmaier, D.R. Information Technology and Consumer Behaviour in Travel and Tourism: Insights from Travel Planning Using the Internet. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2015, 22, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębski, M.; Krawczyk, A.; Dworak, D. Tourist behavior patterns Generation Y representatives (Wzory zachowań turystycznych przedstawicieli Pokolenia, Y.), Studia i Prace. Kolegium Zarządzania i Finansów. Zesz. Nauk. 2019, 172, 9–21. [Google Scholar]
- Paliszkiewicz, J. The Role of Social Media in Innovative Education. Available online: http://www.ptzp.org.pl/files/konferencje/kzz/artyk_pdf_2016/T2/t2_0914.pdf (accessed on 25 February 2020).
- Prensky, M. Digital Natives, Digital Immigrants. In On the Horizon; MCB University Press: Bingley, UK, 2001; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Jabłońska, M.; Bilewicz, R.K. Breakthrough generation in WEB 2.0 (Pokolenie przełomu w WEB 2.0). Acta Univ. Lodz. Folia Sociol. 2016, 56, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, S.T.; Schweitzer, L.; Eddy, S.W. How have careers changed? An investigation of changing career patterns across four generations. J. Manag. Psychol. 2015, 30, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, N.; Manuel, R.; Elam, C.; Jones, B. Differences in motives between millennial and Generation X medical students. Med. Educ. 2010, 44, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juchnowicz, M. Cultural Determinants of Human Capital Management; Oficyna Wolters Kluwer Business: Kraków, Poland, 2009; p. 118. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, G.; Smith, R.; Lucas, L. The debut of generation Y in the American workforce. J. Bus. Adm. Online 2002, 1. Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.556.1213&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 25 February 2020).
- Tyler, K. The Tethered Generation. HR Mag. 2007, 52, 55. [Google Scholar]
- Statistics Poland. Available online: www.sat.gov.pl (accessed on 25 February 2020).
- Burkart, A.J.; Medlik, S. Turism: Past, Prestent and Future; Heinemann Publishers: London, UK, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Baloglu, S.; Brinberg, D. Affective Images of Tourism Destinations. J. Travel Res. 1997, 35, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goeldner, C.R.; Ritchie, J.R.B. Tourism: Principles, Practices, Philosophies; Willey: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Jaska, E. Using new media in creating the company’s image. Zeszyty Naukowe Politechniki Częstochowskiej Zarządzanie 2018, 31, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachniewska, M. Potential of social media in the area of popularisation of tourist activity (Potencjał mediów społecznościowych w obszarze popularyzacji aktywności turystycznej). Rozprawy Naukowe Akademii Wychowania Fizycznego we Wrocławiu 2015, 50, 35–48. [Google Scholar]
- Delińska, L. Social media as a determinant of development of tourist services. Ekon. Probl. Usług 2018, 130, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guggenheim, J.; Kremser, S.; Jhunjhunwala, P.; McCaleb, T.; Garcia-Mon, A.A.; McCabe, L. Travel Goes Mobile. 2014. Available online: www.bcgperspectives.com/content/articles/trans-portation_travel_tourism_digital_economy_travel_goes_mobile/ (accessed on 25 February 2020).
- Wearesocial. Available online: https://wearesocial.com/global-digital-report-2019 (accessed on 25 February 2020).
- Chung, Y.; Buhalis, D. Information Needs in Online Social Networks. Inf. Technol. Tour. 2008, 10, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Local Consumer Revive Survey 2018. Available online: https://www.brightlocal.com/learn/local-consumer-review-survey/?SSAID=314743&SSCID=b1k2_vez00#q1 (accessed on 25 February 2020).
- Park, D.H.; Lee, J.; Han, J. The effect of online consumer reviews on consumer purchasing intention: The moderating role of involvement. Int. J. Electron. Commer. 2007, 11, 125–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.; Menon, S.; Sivakumar, K. Online peer and editorial recommendations, trust, and choice in virtual markets. J. Interact. Mark. 2005, 19, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Local Consumer Review. Available online: https://www.brightlocal.com/research/local-consumer-review-survey/ (accessed on 25 February 2020).
- Govers, R.; Go, F.M.; Kumar, K. Promoting Tourism Destination Image. J. Travel Res. 2007, 46, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V. The influencing role of social media in the consumer’s hotel decision-making process. Worldw. Hosp. Tour. Themes 2019, 11, 378–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdowska, M.; Duda-Seifert, M. Tourist Internet portals-a reliable source of information? Turyzm 2016, 26, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matikiti-Manvevery, R.; Kruger, M. The Role of Social Media Sites in Trip Planning and Destination Decision-Making Processes. Afr. J. Hosp. Tour. Leis. 2019, 8. Available online: https://www.ajhtl.com/uploads/7/1/6/3/7163688/article_3_vol_8_5__2019_cut.pdf (accessed on 25 February 2020).
- Jadhav, V.; Raman, S.; Patwa, N.; Moorthy, K.; Pathrose, J. Impact of Facebook on leisure travel behavior of Singapore residents. Int. J. Tour. Cities 2018, 4, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effect of Social Media in Tourism. Available online: https://www.longdom.org/open-access/effect-of-social-media-in-tourism-case-in-cambodia.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Apanowicz, J. General Methodology; Wyd. Bernardinum: Pelplin, Poland, 2002; p. 71. [Google Scholar]
- Whysosocial. Available online: https://www.whysosocial.pl/uzytkownicy-social-media-w-polsce-i-na-swiecie/2019 (accessed on 25 February 2020).
- Instagram Users in Poland. Available online: https://napoleoncat.com/stats/instagram-users-in-poland/2020/01 (accessed on 25 February 2020).
- Youtube. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/intl/pl/about/press/ (accessed on 25 February 2020).
- Werenowska, A. The use of tourist mobile applications by the Y generation. Bus. Inform. 2018, 2, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostonwebdesigners. Available online: https://www.bostonwebdesigners.net/wp-content/uploads/POS_PUBLIC0819-1.pdf (accessed on 25 February 2020).
- Gackowski, T.; Brylska, K.; Patera, M. The Use of Social Media as a Social Practice of Different Media Generations; Wyd. Labolatorium Medioznawcze UW: Warszawa, Poland, 2018; p. 144. [Google Scholar]
- Millenials. Available online: https://socialpress.pl/2018/07/millenialsi-publikuja-zdjecia-z-wakacji-aby-wzbudzic-zazdrosc-u-innych-uzytkownikow (accessed on 25 February 2020).
- Hussain, W. Role of Social Media in COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Front. Sci. 2020, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flachenäcker, R. Social-Media-Marketing—Kunden gewinnen über XING, Facebook & Co. In Mehr Kunden für Kleinunternehmen und Solopreneure; Springer Gabler: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mostered, P. LinkedIn or Facebook. In Managing Authentic Relationships Facing New Challenges in a Changing Context; Wijers, J.P., Ed.; Institute of Strategic Relationship Management (ISRM): The Hague, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shatal, T.V.; Dmytriyev, G.B. SMM as Modern Marketing Technologies. Bus. Inf. 2019, 12, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Nanda, P. Social Media to Social Media Analytics: Ethical Challenges. Int. J. Technoeth. 2019, 10, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebowitz, J.; Paliszkiewicz, J.; Gołuchowski, J. Intuition, Trust, and Analytics, Data Analytics Applications; Taylor & Francis Group: Milton Park, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Reformat, B.; Reformat, P. Wykorzystanie narzędzi mediów społecznościowych w kształtowaniu wizerunku firm turystycznych. Prace Naukowe Uniwersytetu Ekonomicznego w Katowicach 2018, Kierunki rozwoju innowacji w turystyce, 60–75. [Google Scholar]
- Christou, E. Branding Social Media in the Travel Industry. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 175, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littman, S. Welcome to the new Millennials. Response Mag. 2008, 16, 74–80. [Google Scholar]
- Ratajczyk, M. How Generation Y buys? [Jak kupuje Generacja Y?]. Studia Ekon. Zeszyty Naukowe Uniw. Ekon. Katowicach 2017, 330, 184–193. [Google Scholar]
- Badowska, S.; Delińska, L. Smartphone as a tool to support the process of information absorption during shopping-results of research among consumers of generation Y [Smartfon jako narzędzie wsparcia procesu absorpcji informacji podczas zakupów-wyniki badań wśród konsumentów pokolenia Y]. Annales Universitatis Mariae Curie-Skłodowska Lublin-Polonia 2019, 2, 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Song, H. Investigating Young Consumers’ Purchasing Intention of Green Housing in China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikuła-Małachowska, M. The role of the Internet in making purchasing decisions by young adults (Rola Internetu w podejmowaniu decyzji zakupowych przez młodych dorosłych). Marketing i Zarządzanie 2018, 2, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gołąb-Andrzejak, E. Consumers of generation Y—A new challenge for marketing communication (Konsumenci pokolenia Y-nowe wyzwanie dla komunikacji marketingowej). Handel Wewnętrzny 2016, 2, 140–151. [Google Scholar]
- Accenture. Available online: https://www.accenture.com/_acnmedia/PDF-98/Accenture-raport-2019.pdf (accessed on 25 February 2020).
- Maurer, C.; Siller, H. Iscontur Tourism Research Perspectives. Proceedings of the International Student Conference in Tourism Research; Herstellung und Verlag: Demand, Nordersted, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ghandour, R.; Bakalova, R. Social media influence on the holiday decision-making process in the UK. J. Organ. Stud. Innov. 2014, 1, 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Kuczamer-Kłopotowska, S. The role of social media in the communication of generation Y. Handel Wewnętrzny 2016, 3, 216–227. [Google Scholar]
| Name of the Generation | Range of Years | Age |
|---|---|---|
| Silents | 1928–1945 | 75–92 |
| Boomers | 1946–1964 | 56–74 |
| Generation X | 1965–1980 | 40–55 |
| Millennials/Y | 1981–1996 | 24–39 |
| Generation Z | 1997–2012 | 8–22 |
| I | II | III | IV | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preparation of the survey questionnaire | Testing of the questionnaire among 26 respondents | Verification of the survey questionnaire | Selection of respondents | Conducting research among 111 respondents |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Werenowska, A.; Rzepka, M. The Role of Social Media in Generation Y Travel Decision-Making Process (Case Study in Poland). Information 2020, 11, 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11080396
Werenowska A, Rzepka M. The Role of Social Media in Generation Y Travel Decision-Making Process (Case Study in Poland). Information. 2020; 11(8):396. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11080396
Chicago/Turabian StyleWerenowska, Agnieszka, and Maciej Rzepka. 2020. "The Role of Social Media in Generation Y Travel Decision-Making Process (Case Study in Poland)" Information 11, no. 8: 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11080396
APA StyleWerenowska, A., & Rzepka, M. (2020). The Role of Social Media in Generation Y Travel Decision-Making Process (Case Study in Poland). Information, 11(8), 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11080396





