International Strategic Management: A Conceptual Model with Top Managers’ Emotional Intelligence, Cultural Intelligence, and Networking
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Conceptual Model Theoretical Bases
2.1. Upper Echelons Theory
2.2. Resource-Based View
2.3. Network Theory
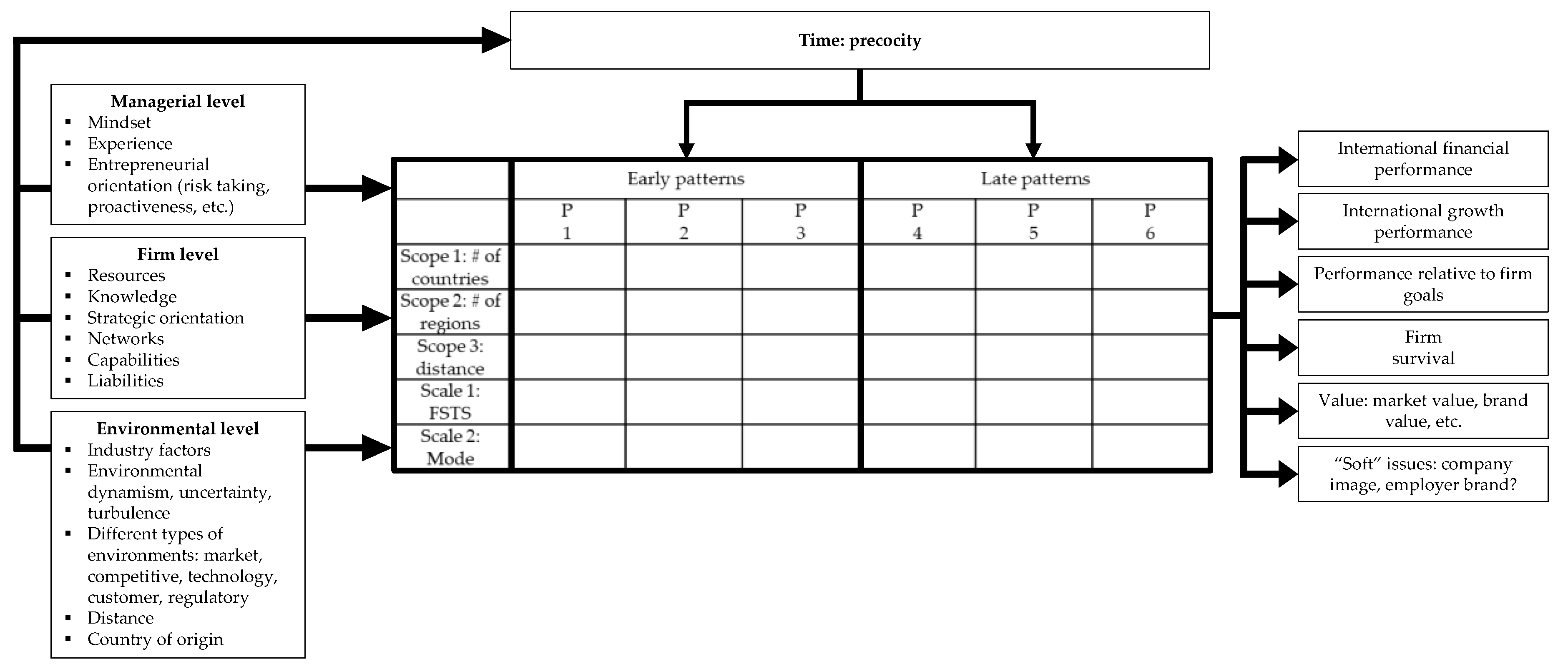
3. Internationalization Framework
3.1. Internationalization Processes
3.2. Internationalization Processes Dimensions
3.3. International Strategy and Strategic Groups
3.3.1. Strategic Groups
3.3.2. International Strategy and the Degree of Internationalization
4. International Performance
International Strategy and International Performance
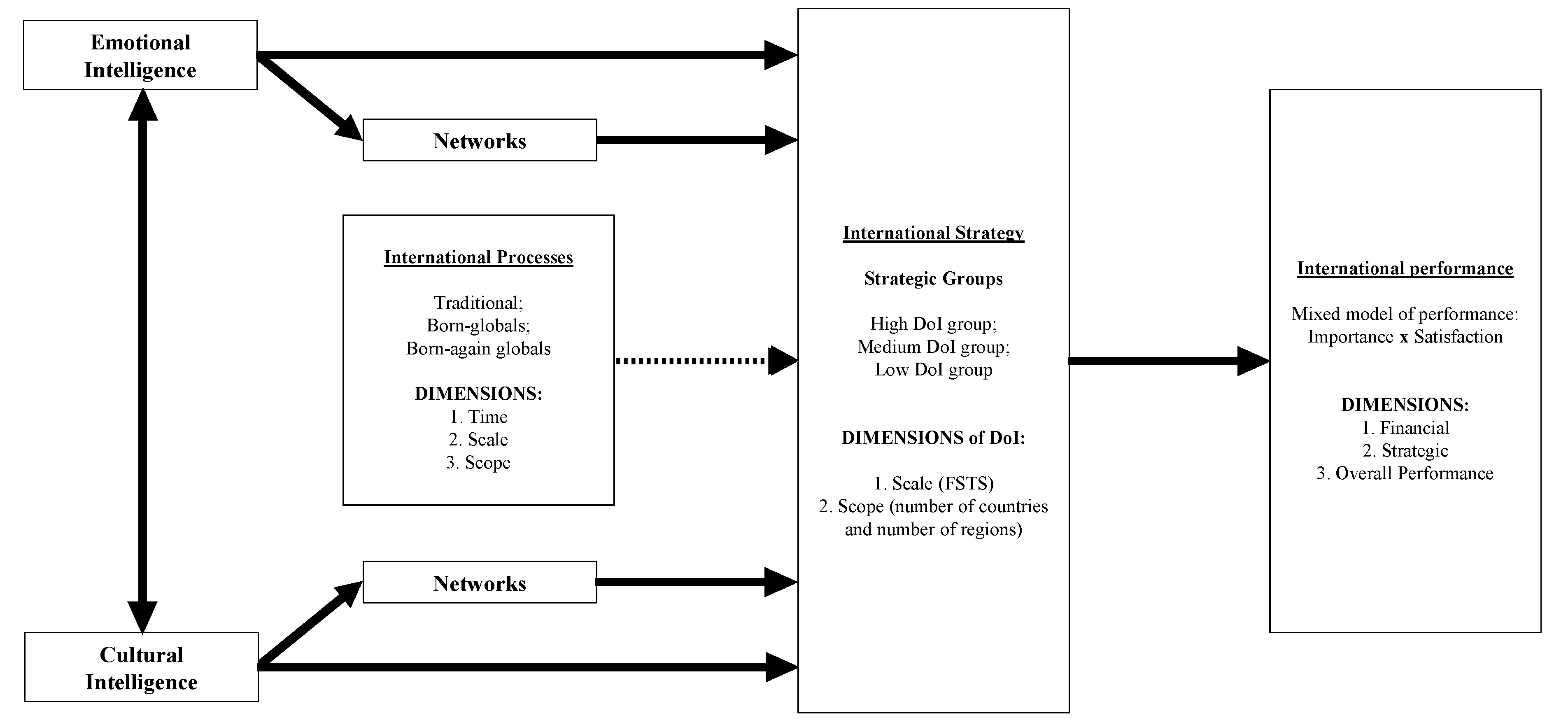
5. Conceptual Model Antecedents
5.1. Intelligence, Emotional Intelligence and Cultural Intelligence
5.1.1. Relationship between Cultural and Emotional Intelligences
5.1.2. Emotional Intelligence
5.1.3. Cultural Intelligence
5.2. Networks
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions and Future Research Avenues
Future Avenues
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuivalainen, O.; Sundqvist, S.; Saarenketo, S.; McNaughton, R. Internationalization patterns of small and medium-sized enterprises. Int. Mark. Rev. 2012, 29, 448–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, J.R.; Rutti, R.M.; Lorenz, M.P.; Barakat, L.L.; Sant’anna, A.S. Developing global transformational leaders. J. World Bus. 2017, 52, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.; Wang, W.; Lewis, J. Emotional intelligence and career decision-making difficulties: The mediating role of career decision self-efficacy. J. Vocat. Behav. 2018, 107, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olejnik, E.; Swoboda, B. SMEs’ internationalisation patterns: Descriptives, dynamics and determinants. Int. Mark. Rev. 2012, 29, 466–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrato, D.; Crosato, L.; Depperu, D. Archetypes of SME internationalization: A configurational approach. Int. Bus. Rev. 2016, 25, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.; Shah, S.Z.A.; Khan, S.Z. The role of personality in SMEs internationalization: Empirical evidence. Rev. Int. Bus. Strategy 2018, 28, 258–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.-T.; Chen, H.-L.; Cheng, C.-Y. Internationalization and firm performance of SMEs: The moderating effects of CEO attributes. J. World Bus. 2013, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.-Y. Top management team characteristics and firm internationalization: The moderating role of the size of middle managers. Int. Bus. Rev. 2018, 27, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oesterle, M.-J.; Elosge, C.; Elosge, L. Me, myself and I: The role of CEO narcissism in internationalization decisions. Int. Bus. Rev. 2016, 25, 1114–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.; Ziaulhaq, H.M. The impact of CEO characteristics on the internationalization of SMEs: Evidence from the UK. Can. J. Adm. Sci. 2019, 36, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambrick, D.C.; Mason, P.A. Upper echelons: The organization as a reflection of its top managers. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1984, 9, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hambrick, D.C. Upper echelons theory: An update. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2007, 32, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S. Top management team internationalization and firm performance: The mediating role of foreign market entry. Manag. Int. Rev. 2010, 50, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prange, C.; Pinho, J.C. How personal and organizational drivers impact on SME international performance: The mediating role of organizational innovation. Int. Bus. Rev. 2017, 26, 1114–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adomako, S.; Frimpong, K.; Mohammed, R.A.; Opoku, R.A.; Hussain, R. Chief executive officers’ dispositional optimism, host country’s rule of law, and foreign market equity mode choice of Ghanaian small and medium-sized enterprises. Thunderbird Int. Bus. Rev. 2019, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, L.; Gelfand, M.J. The culturally intelligent negotiator: The impact of cultural intelligence (CQ) on negotiation sequences and outcomes. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 2010, 112, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, T. Emotional intelligence correlates of the four-factor model of cultural intelligence. J. Manag. Psychol. 2010, 25, 876–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowne, K.A. An empirical analysis of three intelligences. Can. J. Behav. Sci. Rev. Can. Sci. Comport. 2013, 45, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundling, E.; Hogan, T.; Cvitkovich, K. What Is Global Leadership? 10 Key Behaviors That Define Great Global Leaders; Nicholas Brealey Publishing: Boston, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, M.V.; Coviello, N.; Tang, Y.K. International entrepreneurship research (1989–2009): A domain ontology and thematic analysis. J. Bus. Ventur. 2011, 26, 632–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.; Cesinger, B.; Cheng, C.-F.; Schuessler, F.; Kraus, S. A configurational analysis of network and knowledge variables explaining Born Globals’ and late internationalizing SMEs’ international performance. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2019, 80, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, B.; Jung, S. Toward a deeper understanding of the roles of personal and business networks and market knowledge in SMEs’ international performance. J. Small Bus. Enterp. Dev. 2016, 23, 812–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musteen, M.; Datta, D.K.; Butts, M.M. Do international networks and foreign market knowledge facilitate SME internationalization? Evidence from the Czech Republic. Entrep. Theory Pract. 2014, 38, 749–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiello, B.; Izzo, F. Interpersonal social networks and internationalization of traditional SMEs. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2019, 57, 658–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.A.; Kuivalainen, O. The effect of internal capabilities and external environment on small- and medium-sized enterprises’ international performance and the role of the foreign market scope: The case of the Malaysian halal food industry. J. Int. Entrep. 2015, 13, 418–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnizy, I.; Shoham, A. Uncovering the influence of the international marketing function in international firms. Int. Mark. Rev. 2014, 31, 51–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangarkar, N. Internationalization and performance of small- and medium-sized enterprises. J. World Bus. 2008, 43, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitt, M.A.; Tihanyi, L.; Miller, T.; Connelly, B. International diversification: Antecedents, outcomes, and moderators. J. Manag. 2006, 32, 831–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavusgil, S.T.; Knight, G. The born global firm: An entrepreneurial and capabilities perspective on early and rapid internationalization. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2015, 46, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moen, Ø.; Servais, P. Born global or gradual global? Examining the export behavior of small and medium-sized enterprises. J. Int. Mark. 2002, 10, 49–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontinen, T.; Ojala, A. Internationalization pathways among family-owned SMEs. Int. Mark. Rev. 2012, 29, 496–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schueffel, P.; Baldegger, R.; Amann, W. Behavioral patterns in born-again global firms. Multinatl. Bus. Rev. 2014, 22, 418–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuivalainen, O.; Saarenketo, S.; Puumalainen, K. Start-up patterns of internationalization: A framework and its application in the context of knowledge-intensive SMEs. Eur. Manag. J. 2012, 30, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, M.; Schwens, C.; Kabst, R. A latent class analysis of small firms’ internationalization patterns. J. World Bus. 2015, 50, 754–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelsson, M.; Söderblom, A.; McKelvie, A. Path dependence in new ventures’ capital structures. Entrep. Theory Pract. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintzberg, H.; Waters, J.A. Of strategies, deliberate and emergent. Strateg. Manag. J. 1985, 6, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrato, D.; Fernhaber, S.A. Depth versus breadth: Exploring variation and performance differences among internationalising new ventures. Int. Small Bus. J. Res. Entrep. 2018, 36, 758–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genc, E.; Dayan, M.; Genc, O.F. The impact of SME internationalization on innovation: The mediating role of market and entrepreneurial orientation. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2019, 82, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- der Casado-Belmonte, M.P.; Marín-Carrillo, G.M.; Terán-Yépez, E.; Capobianco-Uriarte, M.d.l.M. What is going on with the research into the internationalization of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs)? An intellectual structure analysis into the state-of-the-art (1990–2018). Publications 2020, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hennart, J.-F. The theoretical rationale for a multinationality-performance relationship. Manag. Int. Rev. 2007, 47, 423–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barney, J. Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. J. Manag. 1991, 17, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetty, S.; Holm, D.B. Internationalisation of small to medium-sized manufacturing firms: A network approach. Int. Bus. Rev. 2000, 9, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, Y.; Shirasaka, S.; Yamamoto, S.; Hardjono, T. Risk management for digital transformation in architecture board: A case study on global enterprise. In Proceedings of the 2017 6th IIAI International Congress on Advanced Applied Informatics (IIAI-AAI), Hamamatsu, Japan, 9–13 July 2017; pp. 255–262. [Google Scholar]
- Lapalme, J.; Gerber, A.; Van der Merwe, A.; Zachman, J.; De Vries, M.; Hinkelmann, K. Exploring the future of enterprise architecture: A Zachman perspective. Comput. Ind. 2016, 79, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Assar, S.; Hafsi, M. Managing strategy in digital transformation context: An exploratory analysis of enterprise architecture management support. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 21st Conference on Business Informatics (CBI), Moscow, Russia, 15–17 July 2019; pp. 165–173. [Google Scholar]
- Goerzig, D.; Bauernhansl, T. Enterprise architectures for the digital transformation in small and medium-sized enterprises. Procedia CIRP 2018, 67, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrouz, F.; Fathollah, M. A systematic approach to enterprise architecture using axiomatic design. Procedia CIRP 2016, 53, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikpay, F.; Selamat, H.; Rouhani, B.D.; Nikfard, P. A review of critical success factors of enterprise architecture implementation. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Informatics and Creative Multimedia, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 3–6 September 2013; pp. 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Zahra, S.A.; Matherne, B.P.; Carleton, J.M. Technological resource leveraging and the internationalisation of new ventures. J. Int. Entrep. 2003, 1, 163–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviatt, B.M.; McDougall, P.P. Toward a theory of international new ventures. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 1994, 25, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstede, G. Dimensionalizing cultures: The hofstede model in context. Online Read. Psychol. Cult. 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, M.A.; Geletkanycz, M.A.; Sanders, W.G. Upper echelons research revisited: Antecedents, elements, and consequences of top management team composition. J. Manag. 2004, 30, 749–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martineau, C.; Pastoriza, D. International involvement of established SMEs: A systematic review of antecedents, outcomes and moderators. Int. Bus. Rev. 2016, 25, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acedo, F.J.; Jones, M.V. Speed of internationalization and entrepreneurial cognition: Insights and a comparison between international new ventures, exporters and domestic firms. J. World Bus. 2007, 42, 236–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omri, W.; Becuwe, A. Managerial characteristics and entrepreneurial internationalization: A study of Tunisian SMEs. J. Int. Entrep. 2014, 12, 8–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutzschenreuter, T.; Horstkotte, J. Performance effects of international expansion processes: The moderating role of top management team experiences. Int. Bus. Rev. 2013, 22, 259–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-García, A. Drivers of export entrepreneurship. Int. Bus. Rev. 2016, 25, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedziniauskiene, R.; Sekliuckiene, J.; Zucchella, A. Networks’ impact on the entrepreneurial internationalization: A literature review and research agenda. Manag. Int. Rev. 2019, 59, 779–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerschewski, S.; Rose, E.L.; Lindsay, V.J. Understanding the drivers of international performance for born global firms: An integrated perspective. J. World Bus. 2015, 50, 558–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barney, J. Resource-based theories of competitive advantage: A ten-year retrospective on the resource-based view. J. Manag. 2001, 27, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoensukmongkol, P. Cultural intelligence of entrepreneurs and international network ties: The case of small and medium manufacturing firms in Thailand. Manag. Res. Rev. 2015, 38, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, G.A.; Cavusgil, S.T. Innovation, organizational capabilities, and the born-global firm. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2004, 35, 124–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, S.W. Types of foreign networks and internationalization performance of Korean SMEs. Multinatl. Bus. Rev. 2016, 24, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.F.L.; Kuo, T. When and how managerial ties matter in international competitive strategy, export financial and strategic performance framework: A standardized or customized approach? Eur. J. Mark. 2018, 52, 260–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johanson, J.; Vahlne, J.-E. The Uppsala internationalization process model revisited: From liability of foreignness to liability of outsidership. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2009, 40, 1411–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naudé, P.; Zaefarian, G.; Tavani, Z.N.; Neghabi, S.; Zaefarian, R. The influence of network effects on SME performance. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2014, 43, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che Senik, Z.; Scott-Ladd, B.; Entrekin, L.; Adham, K.A. Networking and internationalization of SMEs in emerging economies. J. Int. Entrep. 2011, 9, 259–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.; McNaughton, R.; Young, S. ‘Born-again global’ firms: An extension to the “born global” phenomenon. J. Int. Manag. 2001, 7, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitt, M.A.; Hoskisson, R.E.; Kim, H. International diversification: Effects on innovation and firm performance in product-diversified firms. Acad. Manag. J. 1997, 40, 767–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zahra, S.A.; George, G. International entrepreneurship: The current status of the field and future research agenda. In Strategic Entrepreneurship: Creating a New Mindset; Hitt, M.A., Ireland, R.D., Camp, S.M., Sexton, D.L., Eds.; Blackwell Publishers Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2002; pp. 255–288. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, J.; McNaughton, R.; Young, S.; Crick, D. Towards an integrative model of small firm internationalisation. J. Int. Entrep. 2003, 1, 339–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johanson, J.; Vahlne, J.-E. The internationalization process of the firm—A model of knowledge development and increasing foreign market commitments. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 1977, 8, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, S.A.; Ireland, R.D.; Hitt, M.A. International expansion by new venture firms: International diversity, mode of market entry, technological learning, and performance. Acad. Manag. J. 2000, 43, 925–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuivalainen, O.; Sundqvist, S.; Servais, P. Firms’ degree of born-globalness, international entrepreneurial orientation and export performance. J. World Bus. 2007, 42, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapienza, H.J.; Autio, E.; George, G.; Zahra, S.A. A capabilities perspective on the effects of early internationalization on firm survival and growth. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2006, 31, 914–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerschewski, S.; Xiao, S.S. Beyond financial indicators: An assessment of the measurement of performance for international new ventures. Int. Bus. Rev. 2015, 24, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, G.A.; Cavusgil, S.T. A taxonomy of born-global firms. Manag. Int. Rev. 2005, 45, 15–35. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, S.L.; Javalgi, R.G.; Cavusgil, E. Marketing capabilities, positional advantage, and performance of born global firms: Contingent effect of ambidextrous innovation. Int. Bus. Rev. 2017, 26, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, S.A. A theory of international new ventures: A decade of research. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2005, 36, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, D. Measuring the degree of internationalization of a firm. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 1994, 25, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunisch, S.; Menz, M.; Cannella, A.A. The CEO as a key microfoundation of global strategy: Task demands, CEO origin, and the CEO’s international background. Glob. Strateg. J. 2019, 9, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, M.V.; Coviello, N.E. Internationalisation: Conceptualising an entrepreneurial process of behaviour in time. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2005, 36, 284–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contractor, F.J.; Kumar, V.; Kundu, S.K. Nature of the relationship between international expansion and performance: The case of emerging market firms. J. World Bus. 2007, 42, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-T.; Liu, Y. Successor characteristics, organisational slack, and change in the degree of firm internationalisation. Int. Bus. Rev. 2012, 21, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugman, A.M.; Verbeke, A. A perspective on regional and global strategies of multinational enterprises. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2004, 35, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parnell, J.A.; Hershey, L. The strategy-performance relationship revisited: The blessing and curse of the combination strategy. Int. J. Commer. Manag. 2005, 15, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, N.V. Export barriers and strategic grouping. J. Glob. Mark. 2007, 20, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGee, J.; Thomas, H.; Pruett, M. Strategic groups and the analysis of market structure and industry dynamics. Br. J. Manag. 1995, 6, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leask, G.; Parnell, J.A. Integrating strategic groups and the resource based perspective: Understanding the competitive process. Eur. Manag. J. 2005, 23, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallman, S.; Li, J. Effects of international diversity and product diversity on the performance of multinational firms. Acad. Manag. J. 1996, 39, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, S.A. Technological capabilities and international expansion: The moderating role of family and non-family firms’ social capital. Asia Pacific J. Manag. 2020, 37, 391–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.; Brege, S.; Nord, T. A combined focused industry and company size investigation of the internationalization-performance relationship: The case of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) within the Swedish wood manufacturing industry. For. Policy Econ. 2018, 97, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freixanet, J.; Renart, G. A capabilities perspective on the joint effects of internationalization time, speed, geographic scope and managers’ competencies on SME survival. J. World Bus. 2020, 55, 101110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, F.; Ferreira, J.J. SME internationalisation process: Key issues and contributions, existing gaps and the future research agenda. Eur. Manag. J. 2020, 38, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lages, L.F.; Silva, G.; Styles, C.; Pereira, Z.L. The NEP scale: A measure of network export performance. Int. Bus. Rev. 2009, 18, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hult, G.T.M.; Ketchen, D.J., Jr.; Griffith, D.A.; Chabowski, B.R.; Hamman, M.K.; Dykes, B.J.; Pollitte, W.A.; Cavusgil, S.T. An assessment of the measurement of performance in international business research. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2008, 39, 1064–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamantopoulos, A.; Kakkos, N. Managerial assessments of export performance: Conceptual framework and empirical illustration. J. Int. Mark. 2007, 15, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larimo, J.; Nguyen, H.L.; Ali, T. Performance measurement choices in international joint ventures: What factors drive them? J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsikeas, C.S.; Leonidou, L.C.; Morgan, N.A. Firm-level export performance assessment: Review, evaluation, and development. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2000, 28, 493–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Taylor, C.R.; Osland, G.E. The EXPERF scale: A cross-national generalized export performance measure. J. Int. Mark. 1998, 6, 37–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madsen, T.K. Executive insights: Managerial judgment of export performance. J. Int. Mark. 1998, 6, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dess, G.G.; Robinson, R.B. Measuring organizational performance in the absence of objective measures: The case of the privately-held firm and conglomerate business unit. Strateg. Manag. J. 1984, 5, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oura, M.M.; Zilber, S.N.; Lopes, E.L. Innovation capacity, international experience and export performance of SMEs in Brazil. Int. Bus. Rev. 2016, 25, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamed, A.F.M.J.; Skallerud, K. The link between export relationship quality, performance and expectation of continuing the relationship: A South Asia exporters’ perspective. Int. J. Emerg. Mark. 2015, 10, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wall, T.D.; Michie, J.; Patterson, M.; Wood, S.J.; Sheehan, M.; Clegg, C.W.; West, M. On the validity of subjective measures of company performance. Pers. Psychol. 2004, 57, 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, L. Internationalization effects on financial performance: The case of portuguese industrial SMEs. J. Small Bus. Strateg. 2019, 29, 97–116. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.W.; Beamish, P.W. International diversification and firm performance: The s-curve hypothesis. Acad. Manag. J. 2004, 47, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito-Osorio, D.; Colino, A.; Guerras-Martín, L.Á.; Zúñiga-Vicente, J.Á. The international diversification-performance link in Spain: Does firm size really matter? Int. Bus. Rev. 2016, 25, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, A.; Losada, F.; Ruzo, E.; Díez, J.A. Implications of perceived competitive advantages, adaptation of marketing tactics and export commitment on export performance. J. World Bus. 2010, 45, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzzier, M.; Antoncic, B.; Hisrich, R.D.; Konecnik, M. Human capital and SME internationalization: A structural equation modeling study. Can. J. Adm. Sci. 2007, 24, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, C.A.; Fernandes, C.I.M.A.S.; Ferreira, J.J.M.; Peris-Ortiz, M. Factors affecting SMEs’ strategic decisions to approach international markets. Eur. J. Int. Manag. 2020, 14, 617–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karroubi, M.; Hadinejad, A.; Mahmoudzadeh, S.M. A study on relationship between cultural intelligence and cross-cultural adjustment in tour management. Manag. Sci. Lett. 2014, 4, 1233–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alon, I.; Higgins, J.M. Global leadership success through emotional and cultural intelligences. Bus. Horiz. 2005, 48, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Chen, A.S.; Song, Y. Does your intelligence help to survive in a foreign jungle? The effects of cultural intelligence and emotional intelligence on cross-cultural adjustment. Int. J. Intercult. Relat. 2012, 36, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, R.J. (Ed.) Integration and implications. In Beyond IQ: A Triarchic Theory of Human Intelligence; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 317–344. ISBN 0521262542. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, J.D.; Salovey, P. What is emotional intelligence? In Emotional Development and Emotional Intelligence: Educational Implications; Salovey, P., Sluyter, D.J., Eds.; Harper Collins: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 3–34. [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg, R.J. Managerial intelligence: Why IQ isn’t enough. J. Manag. 1997, 23, 475–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, J.D.; Caruso, D.R.; Salovey, P. Emotional intelligence meets traditional standards for an intelligence. Intelligence 1999, 27, 267–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.-S.; Law, K.S. The effects of leader and follower emotional intelligence on performance and attitude: An exploratory study. Leadersh. Q. 2002, 13, 243–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ang, S.; Van Dyne, L.; Koh, C.; Ng, K.Y.; Templer, K.J.; Tay, C.; Chandrasekar, N.A. Cultural intelligence: Its measurement and effects on cultural judgment and decision making, cultural adaptation and task performance. Manag. Organ. Rev. 2007, 3, 335–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabel, R.S.; Dolan, S.L.; Cerdin, J.L. Emotional intelligence as predictor of cultural adjustment for success in global assignments. Career Dev. Int. 2005, 10, 375–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.M.; Polesello, D. Emotional and cultural intelligence in diverse workplaces: Getting out of the box. Ind. Commer. Train. 2017, 49, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earley, P.C.; Mosakowski, E. Cultural intelligence. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2004, 82, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Jyoti, J.; Kour, S. Factors affecting cultural intelligence and its impact on job performance: Role of cross-cultural adjustment, experience and perceived social support. Pers. Rev. 2017, 46, 767–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockstuhl, T.; Seiler, S.; Ang, S.; Van Dyne, L.; Annen, H. Beyond general intelligence (IQ) and emotional intelligence (EQ): The role of cultural intelligence (CQ) on cross-border leadership effectiveness in a globalized world. J. Soc. Issues 2011, 67, 825–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowne, K.A. The relationships among social intelligence, emotional intelligence and cultural intelligence. Organ. Manag. J. 2009, 6, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyne, L.; Ang, S.; Ng, K.Y.; Rockstuhl, T.; Tan, M.L.; Koh, C. Sub-dimensions of the four factor model of cultural intelligence: Expanding the conceptualization and measurement of cultural intelligence. Soc. Personal. Psychol. Compass 2012, 6, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, K.S.; Wong, C.-S.; Huang, G.-H.; Li, X. The effects of emotional intelligence on job performance and life satisfaction for the research and development scientists in China. Asia Pacific J. Manag. 2008, 25, 51–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, S.; Drasgow, F.; Cao, M. An investigation of emotional intelligence measures using item response theory. Psychol. Assess. 2015, 27, 1241–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, G.; Zeidner, M.; Roberts, R.D. Emotional intelligence: A promise unfulfilled? Jpn. Psychol. Res. 2012, 54, 105–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devonish, D.; Greenidge, D. The effect of organizational justice on contextual performance, counterproductive work behaviors, and task performance: Investigating the moderating role of ability-based emotional intelligence. Int. J. Sel. Assess. 2010, 18, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salovey, P.; Mayer, J.D. Emotional intelligence. Imagin. Cogn. Pers. 1990, 9, 185–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, Â.M.R.; Carvalho, F.M.P.O. Emotional intelligence and ethics on organizations. Open J. Bus. Manag. 2014, 2, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.J.; Chen, Y.Q.; Sun, H. Emotional intelligence, conflict management styles, and innovation performance: An empirical study of Chinese employees. Int. J. Confl. Manag. 2015, 26, 450–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunkel, M.; Schlaegel, C.; Taras, V. Cultural values, emotional intelligence, and conflict handling styles: A global study. J. World Bus. 2016, 51, 568–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darvishmotevali, M.; Altinay, L.; De Vita, G. Emotional intelligence and creative performance: Looking through the lens of environmental uncertainty and cultural intelligence. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2018, 73, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, A.; Peake, W.O.; Stewart, W.; Watson, W. Emotional intelligence and venture performance. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2019, 57, 780–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonidou, L.C.; Aykol, B.; Fotiadis, T.A.; Zeriti, A.; Christodoulides, P. The role of exporters’ emotional intelligence in building foreign customer relationships. J. Int. Mark. 2019, 27, 58–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, K.S.; Feyerherm, A.; Gu, M. Examining cultural intelligence and cross-cultural negotiation effectiveness. J. Manag. Educ. 2015, 39, 209–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowne, K.A. Cultural exposure, emotional intelligence, and cultural intelligence: An exploratory study. Int. J. Cross Cult. Manag. 2013, 13, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Earley, P.C.; Ang, S. (Eds.) A theory of cultural intelligence. In Cultural Intelligence: Individual Interactions Across Cultures; Standford University Press: Standford, CA, USA, 2003; pp. 59–92. ISBN 0-8047-4300-2. [Google Scholar]
- Caputo, A.; Ayoko, O.B.; Amoo, N. The moderating role of cultural intelligence in the relationship between cultural orientations and conflict management styles. J. Bus. Res. 2018, 89, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, M.P.; Ramsey, J.R.; Richey, R.G. Expatriates’ international opportunity recognition and innovativeness: The role of metacognitive and cognitive cultural intelligence. J. World Bus. 2018, 53, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bembom, M.; Schwens, C. The role of networks in early internationalizing firms: A systematic review and future research agenda. Eur. Manag. J. 2018, 36, 679–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, H.-G.; Moser, K.; Grau, A. Networking: Theoretical foundations and construct validity. In Readings in Applied Organizational Behavior from the Lüneburg Symposium—Personality at Work; Deller, J., Ed.; Rainer Hampp: Mering, Germany, 2008; pp. 101–118. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, M.; Shaheen, M.; Reddy, P.K. Impact of psychological capital on organizational citizenship behavior: Moderating role of emotional intelligence. Cogent Bus. Manag. 2016, 3, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Kwon, J.-W. Overview of Hofstede-inspired research over the past 40 years: The network diversity perspective. SAGE Open 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosik, J.J.; Gentry, W.A.; Chun, J.U. The value of virtue in the upper echelons: A multisource examination of executive character strengths and performance. Leadersh. Q. 2012, 23, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cabral, Â.M.R.; Carvalho, F.M.P.O.; Ferreira, J.A.V. International Strategic Management: A Conceptual Model with Top Managers’ Emotional Intelligence, Cultural Intelligence, and Networking. Information 2020, 11, 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11120577
Cabral ÂMR, Carvalho FMPO, Ferreira JAV. International Strategic Management: A Conceptual Model with Top Managers’ Emotional Intelligence, Cultural Intelligence, and Networking. Information. 2020; 11(12):577. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11120577
Chicago/Turabian StyleCabral, Ângelo Miguel R., Fernando Manuel P. O. Carvalho, and José António Vasconcelos Ferreira. 2020. "International Strategic Management: A Conceptual Model with Top Managers’ Emotional Intelligence, Cultural Intelligence, and Networking" Information 11, no. 12: 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11120577
APA StyleCabral, Â. M. R., Carvalho, F. M. P. O., & Ferreira, J. A. V. (2020). International Strategic Management: A Conceptual Model with Top Managers’ Emotional Intelligence, Cultural Intelligence, and Networking. Information, 11(12), 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11120577





