A New Method for Refined Recognition for Heart Disease Diagnosis Based on Deep Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Disease Diagnosis Based on Refined Recognition
2.1. Research Object
2.2. Diagnosis Model
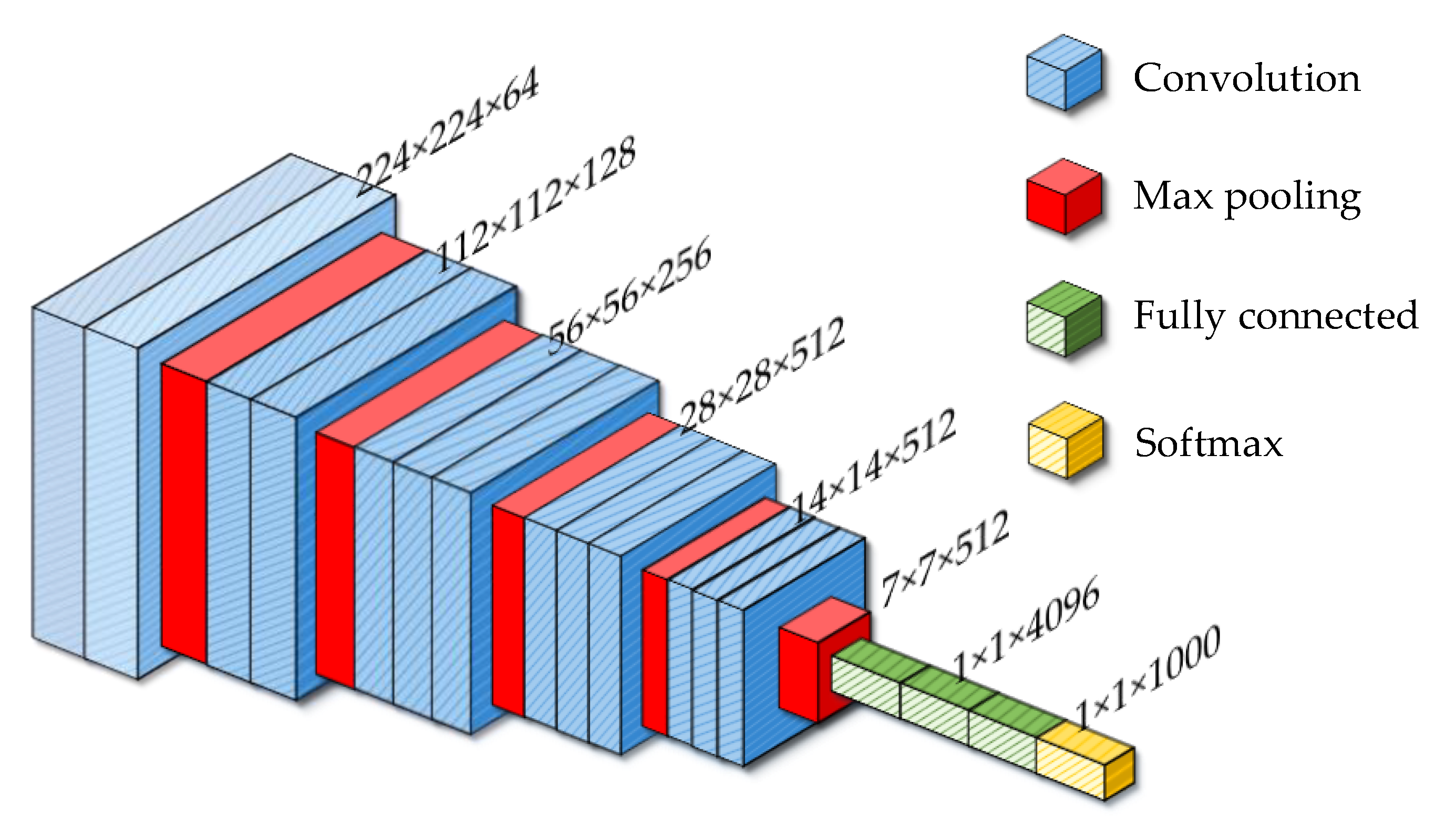
2.2.1. Convolution Neural Network
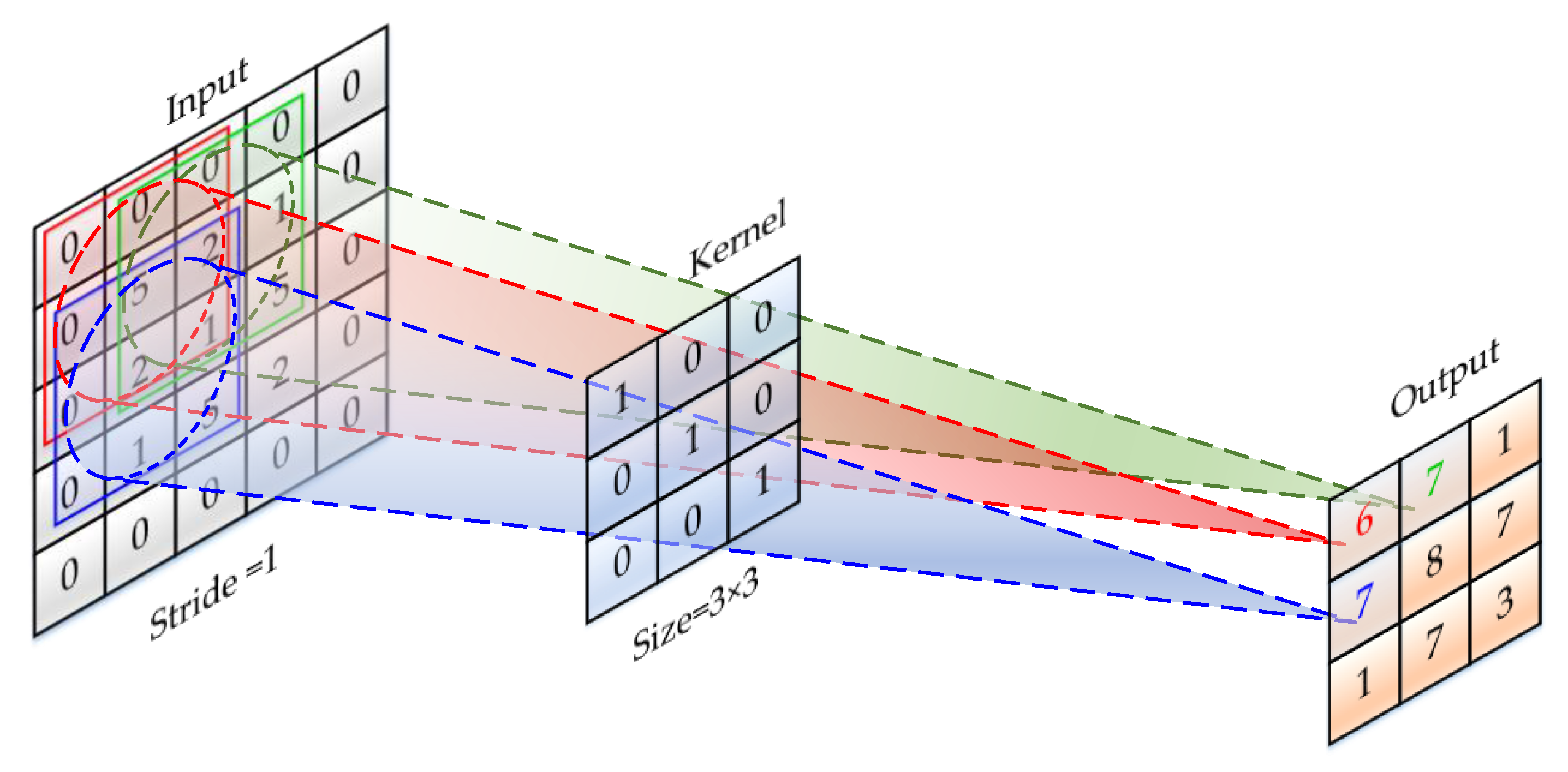
2.2.2. Convolution Layer
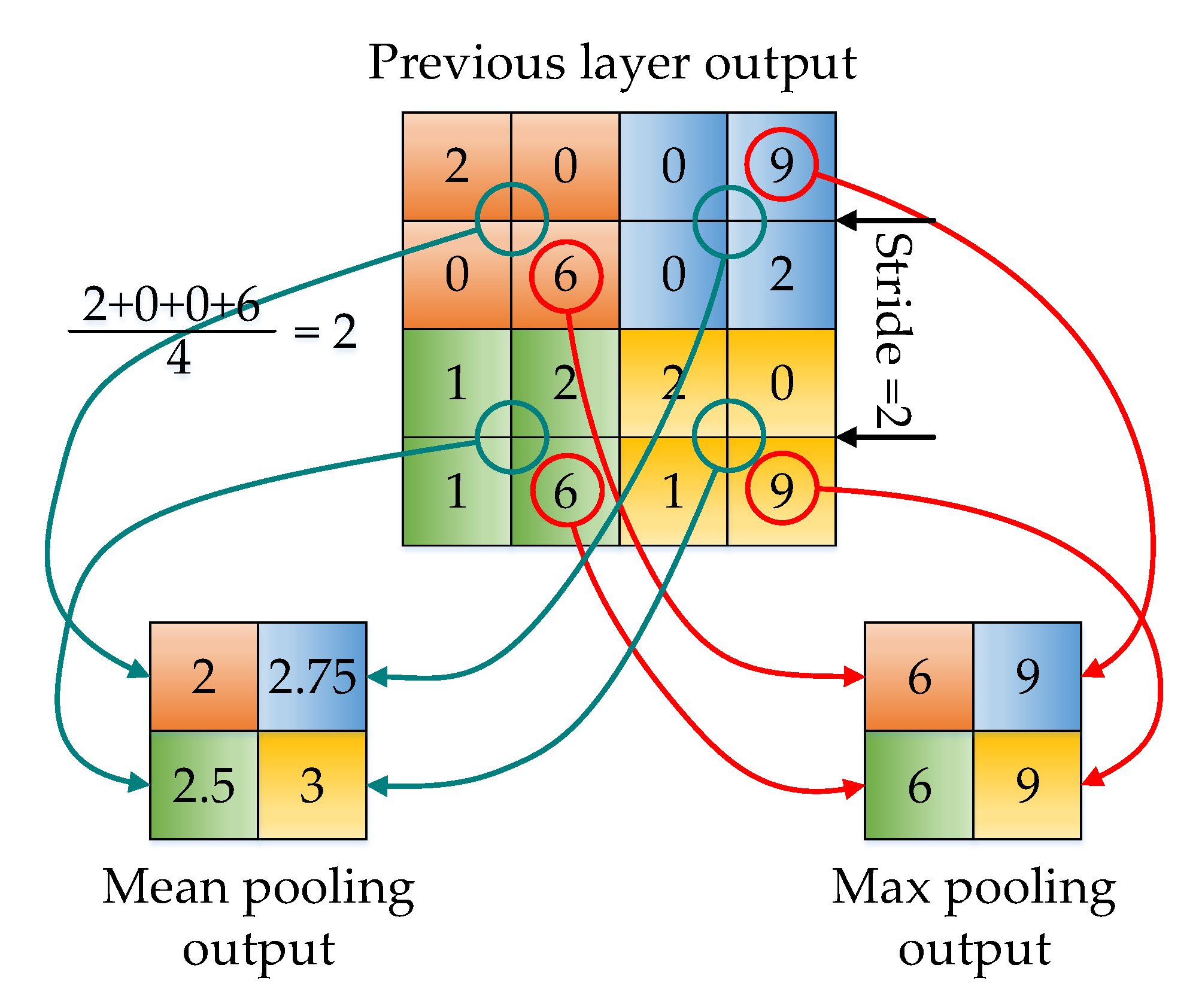
2.2.3. Pooling Layer
2.2.4. Full Connection Layer
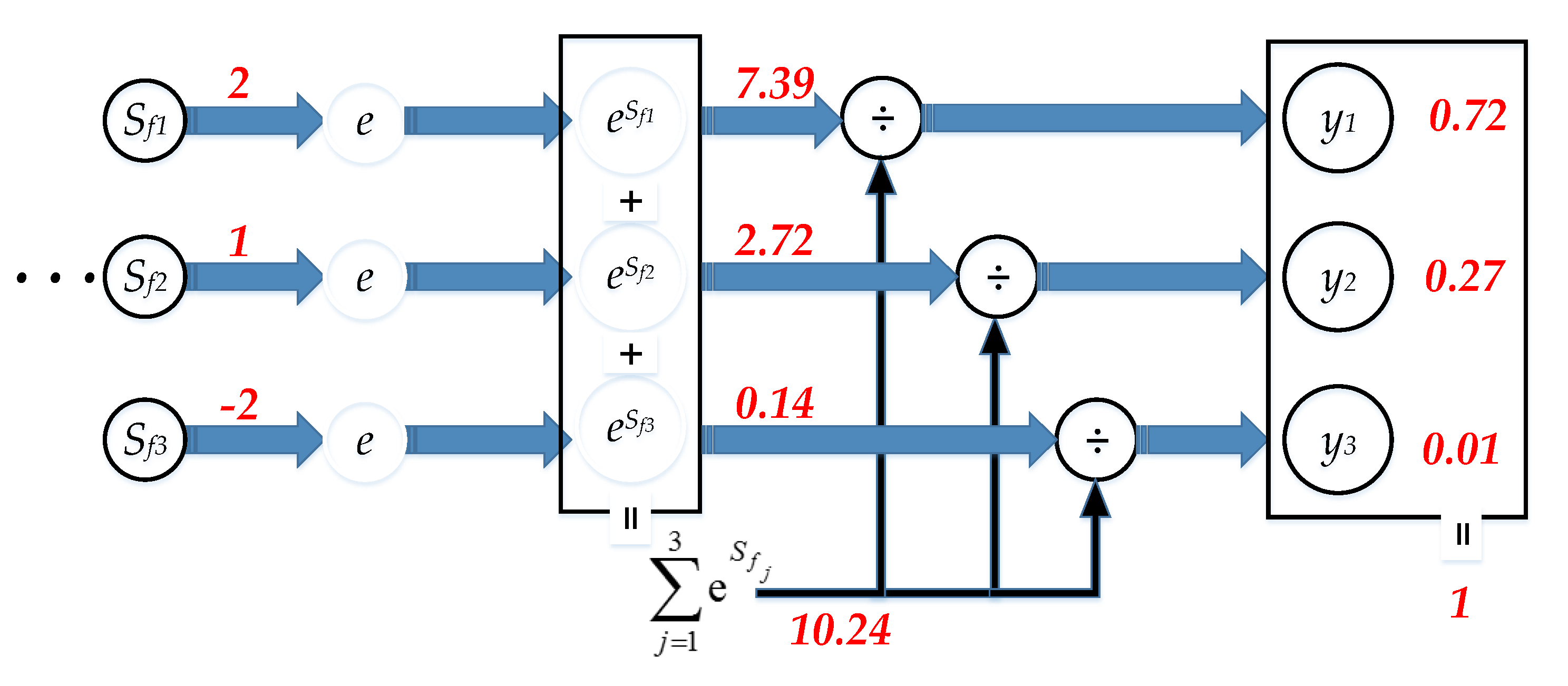
2.2.5. Softmax Layer
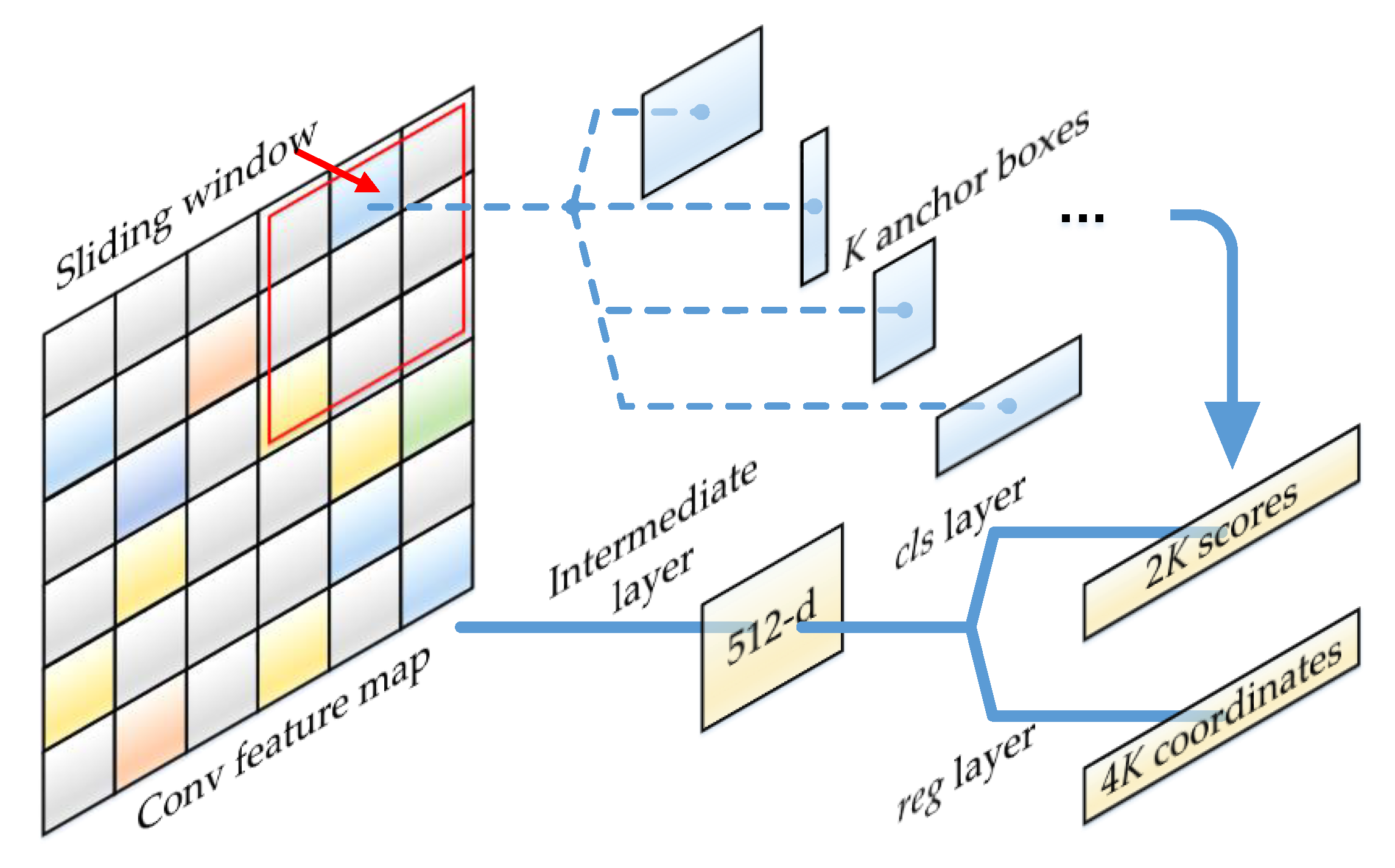
2.3. Region Proposal Network
3. Verification Experiment
3.1. Dataset of Refined Recognition
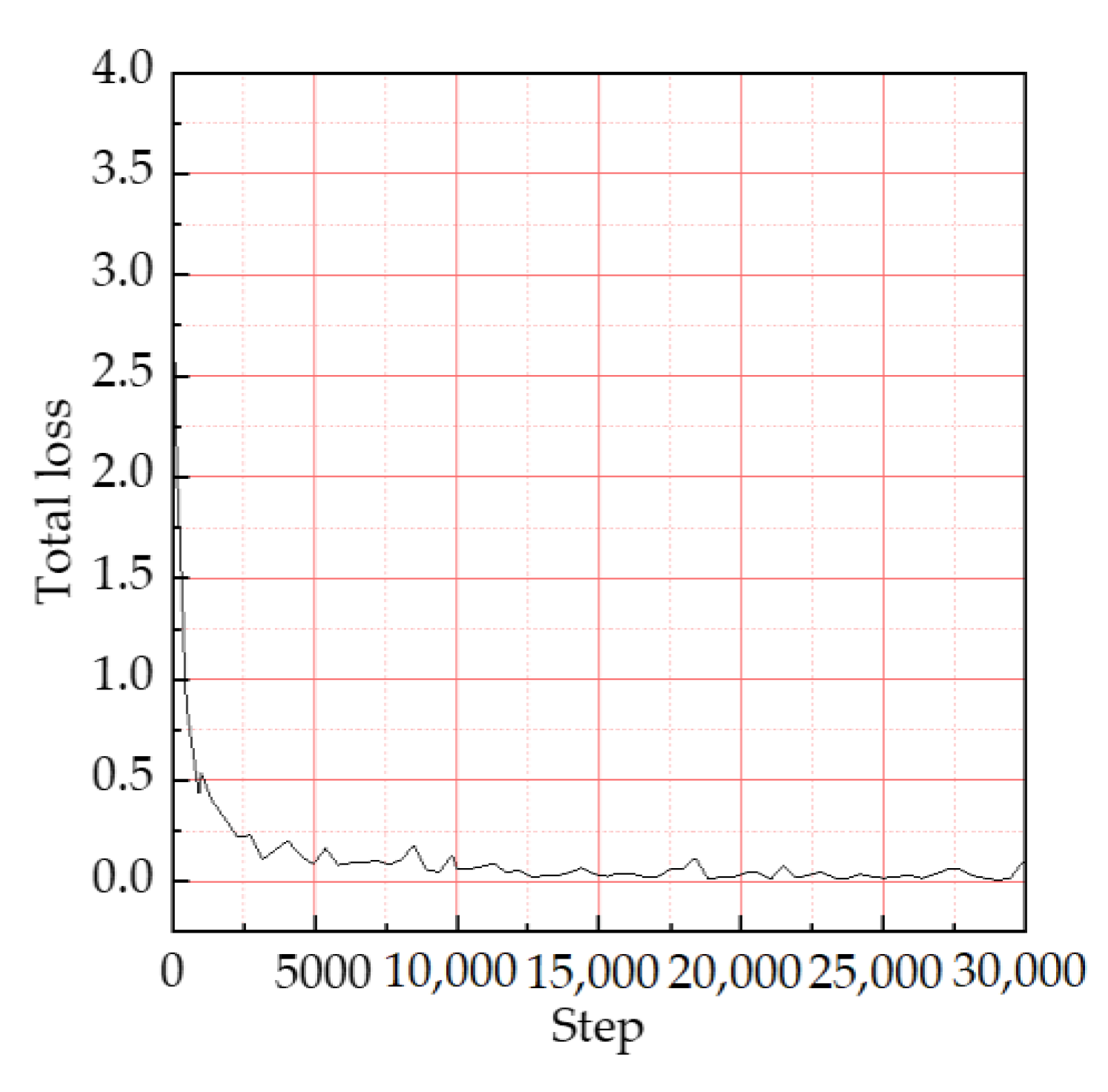
3.2. Training Results
4. Analysis and Diagnosis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oh, S.L.; Hagiwara, Y.; Raghavendra, U.; Yuvaraj, R.; Arunkumar, N.; Murugappan, M.; Acharya, U.R. A deep learning approach for Parkinson’s disease diagnosis from EEG signals. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 10927–10933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vani, S.; Suresh, G.R.; Balakumaran, T.; Ashawise, C.T. EEG Signal Analysis for Automated Epilepsy Seizure Detection Using Wavelet Transform and Artificial Neural Network. Med. Imaging Health Inform. 2019, 9, 1301–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, I.M.; Abu-Naser, S.S. Lung Cancer Detection Using Artificial Neural Network. Int. J. Eng. Inf. Syst. 2019, 3, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, P.; Hu, J.; Peng, Y. EMG-based estimation of limb movement using deep learning with recurrent convolutional neural networks. Artif. Organs 2018, 42, E67–E77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.Z.U.; Waris, A.; Gilani, S.O.; Jochumsen, M.; Niazi, I.K.; Jamil, M.; Farina, D.; Kamavuako, E.N. Multiday EMG-based classification of hand motions with deep learning techniques. Sensors 2018, 18, 2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmanaprabu, S.K.; Mohanty, S.N.; Shankar, K.; Arunkumar, N.; Ramirez, G. Optimal deep learning model for classification of lung cancer on CT images. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 92, 374–382. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.; Wei, B.; Zheng, Y.; Yin, Y.; Li, K.; Li, S. Breast cancer multi-classification from histopathological images with structured deep learning model. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustaqeem, A.; Anwar, S.M.; Majid, M. Multiclass classification of cardiac arrhythmia using improved feature selection and SVM invariants. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2018, 2018, 7310496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J. The dominant T wave cluster and One-Class SVM based analysis of multilead ECG for classification of myocardial infarction. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Biological Information and Biomedical Engineering, Hangzhou, China, 20–22 June 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Saadawy, E.I.; Tantawi, M.; Shedeed, H.A.; Tolba, M.F. Electrocardiogram (ECG) classification based on dynamic beats segmentation. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Informatics and Systems, Cairo, Egypt, 6–25 February 2016; pp. 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Baloglu, U.B.; Talo, M.; Yıldırım, Ö.; Tan, R.S.; Acharya, U.R. Classification of myocardial infarction with multi-lead ECG signals and deep CNN. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2019, 122, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, N.; D’Souza, A.; Wang, Y.; Piggins, H.; Dobrzynski, H.; Morris, G.; Boyett, M.R. Circadian rhythm of cardiac electrophysiology, arrhythmogenesis, and the underlying mechanisms. Heart Rhythm 2019, 16, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrichs, E.S.; McGlynn, K.; Allan, A.; Connolly, A.; Bishop, M.; Burton, F.; Kettlewell, S.; Myles, R.; Tveita, T.; Smith, G.L. Moderate but not severe hypothermia causes pro-arrhythmic changes in cardiac electrophysiology. Cardiovasc. Res. 2020, 116, 2081–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyakillya, B.; Kazachenko, N.; Mikhailovsky, N. Deep learning for ECG classification. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. IOP Publ. 2017, 913, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.; Afghah, F. Inter-and intra-patient ecg heartbeat classification for arrhythmia detection: A sequence to sequence deep learning approach. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019–2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1308–1312. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhou, D.; Zeng, X.; Heart, I.D. A multiresolution convolutional neural network for ECG-based biometric human identification in smart health applications. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 11805–11816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, U.R.; Fujita, H.; Lih, O.S.; Hagiwara, Y.; Tan, J.H.; Adam, M. Automated detection of arrhythmias using different intervals of tachycardia ECG segments with convolutional neural network. Inf. Sci. 2017, 405, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhurane, A.A.; Sharma, M.; Tan, R.-S.; Acharya, U.R. An efficient detection of congestive heart failure using frequency localized filter banks for the diagnosis with ECG signals. Cogn. Syst. Res. 2019, 55, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M. Wavelet de-noising and genetic algorithm-based least squares twin SVM for classification of arrhythmias. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 36, 2828–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliner, V.; Yaniv, Y. An SVM approach for identifying atrial fibrillation. Physiol. Meas. 2018, 39, 094007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, J.A.; Granados, Y.C.; Ariza, C.A.F. Patient-Specific Detection of Atrial Fibrillation in Segments of ECG Signals using Deep Neural Networks. Ciencia E Ingenieria Neogranadina 2020, 30, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labati, R.D.; Muñoz, E.; Piuri, V.; Sassi, R.; Scotti, F. Deep-ECG: Convolutional neural networks for ECG biometric recognition. Pattern Recognition Letters 2019, 126, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, T.; Fattah, S.A.; Saquib, M. DeepArrNet: An Efficient Deep CNN Architecture for Automatic Arrhythmia Detection and Classification from Denoised ECG Beats. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 104788–104800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–10 December 2015; pp. 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2015, arXiv:14091556. [Google Scholar]
- Avanzato, R.; Beritelli, F. Automatic ECG Diagnosis Using Convolutional Neural Network. Electronics 2020, 9, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaragnella, C.; Rizzi, M.; Giorgio, A. Marginal Component Analysis of ECG Signals for Beat-to-Beat Detection of Ventricular Late Potentials. Electronics 2019, 8, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharshid, A.; Alhichri, H.S.; Ouni, R.; Bazi, Y. Classification of Short-time Single-lead ECG Recordings Using Deep Residual CNN. In Proceedings of the 2019 2nd International Conference on new Trends in Computing Sciences (ICTCS), Amman, Jordan, 9–11 October 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, C.; Jiang, H.; Li, Q.; Rao, N. Multi-label Classification of Abnormalities in 12-Lead ECG Using 1D CNN and LSTM. In Machine Learning and Medical Engineering for Cardiovascular Health and Intravascular Imaging and Computer Assisted Stenting; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Abrishami, H.; Han, C.; Zhou, X.; Campbell, M.; Czosek, R. Supervised ecg interval segmentation using lstm neural network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bioinformatics & Computational Biology (BIOCOMP), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 19–21 March 2018; pp. 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Peimankar, A.; Puthusserypady, S. An Ensemble of Deep Recurrent Neural Networks for P-wave Detection in Electrocardiogram. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019–2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 1284–1288. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.; Tan, B. Electrocardiogram soft computing using hybrid deep learning CNN-ELM. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 86, 105778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shdefat, A.; Joo, M.; Kim, H. A Method of Analyzing ECG to Diagnose Heart Abnormality utilizing SVM and DWT. J. Multimed. Inf. Syst. 2016, 3, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Yuen, B.; Dong, X.; Lu, T. Inter-Patient CNN-LSTM for QRS Complex Detection in Noisy ECG Signals. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 169359–169370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvan, Ç.; Özkurt, N. ECG Beat Arrhythmia Classification by using 1-D CNN in case of Class Imbalance. In Proceedings of the 2019 Medical Technologies Congress (TIPTEKNO), Izmir, Turkey, 3–5 October 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Li, X.; Xie, X.; Wang, Q. Research on arrhythmia detection algorithm based on deep learning. Med. Health Equip. 2018, 39, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Hu, F.; Zhu, J.; Tang, Q.; Liang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Hu, F.; Zhu, J.; et al. An Automatic Diagnosis of Arrhythmias Using a Combination of CNN and LSTM Technology. Electronics 2020, 9, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
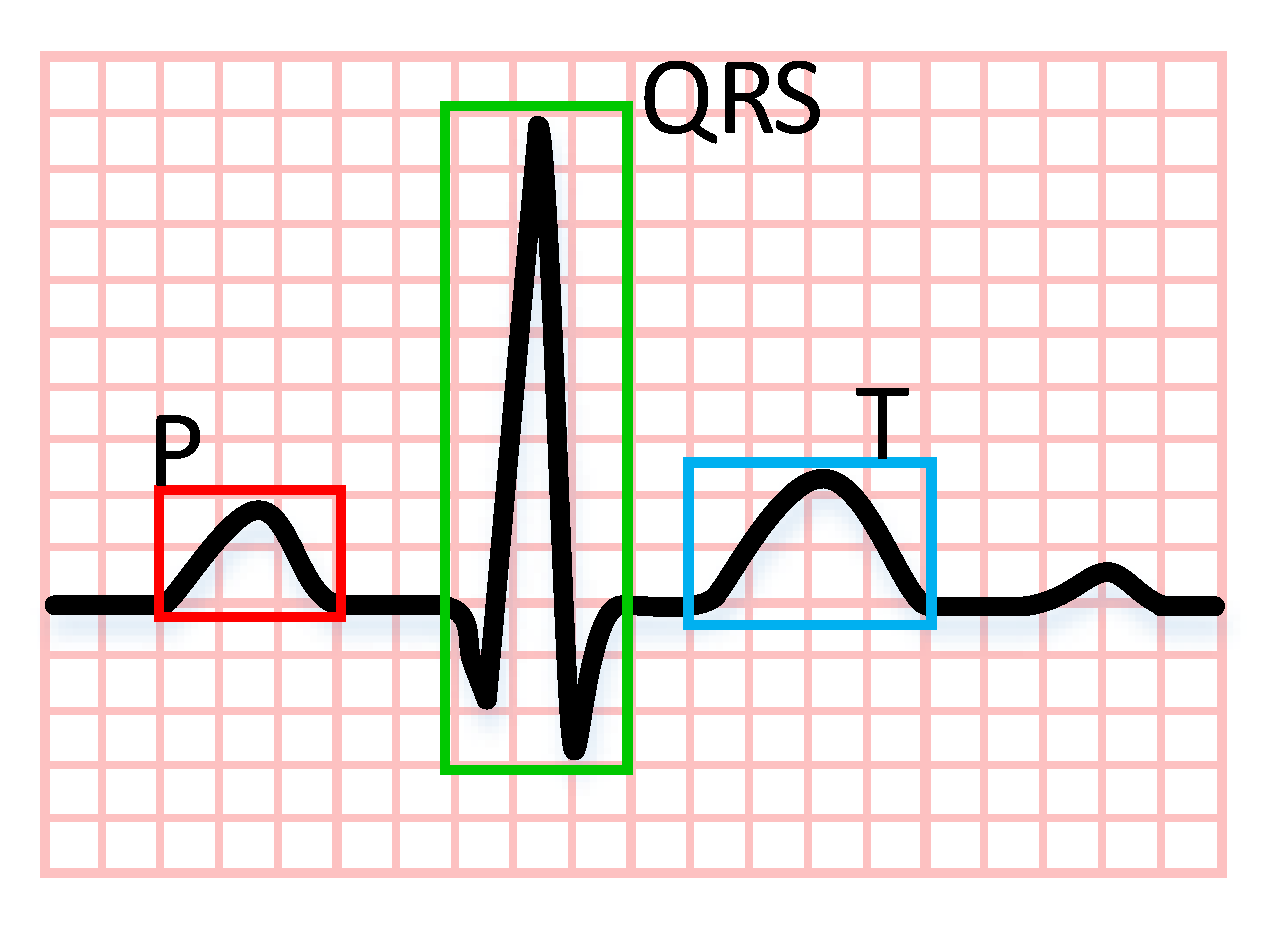
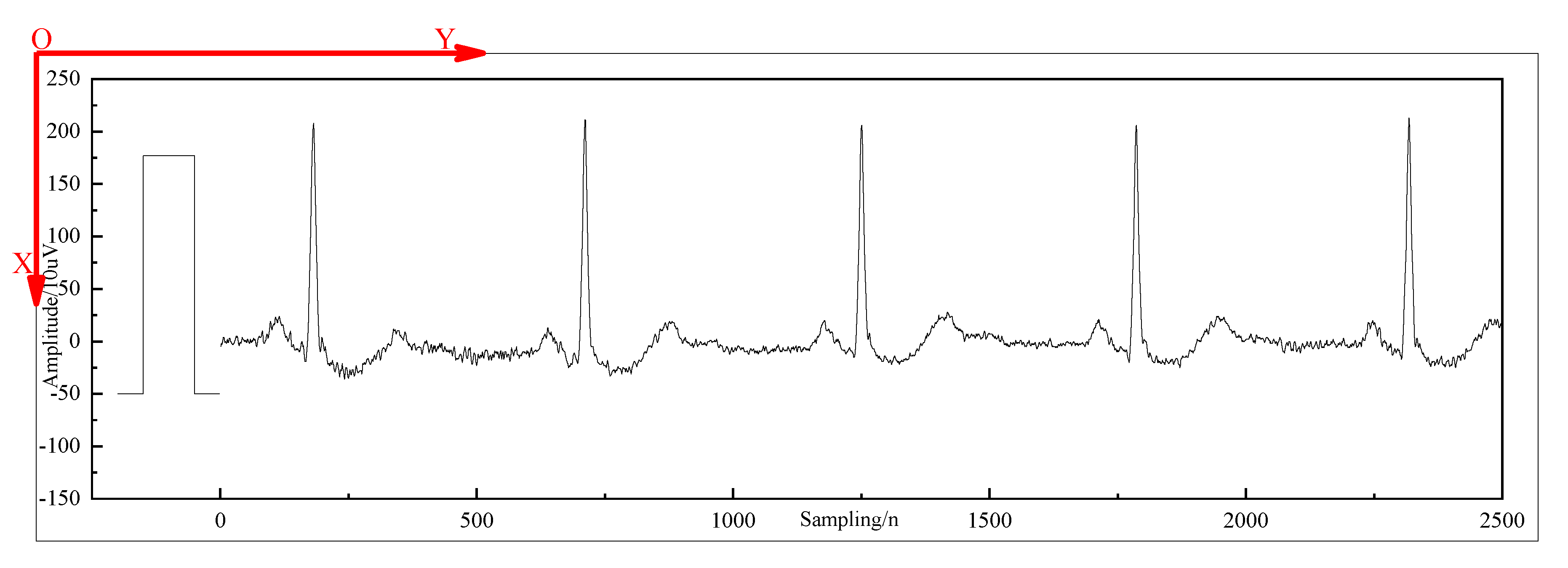
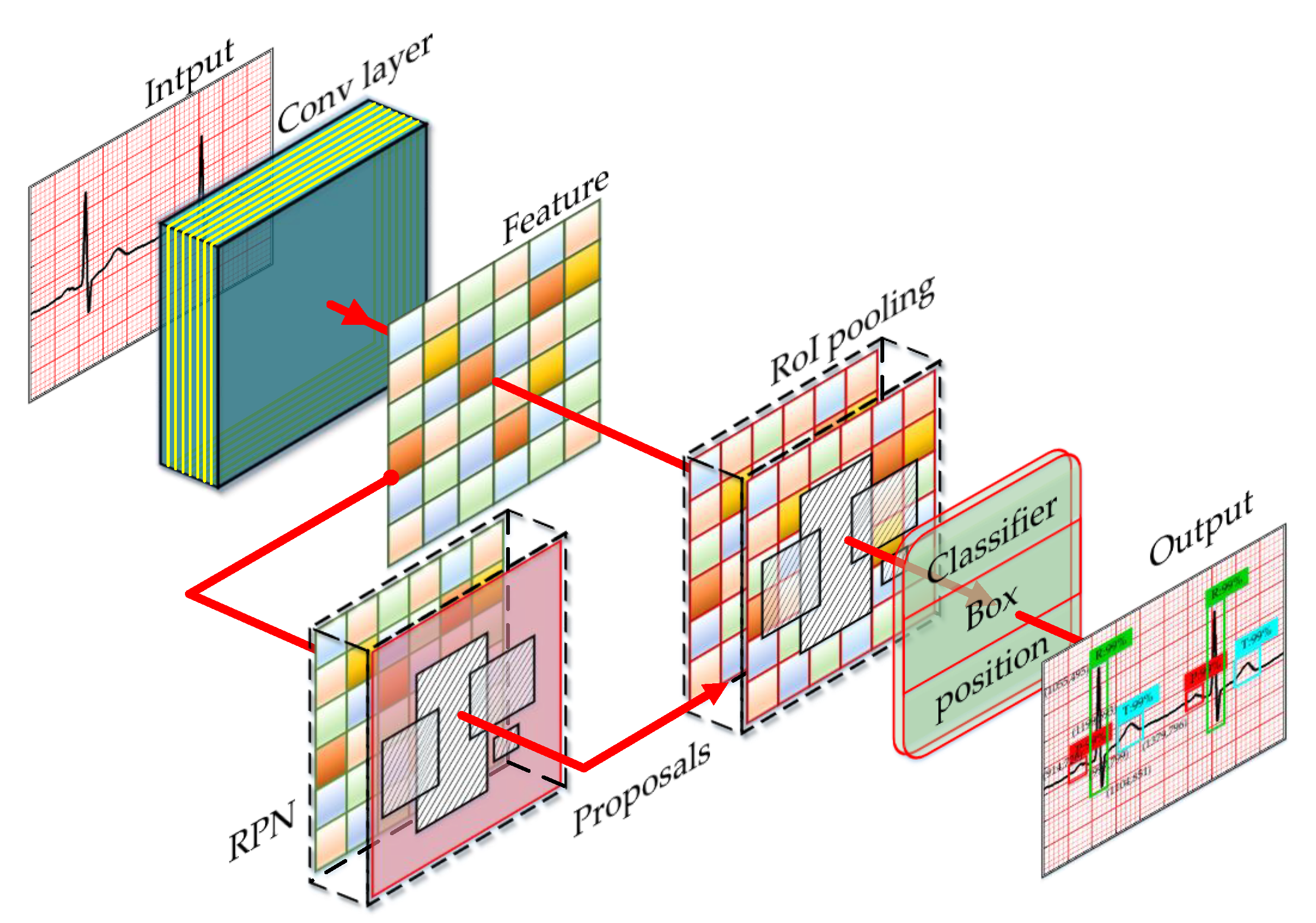
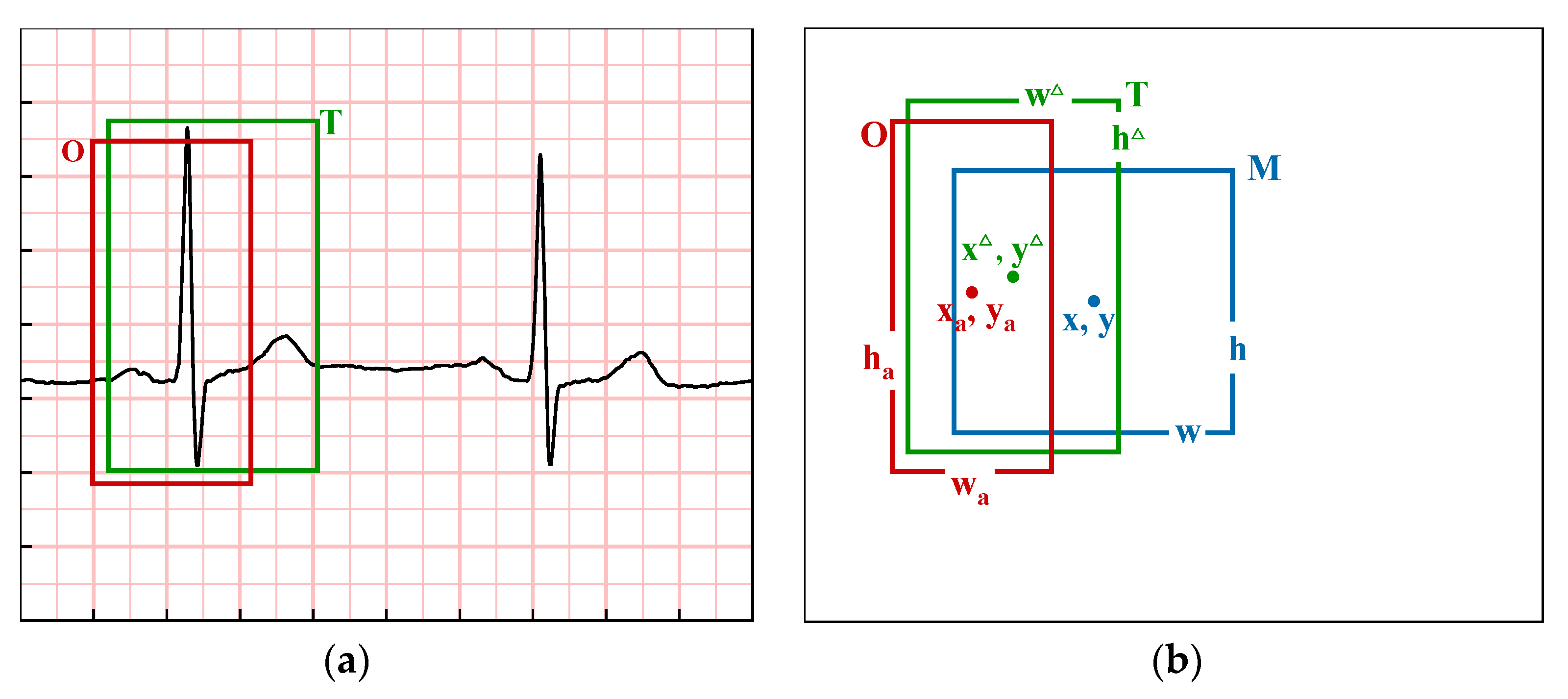
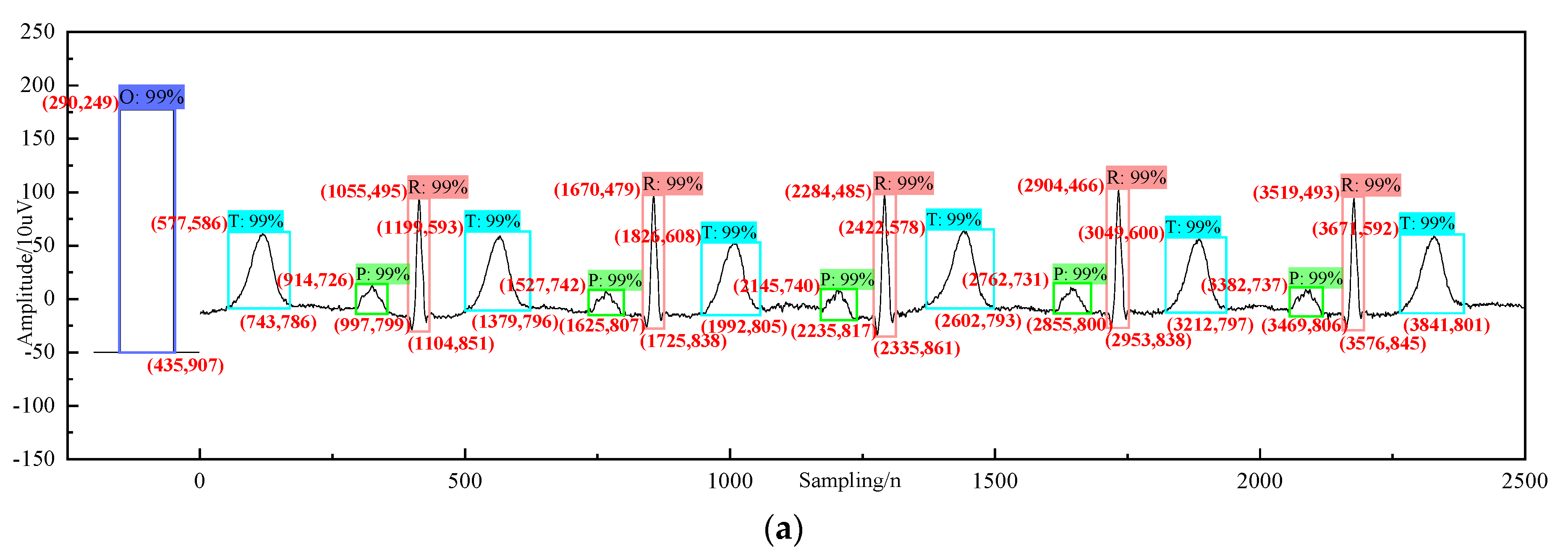
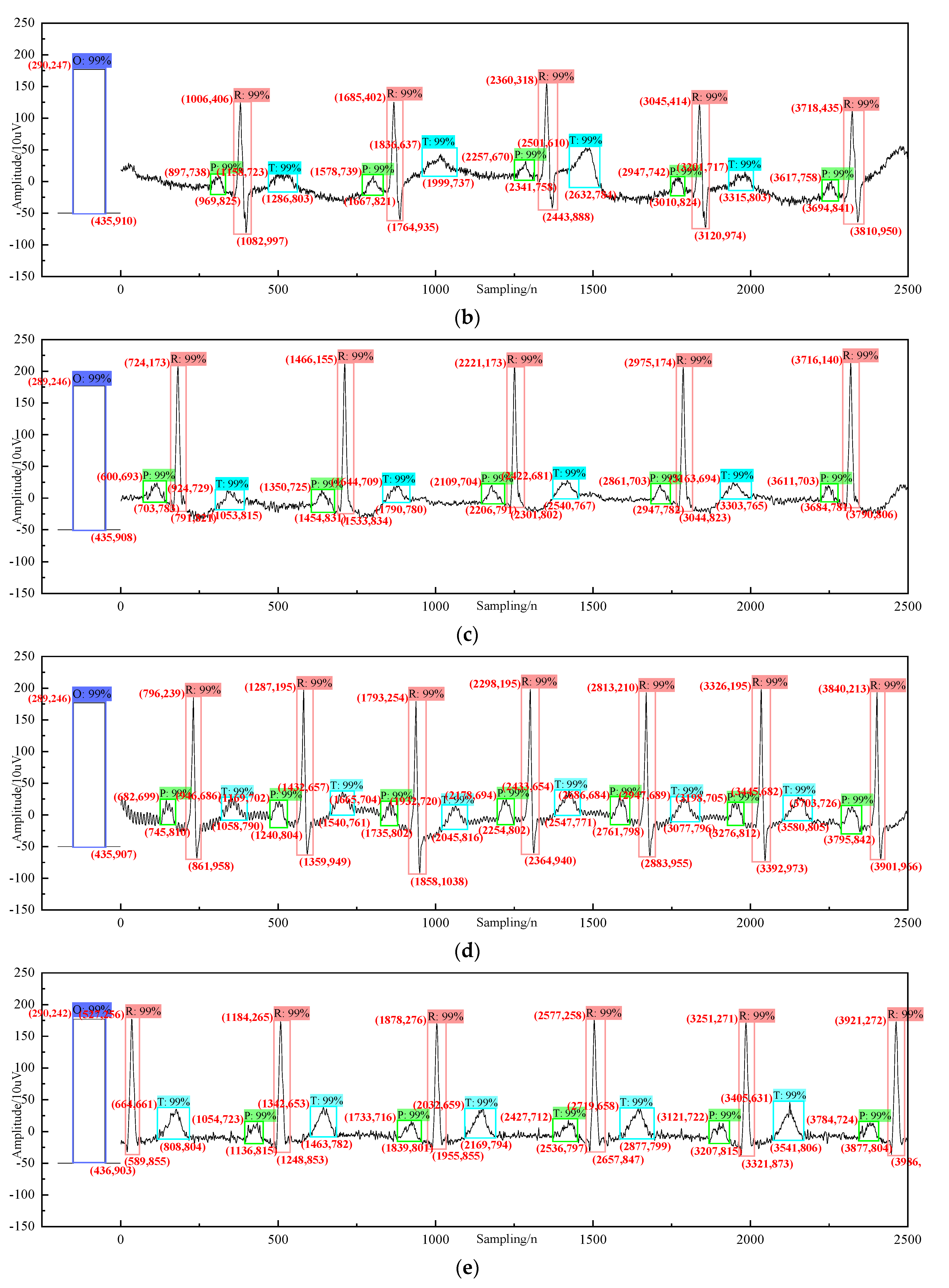
| Category | Description | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| O | calibration curve | 0.9968 |
| P | P wave | 0.9832 |
| R | QRS complex | 0.9885 |
| T | T wave | 0.9890 |
| Average accuracy | - | 0.9894 |
| Recognition Method | Average Accuracy (%) | Waveform Type | Waveform Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Faster R-CNN | 98.94 | O, P, QRS, T | 4 |
| LSTM [30] | 92.00 | P, QRS, T | 3 |
| 4-LSTM [31] | 98.48 | P | 1 |
| CNN + ELM [32] | 98.77 | QRS | 1 |
| SVM [33] | 95.26 | QRS | 1 |
| Parameters | Time (Width) s/Amplitude (Height) mm |
|---|---|
| 1 cell width | 0.04 s |
| 1 big grid width | 0.2 s |
| 5 big grid width | 1 s |
| Duration width of sampling period | 0.002 s |
| Calibration curve high level width | 0.2 s |
| Calibration curve height with 2 grids | 10 mm |
| Parameter N | Calculation by Formula | |
|---|---|---|
| tN (s) | hN (mm) | |
| O | 0.2 | 10 |
| P | 0.114 | 1.11 |
| QRS | 0.068 | 5.410 |
| T | 0.229 | 3.040 |
| P-P | 0.846 | - |
| P–R interval | 0.194 | - |
| P–R segment | 0.08 | - |
| S–T segment | 0.131 | - |
| S–T interval | 0.379 | - |
| Q–T interval | 0.447 | - |
| Type of N | Diagnostic Basis | Possible Disease Category |
|---|---|---|
| P | Calculate P shape, width, height, etc. | Atrial hypertrophy, hyperkalemia, etc. |
| Q | The calculated Q width is out of the normal range. | Myocardial infarction, myocarditis, etc. |
| QRS | Amplitude increase/decrease Width increased. | Myocardial hypertrophy/electrolyte disorder, etc. Bundle branch block, myocardial drugs, etc. |
| S-T | Morphological changes, elevation or depression, lengthening and shortening, etc. | Myocardial ischemia, etc. |
| T | Morphological changes, such as towering, low flat, inverted, etc. | Hyperkalemia, etc. |
| U | The U-wave enlarged obviously. | Hypokalemia, etc. |
| Q–T | Span extension. | Myocardial ischemia, drugs, etc. |
| P, R, P–R, P–P, QRS | The calculated P-R value was greater than 0.21s and increased continuously. | I-atrioventricular block, etc. |
| Periodic calculation of P-R prolongation, continuous recognition of conduction cycle waveform, until a QRS missing after P. | II-1 atrioventricular block, etc. | |
| P–R was constant and QRS missing was proportional to P. | II-2 atrioventricular block, etc. | |
| The adjacent P is equidistant and R is equidistant. P is not related to R. | III-atrioventricular block, etc. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, W. A New Method for Refined Recognition for Heart Disease Diagnosis Based on Deep Learning. Information 2020, 11, 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11120556
Song W. A New Method for Refined Recognition for Heart Disease Diagnosis Based on Deep Learning. Information. 2020; 11(12):556. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11120556
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Weibo. 2020. "A New Method for Refined Recognition for Heart Disease Diagnosis Based on Deep Learning" Information 11, no. 12: 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11120556
APA StyleSong, W. (2020). A New Method for Refined Recognition for Heart Disease Diagnosis Based on Deep Learning. Information, 11(12), 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11120556




