Document Summarization Based on Coverage with Noise Injection and Word Association
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
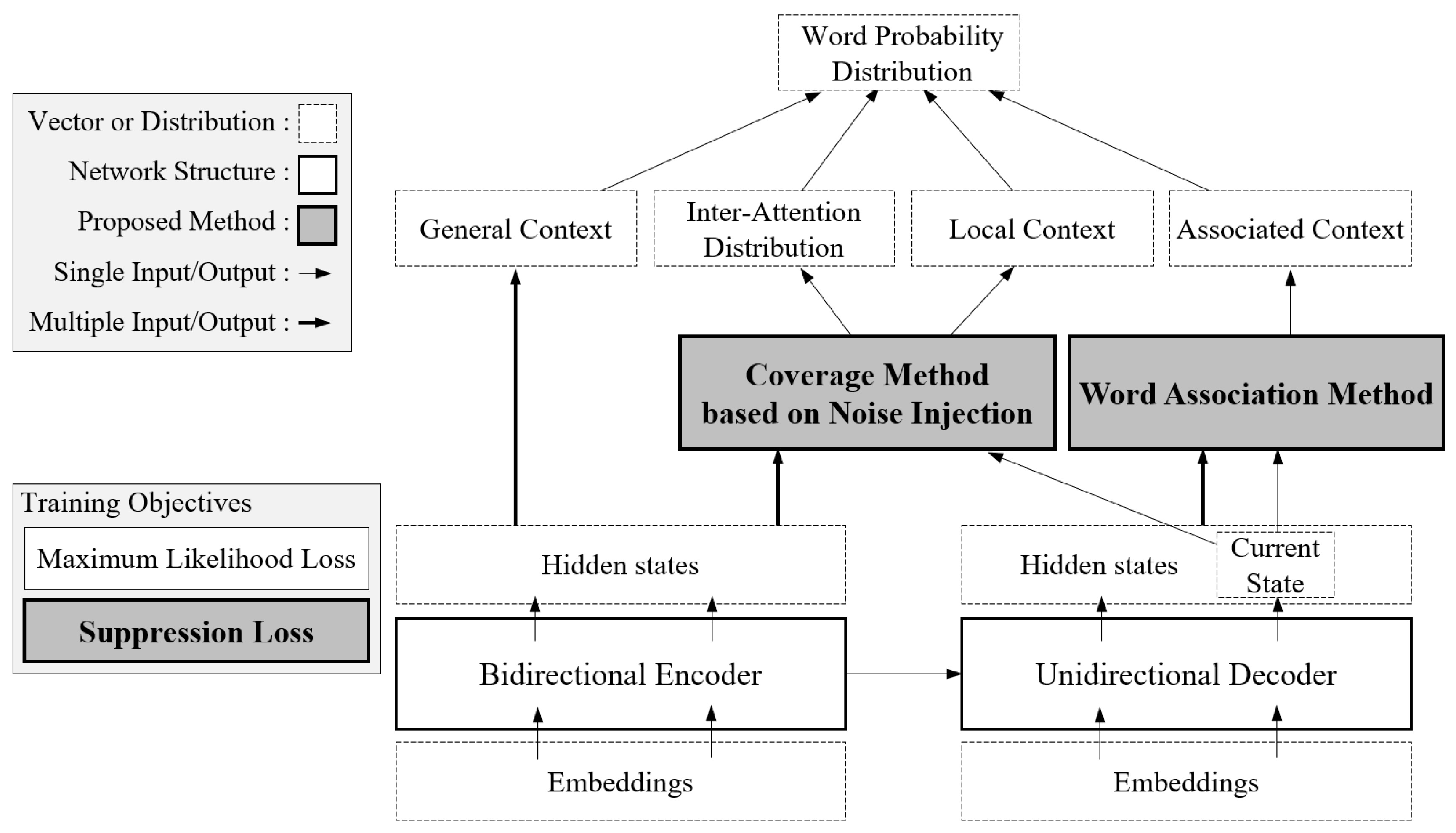
3. Proposed Model
3.1. Notation and Basic Network
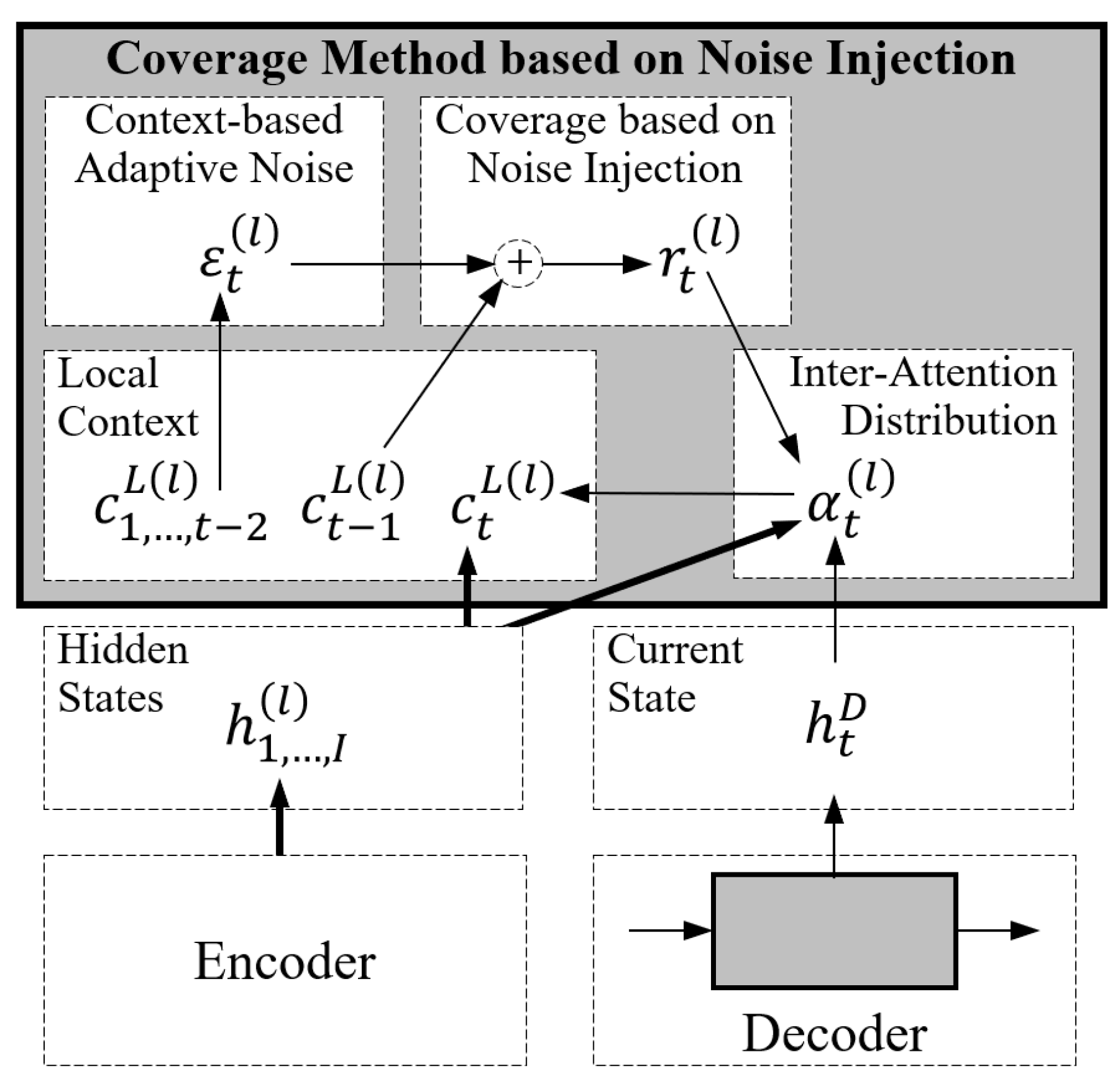
3.2. Coverage Method Based on Noise Injection
3.3. Word Association Method
3.4. Suppression Loss Function
3.5. Decoding Algorithm
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Experimental Settings
4.3. Evaluation Measure: ROUGE Metric
4.4. Optimal Parameter Search
4.5. Experimental Results
4.5.1. Quantitative Results
4.5.2. Qualitative Results
4.6. Comparison between Proposed Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. The Tables about Validation Results
| ROUGE-L | Epoch | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | ||
| 0.1 | 38.26 | 38.41 | 38.68 | 38.59 | 38.49 | 38.45 | |
| 0.2 | 38.34 | 38.40 | 38.20 | 38.19 | 38.17 | 37.78 | |
| 0.3 | 37.16 | 37.23 | 37.98 | 38.07 | 38.13 | 37.77 | |
| 0.4 | 35.99 | 36.85 | 36.41 | 36.50 | 36.17 | 36.07 | |
| 0.5 | 38.09 | 38.73 | 38.47 | 38.36 | 38.26 | 38.41 | |
| 0.6 | 37.16 | 37.26 | 37.75 | 37.28 | 37.30 | 37.37 | |
| 0.7 | 37.17 | 37.55 | 38.24 | 38.03 | 38.22 | 38.20 | |
| 0.8 | 37.57 | 37.91 | 38.14 | 38.45 | 37.53 | 38.03 | |
| 0.9 | 36.96 | 37.35 | 37.18 | 36.44 | 37.08 | 36.84 | |
| 1.0 | 37.49 | 37.48 | 37.26 | 37.12 | 37.65 | 37.63 | |
| 1.1 | 37.65 | 37.87 | 36.73 | 37.70 | 37.97 | 37.84 | |
| ROUGE-L | |
|---|---|
| 0.7 | 38.67 |
| 0.8 | 38.68 |
| 0.9 | 38.69 |
| 1.0 | 38.71 |
| 1.1 | 38.75 |
| 1.2 | 38.80 |
| 1.3 | 38.83 |
| 1.4 | 38.87 |
| 1.5 | 38.88 |
| 1.6 | 38.86 |
| 1.7 | 38.82 |
| ROUGE-L | Epoch | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Models | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| C model | 36.28 | 37.07 | 36.30 | 37.67 | 35.53 | 37.21 | |
| C-A model | 37.21 | 37.89 | 37.38 | 37.50 | 37.70 | 37.04 | |
| C-L model | |||||||
| 0.1 | 36.71 | 36.80 | 35.80 | 37.12 | 36.05 | 36.65 | |
| 0.2 | 36.74 | 36.45 | 35.83 | 37.42 | 36.55 | 36.68 | |
| 0.3 | 36.91 | 36.94 | 35.80 | 37.30 | 36.22 | 36.93 | |
| 0.4 | 35.64 | 36.70 | 35.71 | 36.68 | 35.91 | 36.80 | |
| 0.5 | 35.89 | 37.73 | 36.39 | 38.37 | 36.42 | 37.36 | |
| 0.6 | 35.99 | 36.99 | 35.92 | 37.56 | 36.08 | 36.89 | |
| 0.7 | 36.71 | 36.57 | 35.69 | 36.84 | 36.05 | 36.73 | |
| 0.8 | 36.39 | 36.09 | 35.04 | 36.69 | 35.76 | 36.75 | |
| 0.9 | 36.37 | 37.32 | 36.44 | 37.74 | 36.08 | 37.36 | |
| 1.0 | 35.91 | 37.08 | 36.02 | 37.67 | 35.83 | 36.99 | |
| 1.1 | 36.29 | 36.12 | 35.44 | 37.07 | 36.46 | 36.46 | |
| Models | ROUGE-L | |
|---|---|---|
| C model | 1.7 | 37.90 |
| C-A model | 1.1 | 37.88 |
| C-L model | 1.7 | 38.90 |
References
- Radev, D.R.; Hovy, E.; McKeown, K. Introduction to the special issue on summarization. Comput. Linguist. 2002, 28, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutskever, I.; Vinyals, O.; Le, Q.V. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Bangkok, Thailand, 23–27 November 2014; Volume 2, pp. 3104–3112. [Google Scholar]
- Bahdanau, D.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.0473. [Google Scholar]
- See, A.; Liu, P.J.; Manning, C.D. Get to the point: Summarization with pointer-generator networks. In Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 July–4 August 2017; Volume 1, pp. 1073–1083. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Lee, S. A context based coverage model for abstractive document summarization. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence, Jeju Island, Korea, 16–18 October 2019; pp. 1129–1132. [Google Scholar]
- Paulus, R.; Xiong, C.; Socher, R. A deep reinforced model for abstractive summarization. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Lee, S. Document summarization model based on general context in RNN. J. Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 15, 1378–1391. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, T.; Liu, Y.; Xu, B. Monotonic alignments for summarization. Knowl. Based Syst. 2020, 192, 105363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrmann, S.; Deng, Y.; Rush, A. Bottom-up abstractive summarization. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 31 October–4 November 2018; pp. 4098–4109. [Google Scholar]
- Celikyilmaz, A.; Bosselut, A.; He, X.; Choi, Y. Deep communicating agents for abstractive summarization. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, New Orleans, LA, USA, 1–6 June 2018; Volume 1, pp. 1662–1675. [Google Scholar]
- Pasunuru, R.; Bansal, M. Multi-reward reinforced summarization with saliency and entailment. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, New Orleans, LA, USA, 1–6 June 2018; Volume 2, pp. 646–653. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 6000–6010. [Google Scholar]
- You, Y.; Jia, W.; Liu, T.; Yang, W. Improving abstractive document summarization with salient information modeling. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 2132–2141. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Z.; Lu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, H. Modeling coverage for neural machine translation. In Proceedings of the 54th Annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Berlin, Germany, 7–12 August 2016; Volume 1, pp. 76–85. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.B.; Mann, B.; Ryer, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam., P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language models are few-shot learners. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.14165. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Hu, Y. Extractive summarization with very deep pretrained language model. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Appl. 2019, 10, 2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D. Leveraging BERT for extractive text summarization on lectures. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.04165. [Google Scholar]
- Stiennon, N.; Ouyang, L.; Wu, J.; Ziegler, D.M.; Lowe, R.; Voss, C.; Radford, A.; Amodei, D.; Christiano, P. Learning to summarize with human feedback. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 6–12 December 2020; Volume 33. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, R.S.; McAllester, D.A.; Singh, S.P.; Mansour, Y. Policy gradient methods for reinforcement learning with function approximation. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems; 1999; pp. 1057–1063. Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/1999/file/464d828b85b0bed98e80ade0a5c43b0f-Paper.pdf (accessed on 18 November 2020).
- Lin, C.Y. ROUGE: A package for automatic evaluation of summaries. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Text Summarization Branches Out, Barcelona, Spain, 25–26 July 2004; pp. 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, R.J. Simple statistical gradient-following algorithms for connectionist reinforcement learning. Mach. Learn. 1992, 8, 229–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rennie, S.J.; Marcheret, E.; Mroueh, Y.; Ross, J.; Goel, V. Self-critical sequence training for image captioning. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1179–1195. [Google Scholar]
- Gulcehre, C.; Ahn, S.; Nallapati, R.; Zhou, B.; Bengio, Y. Pointing the unknown words. In Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Berlin, Germany, 7–12 August 2016; Volume 1, pp. 140–149. [Google Scholar]
- Vinyals, O.; Fortunato, M.; Jaitly, N. Pointer networks. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; Volume 2, pp. 2692–2700. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, M.E.; Neumann, M.; Iyyer, M.; Gardner, M.; Clark, C.; Lee, K.; Zettlemoyer, L. Deep contextualized word representations. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.05365. [Google Scholar]
- Dieng, A.B.; Ranganath, R.; Altosaar, J.; Blei, D.M. Noisin: Unbiased regularization for recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; Volume 3, pp. 2030–2039. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Schuster, M.; Chen, Z.; Le, Q.V.; Norouzi, M.; Macherey, W.; Krikun, M.; Cao, Y.; Gao, Q.; Macherey, K.; et al. Google’s neural machine translation system: Bridging the gap between human and machine translation. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.08144. [Google Scholar]
- Hermann, K.M.; Kocisky, T.; Grefenstette, E.; Espeholt, L.; Kay, W.; Suleyman, M.; Blunsom, P. Teaching machines to read and comprehend. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; Volume 1, pp. 1693–1701. [Google Scholar]
- Glorot, X.; Bengio, Y. Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Sardinia, Italy, 13–15 May 2010; pp. 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Pascanu, R.; Mikolov, T.; Bengio, Y. On the difficulty of training recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Machine Learning, Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–21 June 2013; Volume 28, pp. 1310–1318. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Pennington, J.; Socher, R.; Manning, C.D. Glove: Global vectors for word representation. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014; pp. 1532–1543. [Google Scholar]

| Various Models | ROUGE-1 | ROUGE-2 | ROUGE-L |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pointer-generator without coverage [4] | 36.44 | 15.66 | 33.42 |
| RL, with intra-attention [6] | 41.16 | 15.75 | 39.08 |
| ML+RL, with intra-attention [6] | 39.87 | 15.82 | 36.90 |
| Monotonic alignments [8] | 39.91 | 17.06 | 36.24 |
| Pointer-generator with coverage [4] | 39.53 | 17.28 | 36.38 |
| Context-based coverage [5] | 39.64 | 17.54 | 36.52 |
| Lead-3 [4] | 40.34 | 17.70 | 36.57 |
| ROUGESal+Ent (ML+RL) [12] | 40.43 | 18.00 | 37.10 |
| Deep communicating agents (ML) [11] | 41.11 | 18.21 | 36.03 |
| Bottom-up summarization [10] | 41.22 | 18.68 | 38.34 |
| ETADS [13] | 41.75 | 19.01 | 38.89 |
| Deep communicating agents (ML+RL) [11] | 41.69 | 19.47 | 37.92 |
| Proposed model | 41.63 | 19.14 | 38.84 |
| Article |
|---|
| a 46-year-old man was sentenced to life in prison on monday after shooting dead a father and son because they were related to a driver who killed his nine-year-old sister in a crash 45 years ago |
| alfred guy vuozzo swore loudly as he was told he would not be eligible for parole for 35 yearsfor murderingbrent mcguigan, 68, and his son, brendon, 39, on prince edward island last august |
| as he was escorted from the courtroom, he screamed: ‘you′ve sentenced me to life and I sent them to death’, while the judge called the brutal double-murder an act of ‘hatred and misdirected vengeance’ |
| vuozzo was two years old when his older sister, cathy, was killed in a crash in 1970 |
| Brent′s father, herbert, who was behind the wheel, later received a nine-month sentence for dangerous driving |
| scroll down for video |
| ‘revenge’: alfred guy vuozzo, 46, has been sentenced to life in prison after shooting dead brent mcguigan, 68, and his son, brendon -lrb- both pictured -rrb-, 39, because they were related to a driver who killed his nine-year-old sister in a crash 45 years ago |
| Models | Summaries |
|---|---|
| Proposed model | alfred guy vuozzo swore loudly as he was told he would not be eligible for parole for 35 years. |
| he was sentenced to life in prisonafter shooting deadbrent mcguigan, 68, and his son, brendon, 39, on prince edward island last august. | |
| judge called the brutal double-murder an act of ‘hatred and misdirected vengeance’ | |
| BU | alfred guy vuozzo, 46, swore loudly as he was told he would not be eligible for parole for 35 years. |
| vuozzo was two years old when his older sister, cathy, was killed in a crash in 1970. | |
| Brent′s father, herbert, received a nine-month sentence for dangerous driving. | |
| PGC | alfred guy vuozzo, 46, swore loudly as he was told he would not be eligible for parole for murdering brent mcguigan, 68, and his son, brendon, 39, on prince edward island last august. |
| vuozzo was two years old when his older sister, cathy, was killed in a crash in 1970. | |
| Brent′s father, herbert, who was behind the wheel, received a nine-month sentence for dangerous driving. |
| Various Models | ROUGE-1 | ROUGE-2 | ROUGE-L |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 39.93 | 17.71 | 36.68 |
| C model | 41.04 | 18.62 | 38.07 |
| C-A model | 40.84 | 18.78 | 37.85 |
| C-L model | 41.70 | 19.00 | 38.67 |
| C-A-L model (Proposed Model) | 41.63 | 19.14 | 38.84 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.; Lee, S. Document Summarization Based on Coverage with Noise Injection and Word Association. Information 2020, 11, 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11110536
Kim H, Lee S. Document Summarization Based on Coverage with Noise Injection and Word Association. Information. 2020; 11(11):536. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11110536
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Heechan, and Soowon Lee. 2020. "Document Summarization Based on Coverage with Noise Injection and Word Association" Information 11, no. 11: 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11110536
APA StyleKim, H., & Lee, S. (2020). Document Summarization Based on Coverage with Noise Injection and Word Association. Information, 11(11), 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11110536





